Maternal Folate Status and the Relation between Gestational Arsenic Exposure and Child Health Outcomes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. Maternal Urinary Arsenic Concentrations
2.3. Maternal Folate Status
2.3.1. Maternal Plasma Folate Status
2.3.2. Maternal Folic Acid Intake from Supplements
2.4. Child Neurodevelopmental and Anthropometric Health Outcomes
Classes of Child Neurodevelopmental and Anthropometric Health Outcomes
2.5. Covariates
2.6. Statistical Analyses
Secondary and Sensitivity Analyses
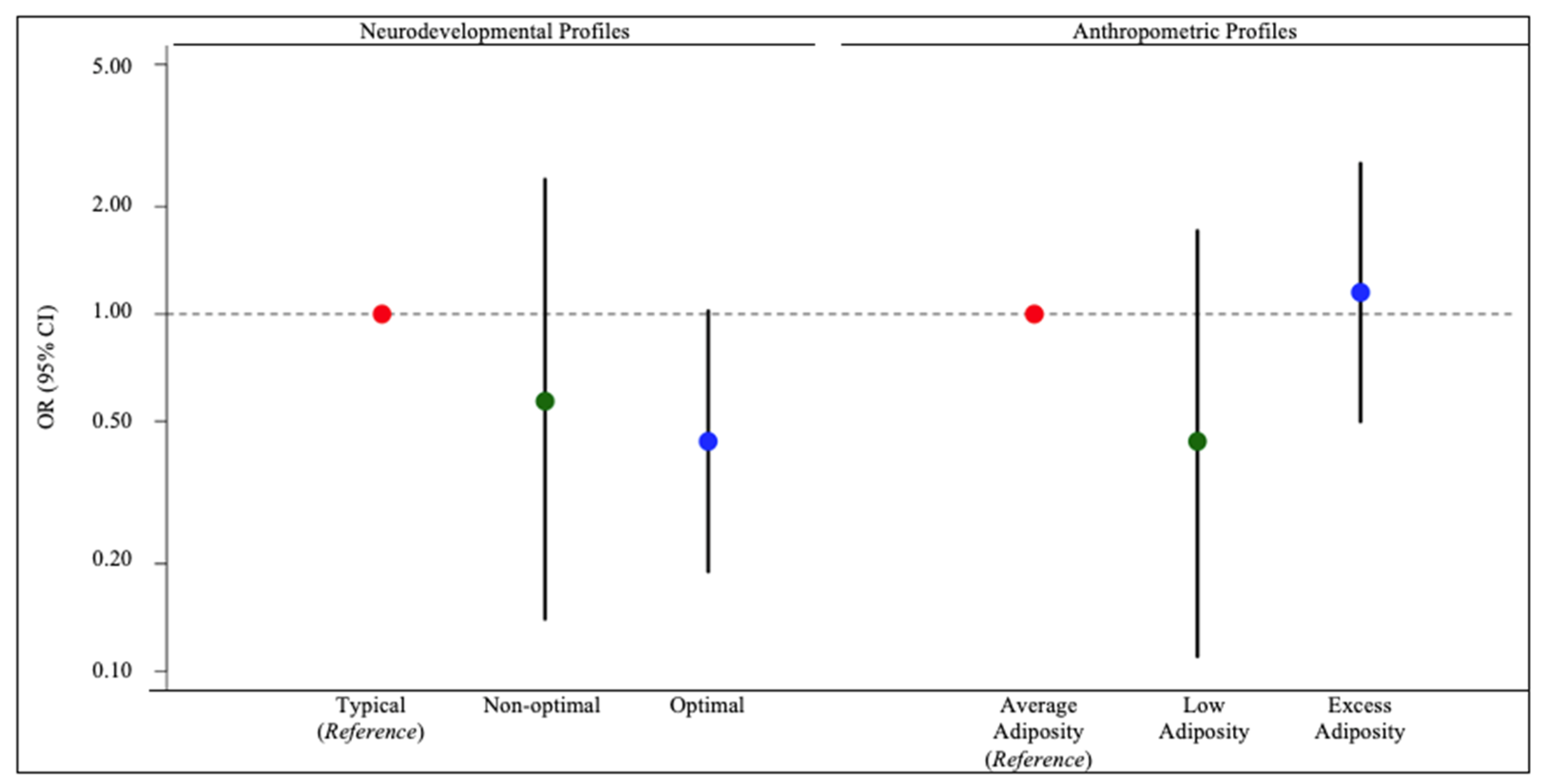
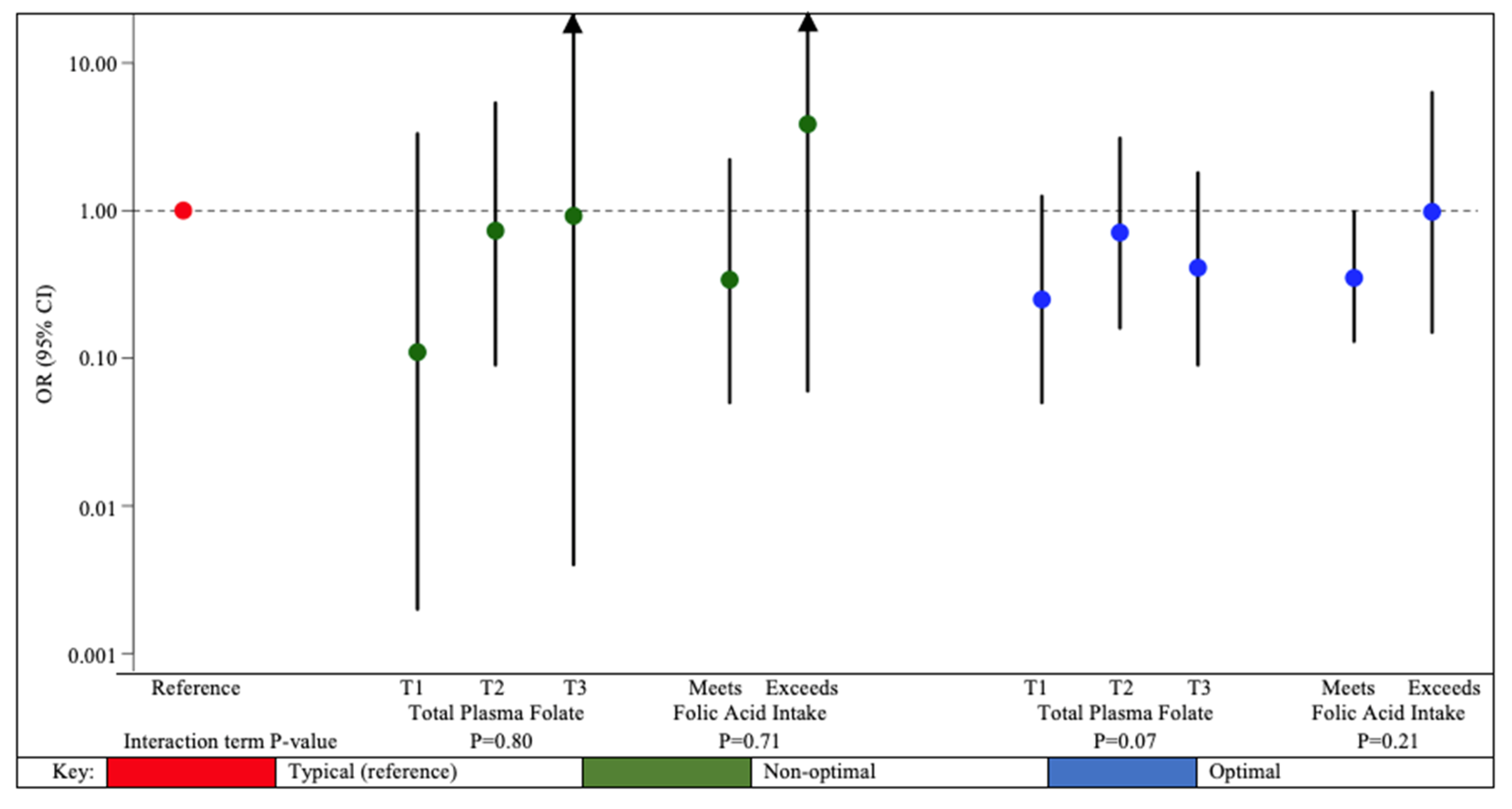
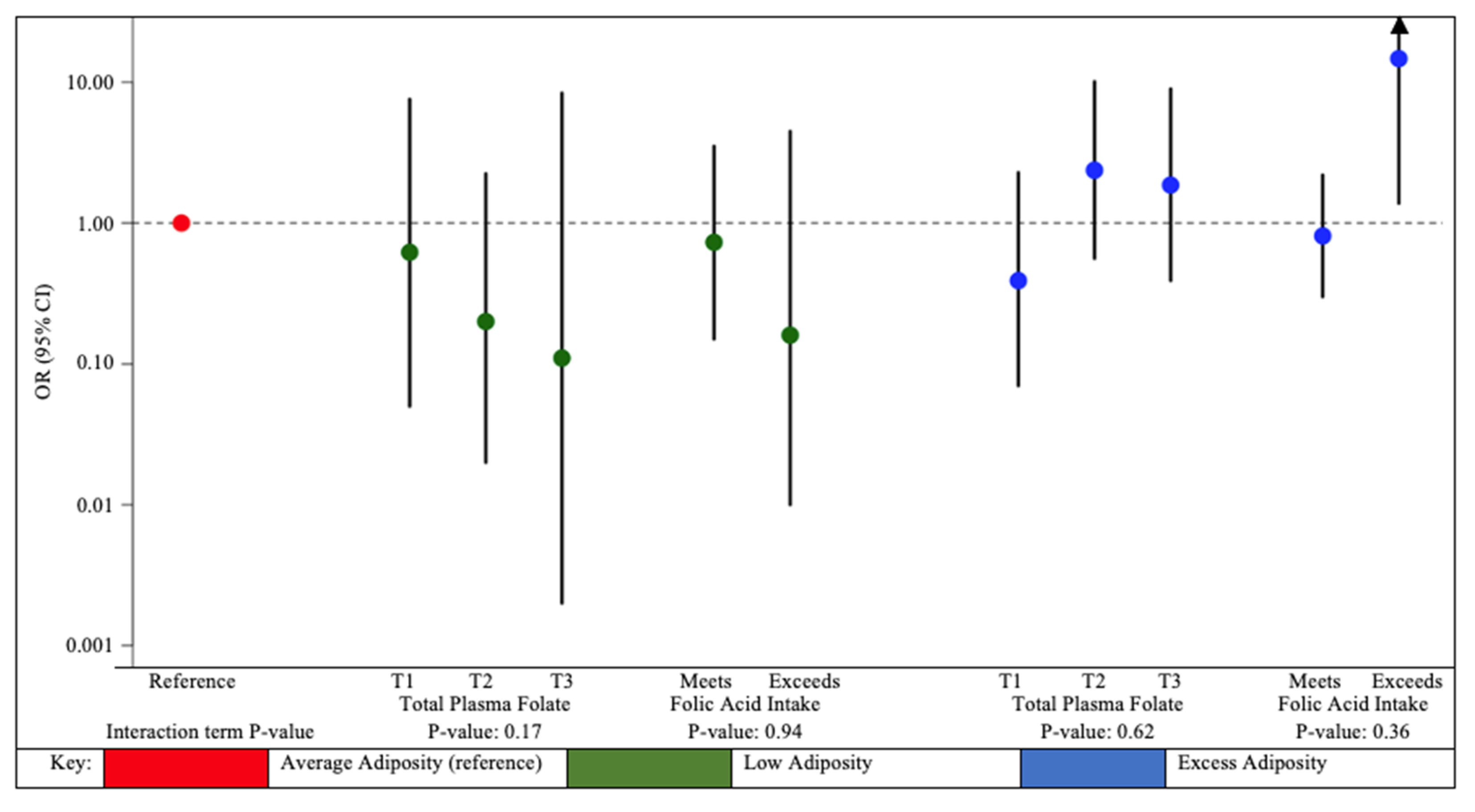
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- McDermott, S.; Bao, W.; Marjorie Aelion, C.; Cai, B.; Lawson, A. When Are Fetuses and Young Children Most Susceptible to Soil Metal Concentrations of Arsenic, Lead and Mercury? Spat. Spatio-Temporal Epidemiol. 2012, 3, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasserman, G.A.; Liu, X.; Parvez, F.; Ahsan, H.; Factor-Litvak, P.; Kline, J.; van Geen, A.; Slavkovich, V.; Loiacono, N.J.; Levy, D.; et al. Water Arsenic Exposure and Intellectual Function in 6-Year-Old Children in Araihazar, Bangladesh. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, R.O.; Amarasiriwardena, C.; Woolf, A.D.; Jim, R.; Bellinger, D.C. Neuropsychological Correlates of Hair Arsenic, Manganese, and Cadmium Levels in School-Age Children Residing near a Hazardous Waste Site. NeuroToxicology 2006, 27, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Z. Blood Mercury, Arsenic, Cadmium, and Lead in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2018, 181, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Barranco, M.; Gil, F.; Hernández, A.F.; Alguacil, J.; Lorca, A.; Mendoza, R.; Gómez, I.; Molina-Villalba, I.; González-Alzaga, B.; Aguilar-Garduño, C.; et al. Postnatal Arsenic Exposure and Attention Impairment in School Children. Cortex J. Devoted Study Nerv. Syst. Behav. 2016, 74, 370–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.L.; Valeri, L.; Kile, M.L.; Mazumdar, M.; Mostofa, G.; Qamruzzaman, Q.; Rahman, M.; Baccarelli, A.; Liang, L.; Hauser, R.; et al. Investigating Causal Relation between Prenatal Arsenic Exposure and Birthweight: Are Smaller Infants More Susceptible? Environ. Int. 2017, 108, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Ehrenstein, O.S.; Guha Mazumder, D.N.; Hira-Smith, M.; Ghosh, N.; Yuan, Y.; Windham, G.; Ghosh, A.; Haque, R.; Lahiri, S.; Kalman, D.; et al. Pregnancy Outcomes, Infant Mortality, and Arsenic in Drinking Water in West Bengal, India. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2006, 163, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, K.K.; Engström, A.; Hamadani, J.D.; Tofail, F.; Rasmussen, K.M.; Vahter, M. Pre- and Postnatal Arsenic Exposure and Body Size to 2 Years of Age: A Cohort Study in Rural Bangladesh. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 1208–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, R.M.; Kippler, M.; Tofail, F.; Bottai, M.; Hamadani, J.; Grandér, M.; Nermell, B.; Palm, B.; Rasmussen, K.M.; Vahter, M. Environmental Exposure to Metals and Children’s Growth to Age 5 Years: A Prospective Cohort Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 177, 1356–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kile, M.L.; Cardenas, A.; Rodrigues, E.; Mazumdar, M.; Dobson, C.; Golam, M.; Quamruzzaman, Q.; Rahman, M.; Christiani, D.C. Estimating Effects of Arsenic Exposure during Pregnancy on Perinatal Outcomes in a Bangladeshi Cohort. Epidemiology 2016, 27, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saxena, R.; Bozack, A.K.; Gamble, M.V. Nutritional Influences on One-Carbon Metabolism: Effects on Arsenic Methylation and Toxicity. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2018, 38, 401–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Shi, Q.; Nix, F.B.; Styblo, M.; Beck, M.A.; Herbin-Davis, K.M.; Hall, L.L.; Simeonsson, J.B.; Thomas, D.J. A Novel S-Adenosyl-L-Methionine:Arsenic(III) Methyltransferase from Rat Liver Cytosol. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 10795–10803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Challenger, F. Biological Methylation. Chem. Rev. 1945, 36, 315–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.J.; Waters, S.B.; Styblo, M. Elucidating the Pathway for Arsenic Methylation. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2004, 198, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, K.; Naranmandura, H. Arsenic Metabolism and Thioarsenicals. Met. Integr. Biometal Sci. 2012, 4, 881–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Cui, X.; Hirano, S. A New Metabolic Pathway of Arsenite: Arsenic-Glutathione Complexes Are Substrates for Human Arsenic Methyltransferase Cyt19. Arch. Toxicol. 2005, 79, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, R.J.; Tancredi, D.J.; Ozonoff, S.; Hansen, R.L.; Hartiala, J.; Allayee, H.; Schmidt, L.C.; Tassone, F.; Hertz-Picciotto, I. Maternal Periconceptional Folic Acid Intake and Risk of Autism Spectrum Disorders and Developmental Delay in the CHARGE (CHildhood Autism Risks from Genetics and Environment) Case-Control Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 96, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, R.J.; Kogan, V.; Shelton, J.F.; Delwiche, L.; Hansen, R.L.; Ozonoff, S.; Ma, C.C.; McCanlies, E.C.; Bennett, D.H.; Hertz-Picciotto, I.; et al. Combined Prenatal Pesticide Exposure and Folic Acid Intake in Relation to Autism Spectrum Disorder. Environ. Health Perspect. 2017, 125, 097007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oulhote, Y.; Lanphear, B.; Braun, J.M.; Webster, G.M.; Arbuckle, T.E.; Etzel, T.; Forget-Dubois, N.; Seguin, J.R.; Bouchard, M.F.; MacFarlane, A.; et al. Gestational Exposures to Phthalates and Folic Acid, and Autistic Traits in Canadian Children. Environ. Health Perspect. 2020, 128, 27004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodrich, A.J.; Volk, H.E.; Tancredi, D.J.; McConnell, R.; Lurmann, F.W.; Hansen, R.L.; Schmidt, R.J. Joint Effects of Prenatal Air Pollutant Exposure and Maternal Folic Acid Supplementation on Risk of Autism Spectrum Disorder. Autism Res. Off. J. Int. Soc. Autism Res. 2018, 11, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftus, C.T.; Hazlehurst, M.F.; Szpiro, A.A.; Ni, Y.; Tylavsky, F.A.; Bush, N.R.; Sathyanarayana, S.; Carroll, K.N.; Karr, C.J.; LeWinn, K.Z. Prenatal Air Pollution and Childhood IQ: Preliminary Evidence of Effect Modification by Folate. Environ. Res. 2019, 176, 108505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, G.; Barg, G.; Queirolo, E.I.; Vahter, M.; Peregalli, F.; Mañay, N.; Kordas, K. A Cross-Sectional Study of General Cognitive Abilities among Uruguayan School Children with Low-Level Arsenic Exposure, Potential Effect Modification by Methylation Capacity and Dietary Folate. Environ. Res. 2018, 164, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, G.; Barg, G.; Vahter, M.; Queirolo, E.; Peregalli, F.; Manay, N.; Millen, A.; Yu, J.; Browne, R.; Kordas, K. Low Level Arsenic Exposure, B-Vitamins, and Achievement among Uruguayan School Children. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2020, 223, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, J.M.; Kalloo, G.; Kingsley, S.L.; Li, N. Using Phenome-Wide Association Studies to Examine the Effect of Environmental Exposures on Human Health. Environ. Int. 2019, 130, 104877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuthbert, B.N.; Insel, T.R. Toward the Future of Psychiatric Diagnosis: The Seven Pillars of RDoC. BMC Med. 2013, 11, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Insel, T.; Cuthbert, B.; Garvey, M.; Heinssen, R.; Pine, D.S.; Quinn, K.; Sanislow, C.; Wang, P. Research Domain Criteria (RDoC): Toward a New Classification Framework for Research on Mental Disorders. Am. J. Psychiatry 2010, 167, 748–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, L.A.; Watson, D.; Reynolds, S. Diagnosis and Classification of Psychopathology: Challenges to the Current System and Future Directions. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 1995, 46, 121–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wing, L.; Gould, J.; Gillberg, C. Autism Spectrum Disorders in the DSM-V: Better or Worse than the DSM-IV? Res. Dev. Disabil. 2011, 32, 768–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sl, K.; Jt, N. Heterogeneity and Subtyping in Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder-Considerations for Emerging Research Using Person-Centered Computational Approaches. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31924323/ (accessed on 16 September 2020).
- Arbuckle, T.E.; Fraser, W.D.; Fisher, M.; Davis, K.; Liang, C.L.; Lupien, N.; Bastien, S.; Velez, M.P.; von Dadelszen, P.; Hemmings, D.G.; et al. Cohort Profile: The Maternal-Infant Research on Environmental Chemicals Research Platform. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 2013, 27, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belanger, P.; Dumas, P. Fast Determination of Urine Arsenic Species by Ion Exchange Chromatography and HPLC-ICP-MS Using Collision-Reactive Interface. At. Spectrosc. 2010, 31, 175–181. [Google Scholar]
- Ettinger, A.S.; Arbuckle, T.E.; Fisher, M.; Liang, C.L.; Davis, K.; Cirtiu, C.-M.; Bélanger, P.; LeBlanc, A.; Fraser, W.D. MIREC Study Group Arsenic Levels among Pregnant Women and Newborns in Canada: Results from the Maternal-Infant Research on Environmental Chemicals (MIREC) Cohort. Environ. Res. 2017, 153, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Just, A.C.; Adibi, J.J.; Rundle, A.G.; Calafat, A.M.; Camann, D.E.; Hauser, R.; Silva, M.J.; Whyatt, R.M. Urinary and Air Phthalate Concentrations and Self-Reported Use of Personal Care Products among Minority Pregnant Women in New York City. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2010, 20, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komorowicz, I.; Sajnóg, A.; Barałkiewicz, D. Total Arsenic and Arsenic Species Determination in Freshwater Fish by ICP-DRC-MS and HPLC/ICP-DRC-MS Techniques. Molecules 2019, 24, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankong, P.; Chalhoub, C.; Kienzl, N.; Goessler, W.; Francesconi, K.A.; Visoottiviseth, P.; Jankong, P.; Chalhoub, C.; Kienzl, N.; Goessler, W.; et al. Arsenic Accumulation and Speciation in Freshwater Fish Living in Arsenic-Contaminated Waters. Environ. Chem. 2007, 4, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazili, Z.; Whitehead, R.D.; Paladugula, N.; Pfeiffer, C.M. A High-Throughput LC-MS/MS Method Suitable for Population Biomonitoring Measures Five Serum Folate Vitamers and One Oxidation Product. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 4549–4560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazili, Z.; Pfeiffer, C.M. Measurement of Folates in Serum and Conventionally Prepared Whole Blood Lysates: Application of an Automated 96-Well Plate Isotope-Dilution Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method. Clin. Chem. 2004, 50, 2378–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, M.S.Q.; Muldoon, K.A.; Sheyholislami, H.; Behan, N.; Lamers, Y.; Rybak, N.; White, R.R.; Harvey, A.L.J.; Gaudet, L.M.; Smith, G.N.; et al. Impact of High-Dose Folic Acid Supplementation in Pregnancy on Biomarkers of Folate Status and 1-Carbon Metabolism: An Ancillary Study of the Folic Acid Clinical Trial (FACT). Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 113, 1361–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, R.; Robichaud, A.; Arbuckle, T.E.; Fraser, W.D.; MacFarlane, A.J. Total Folate and Unmetabolized Folic Acid in the Breast Milk of a Cross-Section of Canadian Women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 105, 1101–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warschausky, S. Wechsler Preschool and Primary Scale of Intelligence. In Encyclopedia of Clinical Neuropsychology; Kreutzer, J.S., DeLuca, J., Caplan, B., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 2690–2693. ISBN 978-0-387-79948-3. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, C.R.; Kamphaus, R.W. BASC-2 Parent Rating Scales—Child Behavior Assessment System for Children, Second Edition Clinical Report; NCS Pearson, Inc.: Bloomington, MN, USA, 2008; 42p. [Google Scholar]
- Constantino, J.; Scale, G.S. (SRS-2) Social Responsiveness Scale, 2nd ed.; Western Psychological Services: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. WHO Child Growth Standards: Head Circumference-for-Age, Arm Circumference-for-Age, Triceps Skinfold-for-Age and Subscapular Skinfold-for-Age: Methods and Development; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007; ISBN 978-92-4-154718-5. [Google Scholar]
- Schorr, I.J. United Nations National Household Survey Capability Programme. How to Weigh and Measure Children: Assessing the Nuritional Status of Young Children in Household Surveys; United Nationas Department of Technical Co-Operation for Development and Statistical Office: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Arbuckle, T.E.; Liang, C.L.; Fisher, M.; Caron, N.J.; Fraser, W.D.; The MIREC Study Group. Exposure to Tobacco Smoke and Validation of Smoking Status during Pregnancy in the MIREC Study. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2018, 28, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benowitz, N.L.; Bernert, J.T.; Caraballo, R.S.; Holiday, D.B.; Wang, J. Optimal Serum Cotinine Levels for Distinguishing Cigarette Smokers and Nonsmokers within Different Racial/Ethnic Groups in the United States between 1999 and 2004. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2009, 169, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totsika, V.; Sylva, K. The Home Observation for Measurement of the Environment Revisited. Child Adolesc. Ment. Health 1978, 9, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radloff, L.S. The CES-D Scale: A Self Repoort Depression Scale for Research in the General Population. Appl. Psychol. Meas. 1977, 1, 385–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Mari, R.; Oberski, D.L.; Vermunt, J.K. Bias-Adjusted Three-Step Latent Markov Modeling With Covariates. Struct. Equ. Model. Multidiscip. J. 2016, 23, 649–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermunt, J.K. Latent Class Modeling with Covariates: Two Improved Three-Step Approaches. Polit. Anal. 2010, 18, 450–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumley, T. Design-Based Inference in Vector Generalised Linear Models; GitHub: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Daly, L.E.; Kirke, P.N.; Molloy, A.; Weir, D.G.; Scott, J.M. Folate Levels and Neural Tube Defects. Implications for Prevention. JAMA 1995, 274, 1698–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Optimal Serum and Red Blood Cell Folate Concentrations in Women of Reproductive Age for Prevention of Neural Tube Defects. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2015, 64, 421. [Google Scholar]
- Arsenic Contamination of Groundwater in Bangladesh|British Geological Survey (BGS). Available online: https://www.bgs.ac.uk/arsenic/bangladesh/ (accessed on 1 July 2020).
- Almberg, K.S.; Turyk, M.E.; Jones, R.M.; Rankin, K.; Freels, S.; Graber, J.M.; Stayner, L.T. Arsenic in Drinking Water and Adverse Birth Outcomes in Ohio. Environ. Res. 2017, 157, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milton, A.H.; Smith, W.; Rahman, B.; Hasan, Z.; Kulsum, U.; Dear, K.; Rakibuddin, M.; Ali, A. Chronic Arsenic Exposure and Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes in Bangladesh. Epidemiology 2005, 16, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserman, G.A.; Liu, X.; Parvez, F.; Ahsan, H.; Factor-Litvak, P.; van Geen, A.; Slavkovich, V.; LoIacono, N.J.; Cheng, Z.; Hussain, I.; et al. Water Arsenic Exposure and Children’s Intellectual Function in Araihazar, Bangladesh. Environ. Health Perspect. 2004, 112, 1329–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaurock-Busch, E.; Amin, O.R.; Dessoki, H.H.; Rabah, T. Toxic Metals and Essential Elements in Hair and Severity of Symptoms among Children with Autism. Maedica 2012, 7, 38–48. [Google Scholar]
- Hamadani, J.D.; Tofail, F.; Nermell, B.; Gardner, R.; Shiraji, S.; Bottai, M.; Arifeen, S.E.; Huda, S.N.; Vahter, M. Critical Windows of Exposure for Arsenic-Associated Impairment of Cognitive Function in Pre-School Girls and Boys: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 40, 1593–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolins, M.; Ruchirawat, M.; Landrigan, P. The Developmental Neurotoxicity of Arsenic: Cognitive and Behavioral Consequences of Early Life Exposure. Ann. Glob. Health 2014, 80, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forns, J.; Fort, M.; Casas, M.; Cáceres, A.; Guxens, M.; Gascon, M.; Garcia-Esteban, R.; Julvez, J.; Grimalt, J.O.; Sunyer, J. Exposure to Metals during Pregnancy and Neuropsychological Development at the Age of 4 Years. Neurotoxicology 2014, 40, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parajuli, R.; Fujiwara, T.; Umezaki, M.; Shimizu-Furusawa, H.; Watanabe, C. Home Environment and Prenatal Exposure to Lead, Arsenic and Zinc on the Neurodevelopment of Six-Month-Old Infants Living in Chitwan Valley, Nepal. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2014, 41, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parajuli, R.P.; Umezaki, M.; Fujiwara, T.; Watanabe, C. Association of Cord Blood Levels of Lead, Arsenic, and Zinc and Home Environment with Children Neurodevelopment at 36 Months Living in Chitwan Valley, Nepal. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuji, J.S.; Garry, M.R.; Perez, V.; Chang, E.T. Low-Level Arsenic Exposure and Developmental Neurotoxicity in Children: A Systematic Review and Risk Assessment. Toxicology 2015, 337, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folic Acid Supplementation for the Prevention of Neural Tube Defects: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement|Guidelines|J.A.M.A|J.A.M.A Network. Available online: https://J.A.M.anetwork.com/journals/J.A.M.a/fullarticle/2596300 (accessed on 1 July 2020).
- Folic Acid Supplementation: An Evidence Review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force [Internet]—PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28151610/ (accessed on 1 July 2020).
- Updated Estimates of Neural Tube Defects Prevented by Mandatory Folic Acid Fortification—United States, 1995–2011. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/mm6401a2.htm (accessed on 1 July 2020).
- Colapinto, C.K.; O’Connor, D.L.; Dubois, L.; Tremblay, M.S. Prevalence and Correlates of Folic Acid Supplement Use in Canada. Health Rep. 2012, 23, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; He, Y.; Sun, X.; He, Y.; Li, Y.; Sun, C. Maternal High Folic Acid Supplement Promotes Glucose Intolerance and Insulin Resistance in Male Mouse Offspring Fed a High-Fat Diet. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 6298–6313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnaveni, G.V.; Veena, S.R.; Karat, S.C.; Yajnik, C.S.; Fall, C.H.D. Association between Maternal Folate Concentrations during Pregnancy and Insulin Resistance in Indian Children. Diabetologia 2014, 57, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghavan, R.; Zuckerman, B.; Hong, X.; Wang, G.; Ji, Y.; Paige, D.; DiBari, J.; Zhang, C.; Fallin, M.D.; Wang, X. Fetal and Infancy Growth Pattern, Cord and Early Childhood Plasma Leptin, and Development of Autism Spectrum Disorder in the Boston Birth Cohort. Autism Res. Off. J. Int. Soc. Autism Res. 2018, 11, 1416–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute of Medicine (US) Food and Nutrition Board. Dietary Reference Intakes: A Risk Assessment Model for Establishing Upper Intake Levels for Nutrients; The National Academies Collection: Reports funded by National Institutes of Health; National Academies Press (US): Washington, DC, USA, 1998; ISBN 978-0-309-06348-7. [Google Scholar]
- Gamble, M.V.; Liu, X.; Slavkovich, V.; Pilsner, J.R.; Ilievski, V.; Factor-Litvak, P.; Levy, D.; Alam, S.; Islam, M.; Parvez, F.; et al. Folic Acid Supplementation Lowers Blood Arsenic. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 86, 1202–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamble, M.V.; Liu, X.; Ahsan, H.; Pilsner, J.R.; Ilievski, V.; Slavkovich, V.; Parvez, F.; Levy, D.; Factor-Litvak, P.; Graziano, J.H. Folate, Homocysteine, and Arsenic Metabolism in Arsenic-Exposed Individuals in Bangladesh. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 1683–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamble, M.V.; Liu, X.; Ahsan, H.; Pilsner, J.R.; Ilievski, V.; Slavkovich, V.; Parvez, F.; Chen, Y.; Levy, D.; Factor-Litvak, P.; et al. Folate and Arsenic Metabolism: A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Folic Acid-Supplementation Trial in Bangladesh. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 84, 1093–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saravanabhavan, G.; Werry, K.; Walker, M.; Haines, D.; Malowany, M.; Khoury, C. Human Biomonitoring Reference Values for Metals and Trace Elements in Blood and Urine Derived from the Canadian Health Measures Survey 2007–2013. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2017, 220, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, C.V.; Lewin, M.; Ragin-Wilson, A.; Jones, R.; Jarrett, J.M.; Wallon, K.; Ward, C.; Hilliard, N.; Irvin-Barnwell, E. Characterization of Trace Elements Exposure in Pregnant Women in the United States, NHANES 1999–2016. Environ. Res. 2020, 183, 109208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.H.; Steinmaus, C.M. Health Effects of Arsenic and Chromium in Drinking Water: Recent Human Findings. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2009, 30, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moe, B.; Peng, H.; Lu, X.; Chen, B.; Chen, L.W.L.; Gabos, S.; Li, X.-F.; Le, X.C. Comparative Cytotoxicity of Fourteen Trivalent and Pentavalent Arsenic Species Determined Using Real-Time Cell Sensing. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 49, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, C.W. Low-Dose Arsenic: In Search of a Risk Threshold. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, A130–A134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahter, M. Mechanisms of Arsenic Biotransformation. Toxicology 2002, 181–182, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, B.A.; Selene, C.-H.; Chou, R.J.; Jones, D.L.; Sullivan Jr, W.; Chen, C.-J. Chapter 28—Arsenic. In Handbook on the Toxicology of Metals, 4th ed.; Nordberg, G.F., Fowler, B.A., Nordberg, M., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2015; pp. 581–624. ISBN 978-0-444-59453-2. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Lu, S.; Zhang, B.; Xia, W.; Liu, W.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wu, K.; Xu, S.; Li, Y. Maternal Arsenic Exposure and Birth Outcomes: A Birth Cohort Study in Wuhan, China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 236, 817–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, R.M.; Nermell, B.; Kippler, M.; Grandér, M.; Li, L.; Ekström, E.-C.; Rahman, A.; Lönnerdal, B.; Hoque, A.M.W.; Vahter, M. Arsenic Methylation Efficiency Increases during the First Trimester of Pregnancy Independent of Folate Status. Reprod. Toxicol. 2011, 31, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, M.R.; Shorvon, S.D. Heredity in Epilepsy: Neurodevelopment, Comorbidity, and the Neurological Trait. Epilepsy Behav. EB 2011, 22, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elrod, M.G.; Hood, B.S. Sleep Differences among Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders and Typically Developing Peers: A Meta-Analysis. J. Dev. Behav. Pediatr. JDBP 2015, 36, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadman, T.; Findon, J.; Eklund, H.; Hayward, H.; Howley, D.; Cheung, C.; Kuntsi, J.; Glaser, K.; Murphy, D.; Asherson, P. Six-Year Follow-up Study of Combined Type ADHD from Childhood to Young Adulthood: Predictors of Functional Impairment and Comorbid Symptoms. Eur. Psychiatry J. Assoc. Eur. Psychiatr. 2016, 35, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, D.R.; Yang, H.; Serena, G.; Sturgeon, C.; Ma, B.; Careaga, M.; Hughes, H.K.; Angkustsiri, K.; Rose, M.; Hertz-Picciotto, I.; et al. Differential Immune Responses and Microbiota Profiles in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders and Co-Morbid Gastrointestinal Symptoms. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2018, 70, 354–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKeown, C.; Hisle-Gorman, E.; Eide, M.; Gorman, G.H.; Nylund, C.M. Association of Constipation and Fecal Incontinence With Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Pediatrics 2013, 132, e1210–e1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvez, F.; Akhtar, E.; Khan, L.; Haq, M.A.; Islam, T.; Ahmed, D.; Eunus, H.M.; Hasan, A.R.; Ahsan, H.; Graziano, J.H.; et al. Exposure to Low-Dose Arsenic in Early Life Alters Innate Immune Function in Children. J. Immunotoxicol. 2019, 16, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, L.; Plötner, M.; In-Albon, T.; Stadelmann, S.; Schmitz, J. The Perspective Matters: A Multi-Informant Study on the Relationship Between Social-Emotional Competence and Preschoolers’ Externalizing and Internalizing Symptoms. Child Psychiatry Hum. Dev. 2019, 50, 1021–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.D.; Wilson, R.D.; Audibert, F.; Brock, J.-A.; Carroll, J.; Cartier, L.; Gagnon, A.; Johnson, J.-A.; Langlois, S.; Murphy-Kaulbeck, L.; et al. Pre-Conception Folic Acid and Multivitamin Supplementation for the Primary and Secondary Prevention of Neural Tube Defects and Other Folic Acid-Sensitive Congenital Anomalies. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Can. 2015, 37, 534–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakk, Z.; Tekle, F.B.; Vermunt, J.K. Estimating the Association between Latent Class Membership and External Variables Using Bias-Adjusted Three-Step Approaches. Sociol. Methodol. 2013, 43, 272–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Full Sample | Urinary DMA (μg As/L) | Total Plasma Folate a (nmol/L) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | N (%) | Median (1st Q, 3rd Q) | Median (1st Q, 3rd Q) |
| 364 (100) | 2.23 (1.53, 3.38) | 99 (81, 120) | |
| Maternal age (years) | |||
| <30 | 81 (22) | 2.00 (1.41, 3.01) | 91 (78, 113) |
| 30–<35 | 155 (43) | 2.25 (1.50, 3.25) | 100 (83, 118) |
| 35 | 128 (35) | 2.47 (1.59, 3.75) | 99 (81, 122) |
| Education b | |||
| High school or less | 12 (3) | 1.83 (1.83, 3.42) | 97 (84, 126) |
| Some college | 11 (3) | 2.31 (2.31, 3.46) | 91 (80, 198) |
| College/trade school | 85 (23) | 2.06 (2.06, 2.85) | 100 (79, 124) |
| University degree | 254 (70) | 2.37 (2.37, 3.70) | 100 (82, 120) |
| Maternal birth country | |||
| Canadian-born | 304 (84) | 2.19 (1.52, 3.19) | 99 (81, 118) |
| Foreign-born | 60 (16) | 2.48 (1.57, 4.18) | 97 (80, 122) |
| Household income | |||
| <$70,000 | 86 (24) | 2.06 (1.43, 3.17) | 95 (75, 111) |
| $70,000–<$100,000 | 117 (32) | 2.20 (1.53, 3.18) | 100 (80, 124) |
| ≥$100,000 | 161 (44) | 2.45 (1.59, 4.00) | 100 (83, 122) |
| Plasma cotinine c | |||
| Unexposed | 254 (70) | 2.20 (1.54, 3.40) | 99 (81, 119) |
| Second-hand smoking | 100 (27) | 2.43 (1.51, 3.61) | 101 (80, 120) |
| Active smoking | 10 (3) | 1.83 (1.43, 2.14) | 85 (78, 129) |
| Pre-pregnancy BMI | |||
| Normal/underweight | 226 (62) | 2.30 (1.56, 3.37) | 95 (80, 114) |
| Overweight | 79 (22) | 2.17 (1.54, 3.87) | 104 (82, 129) |
| Obese | 59 (16) | 2.12 (1.40, 2.96) | 99 (88, 119) |
| Parity | |||
| 0 | 174 (48) | 2.35 (1.59, 3.68) | 103 (82, 125) |
| 1 | 150 (41) | 2.12 (1.47, 3.18) | 98 (79, 114) |
| 2 | 40 (11) | 2.28 (1.49, 3.23) | 92 (78, 117) |
| Prenatal vitamin use | |||
| Yes | 326 (90) | 2.25 (1.55, 3.41) | 100 (82, 122) |
| No | 38 (10) | 1.86 (1.40, 3.27) | 83 (70, 97) |
| Folic acid supplementation d | |||
| 0–400 (μg/day) | 19 (5) | 3.77 (2.77, 5.56) | 80 (71, 106) |
| ≥400–1000 (μg/day) | 254 (70) | 2.14 (1.51, 3.18) | 98 (80, 118) |
| >1000 (μg/day) | 91 (25) | 2.43 (1.52, 3.35) | 104 (87, 122) |
| Child sex | |||
| Girls | 178 (49) | 2.26 (1.55, 3.19) | 100 (80, 123) |
| Boys | 186 (51) | 2.13 (1.49, 3.65) | 98 (81, 117) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Patti, M.A.; Kelsey, K.T.; MacFarlane, A.J.; Papandonatos, G.D.; Arbuckle, T.E.; Ashley-Martin, J.; Fisher, M.; Fraser, W.D.; Lanphear, B.P.; Muckle, G.; et al. Maternal Folate Status and the Relation between Gestational Arsenic Exposure and Child Health Outcomes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11332. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191811332
Patti MA, Kelsey KT, MacFarlane AJ, Papandonatos GD, Arbuckle TE, Ashley-Martin J, Fisher M, Fraser WD, Lanphear BP, Muckle G, et al. Maternal Folate Status and the Relation between Gestational Arsenic Exposure and Child Health Outcomes. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(18):11332. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191811332
Chicago/Turabian StylePatti, Marisa A., Karl T. Kelsey, Amanda J. MacFarlane, George D. Papandonatos, Tye E. Arbuckle, Jillian Ashley-Martin, Mandy Fisher, William D. Fraser, Bruce P. Lanphear, Gina Muckle, and et al. 2022. "Maternal Folate Status and the Relation between Gestational Arsenic Exposure and Child Health Outcomes" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 18: 11332. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191811332
APA StylePatti, M. A., Kelsey, K. T., MacFarlane, A. J., Papandonatos, G. D., Arbuckle, T. E., Ashley-Martin, J., Fisher, M., Fraser, W. D., Lanphear, B. P., Muckle, G., & Braun, J. M. (2022). Maternal Folate Status and the Relation between Gestational Arsenic Exposure and Child Health Outcomes. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(18), 11332. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191811332






