Development and Validation of a Machine Learning Model Predicting Arteriovenous Fistula Failure in a Large Network of Dialysis Clinics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Description of the Arteriovenous Fistula Failure Model (AVF-FM)
2.2. AVF-FM Training
2.3. Measures
2.3.1. Endpoint Definition
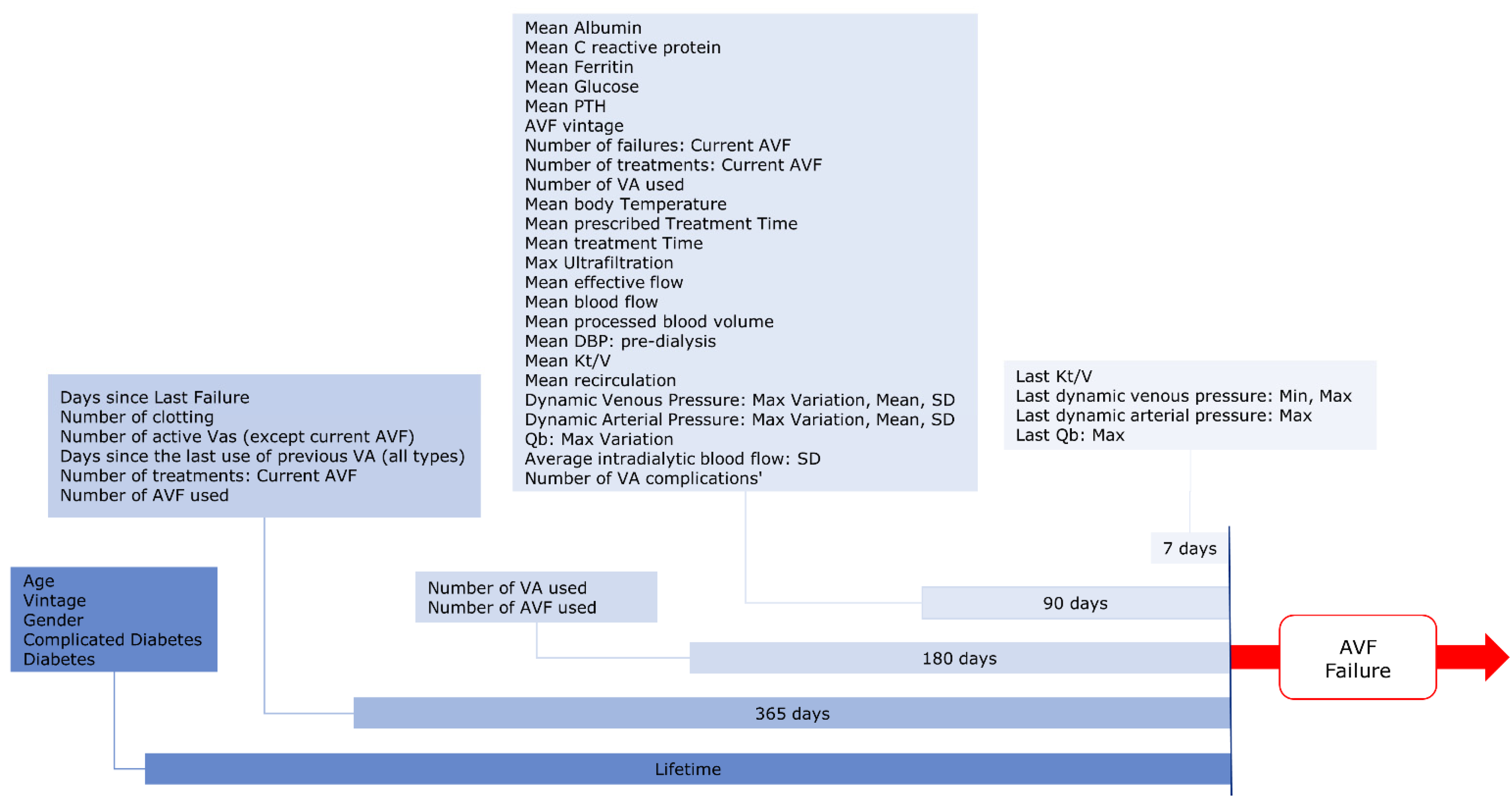
2.3.2. Input Variables
- -
- Socio-demographic and anthropometric parameters;
- -
- Biochemical parameters;
- -
- Vital Signs;
- -
- Dialysis Treatment parameters;
- -
- AVF-related parameters;
- -
- Comorbidities.
2.3.3. Features Generation
2.3.4. Features Selection
2.3.5. Missing Variables Handling
2.4. Statistical Analysis and Model Performance Evaluation
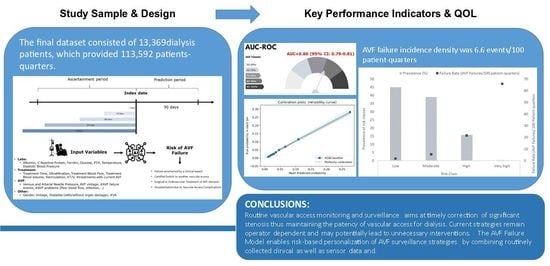
3. Results
3.1. Derivation & Test Dataset
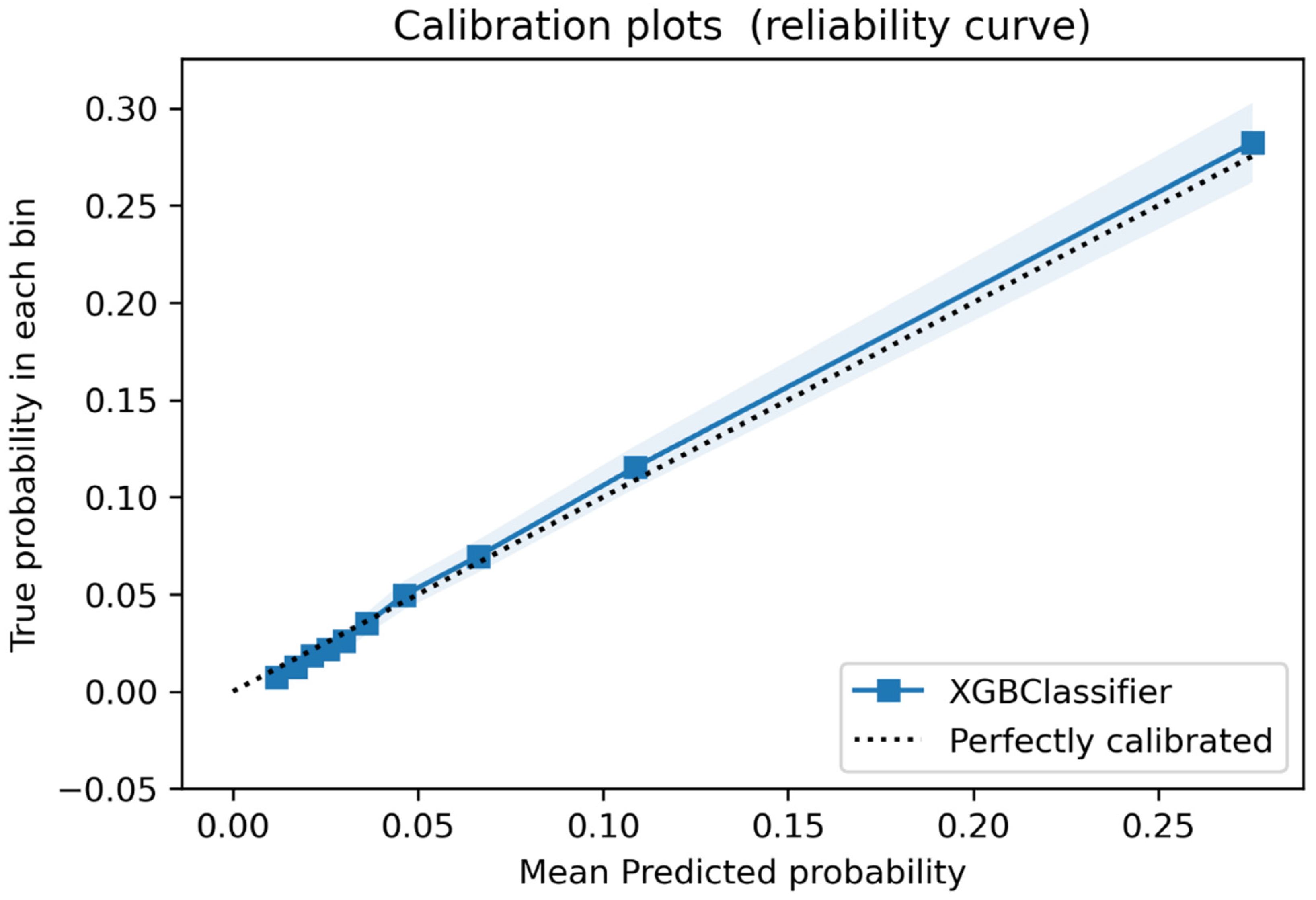
3.2. Discrimination and Calibration in the Validation Sample
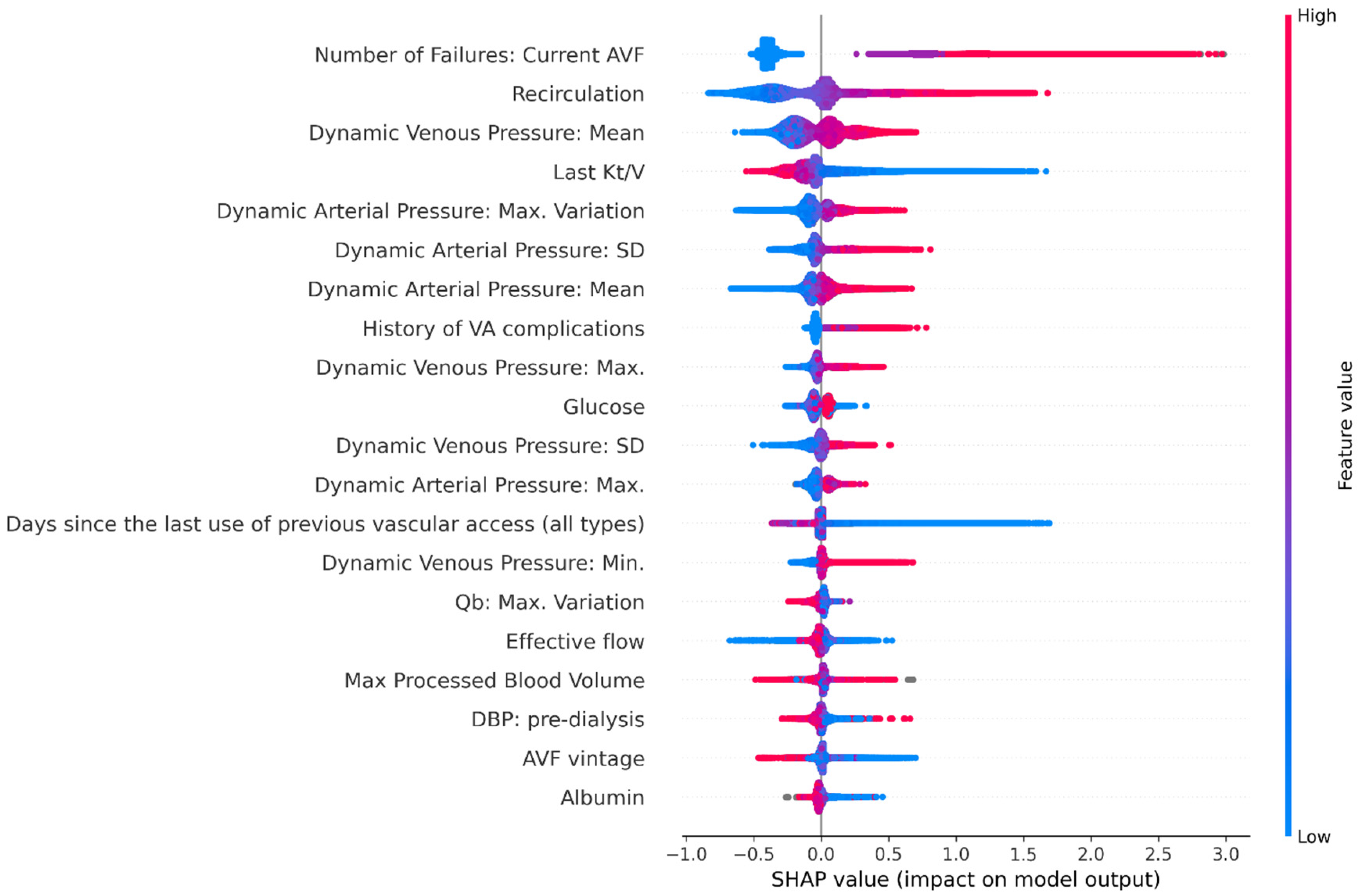
3.3. Feature Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lok, C.E.; Huber, T.S.; Lee, T.; Shenoy, S.; Yevzlin, A.S.; Abreo, K.; Allon, M.; Asif, A.; Astor, B.C.; Glickman, M.H.; et al. KDOQI Clinical Practice Guideline for Vascular Access: 2019 Update. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 75, S1–S164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gallieni, M.; Hollenbeck, M.; Inston, N.; Kumwenda, M.; Powell, S.; Tordoir, J.; Al Shakarchi, J.; Berger, P.; Bolignano, D.; Cassidy, D.; et al. Clinical practice guideline on peri- and postoperative care of arteriovenous fistulas and grafts for haemodialysis in adults. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2019, 34 (Suppl. 2), II1–II42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibeas, J.; Roca-Tey, R.; Vallespín, J.; Moreno, T.; Moñux, G.; Martí-Monrós, A. por la Guía Clínica Española del Acceso Vascular para Hemodiálisis. Spanish Clinical Guidelines on Vascular Access for Haemodialysis. Nefrología 2017, 37, 1–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidli, J.; Widmer, M.K.; Basile, C.; de Donato, G.; Gallieni, M.; Gibbons, C.P.; Haage, P.; Hamilton, G.; Hedin, U.; Kamper, L.; et al. Editor’s Choice—Vascular Access: 2018 Clinical Practice Guidelines of the European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS). Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2018, 55, 757–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paulson, W.D.; Moist, L.; Lok, C.E. Vascular access surveillance: An ongoing controversy. Kidney Int. 2012, 81, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmidli, J.; Widmer, M.K.; Basile, C.; de Donato, G.; Gallieni, M.; Gibbons, C.P.; Haage, P.; Hamilton, G.; Hedin, U.; Kamper, L.; et al. How to Carry out Monthly Blood Flow Surveillance of Fistula in Large-Scale Hemodialysis Units: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Vasc. Access 2021, 22, 75–80. [Google Scholar]
- Aragoncillo, I.; Amézquita, Y.; Caldés, S.; Abad, S.; Vega, A.; Cirugeda, A.; Moratilla, C.; Ibeas, J.; Roca-Tey, R.; Fernández, C.; et al. The impact of access blood flow surveillance on reduction of thrombosis in native arteriovenous fistula: A randomized clinical trial. J. Vasc. Access. 2016, 17, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.D.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.W.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, M.J.; Song, J.H. Comparison of ultrasound scan blood flow measurement versus other forms of surveillance in the thrombosis rate of hemodialysis access: A systemic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2018, 97, e11194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessitore, N.; Poli, A. Pro: Vascular access surveillance in mature fistulas: Is it worthwhile? Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2019, 34, 1102–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, L.; Rizvi, A.; Contreras, G.; Manning, C.; Feustel, P.J.; Machado, I.; Briones, P.L.; Jamal, A.; Bateman, N.; Martinez, L.; et al. A Multicenter Randomized Clinical Trial of Hemodialysis Access Blood Flow Surveillance Compared to Standard of Care: The Hemodialysis Access Surveillance Evaluation (HASE) Study. Kidney Int. Rep. 2020, 5, 1937–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimann, J.G.; Waldron, L.; Koh, E.; Miller, G.A.; Sor, M.H.; Gray, R.J.; Kotanko, P. Meta-analysis and commentary: Preemptive correction of arteriovenous access stenosis. Hemodial. Int. 2018, 22, 279–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ravani, P.; Quinn, R.R.; Oliver, M.J.; Karsanji, D.J.; James, M.T.; Macrae, J.M.; Palmer, S.C.; Strippoli, G.F. Pre-emptive correction for haemodialysis arteriovenous access stenosis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 2016, CD010709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ram, S.J.; Nassar, R.; Work, J.; Abreo, K.; Dossabhoy, N.R.; Paulson, W.D. Risk of Hemodialysis Graft Thrombosis: Analysis of Monthly Flow Surveillance. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2008, 52, 930–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.J.; Ko, P.J.; Hsu, L.A.; Ko, Y.S.; Ko, Y.L.; Chen, C.F.; Huang, C.C.; Hsu, T.S.; Lee, Y.S.; Pang, J.H. Highly Increased Cell Proliferation Activity in the Restenotic Hemodialysis Vascular Access after Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty: Implication in Prevention of Restenosis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2004, 43, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tessitore, N.; Bedogna, V.; Verlato, G.; Poli, A. The rise and fall of access blood flow surveillance in arteriovenous fistulas. Semin. Dial. 2014, 27, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eloot, S.; Dhondt, A.; Hoeben, H.; Vanholder, R. Comparison of different methods to assess fistula flow. Blood Purif. 2010, 30, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tessitore, N.; Bedogna, V.; Verlato, G.; Poli, A. Clinical access assessment. J. Vasc. Access. 2014, 15 (Suppl. 7), S20–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ćosović, A.; van der Kleij, F.G.; Callenbach, P.M.; Hoekstra, M.C.; Hissink, R.J.; van den Berg, M. The diagnostic value of duplex ultrasound in detecting the presence and location of a stenosis in an autologous arteriovenous fistula. J. Vasc. Access 2019, 21, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalesso, F.; Garzotto, F.; Petrucci, I.; Samoni, S.; Virzì, G.M.; Gregori, D.; Meola, M.; Ronco, C. Standardized Protocol for Hemodialysis Vascular Access Assessment: The Role of Ultrasound and ColorDoppler. Blood Purif. 2018, 45, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon, C.; Asif, A. Physical examination of arteriovenous fistulae by a renal fellow: Does it compare favorably to an experienced interventionalist? Semin. Dial. 2008, 21, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coentrão, L.; Faria, B.; Pestana, M. Physical examination of dysfunctional arteriovenous fistulae by non-interventionalists: A skill worth teaching. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27, 1993–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Asif, A.; Leon, C.; Orozco-Vargas, L.C.; Krishnamurthy, G.; Choi, K.L.; Mercado, C.; Merrill, D.; Thomas, I.; Salman, L.; Artikov, S.; et al. Accuracy of physical examination in the detection of arteriovenous fistula stenosis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 2, 1191–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Campos, R.P.; Chula, D.C.; Perreto, S.; Riella, M.C.; Do Nascimento, M.M. Accuracy of physical examination and intra-access pressure in the detection of stenosis in hemodialysis arteriovenous fistula. Semin. Dial. 2008, 21, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonelli, M.; James, M.; Wiebe, N.; Jindal, K.; Hemmelgarn, B.; Kidney, A. Ultrasound Monitoring to Detect Access Stenosis in Hemodialysis Patients: A Systematic Review. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2008, 51, 630–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessitore, N.; Lipari, G.; Poli, A.; Bedogna, V.; Baggio, E.; Loschiavo, C.; Mansueto, G.; Lupo, A. Can blood flow surveillance and pre-emptive repair of subclinical stenosis prolong the useful life of arteriovenous fistulae? A randomized controlled study. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2004, 19, 2325–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polkinghorne, K.R.; Lau, K.K.P.; Saunder, A.; Atkins, R.C.; Kerr, P.G. Does monthly native arteriovenous fistula blood-flow surveillance detect significant stenosis—A randomized controlled trial. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2006, 19, 2498–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jackson, V.E.; Hurst, H.; Mitra, S. Structured physical assessment of arteriovenous fistulae in haemodialysis access surveillance: A missed opportunity? J. Vasc. Access 2018, 19, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreo, K.; Amin, B.M.; Abreo, A.P. Physical examination of the hemodialysis arteriovenous fistula to detect early dysfunction. J. Vasc. Access. 2018, 20, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Lee, S. A Unified Approach to Interpreting Model Predictions. In Proceedings of the 31st Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS 2017), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4 December 2017; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Stopper, A.; Amato, C.; Gioberge, S.; Giordana, G.; Marcelli, D.; Gatti, E. Managing complexity at dialysis service centers across Europe. Blood Purif. 2006, 25, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, H.; Sundararajan, V.; Halfon, P.; Fong, A.; Burnand, B.; Luthi, J.C.; Saunders, L.D.; Beck, C.A.; Feasby, T.E.; Ghali, W.A. Coding algorithms for defining comorbidities in ICD-9-CM and ICD-10 administrative data. Med. Care 2005, 43, 1130–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusdah, D.A.; Murfi, H. XGBoost in handling missing values for life insurance risk prediction. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Kurita, T.; Meyer, F.; Berthouze, L.; Kawabe, T. Stepwise feature selection by cross validation for EEG-based brain computer interface. 2006 IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Network Proceedings, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 16–21 July 2006; 2006; pp. 4672–4677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turmel-Rodrigues, L.; Pengloan, J.; Baudin, S.; Testou, D.; Abaza, M.; Dahdah, G.; Mouton, A.; Blanchard, D. Treatment of stenosis and thrombosis in haemodialysis fistulas and grafts by interventional radiology. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2000, 15, 2029–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balamuthusamy, S.; Reddi, A.L.; Madhrira, M.H.; Sankarapandian, B.; Nguyen, P.; Vallurupalli, A.; Gabbard, W.; Jalandhara, N.; Yurvati, A. Clinical predictors of recurrent stenosis and need for re-intervention in the cephalic arch in patients with brachiocephalic AV fistulas. J. Vasc. Access. 2017, 18, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Depner, T.A.; Krivitski, N.M.; MacGibbon, D. Hemodialysis Access Recirculation Measured by Ultrasound Dilution. ASAIO J. 1995, 41, M749–M753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tessitore, N.; Bedogna, V.; Poli, A.; Impedovo, A.; Antonucci, F.; Teodori, T.; Lupo, A. Practice patterns in the management of arteriovenous fistula stenosis: A northern Italian survey. J. Nephrol. 2006, 19, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ekart, R.; Varda, L.; Vodošek Hojs, N.; Dvoršak, B.; Piko, N.; Bevc, S.; Hojs, R. Early Detection of Arteriovenous Fistula Stenosis in Hemodialysis Patients through Routine Measurements of Dialysis Dose (Kt/V). Blood Purif. 2021, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, A.; Gadalean, F.N.; Merrill, D.; Cherla, G.; Cipleu, C.D.; Epstein, D.L.; Roth, D. Inflow stenosis in arteriovenous fistulas and grafts: A multicenter, prospective study. Kidney Int. 2005, 67, 1986–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stirbu, O.; Gadalean, F.; Pitea, I.V.; Ciobanu, G.; Schiller, A.; Grosu, I.; Nes, A.; Bratescu, R.; Olariu, N.; Timar, B.; et al. C-reactive protein as a prognostic risk factor for loss of arteriovenous fistula patency in hemodialyzed patients. J. Vasc. Surg. 2019, 70, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidawy, A.N.; Gray, R.; Besarab, A.; Henry, M.; Ascher, E.; Silva, M., Jr.; Miller, A.; Scher, L.; Trerotola, S.; Gregory, R.T.; et al. Recommended standards for reports dealing with arteriovenous hemodialysis accesses. J. Vasc. Surg. 2002, 35, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Variables | Values |
|---|---|
| Socio-Demographics, vital signs and Comorbidities | |
| Age (years), median (IQR) | 70 (58–78) |
| Male, n (%) | 8971 (67.1) |
| Body temperature, median (IQR) | 36.1 (35.9–36.3) |
| Renal Replacement Therapy Vintage (months), median (IQR) | 17.3 (5.3–59.3) |
| AVF vintage (months), median (IQR) | 9.3 (3.7–42.7) |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 4959 (37.1) |
| Complicated Diabetes, n (%) | 4238 (31.7) |
| Biochemical parameters | |
| Albumin (g/dL), mean (IQR) | 3.9 (3.6–4.1) |
| C-reactive protein (mg/L), mean (IQR) | 5.1 (2.1–12) |
| Ferritin (ng/mL), median (IQR) | 391 (204–615) |
| Glucose (mg/dL), median (IQR) | 113 (94–152) |
| PTH (pg/mL), median (IQR) | 245 (143–392) |
| HD treatment parameters | |
| Treatment time (min), median (IQR) | 240 (239–242) |
| Ultrafiltration (L), median (IQR) | 3.3 (2.8–4) |
| Effective blood flow (mL/min), median (IQR) | 397 (357–428) |
| Effective processed blood volume (L), median (IQR) | 95.7 (85.1–103.9) |
| Kt/V, mean (SD) | 1.8 (0.4) |
| Recirculation, median (IQR) | 13.9 (11.4–17.7) |
| Characteristics of AVF in use | |
| Days since the last use of previous vascular access, median (IQR) | 74 (38–115) |
| Number of vascular accesses used in the past 6 months, mean (SD) | 1.3 (0.5) |
| Number of treatments with AVF in the past 6 months, mean (SD) | 88.6 (56.3) |
| AVF hemodynamic properties | |
| Dynamic venous pressure: Mean (mmHg), median (IQR) | 182 (165–202) |
| Dynamic arterial pressure: Mean (mmHg), median (IQR) | −200 (−216–−181) |
| AVF failure history and previous adverse events | |
| Number of failures: current AVF, mean (SD) | 0.6 (1.5) |
| Days since the last failure, mean (SD) | 168 (88.6) |
| Number of previous thrombosis, mean (SD) | 0.4 (1) |
| Other active vascular access, mean (SD) | 0.4 (0.7) |
| History of vascular access complications, mean (SD) | 0.5 (1.4) |
| Risk Class | Prevalence (%) | AVF Failure Risk * | Risk Rate Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low | 45.0 (95% CI: 44.9–45.1) | 1.61 (95% CI: 1.57–1.64) | Ref. |
| Moderate | 38.9 (95% CI: 38.8–39.0) | 5.29 (95% CI: 5.22–5.36) | 3.29 (95% CI: 3.2–3.38) |
| High | 15.7 (95% CI: 15.7–15.8) | 21.46 (95% CI: 21.23–21.68) | 13.37 (95% CI: 13.04–13.72) |
| Very high | 0.4 (95% CI: 0.3–0.4) | 65.76 (95% CI: 63.16–68.45) | 41.18 (95% CI: 39.29–43.17) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peralta, R.; Garbelli, M.; Bellocchio, F.; Ponce, P.; Stuard, S.; Lodigiani, M.; Fazendeiro Matos, J.; Ribeiro, R.; Nikam, M.; Botler, M.; et al. Development and Validation of a Machine Learning Model Predicting Arteriovenous Fistula Failure in a Large Network of Dialysis Clinics. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12355. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182312355
Peralta R, Garbelli M, Bellocchio F, Ponce P, Stuard S, Lodigiani M, Fazendeiro Matos J, Ribeiro R, Nikam M, Botler M, et al. Development and Validation of a Machine Learning Model Predicting Arteriovenous Fistula Failure in a Large Network of Dialysis Clinics. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(23):12355. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182312355
Chicago/Turabian StylePeralta, Ricardo, Mario Garbelli, Francesco Bellocchio, Pedro Ponce, Stefano Stuard, Maddalena Lodigiani, João Fazendeiro Matos, Raquel Ribeiro, Milind Nikam, Max Botler, and et al. 2021. "Development and Validation of a Machine Learning Model Predicting Arteriovenous Fistula Failure in a Large Network of Dialysis Clinics" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 23: 12355. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182312355
APA StylePeralta, R., Garbelli, M., Bellocchio, F., Ponce, P., Stuard, S., Lodigiani, M., Fazendeiro Matos, J., Ribeiro, R., Nikam, M., Botler, M., Schumacher, E., Brancaccio, D., & Neri, L. (2021). Development and Validation of a Machine Learning Model Predicting Arteriovenous Fistula Failure in a Large Network of Dialysis Clinics. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(23), 12355. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182312355