Malacological and Parasitological Surveys on Ethiopian Rift Valley Lakes: Implications for Control and Elimination of Snail-Borne Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling Site Selection
2.3. Environmental Variables
2.4. Snail Collection and Examination of Cercarial Infection
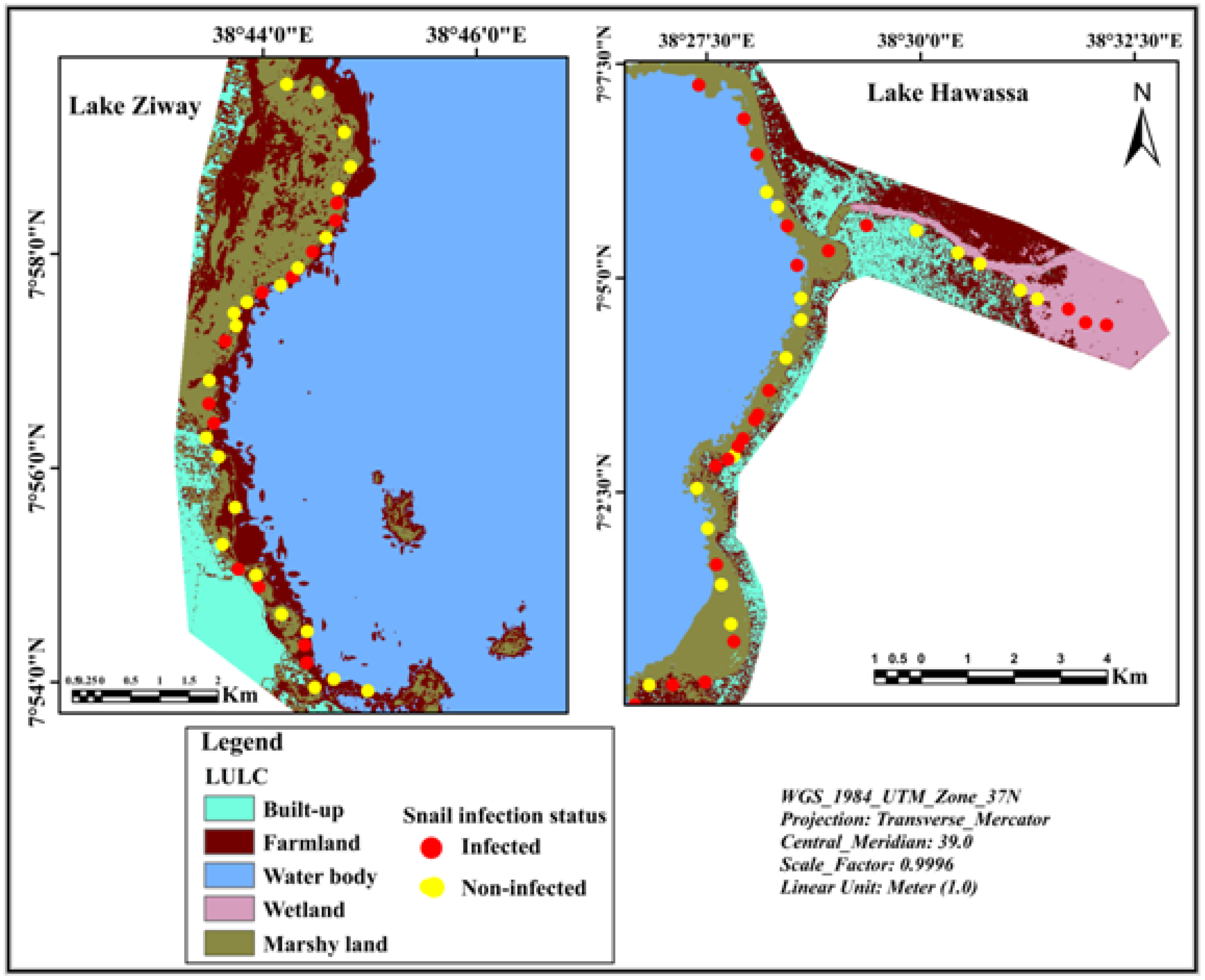
2.5. Mapping Spatial Distribution of Sampling Sites
2.6. Parasitological Survey and Assessment of Risk Factors
2.7. Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cercarial Infection in Snails
3.2. Spatial Distribution of Infected Snails
3.3. Factors Affecting the Occurrence of Infected Snails
3.4. Schistosoma Mansoni Infection and Associated Risk Factors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, X.T.; Gu, Q.Y.; Limpanont, Y.; Song, L.G.; Wu, Z.D.; Okanurak, K.; Lv, Z.Y. Snail-borne parasitic diseases: An update on global epidemiological distribution, transmission interruption and control methods. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2018, 7, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Accelerating Work to Overcome the Global Impact of Neglected Tropical Diseases: A Roadmap for Implementation: Executive Summary; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gryseels, B.; Polman, K.; Clerinx, J.; Kestens, L. Human schistosomiasis. Lancet 2006, 368, 1106–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Schistosomiasis; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/en/news-room/factsheets/detail/schistosomiasis (accessed on 15 July 2021).
- Dida, G.O.; Gelder, F.B.; Anyona, D.N.; Matano, A.S.; Abuom, P.O.; Adoka, S.O.; Ouma, C.; Kanangire, C.K.; Owuor, P.O.; Ofulla, A.V. Distribution and abundance of schistosomiasis and fascioliasis host snails along the Mara River in Kenya and Tanzania. Infect. Ecol. Epidemiol. 2014, 1, 24281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, M.W.; Dalton, J.P. Zoonotic helminth infections with particular emphasis on fasciolosis and other trematodiases. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2763–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degheidy, N.S.; Al-Malki, J.S. Epidemiological studies of fasciolosis in human and animals at Taif, Saudi Arabia. World Appl. Sci. J. 2012, 19, 1099–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arancha, A.; Anegagrie, M.; Zewdie, D.; Benito, A. Schistosoma mansoni in a rural community of Ethiopia. In Proceedings of the 27th European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, Veinna, Austria, 22–25 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gordy, M.A.; Kish, L.; Tarrabain, M.; Hanington, P.C. A comprehensive survey of larval digenean trematodes and their snail hosts in central Alberta, Canada. Parasit. Res. 2016, 115, 3867–3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krauth, S.J.; Wandel, N.; Traoré, S.I.; Vounatsou, P.; Hattendorf, J.; Achi, L.Y.; McNeill, K.; N’Goran, E.K.; Utzinger, J. Distribution of intermediate host snails of schistosomiasis and fascioliasis in relation to environmental factors during the dry season in the Tchologo region, Côte d’Ivoire. Adv. Water Resour. 2017, 108, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loker, E.S. Research on the Molluscan Intermediate Hosts for Schistosomiasis: What Are the Priorities? Presented to the Scientific Working Group on Schistosomiasis; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kloos, H.; Souza, C.D.; Gazzinelli, A.; Soares Filho, B.S.; Temba, P.D.C.; Bethony, J. The distribution of Biomphalaria spp. in different habitats in relation to physical, biological, water contact and cognitive factors in a rural area in Minas Gerais, Brazil. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz. 2001, 96, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aliyu, A.A.; Ajogi, I.A.; Ajanusi, O.J.; Reuben, R.C. Epidemiological studies of Fasciola gigantica in cattle in Zaria, Nigeria using coprology and serology. J. Public Health Epidemiol. 2014, 6, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayalneh, B.; Bogale, B.; Dagnachew, S. Review on Ovine fasciolosis in Ethiopia. Acta Parasitol. Glob. 2018, 9, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Integrating Neglected Tropical Diseases into Global Health and Development: Fourth WHO Report on Neglected Tropical Diseases; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, D.S. Freshwater Snails of Africa and Their Medical Importance; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ekpo, U.F.; Laja-Deile, A.; Oluwole, A.S.; Sam-Wobo, S.O.; Mafiana, C.F. Urinary schistosomiasis among preschool children in a rural community near Abeokuta, Nigeria. Parasit. Vectors 2010, 3, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, M.; Allen, T. Does mass drug administration for the integrated treatment of neglected tropical diseases really work? Assessing evidence for the control of schistosomiasis and soil-transmitted helminths in Uganda. Health Res. Policy Syst. 2011, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, J.P.; Molyneux, D.H.; Hotez, P.J.; Fenwick, A. The contribution of mass drug administration to global health: Past, present and future. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 369, 20130434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Uniting to Combat Neglected Tropical Diseases. London: Declaration on Neglected Tropical Diseases; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- FMoH. National Master Plan for Neglected Tropical Disease (2013–2015); Federal Ministry of Health of Ethiopia: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hotez, P. Mass drug administration and integrated control for the world’s high-prevalence neglected tropical diseases. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2009, 85, 659–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotez, P.J.; Kamath, A. Neglected tropical diseases in sub-Saharan Africa: Review of their prevalence, distribution, and disease burden. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2009, 3, e412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.M.; El Tash, L.A.; Mohamed, E.Y.; Adam, I. High levels of Schistosoma mansoni infections among school children in central Sudan one year after treatment with praziquantel. J. Helminthol. 2012, 86, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melman, S.D.; Steinauer, M.L.; Cunningham, C.; Kubatko, L.S.; Mwangi, I.N.; Wynn, N.B.; Mutuku, M.W.; Karanja, D.M.; Colley, D.G.; Black, C.L. Reduced susceptibility to praziquantel among naturally occurring Kenyan isolates of Schistosoma mansoni. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2009, 3, e504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evan Secor, W. Water-based interventions for schistosomiasis control. Pathog. Glob. Health 2014, 108, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, C.H.; Sutherland, L.J.; Bertsch, D. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the impact of chemical-based mollusciciding for control of Schistosoma mansoni and S. haematobium transmission. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0004290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, D.J.; McManus, D.P.; Li, Y.; Williams, G.M.; Bergquist, R.; Ross, A.G. Schistosomiasis elimination: Lessons from the past guide the future. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2010, 10, 733–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, C.H.; Bertsch, D. Historical perspective: Snail control to prevent schistosomiasis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokolow, S.H.; Wood, C.L.; Jones, I.J.; Swartz, S.J.; Lopez, M.; Hsieh, M.H.; Lafferty, K.D.; Kuris, A.M.; Rickards, C.; De Leo, G.A. Global assessment of schistosomiasis control over the past century shows targeting the snail intermediate host works best. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, K.Y. Trials of ecological and chemical measures for the control of Schistosoma haematobium transmission in a Volta Lake village. Bull. World Health Organ. 1978, 56, 313. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Angelo, T.; Shahada, F.; Kassuku, A.; Mazigo, H.; Kariuki, C.; Gouvras, A. Population abundance and disease transmission potential of snail intermediate hosts of human schistosomiasis in fishing communities of Mwanza region, north-western, Tanzania. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2014, 3, 1230–1236. [Google Scholar]
- Kazibwe, F.; Makanga, B.; Rubaire-Akiiki, C.; Ouma, J.; Kariuki, C.; Kabatereine, N.B.; Booth, M.; Vennervald, B.J.; Sturrock, R.F.; Stothard, J.R. Ecology of Biomphalaria (Gastropoda: Planorbidae) in Lake Albert, Western Uganda: Snail distributions, infection with schistosomes and temporal associations with environmental dynamics. Hydrobiologia 2006, 568, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opisa, S.; Odiere, M.R.; Jura, W.G.; Karanja, D.M.; Mwinzi, P.N. Malacological survey and geographical distribution of vector snails for schistosomiasis within informal settlements of Kisumu City, western Kenya. Parasit. Vectors 2011, 4, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawassa City: Natural Resource Management and Environmental Protection Authority, Hawassa, Ethiopia. 2015; Unpublished report.
- Worako, A.W. Evaluation of the water quality status of Lake Hawassa by using water quality index, Southern Ethiopia. J. Water Res. Environ. Res. 2015, 7, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desta, H.; Lemma, B.; Stellmacher, T.; Gebremariam, E. Water use and management of Lake Ziway and its watershed, Ethiopia: The perception of experts vis-à-vis the latest state of research. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2020, 22, 3621–3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengesha, G.; Mamo, Y.; Bekele, K.S. Effects of Land-use on Birds Diversity in and around Lake Zeway, Ethiopia. J. Sci. Dev. 2014, 2, 5–22. [Google Scholar]
- Mereta, S.T.; Bedewi, J.; Yewhalaw, D.; Mandefro, B.; Abdie, Y.; Tegegne, D.; Birke, W.; Mulat, W.L.; Kloos, H. Environmental determinants of distribution of freshwater snails and trematode infection in the Omo Gibe River Basin, southwest Ethiopia. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2019, 8, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itagaki, H.; Suzuki, N.; Ito, Y.; Hara, T.; Wonde, T. Study on the Ethiopian freshwater molluscs, especially on identification, distribution and ecology of vector snails of human schistosomiasis. Jpn. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1975, 3, 107–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutuku, M.W.; Laidemitt, M.R.; Mwangi, I.N.; Otiato, F.O.; Agola, E.L.; Steinauer, M.L.; Ochanda, H.; Kamel, B.; Loker, E.S.; Mkoji, G.M. Persistent hotspots of Schistosoma mansoni transmission in the Kenyan waters of Lake Victoria: A search for snail-related answers beneath the waves. BioRxiv 2018, 394031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frandsen, F.; Christensen, N.O. Introductory guide to the identification of cercariae from African freshwater snails with special reference to cercariae of trematode species of medical and veterinary importance Taxonomic key. Acta Trop. 1984, 41, 181–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- APHA; AWWA; WPCF. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 19th ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin, D.S.; Nielsen, D.L.; Bowen, T.; Williams, J. Recommended Methods for Monitoring Floodplains and Wetlands; Murray-Darling Basin Commission: Canberra, Australia, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Parsons, M.; Ransom, G.; Thoms, M.; Norris, R. Australian River Assessment System: AusRivAS Physical and Chemical Assessment Module; Environmental Australia: Canberra, Australia, 2001; p. 47. [Google Scholar]
- Posa, M.R.C.; Sodhi, N.S. Effects of anthropogenic land use on forest birds and butterflies in Subic Bay, Philippines. Biol. Conserv. 2006, 129, 256–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCreadie, J.W.; Adler, P.H. The roles of abiotic factors, dispersal, and species interactions in structuring stream assemblages of black flies (Diptera: Simuliidae). Aquat. Biosyst. 2012, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO. Global Forest Resource Assessment. FAO Forestry Paper 163; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, P.; Krogsgaard, M.R.; Christiansen, J.; Brændstrup, O.; Johansen, A.; Olsen, J. Observer variability in the assessment of type and dysplasia of colorectal adenomas, analyzed using kappa statistics. Dis. Colon Rectum 1995, 38, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J. A coefficient of agreement for nominal scales. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1960, 20, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montresor, A.; Crompton, D.W.; Hall, A.; Bundy, D.A.; Savioli, L.; WHO. Guidelines for the Evaluation of Soil-Transmitted Helminthiasis and Schistosomiasis at Community Level: A Guide for Managers of Control Programmes; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Katz, N.; Chaves, A.; Pellegrino, J.A. simple device for quantitative stool thick-smear technique in Schistosomiasis mansoni. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 1972, 14, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- WHO Expert Committee. Prevention and Control of Schistosomiasis and Soil-Transmitted Helminthiasis; WHO Technical Report Series; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002; p. 912. [Google Scholar]
- Venables, W.; Smith, D.M. An Introduction to R: Notes on R, A Programming Environment for Data Analysis and Graphics; R Development: Viena, Austria, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Devkota, R.; Budha, P.B.; Gupta, R. Trematode cercariae infections in freshwater snails of Chitwan district, central Nepal. J. Himal. Sci. 2011, 7, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, K. Prevalence of Fasciolosis in Buffaloes in Relation to Fasciola Larvae Infection in Lymnaea Snails in Dev Bhumi Baluwa VDC of Kavre District. Master’s Dissertation, Tribhuvan University, Kathmandu, Nepal, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Grimes, J.E.; Croll, D.; Harrison, W.E.; Utzinger, J.; Freeman, M.C.; Templeton, M.R. The roles of water, sanitation and hygiene in reducing schistosomiasis: A review. Parasit. Vectors 2015, 8, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hechinger, R.F.; Lafferty, K.D. Host diversity begets parasite diversity: Bird final hosts and trematodes in snail intermediate hosts. Proc. R. Soc. B 2005, 272, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siama, A.; Saotoing, P.; Nloga, A.M. Malacological survey and dynamic of Lymnaeanatalensis population intermediate host of Fasciola gigantica in the Douvar dam freshwater of Farth Nord region Cameroon. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2020, 8, 1213–1221. [Google Scholar]
- De Troyer, N.; Mereta, S.T.; Goethals, P.L.; Boets, P. Water quality assessment of streams and wetlands in a fast growing east African city. Water 2016, 8, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zongo, D.; Kabré, B.G.; Poda, J.N.; Dianou, D. Schistosomiasis among farmers and fisherman in the West part of Burkina Faso (West Africa). J. Biol. Sci. 2008, 8, 482–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ayanda, O.I. Prevalence of snail vectors of schistosomiasis and their infection rates in two localities within Ahmadu Bello University (ABU) Campus, Zaria, Kaduna State, Nigeria. J. Cell Anim.Biol. 2009, 3, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soboksa, N.E.; Yimam, G.N. Assessment of household level sanitation practice of mothers’ and associated factors in Gedeo Zone, South Ethiopia. Am. J. Public Health Res. 2017, 5, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayalew, A.M.; Mekonnen, W.T.; Abaya, S.W.; Mekonnen, Z.A. Assessment of diarrhea and its associated factors in under-five children among open defecation and open defecation-free rural settings of Dangla District, Northwest Ethiopia. J. Environ. Public Health 2018, 2018, 4271915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmann, P.; Keiser, J.; Bos, R.; Tanner, M.; Utzinger, J. Schistosomiasis and water resources development: Systematic review, meta-analysis, and estimates of people at risk. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2006, 6, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alebie, G.; Erko, B.; Aemero, M.; Petros, B. Epidemiological study on Schistosoma mansoni infection in Sanja area, Amhara region, Ethiopia. Parasit. Vectors 2014, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadege, B.; Shimelis, T. Infections with Schistosoma mansoni and geohelminths among school children dwelling along the shore of the Lake Hawassa, southern Ethiopia. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chimbari, M.J.; Dhlomo, E.; Mwadiwa, E.; Mubila, L. Transmission of schistosomiasis in Kariba, Zimbabwe, and a cross-sectional comparison of schistosomiasis prevalences and intensities in the town with those in Siavonga in Zambia. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasit. 2003, 97, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menjetta, T.; Dana, D.; Debalke, S. Schistosoma mansoni infection and risk factors among fishermen at Lake Hawassa, Southern Ethiopia. BioRxiv 2018, 51, 817–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taman, A.; El-Tantawy, N.; Besheer, T.; Taman, S.; Helal, R. Schistosoma mansoni infection in a fishermen community, the Lake Manzala region-Egypt. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Dis. 2014, 4, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, S.J.; Biritwum, N.-K.; Woods, G.; Velleman, Y.; Fleming, F.; Stothard, J.R. Tailoring water, sanitation, and hygiene (WASH) targets for soil-transmitted helminthiasis and schistosomiasis control. Trends Parasitol. 2018, 34, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rollinson, D.; Knopp, S.; Levitz, S.; Stothard, J.R.; Tchuenté, L.A.; Garba, A. Time to set the agenda for schistosomiasis elimination. Acta Trop. 2013, 128, 423–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forio, M.A.; Goethals, P.L. An integrated approach of multi-community monitoring and assessment of aquatic ecosystems to support sustainable development. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebremedhin, S.; Bruneel, S.; Getahun, A.; Anteneh, W.P.; Goethals, P. Scientific Methods to Understand Fish Population Dynamics and Support Sustainable Fisheries Management. Water 2021, 13, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maasri, A.; Jähnig, S.C.; Adamescu, M.C.; Adrian, R.; Baigun, C.; Baird, D.J.; Worischka, S. A global agenda for advancing freshwater biodiversity research. Ecol. Let. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Study Area | Season | Snail Species | Infection Prevalence with a Type of Cercaria (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BAD | Echis | Xior | Gymn | Amph | Meta | |||
| Lake Hawassa | Wet | B. pfeifferi | 9 | 30 | 7 | 2 | 12 | 5 |
| B. sudanica | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 13 | 0 | ||
| Dry | B. pfeifferi | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| B. sudanica | 6 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 0 | ||
| Lake Ziway | Wet | B. pfeifferi | 4 | 16 | 4 | 6 | 12 | 0 |
| B. sudanica | 0 | 14 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | ||
| Environmental Variable | Unit | Mean | SD | Minimum | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | - | 9 | 1 | 6 | 10 |
| Turbidity | NTU | 20 | 31 | 2 | 247 |
| Dissolved oxygen | mg/L | 5 | 3 | 0.5 | 17 |
| Chlorophyll-a | µg/L | 25 | 13 | 11 | 76 |
| Electrical conductivity | µs/cm | 564 | 243 | 71 | 940 |
| BOD5 | mg/L | 26 | 40 | 0.3 | 184 |
| TSS | mg/L | 43 | 31 | 5.2 | 136 |
| Total hardness | mg/L | 68 | 22 | 24 | 120 |
| Calcium ion | mg/L | 49 | 18 | 16 | 100 |
| Magnesium ion | mg/L | 19 | 8 | 0 | 36 |
| Chloride ion | mg/L | 29 | 9 | 11 | 48 |
| Water depth | m | 0.6 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 2 |
| Water transparency | m | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0 | 0.6 |
| Water temperature | °C | 24 | 3 | 19 | 30 |
| Ambient temperature | °C | 26 | 2 | 20 | 31 |
| Canopy cover | % | 16 | 21 | 0 | 100 |
| Variable | Estimate | Std. Error | z Value | Pr (>|z|) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dissolved oxygen | −0.29322 | 0.11558 | −2.537 | 0.0112 * |
| BOD5 | 0.011696 | 0.005558 | 2.104 | 0.0354 * |
| Study Area | Infection Intensity of S. mansoni, n (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Light | Moderate | Heavy | |
| Lake Hawassa | 22 (35) | 19 (31) | 21 (34) |
| Lake Ziway | 17 (71) | 4 (17) | 3 (13) |
| Both lakes | 39 (45) | 23 (27) | 24 (28) |
| Risk Factor | Category | S. mansoni Infection Status | COR (95% CI) | AOR (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive, n (%) | Negative, n (%) | ||||
| Age group (years) | 18–27 | 19 (15) | 104 (85) | 0.40 (0.17–0.95) * | 0.21 (0.07–0.64) * |
| 28–37 | 57 (24) | 185 (76) | 0.67 (0.31–1.46) | 0.38 (0.13–0.96) * | |
| 38 and above | 11 (31) | 24 (69) | 1 | 1 | |
| Level of education | No formal education | 11 (27) | 30 (73) | 1.1 (0.35–3.45) | 1.77 (0.45–7.19) |
| Primary education | 70 (21) | 265 (79) | 0.79 (0.30–2.1) | 0.97 (0.32–2.97) | |
| Secondary education and above | 6 (25) | 18 (75) | 1 | 1 | |
| Residence | Urban | 46 (22) | 160 (78) | 1.07 (0.67–1.74) | 1.29 (0.73–2.27) |
| Rural | 41 (21) | 153 (79) | 1 | 1 | |
| Type of activity | Fishing | 58 (27) | 160 (73) | 1.91 (1.16–3.15) * | 2.24 (1.29–3.92) * |
| Fish processing | 29 (16)) | 153 (84) | 1 | 1 | |
| Swimming/bathing in lake | Yes | 75 (22) | 264 (78) | 1.16 (0.59–2.29) | 1.08 (0.49–2.38) |
| No | 12 (20) | 49 (80) | 1 | 1 | |
| Open defecation/urination in lake | Yes | 32 (32) | 68 (68) | 2.10 (1.26–3.50) * | 2.37 (1.35–4.16) * |
| No | 55 (18) | 245 (82) | 1 | 1 | |
| Using water from lake for domestic purposes | Yes | 13 (16) | 70 (84) | 0.61 (0.32–1.14) | 0.33 (0.14–0.76) * |
| No | 74 (23) | 243 (77) | 1 | 1 | |
| Boiling water before drinking | Yes | 3 (19) | 13 (81) | 0.84 (0.23–2.96) | 0.67 (0.18–2.51) |
| No | 84 (22) | 300 (78) | 1 | 1 | |
| Defecating in bush | Yes | 59 (21) | 220 (79) | 0.89 (0.53–1.49) | 0.79 (0.42–1.48) |
| No | 28 (23) | 93 (77) | 1 | 1 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Olkeba, B.K.; Boets, P.; Mereta, S.T.; Mandefro, B.; Debesa, G.; Ahmednur, M.; Ambelu, A.; Korma, W.; Goethals, P.L.M. Malacological and Parasitological Surveys on Ethiopian Rift Valley Lakes: Implications for Control and Elimination of Snail-Borne Diseases. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19010142
Olkeba BK, Boets P, Mereta ST, Mandefro B, Debesa G, Ahmednur M, Ambelu A, Korma W, Goethals PLM. Malacological and Parasitological Surveys on Ethiopian Rift Valley Lakes: Implications for Control and Elimination of Snail-Borne Diseases. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(1):142. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19010142
Chicago/Turabian StyleOlkeba, Beekam Kebede, Pieter Boets, Seid Tiku Mereta, Belayhun Mandefro, Gemechu Debesa, Mahmud Ahmednur, Argaw Ambelu, Wolyu Korma, and Peter L. M. Goethals. 2022. "Malacological and Parasitological Surveys on Ethiopian Rift Valley Lakes: Implications for Control and Elimination of Snail-Borne Diseases" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 1: 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19010142
APA StyleOlkeba, B. K., Boets, P., Mereta, S. T., Mandefro, B., Debesa, G., Ahmednur, M., Ambelu, A., Korma, W., & Goethals, P. L. M. (2022). Malacological and Parasitological Surveys on Ethiopian Rift Valley Lakes: Implications for Control and Elimination of Snail-Borne Diseases. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(1), 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19010142








