Assessing the Ecosystem Health of Coastal Wetland Vegetation (Suaeda salsa) Using the Pressure State Response Model, a Case of the Liao River Estuary in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
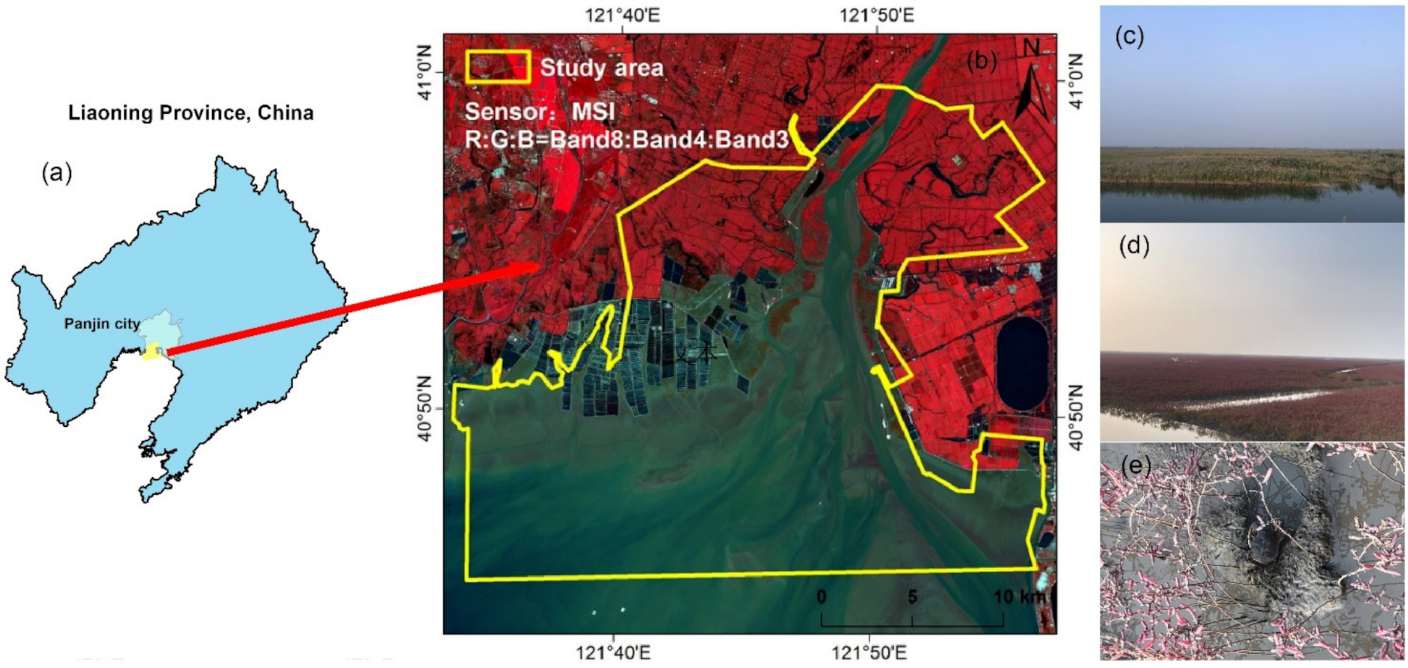
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Data Sources and Preprocessing
2.3. Remote Sensing Image Classification Method and Classification System
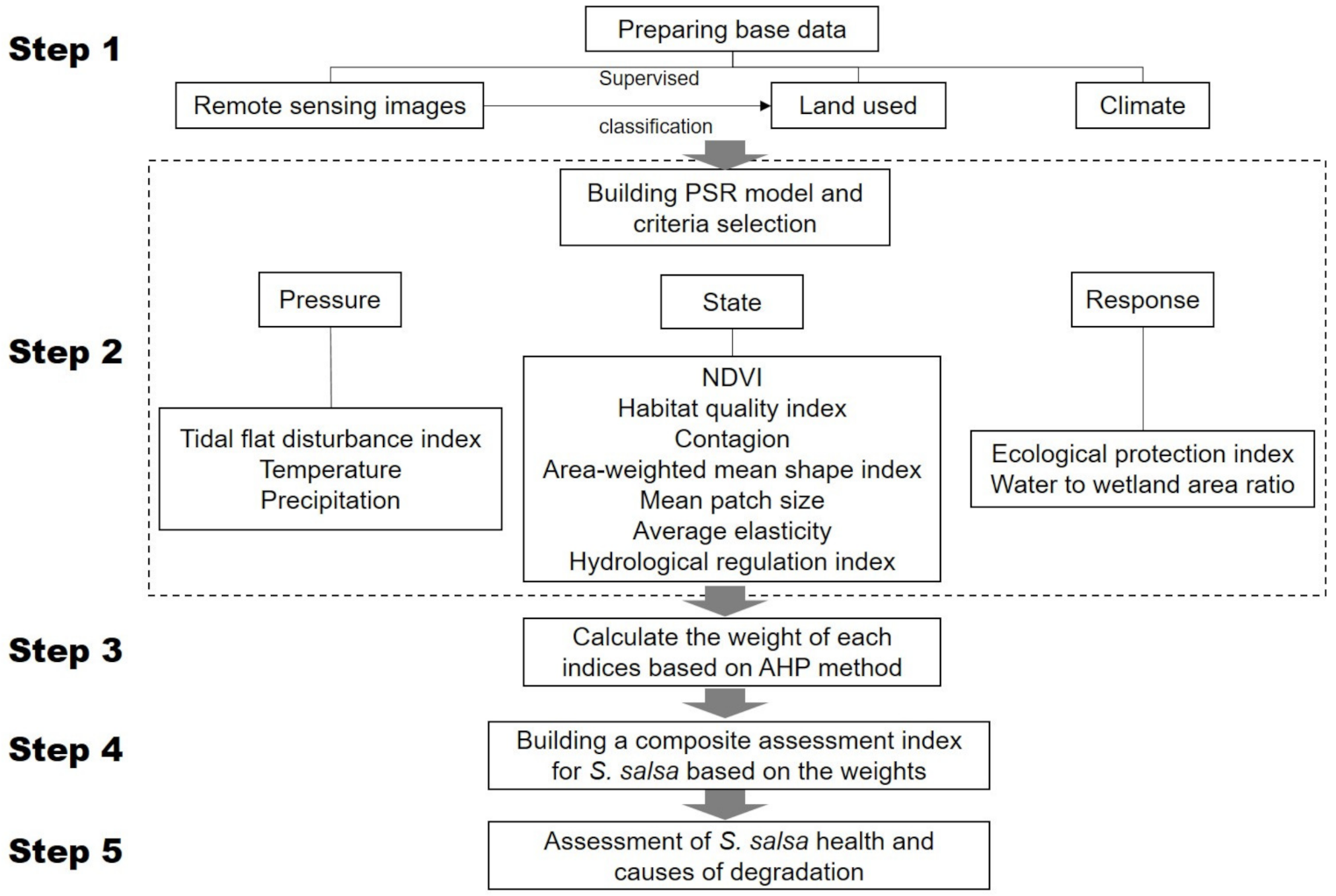
2.4. Construction of Assessment Index System
2.5. Calculation of Index Weight
2.6. Composite Assessment of the S. salsa Community Health
3. Results
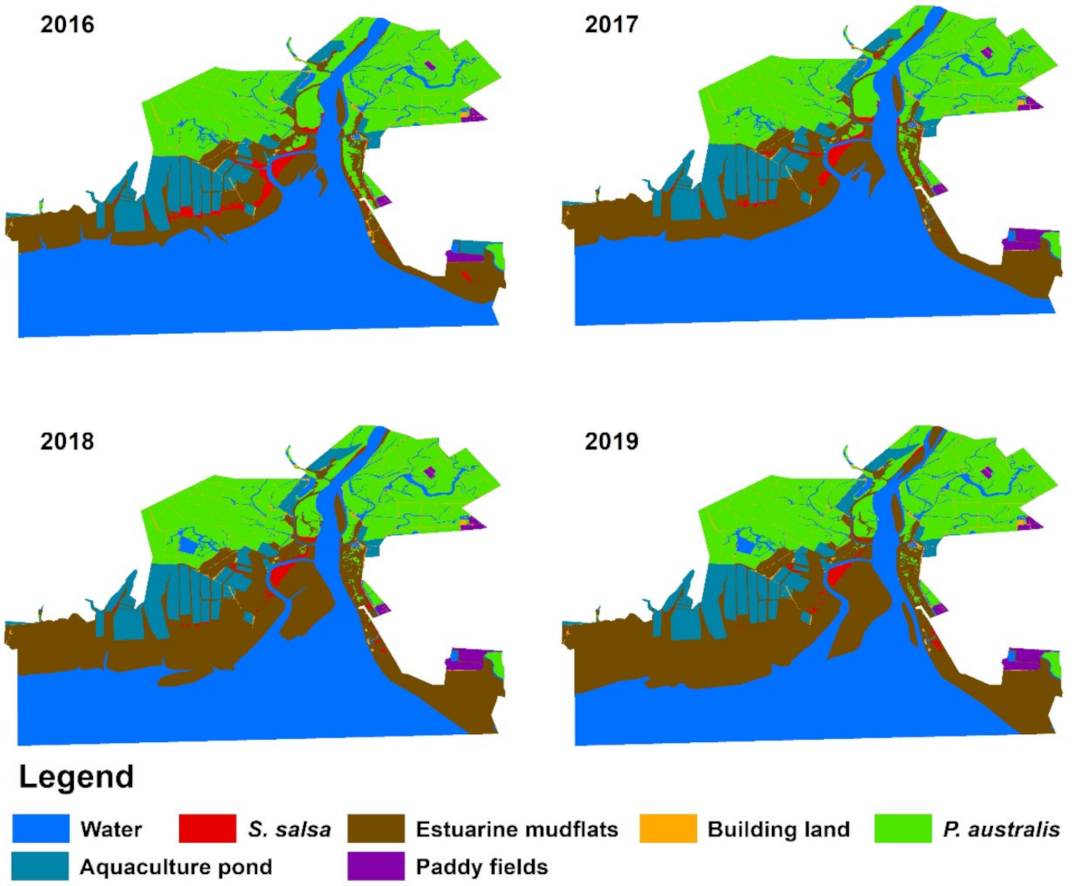
3.1. Landscape Pattern Change of the Liao River Estuary National Nature Reserve
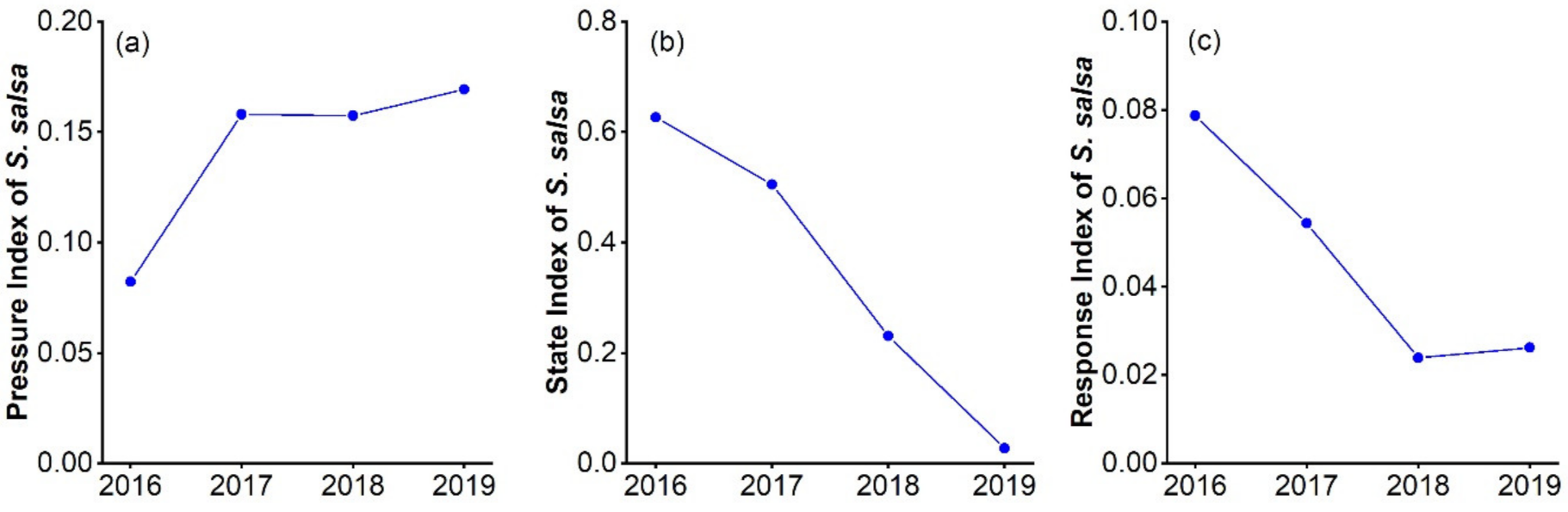
3.2. Assessing S. salsa Community Health from Pressure, State and Response Indicators
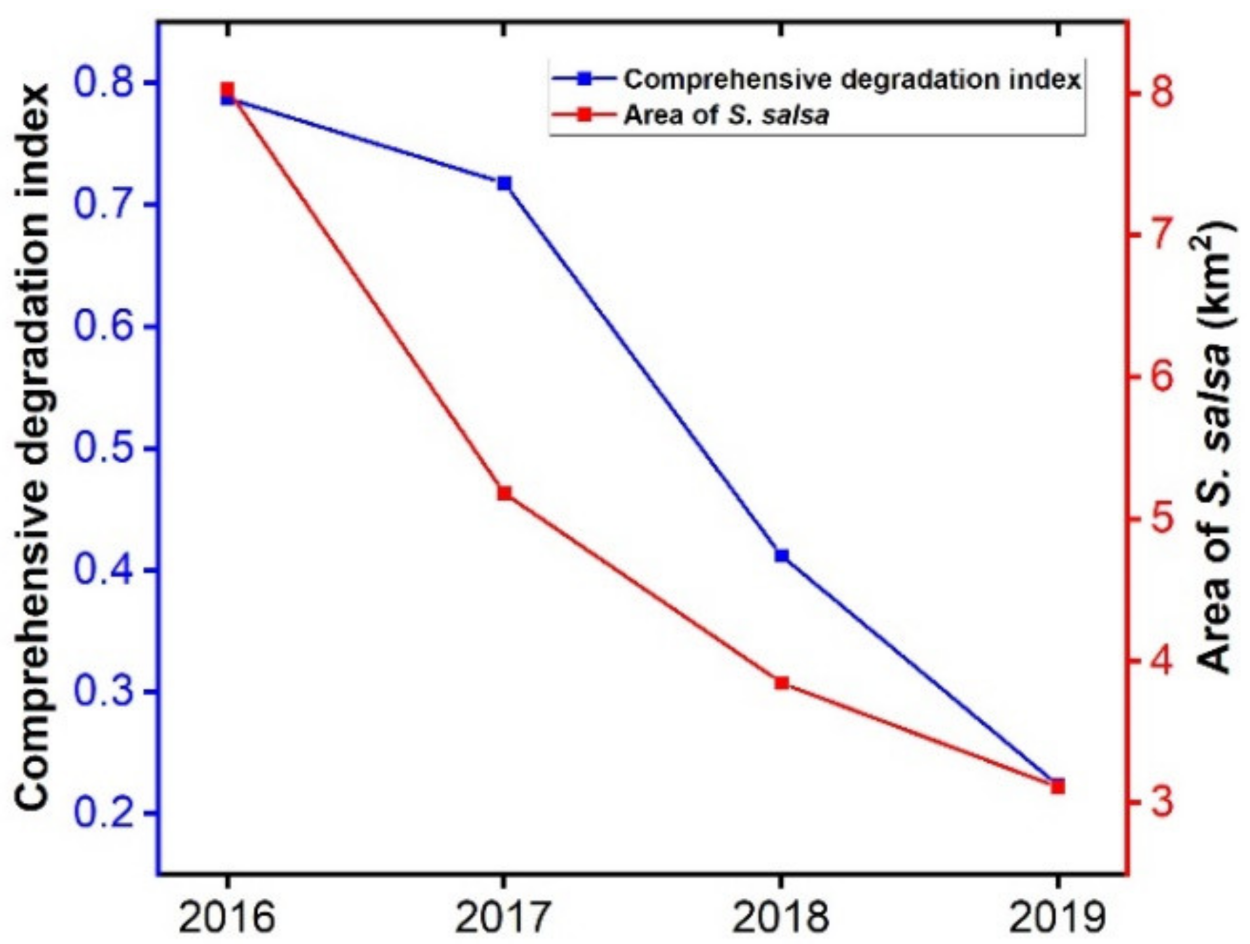
3.3. Composite Health Index of the S. salsa Community
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gedan, K.B.; Kirwan, M.L.; Wolanski, E.; Barbier, E.B.; Silliman, B.R. The present and future role of coastal wetland vegetation in protecting shorelines: Answering recent challenges to the paradigm. Clim. Chang. 2011, 106, 7–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Bellerby, R.; Craft, C.; Widney, S.E. Coastal wetland loss, consequences, and challenges for restoration. Anthr. Coasts 2018, 1, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, J.; Shi, W. Cotton/halophytes intercropping decreases salt accumulation and improves soil physicochemical properties and crop productivity in saline-alkali soils under mulched drip irrigation: A three-year field experiment. Field Crops Res. 2021, 262, 108027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moomaw, W.R.; Chmura, G.L.; Davies, G.T.; Finlayson, C.M.; Middleton, B.A.; Natali, S.M.; Perry, J.E.; Roulet, N.; Sutton-Grier, A.E. Wetlands in a Changing Climate: Science, Policy and Management. Wetlands 2018, 38, 183–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, J.; Jin, R.; Chen, G.; Ye, Z.; Li, Q.; Wang, H.; Li, D.; Christakos, G.; Agusti, S.; Duarte, C.M.; et al. Areal Extent, Species Composition, and Spatial Distribution of Coastal Saltmarshes in China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 7085–7094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Wang, Z.; Liu, D.; Ren, C.; Tang, X.; Dong, Z. Monitoring Loss and Recovery of Salt Marshes in the Liao River Delta, China. J. Coast. Res. 2015, 31, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Wang, Z.; Li, L.; Wu, P.; Mao, D.; Jia, M.; Dong, Z. Assessing the conservation effectiveness of wetland protected areas in Northeast China. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 24, 381–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lloyd, H.; Zhang, Z.; Li, D. Rapid Reclamation and Degradation of Suaeda salsa Saltmarsh along Coastal China’s Northern Yellow Sea. Land 2021, 10, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, L.T.; Knight, C.G.; O’Neill, R.V.; Smith, E.R.; Riitters, K.H.; Wickham, J. Fuzzy decision analysis for integrated environmental vulnerability assessment of the Mid-Atlantic region. Environ. Manag. 2002, 29, 845–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steele, K.; Carmel, Y.; Cross, J.; Wilcox, C. Uses and Misuses of Multicriteria Decision Analysis (MCDA) in Environmental Decision Making. Risk Anal. 2009, 29, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Cai, H.; Wu, P.; Geng, Q.; Xu, L. Sustainability assessment of regional water resources under the DPSIR framework. J. Hydrol. 2016, 532, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Lin, W.; Chen, G.; Guo, P.; Zeng, Y. Wetland ecosystem health assessment through integrating remote sensing and inventory data with an assessment model for the Hangzhou Bay, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566, 627–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.-Y.; Qian, H.; Wu, J.-H. Application of Set Pair Analysis Method Based on Entropy Weight in Groundwater Quality Assessment—A Case Study in Dongsheng City, Northwest China. E-J. Chem. 2011, 8, 851–858. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C.Y.; Gu, W.; Dai, A.H.; Wei, H.Y. Assessing habitat suitability based on geographic information system (GIS) and fuzzy: A case study of Schisandra sphenanthera Rehd. et Wils. in Qinling Mountains, China. Ecol. Model. 2012, 242, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Ji, G.; Tian, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z. Environmental vulnerability assessment for mainland China based on entropy method. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 91, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Pradhan, B.; Shit, P.K.; Alamri, A.M. Assessment of Wetland Ecosystem Health Using the Pressure–State–Response (PSR) Model: A Case Study of Mursidabad District of West Bengal (India). Sustainability 2020, 12, 5932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-T.; Wang, Y.-S.; Wu, M.-L.; Sun, C.-C.; Gu, J.-D. Assessing ecological health of mangrove ecosystems along South China Coast by the pressure–state–response (PSR) model. Ecotoxicology 2021, 30, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, X.; Tang, J. Ecological Security Assessment of Tianjin by PSR Model. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2010, 2, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, M.; Chen, W.; Chen, B. Ecological risk assessment of wetland vegetation under projected climate scenarios in the Sanjiang Plain, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 273, 111108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukdar, S.; Pal, S. Wetland habitat vulnerability of lower Punarbhaba river basin of the uplifted Barind region of Indo-Bangladesh. Geocarto Int. 2020, 35, 857–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortin, M.J.; Olson, R.J.; Ferson, S.; Iverson, L.; Hunsaker, C.; Edwards, G.; Levine, D.; Butera, K.; Klemas, V. Issues related to the detection of boundaries. Landsc. Ecol. 2000, 15, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, K.R.; Hill, G.J.E. Vegetation mapping of a tropical freshwater swamp in the Northern Territory, Australia: A comparison of aerial photography, Landsat TM and SPOT satellite imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 22, 2911–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belluco, E.; Camuffo, M.; Ferrari, S.; Modenese, L.; Silvestri, S.; Marani, A.; Marani, M. Mapping salt-marsh vegetation by multispectral and hyperspectral remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 105, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, E.; Mutanga, O.; Rugege, D. Multispectral and hyperspectral remote sensing for identification and mapping of wetland vegetation: A review. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2010, 18, 281–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hird, J.N.; DeLancey, E.R.; McDermid, G.J.; Kariyeva, J. Google Earth Engine, Open-Access Satellite Data, and Machine Learning in Support of Large-Area Probabilistic Wetland Mapping. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bunting, P.; Rosenqvist, A.; Lucas, R.M.; Rebelo, L.-M.; Hilarides, L.; Thomas, N.; Hardy, A.; Itoh, T.; Shimada, M.; Finlayson, C.M. The Global Mangrove WatchA New 2010 Global Baseline of Mangrove Extent. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, D.; Wan, B.; Qiu, P.; Su, Y.; Guo, Q.; Wang, R.; Sun, F.; Wu, X. Evaluating the Performance of Sentinel-2, Landsat 8 and Pleiades-1 in Mapping Mangrove Extent and Species. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahdianpari, M.; Salehi, B.; Mohammadimanesh, F.; Homayouni, S.; Gill, E. The First Wetland Inventory Map of Newfoundland at a Spatial Resolution of 10 m Using Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 Data on the Google Earth Engine Cloud Computing Platform. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chatziantoniou, A.; Petropoulos, G.P.; Psomiadis, E. Co-Orbital Sentinel 1 and 2 for LULC Mapping with Emphasis on Wetlands in a Mediterranean Setting Based on Machine Learning. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whyte, A.; Ferentinos, K.P.; Petropoulos, G.P. A new synergistic approach for monitoring wetlands using Sentinels-1 and 2 data with object-based machine learning algorithms. Environ. Model. Softw. 2018, 104, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Gong, Z.; Qiu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, D. Mapping typical salt-marsh species in the Yellow River Delta wetland supported by temporal-spatial-spectral multidimensional features. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 783, 147061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heimhuber, V.; Vos, K.; Fu, W.; Glamore, W. InletTracker: An open-source Python toolkit for historic and near real-time monitoring of coastal inlets from Landsat and Sentinel-2. Geomorphology 2021, 389, 107830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarigal, K. FRAGSTATS: Spatial Pattern Analysis Program for Quantifying Landscape Structure; US Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Pacific Northwest Research Station: Portland, OR, USA, 1995; Volume 351. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, P.-H.; Tsai, J.-S.; Lin, W.-T. Using multiple-criteria decision-making techniques for eco-environmental vulnerability assessment: A case study on the Chi-Jia-Wan Stream watershed, Taiwan. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 168, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Jin, H.; Cai, D.; Jiang, C. The comparative study on the ecological sensitivity analysis in Huixian karst wetland, China. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2010, 2, 386–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peker, F.; Kurucu, Y.; Tok, H.H.; Saygili, E.; Tok, E. An application of gis-supported analytic hierarchy process to determine the ecological thresholds in the edirne province. J. Environ. Prot. Ecol. 2013, 14, 713–722. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, N.-F.; Ji, X.-Y.; Jiang, J.-X.; Deng, X.; Huang, K.-H.; Li, B. An eco-engineering assessment index for chemical pesticide pollution management strategies to complex agro-ecosystems. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 52, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marre, J.-B.; Pascoe, S.; Thebaud, O.; Jennings, S.; Boncoeur, J.; Coglan, L. Information preferences for the evaluation of coastal development impacts on ecosystem services: A multi-criteria assessment in the Australian context. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 173, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, Y.; Li, J.; Xie, M. Evaluation of the ecological sensitivity and security of tidal flats in Shanghai. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 85, 729–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; Yang, X.; Jin, Y.; Xu, B.; Zhou, Q. Remote sensing and evaluation of the wetland ecological degradation process of the Zoige Plateau Wetland in China. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 104, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Tang, J.; Yu, D.; Song, Z.; Wang, P. Ecosystem health assessment: A PSR analysis combining AHP and FCE methods for Jiaozhou Bay, China. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2019, 168, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, X.; Yang, J.; Yuan, H. Wetland ecosystem stability evaluation by using Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP) approach in Yinchuan Plain, China. Math. Comput. Model. 2013, 57, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Cui, B.; He, Q. Shifting paradigms in coastal restoration: Six decades’ lessons from China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566-567, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, J.; Luo, M.; Zhang, X.; Christakos, G.; Agusti, S.; Duarte, C.M.; Wu, J. Losses of salt marsh in China: Trends, threats and management. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2018, 214, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Fagherazzi, S.; Ma, X.; Xie, C.; Li, J.; Cui, B. Consumer control and abiotic stresses constrain coastal saltmarsh restoration. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 274, 111110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tong, S.; Liu, X. Early establishment of Suaeda salsa population as affected by soil moisture and salinity: Implications for pioneer species introduction in saline-sodic wetlands in Songnen Plain, China. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 107, 105654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Silliman, B.R.; Cui, B. Incorporating thresholds into understanding salinity tolerance: A study using salt-tolerant plants in salt marshes. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 6326–6333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, Q.; Yu, S. Losses of natural coastal wetlands by land conversion and ecological degradation in the urbanizing Chinese coast. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lei, G.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tan, Z. Assessing hydrodynamic effects of ecological restoration scenarios for a tidal-dominated wetland in Liaodong Bay (China). Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 142339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopeć, D.; Michalska-Hejduk, D.; Krogulec, E. The relationship between vegetation and groundwater levels as an indicator of spontaneous wetland restoration. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 57, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, F.T.; Neckles, H.A. The effects of global climate change on seagrasses. Aquat. Bot. 1999, 63, 169–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Ye, S.; Li, G.; Yu, X.; McClellan, S.A. Soil Organic Carbon Storage Changes in Coastal Wetlands of the Liaohe Delta, China, Based on Landscape Patterns. Estuaries Coasts 2017, 40, 967–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombano, D.D.; Litvin, S.Y.; Ziegler, S.L.; Alford, S.B.; Baker, R.; Barbeau, M.A.; Cebrián, J.; Connolly, R.M.; Currin, C.A.; Deegan, L.A.; et al. Climate Change Implications for Tidal Marshes and Food Web Linkages to Estuarine and Coastal Nekton. Estuaries Coasts 2021, 44, 1637–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, L.J.R.; Raposo, M.A.M.; Gomes, C.J.P. The Impact of Tourism Activity on Coastal Biodiversity: A Case Study at Praia da Cova Redonda (Algarve—Portugal). Environments 2020, 7, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, T.C.; Muhar, A.; Arnberger, A.; Aznar, O.; Boyd, J.W.; Chan, K.M.A.; Costanza, R.; Elmqvist, T.; Flint, C.G.; Gobster, P.H.; et al. Contributions of cultural services to the ecosystem services agenda. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 8812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fish, R.; Church, A.; Winter, M. Conceptualising cultural ecosystem services: A novel framework for research and critical engagement. Ecosyst. Serv. 2016, 21, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Year | Images Acquisition Data | Cloud Coverage (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 22 August 2016 | <10% |
| 2017 | 25 August 2017 | <10% |
| 2018 | 25 August 2018 | <10% |
| 2019 | 25 August 2019 | <10% |
| Year | Overall Accuracy | Kappa Accuracy | User Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.917 |
| 2017 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.933 |
| 2018 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.967 |
| 2019 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.917 |
| Criteria | Indicator | Data Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure | Tidal flat disturbance index | The area of river changing into tidal flat |
| Temperature change | China Meteorological Data Service Center | |
| Precipitation | China Meteorological Data Service Center | |
| State | NDVI | |
| Habitat quality index | ||
| Contagion | Fragstats4.2 | |
| Area-weighted mean shape index | Fragstats4.2 | |
| Mean patch size | Fragstats4.2 | |
| Average elasticity | ||
| Hydrological regulation index | ||
| Response | Ecological protection index | |
| Water to wetland area ratio |
| Higher-Level Indicator | Lower-Level Indicator | Judgement Matrix | Priority | Weight | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. salsa health | Pressure | 1 | 1/3 | 3 | 0.258 | |||||
| State | 3 | 1 | 5 | 0.637 | ||||||
| Response | 1/3 | 1/5 | 1 | 0.105 | ||||||
| Pressure | Tidal flat disturbance index | 1 | 3/4 | 3/4 | 0.4 | 0.103 | ||||
| Temperature change | 4/3 | 1 | 1 | 0.3 | 0.077 | |||||
| Precipitation | 4/3 | 1 | 1 | 0.3 | 0.077 | |||||
| State | NDVI | 1 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0.2 | 0.127 |
| Habitat quality index | 1 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0.2 | 0.127 | |
| Contagion | 1/3 | 1/3 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1/3 | 1/3 | 0.081 | 0.052 | |
| Area-weighted mean shape index | 1/3 | 1/3 | 1/2 | 1 | 1 | 1/3 | 1/3 | 0.06 | 0.038 | |
| Mean patch size | 1/3 | 1/3 | 1/2 | 1 | 1 | 1/3 | 1/3 | 0.06 | 0.038 | |
| Average elasticity | 1 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0.2 | 0.127 | |
| Hydrological regulation index | 1 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0.2 | 0.127 | |
| Response | Ecological protection index | 1 | 3 | 0.75 | 0.079 | |||||
| Water to wetland area ratio | 1/3 | 1 | 0.25 | 0.027 | ||||||
| Type | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | 271.737 | 255.755 | 221.423 | 201.917 |
| Estuarine mudflats | 95.548 | 112.598 | 150.756 | 170.593 |
| Building land | 7.279 | 7.172 | 7.209 | 7.209 |
| P. australis | 123.089 | 121.804 | 117.411 | 117.079 |
| Aquaculture ponds | 44.988 | 43.078 | 43.669 | 43.669 |
| S. salsa | 8.027 | 5.185 | 3.851 | 3.115 |
| Paddy field | 3.675 | 5.907 | 5.907 | 5.907 |
| Criteria | Indicator | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pressure | Tidal flat disturbance index | 2.543 | 17.344 | 35.712 | 45.301 |
| Temperature change | 11.41 | 12.07 | 11.26 | 11.953 | |
| Precipitation | 76.28 | 72.15 | 77.98 | 64.1 | |
| State | NDVI | 0.335 | 0.356 | 0.283 | 0.117 |
| Habitat quality index | 48.539 | 47.20821 | 44.823 | 43.617 | |
| Contagion | 59.372 | 58.328 | 53.783 | 56.746 | |
| Area-weighted mean shape index | 14,426.837 | 13,162.932 | 10,943.731 | 7306.996 | |
| Mean patch size | 25.573 | 25.328 | 25.324 | 25.255 | |
| Mean resilience | 0.766 | 0.764 | 0.759 | 0.755 | |
| Hydroregulation index | 0.369 | 0.364 | 0.354 | 0.347 | |
| Response | Ecological protection index | 50.389 | 50.403 | 50.472 | 50.863 |
| Water to wetland area ratio | 37.864 | 37.343 | 36.340 | 35.631 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, Z.; Sun, Y.; Chen, P.; Jia, M. Assessing the Ecosystem Health of Coastal Wetland Vegetation (Suaeda salsa) Using the Pressure State Response Model, a Case of the Liao River Estuary in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 546. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19010546
Song Z, Sun Y, Chen P, Jia M. Assessing the Ecosystem Health of Coastal Wetland Vegetation (Suaeda salsa) Using the Pressure State Response Model, a Case of the Liao River Estuary in China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(1):546. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19010546
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Ziming, Yingyue Sun, Peng Chen, and Mingming Jia. 2022. "Assessing the Ecosystem Health of Coastal Wetland Vegetation (Suaeda salsa) Using the Pressure State Response Model, a Case of the Liao River Estuary in China" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 1: 546. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19010546
APA StyleSong, Z., Sun, Y., Chen, P., & Jia, M. (2022). Assessing the Ecosystem Health of Coastal Wetland Vegetation (Suaeda salsa) Using the Pressure State Response Model, a Case of the Liao River Estuary in China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(1), 546. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19010546







