Performance of the Hendrich Fall Risk Model II in Patients Discharged from Rehabilitation Wards. A Preliminary Study of Predictive Ability
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Setting
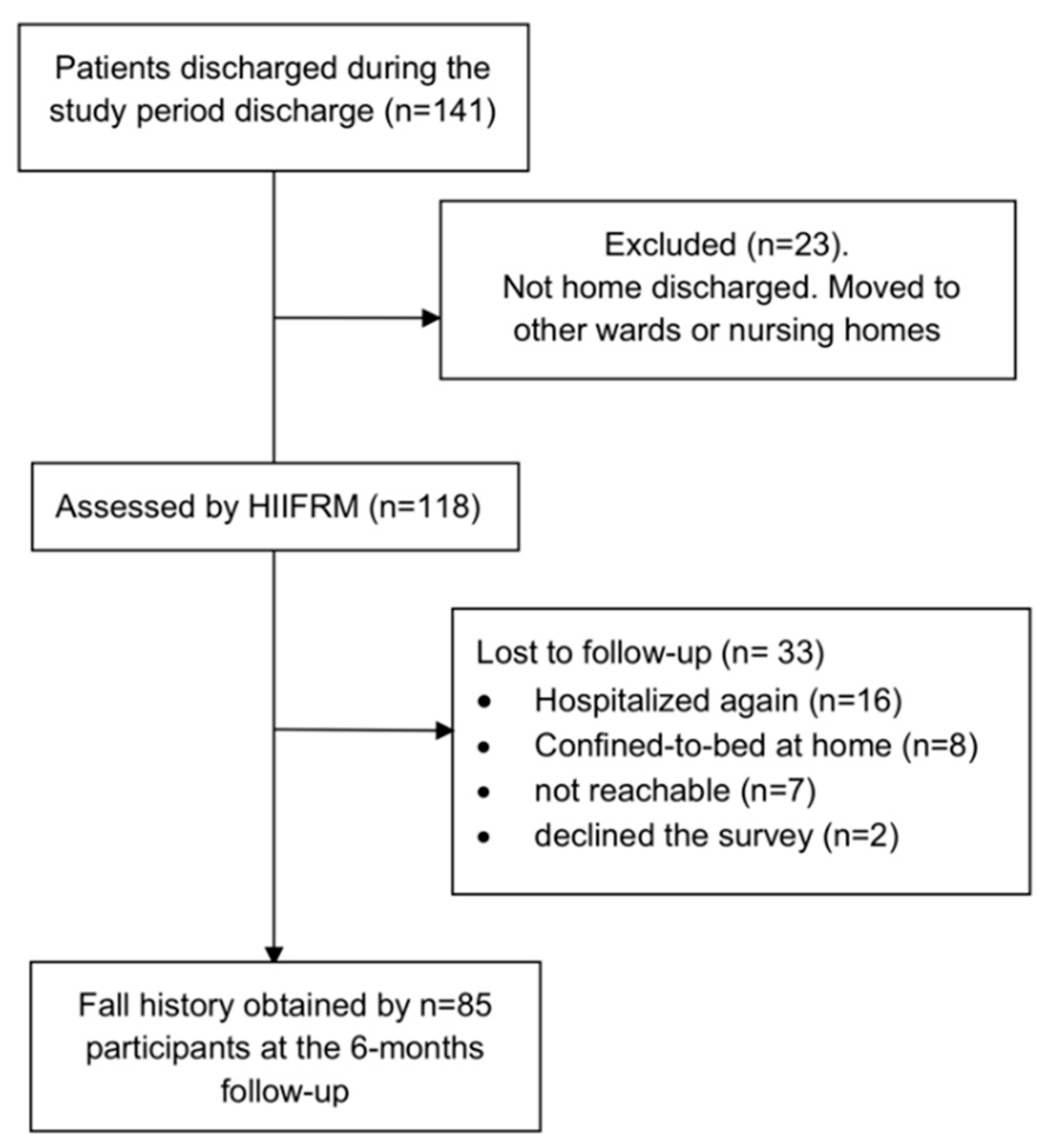
2.2. Patients
2.3. Fall Risk Assessment Procedure at Discharge
2.4. Survey on Post-Discharge Falls
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Sample Size Computation for Future Studies
3. Results
3.1. Sample Characteristics
3.2. Fall Risk Classification at Discharge
3.3. Fall History and Characteristics of Fall Dynamics
3.4. Between Groups Comparison
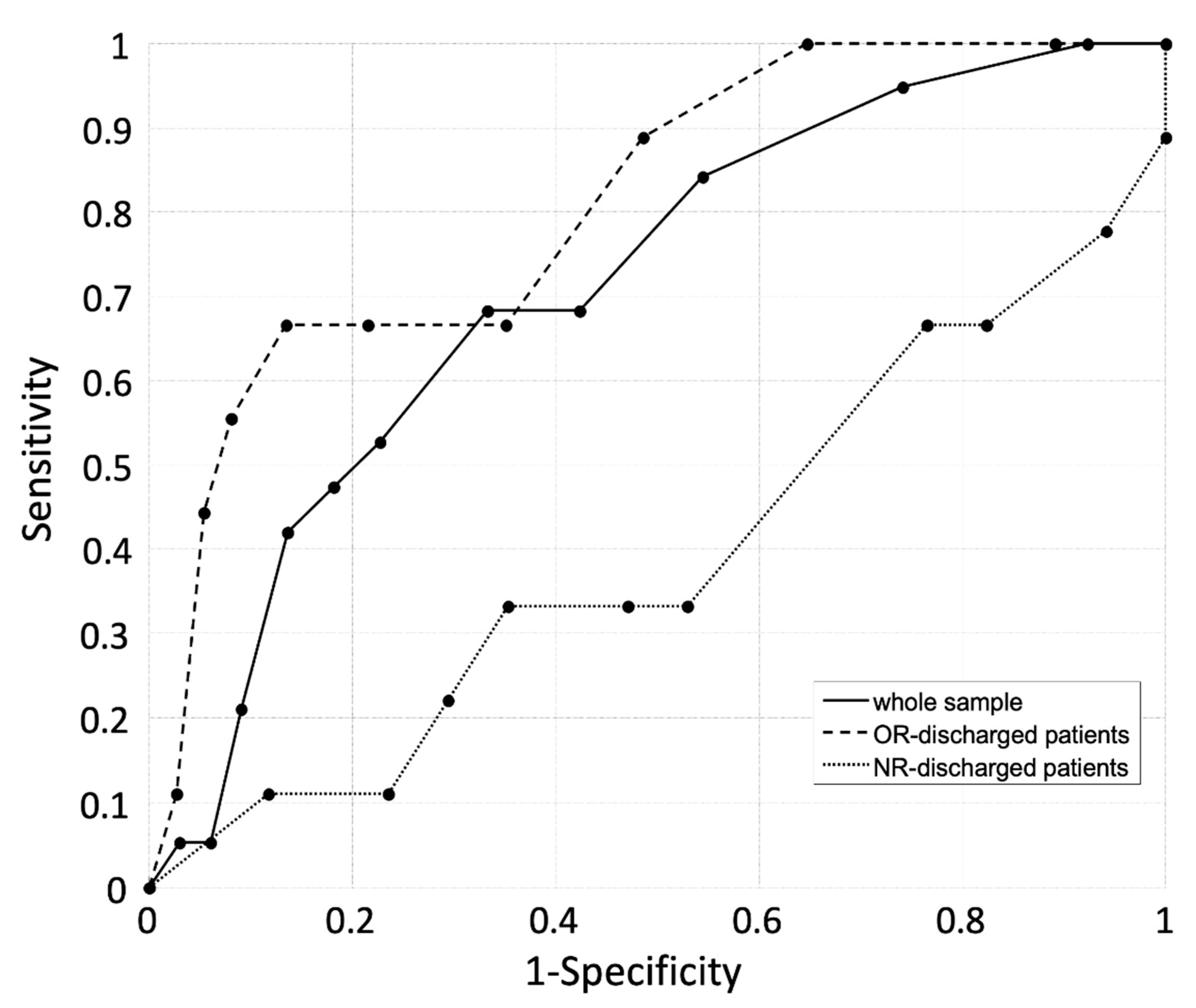
3.5. Predictive Perfomrance of the HIIFRM When Administerd at Discharge
3.6. Sample Size Calculation for a Study of Predictive Ability
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aranda-Gallardo, M.; Asencio, J.M.M.; Canca-Sanchez, J.C.; Mora-Banderas, A.M.; Moya-Suarez, A.B.; Barrero-Sojo, S.; Perez-Jimenez, C.; Morales-Fernandez, A.; de Luna-Rodriguez, M.E.; Moya-Suarez, A.B.; et al. Instruments for assessing the risk of falls in acute hospitalized patients: A systematic review protocol. J. Adv. Nurs. 2013, 69, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, I.D.; Dyer, S.M.; Panagoda, C.E.; Murray, G.R.; Hill, K.D.; Cumming, R.G.; Kerse, N. Interventions for preventing falls in older people in care facilities and hospitals. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 9, CD005465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwendimann, R.; Bühler, H.; De Geest, S.; Milisen, K. Characteristics of Hospital Inpatient Falls across Clinical Departments. Gerontology 2008, 54, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, A.M.; McPhail, S.M.; Waldron, N.; Etherton-Beer, C.; Ingram, K.; Flicker, L.; Bulsara, M.; Haines, T.P. Fall rates in hospital rehabilitation units after individualised patient and staff education programmes: A pragmatic, stepped-wedge, cluster-randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2015, 385, 2592–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healey, F.; Monro, A.; Cockram, A.; Adams, V.; Heseltine, D. Using targeted risk factor reduction to prevent falls in older in-patients: A randomised controlled trial. Age Ageing 2004, 33, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haines, T.; Kuys, S.S.; Morrison, G.; Clarke, J.; Bew, P. Balance impairment not predictive of falls in geriatric rehabilitation wards. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2008, 63, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teasell, R.; McRae, M.; Foley, N.; Bhardwaj, A. The incidence and consequences of falls in stroke patients during inpatient rehabilitation: Factors associated with high risk. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2002, 83, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naseri, C.; Haines, T.P.; Etherton-Beer, C.; McPhail, S.; Morris, M.E.; Flicker, L.; Netto, J.; Francis-Coad, J.; Lee, D.-C.A.; Shorr, R.; et al. Reducing falls in older adults recently discharged from hospital: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Age Ageing 2018, 47, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahoney, J.E.; Palta, M.; Johnson, J.; Jalaluddin, M.; Gray, S.; Park, S.; Sager, M. Temporal Association Between Hospitalization and Rate of Falls After Discharge. Arch. Intern. Med. 2000, 160, 2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackintosh, S.F.; Hill, K.D.; Dodd, K.J.; Goldie, P.A.; Culham, E.G. Balance Score and a History of Falls in Hospital Predict Recurrent Falls in the 6 Months Following Stroke Rehabilitation. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2006, 87, 1583–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, A.; Young, J. Incidence and consequences of falls due to stroke: A systematic inquiry. BMJ Br. Med. J. 1995, 311, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchelor, F.A.; Hill, K.D.; MacKintosh, S.F.; Said, C.M.; Whitehead, C.H. Effects of a multifactorial falls prevention program for people with stroke returning home after rehabilitation: A randomized controlled trial. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2012, 93, 1648–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, S.D.; Miller, R.R. Falls: Epidemiology, pathophysiology, and relationship to fracture. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2008, 6, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.-H. Tools for assessing fall risk in the elderly: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2018, 30, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maranesi, E.; Merlo, A.; Fioretti, S.; Zemp, D.D.; Campanini, I.; Quadri, P. A statistical approach to discriminate between non-fallers, rare fallers and frequent fallers in older adults based on posturographic data. Clin. Biomech. 2016, 32, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendrich, A.L.; Bender, P.S.; Nyhuis, A. Validation of the Hendrich II Fall Risk Model: A large concurrent case/control study of hospitalized patients. Appl. Nurs. Res. 2003, 16, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver, D.; Britton, M.; Seed, P.; Martin, F.C.; Hopper, A.H. Development and evaluation of evidence based risk assessment tool (STRATIFY) to predict which elderly inpatients will fall: Case-control and cohort studies. BMJ 1997, 315, 1049–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breisinger, T.P.; Skidmore, E.R.; Niyonkuru, C.; Terhorst, L.; Campbell, G.B. The Stroke Assessment of Fall Risk (SAFR): Predictive validity in inpatient stroke rehabilitation. Clin. Rehabil. 2014, 28, 1218–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, W.K.; Mordiffi, S.Z.; Wong, H.C.; Ang, E.N.K. Development and Validation of a Simplified Falls Assessment Tool in an Acute Care Setting. J. Nurs. Care Qual. 2016, 31, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanini, I.; Mastrangelo, S.; Bargellini, A.; Bassoli, A.; Bosi, G.; Lombardi, F.; Tolomelli, S.; Lusuardi, M.; Merlo, A. Feasibility and predictive performance of the Hendrich Fall Risk Model II in a rehabilitation department: A prospective study. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2018, 18, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrich, A.L.; Bufalino, A.; Groves, C. Validation of the Hendrich II Fall Risk Model: The imperative to reduce modifiable risk factors. Appl. Nurs. Res. 2020, 713, 151243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrich, A. Predicting Patient Falls. AJN Am. J. Nurs. 2007, 107, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yardley, L.; Bishop, F.L.; Beyer, N.; Hauer, K.; Kempen, G.I.J.M.; Piot-Ziegler, C.; Todd, C.J.; Cuttelod, T.; Horne, M.; Lanta, K.; et al. Older People’s Views of Falls-Prevention Interventions in Six European Countries. Gerontologist 2006, 46, 650–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buderer, N.M.F. Statistical Methodology: I. Incorporating the Prevalence of Disease into the Sample Size Calculation for Sensitivity and Specificity. Acad. Emerg. Med. 1996, 3, 895–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimundić, A.-M. Measures of Diagnostic Accuracy: Basic Definitions. EJIFCC 2009, 19, 203–211. [Google Scholar]
- Morse, J.M. Enhancing the safety of hospitalization by reducing patient falls. Am. J. Infect. Control 2002, 30, 376–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reider, N.; Gaul, C. Fall risk screening in the elderly: A comparison of the minimal chair height standing ability test and 5-repetition sit-to-stand test. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2016, 65, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melzer, I.; Kurz, I.; Oddsson, L.I.E. A retrospective analysis of balance control parameters in elderly fallers and non-fallers. Clin. Biomech. 2010, 25, 984–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, M.A.; Hill, K.D.; Blackberry, I.; Day, L.M.; Dharmage, S.C. The reliability and predictive accuracy of the falls risk for older people in the community assessment (FROP-Com) tool. Age Ageing 2008, 37, 634–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Ng, M.M.; Hill, K.D.; Batchelor, F.; Burton, E. Factors Predicting Falls and Mobility Outcomes in Patients With Stroke Returning Home After Rehabilitation Who are at Risk of Falling. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2017, 98, 2433–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, A.-M.; Hoffmann, T.; McPhail, S.; Beer, C.; Hill, K.D.; Oliver, D.; Brauer, S.G.; Haines, T.P. Evaluation of the Sustained Effect of Inpatient Falls Prevention Education and Predictors of Falls After Hospital Discharge–Follow-up to a Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2011, 66, 1001–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, A.C.M.; Jehu, D.A.; Pang, M.Y.C. Falls After Total Knee Arthroplasty: Frequency, Circumstances, and Associated Factors–A Prospective Cohort Study. Phys. Ther. 2018, 98, 767–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikutomo, H.; Nagai, K.; Nakagawa, N.; Masuhara, K. Falls in patients after total hip arthroplasty in Japan. J. Orthop. Sci. 2015, 20, 663–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, S.J.; Botte, M.J. Management of the Adult, Spastic, Equinovarus Foot Deformity. Foot Ankle Int. 1994, 15, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannotti, E.; Merlo, A.; Zerbinati, P.; Prati, P.; Masiero, S.; Mazzoli, D. Safety and long term effects on gait of hemiplegic patients in equino varus foot deformity surgical correction followed by immediate rehabilitation. A prospective observational study. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2018, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanini, I.; Merlo, A.; Damiano, B. A method to differentiate the causes of stiff-knee gait in stroke patients. Gait Posture 2013, 38, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, C.M.; Batchelor, F.; Shaw, K.; Blennerhassett, J. Preparing patients at high risk of falls for discharge home after rehabilitation: Do we meet the guidelines? Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2016, 16, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gitlin, L.N.; Corcoran, M.; Winter, L.; Boyce, A.; Hauck, W.W. A Randomized, Controlled Trial of a Home Environmental Intervention. Gerontologist 2001, 41, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, B.L.; Gleason, C.E.; Gangnon, R.E.; Janczewski, J.; Shea, T.; Mahoney, J.E. Declining Cognition and Falls: Role of Risky Performance of Everyday Mobility Activities. Phys. Ther. 2014, 94, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlenstedt, C.; Brombacher, S.; Hartwigsen, G.; Weisser, B.; Möller, B.; Deuschl, G. Comparison of the Fullerton Advanced Balance Scale, Mini-BESTest, and Berg Balance Scale to Predict Falls in Parkinson Disease. Phys. Ther. 2016, 96, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivziku, D.; Matarese, M.; Pedone, C. Predictive validity of the Hendrich fall risk model II in an acute geriatric unit. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2011, 48, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muir, S.W.; Berg, K.; Chesworth, B.; Klar, N.; Speechley, M. Balance Impairment as a Risk Factor for Falls in Community-Dwelling Older Adults Who Are High Functioning: A Prospective Study. Phys. Ther. 2010, 90, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variable | Whole Sample Characteristics | Sample Characteristics Split by Wards | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NR | OR | PR | ||
| Patients, n | 85 | 26 | 46 | 13 |
| Age, years, mean (SD); min, 25th, 50th, 75th percentile, max | 67 (16); 20, 60, 72, 77, 91 | 56 (18); 20, 55, 64, 71, 91 | 70 (16); 20, 67, 74, 79, 91 | 69 (10); 54, 59, 72, 75, 86 |
| Gender female/male; n | 51/34 | 14/12 | 31/15 | 6/7 |
| HIIFRM score; median (IQR); range | 3 (4); 0–11 | 5 (4); 1–11 | 3 (4); 0–9 | 2 (1); 0–9 |
| Subjects classified at high risk of falling; n (%) | 35 (41%) | 19 (73%) | 14 (30%) | 2 (15%) |
| Item | Score | Occurrences | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NR (n = 26) | OR (n = 46) | PR (n = 13) | ||
| Confusion/Disorientation | (4) | 19% | 4% | 8% |
| Symptomatic Depression | (2) | 8% | 20% | 8% |
| Altered Elimination | (1) | 35% | 54% | 46% |
| Dizziness/Vertigo | (1) | 77% | 41% | 15% |
| Male Gender | (1) | 46% | 33% | 54% |
| Antiepileptics | (2) | 15% | 7% | 8% |
| Benzodiazepines | (1) | 54% | 35% | 46% |
| Chair test = 0 | (0) | 23% | 17% | 69% |
| Chair test = 1 | (1) | 4% | 7% | 23% |
| Chair test = 3 | (3) | 15% | 2% | 8% |
| Chair test = 4 | (4) | 58% | 26% | 0% |
| Chair test = not feasible | (0) | 0% | 48% | 0% |
| Variable | Whole Sample | Sample by Ward | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 85) | NR (n = 26) | OR (n = 46) | PR (n = 13) | |
| Observed falls, n (%) | 19 (22%) | 9 (35%) | 9 (20%) | 1 (8%) |
| Age, years, mean (SD); min, 25th, 50th, 75th percentile, max | 64 (18); 20, 56, 67, 79, 91 | 56 (19); 20, 54, 63, 67, 75 | 72 (15); 41, 73, 75, 79, 91 | 64 |
| Fallen subjects median HIIFRM | 6 | 5 | 7 | 9 |
| Fractures, n (%fallen) | 5 (26%) | 3 (11%) | 2 (4%) | - |
| Hospitalization, n (%fallen) | 5 (26%) | 3 (11%) | 2 (4%) | - |
| Surgery, n (%fallen) | 3 (17%) | 2 (8%) | 1 (2%) | - |
| Discharge Ward | HIIFRM Score | No. of Falls | Causes of Falls | Service Accessed | Fractures | Surgery |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NR | 11 | 1 | Falling off the bed when adjusting position | none | ||
| NR | 9 | 4 | #1 getting up from a chair; #2 getting up from a wheelchair; #3 getting up from a chair; #4 getting up from a wheelchair | GP | ||
| NR | 8 | 2 | Slipping on a wet floor, trips when walking briskly and with the aid of a walking stick | ES | Leg | |
| NR | 5 | 1 | Epileptic seizure after getting up from a chair | ES; H | Leg | Yes |
| NR | 5 | 1 | Walking briskly with the aid of a walking stick and slipping on a wet floor | GP | ||
| NR | 5 | 2 | #1 slips on a wet surface; #2 slips and falls in the bathroom | GP | ||
| NR | 3 | 1 | Trips and falls down the stairs | ES; H | Femur | Yes |
| NR | 2 | 1 | Walking on a rough and uneven surface | GP | ||
| NR | 1 | 1 | Walking on a wet floor | GP | ||
| OR | 9 | 2 | #1 trips at home whilst walking without the aid of a walker; #2 trips outdoors whilst walking without the aid of a walker | GP | ||
| OR | 8 | 1 | Hypotension caused by standing up to an upright position | GP | ||
| OR | 8 | 1 | Epileptic seizure | ES; H | Traumatic Brain Injury | |
| OR | 8 | 1 | Getting dressed in the bathroom | ES; H | Femur | Yes |
| OR | 7 | 1 | Getting up and off the bed | GP | ||
| OR | 6 | 1 | Rushing to the bathroom due to bowel incontinence | ES | Ribs | |
| OR | 3 | 1 | Fainting spell due additional medication intake (pain killers) | GP | ||
| OR | 3 | 1 | Hopping on a bicycle and the skirt gets stuck in the gears or spokes | GP | ||
| OR | 2 | 1 | Getting up from a lift chair or electric recliner | ES | ||
| PR | 9 | 1 | Whilst walking | - |
| Whole Sample | NR-Discharged Patients | OR-Discharged Patients | PR-Discharged Patients | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Predicted falls | True Falls | True Falls | True Falls | True Falls | |||||||||
| Y | N | tot | Y | N | tot | Y | N | tot | Y | N | tot | ||
| Y | 13 | 22 | 35 | 6 | 13 | 19 | 6 | 8 | 14 | 1 | 1 | 2 | |
| N | 6 | 44 | 50 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 3 | 30 | 33 | 0 | 11 | 11 | |
| tot | 19 | 66 | 85 | 9 | 17 | 26 | 9 | 38 | 47 | 1 | 12 | 13 | |
| C.I. 95% | C.I. 95% | C.I. 95% | C.I. 95% | ||||||||||
| Se (%) | 68% | 43% | 87% | 60% | 26% | 88% | 67% | 30% | 93% | - | |||
| Sp (%) | 67% | 54% | 78% | 35% | 15% | 59% | 79% | 63% | 90% | 92% | 65% | 99% | |
| PPV (%) | 37% | 27% | 48% | 32% | 20% | 45% | 43% | 26% | 62% | - | |||
| NPV (%) | 88% | 79% | 95% | 64% | 40% | 82% | 91% | 80% | 96% | - | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Campanini, I.; Bargellini, A.; Mastrangelo, S.; Lombardi, F.; Tolomelli, S.; Lusuardi, M.; Merlo, A. Performance of the Hendrich Fall Risk Model II in Patients Discharged from Rehabilitation Wards. A Preliminary Study of Predictive Ability. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1444. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18041444
Campanini I, Bargellini A, Mastrangelo S, Lombardi F, Tolomelli S, Lusuardi M, Merlo A. Performance of the Hendrich Fall Risk Model II in Patients Discharged from Rehabilitation Wards. A Preliminary Study of Predictive Ability. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(4):1444. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18041444
Chicago/Turabian StyleCampanini, Isabella, Annalisa Bargellini, Stefano Mastrangelo, Francesco Lombardi, Stefano Tolomelli, Mirco Lusuardi, and Andrea Merlo. 2021. "Performance of the Hendrich Fall Risk Model II in Patients Discharged from Rehabilitation Wards. A Preliminary Study of Predictive Ability" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 4: 1444. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18041444
APA StyleCampanini, I., Bargellini, A., Mastrangelo, S., Lombardi, F., Tolomelli, S., Lusuardi, M., & Merlo, A. (2021). Performance of the Hendrich Fall Risk Model II in Patients Discharged from Rehabilitation Wards. A Preliminary Study of Predictive Ability. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(4), 1444. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18041444







