Reliability and Validity of Mini-Balance Evaluation System Test in Type 2 Diabetic Patients with Peripheral Neuropathy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
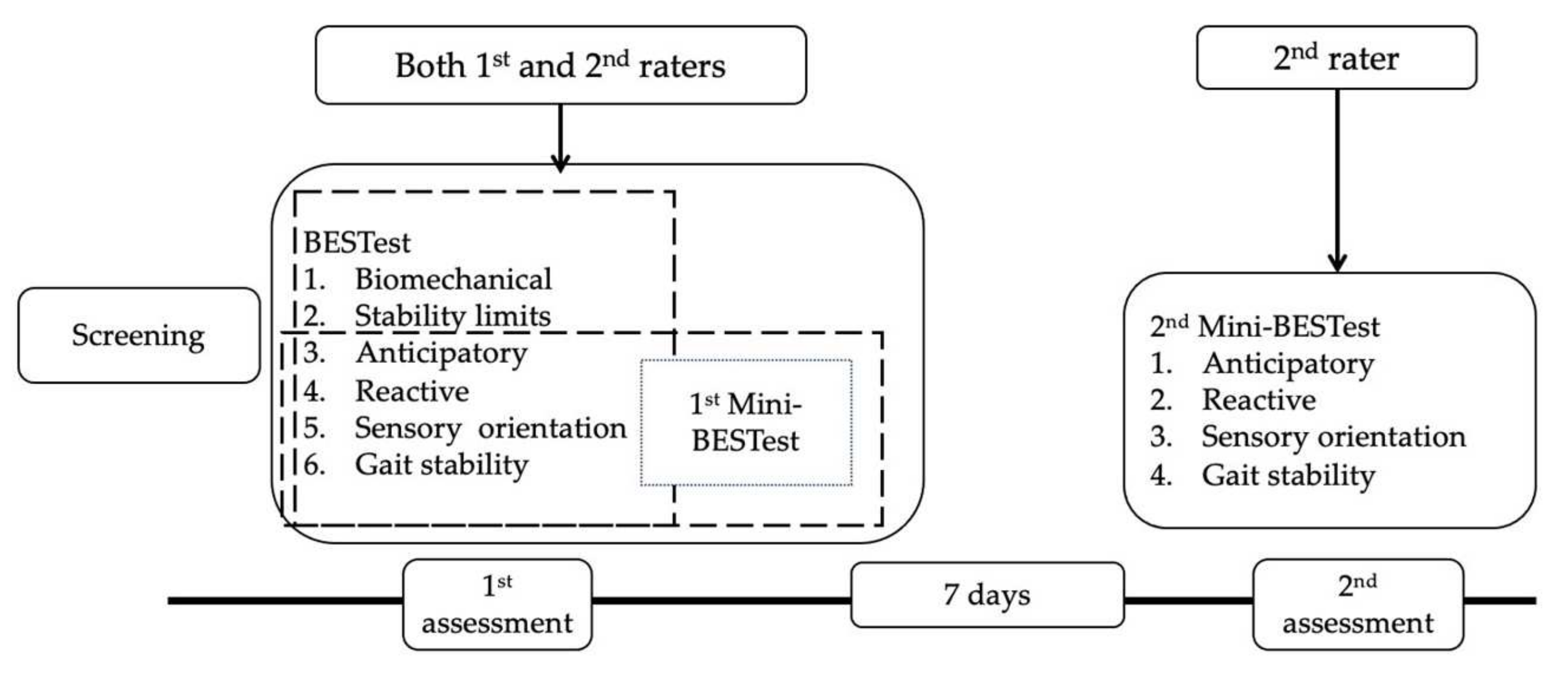
2.3. Procedures
2.4. Sample Size
2.5. Material and Assessment Tools
2.5.1. Balance Evaluation System Test (BESTest)
2.5.2. Mini-Balance Evaluation System Test (Mini-BESTest)
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saeedi, P.; Petersohn, I.; Salpea, P.; Malanda, B.; Karuranga, S.; Unwin, N.; Colagiuri, S.; Guariguata, L.; Motala, A.A.; Ogurtsova, K.; et al. Global and Regional Diabetes Prevalence Estimates for 2019 and Projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th Edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 157, 107843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Magliano, D.J.; Zimmet, P.Z. The Worldwide Epidemiology of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus—Present and Future Perspectives. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2012, 8, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfaye, S.; Selvarajah, D. Advances in the Epidemiology, Pathogenesis and Management of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy. Diabetes/Metab. Res. Rev. 2012, 28, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Win, M.M.T.M.; Fukai, K.; Nyunt, H.H.; Hyodo, Y.; Linn, K.Z. Prevalence of Peripheral Neuropathy and Its Impact on Activities of Daily Living in People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Nurs. Health Sci. 2019, 21, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takakusaki, K. Functional Neuroanatomy for Posture and Gait Control. J. Mov. Disord. 2017, 10, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Prevention National Diabetes Fact Sheet: National Estimates and General Information on Diabetes and Prediabetes in the United States. 2010. Available online: http://www.caldiabetes.org/content_display.cfm?FontSize=normal&contentID=562&CategoriesID=31 (accessed on 14 November 2020).
- Gregg, E.W.; Sorlie, P.; Paulose-Ram, R.; Gu, Q.; Eberhardt, M.S.; Wolz, M.; Burt, V.; Curtin, L.; Engelgau, M.; Geiss, L. Prevalence of Lower-Extremity Disease in the US Adult Population ≥ 40 Years of Age with and without Diabetes: 1999–2000 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 1591–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.-B.; Kim, D.J.; Noh, J.; Yoo, J.; Moon, J.-W. Comparison of Balance Ability Between Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and With and Without Peripheral Neuropathy. PM R 2014, 6, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timar, B.; Timar, R.; Gaiță, L.; Oancea, C.; Levai, C.; Lungeanu, D. The Impact of Diabetic Neuropathy on Balance and on the Risk of Falls in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Cross-Sectional Study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Hussain, E.; Singla, D.; Verma, S.; Ali, K. Balance Training in Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: A Narrative Review. JSM Diabetol. Manag. 2017, 2, 1002. [Google Scholar]
- Roman de Mettelinge, T.; Cambier, D.; Calders, P.; Van Den Noortgate, N.; Delbaere, K. Understanding the Relationship between Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Falls in Older Adults: A Prospective Cohort Study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, J.K. Factors Associated with Falls in Older Patients with Diffuse Polyneuropathy. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2002, 50, 1767–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, A.V.; Hillier, T.A.; Sellmeyer, D.E.; Resnick, H.E.; Gregg, E.; Ensrud, K.E.; Schreiner, P.J.; Margolis, K.L.; Cauley, J.A.; Nevitt, M.C. Older Women with Diabetes Have a Higher Risk of Falls: A Prospective Study. Diabetes Care 2002, 25, 1749–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilling, L.M.; Darawil, K.; Britton, M. Falls as a Complication of Diabetes Mellitus in Older People. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2006, 20, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jernigan, S.D.; Pohl, P.S.; Mahnken, J.D.; Kluding, P.M. Diagnostic Accuracy of Fall Risk Assessment Tools in People with Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy. Phys. Ther. 2012, 92, 1461–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Horak, F.B.; Wrisley, D.M.; Frank, J. The Balance Evaluation Systems Test (BESTest) to Differentiate Balance Deficits. Phys. Ther. 2009, 89, 484–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, C.J.; Knight, T.; Binns, E.; Ihaka, B.; O’Brien, D. Clinical Measures of Balance in People with Type Two Diabetes: A Systematic Literature Review. Gait Posture 2017, 58, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franchignoni, F.; Horak, F.; Godi, M.; Nardone, A.; Giordano, A. Using Psychometric Techniques to Improve the Balance Evaluation Systems Test: The Mini-BESTest. J. Rehabil. Med. 2010, 42, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibley, K.M.; Beauchamp, M.K.; Van Ooteghem, K.; Straus, S.E.; Jaglal, S.B. Using the Systems Framework for Postural Control to Analyze the Components of Balance Evaluated in Standardized Balance Measures: A Scoping Review. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2015, 96, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horak, F.B. Postural Orientation and Equilibrium: What Do We Need to Know about Neural Control of Balance to Prevent Falls? Age Ageing 2006, 35, ii7–ii11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, A.; Silva, A.; Oliveira, A.; Cruz, J.; Machado, A.; Jácome, C. Validity and Relative Ability of 4 Balance Tests to Identify Fall Status of Older Adults with Type 2 Diabetes. J. Geriatr. Phys. Ther. 2017, 40, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, W.H.; Pop-Busui, R.; Braffett, B.H.; Martin, C.L.; Cleary, P.A.; Albers, J.W.; Feldman, E.L.; DCCT/EDIC Research Group. Use of the Michigan Neuropathy Screening Instrument as a Measure of Distal Symmetrical Peripheral Neuropathy in Type 1 Diabetes: Results from the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications. Diabet. Med. 2012, 29, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatchawan, U.; Eungpinichpong, W.; Plandee, P.; Yamauchi, J. Effects of Thai Foot Massage on Balance Performance in Diabetic Patients with Peripheral Neuropathy: A Randomized Parallel-Controlled Trial. Med. Sci. Monit. Basic Res. 2015, 21, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leddy, A.L.; Crowner, B.E.; Earhart, G.M. Utility of the Mini-BESTest, BESTest, and BESTest Sections for Balance Assessments in Individuals with Parkinson Disease. J. Neurol. Phys. Ther. 2011, 35, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, L.; Horak, F. On the Mini-BESTest: Scoring and the Reporting of Total Scores. Phys. Ther. 2013, 93, 571–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunnally, J.C. Psychometric Theory, 2nd ed.; McGraw: New York, NY, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Nurosis, M. Statistical Data Analysis; SPSS Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson, G.; Nevill, A.M. Statistical Methods for Assessing Measurement Error (Reliability) in Variables Relevant to Sports Medicine. Sports Med. 1998, 26, 217–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myles, P.S.; Cui, J.I. Using the Bland–Altman Method to Measure Agreement with Repeated Measures. Br. J. Anaesth. 2007, 99, 309–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godi, M.; Franchignoni, F.; Caligari, M.; Giordano, A.; Turcato, A.M.; Nardone, A. Comparison of Reliability, Validity, and Responsiveness of the Mini-BESTest and Berg Balance Scale in Patients With Balance Disorders. Phys. Ther. 2013, 93, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portney, L.G.; Watkins, M.P. Foundations of Clinical Research: Applications to Practice; Pearson & Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2009; Volume 892. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, A.C.M.; Pang, M.Y.C. Assessing Balance Function in Patients with Total Knee Arthroplasty. Phys. Ther. 2015, 95, 1397–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lampropoulou, S.I.; Billis, E.; Gedikoglou, I.A.; Michailidou, C.; Nowicky, A.V.; Skrinou, D.; Michailidi, F.; Chandrinou, D.; Meligkoni, M. Reliability, Validity and Minimal Detectable Change of the Mini-BESTest in Greek Participants with Chronic Stroke. Physiother. Theory Pract. 2019, 35, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, C.S.L.; Liao, L.-R.; Chung, R.C.K.; Pang, M.Y.C. Psychometric Properties of the Mini-Balance Evaluation Systems Test (Mini-BESTest) in Community-Dwelling Individuals with Chronic Stroke. Phys. Ther. 2013, 93, 1102–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyama, C.; Otaka, Y.; Onitsuka, K.; Takagi, H.; Tan, E.; Otaka, E. Reliability and Validity of the Japanese Version of the Mini-Balance Evaluation Systems Test in Patients with Subacute Stroke. Prog. Rehabil. Med. 2018, 3, 20180015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viveiro, L.A.P.; Gomes, G.C.V.; Bacha, J.M.R.; Carvas Junior, N.; Kallas, M.E.; Reis, M.; Jacob Filho, W.; Pompeu, J.E. Reliability, Validity, and Ability to Identity Fall Status of the Berg Balance Scale, Balance Evaluation Systems Test (BESTest), Mini-BESTest, and Brief-BESTest in Older Adults Who Live in Nursing Home. J. Geriatr. Phys. Ther. 2019, 42, E45–E54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Löfgren, N.; Lenholm, E.; Conradsson, D.; Ståhle, A.; Franzén, E. The Mini-BESTest—A Clinically Reproducible Tool for Balance Evaluations in Mild to Moderate Parkinson’s Disease? BMC Neurol. 2014, 14, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahl, S.S.H.; Jørgensen, L. Intra-and Inter-Rater Reliability of the Mini-Balance Evaluation Systems Test in Individuals with Stroke. Int. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2013, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Marques, A.; Almeida, S.; Carvalho, J.; Cruz, J.; Oliveira, A.; Jácome, C. Reliability, Validity, and Ability to Identify Fall Status of the Balance Evaluation Systems Test, Mini–Balance Evaluation Systems Test, and Brief–Balance Evaluation Systems Test in Older People Living in the Community. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2016, 97, 2166–2173.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinsongkram, B.; Chaikeeree, N.; Saengsirisuwan, V.; Viriyatharakij, N.; Horak, F.B.; Boonsinsukh, R. Reliability and Validity of the Balance Evaluation Systems Test (BESTest) in People with Subacute Stroke. Phys. Ther. 2014, 94, 1632–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Carlo, S.; Bravini, E.; Vercelli, S.; Massazza, G.; Ferriero, G. The Mini-BESTest: A Review of Psychometric Properties. Int. J. Rehabil. Res. 2016, 39, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristics | n (%) | Mean ± SD |
|---|---|---|
| Gender, n (%) | ||
| Male | 4 (9.1) | |
| Female | 40 (90.9) | |
| Age (years) | 56.61 ± 7.70 | |
| ≥60 years | 16 (36.3) | |
| <60 years | 28 (63.6) | |
| Marital Status | ||
| Single | 6 (13.6) | |
| Married | 20 (45.5) | |
| Divorced | 2 (4.5) | |
| Widowed | 16 (36.4) | |
| Education, n (%) | ||
| Primary | 7 (15.9) | |
| Secondary | 21 (47.7) | |
| Higher | 13 (29.5) | |
| Graduate | 3 (6.8) | |
| Occupation | ||
| Unemployed | 29 (65.9) | |
| Employed (e.g., government, business, worker, etc.) | 15 (34.1) | |
| Weight (kg) | 57.57 ± 10.68 | |
| Height (m) | 1.56 ± 0.06 | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.77 ± 4.39 | |
| Smoking | 3 (6.8) | |
| Alcohol drinking | 3 (6.8) | |
| Duration of DM (years) | 8.43 ± 3.30 | |
| Blood sugar level (mg/dL) | 142 ± 39.52 | |
| Drugs controlling DM (how many tablets per time) | 3.34 ± 0.99 | |
| HbA1C (mg/dL) | 8.34 ± 2.01 | |
| MNSI Questionnaires; mean ± SD | 4.16 ± 2.07 | |
| <4 | 17 (38.6) | |
| ≥4 | 27 (61.4) | |
| MNSI Physical assessment | 3.09 ± 0.66 | |
| Other underlying comorbidities (e.g., hypertension, heart disease, etc.) | 37 (84.1) | |
| History of foot ulcer (no ulcer at present) n (%) | 2 (4.5) |
| Item | Single Item Agreement (Weighted Kappa) | Item-Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inter-Rater | Test-Retest | ||
| 1 | - | - | 0.000 |
| 2 | 0.723 | 0.906 | 0.522 |
| 3 | 0.848 | 0.729 | 0.404 |
| 4 | 0.596 | 0.585 | 0.267 |
| 5 | 0.860 | 0.665 | 0.529 |
| 6 | 0.691 | 0.909 | 0.309 |
| 7 | - | - | 0.000 |
| 8 | 0.815 | 0.909 | 0.422 |
| 9 | 0.643 | 0.660 | 0.418 |
| 10 | 0.891 | 0.944 | 0.460 |
| 11 | 0.633 | 0.679 | 0.313 |
| 12 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.022 |
| 13 | 0.758 | 0.809 | 0.445 |
| 14 | 0.656 | 0.656 | 0.333 |
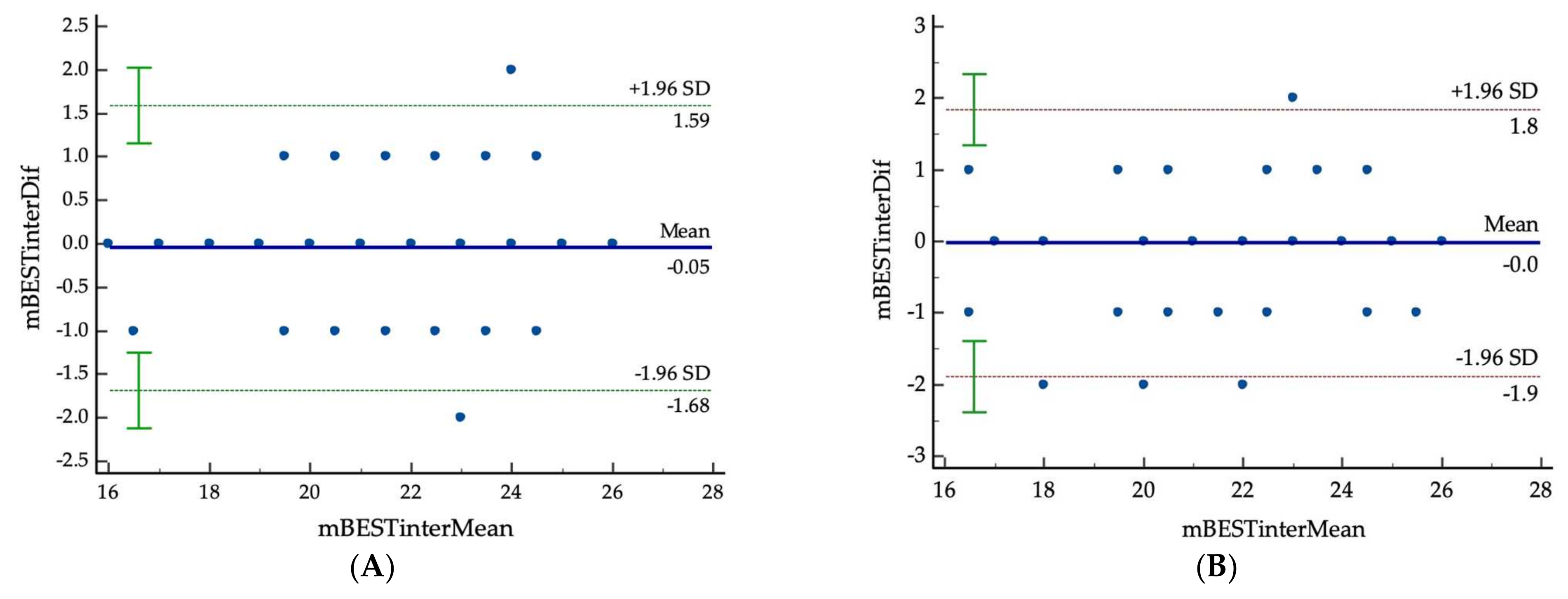
| Rater | Mini-BESTest Mean ± SD | Inter-Rater Reliability ICC2,1 (95% CI) p-Value | Intra-Rater Reliability ICC3,1 (95% CI) p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| First assessment | 1 | 21.39 ± 2.71 | 0.95 (0.91–0.97) p < 0.001 | 0.93 (0.87–0.96) p < 0.001 |
| 2 | 21.41 ± 2.50 | |||
| Second assessment | 2 | 21.43 ± 2.43 | ||
| MDC95 * | 2.16 |
| Subjective Examination of the Michigan Neuropathy Screening Instrument (MNSI) | The Different (95% CI) | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| <4 Score (n = 17) | ≥4 Score (n = 27) | |||
| Mini-BESTest | 22.65 ± 2.26 | 205.6 ± 2.65 | 2.09 (0.52 to 3.66) | 0.0102 |
| BESTest | 91.47 ± 6.93 | 87.07 ± 8.12 | 4.40 (−0.41 to 9.20) | 0.0718 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Phyu, S.N.; Peungsuwan, P.; Puntumetakul, R.; Chatchawan, U. Reliability and Validity of Mini-Balance Evaluation System Test in Type 2 Diabetic Patients with Peripheral Neuropathy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6944. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19116944
Phyu SN, Peungsuwan P, Puntumetakul R, Chatchawan U. Reliability and Validity of Mini-Balance Evaluation System Test in Type 2 Diabetic Patients with Peripheral Neuropathy. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(11):6944. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19116944
Chicago/Turabian StylePhyu, Sitt Nyein, Punnee Peungsuwan, Rungthip Puntumetakul, and Uraiwan Chatchawan. 2022. "Reliability and Validity of Mini-Balance Evaluation System Test in Type 2 Diabetic Patients with Peripheral Neuropathy" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 11: 6944. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19116944
APA StylePhyu, S. N., Peungsuwan, P., Puntumetakul, R., & Chatchawan, U. (2022). Reliability and Validity of Mini-Balance Evaluation System Test in Type 2 Diabetic Patients with Peripheral Neuropathy. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(11), 6944. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19116944






