Analysis of Injury Patterns in Men’s Football between the English League and the Spanish League
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Instruments
2.4. Procedure
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Statistical Analysis
3.2. Identification of Temporal Patterns (T-Patterns)
3.2.1. General Description of T-Patterns
3.2.2. T-Patterns in Defenders
3.2.3. T-Patterns in Midfields
3.2.4. T-Patterns in Forwards
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitations and Future Perspectives
4.2. Practical Implications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leventer, L.; Eek, F.; Hofstetter, S.; Lames, M. Injury Patterns among Elite Football Players: A Media-based Analysis over 6 Seasons with Emphasis on Playing Position. Int. J. Sports Med. 2016, 37, 898–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tscholl, P.; O’Riordan, D.; Fuller, C.W.; Dvorak, J.; Gutzwiller, F.; Junge, A. Causation of injuries in female football players in top-level tournaments. Br. J. Sports Med. 2007, 41, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carling, C.; Orhant, E.; Legall, F. Match injuries in professional soccer: Inter-seasonal variation and effects of competition type, match congestion and positional role. Int. J. Sports Med. 2010, 31, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahínos, J.I.; González, C.; Salinero, J. Epidemiological study of the injuries, the processes of readaptation and prevention of the injury of anterior cruciate ligamento in the professional football. J. Sport Health Res. 2010, 2, 139–150. [Google Scholar]
- Ekstrand, J.; Hägglund, M.; Waldén, M. Injury incidence and injury patterns in professional football: The UEFA injury study. Br. J. Sports Med. 2011, 45, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Valenciano, A.; Ruiz-Pérez, I.; Garcia-Gómez, A.; Vera-Garcia, F.J.; De Ste Croix, M.; Myer, G.D.; Ayala, F. Epidemiology of injuries in professional football: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Sports Med. 2020, 54, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UEFA. Association Club Coefficients. Available online: https://www.uefa.com/nationalassociations/uefarankings/country/seasons/#/yr/2019 (accessed on 23 August 2022).
- Jain, N.; Murray, D.; Kemp, S.; Calder, J. Frequency and trends in foot and ankle injuries within an English Premier League Football Club using a new impact factor of injury to identify a focus for injury prevention. Foot Ankle Surg. 2014, 20, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riepenhof, H.; Lindenmeyer, A.; Bloch, H.; McAleer, S.; Delvescovo, R.; Flammini, V.; Bark, S.; Gille, J.; Oheim, R.; Kienast, B. Profifußball im europäischen Vergleich—Auswirkungen von Verletzungen. Sports Orthop. Traumatol. 2018, 34, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hägglund, M.; Waldén, M.; Bahr, R.; Ekstrand, J. Methods for epidemiological study of injuries to professional football players: Developing the UEFA model. Br. J. Sports Med. 2005, 39, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnason, A.; Sigurdsson, S.B.; Gudmundsson, A.; Holme, I.; Engebretsen, L.; Bahr, R. Risk Factors for Injuries in Football. Am. J. Sports Med. 2004, 32, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, G.; Barnes, C.A.; Portas, M.D. Factors associated with increased propensity for hamstring injury in English Premier League soccer players. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2010, 13, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hägglund, M.; Waldén, M.; Ekstrand, J. Risk factors for lower extremity muscle injury in professional soccer: The UEFA injury study. Am. J. Sports Med. 2013, 41, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benito del Pozo, L.; Ayán Pérez, C.; Revuelta Benzanilla, G.; Maestro Fernández, A.; Fernández Villa, T.; Martín Sánchez, V. Influence of the soccer players’ professional status on the frequency and severity of injuries: A comparative pilot study. Apunt. Med. l’Esport 2014, 49, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, R.R.; Fuller, C.C. A prospective epidemiological study of injuries in four English professional football clubs. Br. J. Sports Med. 1999, 33, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekstrand, J.; Hägglund, M.; Waldén, M. Epidemiology of muscle injuries in professional football (soccer). Am. J. Sports Med. 2011, 39, 1226–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, R.; Hulse, M.; Wilkinson, C.; Hodson, A.; Gibson, M. The association football medical research programme: An audit of injuries in professional football. Br. J. Sports Med. 2001, 35, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.; Jones, G.; Greig, N.; Bower, P.; Brown, J.; Hind, K.; Francis, P. Epidemiology of injury in English Professional Football players: A cohort study. Phys. Ther. Sport 2019, 35, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stubbe, J.H.; Van Beijsterveldt, A.M.M.C.; Van Der Knaap, S.; Stege, J.; Verhagen, E.A.; Van Mechelen, W.; Backx, F.J.G. Injuries in professional male soccer players in the Netherlands: A prospective cohort study. J. Athl. Train. 2015, 50, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belloch, L. The Epidemiology on Soccer: A Systematic Review. Rev. Int. Med. Cienc. Act. Física Deport. 2010, 10, 22–40. [Google Scholar]
- Noya-Salces, J.; Gómez-Carmona, P.M.; Gracia-Marco, L.; Moliner-Urdiales, D.; Sillero-Quintana, M. Epidemiology of injuries in First Division Spanish football. J. Sports Sci. 2014, 32, 1263–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, B.E.; Oberlander, M.A. An Examination of Injuries in Major League Soccer. Am. J. Sports Med. 2001, 29, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldén, M.; Hägglund, M.; Ekstrand, J. UEFA Champions League study: A prospective study of injuries in professional football during the 2001-2002 season. Br. J. Sports Med. 2005, 39, 542–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldén, M.; Hägglund, M.; Ekstrand, J. Football injuries during European Championships 2004–2005. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2007, 15, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Piqueras, P.; López, A.N.; Gonzalez-Rubio, J.; Arribas, E. How, When, and Where do Football Players get Injured?: A Descriptive Epidemiological Study on Male Professional Football Players in Spain for Four Seasons. Ann. Appl. Sport Sci. 2017, 5, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mallo, J.; González, P.; Veiga, S.; Navarro, E. Injury incidence in a spanish sub-elite professional football team: A prospective study during four consecutive seasons. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2011, 10, 731–736. [Google Scholar]
- Ekstrand, J. Keeping your top players on the pitch: The key to football medicine at a professional level. Br. J. Sports Med. 2013, 47, 723–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorborg, K.; Krommes, K.K.; Esteve, E.; Clausen, M.B.; Bartels, E.M.; Rathleff, M.S. Effect of specific exercise-based football injury prevention programmes on the overall injury rate in football: A systematic review and meta-analysis of the FIFA 11 and 11+ programmes. Br. J. Sports Med. 2017, 51, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anguera, M.T.; Blanco-Villaseñor, A.; Losada, J.L.; Portell, M. Guidelines for designing and conducting a study that applies observational methodology. UB J. Psychol. 2018, 48, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anguera, M.T.; Villaseñor, A.B.; Mendo, A.H.; López, J.L.L. Observational designs: Their suitability and application in sports psychology. Cuad. Psicol. Deport. 2011, 11, 63–76. [Google Scholar]
- Harriss, D.J.; Atkinson, G. Ethical Standards in Sport and Exercise Science Research: 2016 Update. Int. J. Sports Med. 2015, 36, 1121–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Psychological Association. Ethical principles of psychologists and code of conduct. Am. Psychol. 2002, 57, 1060–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto-Lage, I.; Argibay-González, J.C.; Paramés-González, A.; Pichel-Represas, A.; Bermúdez-Fernández, D.; Gutiérrez-Santiago, A. Patterns of Injury in the Spanish Football League Players. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 19, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horan, D.; Blake, C.; Hägglund, M.; Kelly, S.; Roe, M.; Delahunt, E. Injuries in elite-level women’s football—A two-year prospective study in the Irish Women’s National League. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2022, 32, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prieto-Lage, I.; Louzao-Neira, I.; Argibay-González, J.C.; Gutiérrez-Santiago, A. Injury patterns of professional footballers in the Spanish first division during the 2017–2018 seasons. Physiol. Behav. 2020, 224, 113052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibikunle, P.O.; Efobi, K.C.; Nwankwo, M.J.; Ani, K.U. Uefa model in identification of types, severity and mechanism of injuries among footballers in the nigerian women’s premier league. BMJ Open Sport Exerc. Med. 2019, 5, e000386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabin, B.; Camerino, O.; Anguera, M.T.; Castañer, M. Lince: Multiplatform Sport Analysis Software. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2012, 46, 4692–4694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañer, M.; Barreira, D.; Camerino, O.; Teresa Anguera, M.; Fernandes, T.; Hileno, R. Mastery in goal scoring, T-pattern detection, and polar coordinate analysis of motor skills used by Lionel Messi and Cristiano Ronaldo. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto-Lage, I.; Bermúdez-Fernández, D.; Paramés-González, A.; Gutiérrez-Santiago, A. Analysis of the corner kick in football in the main European leagues during the 2017-2018 season. Int. J. Perform. Anal. Sport 2021, 21, 611–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radicchi, E.; Mozzachiodi, M. Social talent scouting: A new opportunity for the identification of football players? Phys. Cult. Sport Stud. Res. 2016, 70, 28–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Villaseñor, A.; Anguera, M.T. Evaluación de la calidad en el registro del comportamiento: Aplicación a deportes de equipo. In Métodos Numéricos en Ciencias Sociales; Oñate, E., García-Sicilia, F., Ramallo, L., Eds.; Centro Internacional de Métodos Numéricos en Ingeniería: Barcelona, Spain, 2000; pp. 30–48. [Google Scholar]
- Mukaka, M.M. Statistics corner: A guide to appropriate use of correlation coefficient in medical research. Malawi Med. J. 2012, 24, 69–71. [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson, M.S.; Burgoon, J.K.; Casarrubea, M. Discovering Hidden Temporal Patterns in Behavior and Interaction: T-Pattern Detection and Analysis with THEME; Magnusson, M.S., Burgoon, J.K., Casarrubea, M., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-1-4939-3248-1. [Google Scholar]
- PatternVision Ltd. & Noldus Information Technology. Theme: Powerful Tool for Detection and Analysis of Hidden Patterns in Behavior. Reference Manual, Version 5.0; Noldus InformationTechnology bv: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2004; ISBN 90-74821-60-X. [Google Scholar]
- Borrie, A.; Jonsson, G.K.; Magnusson, M.S. Temporal pattern analysis and its applicability in sport: An explanation and preliminary data. J. Sport Sci. 2002, 20, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larruskain, J.; Lekue, J.A.; Diaz, N.; Odriozola, A.; Gil, S.M. A comparison of injuries in elite male and female football players: A five-season prospective study. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2018, 28, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woods, C.; Hawkins, R.D.; Maltby, S.; Hulse, M.; Thomas, A.; Hodson, A. The Football Association Medical Research Programme: An audit of injuries in professional football--analysis of hamstring injuries. Br. J. Sports Med. 2004, 38, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foreman, T.K.; Addy, T.; Baker, S.; Burns, J.; Hill, N.; Madden, T. Prospective studies into the causation of hamstring injuries in sport: A systematic review. Phys. Ther. Sport 2006, 7, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.A. Hamstring injuries: Risk assessment and injury prevention. Ann. Acad. Med. Singap. 2008, 37, 341–346. [Google Scholar]
- Croisier, J.L.; Ganteaume, S.; Binet, J.; Genty, M.; Ferret, J.M. Strength imbalances and prevention of hamstring injury in professional soccer players: A prospective study. Am. J. Sports Med. 2008, 36, 1469–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson, H.; Ekstrand, J.; Waldén, M.; Hägglund, M. Muscle injury rate in professional football is higher in matches played within 5 days since the previous match: A 14-year prospective study with more than 130 000 match observations. Br. J. Sports Med. 2018, 52, 1116–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falese, L.; Della Valle, P.; Federico, B. Epidemiology of football (soccer) injuries in the 2012/2013 and 2013/2014 seasons of the Italian Serie A. Res. Sports Med. 2016, 24, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson, H.; Ekstrand, J.; Waldén, M.; Hägglund, M. Muscle injury rates in professional football increase with fixture congestion: An 11-year follow-up of the UEFA Champions League injury study. Br. J. Sports Med. 2014, 48, 560–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekstrand, J.; Waldén, M.; Hägglund, M. A congested football calendar and the wellbeing of players: Correlation between match exposure of European footballers before the World Cup 2002 and their injuries and performers during that World Cup. Br. J. Sports Med. 2004, 38, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloomfield, J.; Polman, R.; O’Donoghue, P. Physical Demands of Different Positions in FA Premier League Soccer. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2007, 6, 63. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reilly, T. Motion analysis and physiological demands. In Science and Soccer; Williams, A.M., Reilly, T., Eds.; E & FN Spon: London, UK, 2003; pp. 59–72. [Google Scholar]
- Ferenczi, A.; Moraux, A.; Le Gall, F.; Thevenon, A.; Wieczorek, V. Relationship Between Spinal-Pelvic Sagittal Balance and Pelvic-Femoral Injuries in Professional Soccer Players. Orthop. J. Sports Med. 2020, 8, 2325967119894962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maderer, D.; Holtbrügge, D.; Schuster, T. Professional football squads as multicultural teams: Cultural diversity, intercultural experience, and team performance. Int. J. Cross Cult. Manag. 2014, 14, 215–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renshaw, A.; Goodwin, P.C. Injury incidence in a Premier League youth soccer academy using the consensus statement: A prospective cohort study. BMJ Open Sport Exerc. Med. 2016, 2, e000132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekstrand, J.; Waldén, M.; Hägglund, M. Hamstring injuries have increased by 4% annually in men’s professional football, since 2001: A 13-year longitudinal analysis of the UEFA Elite Club injury study. Br. J. Sports Med. 2016, 50, 731–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapp, R.M.; Spangenburg, E.E.; Hagberg, J.M. Trends in aggressive play and refereeing among the top five European soccer leagues. J. Sports Sci. 2018, 36, 1346–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorak, J.; Junge, A.; Chomiak, J.; Graf-Baumann, T.; Peterson, L.; Rosch, D.; Hodgson, R. Risk Factor Analysis for Injuries in Football Players. Am. J. Sports Med. 2000, 28, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Criteria | Category | Subcategory | Spain | Intra-Criteria | England | Intra-Criteria | Inter-Criteria | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | χ2 (p) | n | % | χ2 (p) | χ2 (p); Contin. Coef. | |||
| Location and type of injuries | |||||||||
| Injury location | Head, face or neck | 6 | 4.2 | 182.634 (0.000) | 10 | 7.4 | 80.881 (0.000) | 13.075 (0.109); 0.212 | |
| Upper limb | 6 | 4.2 | 9 | 6.7 | |||||
| Trunk-back | 1 | 0.7 | 5 | 3.7 | |||||
| Lumbopelvis | 18 | 12.7 | 8 | 5.9 | |||||
| Thigh | 63 | 44.4 | 48 | 35.6 | |||||
| Knee | 19 | 13.4 | 18 | 13.3 | |||||
| Calf | 13 | 9.2 | 13 | 9.6 | |||||
| Ankle | 15 | 10.6 | 24 | 17.8 | |||||
| Foot | 1 | 0.7 | 10 | 7.4 | |||||
| Injured leg | Right leg injuries | 59 | 41.5 | 0.392 (0.531) a | 61 | 45.2 | 1.309 (0.253) a | 1.595 (0.207); 0.082 a | |
| Left leg injuries | 66 | 46.5 | 49 | 36.3 | |||||
| No leg injury | 17 | 12.0 | 25 | 18.5 | |||||
| Type of injury | SPRAIN | 28 | 19.7 | 70.508 (0.000) b | 28 | 20.7 | 4.812 (0.186) b | 16.087 (0.001); 0.249 b | |
| Ankle sprain | 5 | 3.5 | 9 | 6.7 | |||||
| Knee sprain | 13 | 9.2 | 16 | 11.9 | |||||
| Acromioclavicular sprain | 2 | 1.4 | - | - | |||||
| Cruciate ligament rupture | 8 | 5.6 | 3 | 2.2 | |||||
| STRAIN | 71 | 50.0 | 39 | 28.9 | |||||
| Hamstring fibrillar rupture | 42 | 29.6 | 32 | 23.7 | |||||
| Quadricep fibrillar rupture | 9 | 6.3 | - | - | |||||
| Soleus-gastrocnemius fibrillar rupture | 9 | 6.3 | - | - | |||||
| Adductor fibrillar rupture | 11 | 7.7 | 7 | 5.2 | |||||
| CONTUSION | 13 | 9.2 | 27 | 20.0 | |||||
| Head, face or neck contusion | 2 | 1.4 | 3 | 2.2 | |||||
| Upper extremity contusion | - | - | 3 | 2.2 | |||||
| Trunk-back contusion | 1 | 0.7 | 5 | 3.7 | |||||
| Lower extremity contusion | 10 | 7.0 | 16 | 11.9 | |||||
| FRACTURE | 5 | 3.5 | 4 | 3.0 | |||||
| Head, face or neck fracture | 2 | 1.4 | 2 | 1.5 | |||||
| Upper extremity fracture | 2 | 1.4 | 1 | 0.7 | |||||
| Lower extremity fracture | 1 | 0.7 | 1 | 0.7 | |||||
| DISLOCATION | 2 | 1.4 | 5 | 3.7 | |||||
| Upper extremity dislocation | 2 | 1.4 | 5 | 3.7 | |||||
| OVERUSE | 14 | 9.9 | 23 | 17.0 | |||||
| Hamstring overuse | 7 | 4.9 | 12 | 8.9 | |||||
| Adductor overuse | 3 | 2.1 | - | - | |||||
| Quadriceps overuse | 2 | 1.4 | 2 | 1.5 | |||||
| Gastrocnemius overuse | 2 | 1.4 | 9 | 6.7 | |||||
| CONCUSSION | 1 | 0.7 | 5 | 3.7 | |||||
| OTHERS (wound, etc.) | 8 | 5.6 | 4 | 3.0 | |||||
| Not categorized injuries | 7 | 4.9 | - | - | |||||
| Meniscus Tear | 1 | 0.7 | 2 | 1.5 | |||||
| Achilles tendon rupture | - | - | 2 | 1.5 | |||||
| Intrinsic injury risk factors | |||||||||
| Age | <21 years | 1 | 0.7 | 17.149 (0.000) a | 2 | 1.5 | 25.549 (0.000) a | 9.038 (0.011); 0.179 a | |
| 21–25 years | 28 | 19.7 | 40 | 29.6 | |||||
| 26–30 years | 68 | 47.9 | 70 | 51.9 | |||||
| >30 years | 45 | 31.7 | 23 | 17.0 | |||||
| Position | Goalkeeper | 2 | 1.4 | 27.829 (0.000) a | 1 | 0.7 | 1.806 (0.405) a | 6.729 (0.035); 0.155 a | |
| Defender | 76 | 53.5 | 52 | 38.5 | |||||
| Midfielder | 30 | 21.1 | 41 | 30.4 | |||||
| Forward | 34 | 23.9 | 41 | 30.4 | |||||
| Player laterality | Right footed | 100 | 70.4 | 28.971 (0.000) a | 95 | 70.4 | 33.800 (0.000) a | 0.311 (0.577); 0.034 a | |
| Left footed | 37 | 26.1 | 30 | 22.2 | |||||
| Ambidextrous | 5 | 3.5 | 10 | 7.4 | |||||
| Extrinsic injury risk factors | |||||||||
| Moment in the season | Days 1–19 | 74 | 52.1 | 0.254 (0.615) | 101 | 74.8 | 33.252 (0.000) | 15.332 (0.000); 0.229 | |
| Days 20–38 | 68 | 47.9 | 34 | 25.2 | |||||
| Month | August | 4 | 2.8 | 18.704 (0.028) | 18 | 13.3 | 82.111 (0.000) | 37.047 (0.000); 0.343 | |
| September | 13 | 9.2 | 12 | 8.9 | |||||
| October | 19 | 13.4 | 17 | 12.6 | |||||
| November | 14 | 9.9 | 18 | 13.3 | |||||
| December | 19 | 13.4 | 40 | 29.6 | |||||
| January | 11 | 7.7 | 5 | 3.7 | |||||
| February | 13 | 9.2 | 6 | 4.4 | |||||
| March | 12 | 8.5 | 4 | 3.0 | |||||
| April | 24 | 16.9 | 13 | 9.6 | |||||
| May | 13 | 9.2 | 2 | 1.5 | |||||
| Stadium | Local | 72 | 50.7 | 0.028 (0.867) | 68 | 50.4 | 0.007 (0.931) | 0.003 (0.956); 0.003 | |
| Visitor | 70 | 49.3 | 67 | 49.6 | |||||
| Time | 1st half: 0′–45′ | 81 | 57.0 | 2.817 (0.093) | 53 | 39.3 | 6.230 (0.013) | 8.763 (0.003); 0.175 | |
| 0′–15′ | 29 | 20.4 | 6 | 4.4 | |||||
| 16′–30′ | 23 | 16.2 | 19 | 14.1 | |||||
| 31′–45′ + added time | 29 | 20.4 | 28 | 20.7 | |||||
| 2nd half: 46′–90′ | 61 | 43.0 | 82 | 60.7 | |||||
| 46′–60′ | 26 | 18.3 | 20 | 14.8 | |||||
| 61′–75′ | 18 | 12.7 | 34 | 25.2 | |||||
| 76′–90′ + added time | 17 | 12.0 | 28 | 20.7 | |||||
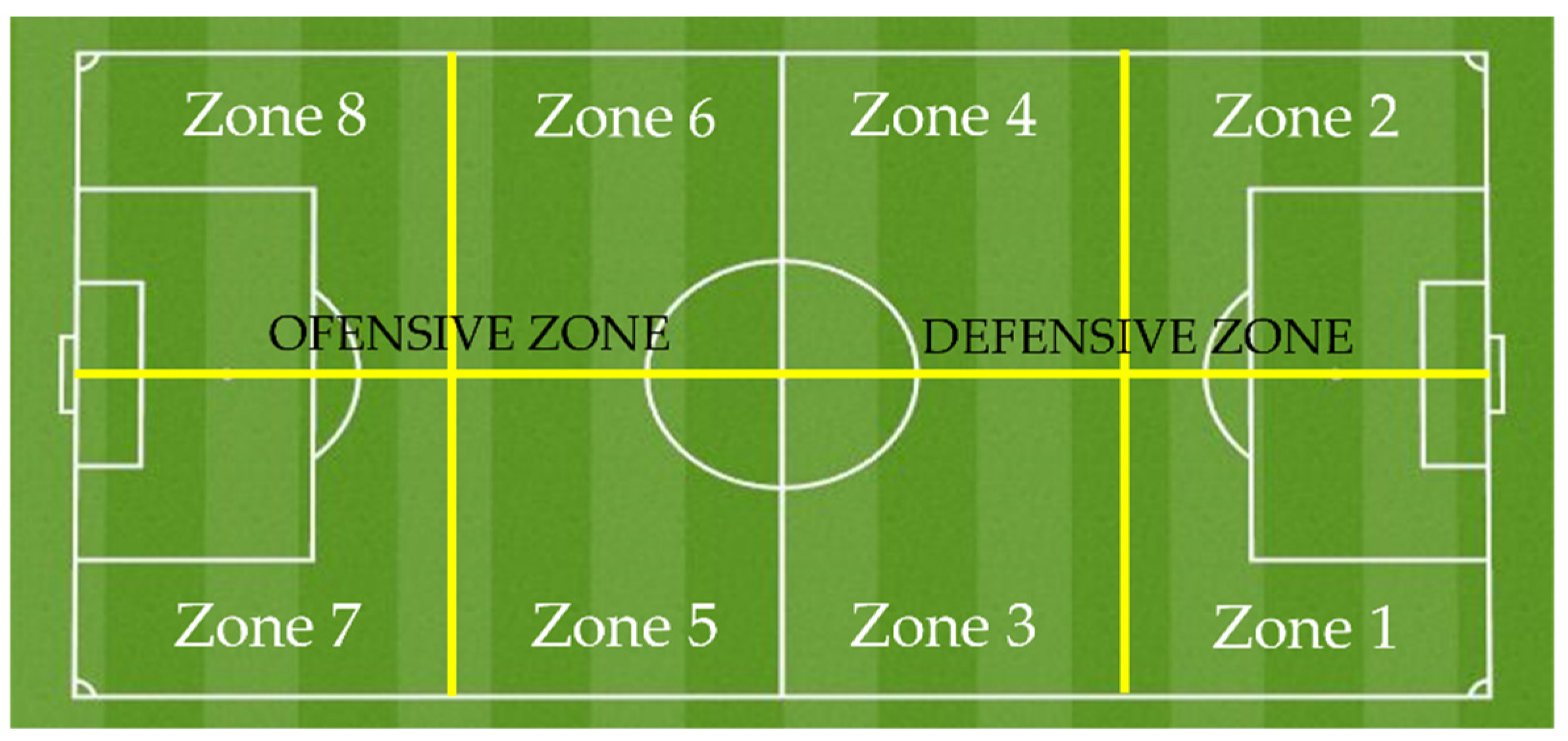
| Zone | Defensive zone | 77 | 54.2 | 1.014 (0.314) | 69 | 51.1 | 0.067 (0.796) | 0.269 (0.604); 0.031 | |
| Zone 1 | 27 | 19.0 | 16 | 11.9 | |||||
| Zone 2 | 21 | 14.8 | 20 | 14.8 | |||||
| Zone 3 | 14 | 9.9 | 12 | 8.9 | |||||
| Zone 4 | 15 | 10.6 | 22 | 16.3 | |||||
| Offensive zone | 65 | 45.8 | 66 | 48.9 | |||||
| Zone 5 | 16 | 11.3 | 13 | 9.6 | |||||
| Zone 6 | 17 | 12.0 | 18 | 13.3 | |||||
| Zone 7 | 17 | 12.0 | 16 | 11.9 | |||||
| Zone 8 | 15 | 10.6 | 18 | 13.3 | |||||
| Total accumulated minutes c | 0′–500′ | 30 | 21.1 | 19.690 (0.000) | 45 | 33.3 | 6.600 (0.086) | 18.496 (0.000); 0.250 | |
| 501′–1000′ | 30 | 21.1 | 33 | 24.4 | |||||
| 1001′–1500′ | 24 | 16.9 | 33 | 24.4 | |||||
| >1500′ | 58 | 40.8 | 24 | 17.8 | |||||
| Accumulated minutes after resting (>7 days) c | 0′–200′ | 64 | 45.1 | 39.014 (0.000) | 91 | 67.4 | 136.141 (0.000) | 17.887 (0.000); 0.246 | |
| 201′ –400′ | 40 | 28.2 | 26 | 19.3 | |||||
| 401′–600′ | 21 | 14.8 | 5 | 3.7 | |||||
| >600′ | 17 | 12.0 | 13 | 9.6 | |||||
| Cause of injuries | |||||||||
| Causative agent of the injury | Alone | 99 | 69.7 | 26.087 (0.000) a | 77 | 57.0 | 4.038 (0.044) a | 4.991 (0.025); 0.135 a | |
| Opponent | 39 | 27.5 | 54 | 40.0 | |||||
| Partner | 4 | 2.8 | 4 | 3.0 | |||||
| How the injury is caused | Sprint | 41 | 28.9 | 118.915 (0.000) | 25 | 18.5 | 63.667 (0.000) | 16.635 (0.164); 0.238 | |
| Dribbling | 4 | 2.8 | 3 | 2.2 | |||||
| Sliding | 4 | 2.8 | 4 | 3.0 | |||||
| Turning | 11 | 7.7 | 5 | 3.7 | |||||
| Tackled by other | 13 | 9.2 | 21 | 15.6 | |||||
| Shooting | 17 | 12.0 | 17 | 12.6 | |||||
| Falling | 6 | 4.2 | 2 | 1.5 | |||||
| Hit by ball | 2 | 1.4 | - | - | |||||
| Tackling other player | 18 | 12.7 | 20 | 14.8 | |||||
| Stretching | 6 | 4.2 | 5 | 3.7 | |||||
| Collision | 10 | 7.0 | 16 | 11.9 | |||||
| Kicked by other | 3 | 2.1 | 9 | 6.7 | |||||
| Unknown | 7 | 4.9 | 8 | 5.9 | |||||
| Spain (LaLiga) | England (Premier League) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 31+ | 26–30 | 21–25 | 20− | 31+ | 26–30 | 21–25 | 20− | |
| Players (n) | 74 | 142 | 107 | 8 | 55 | 166 | 104 | 11 | |
| Players (%) | 22.4 | 42.9 | 32.3 | 2.4 | 16.4 | 49.3 | 31.0 | 3.3 | |
| Injured players (n) | 45 | 68 | 28 | 1 | 23 | 70 | 40 | 2 | |
| Injured players (%) | 31.7 | 47.9 | 19.7 | 0.7 | 17.0 | 51.9 | 29.6 | 1.5 | |
| Difference (%) | +9.3 | +5.0 | −12.6 | −1.7 | +0.6 | +2.6 | −1.4 | −1.8 | |
| Position | Gk | Def | Mid | For | Gk | Def | Mid | For | |
| Players (n) | 34 | 134 | 92 | 105 | 26 | 139 | 105 | 92 | |
| Players (%) | 9.3 | 36.7 | 25.2 | 28.8 | 7.2 | 38.4 | 29.0 | 25.4 | |
| Injured players (n) | 2 | 76 | 30 | 34.0 | 1 | 52 | 41 | 41 | |
| Injured players (%) | 1.4 | 53.5 | 21.2 | 23.9 | 0.7 | 38.5 | 30.4 | 30.4 | |
| Difference (%) | −7.9 | +16.8 | −4.0 | −4.9 | −6.5 | +0.1 | +1.4 | +5.0 | |
| Ranking | Club | Points | Injuries (n) | Club | Points | Injuries (n) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Barcelona | 87 | 9 | Manchester City | 98 | 5 |
| 2 | Atlético de Madrid | 76 | 10 | Liverpool | 97 | 8 |
| 3 | Real Madrid | 68 | 11 | Chelsea | 72 | 8 |
| 4 | Valencia | 61 | 10 | Tottenham Hotspur | 71 | 9 |
| 5 | Getafe | 59 | 4 | Arsenal | 70 | 12 |
| 6 | Sevilla | 59 | 7 | Manchester United | 66 | 10 |
| 7 | Espanyol | 53 | 9 | Wolverhampton W. | 57 | 5 |
| 8 | Athletic Club | 53 | 7 | Everton | 54 | 4 |
| 9 | Real Sociedad | 50 | 14 | Leicester City | 52 | 3 |
| 10 | Real Betis | 50 | 8 | West Ham United | 52 | 7 |
| 11 | Deportivo Alavés | 50 | 6 | Watford | 50 | 4 |
| 12 | Eibar | 47 | 8 | Crystal Palace | 49 | 1 |
| 13 | Leganés | 45 | 4 | Newcastle United | 45 | 8 |
| 14 | Villarreal | 44 | 5 | Bournemouth | 45 | 0 |
| 15 | Levante | 44 | 9 | Burnley | 40 | 4 |
| 16 | Real Valladolid | 41 | 5 | Southampton | 39 | 9 |
| 17 | Celta de Vigo | 41 | 3 | Brighton & Hove Albion | 36 | 10 |
| 18 | Girona | 37 | 6 | Cardiff City | 34 | 11 |
| 19 | Huesca | 33 | 6 | Fulham | 26 | 7 |
| 20 | Rayo Vallecano | 32 | 2 | Huddersfield Town | 16 | 3 |
| Description of T-Patterns with Five Occurrences | LaLiga | Premier |
|---|---|---|
| N | N | |
| Total T-Patterns detected | 12,686 | 10,818 |
| Non-useful T-Patterns (do not meet selection criterion) | 11,655 (91.9%) | 10,414 (96.3%) |
| T-Patterns not excluded | 1031 (8.1%) | 404 (3.7%) |
| T-Patterns with strain, sprain, contusion or overuse | 4256 | 2254 |
| T-Patterns with defender, midfielder or forward | 3711 | 2761 |
| T-Patterns with defender and strain | 779 | 104 |
| T-Patterns with defender and sprain | 26 | 98 |
| T-Patterns with defender and contusion | 11 | 32 |
| T-Patterns with defender and overuse | 18 | 0 |
| T-Patterns with midfielder and strain | 121 | 9 |
| T-Patterns with midfielder and sprain | 7 | 6 |
| T-Patterns with midfielder and contusion | 0 | 17 |
| T-Patterns with midfielder and overuse | 0 | 62 |
| T-Patterns with forward and strain | 45 | 58 |
| T-Patterns with forward and sprain | 24 | 13 |
| T-Patterns with forward and contusion | 0 | 2 |
| T-Patterns with forward and overuse | 0 | 3 |
| Basic T-Pattern | O | Explanatory T-Pattern | O | L |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LaLiga | ||||
| Defender–strain * | 38 | ((defender (thigh strain))(hamstringfr (alone sprint))) | 14 | 6 |
| ((defender (thigh strain))(hamstringfr alone)) | 23 | 5 | ||
| * (18) years26_30; (14) more30 years; (21) firsthalf; (18) tam_more1500; | ||||
| Defender–sprain * | 11 | (((days1_19 firsthalf)(defender sprain)) opponent) | 5 | 5 |
| ((defender (knee sprain)) cruciateligrupt) | 5 | 4 | ||
| * (8) opponent; (5) tacklingother; (5) tam_more1500; (9) firsthalf; (6) knee | ||||
| Defender–contusion | 8 | (((days20_38 firsthalf)(defender contusion)) tam_more1500) | 5 | 5 |
| (defender (contusion opponent)) | 6 | 3 | ||
| Defender–overuse | 9 | ((((secondhalf defensivezone)(defender thigh))(rightfooted overuse))(hamstringoveruse alone)) | 5 | 8 |
| ((secondhalf (defensivezone defender))(leftleg (overuse alone))) | 6 | 6 | ||
| * (7) leftleg; (8) secondhalf; (8) alone; (7) thigh | ||||
| Midfielder–strain * | 18 | (((days1_19 firsthalf)(more30 years midfielder))(thigh (strain alone))) | 6 | 7 |
| (((firsthalf more30 years)(midfielder thigh)) strain) | 7 | 5 | ||
| (((firsthalf midfielder)(strain alone)) amar_0_200) | 7 | 5 | ||
| (midfielder (strain (alone sprint))) | 9 | 4 | ||
| * (8) more30 years; (16) alone; (12) firsthalf; (11) days1_19; (8) amar_0_200 | ||||
| Midfielder–sprain * | 7 | ((days1_19 offensivezone)(midfielder sprain)) | 5 | 4 |
| * (5) secondhalf; (5) opponent; (6) local; (6) days1_19 | ||||
| Midfielder–contusion | 0 | |||
| Midfielder–overuse | 0 | |||
| Forward–strain * | 13 | (offensivezone (((years26_30 forward)(thigh rightfooted))(strain (hamstringfr alone)))) | 5 | 8 |
| (((offensivezone forward)(thigh strain))(hamstringfr (alone amar_0_200))) | 7 | 7 | ||
| ((forward thigh)(strain hamstringfr)) | 9 | 4 | ||
| * (8) days1_19; (8) years26_30; (10) offensivezone; (5) october; (10) firsthalf; (7) thigh; (9) hamstringfibrillarruptu; (8) amar_0_200 | ||||
| Forward–sprain * | 10 | (days20_38 ((forward ankle)(sprain anklesprain))) | 5 | 5 |
| * (8) alone; (7) secondhalf; (6) anklesprain | ||||
| Forward–contusion | 0 | |||
| Forward–overuse | 0 | |||
| Premier League | ||||
| Defender–strain * | 16 | ((days1_19 defender) (thigh((rightfooted(strainhamstringfibrillarruptu)) (alone amar_0_200)))) | 10 | 8 |
| * (9) secondhalf; (11) 26_30 years; (9) rightleg; (15) alone | ||||
| Defender–sprain * | 13 | ((defender leftleg) (sprain opponent)) | 8 | 4 |
| * (10) days1_19; (9) knee; (10) leftleg; (10) opponent; | ||||
| Defender–contusion | 11 | (days1_19 ((defender contusion)(opponent amar_0_200))) | 8 | 5 |
| Defender–overuse | 0 | |||
| Midfielder–strain * | 8 | ((days20_38 midfielder)((thigh (strain hamstringfibrillarruptu)) alone)) | 5 | 6 |
| * (6) leftleg; (5) 26_30 years; (5) offensivezone; (6) secondhalf; (6) hamstringfibrillarruptu | ||||
| Midfielder–sprain * | 7 | ((days1_19 (26_30 years ((midfielder ankle)(rightleg sprain)))) anklesprain) | 5 | 7 |
| ((days1_19 midfielder)(sprain amar_0_200)) | 6 | 4 | ||
| * (5) opponent; (6) anklesprain; (6) rightleg | ||||
| Midfielder–contusion * | 10 | (secondhalf ((midfielder contusion)(lowerextremitycontusion opponent))) | 7 | 5 |
| * (10) opponent; (9) secondhalf; (8) lowerextremitycontusion | ||||
| Midfielder–overuse * | 13 | ((days1_19 secondhalf)((midfielder overuse)(soleusgastrocnemoveruse (alone amar_0_200)))) | 6 | 7 |
| (secondhalf ((midfielder overuse)(soleusgastrocnemoveruse alone))) | 7 | 5 | ||
| ((days1_19 secondhalf)((midfielder overuse)(alone amar_0_200))) | 7 | 6 | ||
| * (10) secondhalf; (9) days1_19; (7) 21_25 years; (8) amar_0_200 | ||||
| Forward–strain * | 14 | (offensivezone (forward ((thigh (strain hamstringfibrillarruptu)) alone))) | 10 | 6 |
| * (8) days1_19; (5) december; (7) sprint; (5) tam_1001_1500; (12) hamstringfibrillarruptu; (8) secondhalf | ||||
| Forward–sprain * | 8 | (secondhalf ((forward (ankle (sprain anklesprain))) amar_0_200)) | 6 | 6 |
| * (6) visitior; (6) rightleg; (7) secondhalf; (5) days20_38; (5) opponent | ||||
| Forward–contusion | 6 | ((offensivezone forward)(contusion opponent)) | 6 | 4 |
| Forward–overuse | 6 | ((offensivezone forward)(thigh (overuse alone))) | 5 | 5 |
| (days1_19 ((offensivezone forward)(overuse alone))) | 5 | 5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Argibay-González, J.C.; Vázquez-Estévez, C.; Gutiérrez-Santiago, A.; Paramés-González, A.; Reguera-López-de-la-Osa, X.; Prieto-Lage, I. Analysis of Injury Patterns in Men’s Football between the English League and the Spanish League. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11296. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191811296
Argibay-González JC, Vázquez-Estévez C, Gutiérrez-Santiago A, Paramés-González A, Reguera-López-de-la-Osa X, Prieto-Lage I. Analysis of Injury Patterns in Men’s Football between the English League and the Spanish League. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(18):11296. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191811296
Chicago/Turabian StyleArgibay-González, Juan Carlos, Christopher Vázquez-Estévez, Alfonso Gutiérrez-Santiago, Adrián Paramés-González, Xoana Reguera-López-de-la-Osa, and Iván Prieto-Lage. 2022. "Analysis of Injury Patterns in Men’s Football between the English League and the Spanish League" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 18: 11296. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191811296
APA StyleArgibay-González, J. C., Vázquez-Estévez, C., Gutiérrez-Santiago, A., Paramés-González, A., Reguera-López-de-la-Osa, X., & Prieto-Lage, I. (2022). Analysis of Injury Patterns in Men’s Football between the English League and the Spanish League. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(18), 11296. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191811296








