Evolution Mechanism of Arsenic Enrichment in Groundwater and Associated Health Risks in Southern Punjab, Pakistan
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
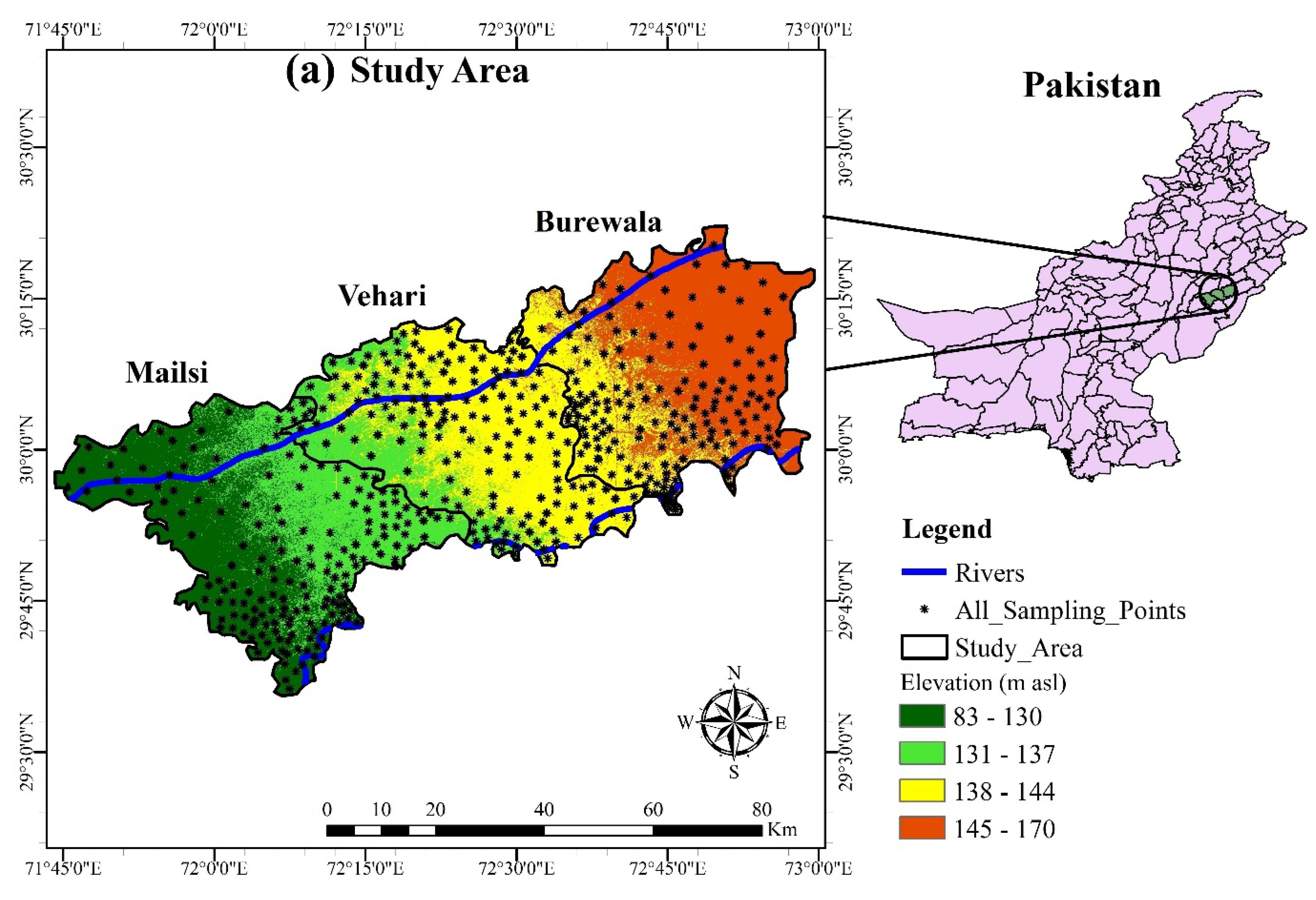
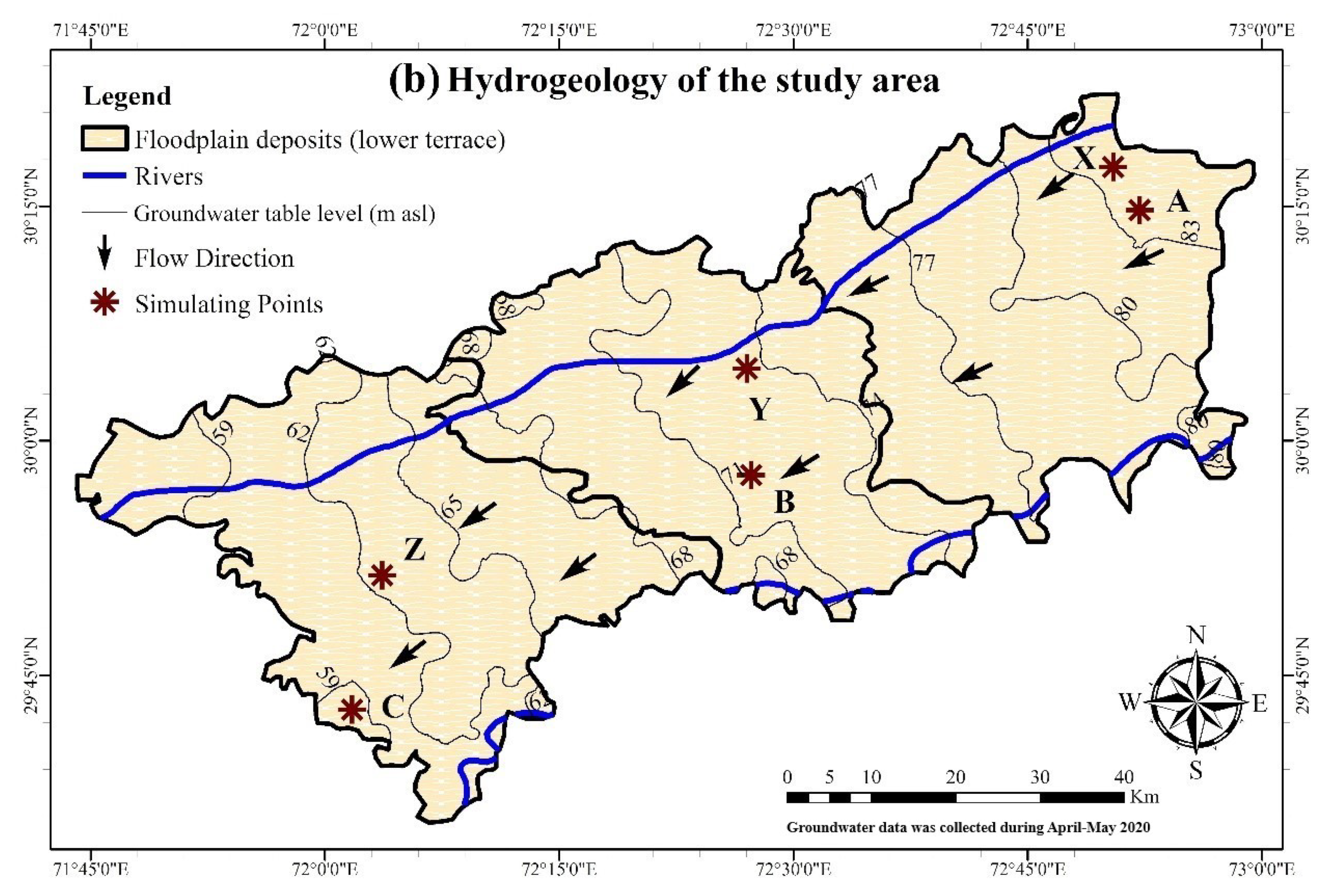
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Groundwater Samples
2.3. Hydrogeochemical Processing and Health Risk Assessment
2.4. Geochemical Modeling
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characteristics of Groundwater Geochemistry
3.2. Hydrogeochemical Origin of Groundwater
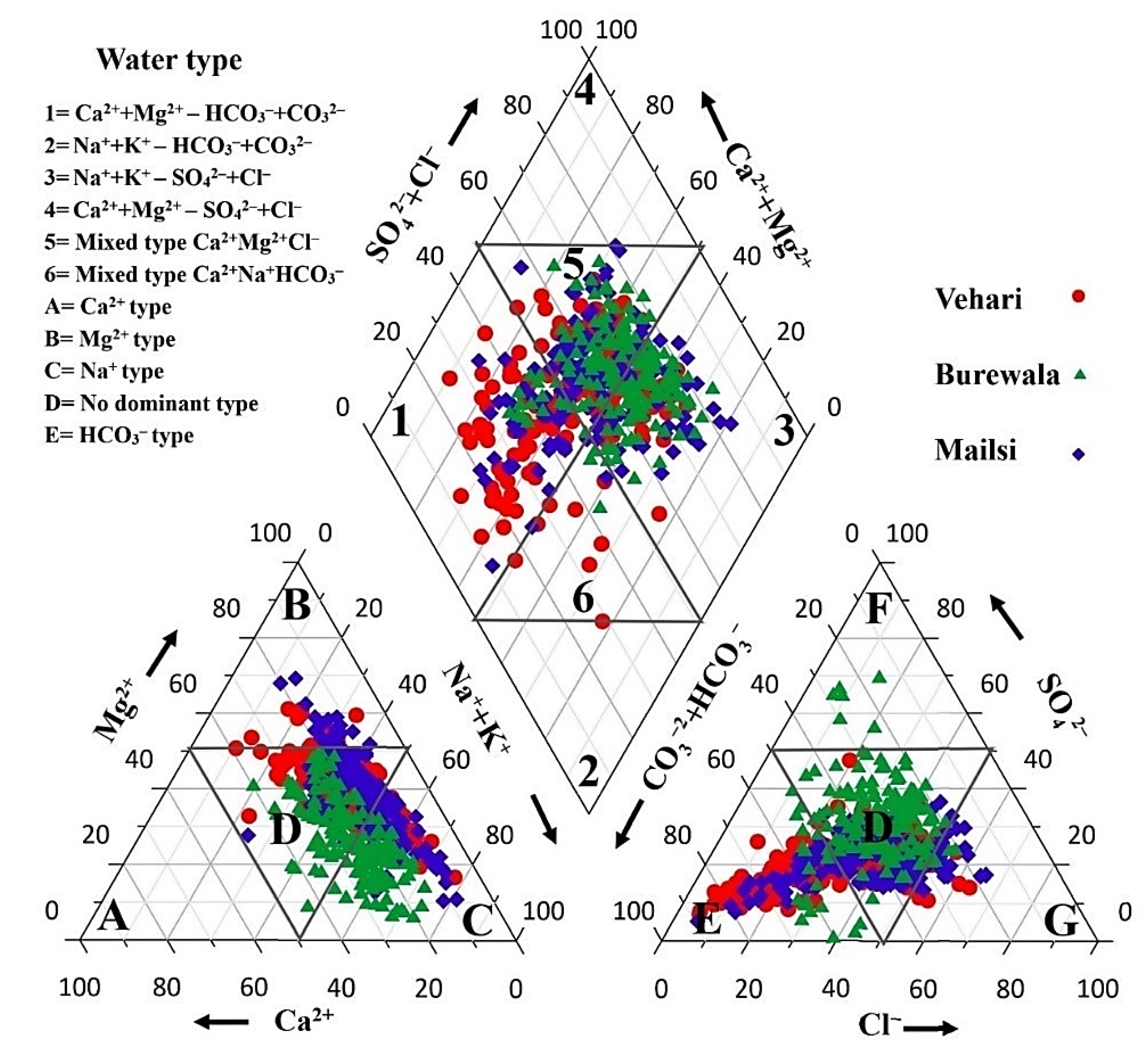
3.2.1. Geochemical Classifications of Groundwater
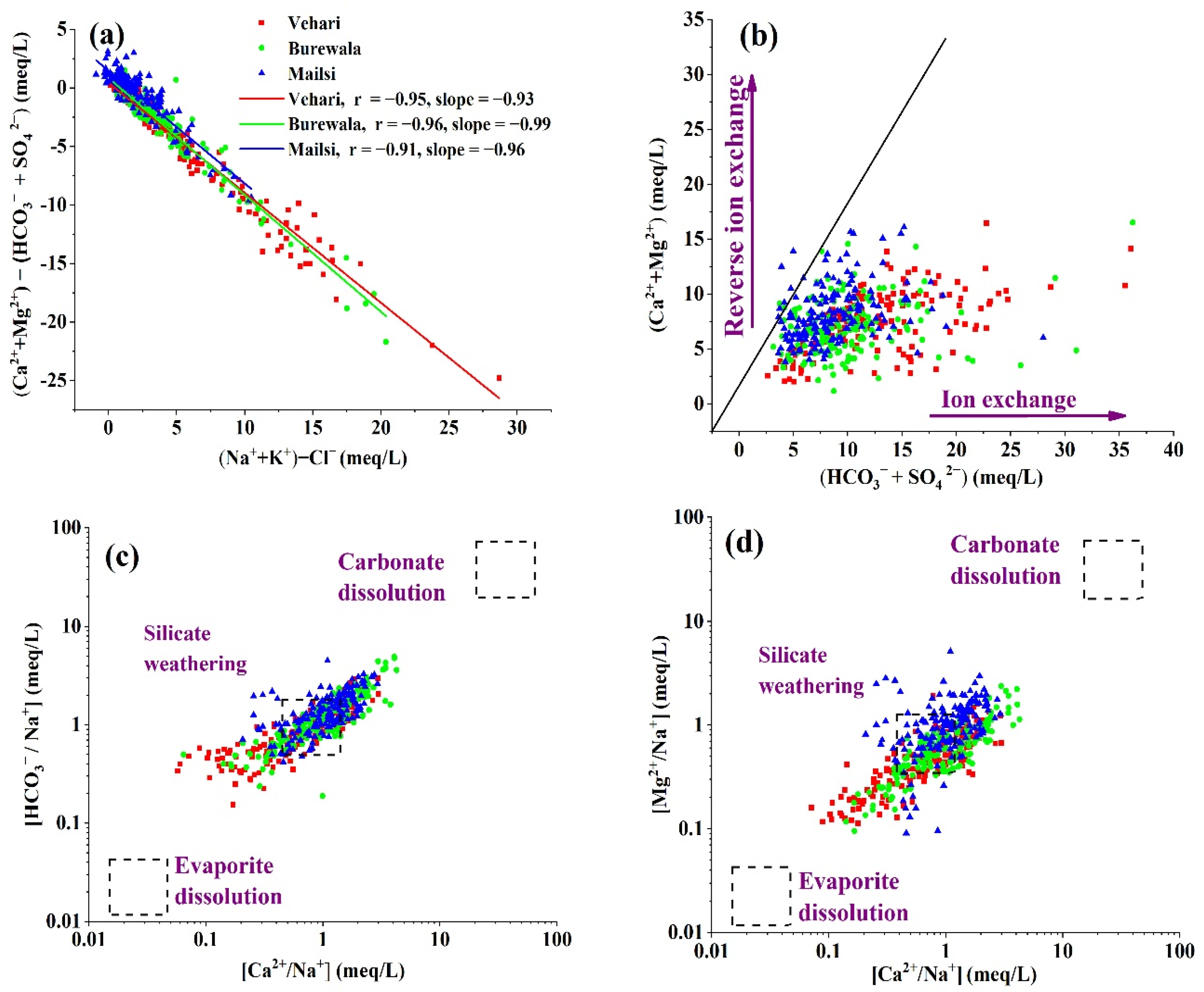
3.2.2. Ionic Ratios and Mineral Phases of Groundwater
3.2.3. Correlation Analysis
3.2.4. Principle Component Analyses (PCA)
3.2.5. Groundwater and Arsenic Evolution along Flow Path
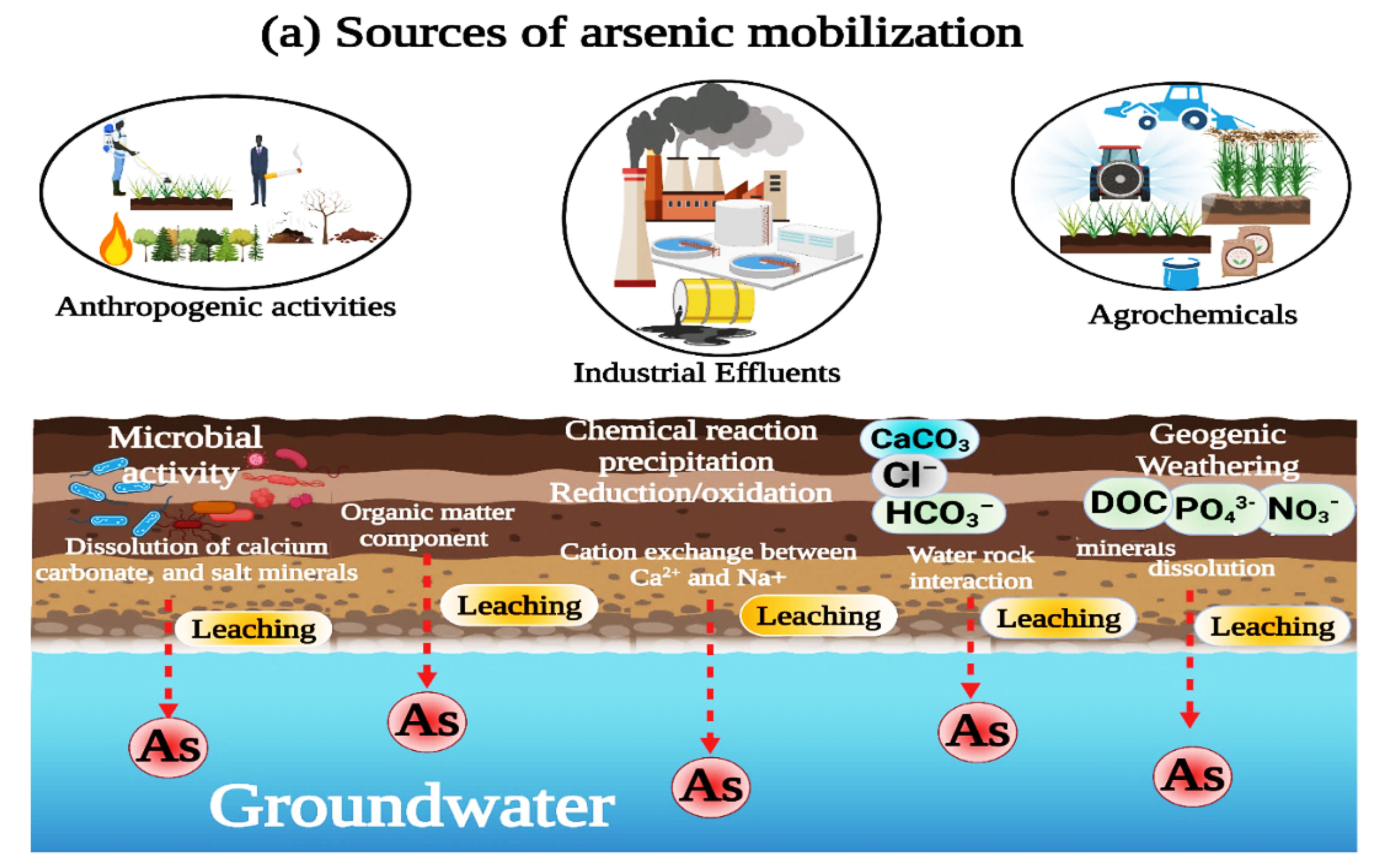
3.3. Mechanism of As Enrichment and Geospatial Distribution
3.4. Health Risk Assessment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Del Olmo, G.; Husband, S.; Sánchez Briones, C.; Soriano, A.; Calero Preciado, C.; Macian, J.; Douterelo, I. The microbial ecology of a Mediterranean chlorinated drinking water distribution systems in the city of Valencia (Spain). Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 142016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Gu, R.; Liang, Z.; Xu, W.; Jat Baloch, M.Y. Health Risk Assessment during In Situ Remediation of Cr(VI)-Contaminated Groundwater by Permeable Reactive Barriers: A Field-Scale Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chai, J.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Wu, S.; Liang, Z.; Baloch, M.Y.J.; Silva, L.F.; Zhang, D. Physiological characteristics, geochemical properties and hydrological variables influencing pathogen migration in subsurface system: What we know or not? Geosci. Front. 2022, 13, 101346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Teng, Y.; Zhai, Y.J.S. Biogeochemistry of Iron Enrichment in Groundwater: An Indicator of Environmental Pollution and Its Management. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Han, Y.; Lu, H.; Du, Q.; Xia, X.; Teng, Y.; Zuo, R.; Wang, J. Interactions between anthropogenic pollutants (biodegradable organic nitrogen and ammonia) and the primary hydrogeochemical component Mn in groundwater: Evidence from three polluted sites. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 808, 152162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Zheng, F.; Li, D.; Cao, X.; Teng, Y. Distribution, Genesis, and Human Health Risks of Groundwater Heavy Metals Impacted by the Typical Setting of Songnen Plain of NE China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talpur, S.A.; Noonari, T.M.; Rashid, A.; Ahmed, A.; Jat Baloch, M.Y.; Talpur, H.A.; Soomro, M.H. Hydrogeochemical signatures and suitability assessment of groundwater with elevated fluoride in unconfined aquifers Badin district, Sindh, Pakistan. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Teng, Y.; Zhai, Y.; Zheng, F.; Cao, X. Influencing factors and mechanism by which DOM in groundwater releases Fe from sediment. Chemosphere 2022, 300, 134524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Cao, X.; Xia, X.; Wang, B.; Teng, Y.; Li, X. Elevated Fe and Mn Concentrations in Groundwater in the Songnen Plain, Northeast China, and the Factors and Mechanisms Involved. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma-Lara, I.; Martínez-Castillo, M.; Quintana-Pérez, J.; Arellano-Mendoza, M.; Tamay-Cach, F.; Valenzuela-Limón, O.; García-Montalvo, E.; Hernández-Zavala, A. Arsenic exposure: A public health problem leading to several cancers. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 110, 104539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodhi, K.K.; Kumar, M.; Agrawal, P.K.; Singh, D.K. Perspectives on arsenic toxicity, carcinogenicity and its systemic remediation strategies. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2019, 16, 100462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Karunanidhi, D.; Subramani, T.; Srinivasamoorthy, K. Sources and consequences of groundwater contamination. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 80, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad Yousuf Jat, B.; Chun, S.; Shakeel Ahmed, T.; Javed, I.; Kulvinder, B. Arsenic Removal from Groundwater using Iron Pyrite: Influences Factors and Removal Mechanism. J. Earth Sci. 2022, 32, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Rahaman, M.S.; Rahman, M.M.; Mise, N.; Sikder, M.T.; Ichihara, G.; Uddin, M.K.; Kurasaki, M.; Ichihara, S. Environmental arsenic exposure and its contribution to human diseases, toxicity mechanism and management. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 289, 117940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, U.; Khan, S.; Muhammad, S. Ingestion of arsenic-contaminated drinking water leads to health risk and traces in human biomarkers (hair, nails, blood, and urine), Pakistan. Expo. Health 2020, 12, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.; Smith, J.; Smith, L.; Biswas, T.; Correll, R.; Naidu, R. Arsenic in Australian environment: An overview. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2003, 38, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, W.; Aslam, M.W.; Feng, C.; Junaid, M.; Ali, K.; Li, S.; Chen, Z.; Yu, Z.; Rasool, A.; Zhang, H.; et al. Unraveling prevalence and public health risks of arsenic, uranium and co-occurring trace metals in groundwater along riverine ecosystem in Sindh and Punjab, Pakistan. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 41, 2223–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Flores, H.; Pariona, N.; Herrera-Trejo, M.; Hdz-García, H.M.; Mtz-Enriquez, A.I. Concrete/maghemite nanocomposites as novel adsorbents for arsenic removal. J. Mol. Struct. 2018, 1171, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aftabtalab, A.; Rinklebe, J.; Shaheen, S.M.; Niazi, N.K.; Moreno-Jiménez, E.; Schaller, J.; Knorr, K.-H. Review on the interactions of arsenic, iron (oxy)(hydr) oxides, and dissolved organic matter in soils, sediments, and groundwater in a ternary system. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savage, K.S.; Bird, D. Inverse geochemical modeling of pit lake evolution in a high-arsenic, alkaline pit lake. In Proceedings of the GSA Abstract Program, Denver, CO, USA, 27–30 October 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Z.; Samper, J.; Ritzi, R., Jr. Identifying geochemical processes by inverse modeling of multicomponent reactive transport in the Aquia aquifer. Geosphere 2006, 2, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakoor, M.B.; Bibi, I.; Niazi, N.K.; Shahid, M.; Nawaz, M.F.; Farooqi, A.; Naidu, R.; Rahman, M.M.; Murtaza, G.; Lüttge, A. The evaluation of arsenic contamination potential, speciation and hydrogeochemical behaviour in aquifers of Punjab, Pakistan. Chemosphere 2018, 199, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, W.; Rasool, A.; Junaid, M.; Zhang, H. A comprehensive review on current status, mechanism, and possible sources of arsenic contamination in groundwater: A global perspective with prominence of Pakistan scenario. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 41, 737–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.; Khalid, M.; Dumat, C.; Khalid, S.; Niazi, N.K.; Imran, M.; Bibi, I.; Ahmad, I.; Hammad, H.M.; Tabassum, R.A.; et al. Arsenic level and risk assessment of groundwater in Vehari, Punjab Province, Pakistan. Expo. Health 2018, 10, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabassum, R.A.; Shahid, M.; Dumat, C.; Niazi, N.K.; Khalid, S.; Shah, N.S.; Imran, M.; Khalid, S.J. Health risk assessment of drinking arsenic-containing groundwater in Hasilpur, Pakistan: Effect of sampling area, depth, and source. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 20018–20029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waqas, H.; Shan, A.; Khan, Y.G.; Nawaz, R.; Rizwan, M.; Rehman, M.S.-U.; Shakoor, M.B.; Ahmed, W.; Jabeen, M. Human health risk assessment of arsenic in groundwater aquifers of Lahore, Pakistan. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2017, 23, 836–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.; Reza, A.; Sattar, G.S.; Ahsan, M.; Akbor, M.; Siddique, M.; Bakar, A. Distribution of arsenic in core sediments and groundwater in the Chapai Nawabganj district, Bangladesh. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, B.; Guo, Z.; Han, J.; Li, H.; Jin, L.; Chen, F.; Xiong, Y. Human health risk assessment of groundwater arsenic contamination in Jinghui irrigation district, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 237, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Embaby, A.; Redwan, M.J. Sources and behavior of trace elements in groundwater in the South Eastern Desert, Egypt. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, P.; Welch, A.H.; Stollenwerk, K.G.; McLaughlin, M.J.; Bundschuh, J.; Panaullah, G.J. Arsenic in the Environment: Biology and Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 109–120. [Google Scholar]
- Rochaddi, B.; Atmodjo, W.; Satriadi, A.; Suryono, C.A.; Irwani, I.; Widada, S. The Heavy Metal Contamination in Shallow Groundwater at Coastal Areas of Surabaya East Java Indonesia. J. Kelaut. Trop. 2019, 22, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, B.; Hug, S.J. Climatic variations and de-coupling between arsenic and iron in arsenic contaminated ground water in the lowlands of Nepal. Chemosphere 2018, 210, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canencia, O.P.; Walag, A.M.P. Coal combustion from power plant industry in Misamis Oriental, Philippines: A potential groundwater contamination and heavy metal detection. Asian J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Environ. Sci. 2016, 18, 55–59. [Google Scholar]
- Fida, M.; Li, P.; Wang, Y.; Alam, S.; Nsabimana, A.J.E. Water Contamination and Human Health Risks in Pakistan: A Review. Exposure Health 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakoor, M.B.; Niazi, N.K.; Bibi, I.; Rahman, M.M.; Naidu, R.; Dong, Z.; Shahid, M.; Arshad, M. Unraveling health risk and speciation of arsenic from groundwater in rural areas of Punjab, Pakistan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 12371–12390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A.H.; Khan, Z.M.; Mahmood, Q.; Nasreen, S.; Bhatti, Z. Perspectives of low cost arsenic remediation of drinking water in Pakistan and other countries. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 168, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbani, U.; Mahar, G.; Siddique, A.; Fatmi, Z. Risk assessment for arsenic-contaminated groundwater along River Indus in Pakistan. Environ. Geochem. Health 2017, 39, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, Z.; Mapoma, H.W.T.; Su, C.; Aziz, S.Z.; Ma, Y.; Abbas, N. Spatial analysis of groundwater suitability for drinking and irrigation in Lahore, Pakistan. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooqi, A.; Masuda, H.; Firdous, N. Toxic fluoride and arsenic contaminated groundwater in the Lahore and Kasur districts, Punjab, Pakistan and possible contaminant sources. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 145, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickson, R.; McArthur, J.; Shrestha, B.; Kyaw-Myint, T.; Lowry, D. Arsenic and other drinking water quality issues, Muzaffargarh District, Pakistan. Appl. Geochem. 2005, 20, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malana, M.A.; Khosa, M.A. Groundwater pollution with special focus on arsenic, Dera Ghazi Khan-Pakistan. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2011, 15, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, J.A.; Kazi, T.G.; Arain, M.B.; Afridi, H.I.; Kandhro, G.A.; Sarfraz, R.A.; Jamal, M.K.; Shah, A.Q. Evaluation of arsenic and other physico-chemical parameters of surface and ground water of Jamshoro, Pakistan. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arain, M.; Kazi, T.; Baig, J.; Jamali, M.; Afridi, H.; Shah, A.; Jalbani, N.; Sarfraz, R. Determination of arsenic levels in lake water, sediment, and foodstuff from selected area of Sindh, Pakistan: Estimation of daily dietary intake. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brahman, K.D.; Kazi, T.G.; Afridi, H.I.; Naseem, S.; Arain, S.S.; Ullah, N. Evaluation of high levels of fluoride, arsenic species and other physicochemical parameters in underground water of two sub districts of Tharparkar, Pakistan: A multivariate study. Water Res. 2013, 47, 1005–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arain, M.; Kazi, T.; Jamali, M.; Jalbani, N.; Afridi, H.; Shah, A. Total dissolved and bioavailable elements in water and sediment samples and their accumulation in Oreochromis mossambicus of polluted Manchar Lake. Chemosphere 2008, 70, 1845–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahid, M.; Niazi, N.K.; Dumat, C.; Naidu, R.; Khalid, S.; Rahman, M.M.; Bibi, I. A meta-analysis of the distribution, sources and health risks of arsenic-contaminated groundwater in Pakistan. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, S.; Hussain, I.; Rasool, A.; Xiao, T.; Farooqi, A. Comparison of two alluvial aquifers shows the probable role of river sediments on the release of arsenic in the groundwater of district Vehari, Punjab, Pakistan. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, M.; Soomro, M.S.; Akhtar, M.S.; Memon, K.S. Drinking water quality assessment in Southern Sindh (Pakistan). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 177, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podgorski, J.E.; Eqani, S.A.M.A.S.; Khanam, T.; Ullah, R.; Shen, H.; Berg, M. Extensive arsenic contamination in high-pH unconfined aquifers in the Indus Valley. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1700935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.H.; Shahid, M.; Khalid, S.; Shabbir, Z.; Bakhat, H.F.; Murtaza, B.; Farooq, A.; Akram, M.; Shah, G.M.; Nasim, W. Assessment of arsenic exposure by drinking well water and associated carcinogenic risk in peri-urban areas of Vehari, Pakistan. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtaza, B.; Amjad, M.; Shahid, M.; Imran, M.; Shah, N.S.; Abbas, G.; Naeem, M.A. Compositional and health risk assessment of drinking water from health facilities of District Vehari, Pakistan. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 2425–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, I.; Falchi, L.; Bühl, V.; Mañay, N. Arsenic levels in groundwater and its correlation with relevant inorganic parameters in Uruguay: A medical geology perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 721, 137787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.; Ahmad, M.; Rafiq, M.; Iqbal, N.; Ali, M.; Sajjad, M.I. Hydrological modeling of the Lahore-Aquifer, using isotopic, chemical and numerical techniques. Back Issues J. Sci. Vis. 2002, 7, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Water Environmental Federation; APHA Association. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; 21p. [Google Scholar]
- Piper, A.M.J.E. Transactions American Geophysical Union, A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water-analyses. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1944, 25, 914–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Arsenic, Inorganic; Integrated Risk Information System (IRIS), CASRN 7440-38-2). 1998. Available online: http://www.epa.gov/iris (accessed on 2 August 2022).
- USEPA. Guidelines for carcinogen risk assessment. In Risk Assessment Forum; EPA/630/P-03 F.; US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Parkhurst, D.L.; Appelo, C.A.J. User’s guide to PHREEQC (Version 2): A computer program for speciation, batch-reaction, one-dimensional transport, and inverse geochemical calculations. Water-Resour. Investig. Rep. 1999, 99, 312. [Google Scholar]
- Sharif, M.; Davis, R.; Steele, K.; Kim, B.; Kresse, T.; Fazio, J.A. Inverse geochemical modeling of groundwater evolution with emphasis on arsenic in the Mississippi River Valley alluvial aquifer, Arkansas (USA). J. Hydrol. 2008, 350, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality: Incorporating the First and Second Addenda; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Adimalla, N.; Qian, H.; Tiwari, D.M. Groundwater chemistry, distribution and potential health risk appraisal of nitrate enriched groundwater: A case study from the semi-urban region of South India. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 207, 111277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smedley, P.L.; Kinniburgh, D.G. A review of the source, behaviour and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Appl. Geochem. 2002, 17, 517–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Naidu, R.; Bhattacharya, P. Arsenic contamination in groundwater in the Southeast Asia region. Environ. Geochem. Health 2009, 31, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, A.; Xiao, T.; Farooqi, A.; Shafeeque, M.; Masood, S.; Ali, S.; Fahad, S.; Nasim, W. Arsenic and heavy metal contaminations in the tube well water of Punjab, Pakistan and risk assessment: A case study. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 95, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, J.; Su, C.; Rashid, A.; Yang, N.; Baloch, M.Y.J.; Talpur, S.A.; Ullah, Z.; Rahman, G.; Rahman, N.U.; Sajjad, M.M. Hydrogeochemical assessment of groundwater and suitability analysis for domestic and agricultural utility in Southern Punjab, Pakistan. Water 2021, 13, 3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Singh, S.; Parihar, P.; Singh, V.P.; Prasad, S.M. Arsenic contamination, consequences and remediation techniques: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 112, 247–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baloch, M.Y.J.; Talpur, S.A.; Talpur, H.A.; Iqbal, J.; Mangi, S.H.; Memon, S.J. Effects of Arsenic Toxicity on the Environment and Its Remediation Techniques: A Review. J. Water Environ. Technol. 2020, 18, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, S.; Guo, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Sun, X.J. Silicate weathering contributed to arsenic enrichment in geotherm-affected groundwater in Pliocene aquifers of the Guide basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2022, 606, 127444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Wu, Y.; Wu, J.J.E.G. Hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater in the Zhangye Basin, Northwestern China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2008, 55, 1713–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anawar, H.M.; Akai, J.; Sakugawa, H.J.C. Mobilization of arsenic from subsurface sediments by effect of bicarbonate ions in groundwater. Chemosphere 2004, 54, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmick, S.; Nath, B.; Halder, D.; Biswas, A.; Majumder, S.; Mondal, P.; Chakraborty, S.; Nriagu, J.; Bhattacharya, P.; Iglesias, M.J. Arsenic mobilization in the aquifers of three physiographic settings of West Bengal, India: Understanding geogenic and anthropogenic influences. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 262, 915–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.A.; Bhattacharya, P.; Sracek, O.; Ahmed, K.M.; Von Brömssen, M.; Jacks, G.J. Geological controls on groundwater chemistry and arsenic mobilization: Hydrogeochemical study along an E–W transect in the Meghna basin, Bangladesh. J. Hydrol. 2009, 378, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jat Baloch, M.Y.; Zhang, W.; Chai, J.; Li, S.; Alqurashi, M.; Rehman, G.; Tariq, A.; Talpur, S.A.; Iqbal, J.; Munir, M. Shallow Groundwater Quality Assessment and Its Suitability Analysis for Drinking and Irrigation Purposes. Water 2021, 13, 3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, J.; Farooqi, A.; Ali, U.J. Arsenic concentration variability, health risk assessment, and source identification using multivariate analysis in selected villages of public water system, Lahore, Pakistan. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 1241–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibi, S.; Farooqi, A.; Ramzan, M.; Javed, A. Health risk of arsenic in the alluvial aquifers of Lahore and Raiwind, Punjab Province, Pakistan: An investigation for safer well water. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2015, 97, 888–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinklebe, J.; Shaheen, S.M.; Yu, K.J.G. Release of As, Ba, Cd, Cu, Pb, and Sr under pre-definite redox conditions in different rice paddy soils originating from the USA and Asia. Geoderma 2016, 270, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, A.; Xiao, T.; Farooqi, A.; Shafeeque, M.; Liu, Y.; Kamran, M.A.; Katsoyiannis, I.A.; Eqani, S.A.M.A.S. Quality of tube well water intended for irrigation and human consumption with special emphasis on arsenic contamination at the area of Punjab, Pakistan. Environ. Geochem. Health 2017, 39, 847–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, M.; Blodau, C. Mobilization of arsenic by dissolved organic matter from iron oxides, soils and sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 354, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lengke, M.F.; Sanpawanitchakit, C.; Tempel, R.N.J.T.C.M. The oxidation and dissolution of arsenic-bearing sulfides. Can. Miner. 2009, 47, 593–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anawar, H.M.; Akai, J.; Komaki, K.; Terao, H.; Yoshioka, T.; Ishizuka, T.; Safiullah, S.; Kato, K.J. Geochemical occurrence of arsenic in groundwater of Bangladesh: Sources and mobilization processes. J. Geochem. Explor. 2003, 77, 109–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Jing, C. A review of arsenic interfacial geochemistry in groundwater and the role of organic matter. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 183, 109550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Wang, H.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, H.; Jiang, Z.; Li, P.; Wang, Y.J. Effects of different dissolved organic matter on microbial communities and arsenic mobilization in aquifers. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 411, 125146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casentini, B.; Pettine, M.; Millero, F.J. Release of arsenic from volcanic rocks through interactions with inorganic anions and organic ligands. Aquat. Geochem. 2010, 16, 373–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arain, G.M.; Aslam, M.; Majidano, S.A.; Khuhawar, M.Y. A preliminary study on the arsenic contamination of underground water of Matiari and Khairpur Districts, Sindh, Pakistan. J. -Chem. Soc. Pak. 2007, 29, 463. [Google Scholar]
- Bandara, U.; Diyabalanage, S.; Hanke, C.; Van Geldern, R.; Barth, J.A.; Chandrajith, R. Arsenic-rich shallow groundwater in sandy aquifer systems buffered by rising carbonate waters: A geochemical case study from Mannar Island, Sri Lanka. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 1352–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Singh, C.K. Arsenic enrichment in groundwater and associated health risk in Bari doab region of Indus basin, Punjab, India. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 256, 113324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, A.; Farooqi, A.; Xiao, T.; Masood, S.; Kamran, M.A. Elevated levels of arsenic and trace metals in drinking water of Tehsil Mailsi, Punjab, Pakistan. J. Geochem. Explor. 2016, 169, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakoor, M.B.; Niazi, N.K.; Bibi, I.; Murtaza, G.; Kunhikrishnan, A.; Seshadri, B.; Shahid, M.; Ali, S.; Bolan, N.S.; Ok, Y.S. Remediation of arsenic-contaminated water using agricultural wastes as biosorbents. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 46, 467–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, S.; Shah, M.T.; Khan, S. Arsenic health risk assessment in drinking water and source apportionment using multivariate statistical techniques in Kohistan region, northern Pakistan. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 2855–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooqi, A.; Masuda, H.; Kusakabe, M.; Naseem, M.; Firdous, N. Distribution of highly arsenic and fluoride contaminated groundwater from east Punjab, Pakistan, and the controlling role of anthropogenic pollutants in the natural hydrological cycle. Geochem. J. 2007, 41, 213–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, M.M. Arsenic in groundwater and health problems in Bangladesh. Water Research 2000, 34, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caylak, E. Health risk assessment for arsenic in water sources of Cankiri Province of Turkey. Clean–Soil Air Water 2012, 40, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameters | Vehari (n = 170) | Burewala (n = 170) | Mailsi (n = 170) | WHO (2022) Standard | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min–Max | Mean ± Standard | Min–Max | Mean ± Standard | Min–Max | Mean ± Standard | ||
| EC | 308–4550 | 1569.94 ± 848.63 | 85–4400 | 1230.78 ± 646.37 | 226–2690 | 1185.059 ± 468.99 | 1000 |
| TDS | 234–3148 | 1072.12 ± 514.8 | 277–3173 | 896.68 ± 429.54 | 359–3298 | 896.64 ± 385.68 | 1000 |
| pH | 6.85–7.61 | 7.17 ± 0.17 | 6.78–7.15 | 6.98 ± 0.07 | 7.2–8.35 | 7.66 ± 0.23 | 6.5–8.5 |
| Turbidity | 0.3–991 | 26.37 ± 86.34 | 0.3–202 | 15.98 ± 38.57 | 0.2–4.2 | 1.22 ± 1.12 | 4.0 |
| Alkalinity | 2.2–610 | 10.82 ± 46.56 | 2.8–13.2 | 5.98 ± 1.81 | 1.4–12.8 | 6.50 ± 1.68 | - |
| Hardness | 100–820 | 368.47 ± 132.94 | 105–820 | 348.85 ± 123.71 | 190–1540 | 414.58 ± 152.34 | - |
| HCO3− | 110–900 | 345.08 ± 116.35 | 80–660 | 299.20 ± 92.78 | 70–640 | 324.23 ± 84.59 | - |
| Cl− | 10–518 | 107.94 ± 88.83 | 10–502 | 74.08 ± 57.8 | 28–336 | 103.51 ± 53.84 | 200–300 |
| SO42– | 41–1300 | 316.87 ± 219.81 | 18–1432 | 244.24 ± 185.36 | 18–840 | 167.49 ± 126.37 | 250 |
| Ca2+ | 24–192 | 86.31 ± 35.40 | 26–208 | 86.44 ± 32.59 | 8–320 | 86.91 ± 40.77 | 200 |
| Mg2+ | 6–98 | 36.65 ± 16.55 | 10–95 | 32.25 ± 14.52 | 2–180 | 48 ± 21.55 | 150 |
| Na+ | 14–850 | 195.29 ± 157.17 | 13–620 | 131.78 ± 109.08 | 21–360 | 107.97 ± 68.98 | 200 |
| K+ | 2.6–42.6 | 9.53 ± 6.53 | 3.7–69 | 8.085 ± 6.24 | 1–74 | 9.49 ± 8.29 | 12 |
| NO3− | BDL-17.66 | 1.51 ± 3.07 | 0.01–15.82 | 1.8 ± 3.31 | BDL-14 | 1.85 ± 2.94 | 50 |
| F− | BDL-3.15 | 0.59 ± 0.37 | 0.18–1.35 | 0.46 ± 0.20 | 0.22–1.24 | 0.51 ± 0.17 | 1.5 |
| Fe2+ | 0.01–2.94 | 0.18 ± 0.39 | 0.01–3.92 | 0.19 ± 0.43 | 0.01–2.94 | 0.23 ± 0.40 | 0.3 |
| As | BDL-45 | 14.0 ± 11.85 | BDL-52 | 11.0 ± 11.62 | BDL-89 | 13.0 ± 15.3 | 10 |
| Tehsil | Vehari | Burewala | Mailsi | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Component | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 |
| EC | 0.964 | −0.199 | 0.092 | 0.957 | −0.094 | −0.185 | 0.869 | 0.063 | 0.195 |
| TDS | 0.981 | 0.051 | 0.131 | 0.962 | 0.141 | −0.16 | 0.972 | −0.074 | 0.027 |
| pH | 0.069 | −0.062 | 0.376 | −0.037 | 0.125 | −0.14 | −0.34 | 0.208 | 0.512 |
| Turbidity | 0.017 | 0.245 | 0.329 | −0.052 | 0.352 | 0.016 | 0.217 | 0.745 | 0.086 |
| Alkalinity | 0.072 | −0.202 | 0.014 | 0.837 | −0.215 | 0.176 | 0.814 | 0.191 | −0.222 |
| HCO3− | 0.707 | −0.067 | −0.108 | 0.821 | −0.254 | 0.182 | 0.823 | 0.178 | −0.209 |
| Cl− | 0.867 | −0.207 | 0.097 | 0.844 | −0.057 | −0.114 | 0.868 | −0.048 | 0.132 |
| SO42– | 0.936 | −0.111 | 0.193 | 0.856 | 0.038 | −0.356 | 0.862 | −0.081 | 0.28 |
| Ca2+ | 0.392 | 0.831 | 0.157 | 0.592 | 0.706 | 0.173 | 0.779 | −0.334 | −0.025 |
| Mg2+ | 0.816 | 0.301 | −0.155 | 0.833 | 0.128 | 0.193 | 0.617 | 0.206 | −0.502 |
| Na+ | 0.856 | −0.433 | 0.121 | 0.859 | −0.307 | −0.332 | 0.792 | 0.13 | 0.383 |
| K+ | 0.331 | 0.108 | −0.556 | 0.301 | −0.124 | 0.481 | 0.573 | −0.097 | 0.291 |
| Hardness | 0.662 | 0.71 | 0.026 | 0.793 | 0.527 | 0.208 | 0.88 | −0.104 | −0.307 |
| NO3− | 0.125 | −0.064 | −0.637 | 0.328 | −0.006 | 0.648 | 0.322 | −0.502 | 0.062 |
| Fe | 0.154 | 0.093 | −0.072 | 0.156 | −0.12 | 0.039 | −0.04 | 0.307 | −0.002 |
| F− | 0.466 | −0.643 | −0.153 | 0.517 | −0.459 | −0.148 | 0.225 | 0.303 | 0.313 |
| As | −0.288 | −0.257 | 0.514 | −0.002 | 0.663 | −0.378 | 0.025 | 0.783 | −0.12 |
| Eigen Value | 6.46 | 2.18 | 1.40 | 7.56 | 1.85 | 1.32 | 7.56 | 1.92 | 1.19 |
| % of Variance | 38.04 | 12.83 | 8.27 | 44.49 | 10.88 | 7.77 | 44.51 | 11.33 | 7.01 |
| Cumulative % | 38.04 | 50.88 | 59.15 | 44.49 | 55.37 | 63.15 | 44.51 | 55.85 | 62.86 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jat Baloch, M.Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, D.; Al Shoumik, B.A.; Iqbal, J.; Li, S.; Chai, J.; Farooq, M.A.; Parkash, A. Evolution Mechanism of Arsenic Enrichment in Groundwater and Associated Health Risks in Southern Punjab, Pakistan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13325. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192013325
Jat Baloch MY, Zhang W, Zhang D, Al Shoumik BA, Iqbal J, Li S, Chai J, Farooq MA, Parkash A. Evolution Mechanism of Arsenic Enrichment in Groundwater and Associated Health Risks in Southern Punjab, Pakistan. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(20):13325. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192013325
Chicago/Turabian StyleJat Baloch, Muhammad Yousuf, Wenjing Zhang, Dayi Zhang, Baig Abdullah Al Shoumik, Javed Iqbal, Shuxin Li, Juanfen Chai, Muhammad Ansar Farooq, and Anand Parkash. 2022. "Evolution Mechanism of Arsenic Enrichment in Groundwater and Associated Health Risks in Southern Punjab, Pakistan" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 20: 13325. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192013325
APA StyleJat Baloch, M. Y., Zhang, W., Zhang, D., Al Shoumik, B. A., Iqbal, J., Li, S., Chai, J., Farooq, M. A., & Parkash, A. (2022). Evolution Mechanism of Arsenic Enrichment in Groundwater and Associated Health Risks in Southern Punjab, Pakistan. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(20), 13325. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192013325