Extreme Climate Shocks and Green Agricultural Development: Evidence from the 2008 Snow Disaster in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review and Theoretical Analysis
2.1. Literature Review
2.2. Theoretical Analysis: How Extreme Climate Shocks Affect GAD
2.2.1. Decreasing Willingness to Cultivate
2.2.2. Increasing Agricultural Energy Consumption
2.2.3. Increasing Agricultural Pollution
3. Methods
3.1. Difference-in-Difference Model
3.2. Calculation of GAD Index
3.3. Independent Variables
3.4. Control Variables
4. Data Sources and Descriptive Statistics
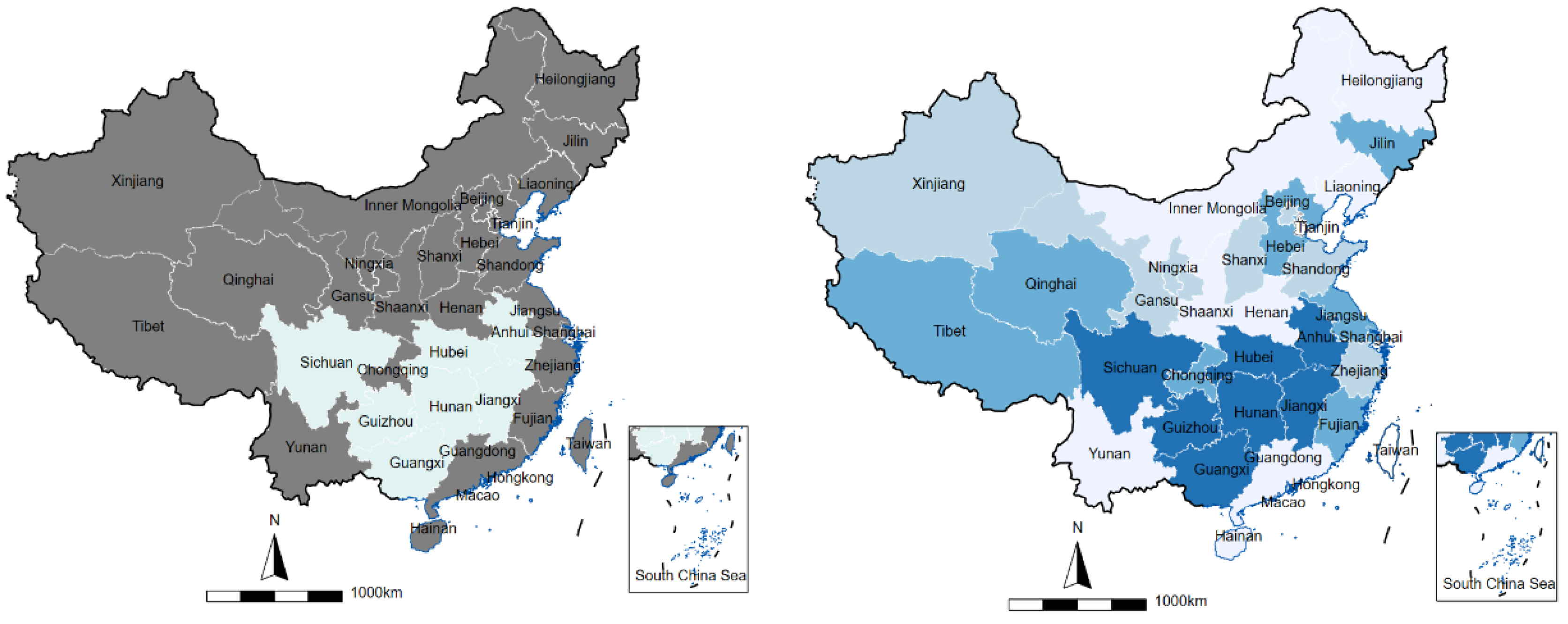
4.1. Sample and Data Source
4.2. Descriptive Statistics
5. Results
5.1. Baseline Estimations
5.2. Robust Checks
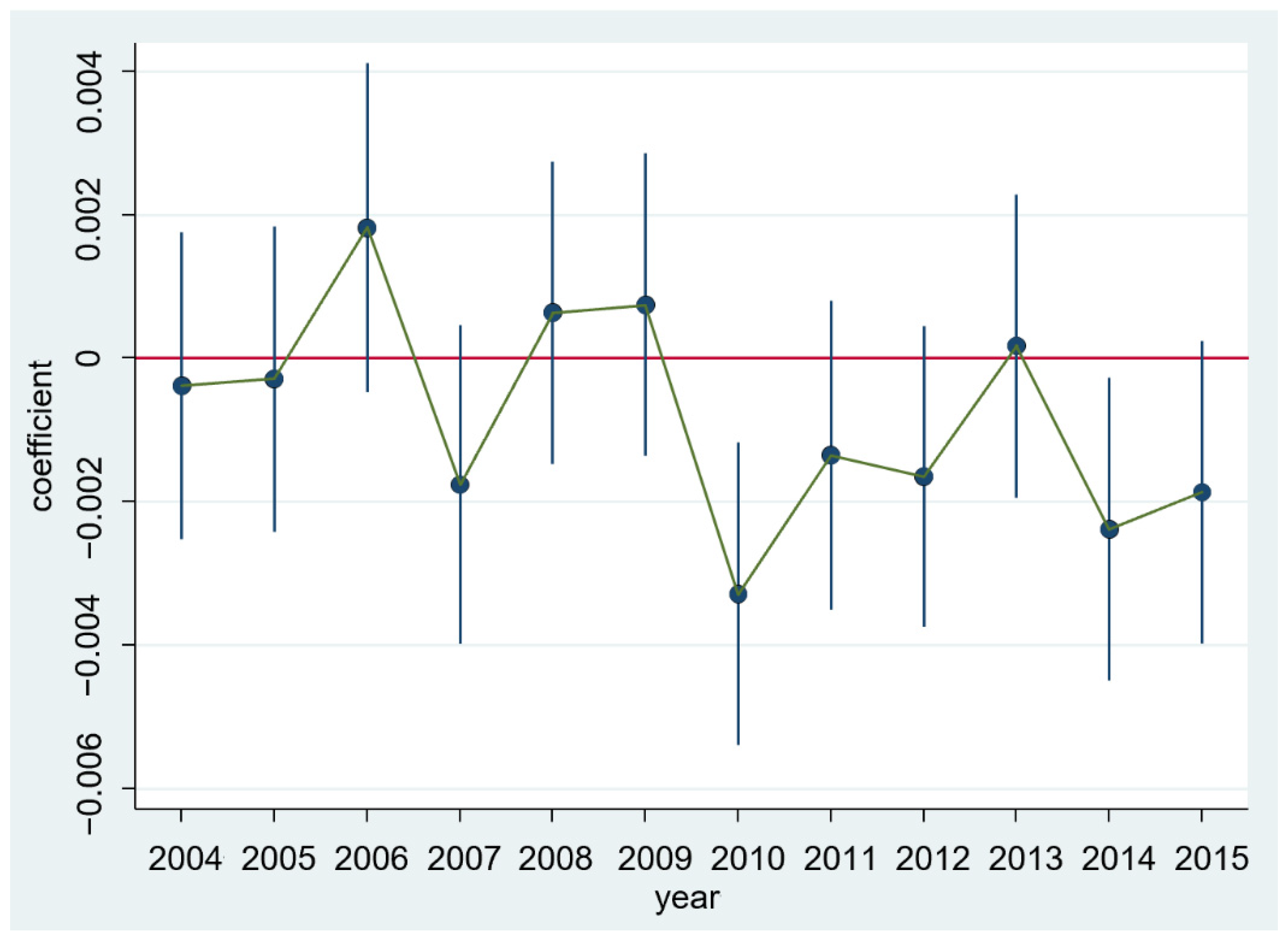
5.2.1. Parallel Trend
5.2.2. Adding Time Trend
5.2.3. Excluding Municipalities
5.2.4. Concurrent Events
5.2.5. Climatic Factors
5.2.6. Propensity Score Matching Method (PSM)
5.2.7. Replace Independent Variables
5.2.8. Instrumental Variable Estimation
5.2.9. Replace the Dependent Variable
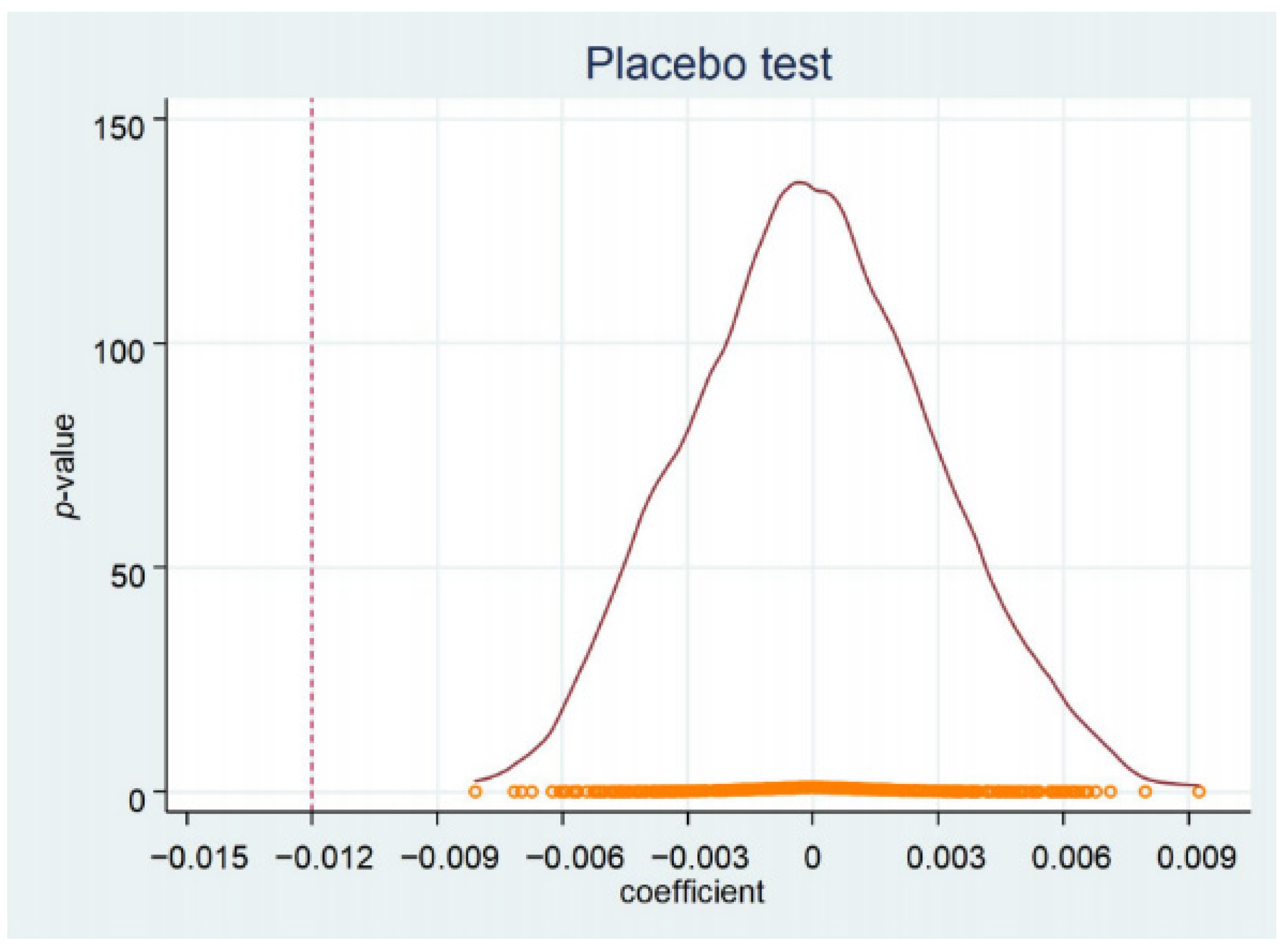
5.2.10. Placebo Tests
5.3. Heterogeneity Analysis
5.3.1. Climate Zone
5.3.2. Poor and Non-Poor Counties
5.3.3. Agricultural and Non-Agricultural Counties
5.3.4. Economic Development
6. Mechanism Analysis
6.1. Farming Willingness
6.2. Production Energy Consumption
6.3. Agricultural Pollution
7. Conclusions and Policy Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Variables | (1) | (2) | (3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Green | Green | Green | |
| −0.010 *** | −0.010 *** | −0.012 *** | |
| (0.002) | (0.001) | (0.001) | |
| Effective irrigation rate | 0.0158 ** | 0.0155 *** | 0.0316 *** |
| (0.007) | (0.002) | (0.004) | |
| County fix | Yes | No | Yes |
| Time fix | No | Yes | Yes |
| Obs | 38,142 | 38,142 | 38,142 |
| R2 | 0.151 | 0.700 | 0.701 |
| Counties | 2077 | 2077 | 2077 |
| Variables | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Green | Green | Green | Green | |
| −0.011 *** | −0.010 *** | −0.011 *** | −0.011 *** | |
| (0.001) | (0.001) | (0.001) | (0.001) | |
| Education | 0.008 *** | 0.002 *** | 0.003 *** | 0.003 *** |
| (0.0004) | (0.0003) | (0.0003) | (0.0003) | |
| Effective irrigation rate | 0.035 *** | |||
| (0.004) | ||||
| County fix | No | No | Yes | Yes |
| Time fix | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Obs | 38,136 | 38,136 | 38,136 | 38,136 |
| R2 | 0.161 | 0.700 | 0.701 | 0.702 |
| Counties | 2077 | 2077 | 2077 | 2077 |
References
- Bergius, M.; Benjaminsen, T.A.; Widgren, M. Green economy, Scandinavian Invests and agricultural modernization in Tanzania. J. Peasant Stud. 2018, 45, 825–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Ishfaq, M.; Zhong, J.; Li, W.; Zhang, F.; Li, X. Green food development in China: Experiences and challenges. Agriculture 2020, 10, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Y. China’s agricultural green total factor productivity based on carbon emission: An analysis of evolution trend and influencing factors. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 123692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhemachena, C.; Nhamo, L.; Matchaya, G.; Nhemachena, C.R.; Muchara, B.; Karuaihe, S.T.; Mpandeli, S. Climate change impacts on water and agriculture sectors in Southern Africa: Threats and opportunities for sustainable development. Water 2020, 12, 2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.F.; Yang, Y.Z.; Wu, K.J.; Sun, B.N. The signal of La Niña in wave transport. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 70, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Strapasson, A.; Rojas, O. Assessment of El Niño and La Niña impacts on China: Enhancing the Early Warning System on Food and Agriculture. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2020, 27, 100208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Sun, H.; Singh, V.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, M. Agricultural Water Resources Management Using Maximum Entropy and Entropy-Weight-Based TOPSIS Methods. Entropy 2019, 21, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, S.; Hu, Y.; Balezentis, T.; Streimikiene, D. A multi-criteria sustainable supplier selection framework based on neutrosophic fuzzy data and entropy weighting. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 28, 1431–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, C.; Bi, R.; Zhu, H.; He, P.; Jing, Y.; Yang, W. Winter wheat yield estimation based on assimilated Sentinel-2 images with the CERES-Wheat model. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 1958–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pingali, P.L. Green Revolution: Impacts, limits, and the path ahead. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 12302–12308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Musvoto, C.; Nortje, K.; de Wet, B.; Mahumani, B.K.; Nahman, A. Imperatives for an agricultural green economy in South Africa. S. Afr. J. Sci. 2014, 111, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lanza, K.; Durand, C.P. Heat-Moderating Effects of Bus Stop Shelters and Tree Shade on Public Transport Ridership. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.B. Environmental consequences of agricultural development: A case study from the Green Revolution state of Haryana, India. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2000, 82, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, L.; Liu, C. The Role of soil N2O emissions in agricultural green total factor productivity: An empirical study from China around 2006 when Agricultural Tax was abolished. Agriculture 2020, 10, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadi, H.; Ghanian, M.; Ghoochani, O.M.; Rafiaani, P.; Taning, C.N.T.; Hajivand, R.Y.; Dogot, T. Genetically modified crops: Towards agricultural growth, agricultural development, or agricultural sustainability? Food Rev. Int. 2015, 31, 195–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaim, M. Role of new plant breeding technologies for food security and sustainable agricultural development. Appl. Econ. Perspect. Policy 2020, 42, 129–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, S.; Bocchi, S. Green revolution impacts in Bangladesh: Exploring adaptation pathways for enhancing national food security. Clim. Dev. 2014, 6, 238–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clay, N.; King, B. Smallholders’ uneven capacities to adapt to climate change amid Africa’s ‘green revolution’: Case study of Rwanda’s crop intensification program. World Dev. 2019, 116, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Deng, G.; Zhou, D.; Zhu, X.; Ma, J.; Cen, G.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, J. Effects of climate change and land-use changes on spatiotemporal distributions of blue water and green water in Ningxia, Northwest China. J. Arid Land 2021, 13, 674–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhassan, S.; Hadwen, W.L. Challenges and opportunities for mainstreaming climate change adaptation into WaSH development planning in Ghana. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorgho, R.; Quiñonez, C.A.M.; Louis, V.R.; Winkler, V.; Dambach, P.; Sauerborn, R.; Horstick, O. Climate change policies in 16 West African countries: A systematic review of adaptation with a focus on agriculture, food security, and nutrition. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinia, N.J.; McShane, P. Ecosystem services management: An evaluation of green adaptations for urban development in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2018, 173, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clay, N.; Zimmerer, K.S. Who is resilient in Africa’s Green Revolution? Sustainable intensification and Climate Smart Agriculture in Rwanda. Land Use Policy 2020, 97, 104558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazurko, A.; Venema, H.D. Financing High Performance Climate adaptation in agriculture: Climate bonds for multi-functional water harvesting infrastructure on the Canadian Prairies. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Locatelli, B.; Fedele, G.; Fayolle, V.; Baglee, A. Synergies between adaptation and mitigation in climate change finance. Int. J. Clim. Chang. Strateg. Manag. 2016, 8, 112–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elum, Z.A.; Momodu, A.S. Climate change mitigation and renewable energy for sustainable development in Nigeria: A discourse approach. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 76, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budhathoki, N.K.; Zander, K.K. Socio-Economic Impact of and Adaptation to Extreme Heat and Cold of Farmers in the Food Bowl of Nepal. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Acosta, A.; Nicolli, F.; Karfakis, P. Coping with climate shocks: The complex role of livestock portfolios. World Dev. 2021, 146, 105546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddig, K.; Stepanyan, D.; Wiebel, M.; Grethe, H.; Zhu, T. Climate change and agriculture in the Sudan: Impact pathways beyond changes in mean rainfall and temperature. Ecol. Econ. 2020, 169, 106566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nasr Ahmed, Y.; Huang, D.; Belford, C.; Shaker, V.; Abdelrahaman, N.A.M. An estimate of the potential economic impacts of climate change on Egypt’s agriculture: A multi-market model approach. Clim. Dev. 2021, 13, 228–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, C.; Ruben, R.; Dijkstra, G. Climate variability and vulnerability to poverty in Nicaragua. J. Environ. Econ. Policy 2018, 7, 324–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olayide, O.E.; Alabi, T. Between rainfall and food poverty: Assessing vulnerability to climate change in an agricultural economy. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 198, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DePaula, G. The distributional effect of climate change on agriculture: Evidence from a Ricardian quantile analysis of Brazilian census data. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2020, 104, 102378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malikov, E.; Miao, R.; Zhang, J. Distributional and temporal heterogeneity in the climate change effects on U.S. agriculture. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2020, 104, 102386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X. Climate change and adaptation in agriculture: Evidence from US cropping patterns. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2020, 101, 102306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogato, A.; Meggio, F.; Migliorati, M.D.; Marinello, F. Extreme Weather Events in Agriculture: A Systematic Review. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, Z.; Huang, H.N.; Wu, Y.J.; Chiu, Y.H.; Qin, S.J. Climate Change Impacts on Agricultural Production and Crop Disaster Area in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falco, C.; Galeotti, M.; Olper, A. Climate change and migration: Is agriculture the main channel? Glob. Environ. Chang. 2019, 59, 101995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutenje, M.J.; Farnworth, C.R.; Stirling, C.; Thierfelder, C.; Mupangwa, W.; Nyagumbo, I. A cost-benefit analysis of climate-smart agriculture options in Southern Africa: Balancing gender and technology. Ecol. Econ. 2019, 163, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, C.A.; Rakotobe, Z.L.; Rao, N.S.; Dave, R.; Razafimahatratra, H.; Rabarijohn, R.H.; Rajaofara, H.; MacKinnon, J.L. Extreme vulnerability of smallholder farmers to agricultural risks and climate change in Madagascar. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 369, 20130089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dodd, W.; Cerna, M.G.; Orellena, P.; Humphries, S.; Sadoine, M.L.; Zombre, D.; Zinszer, K.; Kipp, A.; Cole, D.C. Factors Associated with Seasonal Food Insecurity among Small-Scale Subsistence Farming Households in Rural Honduras. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Srivastav, A.L.; Dhyani, R.; Ranjan, M.; Madhav, S.; Sillanpaa, M. Climate-resilient strategies for sustainable management of water resources and agriculture. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 41576–41595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenzweig, C.; Strzepek, K.M.; Major, D.C.; Iglesias, A.; Yates, D.N.; McCluskey, A.; Hillel, D. Water resources for agriculture in a changing climate: International case studies. Glob. Environ. Chang. Hum. Policy Dimens. 2004, 14, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunn, N.; Qian, N. The potato’s contribution to population and urbanization: Evidence from a historical experiment. Q. J. Econ. 2011, 126, 593–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Xu, S.; Pan, C. Measurement of the Spatial Complexity and Its Influencing Factors of Agricultural Green Development in China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, D.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Yu, G.; Zhao, X. An evaluation of China’s agricultural green production: 1978–2017. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 243, 118483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, X.; Xia, X. Measurement and spatial convergence analysis of China’s agricultural green development index. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 19694–19709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crost, B.; Duquennois, C.; Felter, J.H.; Rees, D.I. Climate change, agricultural production and civil conflict: Evidence from the Philippines. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2018, 88, 379–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Huang, J.; Wang, J.; Cui, Q.; Robertson, R.; Chen, K. Climate change impacts on China’s agriculture: The responses from market and trade. China Econ. Rev. 2020, 62, 101256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Primary Indicators | Secondary Indicators | Measurement Method | Direction |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agricultural endowment | Arable land | Total arable land area | Positive |
| Water resources | Water resources per capita | Positive | |
| Forest resources | Forest coverage rate | Positive | |
| Agricultural production efficiency | Agricultural productivity | Per capita output of major agricultural products | Positive |
| Agricultural output efficiency | Primary industry value-added/Agricultural population | Positive | |
| Arable land utilization | Sown area/arable land area | Positive | |
| Effective irrigation rate | Effective irrigated area/Sown area | Positive | |
| Mechanization level | Agricultural machinery power/Sown area | Positive | |
| Agricultural energy consumption | Diesel consumption | Agricultural diesel consumption/Primary industry value-added | Negative |
| Electricity consumption | Electricity for agriculture/Primary industry value-added | Negative | |
| Water consumption | Water for agriculture/Primary industry value-added | Negative | |
| Agricultural pollution | Fertilizer input | Total fertilizer input/Sown area | Negative |
| Pesticide input | Total pesticide input/Sown area | Negative | |
| Plastic film input | Total agricultural plastic film input/Sown area | Negative | |
| Environmental protection | Afforestation area | Afforestation area | Positive |
| Erosion control | Soil erosion control area | Positive | |
| Farmland governance | Flood removal area/Sown area | Positive |
| Variable | Definition of Variables | Data Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Green | Green agricultural development index | China County Statistical Yearbook, China Statistical Yearbook & Statistical Yearbook of every province |
| Rain | Rainfall fluctuations | FLDAS Noah Land Surface Model L4 Global Monthly |
| Production | Output per capita of major corps | China County Statistical Yearbook and China Rural Statistical Yearbook |
| Perfirst | Per capita primary industry value-added | China County Statistical Yearbook |
| Arable rate | Arable land utilization rate | China Rural Statistical Yearbook and Statistical Yearbook of every province |
| Fertile | Fertilizer input per hectare | China Rural Statistical Yearbook and Statistical Yearbook of every province |
| Pesticide | Pesticide inputs per hectare | China Rural Statistical Yearbook and Statistical Yearbook of every province |
| POP | Total population | China County Statistical Yearbook |
| Machinery | Total agricultural machinery power | China County Statistical Yearbook |
| First | Primary industry value-added | China County Statistical Yearbook |
| Second | Secondary industry value-added | China County Statistical Yearbook |
| Expend | Total government expenditure | China County Statistical Yearbook |
| Invest | Total social investment | China County Statistical Yearbook |
| Variable | Affected Counties | Non-Affected Counties | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |
| Green | 0.39 | 0.18 | 0.39 | 0.17 |
| Production | 509 | 284 | 642 | 531 |
| Perfirst | 3156 | 2689 | 3847 | 3847 |
| Arable rate | 146 | 51 | 145 | 52 |
| Fertile | 347 | 133 | 312 | 103 |
| Pesticide | 10.28 | 7.90 | 9.99 | 6.68 |
| POP | 478 | 386 | 476 | 325 |
| Machinery | 356 | 4362 | 430 | 5145 |
| First | 1475 | 1594 | 1696 | 1617 |
| Second | 4903 | 10,867 | 5662 | 9868 |
| Expend | 1510 | 1967 | 1576 | 1971 |
| Invest | 6245 | 10,720 | 7067 | 11,532 |
| Variables | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Green | Green | Green | Green | Green | Green | |
| −0.008 *** | −0.013 *** | −0.013 *** | −0.012 *** | −0.012 *** | −0.018 *** | |
| (0.001) | (0.001) | (0.001) | (0.001) | (0.001) | (0.002) | |
| POP | −0.007 | 0.012 | 0.012 | 0.004 | ||
| (0.008) | (0.008) | (0.009) | (0.009) | |||
| Machinery | 0.003 | 0.007 *** | 0.007 *** | 0.007 *** | ||
| (0.002) | (0.002) | (0.002) | (0.002) | |||
| First | −0.031 *** | −0.028 *** | −0.029 *** | −0.027 *** | ||
| (0.002) | (0.002) | (0.002) | (0.002) | |||
| Second | −0.005 *** | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | ||
| (0.001) | (0.001) | (0.001) | (0.002) | |||
| Expend | −0.042 *** | −0.043 *** | −0.043 *** | |||
| (0.002) | (0.002) | (0.002) | ||||
| Invest | 0.001 | 0.0004 | ||||
| (0.001) | (0.001) | |||||
| County fix | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Time fix | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Obs | 39,270 | 39,270 | 38,354 | 38,331 | 38,142 | 38,186 |
| R2 | 0.694 | 0.695 | 0.698 | 0.700 | 0.701 | 0.699 |
| Counties | 2078 | 2078 | 2077 | 2077 | 2077 | 2086 |
| Variables | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time Trend | Municipalities | Land Transfer | Rainfall1 | Rainfall2 | |
| Green | Green | Green | Green | Green | |
| −0.012 *** | −0.012 *** | −0.011 *** | −0.012 *** | −0.013 *** | |
| (0.001) | (0.001) | (0.001) | (0.001) | (0.001) | |
| Obs | 38,142 | 37,440 | 32,140 | 38,006 | 38,006 |
| R2 | 0.701 | 0.702 | 0.413 | 0.707 | 0.705 |
| Counties | 2077 | 2040 | 2076 | 2077 | 2077 |
| Variables | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSM-DID | Identify2 | 2SLS-Rainfall | 2SLS-lat&lon | Index2 | |
| Green | Green | Green | Green | Input | |
| −0.013 *** | −0.024 *** | −0.034 *** | −0.041 *** | −0.006 *** | |
| (0.001) | (0.002) | (0.004) | (0.002) | (0.0004) | |
| Obs | 34,500 | 38,186 | 38,053 | 38,112 | 38,142 |
| R2 | 0.726 | 0.700 | 0.701 | 0.703 | 0.800 |
| Counties | 2077 | 2086 | 2067 | 2075 | 2077 |
| Variables | Climate Zone | Poor/Non-Poor | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | |
| Humid | Semi-Humid | Semi-Arid | Poor | Non-Poor | |
| Green | Green | Green | Green | Green | |
| −0.008 *** | −0.017 *** | 0.008 *** | −0.005 *** | −0.018 *** | |
| (0.001) | (0.002) | (0.003) | (0.002) | (0.001) | |
| Obs | 18,858 | 14,373 | 4775 | 13,891 | 24,251 |
| R2 | 0.751 | 0.718 | 0.783 | 0.684 | 0.714 |
| Counties | 1028 | 767 | 282 | 761 | 1316 |
| Variables | Agriculture/Non-Agriculture | East/Middle/West | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | |
| Agriculture | Non-Agriculture | East | Middle | West | |
| Green | Green | Green | Green | Green | |
| −0.010 *** | −0.014 *** | −0.031 *** | −0.015 *** | 0.001 | |
| (0.001) | (0.002) | (0.002) | (0.002) | (0.001) | |
| Obs | 20,176 | 17,877 | 10,541 | 11,419 | 16,182 |
| R2 | 0.690 | 0.718 | 0.719 | 0.726 | 0.736 |
| Counties | 1108 | 959 | 563 | 611 | 903 |
| Variables | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arable Rate | Consumption | Fertilizer | Pesticide | |
| Arable Rate | Consumption | lFertile | lPesticide | |
| −2.013 *** | 0.003 *** | 0.013 *** | 0.047 *** | |
| (0.266) | (0.0003) | (0.001) | (0.002) | |
| Obs | 37,375 | 38,142 | 38,142 | 38,142 |
| R2 | 0.255 | 0.638 | 0.717 | 0.493 |
| Counties | 2077 | 2077 | 2077 | 2077 |
| Variables | (1) | (2) | (3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Products | Per Products | Primary Value | |
| lProduction | lpro | lFirst | |
| 0.068 *** | 0.068 *** | −0.019 *** | |
| (0.004) | (0.004) | (0.002) | |
| Obs | 38,140 | 38,140 | 38,142 |
| R2 | 0.074 | 0.093 | 0.875 |
| Counties | 2077 | 2077 | 2077 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, L.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Z. Extreme Climate Shocks and Green Agricultural Development: Evidence from the 2008 Snow Disaster in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12055. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182212055
Feng L, Li Z, Zhao Z. Extreme Climate Shocks and Green Agricultural Development: Evidence from the 2008 Snow Disaster in China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(22):12055. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182212055
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Litao, Zhuo Li, and Zhihui Zhao. 2021. "Extreme Climate Shocks and Green Agricultural Development: Evidence from the 2008 Snow Disaster in China" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 22: 12055. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182212055
APA StyleFeng, L., Li, Z., & Zhao, Z. (2021). Extreme Climate Shocks and Green Agricultural Development: Evidence from the 2008 Snow Disaster in China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(22), 12055. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182212055






