Research on Environmental Regulation and Green Total Factor Productivity in Yangtze River Delta: From the Perspective of Financial Development
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Theoretical Mechanism and Research Design
3.1. Theoretical Mechanism
3.2. Model Construction
3.3. Index Selection
3.3.1. The Explained Variable
3.3.2. Explanatory Variable
- Entropy weight method to determine the weight
- 2.
- Use the TOPSIS method to evaluate relevant data
3.3.3. Control Variables
4. Result from Analysis
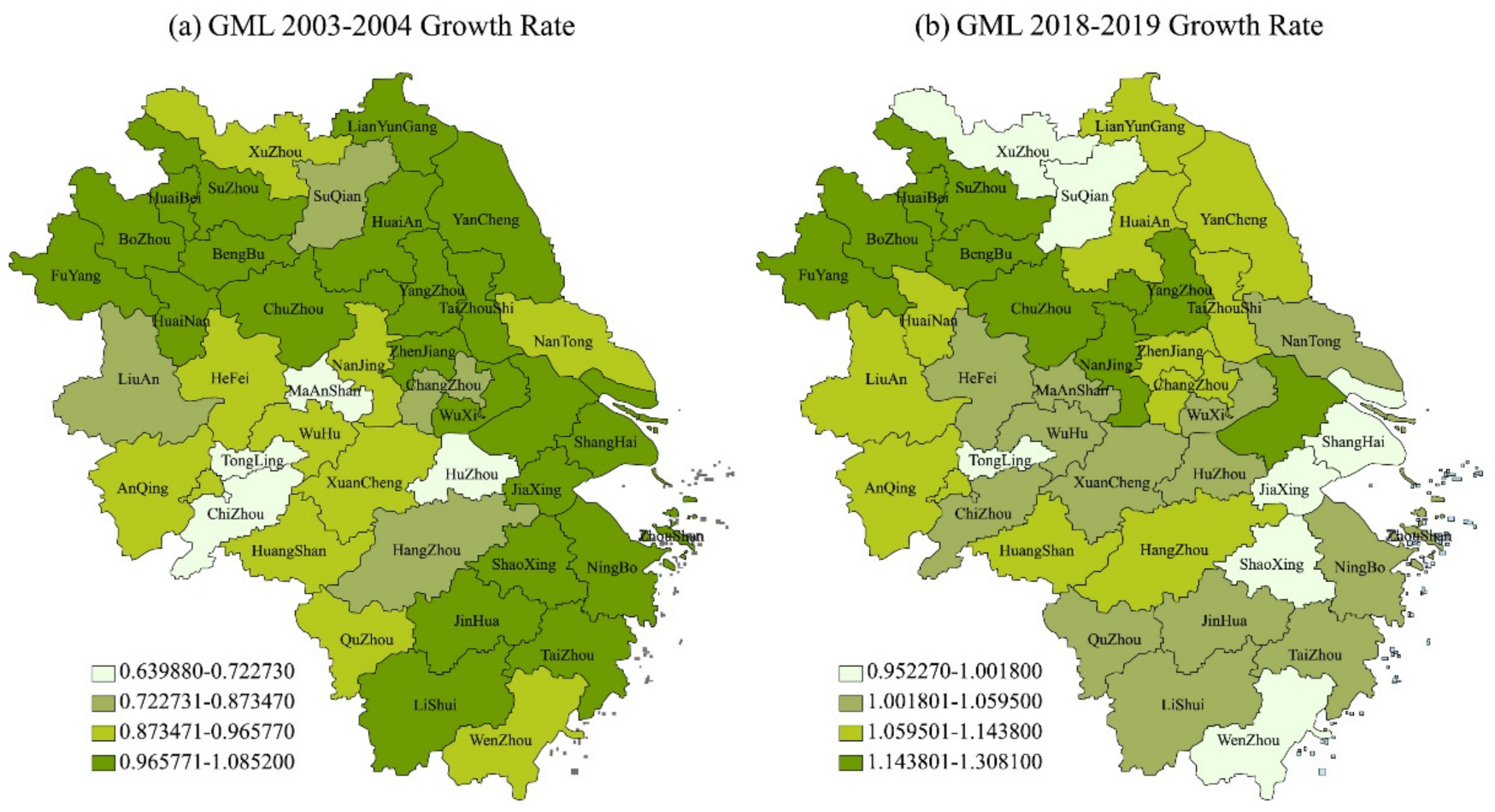
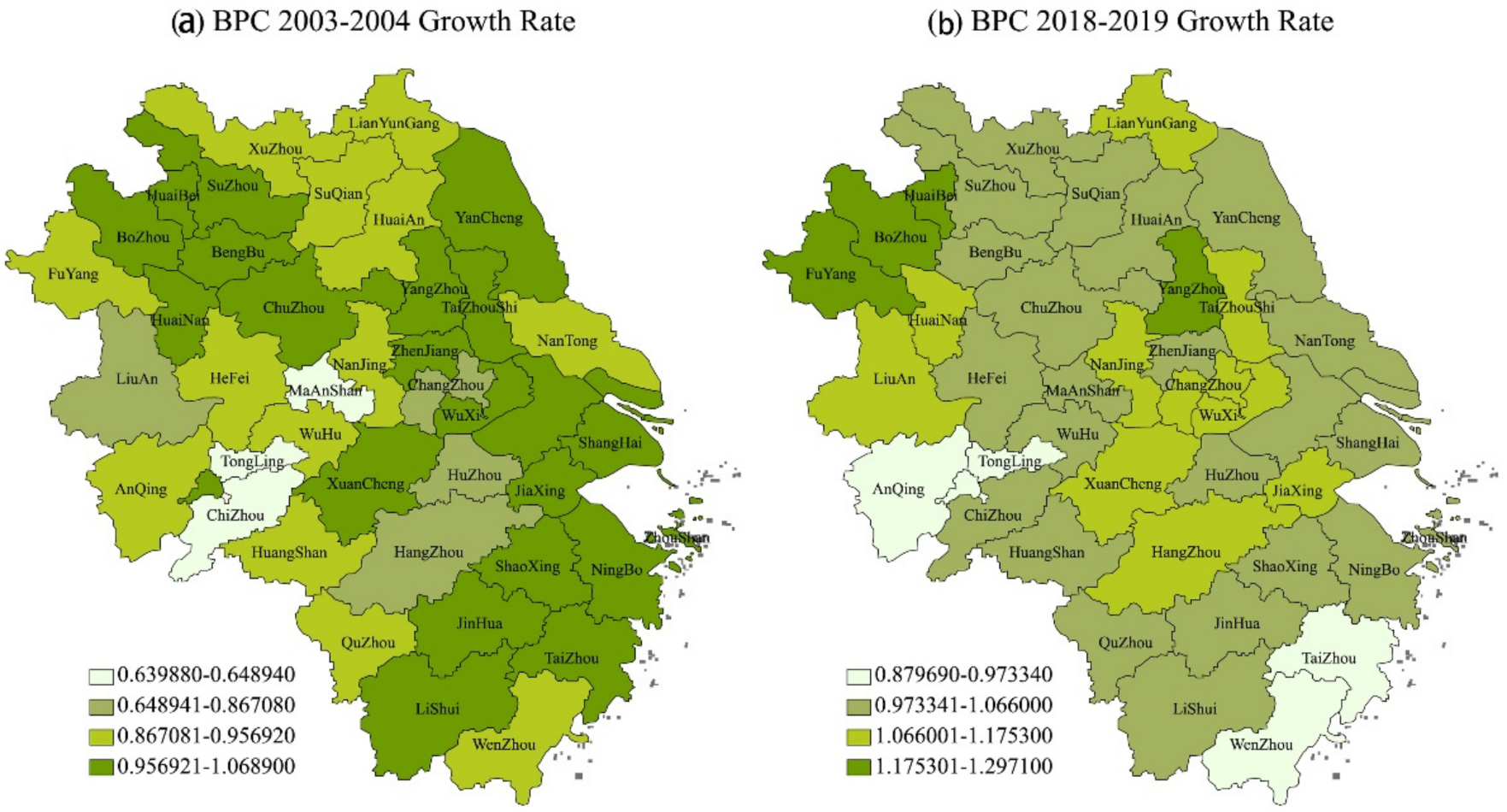
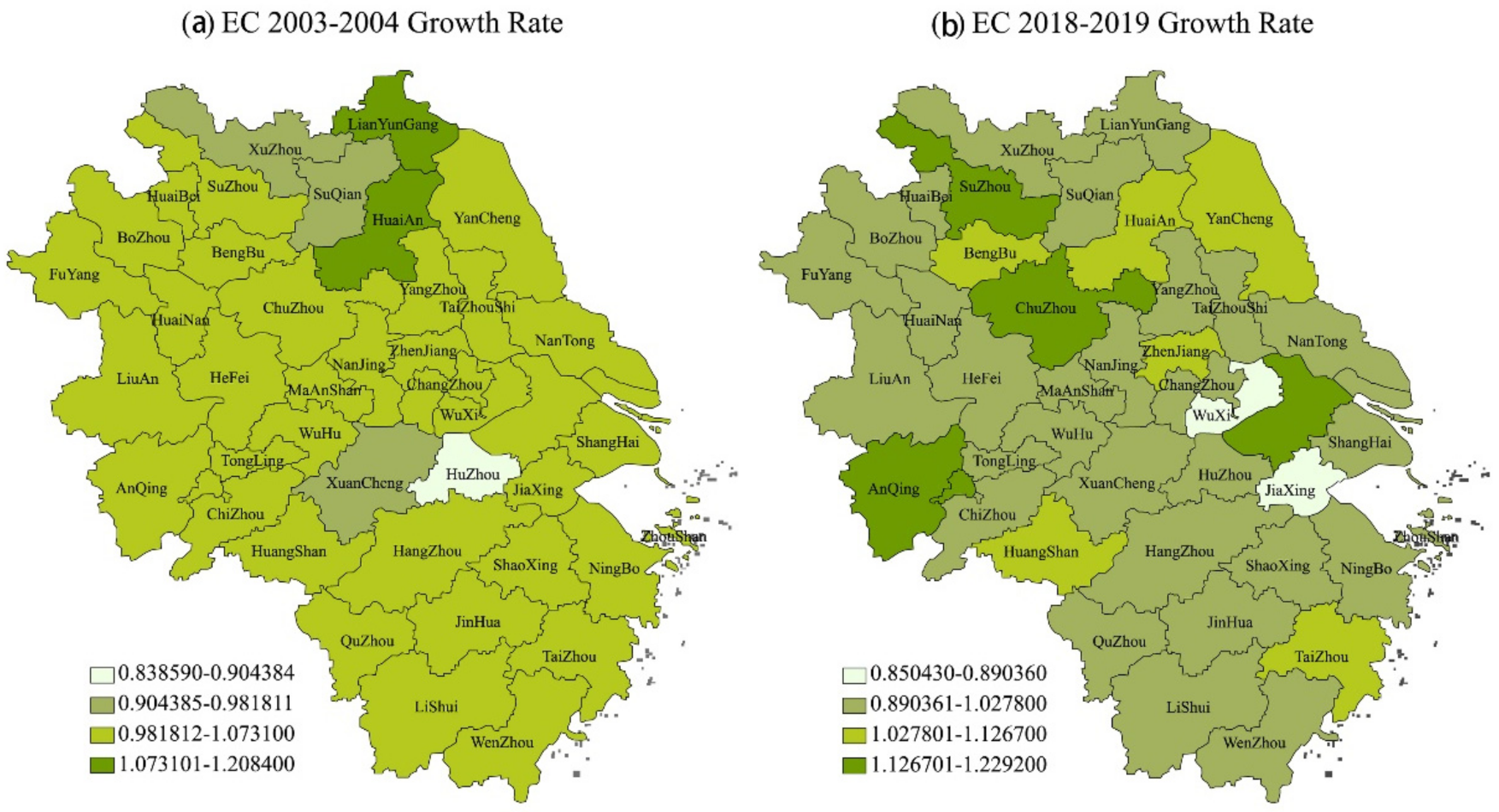
4.1. Spatial Difference Analysis of Green Total Factor Productivity in YRD
4.2. Empirical Regression Analysis
4.2.1. Empirical Result Analysis of Single Variable
4.2.2. Analysis of Empirical Results by Adding Control Variables
5. Research Conclusions and Countermeasures
5.1. Research Conclusions
5.2. Countermeasures and Suggestions
5.2.1. Pay Attention to the Strength of Environmental Regulation and Prevent over-Correction
5.2.2. Increase the Guidance of Credit Funds and Deepen the Reform of the Financial System
5.2.3. The Government Intervenes Moderately to Strengthen the Guidance of Foreign Investment
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lorek, S.; Spangenberg, J.H. Sustainable consumption within a sustainable economy beyond green growth and green economies. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 63, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.T.; Liu, Y. Green economy in China: Regional variations and policy drivers. Glob. Environ. Change 2015, 31, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubrova, M.V.; Gusarova, L.V.; Zhylina, N.N.; Shamsutdinova, M.R.; Ignatyev, V.G. Financial instruments of “green” economy development in Russia. In Proceedings of the 1st International Scientific and Practical Conference “lnnovative Technologies in Environmental Engineering and Agroecosystems” (ITEEA 2021), Denver, CO, USA, 24–27 March 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, M.E. America’s Green Strategy. Sci. Am. 1991, 264, 193–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Chiu, Y.-H.; Li, X.; Guo, Q.; Yun, Y. Study on the Effect of Environmental Regulation on the Green Total Factor Productivity of Logistics Industry from the Perspective of Low Carbon. Sustainability 2020, 12, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, X.X.; Du, J.T. Does environmental regulation induce improved financial development for green technological innovation in China? J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 300, 113685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagan, D.S.; Aviral, K.T.; Burak, E.; Hardeep, S.M. Exploring the nexus between non-renewable and renewable energy consumptions and economic development: Evidence from panel estimations. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 146, 111152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.H.; Du, J.T.; Wang, S.H. Environmental Regulations, Enterprise Productivity, and Green Technological Progress: Large-scale Data Analysis in China. J. Oper. Res. Soc. Am. 2020, 290, 369–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.H.; Li, T.H. Impact of Financial Development and Its Spatial Spillover Effect on Green Total Factor Productivity: Evidence from 30 Provinces in China. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 1, 5741387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cropper, M.L.; Oates, W.E. Environmental Economics: A Survey. J. Econ. Lit. 1992, 30, 675–740. [Google Scholar]
- Greenstone, M.; List, J.A.; Syverson, C. The Effects of Environmental Regulation on the Competitiveness of U.S. Manufacturing. NBER 2012, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shen, N. Regulation and Environmental Productivity: The Case of China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 62, 758–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Li, B.Y.; Bai, Q.G. Quantity and Collection Decisions of the Remanufacturing Enterprise under Both the Take-back and Carbon Emission Capacity Regulations. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2020, 141, 102032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.Y.; Jiang, Z.J.; Lan, W.X. How Environmental Regulations Affect Corporate Innovation? The Coupling Mechanism of Mandatory Rules and Voluntary Management. Technol. Soc. 2021, 65, 101575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.; Qiu, Y.; Zhou, D. Does Command-and-control Regulation Promote Green Innovation Performance? Evidence from China’s Industrial Enterprises. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 712, 136362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.Y.; Xu, X.D.; Liang, K.P. The Impact of Environmental Regulation on Firm Performance: Evidence from the Chinese Cement industry. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 299, 113596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Xu, J.C.; Yang, F.X.; Duan, H.B. Environmental Regulation Induces Technological Change and Green Transformation in Chinese Cities. Reg. Environ. Change 2021, 21, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, M.E.; Linder, C. Towards a New Conception of the Environment-competitiveness Relationship. J. Econ. Perspect. 1995, 9, 97–118. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/sTable/2138392 (accessed on 24 November 2021). [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, A.B.; Palmer, K. Environmental Regulation and Innovation: A Panel Data Study. Rev. Econ. Stat. 1997, 79, 610–619. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/sTable/2951413 (accessed on 24 November 2021). [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Bose, S.; Alnes, K. Employment Implications of Stricter Pollution Regulation in China: Theories and Lessons from the USA. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2017, 19, 549–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.L.; Liu, N.; Zhang, Z.B. The Impact of Environmental Regulation on Total Factor Productivity of Firms: An Analysis Based on Technical Distance. Chin. J. Popul. Resour. Environ. 2020, 18, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X. Strategic Interaction of Environmental Regulation and Green Productivity Growth in China: Green Innovation or Pollution Refuge? Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 732, 139200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, M.Q.; You, Z.; Wang, L.; Cheng, J.H. Environmental Regulation, Trade Comparative Advantage, and the Manufacturing Industry’s Green Transformation and Upgrading. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Wang, P. Economic Effects Analysis of Environmental Regulation Policy in the Process of Industrial Structure Upgrading: Evidence from Chinese Provincial Panel Data. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 753, 142004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.Y. Marketization, Environmental Regulation, and Eco-friendly Productivity: A Malmquist-Luenberger Index for Pollution Emissions of Large Chinese Firms. J. Asian Econ. 2021, 76, 101342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manello, A. Productivity Growth, Environmental Regulation and Win-win Opportunities: The Case of Chemical Industry in Italy and Germany. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2017, 262, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Sun, C.Z.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.X.; Zou, W. Going Green or Going Away? A Spatial Empirical Examination of the Relationship between Environmental Regulations, Biased Technological Progress, and Green Total Factor Productivity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, B.; Wu, S.S. Effects of Local and Civil Environmental Regulation on Green Total Factor Productivity in China: A Spatial Durbin Econometric Analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 153, 342–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.L.; Du, J.T.; Kim Hua, T. Impact of Fiscal Decentralization on Green Total Factor Productivity. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2018, 205, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.C.; Tang, D.X.; Xiao, Z.; Ma, T.Y.; Bethel, B.J. Environmental Regulation Efficiency and Total Factor Productivity-Effect Analysis Based on Chinese Data From 2003 to 2013. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 73, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Tang, D.C.; Bethel, B.J. Impact of Urbanization on the Environmental Regulation Efficiency in the Yangtze River Basin Based on the Empirical Analysis of Spatial Econometrics. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.C.; Brandon, J.B. Yangtze River Economic Belt Environmental Remediation Efficiency Based on an Input-output Optimization Analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 16734–16743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.L.; Xiang, Q.L. Environmental Regulation, Industrial Innovation and Green Development of Chinese Manufacturing: Based on An Extended CDM Model. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 176, 895–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.S.; Chen, Y.Y. The influence of Enterprises’ Bargaining Power on the Green Total Factor Productivity Effect of Environmental Regulation: Evidence from China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, X.H.; Guo, X. Environmental Regulation and Green Productivity Growth: Empirical Evidence on the Porter Hypothesis from OECD Industrial Sectors. Energy Policy 2019, 132, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.J.; Li, B. The Threshold Effect of Environmental Regulation on the Green Transition of the Industrial Economy in China. Econ Res.-Ekon. Istraz. 2019, 32, 3128–3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lei, X.B.; Wu, S.S. Nonlinear Effects of Governmental and Civil Environmental Regulation on Green Total Factor Productivity in China. Adv. Meteorol. 2019, 11, 8351512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.L.; Liu, F.Y. The Relationship between Environmental Regulation and Green Total Factor Productivity in China: An Empirical Study Based on the Panel Data of 177 Cities. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, K.; Zhou, D.J.; Wang, Q.W.; Zhou, D.Q.; Wei, X.Z. What Comes After Picking Pollution Intensive Low-hanging Fruits? Transfer Direction of Environmental Regulation in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 120405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.F.; Cheng, B.D.; Hong, Q.L.; Xu, C. Can a Win-Win Situation of Economy and Environment Be Achieved in Cities by the Government’s Environmental Regulations? Sustainability 2021, 13, 5829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, S.Y. The Influence Study on Environmental Regulation and Green Total Factor Productivity of China’s Manufacturing Industry. Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2021, 4, 5580414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Chen, K.; Waggoner, D.F. Trends and Cycles in China’s Macroeconomy. NBER Macroecon. Annu. 2016, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, Q.M.; Wen, S.Y.; Liu, X.L. Credit Allocation, Pollution, and Sustainable Growth: Theory and Evidence from China. Emerg. Mark. Financ. Trade 2020, 56, 2793–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.Y.; Xu, Y.R.; Liu, C.Z. The Threshold Effect of China’s Financial Development on Green Total Factor Productivity. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, T.H.; Liang, G.K. The Heterogeneous Impact of Financial Development on Green Total Factor Productivity. Front. Energy Res. 2020, 8, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, D.Y. Green Credit Regulation, Induced R & D and Green Productivity: Revisiting the Porter Hypothesis. Int. Rev. Financ. Anal. 2021, 75, 101723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Tang, D.C.; Bethel, B.J. Yangtze River Basin Environmental Regulation Efficiency Based on the Empirical Analysis of 97 Cities from 2005 to 2016. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.M.; Upadhyay, M.P. The Effects of Openness, Trade Orientation and Human Capital on Total Factor Productivity. J. Dev. Econ. 2000, 63, 399–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittman, R.W. Multilateral Productivity Comparisons with Undesirable Outputs. Econ. J. 1983, 93, 933–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, M.; Qu, D.L. Understanding the Green Energy Efficiencies of Provinces in China: A Super-SBM and GML Analysis. Energy 2022, 239, 121912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, J.; Lovell, A. Global Malmquist Productivity Index. Econ. Lett. 2005, 88, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, D.A. Global Malmquist-Luenberger Productivity Index. J. Prod. Anal. 2010, 34, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.H.; Färe, R.; Grosskopf, S. Productivity and Undesirable Outputs: A Directional Distance Function Approach. J. Environ. Manag. 1997, 51, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azimifard, A.; Moosavirad, S.H.; Ariafar, S. Selecting Sustainable Supplier Countries for Iran’s Steel Industry at Three Levels by Using AHP and TOPSIS Methods. Resour. Policy 2018, 57, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seker, S.; Aydin, N. Hydrogen Production Facility Location Selection for Black Sea Using Entropy Based TOPSIS under IVPF. Environment. Int. J. Hydrog. Energ. 2020, 45, 15855–15868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, W.; Wang, B. Environmental technology innovation caused by environmental regulation and its bias. J. Ind. Eng. Manag. 2018, 32, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
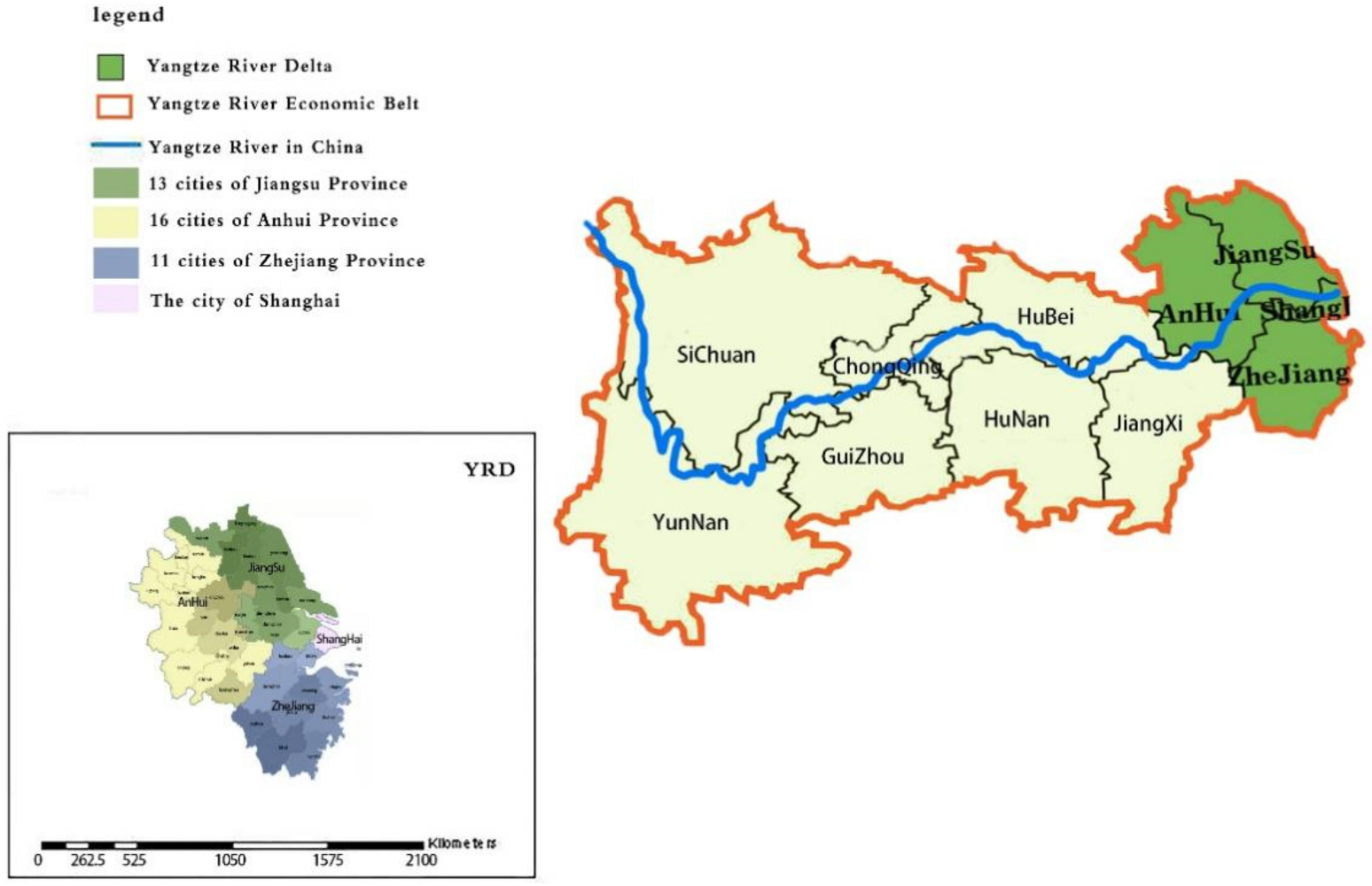

| Variable | Index | Computing Method |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental regulation | ER | Select three indicators: industrial wastewater emission, industrial sulfur dioxide emission and industrial smoke (powder) dust emission, determine the weight of each indicator by using the entropy of the indicator data, and then evaluate the relevant data by TOPSIS method. |
| Financial development | FD | Select three indicators: per capita deposit and loan balance, deposit conversion rate and financial scale, determine the weight of each indicator by using the entropy of the indicator data, and then evaluate the relevant data by TOPSIS method. |
| Financial intervention | FI | The proportion of fiscal expenditure in GDP |
| Foreign capital utilization | FDI | Measured by the proportion of actual foreign direct investment in GDP, the unit of the US dollar is adjusted to RMB based on the annual average exchange rate |
| Degree of openness | OPEN | When using the two indicators of the proportion of total import and export trade in GDP, the unit of the US dollar is adjusted to RMB based on the annual average exchange rate. |
| Green total factor productivity | GML | The input indicators are capital, labor, energy and water resources, the output indicators are actual GDP as the desirable output, and the industrial wastewater and waste gas emission is undesirable output |
| Year | Average Growth Rate of GML in Jiangsu Province | Average Growth Rate of GML in Zhejiang Province | Average Growth Rate of GML in Shanghai | Average Growth Rate of GML in Anhui Province | Mean Value of GML Growth Rate in YRD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2003–2004 | 0.972451 | 0.941206 | 1 | 0.902728 | 0.937531 |
| 2004–2005 | 0.979407 | 0.928238 | 1 | 0.977036 | 0.965256 |
| 2005–2006 | 0.932775 | 1.015935 | 0.9496 | 0.986268 | 0.976371 |
| 2006–2007 | 1.001462 | 1.012674 | 1.0429 | 0.976696 | 0.995816 |
| 2007–2008 | 1.066429 | 1.01081 | 1.0147 | 1.093313 | 1.060736 |
| 2008–2009 | 1.010115 | 0.970909 | 1.003 | 0.991999 | 0.992353 |
| 2009–2010 | 1.044536 | 1.069245 | 0.99219 | 1.039806 | 1.048043 |
| 2010–2011 | 1.020308 | 0.966238 | 1.7954 | 1.022486 | 1.025556 |
| 2011–2012 | 1.041635 | 0.983672 | 0.54311 | 0.989197 | 0.993461 |
| 2012–2013 | 1.037688 | 1.124828 | 1.0256 | 0.954114 | 1.028158 |
| 2013–2014 | 0.939304 | 0.850866 | 0.85125 | 1.011184 | 0.94148 |
| 2014–2015 | 0.988408 | 0.987608 | 0.94781 | 0.951701 | 0.972878 |
| 2015–2016 | 0.974235 | 1.119512 | 1.0664 | 1.078142 | 1.056009 |
| 2016–2017 | 0.910635 | 0.841714 | 1.1622 | 0.914653 | 0.899848 |
| 2017–2018 | 1.062916 | 1.11325 | 1.0013 | 1.019848 | 1.05811 |
| 2018–2019 | 1.080948 | 1.012893 | 0.99874 | 1.129626 | 1.079681 |
| 2013–2019 | 1.003953 | 0.99685 | 1.024638 | 1.002425 | 1.001955 |
| Year | Average Growth Rate of BPC in Jiangsu Province | Average Growth Rate of BPC in Zhejiang Province | Average Growth Rate of BPC in Shanghai | Average Growth Rate of BPC in Anhui Province | Mean Value of BPC Growth Rate in YRD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2003–2004 | 0.94516 | 0.953854 | 1 | 0.895824 | 0.929577 |
| 2004–2005 | 0.981932 | 0.961922 | 1 | 0.943616 | 0.962051 |
| 2005–2006 | 0.953116 | 0.993189 | 0.9496 | 0.993926 | 0.979708 |
| 2006–2007 | 1.002792 | 1.013592 | 1.0429 | 0.982313 | 0.998676 |
| 2007–2008 | 1.066208 | 1.014137 | 1.0147 | 1.091544 | 1.060869 |
| 2008–2009 | 0.987998 | 1.020192 | 1.003 | 1.00557 | 1.003859 |
| 2009–2010 | 1.034151 | 1.073091 | 0.99219 | 1.060014 | 1.053668 |
| 2010–2011 | 1.01863 | 0.936985 | 1.7954 | 1.002838 | 1.009508 |
| 2011–2012 | 1.024138 | 0.972136 | 0.54311 | 0.97269 | 0.978377 |
| 2012–2013 | 1.030305 | 1.137539 | 1.0256 | 0.960765 | 1.031823 |
| 2013–2014 | 0.969436 | 0.835637 | 0.85125 | 1.083184 | 0.975046 |
| 2014–2015 | 0.947829 | 0.989918 | 0.94781 | 0.906176 | 0.942866 |
| 2015–2016 | 0.995758 | 1.192436 | 1.0664 | 1.085362 | 1.085216 |
| 2016–2017 | 0.966127 | 0.928871 | 1.1622 | 0.948786 | 0.954146 |
| 2017–2018 | 1.074291 | 1.176891 | 1.0013 | 1.031944 | 1.083512 |
| 2018–2019 | 1.079854 | 1.027301 | 0.99874 | 1.077131 | 1.062713 |
| 2013–2019 | 1.004858 | 1.014231 | 1.024638 | 1.002605 | 1.006976 |
| Year | Average Growth Rate of EC in Jiangsu Province | Average Growth Rate of EC in Zhejiang Province | Average Growth Rate of EC in Shanghai | Average Growth Rate of EC in Anhui Province | Mean Value of EC Growth Rate in YRD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2003–2004 | 1.030603 | 0.985326 | 1 | 1.007464 | 1.00868 |
| 2004–2005 | 0.99527 | 0.973789 | 1 | 1.039931 | 1.007051 |
| 2005–2006 | 0.978372 | 1.033568 | 1 | 0.992861 | 0.999362 |
| 2006–2007 | 0.999838 | 0.99912 | 1 | 0.994173 | 0.997439 |
| 2007–2008 | 0.999252 | 0.997039 | 1 | 1.00167 | 0.99962 |
| 2008–2009 | 1.023064 | 0.961415 | 1 | 0.988283 | 0.992388 |
| 2009–2010 | 1.010568 | 0.997486 | 1 | 0.986408 | 0.997372 |
| 2010–2011 | 1.001833 | 1.037915 | 1 | 1.023394 | 1.019883 |
| 2011–2012 | 1.017862 | 1.014 | 1 | 1.017733 | 1.01634 |
| 2012–2013 | 1.007531 | 0.983457 | 1 | 0.993271 | 0.995323 |
| 2013–2014 | 0.965725 | 1.019713 | 1 | 0.946419 | 0.973511 |
| 2014–2015 | 1.044835 | 0.997745 | 1 | 1.055799 | 1.035386 |
| 2015–2016 | 0.982194 | 0.953412 | 1 | 0.996111 | 0.980337 |
| 2016–2017 | 0.94732 | 0.913129 | 1 | 0.981236 | 0.952667 |
| 2017–2018 | 0.995302 | 0.951143 | 1 | 0.99121 | 0.981972 |
| 2018–2019 | 1.002077 | 0.987901 | 1 | 1.052734 | 1.017991 |
| 2013–2019 | 1.000103 | 0.987885 | 1 | 1.004294 | 0.998458 |
| Variable | Equation (5) | Equation (6) | Equation (7) | Equation (8) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GML(−1) | −0.276264 *** (0.0000) | −0.278267 *** (0.0000) | −0.281241 *** (0.0000) | −0.288975 *** (0.0000) |
| ER | 0.312018 *** (0.0000) | 0.681847 *** (0.0000) | 0.304650 *** (0.0000) | 0.038850 (0.3053) |
| ER◊ER | −0.553697 *** (0.0000) | |||
| FD | 0.226589 *** (0.0000) | 0.074708 (0.3050) | ||
| ER◊FD | 2.825434 *** (0.0000) | |||
| AR(1) | 0.0010 | 0.0009 | 0.0015 | 0.0008 |
| AR(2) | 0.4860 | 0.4679 | 0.6062 | 0.4709 |
| Hansen-J | 0.398402 | 0.347079 | 0.381883 | 0.374182 |
| Variable | Equation (9) | Equation (10) | Equation (11) | Equation (12) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GML(−1) | −0.282957 *** (0.0000) | −0.275847 *** (0.0000) | −0.293918 *** (0.0000) | −0.295396 *** (0.0000) |
| ER | 0.213317 *** (0.0000) | 0.795267 *** (0.0000) | 0.190924 *** (0.0000) | 0.096351 (0.2681) |
| ER◊ER | −0.789845 *** (0.0000) | |||
| FD | 0.229440 ** (0.0215) | 0.192864 * (0.0613) | ||
| ER◊FD | 1.190128 ** (0.0376) | |||
| FI | 0.071431 * (0.0813) | −0.239431 *** (0.0000) | −0.007582 (0.8779) | −0.035768 (0.6311) |
| FDI | −2.642130 *** (0.0001) | −2.409499 *** (0.0008) | −2.099880 *** (0.0044) | |
| OPEN | 0.034550 *** (0.0025) | 0.034888 *** (0.0001) | 0.037254 *** (0.0028) | 0.036452 *** (0.0096) |
| AR(1) | 0.0003 | 0.0000 | 0.0001 | 0.0000 |
| AR(2) | 0.0597 | 0.0986 | 0.0988 | 0.0683 |
| Hansen-J | 0.336793 | 0.31179 | 0.290363 | 0.270560 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Tang, D.; Tenkorang, A.P.; Shi, Z. Research on Environmental Regulation and Green Total Factor Productivity in Yangtze River Delta: From the Perspective of Financial Development. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12453. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182312453
Li J, Tang D, Tenkorang AP, Shi Z. Research on Environmental Regulation and Green Total Factor Productivity in Yangtze River Delta: From the Perspective of Financial Development. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(23):12453. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182312453
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jia, Decai Tang, Acheampong Paul Tenkorang, and Zhuoran Shi. 2021. "Research on Environmental Regulation and Green Total Factor Productivity in Yangtze River Delta: From the Perspective of Financial Development" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 23: 12453. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182312453
APA StyleLi, J., Tang, D., Tenkorang, A. P., & Shi, Z. (2021). Research on Environmental Regulation and Green Total Factor Productivity in Yangtze River Delta: From the Perspective of Financial Development. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(23), 12453. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182312453






