Effects of Body Mass Index, Waist Circumference, Waist-to-Height Ratio and Their Changes on Risks of Dyslipidemia among Chinese Adults: The Guizhou Population Health Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
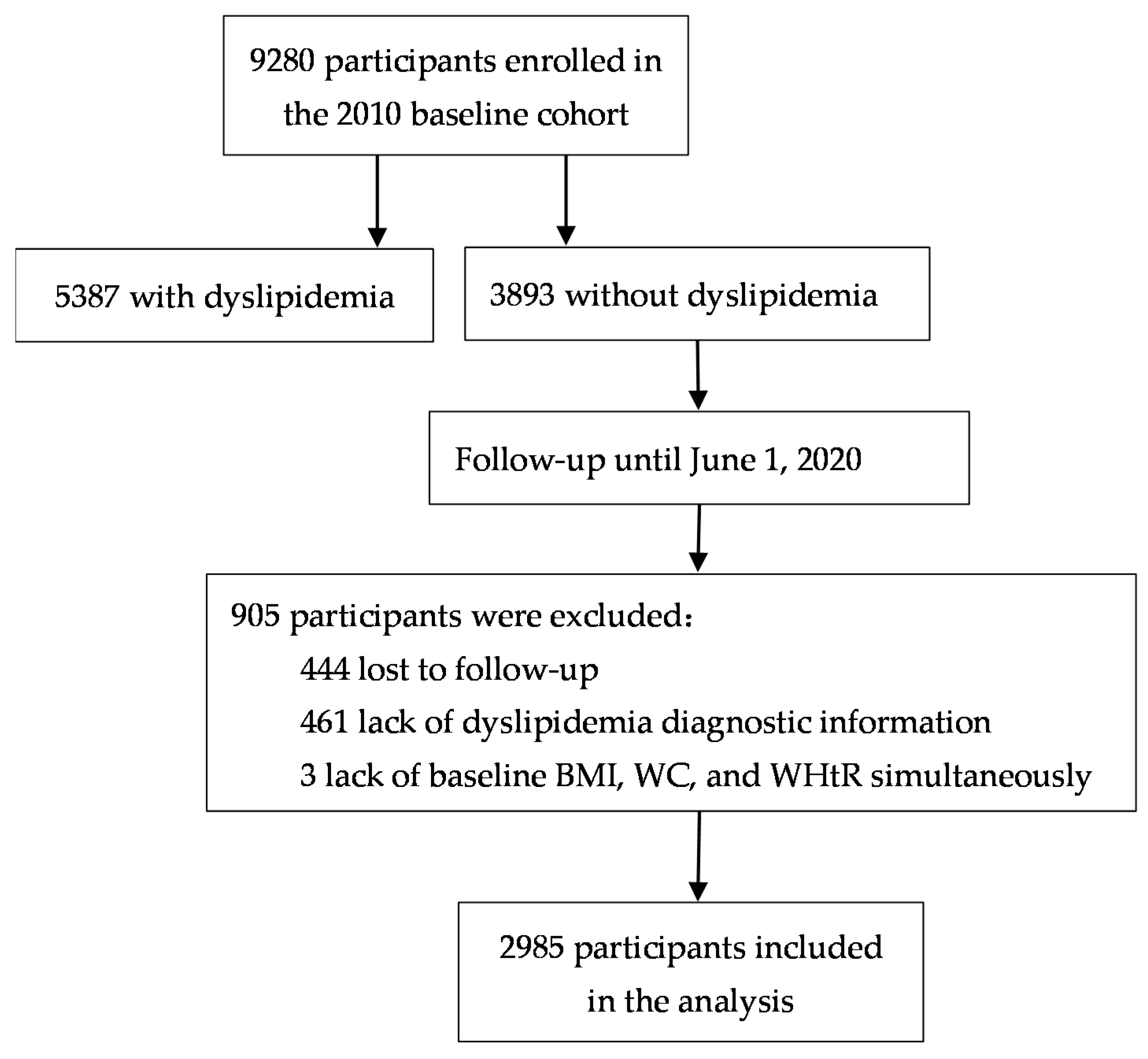
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population and Procedure
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Definition
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of Participants
3.2. Baseline WC, WHtR, and BMI and Risk of Incident Dyslipidemia
3.3. Risk of Incident Dyslipidemia Due to Changes of WHtR and BMI
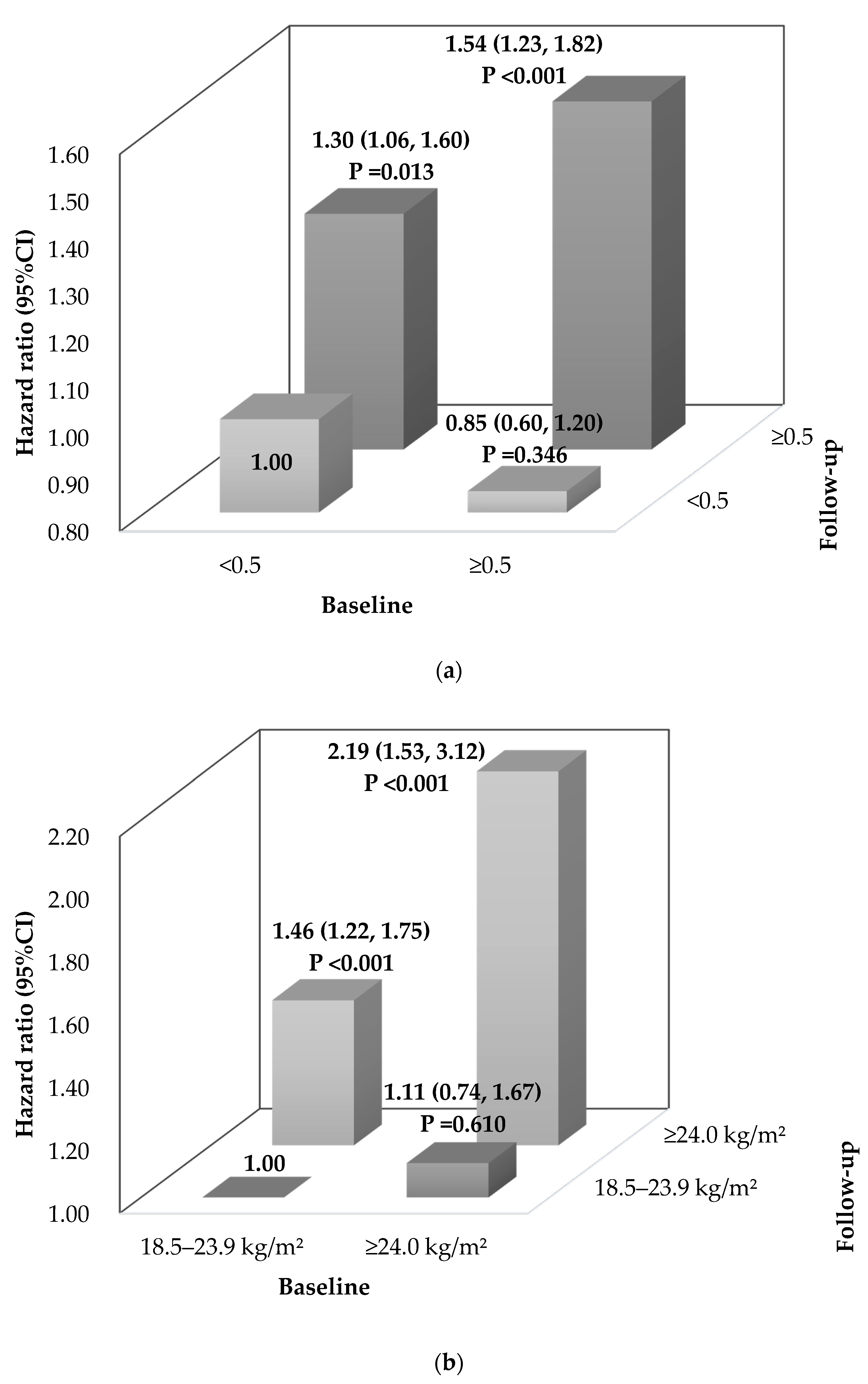
3.4. Stratification Analysis
3.5. Sensitivity Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kopin, L.; Lowenstein, C. Dyslipidemia. Ann. Intern. Med. 2017, 167, itc81–itc96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Ren, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, B.; Zhao, Y.; Han, C.; Zhang, H.; Yang, X.; et al. Association of change in waist circumference and dyslipidaemia risk: The rural Chinese cohort study. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2018, 34, e2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleeman, J.; Grundy, S.; Becker, D.; Clark, L.; Cooper, R.; Denke, M.; Howard, W.; Hunninghake, D.; Illingworth, D. Executive Summary of The Third Report of The National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). JAMA 2001, 285, 2486–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, G.A.; Johnson, C.; Abajobir, A.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abera, S.F.; Abyu, G.; Ahmed, M.; Aksut, B.; Alam, T.; Alam, K.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases for 10 Causes, 1990 to 2015. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 70, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.Y.; Chen, W.W.; Gao, R.L.; Liu, L.S.; Zhu, M.L.; Wang, Y.J.; Wu, Z.S.; Li, H.J.; Gu, D.F.; Yang, Y.J.; et al. China cardiovascular diseases report 2018: An updated summary. J. Geriatr. Cardiol. 2020, 17, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opoku, S.; Gan, Y.; Yobo, E.A.; Tenkorang-Twum, D.; Yue, W.; Wang, Z.; Lu, Z. Awareness, treatment, control, and determinants of dyslipidemia among adults in China. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, Y.; Niu, L.; Cao, N.; Bao, H.; Xu, X.; Zhu, H.; Yan, T.; Zhang, N.; Qiao, L.; Han, K.; et al. Prevalence of dyslipidemia and associated risk factors among adults aged ≥35 years in northern China: A cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Chang, P.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Kizer, J.R.; Best, L.G.; Howard, B.V. Triglyceride and HDL-C Dyslipidemia and Risks of Coronary Heart Disease and Ischemic Stroke by Glycemic Dysregulation Status: The Strong Heart Study. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikula, A.; Beiser, A.S.; Wang, J.; Himali, J.J.; Kelly-Hayes, M.; Kase, C.S.; Yang, Q.; Seshadri, S.; Wolf, P.A. Lipid and lipoprotein measurements and the risk of ischemic vascular events: Framingham Study. Neurology 2015, 84, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vekic, J.; Zeljkovic, A.; Stefanovic, A.; Jelic-Ivanovic, Z.; Spasojevic-Kalimanovska, V. Obesity and dyslipidemia. Metabolism 2019, 92, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, A.; Zhao, T.; Gong, X.; Pang, T.; Zhou, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Yan, Y.; Fan, C.; Teng, W.; et al. Comparison of anthropometric indices for predicting the risk of metabolic syndrome and its components in Chinese adults: A prospective, longitudinal study. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e016062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Li, K.; Li, X.; Luan, R.; Zhou, R. Independent and joint associations of body mass index, waist circumference, waist-height ratio and their changes with risks of hyperuricemia in middle-aged and older Chinese individuals: A population-based nationwide cohort study. Nutr. Metab. 2021, 18, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, W.; Su, Y.; Yang, G.; Ma, Y.; Liu, R.; Zhang, S.; Wang, S.; Fu, Y.; Kou, C.; Yu, Y.; et al. Cross-Sectional Associations between Body Mass Index and Hyperlipidemia among Adults in Northeastern China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, K.; Huang, Y.Q.; Shen, G.; Huang, J.Y.; Liu, L.; Yu, Y.L.; Chen, C.L.; Feng, Y.Q. Effects of waist to height ratio, waist circumference, body mass index on the risk of chronic diseases, all-cause, cardiovascular and cancer mortality. Postgrad. Med. J. 2021, 97, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, S.M.; Ma, G.S.; Li, Y.P.; Fang, H.Y.; Hu, X.Q.; Yang, X.G.; Hu, Y.H. Relationship of body mass index, waist circumference and cardiovascular risk factors in Chinese adult. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2010, 23, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obirikorang, C.; Obirikorang, Y.; Acheampong, E.; Anto, E.O.; Toboh, E.; Asamoah, E.A.; Amakwaa, B.; Batu, E.N.; Brenya, P. Association of Wrist Circumference and Waist-to-Height Ratio with Cardiometabolic Risk Factors among Type II Diabetics in a Ghanaian Population. J. Diabetes Res. 2018, 2018, 1838162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel-Baltazar, E.; Cuevas-Nasu, L.; Shamah-Levy, T.; Rodríguez-Ramírez, S.; Méndez-Gómez-Humarán, I.; Rivera, J.A. Association between High Waist-to-Height Ratio and Cardiovascular Risk among Adults Sampled by the 2016 Half-Way National Health and Nutrition Survey in Mexico (ENSANUT MC 2016). Nutrients 2019, 11, 1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzeidan, R.; Fayed, A.; Rabiee, F.; Hersi, A.; Elmorshedy, H. Diagnostic performance of waist-to-height ratio in identifying cardiovascular risk factors and metabolic syndrome among adult Saudis. A cross-sectional study. Saudi Med. J. 2020, 41, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, G.C.; Shu, X.O.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.L.; Cai, H.; Gao, J.; Gao, Y.T.; Wen, W.Q.; Xiang, Y.B.; Zheng, W. Association of Adult Weight Gain with Major Health Outcomes Among Middle-aged Chinese Persons with Low Body Weight in Early Adulthood. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e1917371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balkau, B.; Picard, P.; Vol, S.; Fezeu, L.; Eschwège, E. Consequences of change in waist circumference on cardiometabolic risk factors over 9 years: Data from an Epidemiological Study on the Insulin Resistance Syndrome (DESIR). Diabetes Care. 2007, 30, 1901–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hemelrijck, M.; Ulmer, H.; Nagel, G.; Peter, R.S.; Fritz, J.; Myte, R.; van Guelpen, B.; Föger, B.; Concin, H.; Häggström, C.; et al. Longitudinal study of body mass index, dyslipidemia, hyperglycemia, and hypertension in 60,000 men and women in Sweden and Austria. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yu, L.; Liu, T.; Fu, C. Is the Efficiency Score an Indicator for Incident Hypertension in the Community Population of Western China? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 10132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.H.; Ning, G. Contents and methods of chronic disease surveillance project in China in 2010. Chin. J. Prev. Med. 2012, 46, 477–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, L.; He, J.; Bi, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, T.; Wang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Dai, M.; Lu, J.; et al. Prevalence and Control of Diabetes in Chinese Adults. JAMA 2013, 310, 948–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Taylor, A.W.; Zhang, T.; Appleton, S.; Shi, Z. Association between Body Mass Index and All-Cause Mortality among Oldest Old Chinese. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2018, 22, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashwell, M.; Lejeune, S.; McPherson, K. Ratio of waist circumference to height may be better indicator of need for weight management. BMJ 1996, 312, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browning, L.M.; Hsieh, S.D.; Ashwell, M. A systematic review of waist-to-height ratio as a screening tool for the prediction of cardiovascular disease and diabetes: 0·5 could be a suitable global boundary value. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2010, 23, 247–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The IPAQ Group Guidelines for Data Processing and Analysis of the International Physical Activity Questionnaire. 2015. Available online: http://www.ipaq.ki.se (accessed on 26 November 2021).
- Prazeres, L.; Brito, R.; Silva, É. Regular physical exercise, sedentarism and characteristics of dismenorrhea and premenstrual syndrome. Fisioter. Mov. 2018, 31, e003118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.S.; Revision, J.C.f.G. 2018 Chinese Guidelines for Prevention and Treatment of Hypertension-A report of the Revision Committee of Chinese Guidelines for Prevention and Treatment of Hypertension. J. Geriatr. Cardiol. 2019, 16, 182–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Weng, J.; Zhu, D.; Ji, L.; Lu, J.; Zhou, Z.; Zou, D.; Guo, L.; Ji, Q.; Chen, L.; et al. Standards of medical care for type 2 diabetes in China 2019. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2019, 35, e3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.R.; Gao, R.L.; Zhao, S.P.; Lu, G.P.; Zhao, D.; Li, J.J. 2016 Chinese guidelines for the management of dyslipidemia in adults. J. Geriatr. Cardiol. 2018, 15, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, T.H. Absolute risk of tobacco deaths: One in two smokers will be killed by smoking: Comment on “Smoking and all-cause mortality in older people”. Arch. Intern. Med. 2012, 172, 845–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Tse, L.A.; Liu, Z.; Rangarajan, S.; Hu, B.; Yin, L.; Leong, D.P.; Li, W. Predictive Values of Anthropometric Measurements for Cardiometabolic Risk Factors and Cardiovascular Diseases Among 44,048 Chinese. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e010870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, R.N.; Zhao, C.; Wang, C.; Niu, Y.C.; Li, K.; Guo, F.C.; Li, S.T.; Sun, C.H.; Li, Y. BMI is strongly associated with hypertension, and waist circumference is strongly associated with type 2 diabetes and dyslipidemia, in northern Chinese adults. J. Epidemiol. 2012, 22, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishizaka, N.; Ishizaka, Y.; Toda, E.; Koike, K.; Nagai, R.; Yamakado, M. Impact of changes in waist circumference and BMI over one-year period on serum lipid data in Japanese individuals. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2009, 16, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ebrahimi, H.; Emamian, M.H.; Hashemi, H.; Fotouhi, A. Dyslipidemia and its risk factors among urban middle-aged Iranians: A population-based study. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2016, 10, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangrós, F.J.; Torrecilla, J.; Giráldez-García, C.; Carrillo, L.; Mancera, J.; Mur, T.; Franch, J.; Díez, J.; Goday, A.; Serrano, R.; et al. Association of General and Abdominal Obesity With Hypertension, Dyslipidemia and Prediabetes in the PREDAPS Study. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirasawa, T.; Ochiai, H.; Yoshimoto, T.; Nagahama, S.; Kobayashi, M.; Ohtsu, I.; Sunaga, Y.; Kokaze, A. Associations between normal weight central obesity and cardiovascular disease risk factors in Japanese middle-aged adults: A cross-sectional study. J. Health Popul. Nutr. 2019, 38, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; He, Y.; Dong, S.; Zhao, X.; Chen, Z.; Song, Z.; Chang, G.; Yang, F.; Wang, Y. Optimal cut-off values of BMI, waist circumference and waist: Height ratio for defining obesity in Chinese adults. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 112, 1735–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, L.; Schnohr, P.; Sørensen, T.I. Longitudinal study of the long-term relation between physical activity and obesity in adults. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2004, 28, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, P.T. Changes in body weight and waist circumference affect incident hypercholesterolemia during 7 years of follow-up. Obesity 2008, 16, 2163–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truesdale, K.P.; Stevens, J.; Lewis, C.E.; Schreiner, P.J.; Loria, C.M.; Cai, J. Changes in risk factors for cardiovascular disease by baseline weight status in young adults who maintain or gain weight over 15 years: The CARDIA study. Int. J. Obes. 2006, 30, 1397–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sogabe, N.; Sawada, S.S.; Lee, I.M.; Kawakami, R.; Ishikawa-Takata, K.; Nakata, Y.; Mitomi, M.; Noguchi, J.; Tsukamoto, K.; Miyachi, M.; et al. Weight change after 20 years of age and the incidence of dyslipidemia: A cohort study of Japanese male workers. J. Public Health 2016, 38, e77–e83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norman, J.E.; Bild, D.; Lewis, C.E.; Liu, K.; West, D.S. The impact of weight change on cardiovascular disease risk factors in young black and white adults: The CARDIA study. Int. J. Obes. 2003, 27, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, Y.; Nakagami, T.; Oya, J.; Takahashi, K.; Isago, C.; Kurita, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Ito, A.; Kasahara, T.; Uchigata, Y. Body Weight Reduction of 5% Improved Blood Pressure and Lipid Profiles in Obese Men and Blood Glucose in Obese Women: A Four-Year Follow-up Observational Study. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2019, 17, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, S.; Genest, J. Effect of obesity on high-density lipoprotein metabolism. Obesity 2007, 15, 2875–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, Y.; Nakagawa, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Takahashi, Y.; Yokoyama, T.; Mizoue, T.; Noda, M. Effect of longitudinal changes in visceral fat area and other anthropometric indices to the changes in metabolic risk factors in Japanese men: The Hitachi Health Study. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 1139–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Su, X.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, G.; Wang, B. Novel insights into the pathological mechanisms of metabolic related dyslipidemia. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 5675–5687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenkilde, M.; Rygaard, L.; Nordby, P.; Nielsen, L.B.; Stallknecht, B. Exercise and weight loss effects on cardiovascular risk factors in overweight men. J. Appl. Physiol. 2018, 125, 901–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | Total (n = 2985) | Dyslipidemia (n = 2089) | Non-Dyslipidemia (n = 896) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female | 1547 (51.8) | 1126 (53.9) | 421 (47.0) | 0.001 |
| Age, years | 44.43 ± 15.44 | 44.27 ± 15.44 | 44.82 ± 15.43 | 0.365 |
| Non-Han Chinese | 1634 (54.7) | 1172 (56.1) | 462 (51.6) | 0.025 |
| Rural residents | 1921 (64.4) | 1294 (61.9) | 627 (70.0) | <0.001 |
| Married | 542 (18.2) | 378 (18.1) | 164 (18.3) | 0.933 |
| Nine education years or longer | 1933 (64.8) | 1362 (65.2) | 571 (63.7) | 0.466 |
| Current smoking | 801 (26.8) | 524 (25.1) | 277 (30.9) | 0.001 |
| Current alcohol drinking * | 884 (29.6) | 565 (27.1) | 319 (35.6) | <0.001 |
| Regular physical exercise | 1194 (40.0) | 863 (41.3) | 331 (36.9) | 0.028 |
| Hypertension * | 636 (21.3) | 433 (20.7) | 203 (22.7) | 0.258 |
| Diabetes mellitus * | 161 (5.4) | 100 (4.8) | 61 (6.9) | 0.030 |
| Cardiovascular disease * | 21 (0.7) | 14 (0.7) | 7 (0.8) | 0.923 |
| Waist circumference, cm * | 74.88 ± 8.63 | 74.68 ± 8.59 | 75.32 ± 8.69 | 0.065 |
| ≥85/90 | 280 (9.5) | 187 (9.1) | 93 (10.6) | 0.237 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 22.21 ± 3.00 | 22.11 ± 2.98 | 22.42 ± 3.03 | 0.011 |
| <18.5 | 208 (7.0) | 156 (7.5) | 52 (5.8) | 0.115 |
| 18.5- | 2099 (70.3) | 1472 (70.5) | 627 (70.0) | |
| 24.0- | 567 (19.0) | 392 (18.8) | 175 (19.5) | |
| ≥28.0 | 111 (3.7) | 69 (3.3) | 42 (4.7) | |
| WHtR * | 0.48 ± 0.06 | 0.48 ± 0.06 | 0.48 ± 0.06 | 0.104 |
| ≥0.5 | 918 (31.2) | 621 (30.1) | 297 (33.7) | 0.062 |
| SBP, mmHg * | 120.91 ± 19.63 | 120.08 ± 19.30 | 122.85 ± 20.25 | <0.001 |
| DBP, mmHg * | 76.38 ± 11.47 | 76.22 ± 11.40 | 76.74 ± 11.63 | 0.258 |
| FPG, mmol/L * | 5.19 ± 1.05 | 5.18 ± 1.07 | 5.21 ± 1.02 | 0.573 |
| TC, mg/dL * | 5.79 ± 0.38 | 5.85 ± 0.37 | 5.75 ± 0.39 | 0.054 |
| TG, mg/dL * | 4.38 ± 3.68 | 4.49 ± 4.29 | 4.31 ± 3.20 | 0.699 |
| HDL-C, mg/dL * | 4.70 ± 0.77 | 4.71 ± 0.78 | 4.67 ± 0.77 | 0.127 |
| LDL-C, mg/dL * | 1.16 ± 0.44 | 1.15 ± 0.44 | 1.17 ± 0.45 | 0.317 |
| Variables | Cases, n | ID/1000 PYs | HR (95%CI) | p Value | aHR * (95%CI) | p Value | aHR # (95%CI) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WC (per 5 cm increment) | 881 | 42.66 | 1.04 (1.01, 1.08) | 0.019 | 1.03 (0.99, 1.07) | 0.112 | 1.02 (0.98, 1.06) | 0.351 |
| <85/90 | 788 | 42.15 | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - |
| ≥85/90 | 93 | 47.53 | 1.17 (0.94, 1.45) | 0.156 | 1.16 (0.94, 1.44) | 0.170 | 1.12 (0.90, 1.39) | 0.323 |
| WHtR (per 0.05 increment) | 881 | 42.66 | 1.07 (1.01, 1.13) | 0.023 | 1.06 (1.00, 1.13) | 0.043 | 1.04 (0.98, 1.11) | 0.157 |
| <0.5 | 584 | 41.03 | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - |
| ≥0.5 | 297 | 46.27 | 1.16 (1.01, 1.33) | 0.037 | 1.16 (1.01, 1.34) | 0.039 | 1.13 (0.98, 1.31) | 0.086 |
| BMI (per 5.0 kg/m2 increment) | 896 | 42.82 | 1.14 (1.03, 1.25) | 0.009 | 1.12 (1.01, 1.23) | 0.024 | 1.10 (1.00, 1.22) | 0.053 |
| <18.5 | 52 | 35.77 | 0.78 (0.59, 1.04) | 0.089 | 0.80 (0.60, 1.06) | 0.116 | 0.84 (0.63, 1.12) | 0.246 |
| 18.5- | 627 | 42.58 | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - |
| 24.0- | 175 | 43.85 | 1.00 (0.85, 1.19) | 0.955 | 1.01 (0.85, 1.19) | 0.947 | 1.00 (0.84, 1.19) | 0.999 |
| ≥28.0 | 42 | 55.42 | 1.53 (1.12, 2.10) | 0.007 | 1.49 (1.09, 2.04) | 0.012 | 1.45 (1.05, 1.99) | 0.023 |
| p for trend | 0.014 | 0.021 | 0.056 |
| Variables | Cases, n | ID/1000 PYs | HR (95%CI) | p Value | aHR * (95%CI) | p Value | aHR # (95%CI) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WHtR change (per 0.05 increase) | 631 | 48.47 | 1.16 (1.10, 1.23) | <0.001 | 1.16 (1.10, 1.23) | <0.001 | 1.25 (1.18, 1.33) | <0.001 |
| <0.02 | 211 | 45.31 | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - |
| [0.02, 0.06) | 155 | 44.36 | 1.02 (0.83, 1.26) | 0.817 | 1.00 (0.81, 1.23) | 0.998 | 1.13 (0.91, 1.41) | 0.267 |
| [0.06, 0.12) | 179 | 52.58 | 1.41 (1.16, 1.73) | 0.001 | 1.39 (1.14, 1.70) | 0.001 | 1.60 (1.29, 1.99) | <0.001 |
| [0.12, 0.20) | 70 | 57.07 | 1.63 (1.24, 2.14) | <0.001 | 1.59 (1.21, 2.08) | 0.001 | 2.00 (1.49, 2.69) | <0.001 |
| ≥0.20 | 16 | 67.39 | 1.96 (1.18, 3.26) | 0.009 | 2.07 (1.24, 3.45) | 0.005 | 2.77 (1.63, 4.71) | <0.001 |
| p for trend | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||||
| BMI change (per 5.0 kg/m2 increase) | 783 | 45.61 | 1.27 (1.15, 1.39) | <0.001 | 1.30 (1.18, 1.42) | <0.001 | 1.43 (1.31, 1.57) | <0.001 |
| <−2 | 105 | 37.71 | 0.78 (0.63, 0.97) | 0.024 | 0.77 (0.62, 0.96) | 0.019 | 0.73 (0.58, 0.91) | 0.007 |
| [−2, 2) | 367 | 42.09 | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - |
| [2, 6) | 225 | 50.79 | 1.09 (0.92, 1.29) | 0.300 | 1.10 (0.93, 1.30) | 0.258 | 1.21 (1.02, 1.44) | 0.026 |
| [6, 12) | 77 | 67.75 | 1.43 (1.12, 1.83) | 0.005 | 1.50 (1.17, 1.93) | 0.001 | 1.86 (1.44, 2.41) | <0.001 |
| p for trend | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Stratification Variable | Effect Variable | aHR (95%CI) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | WC | ||
| <40 | <85/90 | 1.00 | - |
| ≥85/90 | 0.71 (0.46, 1.09) | 0.118 | |
| 40- | <85/90 | 1.00 | - |
| ≥85/90 | 1.19 (0.87, 1.63) | 0.268 | |
| ≥60 | <85/90 | 1.00 | - |
| ≥85/90 | 1.92 (1.19, 3.07) | 0.007 | |
| p for interaction | 0.015 | ||
| Age, years | WHtR | ||
| <40 | <0.5 | 1.00 | - |
| ≥0.5 | 0.92 (0.72, 1.17) | 0.512 | |
| 40- | <0.5 | 1.00 | - |
| ≥0.5 | 1.31 (1.06, 1.62) | 0.014 | |
| ≥60 | <0.5 | 1.00 | - |
| ≥0.5 | 1.12 (0.80, 1.56) | 0.506 | |
| p for interaction | 0.030 | ||
| Rural residents | BMI change | ||
| No | <−2 | 0.67 (0.43, 1.07) | 0.093 |
| [−2, 2) | 1.00 | - | |
| [2, 6) | 1.69 (1.22, 2.36) | 0.002 | |
| [6, 12) | 3.26 (1.99, 5.33) | <0.001 | |
| ≥12 | 2.53 (0.77, 8.26) | 0.126 | |
| Yes | <−2 | 0.71 (0.54, 0.93) | 0.014 |
| [−2, 2) | 1.00 | - | |
| [2, 6) | 1.07 (0.88, 1.31) | 0.501 | |
| [6, 12) | 1.53 (1.13, 2.07) | 0.006 | |
| ≥12 | 2.38 (0.99, 5.68) | 0.052 | |
| p for interaction | 0.045 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, L.; Zhou, J.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, T.; Fu, C. Effects of Body Mass Index, Waist Circumference, Waist-to-Height Ratio and Their Changes on Risks of Dyslipidemia among Chinese Adults: The Guizhou Population Health Cohort Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19010341
Cao L, Zhou J, Chen Y, Wu Y, Wang Y, Liu T, Fu C. Effects of Body Mass Index, Waist Circumference, Waist-to-Height Ratio and Their Changes on Risks of Dyslipidemia among Chinese Adults: The Guizhou Population Health Cohort Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(1):341. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19010341
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Li, Jie Zhou, Yun Chen, Yanli Wu, Yiying Wang, Tao Liu, and Chaowei Fu. 2022. "Effects of Body Mass Index, Waist Circumference, Waist-to-Height Ratio and Their Changes on Risks of Dyslipidemia among Chinese Adults: The Guizhou Population Health Cohort Study" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 1: 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19010341
APA StyleCao, L., Zhou, J., Chen, Y., Wu, Y., Wang, Y., Liu, T., & Fu, C. (2022). Effects of Body Mass Index, Waist Circumference, Waist-to-Height Ratio and Their Changes on Risks of Dyslipidemia among Chinese Adults: The Guizhou Population Health Cohort Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(1), 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19010341






