Diacutaneous Fibrolysis Intervention in Patients with Mild to Moderate Carpal Tunnel Syndrome May Avoid Severe Cases in Elderly: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Ethics
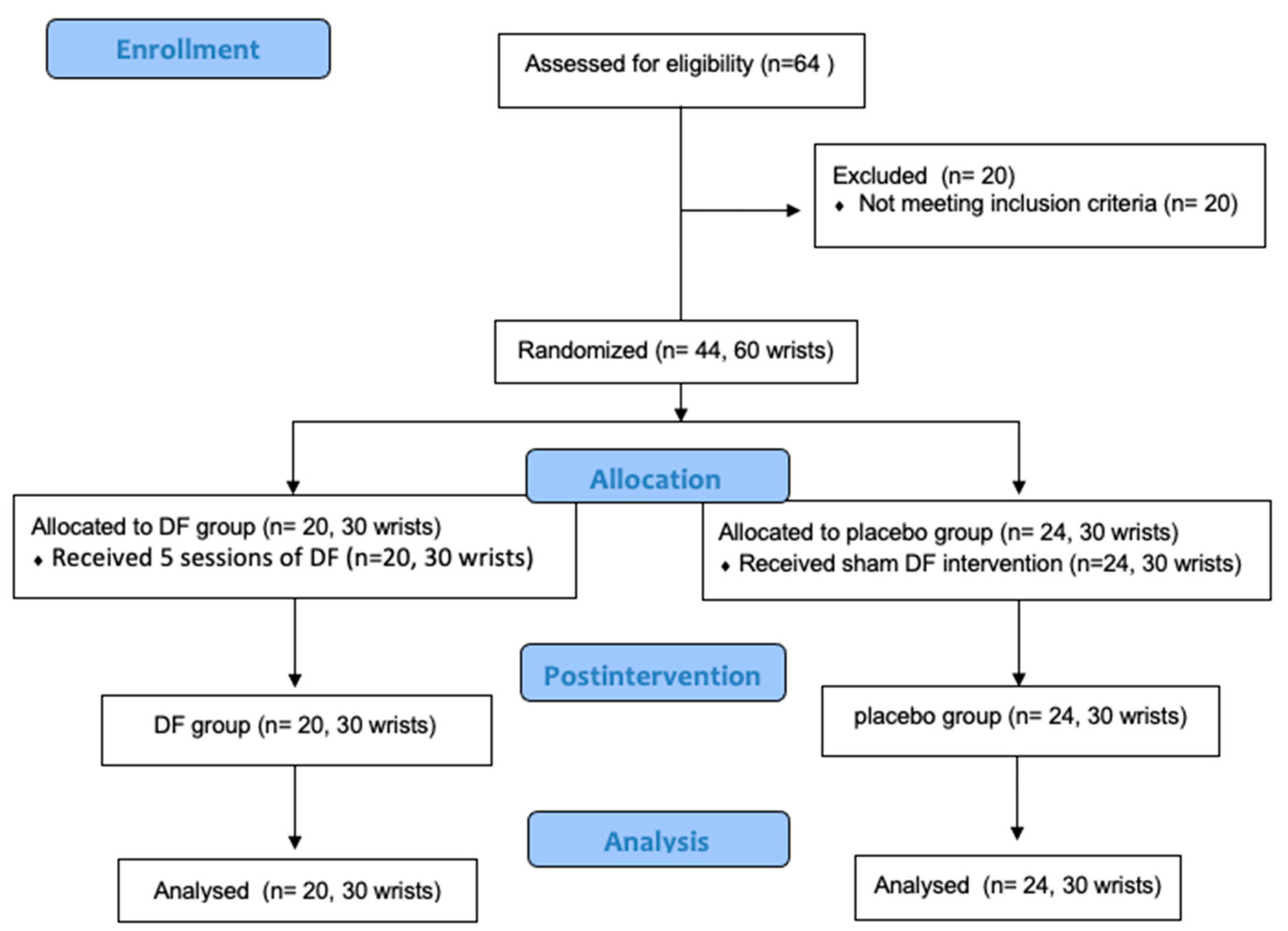
2.2. Participants
2.3. Randomization and Blinding
2.4. Interventions
2.5. Outcome Measures
2.5.1. Ultrasonography Variables: CSA and TCL Thickness
2.5.2. Numbness Intensity
2.5.3. Patient Global Impression Change
2.6. Sample Size
2.7. Statistical Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aroori, S.; Spence, R. Carpal tunnel syndrome. Ulst. Med. J. 2008, 77, 6–17. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, I.; Khan, W.S.; Goddard, N.; Smitham, P. Carpal tunnel syndrome: A review of the recent literature. Open Orthop. J. 2012, 6, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seror, P. Carpal tunnel sonography by the rheumatologist versus nerve conduction study by the neurologist. J. Rheumatol. 2001, 28, 2560. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lam, N.; Thurston, A. Association of obesity, gender, age and occupation with carpal tunnel syndrome. Aust. N. Z. J. Surg. 1998, 68, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeBlanc, K.E.; Cestia, W. Carpal tunnel syndrome. Am. Fam. Physician 2011, 83, 952–958. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.K.; Benstead, T.J. Symptoms experienced by patients with carpal tunnel syndrome. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 1997, 24, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabbagh, A.; MacDermid, J.C.; Yong, J.; Macedo, L.G.; Packham, T.L. Diagnosing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Diagnostic Test Accuracy of Scales, Questionnaires, and Hand Symptom Diagrams-A Systematic Review. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2020, 50, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanatani, T.; Fujioka, H.; Kurosaka, M.; Nagura, I.; Sumi, M. Delayed electrophysiological recovery after carpal tunnel release for advanced carpal tunnel syndrome: A two-year follow-up study. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2013, 30, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, M.W.; Masear, V.; Chung, K.C.; Maupin, K.; Andary, M.; Amadio, P.C.; Watters, W.C., III; Goldberg, M.J.; Haralson, R.H., II; Turkelson, C.M.; et al. American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Clinical Practice Guideline onDiagnosis of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2009, 91, 2478–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonagh, C.; Alexander, M.; Kane, D. The role of ultrasound in the diagnosis and management of carpal tunnel syndrome: A new paradigm. Rheumatology 2015, 54, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beekman, R.; Visser, L.H. Sonography in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome: A critical review of the literature. Muscle Nerve 2003, 27, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bueno-Gracia, E.; Haddad-Garay, M.; Tricas-Moreno, J.M.; Fanlo-Mazas, P.; Malo-Urries, M.; Estebanez-de-Miguel, E.; Hidalgo-Garcia, C. Diagnostic validity of ultrasonography in carpal tunnel syndrome. Rev Neurol. 2015, 61, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ettema, A.M.; Belohlavek, M.; Zhao, C.; Oh, S.H.; Amadio, P.C.; An, K.N. High-resolution ultrasound analysis of subsynovial connective tissue in human cadaver carpal tunnel. J. Orthop. Res. 2006, 24, 2011–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karabay, N.; Kayalar, M.; Ada, S. Sonographic assessment of transverse carpal ligament after open surgical release of the carpal tunnel. Acta Orthop. Et Traumatol. Turc. 2013, 47, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno-Gracia, E.; Ruiz-de-Escudero-Zapico, A.; Malo-Urriés, M.; Shacklock, M.; Estébanez-de-Miguel, E.; Fanlo-Mazas, P.; Caudevilla-Polo, S.; Jiménez-del-Barrio, S. Dimensional changes of the carpal tunnel and the median nerve during manual mobilization of the carpal bones. Musculoskelet. Sci. Pract. 2018, 36, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.L.; Li, Z.-M. Ultrasound assessment of transverse carpal ligament thickness: A validity and reliability study. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2012, 38, 982–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajika, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Yamamoto, A.; Kaneko, T.; Takagishi, K. Diagnostic Utility of Sonography and Correlation Between Sonographic and Clinical Findings in Patients With Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. J. Ultrasound Med. 2013, 32, 1987–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolovos, S.; Tsiotas, D. Ultrasonographic diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome: Introducing a new approach. Eu.r J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. 2016, 26, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhoon, J.T.; Juel, V.C.; Hobson-Webb, L.D. Median nerve ultrasound as a screening tool in carpal tunnel syndrome: Correlation of cross-sectional area measures with electrodiagnostic abnormality. Muscle Nerve 2012, 46, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagami, T.; Higashi, K.; Handa, H.; Minouchi, K.; Fujii, M.; Nishihara, K.; Kaji, R. Carpal tunnel syndrome: Clinical experience of 61 cases. No Shinkei Geka. Neurol. Surg. 1994, 22, 617–620. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari, F.S.; Della Sala, L.; Cozza, S.; Guazzi, G.; Belcapo, L.; Mariottini, A.; Bolognini, A.; Stefani, P. High-resolution ultrasonography in the study of carpal tunnel syndrome. Radiol Med. 1997, 93, 336–341. [Google Scholar]
- Bartolomé-Villar, A.; Pastor-Valero, T.; Fuentes-Sanz, A.; Varillas-Delgado, D.; García-de Lucas, F. Influence of the thickness of the transverse carpal ligament in carpal tunnel syndrome. Rev. Española De Cirugía Ortopédica Y Traumatol. (English Edition) 2018, 62, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-de-Las Peñas, C.; Ortega-Santiago, R.; Ana, I.; Martínez-Perez, A.; Díaz, H.F.S.; Martínez-Martín, J.; Pareja, J.A.; Cuadrado-Pérez, M.L. Manual Physical Therapy Versus Surgery for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Randomized Parallel-Group Trial. J. Pain 2015, 16, 1087–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, J.; Buchberger, D.J.; Carey-Loghmani, M.T.; Dougherty, P.E.; Greco, D.S.; Dishman, J.D. A pilot study comparing two manual therapy interventions for carpal tunnel syndrome. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2007, 30, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allampallam, K.; Chakraborty, J.; Bose, K.K.; Robinson, J. Explant culture, immunofluorescence and electron-microscopic study of flexor retinaculum in carpal tunnel syndrome. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 1996, 38, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yesil, M.; Bacakaoglu, A.K.; Dogan, M. Are myofibroblasts activated in idiopathic carpal tunnel syndrome? an immunohistochemical study. Jt. Dis. Relat. Surg. 2014, 25, 133–140. [Google Scholar]
- Blumenthal, S.; Herskovitz, S.; Verghese, J. Carpal tunnel syndrome in older adults. Muscle Nerve 2006, 34, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyšata, O.; Prochazka, A.; Kunc, P.; Kanta, M.; Ehler, E.; Yadollahi, M.; Vališ, M. Age delays the recovery of distal motor latency after carpal tunnel syndrome surgery. Acta Neurochir. 2014, 156, 1335–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, D.; Marshall, S.; Massy-Westropp, N. Non-surgical treatment (other than steroid injection) for carpal tunnel syndrome. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Barrio, S.J.; Gracia, E.B.; García, C.H.; de Miguel, E.E.; Moreno, J.T.; Marco, S.R.; Laita, L.C. Conservative treatment in patients with mild to moderate carpal tunnel syndrome: A systematic review. Neurologia 2018, 33, 590–601. [Google Scholar]
- López-de-Celis, C.; Barra-López, M.-E.; González-Rueda, V.; Bueno-Gracia, E.; Rodríguez-Rubio, P.-R.; Tricás-Moreno, J.-M. Effectiveness of diacutaneous fibrolysis for the treatment of chronic lateral epicondylalgia: A randomized clinical trial. Clin. Rehabil. 2018, 32, 644–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barra, M.E.; Lopez, C.; Fernandez, G.; Murillo, E.; Villar, E.; Raya, L. The immediate effects of diacutaneous fibrolysis on pain and mobility in patients suffering from painful shoulder: A randomized placebo-controlled pilot study. Clin Rehabil. 2011, 25, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, S.; Shizu, N.; Suzuki, Y.; Asai, T.; Yoshizawa, H. Changes in nerve root motion and intraradicular blood flow during an intraoperative straight-leg-raising test. Spine 2003, 28, 1427–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-de-Celis, C.; Pérez-Bellmunt, A.; Bueno-Gracia, E.; Fanlo-Mazas, P.; Zárate-Tejero, C.A.; Llurda-Almuzara, L.; Cadellans Arróniz, A.; Rodriguez-Rubio, P.R. Effect of diacutaneous fibrolysis on the muscular properties of gastrocnemius muscle. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0243225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, W.R.; Carvalho, M.M.; Mota, M.R.; Cipriano, G.F.B.; Mendes, F.A.D.S.; Diniz, L.R.; CJúnior, G.; Carregaro, R.L.; Durigan, J.L.Q. Diacutaneous fibrolysis versus passive stretching after articular immobilization: Muscle recovery and extracellular matrix remodelling. OA Med. Hypothesis 2013, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cadellans-Arróniz, A.; López-De-celis, C.; Pérez-Bellmunt, A.; Rodríguez-Sanz, J.; Llurda-Almuzara, L.; González-Rueda, V.; Rodríguez-Rubio, P.R. Effects of diacutaneous fibrolysis on passive neuromuscular response and mechanosensitivity in athletes with hamstring shortening: A randomized controlled trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Del-Barrio, S.; Estébanez-de-Miguel, E.; Bueno-Gracia, E.; Haddad-Garay, M.; Tricás-Moreno, J.M.; Hidalgo-García, C. Effects of diacutaneous fibrolysis in patients with mild to moderate symptomatic carpal tunnel syndrome: A randomized controlled trial. Clin. Rehabil. 2018, 32, 1645–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez del Barrio, S.; Ceballos-Laita, L.; Bueno-Gracia, E.; Rodríguez-Marco, S.; Haddad-Garay, M.; Estébanez-de-Miguel, E. Effects of Diacutaneous Fibrolysis on Mechanosensitivity, Disability, and Nerve Conduction Studies in Mild to Moderate Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Controlled Trial. Phys Ther. 2021, 101, pzaa222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jablecki, C.K.; Andary, M.T.; Floeter, M.K.; Miller, R.G.; Quartly, C.A.; Vennix, M.J.; Wilson, J.R. Practice parameter: Electrodiagnostic studies in carpal tunnel syndrome. Report of the American Association of Electrodiagnostic Medicine, American Academy of Neurology, and the American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. Neurology 2002, 58, 1589–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bland, J.D. A neurophysiological grading scale for carpal tunnel syndrome. Muscle Nerve 2000, 23, 1280–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno-Gracia, E.; Malo-Urriés, M.; Ruiz-de-Escudero-Zapico, A.; Rodríguez-Marco, S.; Jiménez-del-Barrio, S.; Shacklock, M.; Estébanez-de-Miguel, E.; Tricás-Moreno, J.M. Reliability of measurement of the carpal tunnel and median nerve in asymptomatic subjects with ultrasound. Musculoskelet. Sci. Pract. 2017, 32, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çatalbaş, N.; Akkaya, N.; Atalay, N.S.; Sahin, F. Ultrasonographic imaging of the effects of continuous, pulsed or sham ultrasound treatments on carpal tunnel syndrome: A randomized controlled study. J. Back Musculoskelet. Rehabil. 2018, 31, 981–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.H.; Kim, T.K.; Yoon, E.S.; Dhong, E.S. Postoperative morphologic analysis of carpal tunnel syndrome using high-resolution ultrasonography. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2005, 54, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrar, J.T.; Young, J.P.; LaMoreaux, L.; Werth, J.L.; Poole, R.M. Clinical importance of changes in chronic pain intensity measured on an 11-point numerical pain rating scale. Pain 2001, 94, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeschke, R.; Singer, J.; Guyatt, G.H. Measurement of health status. Ascertaining the minimal clinically important difference. Control. Clin. Trials 1989, 10, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamper, S.J.; Maher, C.G.; Mackay, G. Global rating of change scales: A review of strengths and weaknesses and considerations for design. J. Man. Manip. Ther. 2009, 17, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hashel, J.Y.; Rashad, H.M.; Nouh, M.R.; Amro, H.A.; Khuraibet, A.J.; Shamov, T.; Tzvetanov, P.; Rousseff, R.T. Sonography in carpal tunnel syndrome with normal nerve conduction studies. Muscle Nerve 2015, 51, 592–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyupek, F.; Yesildag, A.; Kutluhan, S.; Askin, A.; Ozden, A.; Uslusoy, G.A.; Demirci, S. Determining the effectiveness of various treatment modalities in carpal tunnel syndrome by ultrasonography and comparing ultrasonographic findings with other outcomes. Rheumatol. Int. 2012, 32, 3229–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, P.; Dilek, B.; Şahin, E.; Gülbahar, S.; Kizil, R. Ultrasonographic and clinical evaluation of additional contribution of kinesiotaping to tendon and nerve gliding exercises in the treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 48, 925–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volland, L.M.; Zhou, J.Y.; Barnes, R.F.; Kruse-Jarres, R.; Steiner, B.; Quon, D.V.; Bailey, C.; Hughes, T.H.; Moore, R.E.; Chang, E.Y.; et al. Development and Reliability of the Joint Tissue Activity and Damage Examination for Quantitation of Structural Abnormalities by Musculoskeletal Ultrasound in Hemophilic Joints. J. Ultrasound Med. 2019, 38, 1569–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno-Gracia, E.; Pérez-Bellmunt, A.; López-de-Celis, C.; Shacklock, M.; Salas-López, A.; Simon, M.; Álvarez-Díaz, P.; Tricás-Moreno, J.M. Dimensional changes of the carpal tunnel and median nerve during manual mobilization of the carpal bones-Anatomical study. Clin. Biomech. 2018, 59, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Günay, B.; Alp, A. The effectiveness of carpal bone mobilization accompanied by night splinting in idiopathic carpal tunnel syndrome. Turk. Fiz Tip Ve Rehabil. Derg. 2015, 61, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tal-Akabi, A.; Rushton, A. An investigation to compare the effectiveness of carpal bone mobilisation and neurodynamic mobilisation as methods of treatment for carpal tunnel syndrome. Man. Ther. 2000, 5, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mondelli, M.; Filippou, G.; Aretini, A.; Frediani, B.; Reale, F. Ultrasonography before and after surgery in carpal tunnel syndrome and relationship with clinical and electrophysiological findings. A new outcome predictor? Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2008, 37, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.Y.; Xiong, M.X.; Zhao, Y.; He, F.D.; Cheng, X.Q.; Wu, Y.Y.; Chen, K.; Lu, M. Comparison of the Clinical Effectiveness of Ultrasound-Guided Corticosteroid Injection with and without Needle Release of the Transverse Carpal Ligament in Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. Eur. Neurol. 2017, 78, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfonso, C.; Jann, S.; Massa, R.; Torreggiani, A. Diagnosis, treatment and follow-up of the carpal tunnel syndrome: A review. Neurol. Sci. 2010, 31, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de-la-Llave-Rincon, A.I.; Laguarta-Val, S.; Arroyo-Morales, M.; Martinez-Perez, A.; Pareja, J.A.; Fernandez-de-Las-Penas, C. Characterisation of pain in patients with carpal tunnel syndrome according to electromyographic severity criteria. Rev. Neurol. 2012, 54, 407–414. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, B.; Chen, K.; Zhu, X.; Ip, W.Y.; Andersen, L.L.; Page, P.; Wang, Y. Prevalence and risk factors of self-reported wrist and hand symptoms and clinically confirmed carpal tunnel syndrome among office workers in China: A cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caliandro, P.; La Torre, G.; Aprile, I.; Pazzaglia, C.; Commodari, I.; Tonali, P.; Padua, L. Distribution of paresthesias in Carpal Tunnel Syndrome reflects the degree of nerve damage at wrist. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2006, 117, 228–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, R.; Burkett, B. Massage therapy as an effective treatment for carpal tunnel syndrome. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2013, 17, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraska, A.; Chandler, C.; Edmiston-Schaetzel, A.; Franklin, G.; Calenda, E.L.; Enebo, B. Comparison of a targeted and general massage protocol on strength, function, and symptoms associated with carpal tunnel syndrome: A randomized pilot study. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2008, 14, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Field, T.; Diego, M.; Cullen, C.; Hartshorn, K.; Gruskin, A.; Hernandez-Reif, M.; Sunshine, W. Carpal tunnel syndrome symptoms are lessened following massage therapy. J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2004, 8, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padua, L.; Padua, R.; Aprile, I.; Pasqualetti, P.; Tonali, P. Multiperspective follow-up of untreated carpal tunnel syndrome: A multicenter study. Neurology 2001, 56, 1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padua, L.; Lo Monaco, M.; Aprile, I.; Paciello, N.; Tonali, P.; Padua, R.; Nazzaro, M. Natural history of carpal tunnel syndrome according to the neurophysiological classification. Ital. J. Neurol. Sci. 1998, 19, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Corredor, F.; Enríquez, F.; Díaz-Ruíz, J.; Calambas, N. Natural evolution of carpal tunnel syndrome in untreated patients. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2008, 119, 1373–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Features | DF Group n = 20 (30 Wrists) | Sham Group n = 24 (30 Wrists) | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 44.17 (10.00) | 48.9 (8.69) | p = 0.063 a |
| Sex (female/male) | 24/6 | 26/4 | p = 0.731 b |
| Duration of suffering (months) | 24.43 (22.78) | 27.77 (37.73) | p = 0.346 c |
| Body Mass Index (BMI) (Kg/m2) | 24.76 (2.8) | 25.84 (2.92) | p = 0.203 a |
| Work activity (outside home) Active/Not working | 28/2 | 27/3 | p = 0.891 b |
| Use wrist in sports activity Yes/No | 8/22 | 5/25 | p = 0.298 b |
| Wrist circumference (cm) (mean and SD) | 16.00 (1.25) | 16.05 (1.02) | p = 0.731 a |
| Outcomes | Baseline | End of Treatment | Within-Group Changes (95%IC) | Within-Group Effect Sizes | Between-Group p-Values | Between-Group Effect Sizes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VAS Numbness (0–10) | ||||||
| DF group | 3.7 (2.64) | 0.23 (0.54) | 3.47 (2.50–4.44) | 1.8 | <0.01 | 1.46 |
| Sham group | 2.95 (2.2) | 2.87 (2.5) | 0.08 (−0.97–1.1) | 0.0 | ||
| CSA (mm2) | ||||||
| DF group | 9.3 (1.4) | 8.8 (1.5) | 0.45 (0.05–0.86) | 0.34 | <0.01 | 0.70 |
| Sham group | 9.7 (1.0) | 9.7 (1.0) | −0.02 (−0.22–0.18) | −0.2 | ||
| Thickness TCL (mm) | ||||||
| DF group | 22.0 (0.02) | 20.0 (1.6) | 0.4 (0.6–2.1) | 1.0 | <0.03 | 0.89 |
| Sham group | 21.3 (0.01) | 21.3 (1.3) | −0.28 (−0.57–0.02) | −0.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiménez-del-Barrio, S.; Ceballos-Laita, L.; Bueno-Gracia, E.; Rodríguez-Marco, S.; Caudevilla-Polo, S.; Estébanez-de-Miguel, E. Diacutaneous Fibrolysis Intervention in Patients with Mild to Moderate Carpal Tunnel Syndrome May Avoid Severe Cases in Elderly: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10983. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191710983
Jiménez-del-Barrio S, Ceballos-Laita L, Bueno-Gracia E, Rodríguez-Marco S, Caudevilla-Polo S, Estébanez-de-Miguel E. Diacutaneous Fibrolysis Intervention in Patients with Mild to Moderate Carpal Tunnel Syndrome May Avoid Severe Cases in Elderly: A Randomized Controlled Trial. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(17):10983. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191710983
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiménez-del-Barrio, Sandra, Luis Ceballos-Laita, Elena Bueno-Gracia, Sonia Rodríguez-Marco, Santos Caudevilla-Polo, and Elena Estébanez-de-Miguel. 2022. "Diacutaneous Fibrolysis Intervention in Patients with Mild to Moderate Carpal Tunnel Syndrome May Avoid Severe Cases in Elderly: A Randomized Controlled Trial" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 17: 10983. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191710983
APA StyleJiménez-del-Barrio, S., Ceballos-Laita, L., Bueno-Gracia, E., Rodríguez-Marco, S., Caudevilla-Polo, S., & Estébanez-de-Miguel, E. (2022). Diacutaneous Fibrolysis Intervention in Patients with Mild to Moderate Carpal Tunnel Syndrome May Avoid Severe Cases in Elderly: A Randomized Controlled Trial. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(17), 10983. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191710983






