Abstract
The globe is presently reliant on natural resources, fossil fuels, and crude oil to support the world’s energy requirements. Human exploration for oil resources is always associated with irreversible effects. Primary sources of hydrocarbon pollution are instigated through oil exploration, extraction, and transportation in the Arctic region. To address the state of pollution, it is necessary to understand the mechanisms and processes of the bioremediation of hydrocarbons. The application of various microbial communities originated from the Arctic can provide a better interpretation on the mechanisms of specific microbes in the biodegradation process. The composition of oil and consequences of hydrocarbon pollutants to the various marine environments are also discussed in this paper. An overview of emerging trends on literature or research publications published in the last decade was compiled via bibliometric analysis in relation to the topic of interest, which is the microbial community present in the Arctic and Antarctic marine environments. This review also presents the hydrocarbon-degrading microbial community present in the Arctic, biodegradation metabolic pathways (enzymatic level), and capacity of microbial degradation from the perspective of metagenomics. The limitations are stated and recommendations are proposed for future research prospects on biodegradation of oil contaminants by microbial community at the low temperature regions of the Arctic.
1. Introduction
Arctic crude oil resources have become the major interest for exploitation to power the petroleum and other related industries [1,2]. A growing number of areas are being exposed to anthropogenic activities, oil drilling and maritime traffic in the inclement Arctic climate, which pose a high risk for accidental oil spills. The Polar Code discourages the transport and use of heavy fuel oil (HFO) in the Arctic while being explicitly prohibited in the Antarctic under the International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships (MARPOL) [3,4]. Marine vessels operate with two types of fuel oil: (1) distillate fuel including marine diesel oil (MDO) and marine gas oil (MGO) and (2) residual fuel such as IFO variants and HFO, all fuels that are derived from crude oil [5,6].
The degradation rate of hydrocarbon derivatives in the Arctic sea ice, marine, and soil are not feasible enough due to the cold temperatures combined with the perilous environment, reduced solubility, and high viscosity of hydrocarbons. An emergency mechanical technique was implemented to clean up almost 11 million gallons of oil from the infamous Exxon Valdez tanker oil spill, which displayed some drawbacks. The incident left many habitats and wildlife species still recovering and on the verge of being endangered [7,8]. Physical and chemical clean-up of oil spills is complex and expensive, as it is dependent on the water temperature, composition of oil, amount of oil spilled, and other environmental factors. Therefore, biological treatments such as biodegradation of hydrocarbon pollutants by indigenous microorganisms could exploit the contaminants by using them as a source of energy for growth and other metabolic processes. This method has shown promising results as a potential treatment to eradicate hydrocarbon pollutants [9,10].
The bibliometric approach analyzes and evaluates research publications by monitoring the trajectory and development of the literature attributes in a scientific field. Interpreting and mapping a visualization network of research articles, helps to evaluate the productivity of authors, research groups, journals, institutions, countries, and determine the prospective state of knowledge of the field of study [11,12]. Thus, a comparative bibliometric analysis was employed to analyze the current research trends on the biodegradation of hydrocarbons by the microbial communities in the Arctic and Antarctic marine environments. To the best of the authors’ knowledge, no published study has exclusively explored the biodegradation of hydrocarbons by indigenous microbial communities in both the Arctic and Antarctic marine environments by using a bibliometric framework.
Additionally, a literature analysis was carried out to present the various aspects of microbial degradation of hydrocarbons, particularly in the Arctic marine region, since this was hardly reported compared to the Antarctic. The literature analysis compiled the consequences of hydrocarbon pollution in the Arctic marine environment, followed by the application of diverse microbial communities to degrade hydrocarbons, the metabolic pathway of the oil-degrading microbial community at enzymatic levels, microbial degradation capacity at the metagenomic level, and future prospects of bioremediation in the Arctic marine environment.
2. Application of Microbial Community in Biodegradation of Hydrocarbons in Arctic and Antarctic Marine Environments: Comparative Bibliometric Analysis and Literature Review
Comprehensive data mining and analysis of scientific publications for a literature review are the foundation to establish and solve a problem in every aspect of research. A researcher should be able to grasp and understand the overview of a particular field of research. Bibliometrics is a statistical approach used to analyze scientific research or review articles, books, and other publications, which is often referred to as scientometrics [13,14]. This quantitative method mainly entails research assessment in various disciplines by ranking the number of publications according to the authors, source journals, and institutions [15]. The process of exploring scientific information using available information technology (IT) tools or software assists in the analysis and summarization of the gathered data [16].
The present emerging trends in hydrocarbon pollution by microbial communities in cold marine environments are important to evaluate the advancement and dynamics in bioremediation research. This section provides a bibliometrics analysis on the existing literature published during the last 10-year period (from 2009 to 2019). A comparative analysis was performed to highlight the application of microbial communities native to the Arctic and Antarctic cold marine environments in degrading hydrocarbon contaminants. A comparison between both polar regions provides better insights and overview of the proposed study.
The analysis and evaluation of current trends were employed through a data searching of the “Scopus” database produced by Elsevier [17]. This powerful database is reliable and provides substantial information on indexed journals, publications, and a large collection of abstracts and citations encompassing a broad range of subjects [18]. It offers integrated, efficient analytical methods for data extraction, compilation, and content exporting in various formats, which provides an inclusive statistical data of the entire quantity of the world’s research outcomes in the fields of science, medicine, technology, arts, humanities, and social sciences. The premise behind using the Scopus database is that relative to other such databases, at over 23,000 peer-reviewed indexed journals, it has a substantially greater abstract and citation range in interdisciplinary scientific data [19]. In this review, we restricted our assessment to journal articles only, limiting the influence of redundant publications and mitigating false-positive outcomes. Reviews, book chapters, and conference sessions were not taken into consideration, because they contain works that may have been published in multiple sources more than once [13,20].
The process of document collection in relevance to the hydrocarbon degradation by Arctic and Antarctic marine microbial communities as the main theme is represented in the flowchart (Figure 1). The keywords were used as the query string in the Scopus database and analyzed through Microsoft Excel and VOS viewer software (version 1.6.15, Center for Science and Technology Studies, Leiden University, The Netherlands) [21]. A total of 175 and 144 documents pertaining to the Arctic and Antarctic marine environments, respectively, were obtained after search refinement. The occurrence of keywords, publications in countries or territories, affiliations, most productive journals, authors, and most cited documents were analyzed and organized in various visualization representations.
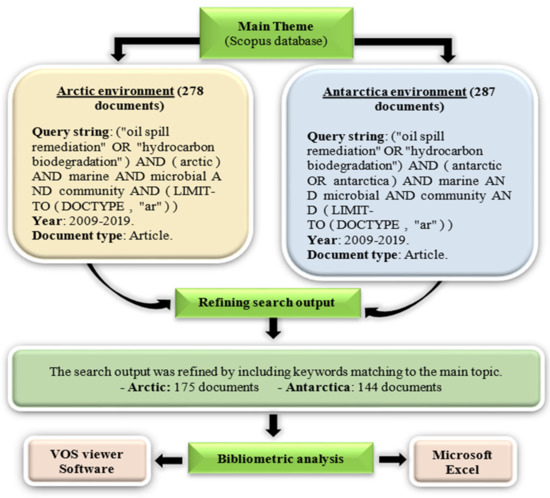
Figure 1.
Flowchart of data collection of documents published in relevance to the main theme: hydrocarbon degradation by microbial communities in both Arctic and Antarctic marine environments.
2.1. Keyword Co-Occurrence Analysis
Analysis of co-occurrence of keywords is a bibliometric technique that determines the association between topics in the research field of interest. The VOS viewer software constructed visualizing bibliometric maps based on the bibliographical, citation, and all keywords information of 175 and 144 articles that were exported separately. This tool is useful in finding the relatedness or connections between different items or pairs that exhibit specific link strength. The larger the value (numerical) of a link, the greater the strength of a link [22]. Figure 2 illustrates the keywords used and the frequency of occurrence represented by the size of nodes that explains high frequency keywords. Nodes of the same colour are part of a cluster. The closer the distance between each node, the stronger the relatedness of the keywords. A total of five clusters were identified for both research topics by forming groups that correlated with one another’s keywords.
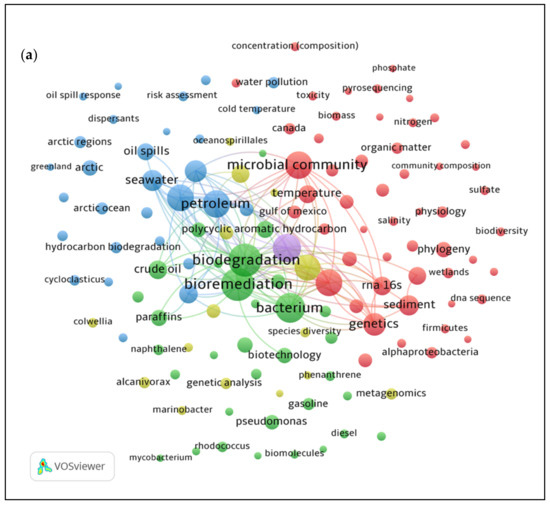
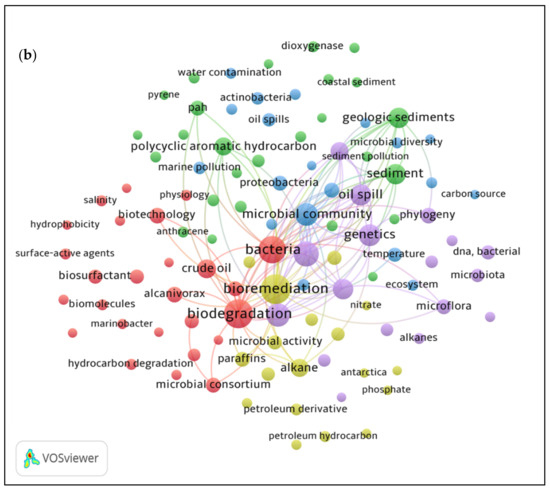
Figure 2.
Keywords occurrence on hydrocarbon degradation by (a) Arctic and (b) Antarctic marine microbial community.
Figure 2a is a bibliometric map of network between the occurrence of keywords in relation to the microbial community that degrades hydrocarbons in the Arctic marine environment. Among the 175 retrieved articles from the Scopus database, 246 keywords were identified that met with a minimum of five occurrences of threshold for mapping. This was presented in different clusters displaying a strong link strength of 49,198. The most frequent keywords indicating the primary clusters were “bioremediation” (green), “microbial community” (red), “hydrocarbons” (purple), “petroleum” (blue), and “microbiology” (yellow). The term “bioremediation” (green) was located in the core of the network and had the greatest interest of this topic, corresponding with the other keywords such as “biodegradation”, “bacterium”, and ‘crude oil’. The main clusters (blue and red), led by “petroleum” and “microbial community”, respectively, have established a high relevance with the “bioremediation” (green) keyword. This suggests that the study of microbial community or bacterium has been exploited in remediating oil pollution in the Arctic sea water. Thus, the occurrence of keywords such as “biodegradation” (95 occurrences, 2424 links), “bioremediation” (94 occurrences, 2498 links), “hydrocarbons” (70 occurrences. 2051 links), “microbial community” (67 occurrences, 1951 links), “marine” (20 occurrences, 527 links), “Arctic” (21 occurrences, 560 links), “Arctic Ocean” (14 occurrences, 345 links) or “Arctic regions” (13 occurrences, 405 links) were highly relevant with other keywords in relatedness to the topic. In comparison, the keywords based on the hydrocarbon degradation by microbial community in the Antarctic marine environment showed 151 keywords that occurred together with 21,229 link strength from a total of 144 publications deposited in Scopus. The most frequently occurred and relevant keywords were selected for network visualization of the keywords co-occurrence in relation to the topic. The bibliometric map in Figure 2b indicates the term “bioremediation” (76 occurrences, 1755 links) occurred the most, followed by other keywords such as “biodegradation” (74 occurrences, 1539 links), hydrocarbon (44 occurrences, 1105 links), “microbial community” (40 occurrences, 1047 links), “marine environment” (12 occurrences, 323 links), and “Antarctica” (five occurrences, 96 links). The main clusters can be depicted by frequently used keywords such as, “biodegradation” (red), “bioremediation” (yellow), “hydrocarbons” (purple), “microbial community” (blue), and “sediments” (green). Our findings elucidated that the terms “bioremediation” and “biodegradation” were often associated with “oil spill”, “bacteria”, and “crude oil”.
The findings showed that the term “bioremediation” was most frequently encountered and was established as the central theme of this topic. The keywords including “microbial community”, “biodegradation”, and “hydrocarbons” were profoundly associated with “bioremediation”. The use of microorganisms to remove or degrade environmental pollutants in oil spill incidents that threaten the marine ecosystem defines bioremediation [23,24]. Biological clean up through microbial biodegradation of hydrocarbons is a promising bioremediation technique, which takes advantage of its own natural mechanisms and is less intrusive and more cost efficient, especially in cold regions [25]. Bioremediation in ice-covered sea and soil during winter is more challenging than in the summer, while most oil drilling and transportation activities are concentrated in the ice-free season. As the temperature rises in summer, oil droplets floating on the surface of the sea are easily attached to the concentrated ice floes and spread even further [26]. The consequences of oil spills in marine environments are further discussed in Section 3.
2.2. Trends of Publications in the Last 10 Years
The pattern in the number of publications published on the topic of oil spill remediation or hydrocarbon degradation in cold marine environments with the application of indigenous microbial communities has been extensively increasing from 2009 to 2019 (Figure 3). Many research groups worldwide are conducting extensive research on bioremediation or biodegradation of oil pollutants in low temperature climate regions. Microbial community applications have been found to be less invasive to treat pollution and in addressing the environmental concerns in the Arctic and Antarctic regions. Based on the articles published from the Scopus database, it was elucidated that the number of publications related to the Antarctic environment (107 cumulative publications) was higher than that in Arctic (81 cumulative publications) between 2009 to 2014. However, more articles were published on topics focusing on the Arctic (40 and 58 publications) compared Antarctic (34 and 44 publications) in 2018 and 2019, respectively. This shows that research on the bioremediation of hydrocarbons in the Antarctic and Arctic marine environments is evolving progressively within the last years five years. The current state of advancement and development in technology has caused growing concerns on the environmental impacts to the cold marine ecosystem resulting from the large number of anthropogenic activities.
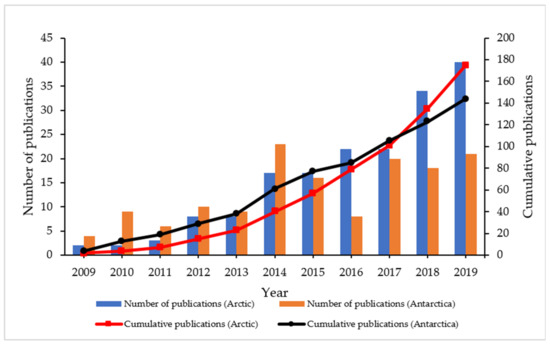
Figure 3.
Number of publications from 2009 till 2019 related to hydrocarbon degradation by microbial communities in Arctic and Antarctic marine environments.
2.3. Analysis of Publications in Subject Areas
The published journal articles in relevance to hydrocarbon degradation by microbial community in cold marine Arctic and Antarctic environments were classified in various subject areas. This highlighted three main areas of knowledge (Figure 4 and Figure 4b), which included environmental sciences, encompassing 36.33% (Arctic) and 26% (Antarctic); immunology and microbiology, encompassing 20.5% (Arctic) and 18% (Antarctica); followed by agricultural and biological sciences, with similar number of publications (17.3% Arctic and 17% Antarctic) in both research areas. Most of the journal articles were attentive in identifying oil-degrading indigenous microorganisms that utilize their metabolic capacity at the genomic and enzymatic levels to naturally degrade hydrocarbon pollutants [27]. Therefore, a large number of papers have been published in the field of environmental science throughout the last decade.
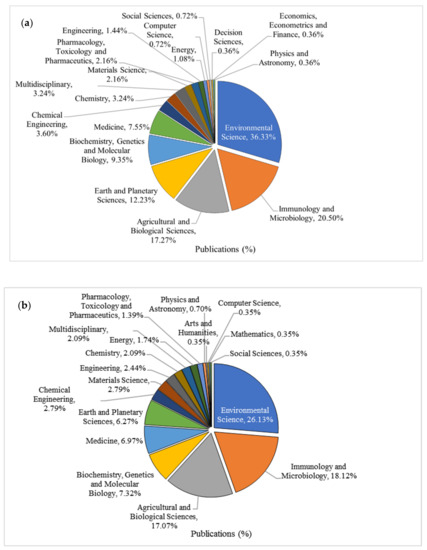
Figure 4.
Distribution of publications by various subject areas based on the hydrocarbon degradation by microbial community in marine environments of (a) Arctic and (b) Antarctica.
2.4. Global Output in Publications and Most Progressive Affiliations
Bibliometric parameters such as countries and affiliated institutions provide opportunities for an international level of collaborations in the particular research field. This also helps some researchers to pursue their research career in established institutions or countries related to their specialization. The trends of publications were analyzed over the last decade based on the 144 and 175 articles related to hydrocarbon pollution in the Antarctic and Arctic marine environments and are presented in a global map (Figure 5). The most productive countries in publishing journal articles were the United States (28% and 23%), China (13% and 16%), and Canada (12% and 11%) for research related to the Arctic (Figure 5a) and Antarctic (Figure 5b) environments, respectively. These countries are the key players in pursuing research in hydrocarbon biodegradation compared to other countries or territories, with their first-rate advancements in technology and scientific research contributing to high publication numbers.
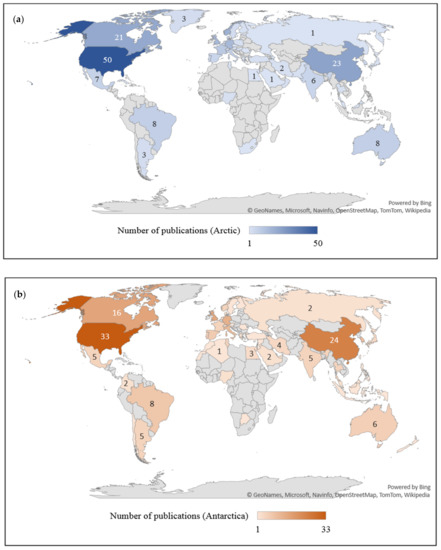
Figure 5.
Number of journal articles published by countries or territories related to hydrocarbon degradation by (a) Arctic and (b) Antarctic marine microbial community.
In addition, the most progressive research affiliated institutions in publishing journal articles are listed in Table 1. Based on the Scopus database, the following institutions, namely the Chinese Academy of Sciences in China (4.6%), SINTEF Ocean in Norway (4.6%), and Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory in the United States (4%) frequently contributed to the publishing of journal articles on this research topic for the Arctic region. Meanwhile, the institutions that have a high impact on this area were Istituto per l’Ambiente Marino Costiero del Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche IAMC-CNR (5.5%) and Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche (5.5%) in Italy, and Chung-Ang University in South Korea (4.2%). The Chinese Academy of Sciences published a total of 752,710 journal articles by affiliations, which has established a gap with other leading countries. Institutions in Canada, Norway, and Italy also participated actively in this research area to continuously address the oil pollution issues that threaten the environment.

Table 1.
Top ten ranked affiliations with the number of publications between 2009 and 2019 based on the research on degradation of hydrocarbon by Arctic and Antarctic marine environments.
2.5. Source Journals Trends, Most Cited Articles Based on Journal Ranks, and Relevance to the Field
The trends of preferred journals from 2009 to 2019 were analyzed based on their number of publications on the topic of hydrocarbon biodegradation through the application of microbial communities in the Arctic and Antarctic marine environments (Figure 6). Figure 6a illustrates the growth of publications in the top 10 journals from 2012 to 2019, with the journal of Marine Pollution Bulletin (8.57%) performing well from 2014 to 2019, producing a total of 15 articles, followed by 12 articles from the journal Frontiers in Microbiology (6.86%), and Applied and Environmental Microbiology (2.86%), with five documents published. The extracted articles from these top 10 source journals were further analyzed to identify the most cited documents related to this research area (Table 2). The citations of a document reflect the quality of the document published [28]. The most cited article with total citations of 105 that was ranked seventh on the list of productive journals was published in 2015 by the International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation journal. At least 80% of the 10 journals demonstrated an emerging growth in published articles within the last five years. Most of the articles were published by Elsevier (50% in Table 2) and Springer, with both equally publishing similar numbers of articles as shown in Table 3. High impact academic journal publishers such as Elsevier and Springer provide large scale of bibliometric electronic databases across various disciplines [28].
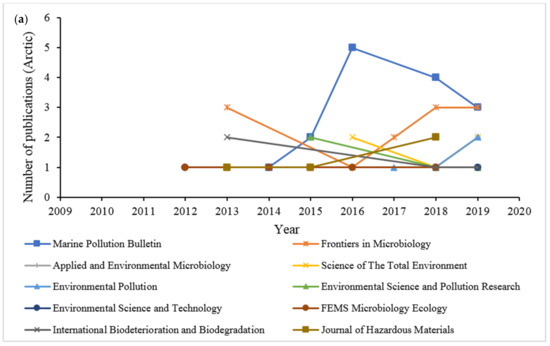
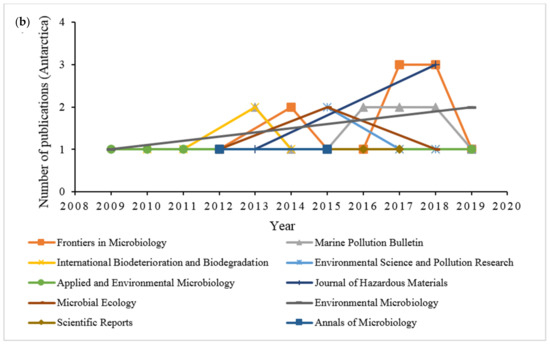
Figure 6.
Trends of the top 10 source journals based on the degradation of hydrocarbon by microbial community in (a) Arctic and (b) Antarctic marine environments between 2009 to 2019.

Table 2.
Top ten most productive journals on degradation of hydrocarbons by Arctic microbial community research with their most cited articles.

Table 3.
Top ten most productive journals on degradation of hydrocarbons by Antarctic microbial community research with their most cited articles.
The literature search from the database of 144 documents showed an extensive publishing by the top 10 journals in the study of hydrocarbon degradation by microbial communities from the Antarctic marine environment. According to Figure 6b, the pattern in number of documents published annually from 2009 to 2019 progressively increased, though with some decline in certain years. By comparing with Figure 6a, the journal Frontiers in Microbiology (8.33%) was ranked first with a total publication of 12 articles, while the journal Marine Pollution Bulletin published 11 articles (7.64%), followed by the journal International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation (4.86%), with seven documents.
In addition to this, the Cite Score (Elsevier-Scopus), Clarivate Analytics of Journal Citation Reports (JCR), and Impact Factor (IF) information were evaluated based on the statistics of number and quality of documents and source journals. According to the Cite Score in 2019, nine journals (Table 2) and eight journals (Table 3) had Cite Scores of above five, and there were two journals that scored above 10, which were the Environmental Science and Technology (12.6) and Journal of Hazardous Materials (13.1). This information allowed authors to select suitable journals to add up the significance and novelty of their research work. The authors should also consider various metrics in measuring the journal impact and compare them with other published articles in the similar research field [29].
2.6. Most Prolific Authors
Leading authors in publishing relevant articles were analyzed from the Scopus database based on the bibliometric parameters including author (Scopus) ID, current affiliations, highest cited document, total citations and publications, h-index, journal, and cited by. The total number of publications (175 and 144 journal articles) on the study of hydrocarbon degradation by microbial community in the Arctic and Antarctic marine environments are summarized in Table 4 and Table 5. These prolific authors produced a high number of articles and achieved high scientific impact in research. The h-index is an important metric used to evaluate the cumulative impact of a researcher’s publication output and performance by comparing the publications to citations [29,30].

Table 4.
Most productive 10 authors that published journal articles between 2009 to 2019 related to degradation of hydrocarbons in the Arctic marine environment by microbial community.

Table 5.
Most productive 10 authors that published journal articles between 2009 to 2019 related to degradation of hydrocarbons in the Antarctic marine environment by microbial community.
Based on Table 4, out of a total of 175 publications, the three most prolific authors who were actively publishing articles related to the study of hydrocarbon degradation in the Arctic marine environment by utilizing native microbial communities were Cappello, S. (5.1%), Jeon, C.O. (4%), and Madsen, E.L. (2.9%). Meanwhile, out of a total of 144 documents retrieved from the database, the top three productive authors who published articles from 2009 to 2019 (Table 5) for the Antarctic environments were Brakstad, O.G. (4.2%), Netzer, R. (3.5%), and Anderson, J.A. (2.8%). Overall, Andersen, G. L., who published an article that was cited 133 times, had the highest h-index (61) and citations per publications (CPP) of 191.43 compared to other authors, whereas Jeon, C.O., had a CPP of 23.21 and a h-index of 49, the highest in comparison to authors listed in Table 5. Moreover, the most productive author in this research study focusing on the Arctic marine environment was Brakstad, O.G, with a h-index of 22, CPP of 28.56, and the author’s highest cited publication was cited by 31 other published articles. For the Antarctic environments, Cappello, S., was the most prolific author, with a h-index of 25 and CPP of 26.22 and cited by 62 other published articles. He is affiliated with the Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche in Rome, Italy, whereas Brakstad, O. G, along with Netzer, R, and Ribicic, D., are affiliated with the SINTEF Ocean in Trondheim, Norway. Both of their affiliations were ranked second in terms of their publications number in last 10 years (Table 1). Three (Almeida, A. P., Cleary, D.F.R., and Cunha, A.) out of the 10 authors have affiliations with the Universidade de Aveiro, Aveiro in Portugal (ranked fifth). This indicated that even though China and Italy (Table 1) produced high quantities of publications, more active authors were linked with institutions in Norway and Portugal that have great interest in investigating the applications of microbial communities in hydrocarbon degradation in the Arctic and Antarctic marine environments.
2.7. Limitations of Bibliometric Study
This study recognizes several shortcomings that could be explored in further research. The results of the bibliometric analysis are characterized by the research area, the selected timeframe, database, keywords and articles analysis, and the evaluated variables. Therefore, comparisons with multiple data outputs such as Web of Science and Scopus will be effective to find notable differences to assess the latest research trends [22,31]. In this study, only published articles have been taken into account; thus, publications such as books, proceedings, and other types of documents could be taken into consideration in the future. This paper utilized a comparative bibliometric study between two different focus of studies by quantifying the articles published over the years followed by extracting the information and then presented using network analysis. However, several other methods such as qualitative measurements using questionnaires on the opinions of people with various backgrounds and seeking experts for constructive discussions could be combined with the traditional bibliometric approach (hybrid model) [30,31]. Alternatively, a topology structure and model mapping could also be used to determine the extent of advancement over different fields or disciplines and increase the robustness of the bibliometric analysis [13,32].
3. Consequences of Hydrocarbon Pollution in Arctic Environments: Seawater, Marine Sediments, and Coastal Environments
Our bibliometric analysis showed that the research output in the bioremediation or biodegradation of hydrocarbons by Arctic marine microbial communities outnumber those for the Antarctic marine environment. Subsequently, an extensive literature analysis will identify various aspects of microbial degradation of hydrocarbons, from the fate of oil spills in the ocean to the enzymes or genes that are responsible for biodegradation (Section 3, Section 4 and Section 5). Oil containment and elimination in the marine setting, especially in cold conditions, pose challenges in removing pollutants completely from the environment. Although much of the spilled oil would have been physically collected through containment booms, a substantial amount of the residual oil during clean-up will wash up to the coast or ashore, while some resurfaced oil will float on the surface of water, while others were deposited in the marine sediments depending on the oceanic currents (Figure 7) [33,34,35].
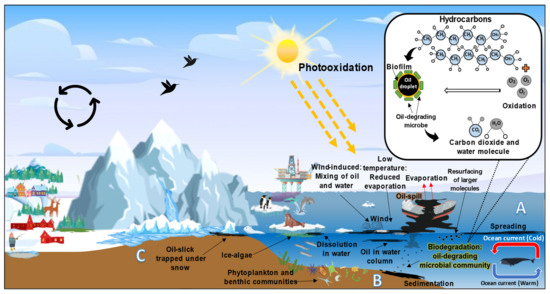
Figure 7.
The fate of oil spills into the Arctic marine environment from the aspects of the (A) seawater, (B) marine sediment, and (C) coastal environments (Adapted from: [34,36]).
In the Arctic, the primary sources of hydrocarbon pollution generally come from offshore drilling, oil tank blowouts or leaks, fuel transportation, leakage from ships, pipeline leakages, runoffs from land or river, discharges from water, and long-range transportation of pollutants via water. The marine ecosystem is largely affected, especially by large-scale oil spill disasters such as the Exxon Valdez tanker oil spill incident in Alaska (1989), Deepwater Horizon oil rig explosion in the Gulf of Mexico (2010), and Norilsk diesel fuel spill in Russia (2020). Such disasters were caused by human errors, illegal disposal of oil waste, and bunkering of oil among the ships [37]. There were other oil spill incidents, from low to high level of discharge of oil, that have been recorded as listed in Table 6.

Table 6.
List of oil spills incidents that occurred recently surrounding the Arctic Circle.
3.1. Seawater of the Marine Environment
The oil hydrocarbons spilled on marine surfaces encounter several weathering processes including photo-oxidation via carbon dioxide and water, emulsification, dissolution dispersion, evaporation, sedimentation, adsorption, as well as microbial biodegradation [44,45]. Oil spills in the marine environment occurs mainly due to ship accidents during the transportation of crude oil, severe or extreme oceanic currents and weather conditions, risky geographical regions (prone to sea ice melting), and possible human errors. The spilled oil could spread further, forming slicks over the surface of the Arctic seawater. Approximately, 5 × 106 m2 of slick can be formed from 1000 kg of oil spilled, which depletes the oxygen level and causes pH changes in the seawater due to the disruption of gaseous (oxygen and carbon dioxide) exchange [46,47].
3.2. Marine Sediment
Accidental or unnecessary waste discharges associated with offshore drilling such as production water may be deposited in the sediments of the marine environment. Moreover, to sustain the pressure and rushing of the hydrocarbons into productions wells, tonnes of injection water are introduced into the system. Despite clean-up efforts that are based on regulatory guidelines, some of the low molecular weight hydrocarbons, inorganic salts, additives, monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (BREX), polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), and other aromatic compounds remained in the environment [47]. Apart from operational waste discharges, huge volumes of natural gas and crude oil leak out of the ocean’s seabed and sedimentary rock, especially in areas rich with oil resources including in the sandstones of Alaska, Timan-Pechora basin in Russia, and submarine seeps in Nuussuaq peninsula of Greenland. Oil seeping from the seabed acts in a similar manner to oil drilling or spills by forming massive slicks that circulate through long-range atmospheric and ocean currents [48].
3.3. Coastal or Shoreline of Arctic Ocean
The integrity of the Arctic’s ecosystem, including marine mammals, birds, corals, fish, and wildlife at coastal and shore regions have been destroyed in the pursuit of natural gas and crude oil exploration. The wildlife, marine animals, and birds manifested behavioral changes in their motility, feeding, and physical activities and were affected by disrupted growth and reproduction. Most of the hydrocarbons are less toxic when present at low amounts, although some aldehydes with low molecular weight, (monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbon) MAHs, and (polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon) PAHs are stable, extremely carcinogenic, and toxic [49]. The clean-up and recovering process are extremely challenging for ice-infested waters in the Arctic and certainly cause diverse negative impacts to the overall ecology. Most carcinogenic hydrocarbons are classified as high molecular weight aromatic compounds, which pose high potential risk and increased toxicity. Among the composition of fuel hydrocarbons, PAHs have higher chances for bioconcentration due to their low volatility, insolubility in aqueous system, and lower rate of degradation. An early study suggested that the toxicity and persistence of PAHs in the environment are mainly caused by their large size due to their more fused benzene ring. Derivates of lighter hydrocarbons are hydrophilic and soluble up to 2000 ppm [50]. Wildlife populations in the Arctic are being chemically exposed to the toxic hydrocarbons and currently threatened at an alarming rate, and thus the potential biological effects need to be assessed. The toxicological effects of hydrocarbons on the marine ecosystem, coastal wildlife, flora, and humans require more attention by researchers.
3.4. Toxicological Effects of Hydrocarbon Pollution on Different Marine Environments.
Various fish are affected by PAHs and their derivatives, including naphthalene that was observed to reduce the larval growth of fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas) [51]; induced genotoxic damages in eel (Anguilla anguilla) [52] and Arctic copepods (Calanus finmarchicus and C. glacialis); damaged deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and inhibition in acetylcholine esterase (AChE) observed in Littoral crab (Carcinus aestuarii) [53], Icelandic scallop (Chlamys islandica), blue mussel (Mytilus edulis), and red king crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus) that led to nervous system damage, behavioral changes in swimming to escape, and induced oxidative stress [54,55,56].
In marine mammals, PAHs induces oxidative enzyme activity in beluga whales (Delphinapterus leucas) [57] and an orca pod (AT 1) [58] was yet to recover from the Exxon Valdez oil spill from 25 years ago. The Arctic coastal and shoreline regions are occupied by a large and diverse number of sea- and shorebirds, which are the most vulnerable and sensitive species to oil pollution due to regular contact with water surfaces. Floating oil covers the thick fur or feathers of polar bears, sea otters, seals, walruses, and seabirds, which prevents them from staying afloat and reducing insulation, leading to hypothermia, drowning, smothering, and toxic hydrocarbons ingestion through the food web [58,59]. Meanwhile, toxic fumes inhalation increased the mortality in harbor seals through stress, brain lesions, and disorientations [8].
Oil spills or pipeline leakages absorbed by the soil at the shorelines resulted in reduced soil fertility that inhibits the growth of some plants. However, oil spreads minimally in soil, as hydrocarbons transform through blending in soil or snow ice, photo-oxidation, and microbial degradation [58]. Plant life in the Arctic suffers much higher consequences compared to other terrestrial or tropical regions. The hydrocarbons from oil spills can severely damage plants due to the vulnerable thin surface cover [8]. Moreover, the Arctic vegetation requires a longer time to recover from exposure to the toxic compounds due to the low temperature and shortage of nutrients. Exposure and potential health effects of PAHs are also of concern in humans due to their chronic effects such as reduced immune system, damage to the liver and kidneys, cataracts, and respiratory abnormalities [60]. General routes of the carcinogens’ exposure are through nasal inhalation, ingestion, and skin contact via oil spills in soil, water, or air. Workers especially at oil drills, transportation, or spill sites suffer from acute symptoms, including vomiting, skin inflammation, and eye irritation [61,62]. Aromatic hydrocarbons are the main contributors of carcinogenicity in humans and animals, which has been made evident through cellular damage via mutations that lead to cancers of the gastrointestinal, lung, bladder, as well as skin due to long term exposures [63].
4. Application of Microbial Community in Biodegradation of Hydrocarbons in Arctic Environments
This section discusses the applications of microbial community that focus mainly on the Arctic environments in degrading or remediating oil pollutants. The treatment of hydrocarbon contaminants, a combination of both mechanical and biological techniques or either one, are used to contain and remediate oil spills in the Arctic soil and ocean. The remoteness of the Arctic environment and its unpredictable conditions make oil spills extremely dangerous to animal habitats. Indigenous microbial floras concentrated in the seabed close to natural seeps have been found to degrade huge volumes of oil spills from the Deepwater Horizon and Exxon Valdez incidents at low temperatures and as deep as 1000 m [64]. Physical booms, skimmers, and chemical dispersant that are used in the initial response to clean up oil spills are expensive, as well as requiring more manpower, prolonged response, and ecological side effects. However, some mechanical and chemical clean-up methods are not able to remove the hydrocarbons once the oil is emulsified in water or soil surfaces, which further increases the damage and recovery period of the ecosystem [65,66,67].
The nature of hydrocarbon compounds is not viable for degradation, especially in low temperatures. Therefore, the factors including temperature, pH, nutrients, and oxygen can influence the microbial activity [68]. Psychrophilic and psychrotolerant bacteria that are derived from cold environments have increased potentials in the decontamination of hydrocarbons from oil-polluted sites in the Arctic. The minimum, optimum, and maximum temperatures in assisting growth are differentiated as follows: for psychrotolerant bacteria, temperatures of <0−5 °C, <15 °C, and <20 °C are required; whereas for psychrophile bacteria, <0 °C, <15 °C, and <20 °C are required [69]. Reduced enzymatic activity is associated with lower degradation rate at low temperatures [65,70]. The maximum level of hydrocarbon metabolism can be achieved at temperatures between 30 to 40 °C. In the Arctic, the growth of hydrocarbon-degrading Proteobacteria, including Psychrobacter, Pseudoalteromonas, and Pseudomonas spp. [71,72] are promoted through the addition of hydrocarbons. The marine bacteria, Marinobacter [73], exhibited degradation capacities of 20–50% at temperatures as low as 1 °C and almost 80% hydrocarbon degradation for Oleispira at 4 °C [74].
Biostimulation, which is the incorporating of nutrients for hydrocarbon degradation, stimulates the nitrogen content for assimilation and induces growth. The oil-contaminated soils in the Arctic have low levels of nitrogen concentrations due to an increase in carbon, which limits the bioremediation process. The carbon sources essential for degradation are supplemented through hydrocarbon and water supplying oxygen and hydrogen [75,76]. Thus, the addition of nutrients is dependent on the mechanisms of the specific bacteria to uptake and promote assimilation for rapid mineralization of hydrocarbons. The effectiveness of PAHs degradation has been observed in diversely growing Sphingomonas strains that can adapt to various nitrogen concentrations [77,78].
The addition of hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria, algae, fungi, algae, or yeast to prevailing population of microbes is known as bioaugmentation, which is inexpensive and allows in-situ bioremediation. The oil-degrading microorganisms isolated from oil spill sites increase the degradation capacity of organic pollutants in conjunction with indigenous microbiota, with high tolerance towards the toxicity of hydrocarbons [79,80]. The presence of various Arctic microorganisms has been observed in crude and diesel oil through stimulation of hydrocarbons that degrade aromatic compounds (Table 7) [81,82,83]. In cold regions, hydrocarbonoclastic bacteria are important in hydrocarbon degradation at low temperatures [84,85,86]. Furthermore, other microbes such as the fungi Phialophora spp. and Hormoconis resinae [87,88] are known to degrade hydrocarbon pollutants in Antarctica. Filamentous fungi and yeast in terrestrial environments can degrade PAHs in the presence of responsible genes for degradation. Experimental research on hydrocarbon-degrading fungi and algae is yet to be thoroughly investigated in the cold regions of the Arctic, but some studies have reported on the ability of fungi and algae to degrade aromatic compounds and other derivatives of hydrocarbon in the Antarctic and terrestrial regions [89,90,91].

Table 7.
List of hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria found in the Arctic.
5. Metabolic Pathways of Oil-Degrading Microbial Community at the Enzymatic Level
Complex hydrocarbon compounds in nature degrade according to the following order of biodegradability (least to most): linear alkanes—branched alkanes—low molecular weight alkyl aromatics—monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (MAHs)—cyclic alkanes—polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs)—high molecular weight asphaltenes [94,95]. Aromatic hydrocarbons are the least biodegradable in comparison to alkanes; therefore, the physico-chemical properties, availability of substrates, and environmental conditions are necessary to eliminate them through eco-friendly and feasible bioremediation techniques. Previous studies largely discussed and reported on the most toxic contaminant, namely, PAH biodegradation, due to its persistency and ubiquitous nature towards the marine ecosystem [96,97].
The petrogenic origins of PAHs were identified in the Arctic sea through an extensive sampling with depths of 367–4320 m, while some low molecular weight PAHs were abundant in the Arctic Ocean North–South Transect, notably close to the land [98]. Moreover, Yunker et al. [98] also revealed deep sea sediment microbial members, namely, Pseudomonas, Dietzia, Pseudoalteromonas, Halomonas, Cycloclasticus, and Marinomonas found in the Arctic Ocean, which were responsible for PAH degradation. Cold-acclimated microorganisms such as PAHs-degrading Pseudomonads (β-Proteobacteria) and Sphingobium sp. C100 (α-Proteobacteria) were enriched in the deep-sea sediments of the Arctic Ocean [99], Marinomonas profundimaris D104 [100], while Colwellia was present in the Svalbard sea ice of the Arctic [101,102]. The majority of hydrocarbons (94%) were degraded by the bacterial communities present in sub-ice seawater of the Arctic by removing almost all the biodegradable alkanes and similarly for the methylated forms of PAHs. It was identified that anaerobic microbial communities of Gammaproteobacteria and Bacteroidetes are the predominant groups underneath the shore-fast ice of the Arctic sub-ice, while Alphaproteobacteria majorly dominates the surface of seawaters [103].
Hydrocarbon degradation involves two common pathways: aerobic (oxygen-dependent) and anaerobic (oxygen-independent) (Figure 8). Microbial degradation of hydrocarbons under aerobic conditions involves an oxidative process performed by oxygenase and peroxidase as an initial attack. This pathway is often necessary in hydrocarbon degradation, as the amount of oxygen is abundant on the surface of seawaters, in contrast with the low availability of oxygen in the water columns and deep seawater [92,104]. The bottom of the ocean bed is anoxic where the oxygen concentrations are limited, depending on the amount of oil and level of oxygen renewal by the ocean current [105]. A previous study reported that the enzymatic attack is highly influenced by the composition of hydrocarbons in oil, as the linear and some branched alkanes are degradable, unlike aromatic compounds [106].
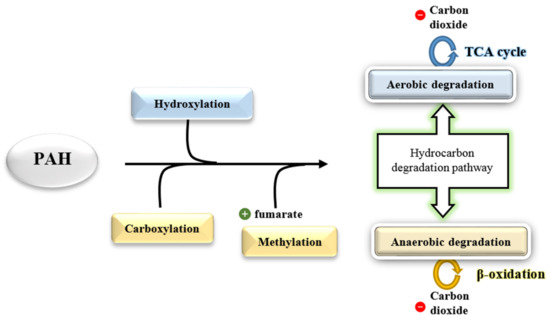
Figure 8.
The primary activation mechanism in PAH degradation via the initial step of activation (reconstructed from [34] through adaption from [115,117]).
Analysis of potential microbial community of PAHs degraders found that they utilized genes encoding for the PAH monooxygenase or dioxygenase (large alpha subunit), which could be utilized as biomarkers [107]. These enzymes are members of the ring-hydroxylating oxygenase (RHOs) or ring-hydroxylating dioxygenase (RHDs), a large enzyme family that activates the compounds to generate a cis-dihydriol from the dihydroxylation of one of the aromatic rings [97,108]. Next, the cis-dihydriol dehydrogenase rearomatizes the aromatic ring of hydrocarbons, forming di-hydroxylated intermediates that are oxidised into catechol, which is the primary intermediate of oxygen-dependent degradation [109]. The metabolic advantage of aerobic catabolism of hydrocarbons is that it is more rapid due to the presence of oxygen (O2) molecule as an electron acceptor through the introduction of one or two atoms of O2 to a substrate (hydrocarbon) [110].
Apart from that, anaerobic biodegradation of hydrocarbons requires compounds other than oxygen that can act as electron acceptors such as sulphate, nitrate, and ferric chloride [111]. A proposed general pathway includes two primary activation mechanisms, namely direct carboxylation of aromatic rings by carboxylase originated from UbiD-like proteins or a methylation pathway that methylates aromatic compounds through methyltransferase [112]. The second mechanism comprises the supplementation to fumarate by the catalysis of a glycyl-radical enzyme identified as naphthyl-2-methyl-succinate synthase [113,114]. Both mechanisms advance with activation of coenzyme A via the process of β-oxidation [115]. Enzymatic pathway activation requires some time to be fully functional for hydrocarbon degradation [116].
Microbial communities possessing high enzymatic capacity can degrade complex hydrocarbons through transformation of contaminants into less toxic forms. The distinctive catalytic properties evolved in the psychrophilic microbial community express cold-adapted enzymes that have enhanced flexibility, reduced thermal stability, and greater catalytic effectiveness in extremely cold environments [118,119]. These enzymes are expressed by genes adapted to the low temperature conditions, which improve the catalytic activity of hydrocarbon degradation through certain environmental adaptation processes [120]. The microorganisms enhance the fluidity of their cell membrane and increase the short-chain fatty acids and unsaturated fatty acids at low temperatures. Psychrophilic enzymes have an elevated specific activity compared to that in mesophilic and thermophilic microorganisms [121,122]. Thus, further investigations are necessary to discover more cold-adapted enzymes capable of degrading hydrocarbons from the polluted environments in the Arctic regions.
6. Microbial Degradation Capacity at the Metagenomic Level
The rate and magnitude of hydrocarbon biodegradation in cold marine environments are considered to be crucial elements and require understanding in the removal of compounds by microbes. Multiple aspects such as pollutants, oxygen, pH, nutrient, temperature, and the wide range of microbial community have been found in the contaminated regions. Microbial communities present in the low temperatures of Arctic marine ecosystems are capable of degrading hydrocarbons as a carbon source and promoting energy production while utilizing the bioavailability of nutrients such as nitrogen [123]. The molecular analysis of functional genes that are active in oil-degrading microbial communities can provide different insights at the metagenomic and enzymatic levels [27,124]. This method can be used to collect information on the distribution and diverse range of potential hydrocarbon-degrading microbial communities in the Arctic marine environments, including coastal, marine sediments, and seawater. These cold adapted marine microbial communities can act as innovative model organisms for the bioremediation of hydrocarbon pollutants.
Recent advancements in analyzing and understanding the metagenomics of the microbial communities are essential to access the taxonomic and composition of functional genes in the biodegradation of oil pollutants. The study of genetic material of intact communities is known as the metagenomics process. Metagenomics involve the use of next-generation sequencing (NGS) with the latest approaches including whole-metagenome sequencing (WMS) [125,126]. The diversity of hydrocarbon degrading-bacteria present in the sediment of the Arctic Ocean has been determined through a large scale of 16s rRNA analysis in a study that assessed the presence of PAHs. Samples collected from 19 various deep-sea sediments (Chukchi Plateau, Makarov Basin, Canada Basin, and Alpha Ridge) showed members of Halomonas, Cycloclasticus, Pseudomonas, Marinomonas, Dietzia, and Pseudoalteromonas genera that exhibited the capability to mineralize PAHs [92]. In another study, the taxa Colwellia and Oleispira were found to have higher responses to oil in the Arctic seawater. These taxa were associated with the functional genes alkB, nagG, and pchCF in hydrocarbon degradation and dispersant Corexit 9500 [127]. In addition, the obligate hydrocarbonoclastic or heterotrophic genera Pseudomonas, Cobetia, Thalassomonas, Marinobacter, Moritella, Shewanella, and Aestuariicella found in the deep-sea water of the Arctic have also been shown to favor oil degradation [98].
The application of metagenomics in the largest oil spill accident to-date, the 2010 Deepwater Horizon drilling rig explosion, provided an opportunity for researchers to explore and deepen the knowledge of the biodegradation of hydrocarbon pollutants. PAH-degrading bacteria such as Cycloclasticus [128], Marinobacter [129], Pseudoalteromonas, Marinomonas, Halomonas [130], Sphingomonas [131], and Vibrio [132] were identified from coastal sediments through metagenomics [133]. The phdCI gene that encoded for carboxylate isomerase responsible for degrading naphthalene was largely found in oil plume samples. Moreover, the Oceanospirillales, which belong to the Y-Proteobacteria, including Oleispira antarctica, Oleiphilus messinensi, and Thalassolituus oleivorans, have been found in Arctic seawater [118]. The Deepwater Horizon incident left a negative impact on the marine environment due to the large portion of oil remaining in deep-sea sediments, including the deep-water plume of oil. Oleophilic bacterial samples, Colwellia rossensis and Oleispira antarctica from natural North Sea fjord seawater and Arctic seawater, are capable of expressing GyrB genes. Through this molecular approach, the identified hydrocarbon-degrading genes could be utilized as a proxy in detecting oil contamination in the seawater of cold environments [134]. The metagenomics approach can also improve the understanding of the fate of oil spills and the dynamics of microbial structure.
7. Future Prospects of Bioremediation in the Arctic: Limitations and Suggestions
Emerging technologies in bioremediation strategies have been introduced with the main purpose to restore contaminated ecosystems in an environmentally sustainable and cost-effective manner. The ecosystem in the extreme Arctic conditions requires a longer time to recover from pollution [135]. Ex-situ bioremediation is widely implemented as the initial response towards accidental oil spills, tanker blowouts, or pipeline leakages to control harmful pollutants and minimize damage to marine and wildlife ecosystems. Bioremediation in the Arctic is governed by time and expense constraints, internal regulations, and guidelines. The time taken for the ecosystem to recover is much longer than temperate environments for the same concentrations of hydrocarbons, for many months or even decades [103]. This is due to the slower rate of natural attenuation and thermal incineration that poses a threat to permafrost and descending pollutant migration [136]. Moreover, based on the literature search and readings, studies on Arctic bacterial degradation of hydrocarbons are prominent; however, less is known about the application of algae, fungi, or other microbial communities. Therefore, with availability of resources and new technologies, it could be feasible to explore more and solve the problem of oil pollution.
Bioaugmentation is one of the in-situ bioremediation techniques that is less common in the Arctic due to limited nutrients levels that inhibit successful bioremediation of hydrocarbon contaminants. Therefore, the addition of nitrogen, carbon, and phosphorous sources is essential to optimize the growth of microbial communities and increase the efficiency of biodegradation of hydrocarbons [137,138]. Biodegradation of hydrocarbons by bacteria [139] is popular in the Arctic owing to their availability and adaptational capability, but less information is available on the functionality of fungi or algae. Phytoremediation is a potential bioremediation method to replace expensive techniques in cold regions. Plant species in cold regions may assist in soil decontamination. However, it is highly dependent on various growth factors such as water, soil nutrients, temperature, soil chemistry, and seasons [140,141]. Similarly, another primary producer is the sea ice algae population that contributes 3% to 50% of nutrients for copepods, zooplanktons, and krill that are then eaten by secondary consumers, fish, and whales [142]. Apart from that, bioreactor-based bioremediation treatments allow biodegradation of hydrocarbons in an optimal condition. The efficiency of bioreactor-based degradation relies on the ability of microbes to bind to inert packing that produces a high biomass [143]. Therefore, various biotechnological approaches can be used as an alternative over mechanical techniques to ensure the sustainability of the Arctic ecosystem.
8. Conclusions
The recent developments in biotechnology and engineering have produced new technologies to deliver novel and effective methods in managing polluted Arctic marine environments. Bibliometric analysis is valuable to identify the gaps of knowledge in the field of study. Polar regions are immensely vulnerable to rising anthropogenic activities that pose risks to the environment because of the high possibility for the next major oil pollution to occur. Bioremediation approaches improve the sustainability of the environment via in-situ remediation, including applications of native cold-acclimated microbial communities that safely degrade harmful hydrocarbons. The investigations on biodegradation of hydrocarbons in cold regions remain limited, and more information through enzymatic and metagenomics insights are required to respond and prepare towards the consequences of oil pollution in the Arctic marine ecosystem. Over the years, studies had proven that biodegradation of hydrocarbon via indigenous microbial communities is able to enhance the remediation process. This review has provided an overview for further scientific research and highlighted future research that are needed for microbial applications in the bioremediation of oil pollutants.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: S.A.A., G.V. and C.-Y.W.; writing–original draft preparation: G.V.; software: G.V.; writing–review and editing: S.A.A., C.-Y.W., N.A.S., C.G.-F. and A.Z.; supervision: S.A.A., C.-Y.W., N.A.S., C.G.-F. and A.Z. All authors have read and agree to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Universiti Putra Malaysia, Matching Grant Putra 9300436 and Putra Berimpak 9678900 and Yayasan Penyelidikan Antartika Sultan Mizan (YPASM) Research Grant 2020 on “Phytoremediation Potential of Antarctic Microalgae on Diesel Hydrocarbons”. C.G. Fuentes is supported by Centro de Investigacion y Monitoreo Ambiental Antàrctico (CIMAA) Project.
Acknowledgments
The authors also would like to thank Universiti Putra Malaysia, International Medical University, Universidad de Magallanes, Sultan Mizan Antarctic Research Foundation, and National Antarctic Research Center. This paper also contributes to the international SCAR research program “State of the Antarctic Ecosystem”.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Klein, D. Organic Chemistry, 3rd ed.; John Wiley and Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; Volume 51, p. 132. [Google Scholar]
- Speight, J.G. Handbook of Petroleum Refining; CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Arctic Council. Heavy Fuel Oil (HFO) Use by Ships in the Arctic 2019; Arctic Council: Tromsø, Norway, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Decola, E.; Robertson, T.; Fisher, M.; Blair, L. Phasing Out the Use and Carriage for Use of Heavy Fuel Oil in the Canadian Arctic: Impacts to Northern Communities; Nuka Research and Planning Group LLC.: Plymouth, MA, USA; Northern Economics: Anchorage, AK, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Comer, B.; Olmer, N.; Mao, X.; Roy, B.; Rutherford, D. Prevalence of Heavy Fuel Oil and Black Carbon in Arctic Shipping, 2015 to 2025; International Council on Clean Transportation: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Deggim, H. The International Code for Ships Operating in Polar Waters (Polar Code); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Guo, J.; Lv, Y.; Li, Y. Biodegradation of marine oil spill residues using aboriginal bacterial consortium based on Penglai 19-3 oil spill accident, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 159, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, C.H.; Rice, S.D.; Short, J.W.; Esler, D.; Bodkin, J.L.; Ballachey, B.E.; Irons, D.B. Long-term ecosystem response to the Exxon Valdez oil spill. Science 2003, 302, 2082–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozhukhova, E.; Litvinova, M.; Makarevich, E.; Malaeva, A. Biodegradation of petroleum hydrocarbons by bioflocculant-producing microorganisms of the aquatic ecosystems in the Arctic region. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 539, 012192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, S.; Deb, B.; Sharma, I. Isolation and characterization of cadmium and lead resistant bacteria. Glob. Adv. Res. J. Microbiol. 2012, 1, 194–198. [Google Scholar]
- Solis, B.P.; Argüello, J.C.C.; Barba, L.G.; Gurrola, M.P.; Zarhri, Z.; TrejoArroyo, D.L. Bibliometric Analysis of the Mass Transport in a Gas Diffusion Layer in PEM Fuel Cells. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingers, J.; Leydesdorff, L. A Review of Theory and Practice in Scientometrics. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2015, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, R.N.; Lima, A.T.C.; Lentini, C.A.D.; Miranda, G.V.; Mendonça, L.F.; Silva, M.A.; Cambuí, E.C.B.; Lopes, J.M.; Porsani, M.J. Oil Spill Detection and Mapping: A 50-Year Bibliometric Analysis. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gläser, J.; Laudel, G. A bibliometric reconstruction of research trails for qualitative investigations of scientific innovations. Hist. Soc. Res. Hist. Sozialforch. 2015, 40, 299–330. [Google Scholar]
- Tsay, M.Y. A bibliometric analysis of hydrogen energy literature, 1965-2005. Scientometrics 2008, 75, 421–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, D.; Picard-Aitken, M.; Côté, G.; Macaluso, B.Î.; Robitaille, J.P.; Bastien, N.; Laframboise, M.C.; Lebeau, L.M.; Mirabel, P.; Larivière, V.; et al. Bibliometrics as a performance measurement tool for research evaluation: The case of research funded by the national cancer institute of Canada. Proc. ISSI 2009, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scopus. Available online: https://www.scopus.com/ (accessed on 19 November 2020).
- Ki Kiduk, Y.; Meho, L.I. Citation analysis: A comparison of Google Scholar, Scopus, and Web of Science. Proc. ASIST Annu. Meet. 2006, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsevier. Scopus: Content Coverage Guide; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Borthakur, A.; Govind, M. Public Understandings of E-Waste and Its Disposal in Urban India: From a Review towards a Conceptual Framework. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 1053–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Viedma, E.; Martinez, M.A.; Herrera, M. Bibliometric tools for discovering information in database. In Trends in Applied Knowledge-Based Systems and Data Science IEA/AIE 2016. Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Fujita, H., Ali, M., Selamat, A., Sasaki, J., Kurematsu, M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; p. 9799. [Google Scholar]
- Md Khudzari, J.; Kurian, J.; Tartakovsky, B.; Raghavan, G.S.V. Bibliometric analysis of global research trends on microbial fuel cells using Scopus database. Biochem. Eng. J. 2018, 136, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Bellver, J.I.; Marín, P.; Delgado, A.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, A.; Reyes, E.; Ramos, J.L.; Marqués, S. Evidence for in situ crude oil biodegradation after the Prestige oil spill. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 7, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leahy, J.G.; Colwell, R.R. Microbial degradation of hydrocarbons in the environment. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. 1990, 54, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, N.; Chandran, P. Microbial degradation of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminants: An overview. Biotechnol. Res. Int. 2011, 2011, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, J.; Beegle-Krause, C.J.; Evers, K.-U.; Hughes, N.; Lewis, A.; Reed, M.; Wadhams, P. Oil spill response capabilities and technologies for ice-covered Arctic marine waters: A review of recent developments and established practices. Ambio 2017, 46, 423–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidalgo, K.J.; Sierra-Garcia, I.N.; Dellagnezze, B.M.; de Oliveira, V.M. Metagenomic insights into the mechanisms for biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the oil supply chain. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larivière, V.; Haustein, S.; Mongeon, P. The Oligopoly of Academic Publishers in the Digital Era. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grech, V.; Rizk, D.E.E. Increasing importance of research metrics: Journal Impact Factor and h-index. Int. Urogynecol. J. 2018, 29, 619–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abad-Segura, E.; Morales, M.E.; Cortés-García, F.J.; Belmonte-Ureña, L.J. Industrial Processes Management for a Sustainable Society: Global Research Analysis. Processes 2020, 8, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhu, D.; Porter, A.L. A Hybrid Visualisation Model for Technology Roadmapping: Bibliometrics, Qualitative Methodology and Empirical Study. Technol. Anal. Strateg. Manag. 2013, 25, 707–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, S.; Caldeira, R. Bibliometric Analysis of Ocean Literacy: An Underrated Term in the Scientific Literature. Mar. Policy 2018, 87, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, D.; Liang, B.; Bao, C.; Ma, M.; Xu, Y.; Yu, C. Marine Oil Spill Risk Mapping for Accidental Pollution and Its Application in a Coastal City. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 96, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran, R.; Cravo-Laureau, C. Role of environmental factors and microorganisms in determining the fate of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the marine environment. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2016, 40, 814–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neethu, C.S.; Saravanakumar, C.; Purvaja, R.; Robin, R.S.; Ramesh, R. Oil-spill triggered shift in indigenous microbial structure and functional dynamics in different marine environmental matrices. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Yu, Y.; Bai, Y.; Wang, L.; Wu, Y. Marine oil-degrading microorganisms and biodegradation process of petroleum hydrocarbon in marine environments: A review. Curr. Microbiol. 2015, 71, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCA. Kystverkets beredskap mot akutt forurensning. In Årsrapport 2012; NCA Preparedness for Acute Pollution. Annual Report 2012; Norwegian Coastal Administration (NCA): Ålesund, Norway, 2013; pp. 1–20. (In Norwegian) [Google Scholar]
- CBC News. Trans Mountain Pipeline Spill in Abbotsford Estimated at up to 190,000 Litres of Crude Oil. Available online: https://www.cbc.ca/news/canada/british-columbia/trans-mountain-pipeline-spill-abbotsford-150000-190000-litres-1.5611973 (accessed on 1 November 2020).
- The New York Times. Russia Declares Emergency After Arctic Oil Spill. Available online: https://www.nytimes.com/2020/06/04/world/europe/russia-oil-spill-arctic.html (accessed on 1 November 2020).
- Independent. Tanker Spills over 4000 Gallons of Crude Oil into Cuyama River. Available online: https://www.independent.com/2020/03/24/tanker-spills-over-4000-gallons-of-crude-oil-into-cuyama-river/ (accessed on 1 November 2020).
- Electrek. EGEB: Keystone Oil Spill in North Dakota, US Green Energy Grows by 6.15% to Date, More. Available online: https://electrek.co/2019/11/01/egeb-keystone-pipeline-oil-spill-north-dakota-us-green-energy-grows/ (accessed on 1 November 2020).
- Huffpost. Newfoundland Oil Spill Now Impossible to Clean Up: Watchdog. Available online: https://www.huffingtonpost.ca/2018/11/20/newfoundland-oil-spill-impossible-clean_a_23595116/ (accessed on 1 November 2020).
- CBC News. Trans Mountain Pipeline Spill in Abbotsford Estimated at up to 190,000 Litres of Crude Oil. Available online: https://www.cbc.ca/news/business/pipeline-leak-fouls-creek-near-grizzly-bear-protection-area-in-northwestern-alberta-1.3634989 (accessed on 1 November 2020).
- Fingas, M.F.; Hollebone, B.P. Review of behaviour of oil in freezing environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2003, 47, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagnolli, R.; Lopes, P.; Bidoia, E. Screening the toxicity and biodegradability of petroleum hydrocarbons by a rapid colorimetric method. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 68, 342–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bargiela, R.; Yakimov, M.M.; Golyshin, P.N. Consequences of Microbial Interactions with Hydrocarbons, Oils, and Lipids: Production of Fuels and Chemicals; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 629–651. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, C.L.; Selin, N.E. Long-range atmospheric transport of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: A global 3-D model analysis including evaluation of Arctic sources. Environ. Sci.Technol. 2012, 46, 9501–9510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakke, T.; Klungsøyr, J.; Sanni, S. Environmental impacts of produced water and drilling waste discharges from Norwegian offshore petroleum industry. Mar. Environ. Res. 2013, 92, 154–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Shafy, H.I.; Mansour, M.S.M. A review on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Source, environmental impact, effect on human health and remediation. Egypt. J. Pet. 2016, 25, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerniglia, C.E.; Heitkamp, M.A. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degradation by Mycobacterium. Meth. Enzymol. 1990, 188, 148–153. [Google Scholar]
- DeGraeve, G.M.; Elder, R.G.; Woods, D.C.; Bergman, H.L. Effects of naphthalene and benzene on fathead minnows and rainbow trout. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1982, 11, 487–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teles, M.; Pacheco, M.; Santos, M.A. Anguilla anguilla L. liver ethoxyresorufin O-deethylation, glutathione S-transferase, erythrocytic nuclear abnormalities, and endocrine responses to naphthalene and b-naphthoflavone. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2003, 55, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossi, M.; Pedà, C.; Compa, M.; Tsangaris, C.; Alomar, C.; Claro, F.; Ioakeimidis, C.; Galgani, F.; Hema, T.; Deudero, S.; et al. Bioindicators for monitoring marine litter ingestion and its impacts on Mediterranean biodiversity. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 1023–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milinkovitch, T.; Geraudie, P.; Camus, L.; Huet, V.; Thomas-Guyon, H. Biomarker modulation associated with marine diesel contamination in the Iceland scallop (Chlamys islandica). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 19292–19296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geraudie, P.; Bakkemo, R.; Milinkovitch, T.; Thomas-Guyon, H. First evidence of marine diesel effects on biomarker responses in the Icelandic scallops, Chlamys islandica. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 16504–16512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagerup, K.; Nahrgang, J.; Frantzen, M.; Larsen, L.-H.; Geraudie, P. Biological effects of marine diesel oil exposure in red king crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus) assessed through a water and foodborne exposure experiment. Mar. Environ. Res. 2016, 119, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.Y.; Cooke, S.R.; Moore, M.J.; Martineau, D.; Mikaelian, I.; Metner, D.A.; Lockhart, W.L.; Stegeman, J.J. Systemic effects of Arctic pollutants in beluga whales indicated by CYP1A1 expression. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 1594–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Morris, B.F.; Loughlin, T.R. Overview of the Exxon Valdez Oil Spill 1989–1992. In Marine Mammals and the Exxon Valdez; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1994; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- ATSDR. Toxicological Profile for Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs); US Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry: Atlanta, GA, USA, 1995.
- Armstrong, B.; Hutchinson, E.; Unwin, J.; Fletcher, T. Lung cancer risk after exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: A review and meta-analysis. Environ. Health Perspect. 2004, 112, 970–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diggs, D.L.; Huderson, A.C.; Harris, K.L.; Myers, J.N.; Banks, L.D.; Rekhadevi, P.V.; Niaz, M.S.; Ramesh, A. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and digestive tract cancers: A perspective. J. Environ. Sci. Health. C Environ. Carcinog. Ecotoxicol. Rev. 2011, 29, 324–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unwin, J.; Cocker, J.; Scobbie, E.; Chambers, H. An assessment of occupational exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the UK. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2006, 50, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bach, P.; Kelley, M.; Tate, R.; McCrory, D. Screening for lung cancer: A review of the current literature. Chest. 2003, 123, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlas, R.; Bragg, J. Bioremediation of marine oil spills: When and when not—The Exxon Valdez experience. Microb. Biotechnol. 2009, 2, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakaria, N.N.; Man, Z.; Zulkharnain, A.; Ahmad, S.A. Psychrotolerant biosurfactant-producing bacteria for hydrocarbon degradation: A mini review. Malays. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 22, 52–59. [Google Scholar]
- Roslee, A.F.A.; Zakaria, N.N.; Convey, P.; Zulkharnain, A.; Lee, G.L.Y.; Gomez-Fuentes, C.; Ahmad, S.A. Statistical optimisation of growth conditions and diesel degradation by the Antarctic bacterium, Rhodococcus sp. strain AQ5‒07. Extremophiles 2020, 24, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Z.S.; Wong., R.R.; Chiew-Yen., W.; Zulkharnian., A.; Shaharuddin, N.A.; Ahmad., S.A. Bibliometric analysis of research on diesel pollution in Antarctica and a review on remediation techniques. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hawash, A.B.; Dragh, M.A.; Li, S.; Alhujaily, A.; Abbood, H.A.; Zhang, X.; Ma, F. Principles of microbial degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons in the environment. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2018, 44, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmke, E.; Weyland, H. Psychrophilic versus psychrotolerant bacteria—Occurrence and significance in polar and temperate marine habitats. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2014, 50, 553–561. [Google Scholar]
- Bisht, S.; Pandey, P.; Bhargava, B.; Sharma, S.; Kumar, V.; Sharma, K.D. Bioremediation of polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) using rhizosphere technology. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2015, 46, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deppe, U.; Richnow, H.-H.; Michaelis, W.; Antranikian, G. Degradation of crude oil by an arctic microbial consortium. Extremophiles 2005, 9, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conte, A.; Papale, M.; Amalfitano, S.; Mikkonen, A.; Rizzo, C.; De Domenico, E.; Michaud, L.; Lo Giudice, A. Bacterial community structure along the subtidal sandy sediment belt of a high Arctic fjord (Kongsfjorden, Svalbard Islands). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619–620, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerdes, B.; Brinkmeyer, R.; Dieckmann, G.; Helmke, E. Influence of crude oil on changes of bacterial community in Arctic sea-ice. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2005, 53, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisafi, F.; Giuliano, L.; Yakimov, M.M.; Azzaro, M.; Denaro, R. Isolation and degradation potential of a cold-adapted oil/PAH degrading marine bacterial consortium from Kongsfjorden (Arctic region). Rend. Lincei Sci. Fis. Nat. 2016, 27, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesnawi, R.M.; Adbeib, M.M. Effect of nutrient source on indigenous biodegradation of diesel fuel contaminated soil. APCBEE Procedia 2013, 5, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantary, R.R.; Mohseni-Bandpi, A.; Esrafili, A.; Nasseri, S.; Ashmagh, F.; Jorfi, S.; Ja’fari, M. Effectiveness of biostimulation through nutrient content on the bioremediation of phenanthrene contaminated soil. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2014, 12, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leys, N.M.; Bastiaens, L.; Verstraete, W.; Springael, D. Influence of the carbon/nitrogen/phosphorus ratio on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degradation by Mycobacterium and Sphingomonas in soil. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2005, 66, 726–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.; Abdul Khalil, K.; Zahri, K.N.M.; Gomez-Fuentes, C.; Convey, P.; Zulkharnain, A.; Sabri, S.; Alias, S.A.; González-Rocha, G.; Ahmad, S.A. Biosurfactant production and growth kinetics studies of the waste canola oil-degrading bacterium Rhodococcus erythropolis AQ5-07 from Antarctica. Molecules 2020, 25, 3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pengcheng, F.; Secundo, F. Algae and their bacterial consortia for soil bioremediation. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2016, 49, 427–432. [Google Scholar]
- Nur Zaida, Z.; Piakong, M.T. Bioaugmentation of Petroleum Hydrocarbon in Contaminated Soil: A Review. In Microbial Action on Hydrocarbons; Kumar, V., Kumar, M., Prasad, R., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, E.M.S.; Guyoneaud, R.; Goñi-Urriza, M.; Ranchou-Peyruse, A.; Verbaere, A.; Crapez, M.A.C.; Wasserman, J.C.A.; Duran, R. Characterization of hydrocarbonoclastic bacterial communities from mangrove sediments in Guanabara Bay, Brazil. Microbiol. Res. 2006, 157, 752–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaRoe, S.L.; Wang, B.; Han, J.I. Isolation and characterization of a novel polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-degrading bacterium, Sphingopyxis sp strain M2R2, capable of passive spreading motility through soil. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2010, 27, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, C.; Malavenda, R.; Gerçe, B.; Papale, M.; Syldatk, C.; Hausmann, R.; Bruni, V.; Michaud, L.; Lo Giudice, A.; Amalfitano, S. Effects of a simulated acute oil spillage on bacterial communities from Arctic and Antarctic marine sediments. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brakstad, O.G.; Lofthus, S.; Ribicic, D.; Netzer, R. Biodegradation of petroleum oil in cold marine environments. In Psychrophiles: From Biodiversity to Biotechnology; Margesin, R., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 613–644. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulrasheed, M.; Zulkharnain, A.; Zakaria, N.N.; Roslee, A.F.A.; Abdul Khalil, K.; Napis, S.; Convey, P.; Gomez-Fuentes, C.; Ahmad, S.A. Response surface methodology optimization and kinetics of diesel degradation by a cold-adapted Antarctic bacterium, Arthrobacter sp. strain AQ5-05. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, N.N.; Roslee, A.F.A.; Gomez-Fuentes, C.; Zulkharnain, A.; Abdulrasheed, M.; Sabri, S.; Ramírez-Moreno, N.; Calisto-Ulloa, N.; Ahmad, S.A. Biodegradation of diesel in the presence of heavy metals by Antarctic marine bacteria. Rev. Mex. Ing. Quím. 2020, 19, 1375–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerry, E. Microorganisms colonizing plants and soil subjected to different degrees of human activity, including petroleum contamination, in the Vestfold Hills and MacRobertson Land, Antarctica. Polar Biol. 1990, 10, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aislabie, J.; Fraser, R.; Duncan, S.; Farrell, R.L. Effects of oil spills on microbial heterotrophs in Antarctic soils. Polar Biol. 2001, 24, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, A.N. Role of fungi in bioremediation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 12, 55–841. [Google Scholar]
- de Jesus, H.E.; Peixoto, R.S. Bioremediation in Antarctic Soils. J. Pet. Environ. Biotechnol. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bramley-Alves, J.; Wasley, J.; King, C.K.; Powell, S.; Robinson, S.A. Phytoremediation of Hydrocarbon Contaminants in Subantarctic Soils: An Effective Management Option. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 142, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Bai, X.; Sheng, H.; Jiao, L.; Zhou, H.; Shao, Z. Distribution of PAHs and the PAH-degrading bacteria in the deep-sea sediments of the high-latitude Arctic Ocean. Biogeosciences 2015, 12, 2163–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchigvintsev, A.; Tran, H.; Popovic, A.; Kovacic, F.; Brown, G.; Flick, R.; Hajighasemi, M.; Egorova, O.; Somody, J.C.; Tchigvintsev, D.; et al. The environment shapes microbial enzymes: Five cold-active and salt-resistant carboxylesterases from marine metagenomes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 2165–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varjani, S.J.; Upasani, V.N. Biodegradation of petroleum hydrocarbons by oleophilic strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa NCIM 5514. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 222, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, H.; Sheng, Y.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Zhao, H.; Gui, X. Metagenomic insights into the microbiota profiles and bioaugmentation mechanism of organics removal in coal gasification wastewater in an anaerobic/anoxic/oxic system by methanol. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 264, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, J.; Jonsson, G.; Porte, C.; Krahn, M.M.; Ariese, F. Analytical methods for determining metabolites of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) pollutants in fish bile: A review. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2010, 30, 224–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosal, D.; Ghosh, S.; Dutta, T.K.; Ahn, Y. Current state of knowledge in microbial degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs): A review. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunker, M.B.; Macdonald, R.W.; Snowdon, L.R.; Fowler, B.R. Alkane and PAH biomarkers as tracers of terrigenous organic carbon in Arctic Ocean sediments. Org. Geochem. 2011, 42, 1109–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Bai, X.; Lai, Q.; Xie, Y.; Chen, X.; Shao, Z. Draft genome sequence of Sphingobium sp. strain C100, a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-degrading bacterium from the deep-sea sediment of the Arctic Ocean. Genome Announc. 2014, 2, e01210–e01213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, C.; Bai, X.; Lai, Q.; Xie, Y.; Chen, X.; Shao, Z. Draft genome sequence of Marinomonas sp. strain D104, a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-degrading bacterium from the deep-sea sediment of the Arctic Ocean. Genome Announc. 2014, 2, e01211–e01213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brakstad, O.G.; Nonstad, I.; Faksness, L.G.; Brandvik, P.J. Responses of microbial communities in Arctic sea ice after contamination by crude petroleum oil. Microb. Ecol. 2008, 55, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez Calderon, L.J.; Gontikaki, E.; Potts, L.D.; Shaw, S.; Gallego, A.; Anderson, J.A.; Witte, U. Pressure and temperature effects on deep-sea hydrocarbon-degrading microbial communities in subarctic sediments. Microbiologyopen 2019, 8, e00768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garneau, M.-È.; Michel, C.; Meisterhans, G.; Fortin, N.; King, T.L.; Greer, C.W.; Lee, K. Hydrocarbon biodegradation by Arctic sea-ice and sub-ice microbial communities during microcosm experiments, Northwest Passage (Nunavut, Canada). FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2016, 92, fiw130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazen, T.C.; Prince, R.C.; Mahmoudi, N. Marine Oil Biodegradation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 2121–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, H.; Kallmeyer, J.; Adhikari, R.R.; Pockalny, R.; Jorgensen, B.B.; D’Hondt, S. Aerobic microbial respiration in 86-million-year-old deep-sea red clay. Science 2012, 336, 922–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghukumar, C.; Vipparty, V.; David, J.J.; Chandramohan, D. Degradation of crude oil by marine cyanobacteria. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2001, 57, 433–436. [Google Scholar]
- Iwai, S.; Johnson, T.A.; Chai, B.; Hashsham, S.A.; Tiedje, J.M. Comparison of the specificities and efficacies of primers for aromatic dioxygenase gene analysis of environmental samples. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 3551–3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parales, R.E.; Resnick, S.M. Aromatic ring hydroxylating dioxygenases. In Pseudomonas; Ramos, J.-L., Levesque, R.C., Eds.; Springer: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 287–340. [Google Scholar]
- Shahsavari, E.; Schwarz, A.; Aburto-Medina, A.; Ball, A.S. Biological degradation of polycyclic aromatic compounds (PAHs) in soil: A current perspective. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2019, 5, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Karthiga, N.; Kai-Chee, L. Biodegradation of aromatic compounds: Current status and opportunities for biomolecular approaches. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 85, 207–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coates, J.D.; Anderson, R.T.; Woodward, J.C.; Phillips, E.J.P.; Lovley, D.R. Anaerobic hydrocarbon degradation in petroleum contaminated harbor sediments under sulfate-reducing and artificially imposed iron-reducing conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1996, 30, 2784–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabus, R.; Boll, M.; Heider, J.; Meckenstock, R.U.; Buckel, W.; Einsle, O.; Ermler, U.; Golding, B.T.; Gunsalus, R.P.; Kroneck, P.M.H.; et al. Anaerobic microbial degradation of hydrocarbons: From enzymatic reactions to the environment. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 26, 5–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safinowski, M.; Meckenstock, R.U. Methylation is the initial reaction in anaerobic naphthalene degradation by a sulfate-reducing enrichment culture. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meckenstock, R.U.; Mouttaki, H. Anaerobic degradation of non-substituted aromatic hydrocarbons. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2011, 22, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meckenstock, R.U.; Boll, M.; Mouttaki, H.; Koelschbach, J.S.; Cunha Tarouco, P.; Weyrauch, P.; Dong, X.; Himmelberg, A.M. Anaerobic degradation of benzene and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 26, 92–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojo, F. Degradation of alkanes by bacteria. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 477–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heider, J.; Schühle, K. Anaerobic biodegradation of hydrocarbons including methane. In The Prokaryotes: Prokaryotic Physiology and Biochemistry; Rosenberg, E., DeLong, E.F., Lory, S., Thompson, F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 605–634. [Google Scholar]
- Vergeynst, L.; Kjeldsen, K.U.; Lassen, P.; Rysgaard, S. Bacterial community succession and degradation patterns of hydrocarbons in seawater at low temperature. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 353, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruno, S.; Coppola, D.; Di Prisco, G.; Giordano, D.; Verde, C. Enzymes from marine polar regions and their biotechnological applications. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phadtare, S. Recent developments in bacterial cold-shock response. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2004, 6, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Collins, T.; Gerday, C. Enzyme Catalysis in Psychrophiles. In Psychrophiles: From Biodiversity to Biotechnology; Margesin, R., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 209–235. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Li, X.; Yu, T.; Wang, F.; Qu, C. Study on Extreme Microbial Degradation of Petroleum Hydrocarbons. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFarlin, K.M.; Prince, R.C.; Perkins, R.; Leigh, M.B. Biodegradation of dispersed oil in Arctic seawater at −1 °C. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahendra, S.; Gedalanga, P.; Kotay, S.M.; Torres, C.I.; Butler, C.S.; Goel, R. Advancements in molecular techniques and applications in environmental engineering. Water. Environ. Res. 2012, 84, 814–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpton, T.J. An introduction to the analysis of shotgun metagenomic data. Front. Plant. Sci. 2014, 5, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguiar-Pulido, V.; Huang, W.; Suarez-Ulloa, V.; Cickovski, T.; Mathee, K.; Narasimhan, G. Metagenomics, metatranscriptomics, and metabolomics approaches for microbiome analysis. Evol. Bioinform. 2016, 12, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFarlin, K.M.; Perkins, M.J.; Field, J.A.; Leigh, M.B. Biodegradation of crude oil and Corexit 9500 in Arctic seawater. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyksterhouse, S.E.; Gray, J.P.; Herwig, R.P.; Lara, J.C.; Staley, J.T. Cycloclasticus pugetii gen. nov., sp. nov., an aromatic hydrocarbon-degrading bacterium from marine sediments. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1995, 45, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedlund, B.P.; Geiselbrecht, A.D.; Staley, J.T. Marinobacter strain NCE312 has a Pseudomonas-like naphthalene dioxygenase. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2001, 201, 47–51. [Google Scholar]
- Melcher, R.J.; Apitz, S.E.; Hemmingsen, B.B. Impact of irradiation and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon spiking on microbial populations in marine sediment for future aging and biodegradability studies. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 2858–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demaneche, S.; Meyer, C.; Micoud, J.; Louwagie, M.; Willison, J.C.; Jouanneau, Y. Identification and functional analysis of two aromatic-ring-hydroxylating dioxygenases from a Sphingomonas strain that degrades various polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 6714–6725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedlund, B.P.; Staley, J.T. Vibrio cyclotrophicus sp. nov., a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH)-degrading marine bacterium. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Micr. 2001, 51, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, G.; Kostka, J.; Hazen, T.; Sobecky, P. Microbial responses to the Deepwater Horizon oil spill: From coastal wetlands to the deep sea. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2015, 7, 377–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazen, T.C.; Dubinsky, E.A.; Desantis, T.Z.; Andersen, G.L.; Piceno, Y.M.; Singh, N.; Jansson, J.K.; Probst, A.; Borglin, S.E.; Fortney, J.L.; et al. Deep-sea oil plume enriches indigenous oil-degrading bacteria. Science 2010, 330, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krolicka, A.; Boccadoro, C.; Mæland, M.; Demir-hilton, E.; Birch, J.; Preston, C.; Scholin, C.; Baussant, T. Identification of microbial key-indicators of oil contamination at sea through tracking of oil biotransformation: An Arctic field and laboratory study. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 696, 133715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautier, D.; Bird, K.; Charpentier, R.; Grantz, A.; Houseknecht, D.; Klett, T. Assessment of undiscovered oil and gas in the Arctic. Science 2009, 324, 1175–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, L.; Niu, J.; Wang, J.; Shen, Z. Pollution assessment and source identifications of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments of the Yellow River Delta, a newly born wetland in China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 158, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naseri, M.; Barabadi, A.; Barabady, J. Bioremediation treatment of hydrocarbon-contaminated Arctic soils: Influencing parameters. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2014, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, G.O.; Fufeyin, P.T.; Okoro, S.E.; Ehinomen, I. Bioremediation, biostimulation and bioaugmention: A review. Int. J. Environ. Bioremediat. Biodegrad. 2015, 3, 28–39. [Google Scholar]
- Gran-Scheuch, A.; Fuentes, E.; Bravo, D.M.; Jiménez, J.C.; Pérez-Donoso, J.M. Isolation and characterization of phenanthrene degrading bacteria from diesel fuel-contaminated Antarctic soils. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 16–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Calvo, A.; Silva-Castro, G.A.; Olicón-Hernández, D.R.; González-López, J.; Calvo, C. Biodegradation and absorption technology for hydrocarbon-polluted water treatment. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosselin, M.; Levasseur, M.; Wheeler, P.A.; Horner, R.A.; Booth, B.C. New measurements of phytoplankton and ice algal production in the Arctic Ocean. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 1997, 44, 1623–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikere, C.B.; Chikere, B.O.; Okpokwasili, G.C. Bioreactor-based bioremediation of hydrocarbon-polluted Niger Delta marine sediment, Nigeria. 3 Biotech 2012, 2, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).