Development of a Conceptual Model of Occupational Stress for Athletic Directors in Sport Contexts
Abstract
1. Introduction
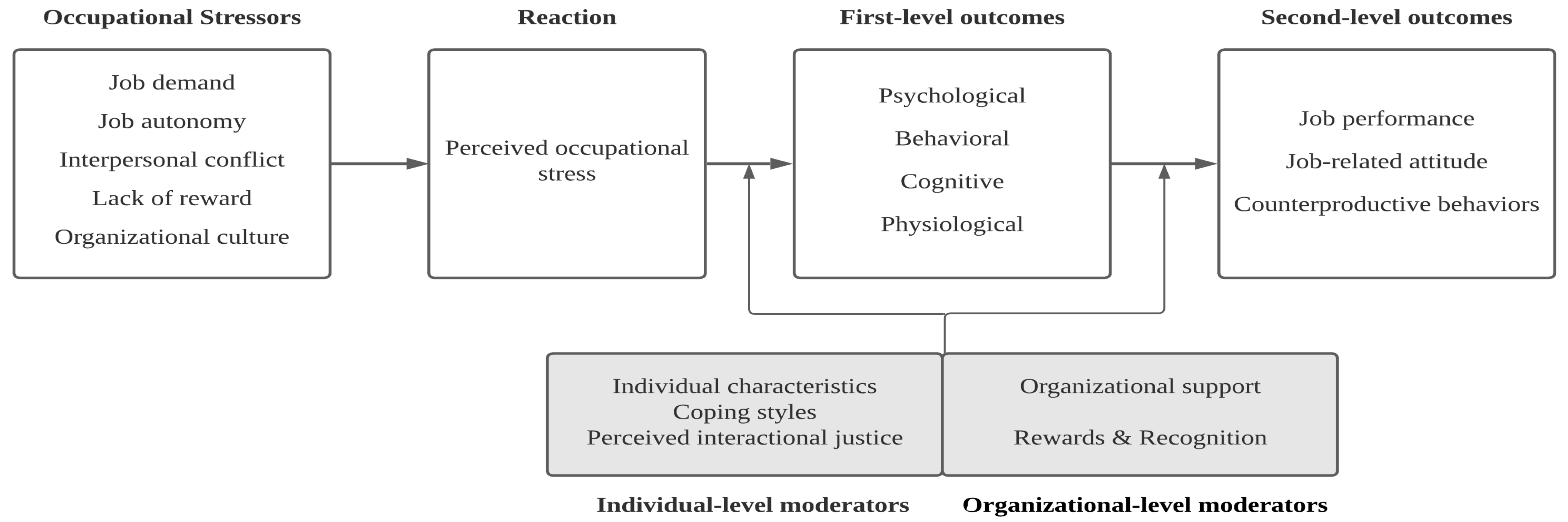
2. Conceptual Model of Occupational Stress in Sport Leadership
2.1. Definition of Occupational Stress
2.2. Sources of Occupational Stress
2.2.1. Job Demands
Administration-Related Job Demands
Competition-Related Job Demands
2.2.2. Job Autonomy
2.2.3. Interpersonal Conflict
Working with Coaches and Student-Athletes
Working with Parents and Booster Clubs
2.2.4. Lack of Rewards
2.2.5. Organizational Culture
2.3. Occupational Stress and Outcomes
2.3.1. First-Level Outcomes
2.3.2. Second-Level Outcomes
2.4. Moderators
3. Conclusions and Future Research Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hunter, S.T.; Tate, B.W.; Dzieweczynski, J.L.; Bedell-Avers, K.E. Leaders make mistakes: A multilevel consideration of why. Leadersh. Q. 2011, 22, 239–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaluza, A.J.; Boer, D.; Buengeler, C.; van Dick, R. Leadership behaviour and leader self-reported well-being: A review, integration and meta-analytic examination. Work Stress 2020, 34, 34–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, M.; Baltes, J.I.; Martin, A.; Meddings, K. The Stress of Leadership; Center Creative Leadership: Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, M.D.; Jackson, C.J. A process model of self-regulation and leadership: How attentional resource capacity and negative emotions influence constructive and destructive leadership. Leadersh. Q. 2015, 26, 386–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eubanks, D.L.; Mumford, M.D. Leader errors and the influence on performance: An investigation of differing levels of impact. Leadersh. Q. 2010, 21, 809–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harms, P.; Credé, M.; Tynan, M.; Leon, M.; Jeung, W. Leadership and stress: A meta-analytic review. Leadersh. Q. 2017, 28, 178–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.J.; Kelley, B.; Eklund, R.C. A model of stress and burnout in male high school athletic directors. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 1999, 21, 280–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ryska, T.A. Leadership styles and occupational stress among college athletic directors: The moderating effect of program goals. J. Psychol. 2002, 136, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Judge, L.W.; Judge, I.L. Understanding the Occupational Stress of Interscholastic Athletic Directors. ICHPER-SD J. Res. 2009, 4, 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan, D. High School Athletic Directors Always Have Their Heads in the Games. New Jersey Monthly. 2017. Available online: http://www.njmonthly.com/articles/towns-schools/athletic-directors-the-game-that-never-ends (accessed on 12 March 2018).
- Covell, D.; Walker, S.; Hess, P.; Siciliano, J. Managing Sports Organizations; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Inter-Agency Task Force on Sport for Development and Peace. Sport for Development and Peace: Towards Achieving the Millennium Development Goals. United Nations. 2003. Available online: http://www.sportanddev.org/en/document/manuals-and-tools/sport-development-and-peace-towards-achieving-millennium-development (accessed on 20 July 2018).
- Driskell, J.E.; Salas, E.; Johnston, J. Does stress lead to a loss of team perspective? Group Dyn. Theory Res. Pract. 1999, 3, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H. The role of mindfulness and occupational stress in the goal orientations of development and winning. Sport Manag. Rev. 2020, 23, 626–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, D.; Scott, M. Psychological stress in sports coaches: A review of concepts, research, and practice. J. Sports Sci. 2010, 28, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olusoga, P.; Kenttä, G. Desperate to quit: A narrative analysis of burnout and recovery in high-performance sports coaching. Sport Psychol. 2017, 31, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caplan, R.; Cobb, S.; French, J.; Van Harrison, R.; Pinneau, S. Demands and Worker Health: Main Effects and Organizational Differences; US Gov. Print. Off: Washington, DC, USA, 1975.
- O’Connor, D.B.; Thayer, J.F.; Vedhara, K. Stress and health: A review of psychobiological processes. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2021, 72, 663–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Fevre, M.; Matheny, J.; Kolt, G.S. Eustress, distress, and interpretation in occupational stress. J. Manag. Psychol. 2003, 18, 726–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneiderman, N.; Ironson, G.; Siegel, S.D. Stress and health: Psychological, behavioral, and biological determinants. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 2005, 1, 607–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NIOSH. Stress at Work; National Institute for Occuaptional Safety and Health: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1999.
- Häusser, J.A.; Mojzisch, A.; Niesel, M.; Schulz-Hardt, S. Ten years on: A review of recent research on the Job Demand–Control (-Support) model and psychological well-being. Work Stress 2010, 24, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hums, M.A.; MacLean, J.C. Governance and Policy in Sport Organizations; Holcombe Hathaway: Scottsdale, AZ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Korn, M. With Budgets Under Pressure, Colleges Cut Country-Club Staples Like Golf and Tennis. The Wall Stress Journal. 2020. Available online: https://www.wsj.com/articles/with-budgets-under-pressure-colleges-cut-country-club-staples-like-golf-and-tennis-11595170801 (accessed on 19 July 2020).
- Pedersen, P.M.; Thibault, L. Contemporary Sport Management, 6th ed.; Human Kinetics: Champagne City, IL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Koehler, M.; Giebel, N. Athletic Director’s Survival Guide; Prentice Hall: Paramus, NJ, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Pilar, P.-M.; Rafael, M.-C.; Félix, Z.-O.; Gabriel, G.-V. Impact of sports mass media on the behavior and health of society. A systematic review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, T. Know how to avoid Title IX violations when eliminating sports. Coll. Athl. Law 2021, 18, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Chelladurai, P.; Kang, C. Emotional labor in the dual role of teaching and coaching. Psychol. Rep. 2018, 121, 952–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, K.A.R. Role socialization theory: The sociopolitical realities of teaching physical education. Eur. Phys. Educ. Rev. 2015, 21, 379–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fried, G.; Kastel, M. Managing Sport Facilities; Human Kinetics: Champagne City, IL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Karasek, R.A., Jr. Job demands, job decision latitude, and mental strain: Implications for job redesign. Adm. Sci. Q. 1979, 24, 285–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, F.W.; Flaxman, P.E.; Bunce, D. The influence of psychological flexibility on work redesign: Mediated moderation of a work reorganization intervention. J. Appl. Psychol. 2008, 93, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirom, A.; Nirel, N.; Vinokur, A.D. Overload, autonomy, and burnout as predictors of physicians’ quality of care. J. Occup. Health Psychol. 2006, 11, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.H.; Cho, H. The roles of different types of passion in emotional exhaustion and turnover intention among athletic coaches. Int. J. Sports Sci. Coach. 2021, 16, 1747954120976955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Press, A. Former Penn State Officials Gary Schultz, Tim Curley Begin Prison Terms. ESPN. 2017. Available online: https://www.espn.com/college-football/story/_/id/20071906/former-penn-state-officials-gary-schultz-tim-curley-begin-jail-terms-jerry-sandusky-case (accessed on 7 August 2018).
- Kerr, Z.Y.; Chandran, A.; Nedimyer, A.K.; Arakkal, A.; Pierpoint, L.A.; Zuckerman, S.L. Concussion incidence and trends in 20 high school sports. Pediatrics 2019, 144, e20192180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jehn, K.A.; Mannix, E.A. The dynamic nature of conflict: A longitudinal study of intragroup conflict and group performance. Acad. Manag. J. 2001, 44, 238–251. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, W.-F.; Lin, Y.-C.; Huang, C.-L.; Chen, L.H. We can make it better: “We” moderates the relationship between a compromising style in interpersonal conflict and well-being. J. Happiness Stud. 2016, 17, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, S.; Spector, P.E.; Miles, D. Counterproductive work behavior (CWB) in response to job stressors and organizational justice: Some mediator and moderator tests for autonomy and emotions. J. Vocat. Behav. 2001, 59, 291–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo, F.; Mulki, J.P.; Boles, J.S. Workplace stressors, job attitude, and job behaviors: Is interpersonal conflict the missing link? J. Pers. Sell. Sales Manag. 2011, 31, 339–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Park, S.M. Determinants of job satisfaction and turnover intentions of public employees: Evidence from US federal agencies. Int. Rev. Public Adm. 2014, 19, 63–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakefield, K.L. Team Sports Marketing; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Peachey, J.W.; Zhou, Y.; Damon, Z.J.; Burton, L.J. Forty years of leadership research in sport management: A review, synthesis, and conceptual framework. J. Sport Manag. 2015, 29, 570–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelladurai, P. Managing Organizations: For Sport and Physical Activity a Systems Perspective; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Staurowsky, E. College athletes’ rights in the age of the super conference: The case of the All Players United campaign. J. Intercoll. Sport 2014, 7, 11–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, J.; Edwards, J.R. Understanding parental support in elite sport: A phenomenological approach to exploring midget triple a hockey in the Canadian Maritimes. Sport Soc. 2020, 24, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, S.K.; Drummond, M.J. Parents in youth sport: What happens after the game? Sport Educ. Soc. 2017, 22, 391–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorsch, T.E.; King, M.Q.; Tulane, S.; Osai, K.V.; Dunn, C.R.; Carlsen, C.P. Parent education in youth sport: A community case study of parents, coaches, and administrators. J. Appl. Sport Psychol. 2019, 31, 427–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, D.; Lauer, L.; Rolo, C.; Jannes, C.; Pennisi, N. Understanding the role parents play in tennis success: A national survey of junior tennis coaches. Br. J. Sports Med. 2006, 40, 632–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coakley, J. Sports in Society: Issues and Controversies, 12th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Dextras-Gauthier, J.; Marchand, A.; Haines, V., III. Organizational culture, work organization conditions, and mental health: A proposed integration. Int. J. Stress Manag. 2012, 19, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, L.J. Underrepresentation of women in sport leadership: A review of research. Sport Manag. Rev. 2015, 18, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta, R.V.; Carpenter, L.J. Women in Intercollegiate Sport: A Longitudinal, National Study. Thirty-Five Year Update, 1977–2012. Acosta-Carpent. 2012. Available online: http://www.acostacarpenter.org/2014%20Status%20of%20Women%20in%20Intercollegiate%20Sport%20-37%20Year%20Update%20-%201977-2014%20.pdf (accessed on 20 July 2018).
- Fagan, K.; Cyphers, L. Five myths about Title IX. ESPN. 2012. Available online: https://www.espn.com/espnw/title-ix/story/_/id/7729603/five-myths-title-ix (accessed on 20 July 2021).
- Adriaenssens, J.; De Gucht, V.; Maes, S. Causes and consequences of occupational stress in emergency nurses, a longitudinal study. J. Nurs. Manag. 2015, 23, 346–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakker, A.B.; Demerouti, E. The job demands-resources model: State of the art. J. Manag. Psychol. 2007, 22, 309–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halbesleben, J.R.; Buckley, M.R. Burnout in organizational life. J. Manag. 2004, 30, 859–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halbesleben, J.R.B.; Leon, M.R. Multilevel models of burnout: Separating group level and individual level effects in burnout research. In Burnout at Work: A Psychological Perspective; Psychology Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 122–144. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, S.; Janicki-Deverts, D.; Miller, G.E. Psychological stress and disease. JAMA 2007, 298, 1685–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melamed, S.; Shirom, A.; Toker, S.; Berliner, S.; Shapira, I. Burnout and risk of cardiovascular disease: Evidence, possible causal paths, and promising research directions. Psychol. Bull. 2006, 132, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortes, A.; Tian, L.; Huebner, S. Occupational stress and employees complete mental health: A cross-cultural empirical study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffeth, R.W.; Hom, P.W.; Gaertner, S. A meta-analysis of antecedents and correlates of employee turnover: Update, moderator tests, and research implications for the next millennium. J. Manag. 2000, 26, 463–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, L.R.; DuBois, D.; Hurrell, J.J. Accident reduction through stress management. J. Bus. Psychol. 1986, 1, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frone, M.R. Are work stressors related to employee substance use? The importance of temporal context assessments of alcohol and illicit drug use. J. Appl. Psychol. 2008, 93, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Izquierdo, M.; Meseguer de Pedro, M.; Ríos-Risquez, M.I.; Sánchez, M.I.S. Resilience as a moderator of psychological health in situations of chronic stress (burnout) in a sample of hospital nurses. J. Nurs. Scholarsh. 2018, 50, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hengartner, M.P.; van der Linden, D.; Bohleber, L.; von Wyl, A. Big five personality traits and the general factor of personality as moderators of stress and coping reactions following an emergency alarm on a Swiss University Campus. Stress Health 2017, 33, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallerand, R.J.; Blanchard, C.; Mageau, G.A.; Koestner, R.; Ratelle, C.; Léonard, M.; Gagné, M.; Marsolais, J. Les passions de l’ame: On obsessive and harmonious passion. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 2003, 85, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucidi, F.; Pica, G.; Mallia, L.; Castrucci, E.; Manganelli, S.; Bélanger, J.; Pierro, A. Running away from stress: How regulatory modes prospectively affect athletes’ stress through passion. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2016, 26, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafrenière, M.-A.K.; Jowett, S.; Vallerand, R.J.; Carbonneau, N. Passion for coaching and the quality of the coach–athlete relationship: The mediating role of coaching behaviors. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2011, 12, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, S.; Kent, A. Passion and pride in professional sports: Investigating the role of workplace emotion. Sport Manag. Rev. 2017, 20, 352–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewe, P.; Cox, T.; Ferguson, E. Individual strategies for coping with stress at work: A review. Work Stress 1993, 7, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandey, A.A. Emotional regulation in the workplace: A new way to conceptualize emotional labor. J. Occup. Health Psychol. 2000, 5, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Proactive and preventive coping in adjustment to college. Psychol. Rec. 2010, 60, 643–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Chelladurai, P. Emotional intelligence, emotional labor, coach burnout, job satisfaction, and turnover intention in sport leadership. Eur. Sport Manag. Q. 2018, 18, 393–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchino, B.N. Understanding the links between social support and physical health: A life-span perspective with emphasis on the separability of perceived and received support. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 2009, 4, 236–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearlin, L.I.; Menaghan, E.G.; Lieberman, M.A.; Mullan, J.T. The stress process. J. Health Soc. Behav. 1981, 22, 337–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenberger, R.; Stinglhamber, F. Perceived Organizational Support: Fostering Enthusiastic and Productive Employees; American Psychological Association: Clark University, MA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Cropanzano, R.; Greenberg, J. Progress in organizational justice: Tunneling through the maze. Int. Rev. Ind. Organ. Psychol. 1997, 12, 317–372. [Google Scholar]
- Bies, R.J. Interactional justice: Communication criteria of fairness. Res. Negot. Organ. 1986, 1, 43–55. [Google Scholar]
- Aryee, S.; Chen, Z.X.; Sun, L.-Y.; Debrah, Y.A. Antecedents and outcomes of abusive supervision: Test of a trickle-down model. J. Appl. Psychol. 2007, 92, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen-Charash, Y.; Spector, P. The role of justice in organizations: A meta-analysis. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Processes 2012, 86, 278–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, J.; Bastounis, M.; Minibas-Poussard, J. Interactional justice and counterproductive work behaviors. The mediating role of negative emotion. Soc. Behav. Personal. Int. J. 2012, 40, 1341–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creswell, J.W.; Poth, C.N. Qualitative Inquiry and Research Design: Choosing among Five Approaches; Sage Publications: Newcastle upon Tyne, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
| Job demand | Administration-related | Time pressure from the paperwork |
| Amount of workloads | ||
| Requirements for business techniques | ||
| Budgetary pressure | ||
| Public relation | ||
| Policy compliance | ||
| Competition-related | Pressure to win | |
| Role conflict | ||
| Facility issues | ||
| Job autonomy | Unpredictable outcomes in the field | Level of opponents |
| Characteristics of umpire | ||
| Weather | ||
| Uncontrollable athletic-related issues outside field | Player/coach turnover | |
| Injuries | ||
| Deviant behaviors | ||
| Interpersonal conflict | Working with coaches and student-athletes | |
| Working with parents and booster clubs | ||
| Lack of rewards | Monetary rewards | |
| Recognition | ||
| Opportunities for professional development | ||
| Organizational culture | Male-oriented culture | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, Y.H.; Kim, H.; Park, Y. Development of a Conceptual Model of Occupational Stress for Athletic Directors in Sport Contexts. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 516. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19010516
Lee YH, Kim H, Park Y. Development of a Conceptual Model of Occupational Stress for Athletic Directors in Sport Contexts. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(1):516. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19010516
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Ye Hoon, Hyungsook Kim, and Yonghyun Park. 2022. "Development of a Conceptual Model of Occupational Stress for Athletic Directors in Sport Contexts" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 1: 516. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19010516
APA StyleLee, Y. H., Kim, H., & Park, Y. (2022). Development of a Conceptual Model of Occupational Stress for Athletic Directors in Sport Contexts. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(1), 516. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19010516






