Heavy Metal Contamination in an Industrially Affected River Catchment Basin: Assessment, Effects, and Mitigation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. River Field Sampling
2.3. Sample Preparation and Analyses for HMs and Macrozoobenthos
2.4. Assessment of HM Contamination, Environmental Hazards, and Macrozoobenthos Diversity
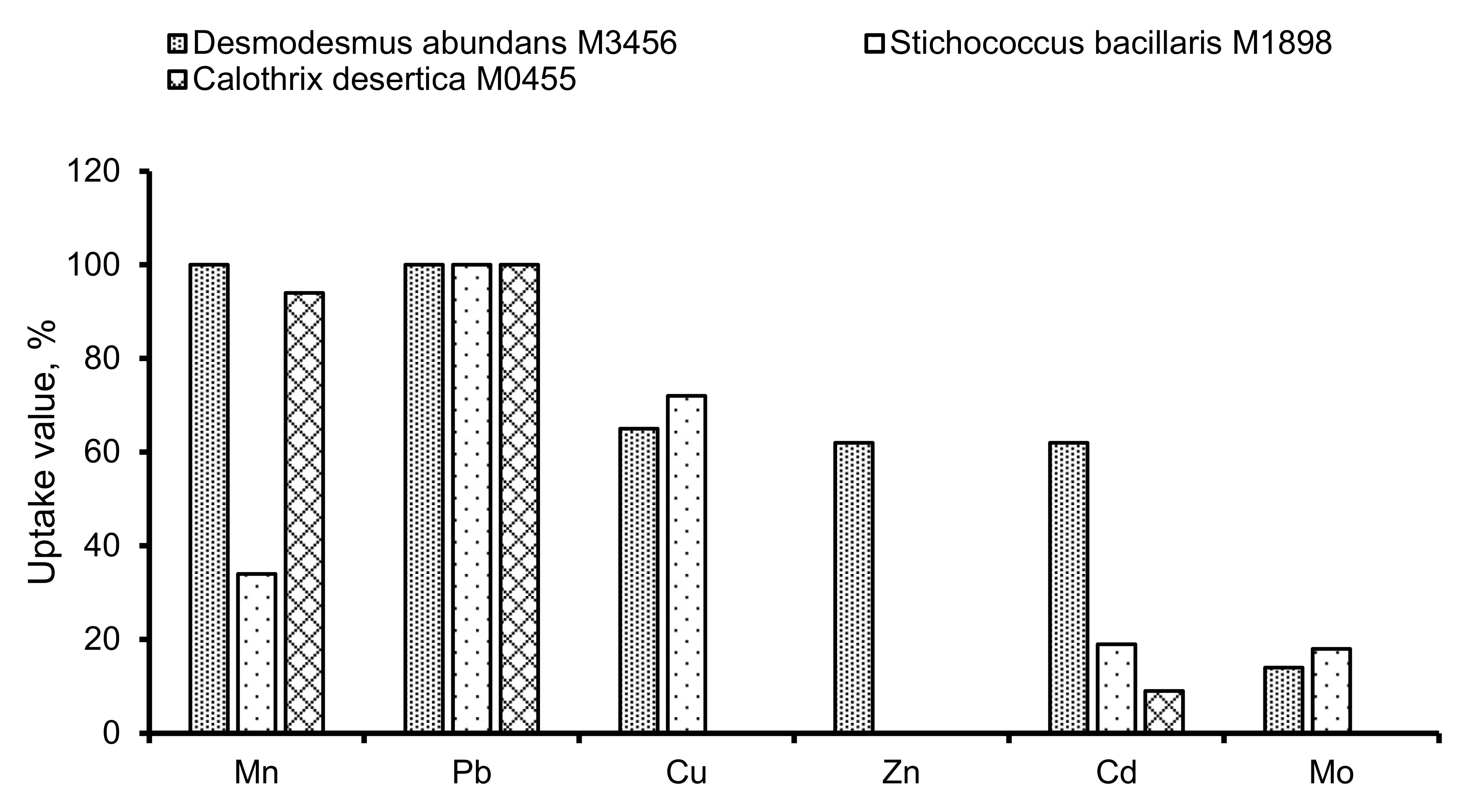
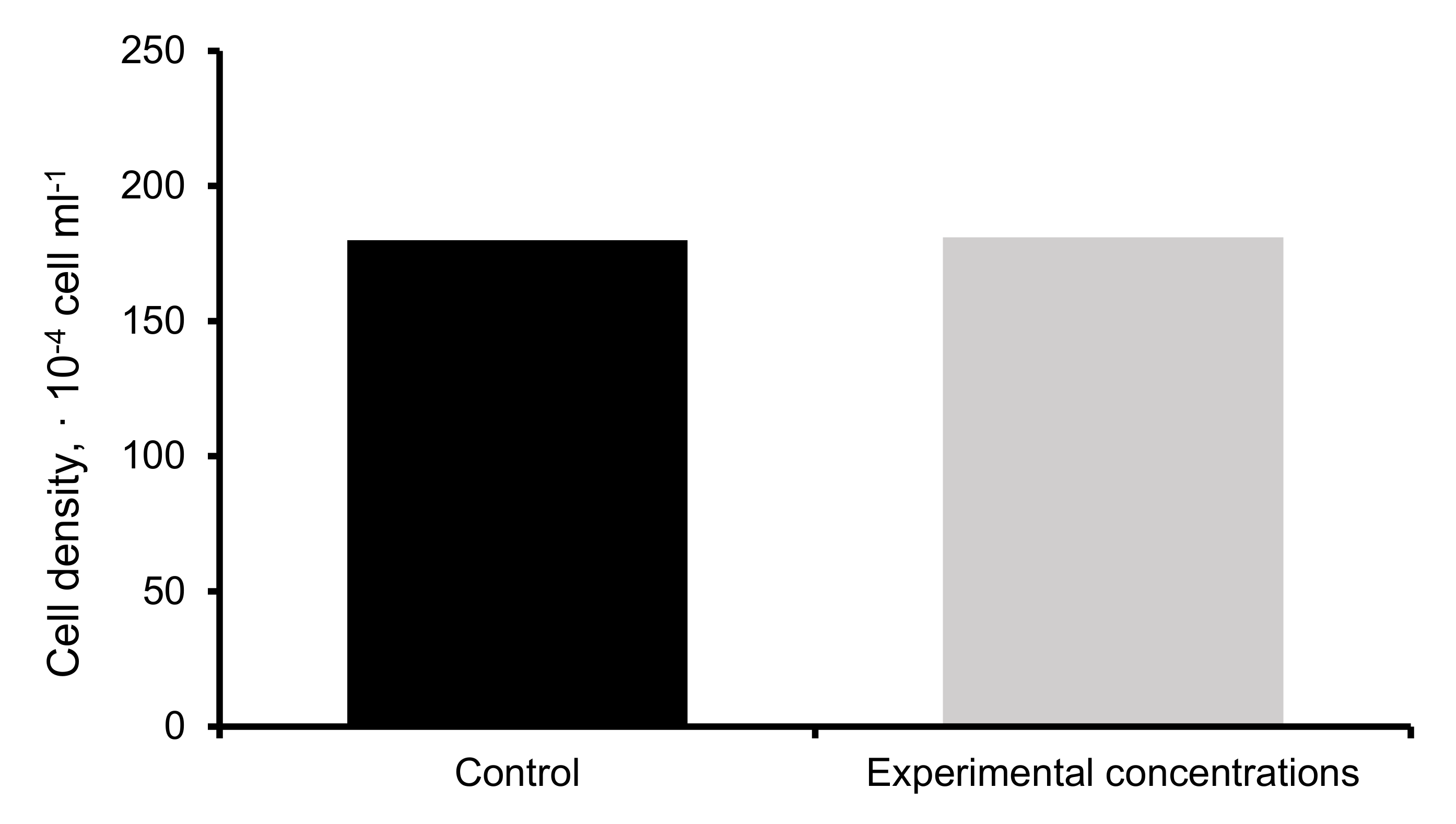
2.5. Phytoextraction of HMs
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. HMs in River Water
3.2. HMs in River Macrozoobenthos and Fish
3.3. Assessment of HM Contamination in River Waters, Macrozoobenthos, and Fish
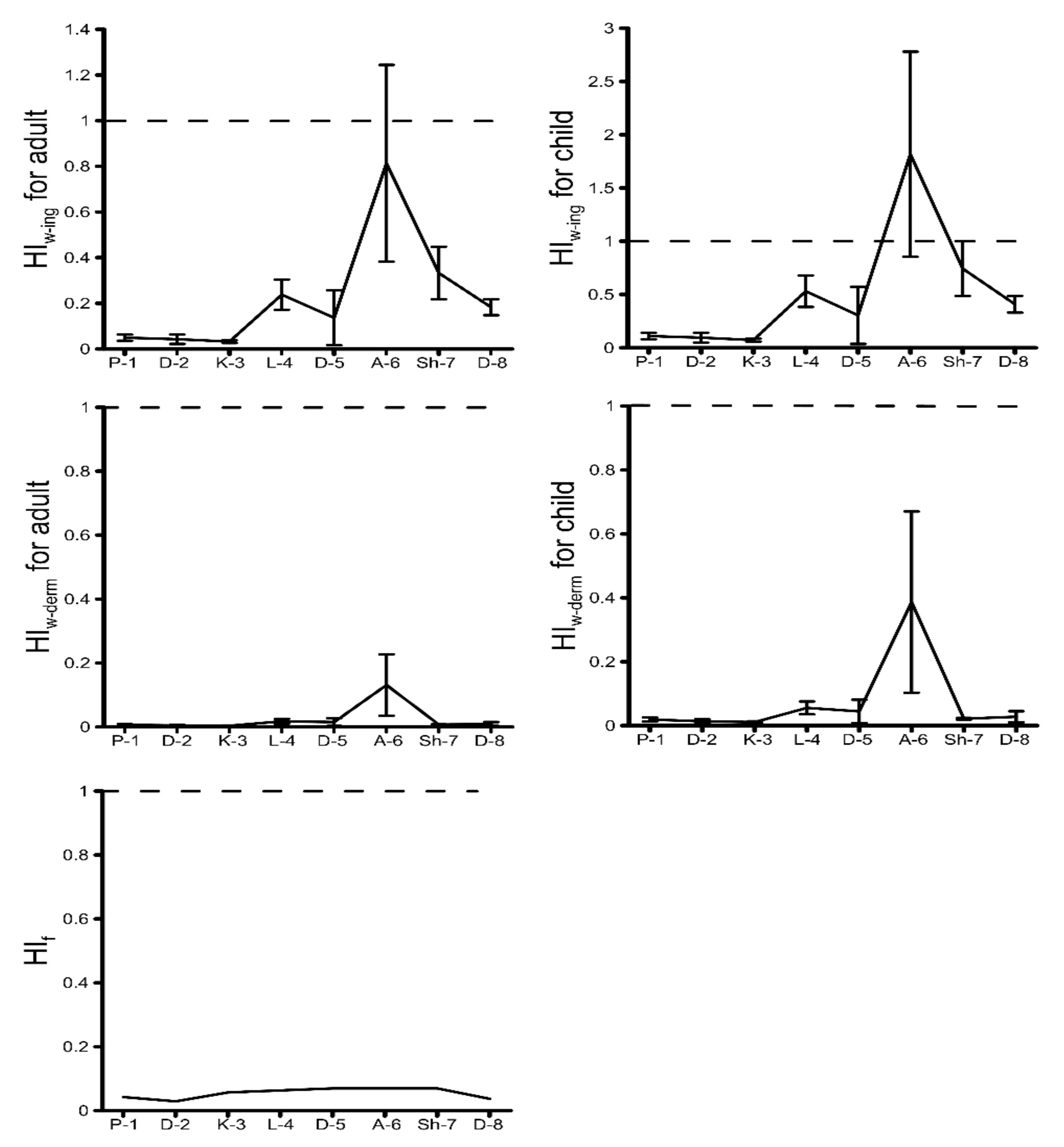
3.4. Adverse Health Effects by HM Contamination in River Water and Fish
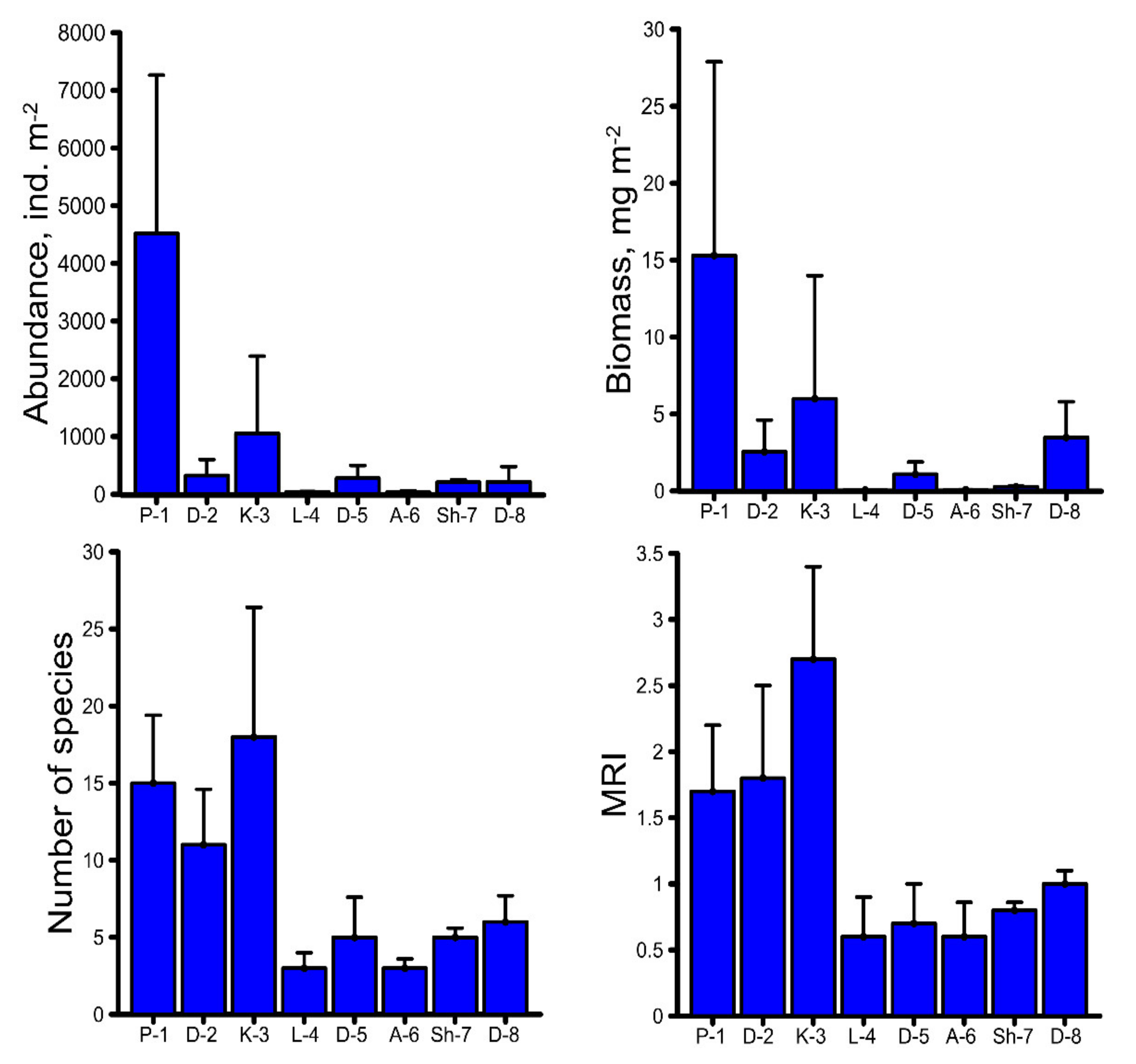
3.5. Adverse Biological Effects by HM Contamination in River
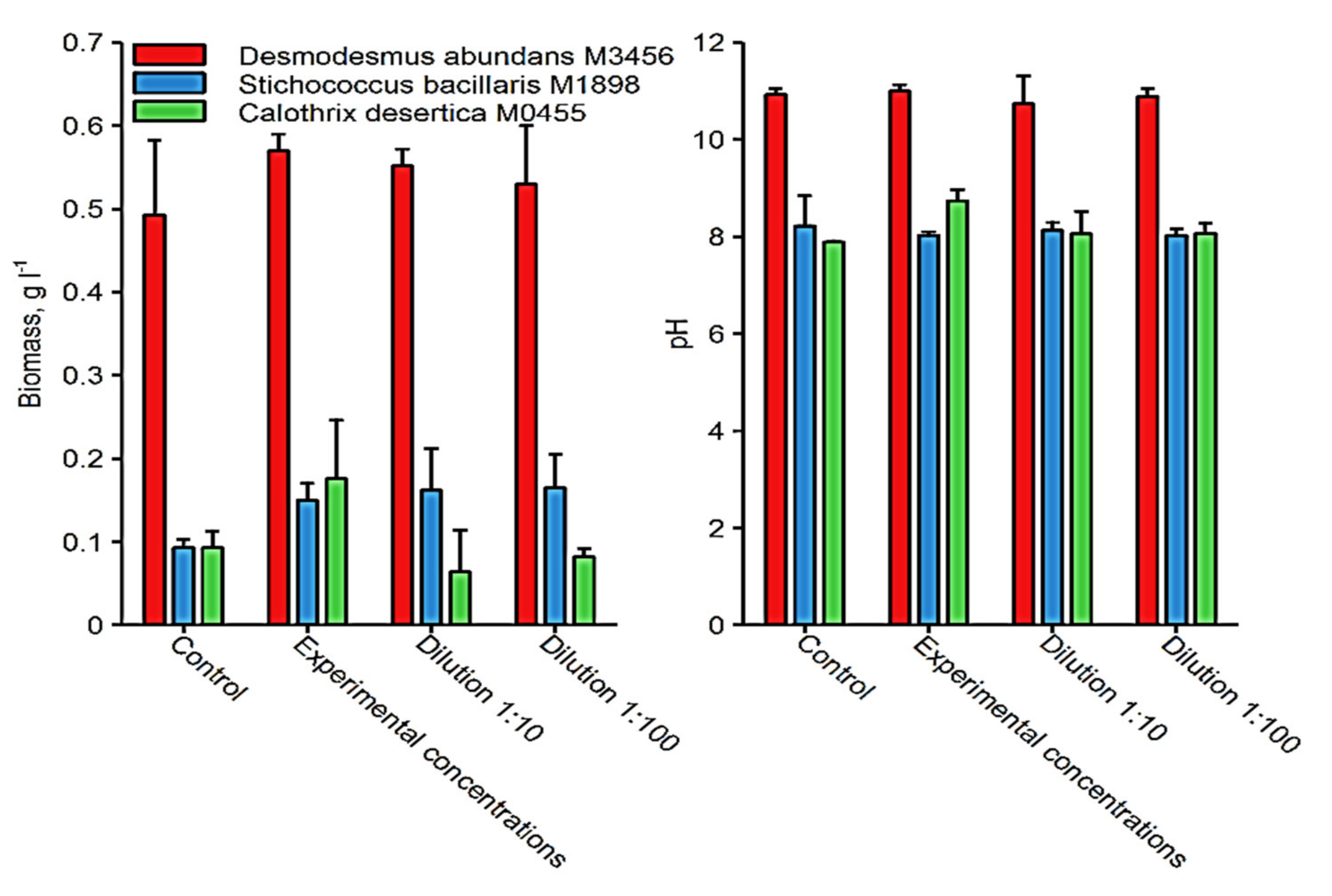
3.6. Phytoextraction of HMs in Water
4. Conclusions and Recommendations
- Setting of new treatment technologies (e.g., microalgal remediation) for improving the quality of wastewaters discharged from the mining industry.
- Implementation of remediation works (i.e., covering with soil and vegetation) in the areas affected by the mining industry.
- Maintenance of the rules for technical operation of the tailing dumps and restoration of their damaged parts.
- Definition of strict regulations for waste storage and emissions for miners.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiao, F.; Ren, L.; Liu, W. Pollution Characteristics and Potential Ecological Risk Assessment of Metals in the Sediments of Xiaoqing River, Jinan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 15001–15011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bo, L.; Wang, D.; Li, T.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Wang, C.; Zhang, S. Accumulation and Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Water, Sediments, and Aquatic Organisms in Rural Rivers in the Taihu Lake Region. China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 6721–6731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, G.; Hoang, H.; Lin, C.; Bui, X.-T.; Tran, H.-T.; Shern, C.-C.; Vu, C.-T. Assessment of Heavy Metal Contamination and Adverse Biological Effects of an Industrially Affected River. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 34770–34780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Liu, C.; Zhao, X.; Dong, J.; Zheng, B. Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in the Surface Sediment at the Drinking Water Source of the Xiangjiang River in South China. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2020, 32, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khallaf, E.A.; Authman, M.M.N.; Alnenaei, A.A. Contamination and Ecological Hazard Assessment of Heavy metals in Freshwater Sediments and Oreochromis niloticus (Linnaeus, 1758) Fish Muscles in a Nile River Canal in Egypt. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 13796–13812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.L.; Fang, L.; Song, J.Y.; Luo, X.; Fu, K.D.; Chen, L.Q. Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Cyprinus carpio (Cyprinidae) from the upper Mekong River. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 9490–9499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, J.; Wang, J.; Pan, H.; Yang, C.; Qu, J.; Lu, N.; Yuan, X. Heavy Metals in Yinma River Sediment in a Major Phaeozems Zone, Northeast China: Distribution, Chemical Fraction, Contamination Assessment and Source Apportionment. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Y.-J.; Sun, J.; Tang, C.-H.; Zhang, S.-H. Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Sediment in the upper Rich of the Yangtze River. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 11002–11013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, A.M.; Salviano, A.M.; Melo, J.F.B.; Felix, W.P.; Belem, C.S.; Ramos, P.N. Seasonal Study of Concentration of Heavy Metals in Waters from Lower São Francisco River Basin, Brazil. Braz. J. Biol. 2016, 76, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taiwo, I.O.; Babajide, S.O.; Taiwo, A.A.; Osunkiyesi, A.A.; Akindele, O.I.; Sojobi, O.A. Phytoremediation of Heavy Metals (Cu, Zn, and Pb) Contaminated Water Using Water Hyacinth (Eichornia crassipes). IOSR JAC 2015, 8, 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Life Cycle of Nanoparticles; Vaseashta, A., Ed.; DEStech Publications: Lancaster, PA, USA, 2015; pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Stefes, C.H.; Theodoratos, P. Armenia: A Case Study on Mining. In Fighting Environmental Crime in Europe and Beyond; Sollund, R., Stefes, C., Germani, A., Eds.; Palgrave Macmillan: London, UK, 2016; pp. 187–216. [Google Scholar]
- Gevorgyan, G.A.; Mamyan, A.S.; Hambaryan, L.R.; Khudaverdyan, S.K.; Vaseashta, A. Environmental Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution in Armenian River Ecosystems: Case Study of Lake Sevan and Debed River Catchment Basins. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2016, 25, 2387–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvaryan, Y.; Sargsyan, V.; Sargsyan, A. The Problem of Heavy Metal Pollution in the Republic of Armenia: Overview and strategies of balancing socioeconomic and ecological development. In Environmental Heavy Metal Pollution and Effects on Child Mental Development; Simeonov, L., Kochubovski, M., Simeonova, B., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 309–316. [Google Scholar]
- Kurkjian, R.; Dunlap, C.; Flegal, A.R. Long-range Downstream Effects of Urban Runoff and Acid Mine Drainage in the Debed River, Armenia: Insights from Lead Isotope Modeling. Appl. Geochem. 2004, 19, 1567–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielyan, A. The Ecological Assessment of the Debed River and Its Catchment Basin and the Perspectives for the Sustainable Development of the Area. Ph.D. Thesis, Scientific Center of Zoology and Hydroecology of NAS RA, Yerevan, Armenia, 2009. In Armenian. [Google Scholar]
- Pipoyan, S.; Arakelyan, A. The Ichthyofauna of Aghstev and Debed River Basins (North Armenia) and the Impact of Separate Factors on Its Transformation. IJOAC 2018, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Arakelyan, A. Ichthyofauna of Aquatic Ecosystems of Tavush and Lori Provinces of the Republic of Armenia. Ph.D. Thesis, Scientific Center of Zoology and Hydroecology of NAS RA, Yerevan, Armenia, 2020. In Armenian. [Google Scholar]
- FSI FCAATI. Methods for Measuring the Mass Concentration of Iron, Cadmium, Cobalt, Manganese, Nickel, Copper, Zinc, Chromium and Lead in Samples of Natural and Waste Waters Using Plasma Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. In Quantitative Chemical Analysis of Water; PND F 14.1:2:4.214-06; Federal State Institution Federal Center for Analysis and Assessment of Technogenic Impact (FSI FCAATI): Moscow, Russia, 2011; In Russian. [Google Scholar]
- Hanna Instruments, Co. Instruction Manual. Available online: http://www.pewa.de/DATENBLATT/DBL_HA_HA83200-02_MANUAL_ENGLISCH.PDF (accessed on 2 March 2021).
- Müller, G. Heavy Metals in the Sediments of the Rhine—Changes since 1971. Umschau 1979, 79, 778–783, In German. [Google Scholar]
- USDOE. The Risk Assessment Information System (RAIS); U.S. Department of Energy (USDOE): Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 2011.
- USEPA. Regional Screening Level (RSL) Table for Chemical Contaminants at Superfund Sites; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA): Washington, DC, USA, 2011.
- USEPA. Human Health Toxicity Values in Superfund Risk Assessments; OSWER Directive 9285.7-53; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA): Washington, DC, USA, 2003.
- Margalef, R. Information Theory in Ecology. Gen. Syst. 1958, 3, 36–71. [Google Scholar]
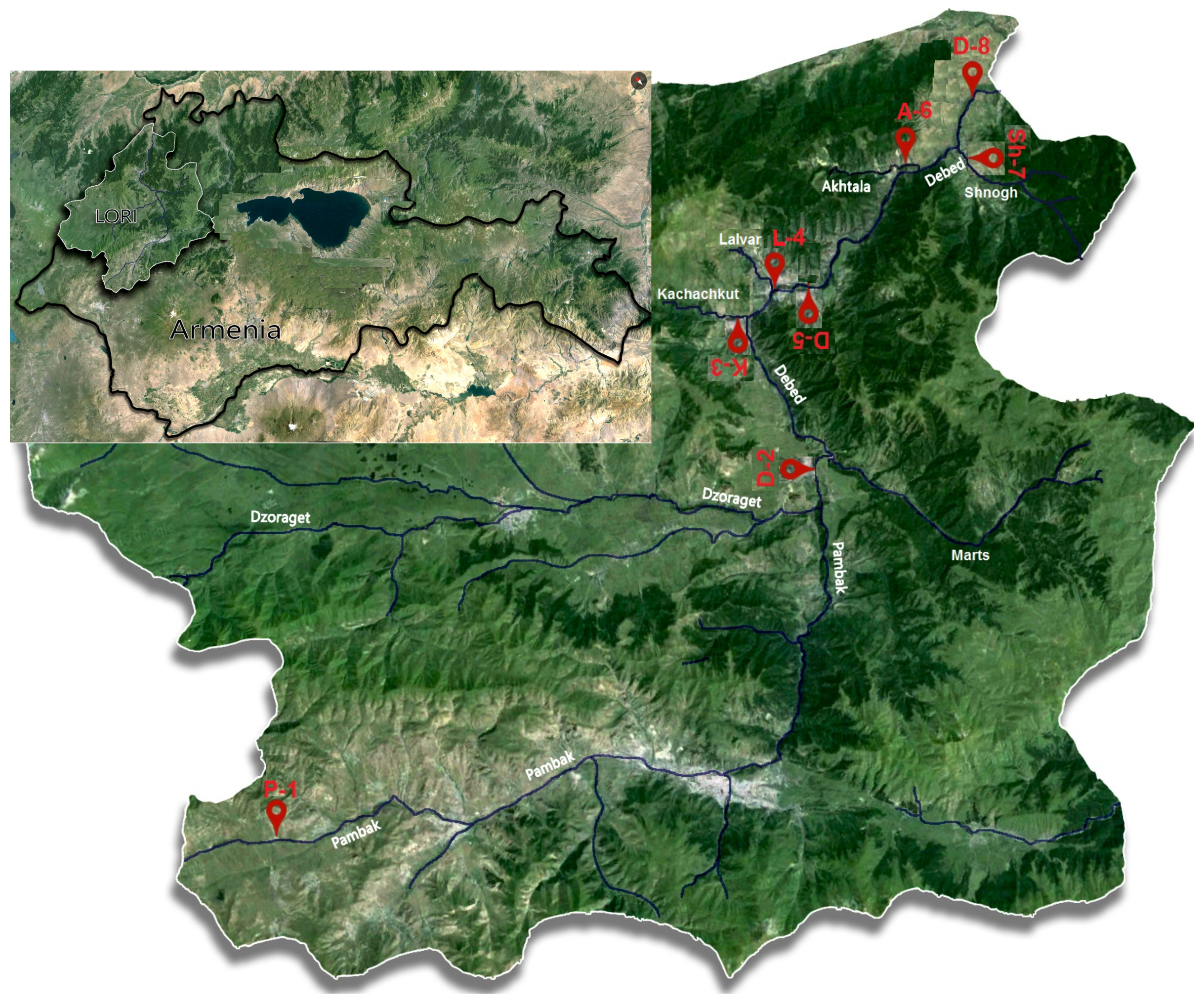

| Sampling Site Code | N/Lat | E/Long | River Site Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| P-1 | 40°50′51.8″ | 44°09′36.6″ | Pambak River site located in the river upstream |
| D-2 | 40°59′08.2″ | 44°39′04.8″ | Debed River site located downstream of the confluence of the Pambak and Dzoraget rivers |
| K-3 | 41°04′55.2″ | 44°37′07.2″ | Kachachkut River site located near the river mouth |
| L-4 | 41°05′56.8″ | 44°39′28.8″ | Lalvar River site located near the river mouth |
| D-5 | 41°06′48.5″ | 44°44′16.2″ | Debed River site located downstream of Alaverdi Town |
| A-6 | 41°08′57.3″ | 44°46′56.0″ | Akhtala River site located in the river downstream |
| Sh-7 | 41°09′04.1″ | 44°49′49.3″ | Shnogh River site located near the river mouth |
| D-8 | 41°12′33.4″ | 44°54′08.8″ | Debed River site located near Ayrum Town |
| Igeo Value | Contamination Degree | Contamination Class |
|---|---|---|
| ˂0 | Uncontaminated | 0 |
| ≥0, ˂1 | Uncontaminated to moderately contaminated | 1 |
| ≥1, ˂2 | Moderately contaminated | 2 |
| ≥2, ˂3 | Moderately to heavily contaminated | 3 |
| ≥3, ˂4 | Heavily contaminated | 4 |
| ≥4, ˂5 | Heavily to extremely contaminated | 5 |
| ≥5 | Extremely contaminated | 6 |
| Metal Compound | MnCl2·2H2O | NiCl2·6H2O | Cr2K2O7 | Na2MoO4·2H2O | VCl3 | ZnCl2 | CuSO4 ·5H2O | PbCl2 | CdCl2 | Co(NO3)2·6H2O | NaAsO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration in environment (µg L−1) | 191.7 | 2.8 | 2.3 | 508.4 | 2.9 | 108.0 | 120 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 1.8 | 2.03 |
| HMs | Fe | Zn | Mn | Cu | Mo | Pb | Cd |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe | 1 | ||||||
| Zn | 0.53 | 1 | |||||
| Mn | 0.41 | 0.96 | 1 | ||||
| Cu | 0.14 | 0.75 | 0.84 | 1 | |||
| Mo | −0.22 | −0.06 | −0.09 | 0.04 | 1 | ||
| Pb | 0.39 | 0.97 | 0.99 | 0.86 | 0.04 | 1 | |
| Cd | 0.34 | 0.94 | 0.98 | 0.75 | −0.06 | 0.97 | 1 |
| Sampling Sites | Fe | Zn | Mn | Cu | Mo | Pb | Cd |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Macrozoobenthos tissues | |||||||
| P-1 | 204.75 | 71.50 | 66.30 | 21.13 | NR | NR | NR |
| D-2 | 1005.00 | 195.00 | 256.00 | 39.50 | NR | Traces | NR |
| K-3 | 750.29 | 200.57 | 110.31 | 74.29 | NR | NR | NR |
| L-4 | 517.36 | 409.57 | 274.22 | 175.85 | NR | 1.40 | NR |
| D-5 | 6364.18 | 329.85 | 395.82 | 203.73 | 5.82 | 1.36 | NR |
| A-6 | 5066.67 | 1311.11 | 284.44 | 133.33 | NR | 1.93 | NR |
| Sh-7 | 627.14 | 272.33 | 105.37 | 104.27 | 21.89 | Traces | NR |
| D-8 | 1827.03 | 165.14 | 107.86 | 86.43 | NR | Traces | NR |
| Kura scraper gills | |||||||
| P-1 | 132.95 | 97.50 | 22.69 | 4.20 | NR | NR | NR |
| D-2 | 243.92 | 115.26 | 47.98 | 6.86 | NR | NR | NR |
| K-3 | 216.67 | 117.62 | 49.03 | 10.52 | Traces | NR | NR |
| D-5 | 222.60 | 113.97 | 36.51 | 8.90 | 1.78 | NR | NR |
| Sh-7 | 168.47 | 77.38 | 31.28 | 11.93 | 0.94 | NR | NR |
| D-8 | 65.80 | 44.94 | 45.10 | 6.58 | NR | NR | NR |
| Kura scraper liver | |||||||
| P-1 | 431.05 | 95.79 | 17.11 | 23.4 | NR | NR | NR |
| D-2 | 469.13 | 96.09 | 40.53 | 20.91 | NR | NR | NR |
| K-3 | 364.00 | 104.00 | 53.17 | 33.80 | NR | NR | NR |
| D-5 | 704.74 | 95.79 | 35.03 | 25.32 | NR | NR | NR |
| Sh-7 | 421.76 | 86.27 | 25.34 | 38.41 | 5.71 | NR | NR |
| D-8 | 239.32 | 339.77 | 7.39 | 27.77 | 14.77 | NR | NR |
| Kura scraper muscles | |||||||
| P-1 | 90.43 | 50.87 | 4.71 | 4.01 | NR | NR | NR |
| D-2 | 90.10 | 47.62 | 11.84 | 3.22 | NR | NR | NR |
| K-3 | 116.07 | 27.57 | 11.14 | 3.05 | NR | NR | NR |
| D-5 | 118.30 | 49.40 | 6.66 | 4.16 | 1.30 | NR | NR |
| Sh-7 | 98.43 | 32.84 | 6.34 | 4.84 | 1.70 | NR | NR |
| D-8 | 144.16 | 30.89 | 3.22 | 3.06 | NR | NR | NR |
| Sampling Sites | Indicator Metals | Contamination Degree (Class) | Indicator Metals | Contamination Degree (Class) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | Macrozoobenthos | |||
| P-1 | Fe, Zn, Cu, Mo, Pb, Cd | UC (0) | Fe, Zn, Mn, Cu, Mo, Pb, Cd | UC (0) |
| Mn | UC-MC (1) | |||
| D-2 | Zn, Mn, Cu, Mo, Pb, Cd | UC (0) | Mo, Cd | UC (0) |
| Pb | ≥UC (≥0) | |||
| Zn, Cu | UC-MC (1) | |||
| Fe | UC-MC (1) | Fe, Mn | MC (2) | |
| K-3 | Fe, Mn, Cu, Mo, Pb, Cd | UC (0) | Mo, Pb, Cd | UC (0) |
| Zn, Mn | UC-MC (1) | |||
| Zn | UC-MC (1) | Fe, Cu | MC (2) | |
| L-4 | Fe | UC (0) | Mo, Cd | UC (0) |
| Mo, Cd | ≥UC (≥0) | Fe | UC-MC (1) | |
| Pb | ≥UC-MC (≥1) | Zn, Mn | MC (2) | |
| Mn | MC (2) | Pb | ≥MC (≥2) | |
| Zn, Cu | HC (4) | Cu | MC-HC (3) | |
| D-5 | Mo, Cd | UC (0) | Cd | UC (0) |
| Mo | ≥UC-MC (≥1) | |||
| Pb | ≥UC (≥0) | Zn, Mn | MC (2) | |
| Pb | ≥MC (≥2) | |||
| Fe, Mn, Cu | MC (2) | Cu | MC-HC (3) | |
| Zn | HC-EC (5) | Fe | HC-EC (5) | |
| A-6 | Fe | UC-MC (1) | Mo, Cd | UC (0) |
| Mo, Pb, Cd | ≥MC-HC (≥3) | Mn | MC (2) | |
| Mn, Cu | HC (4) | Pb | ≥MC (≥2) | |
| Cu | MC-HC (3) | |||
| Zn | EC (6) | Zn | HC (4) | |
| Fe | HC-EC (5) | |||
| Sh-7 | Fe, Mn | UC (0) | Cd | UC (0) |
| Pb, Cd | ≥UC (≥0) | Pb | ≥UC (≥0) | |
| Zn | UC-MC (1) | Mn | UC-MC (1) | |
| Mo | ≥UC-MC (≥1) | Fe, Zn, Cu | MC (2) | |
| Cu | MC (2) | Mo | ≥MC-HC (≥3) | |
| D-8 | Pb, Cd | ≥UC (≥0) | Mo, Cd | UC (0) |
| Pb | ≥UC (≥0) | |||
| Fe, Mn, Cu | UC-MC (1) | Zn, Mn | UC-MC (1) | |
| Mo | ≥UC-MC (≥1) | Cu | MC (2) | |
| Zn | HC-EC (5) | Fe | MC-HC (3) | |
| Sampling Sites | Indicator Metals | Contamination Degree (Class) | Indicator Metals | Contamination Degree (Class) | Indicator Metals | Contamination Degree (Class) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kura Scraper Gills | Kura Scraper Liver | Kura Scraper Muscles | ||||
| P-1 | Mn, Cu, Mo, Pb, Cd | UC (0) | Zn, Cu, Mo, Pb, Cd | UC (0) | Fe, Mn, Cu, Mo, Pb, Cd | UC (0) |
| Fe, Zn, | UC-MC (1) | Fe, Mn | UC-MC (1) | Zn | UC-MC (1) | |
| D-2 | Mo, Pb, Cd | UC (0) | Zn, Cu, Mo, Pb, Cd | UC (0) | Fe, Cu, Mo, Pb, Cd | UC (0) |
| Fe | UC-MC (1) | |||||
| Zn, Mn, Cu | UC-MC (1) | Mn | MC (2) | Zn | UC-MC (1) | |
| Fe | MC (2) | Mn | MC (2) | |||
| K-3 | Pb, Cd | UC (0) | Zn, Mo, Pb, Cd | UC (0) | Fe, Zn, Cu, Mo, Pb, Cd | UC (0) |
| Mo | ≥UC (≥0) | |||||
| Zn, Mn, Cu | UC-MC (1) | Fe, Cu | UC-MC (1) | |||
| Fe | MC (2) | Mn | MC-HC (3) | Mn | MC (2) | |
| D-5 | Pb, Cd | UC (0) | Zn, Cu, Mo, Pb, Cd | UC (0) | Fe, Cu, Pb, Cd | UC (0) |
| Mo | ≥UC (≥0) | |||||
| Zn, Mn, Cu | UC-MC (1) | Fe | UC-MC (1) | Mo | ≥UC (≥0) | |
| Fe | MC (2) | Mn | MC (2) | Zn, Mn | UC-MC (1) | |
| Sh-7 | Mn, Pb, Cd | UC (0) | Zn, Pb, Cd | UC (0) | Fe, Zn, Pb, Cd | UC (0) |
| Mo | ≥UC (≥0) | Mo | ≥UC (≥0) | |||
| Fe, Cu | UC-MC (1) | Mo | ≥UC (≥0) | |||
| Fe, Zn, Cu | UC-MC (1) | Mn | MC (2) | Mn, Cu | UC-MC (1) | |
| D-8 | Fe, Zn, Mo, Pb, Cd | UC (0) | Fe, Mn, Cu, Pb, Cd | UC (0) | Zn, Mn, Cu, Mo, Pb, Cd | UC (0) |
| Mo | ≥UC-MC (≥1) | |||||
| Mn, Cu | UC-MC (1) | Zn | MC (2) | Fe | UC-MC (1) | |
| Macrozoobenthos Parameters | Fe | Zn | Mn | Cu | Mo | Pb | Cd |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abundance | −0.35 | −0.35 | −0.26 | −0.37 | −0.37 | −0.35 | −0.21 |
| Biomass | −0.37 | −0.38 | −0.34 | −0.49 | −0.46 | −0.43 | −0.28 |
| Species number | −0.48 | −0.54 | −0.49 | −0.65 | −0.53 | −0.58 | −0.37 |
| MRI | −0.49 | −0.51 | −0.46 | −0.61 | −0.53 | −0.54 | −0.34 |
| Macrozoobenthos Parameters | Fe | Zn | Mn | Cu | Mo | Pb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abundance | −0.39 | −0.48 | −0.56 | −0.59 | −0.28 | −0.56 |
| Biomass | −0.44 | −0.46 | −0.58 | −0.62 | −0.38 | −0.62 |
| Species number | −0.34 | −0.47 | −0.51 | −0.54 | −0.23 | −0.58 |
| MRI | −0.27 | −0.36 | −0.48 | −0.56 | −0.25 | −0.53 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gevorgyan, G.; Mamyan, A.; Boshyan, T.; Vardanyan, T.; Vaseashta, A. Heavy Metal Contamination in an Industrially Affected River Catchment Basin: Assessment, Effects, and Mitigation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2881. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18062881
Gevorgyan G, Mamyan A, Boshyan T, Vardanyan T, Vaseashta A. Heavy Metal Contamination in an Industrially Affected River Catchment Basin: Assessment, Effects, and Mitigation. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(6):2881. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18062881
Chicago/Turabian StyleGevorgyan, Gor, Armine Mamyan, Tatevik Boshyan, Tigran Vardanyan, and Ashok Vaseashta. 2021. "Heavy Metal Contamination in an Industrially Affected River Catchment Basin: Assessment, Effects, and Mitigation" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 6: 2881. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18062881
APA StyleGevorgyan, G., Mamyan, A., Boshyan, T., Vardanyan, T., & Vaseashta, A. (2021). Heavy Metal Contamination in an Industrially Affected River Catchment Basin: Assessment, Effects, and Mitigation. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(6), 2881. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18062881








