Lipoedema as a Social Problem. A Scoping Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
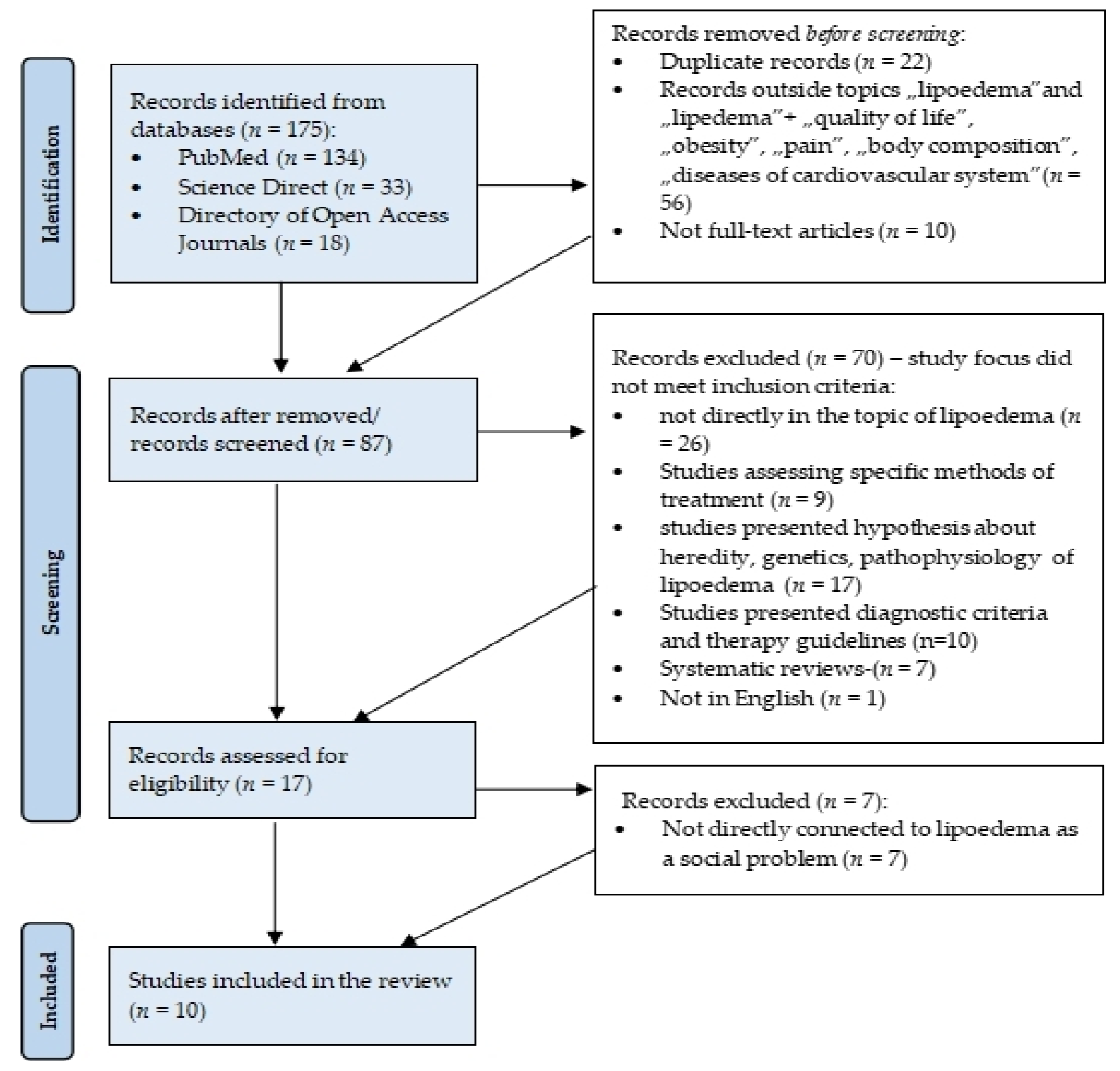
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Lipoedema and Body Weight Relationship
3.2. Lipoedema Associated Comorbidities
3.3. Quality of Life
3.4. Time of Diagnosis
3.5. Psychological Stress and Pain
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bertsch, T.; Erbacher, G.; Elwell, R. Lipoedema: A paradigm shift and consensus. J. Wound Care 2020, 29, 1–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosman, J. Lipoedema: Poor knowledge, neglect or disinterest? J. Lymphoedema 2011, 6, 109–111. [Google Scholar]
- Peled, A.W.; Kappos, E.A. Lipedema: Diagnostic and management challenges. Int. J. Womens Health 2016, 8, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buso, G.; Depairon, M.; Tomson, D.; Raffoul, W.; Vettor, R.; Mazzolai, L. Lipedema: A Call to Action! Obesity 2019, 27, 1567–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shavit, E.; Wollina, U.; Alavi, A. Lipoedema is not lymphoedema: A review of current literature. Int. Wound J. 2018, 15, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapprich, S.; Baum, S.; Kaak, I.; Kottmann, T.; Podda, M. Treatment of lipoedema using liposuction: Results of our own surveys. Phlebologie 2015, 44, 121–132. [Google Scholar]
- Paolacci, S.; Precone, V.; Acquaviva, F.; Chiurazzi, P.; Fulcheri, E.; Pinelli, M.; Buffelli, F.; Michelini, S.; Herbst, K.L.; Unfer, V.; et al. Genetics of lipedema: New perspectives on genetic research and molecular diagnoses. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 5581–5594. [Google Scholar]
- Michelini, S.; Chiurazzi, P.; Marino, V.; Dell’Orco, D.; Manara, E.; Baglivo, M.; Fiorentino, A.; Maltese, P.E.; Pinelli, M.; Herbst, K.L. Aldo-keto reductase 1C1 (AKR1C1) as the first mutated gene in a family with nonsyndromic primary lipedema. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Child, A.H.; Sharpe, P.; Gordon, K.D.; Brice, G.; Ostergaard, P.; Jeffery, S.; Mortimer, P.S. Lipedema: An inherited condition. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2010, 152, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margaret, A.F.; James, W.L.; Gerald, S.L. Lipedema, a frequently unrecognized problem. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2007, 57, S1–S3. [Google Scholar]
- Kruppa, P.; Georgiou, I.; Biermann, N.; Prantl, L.; Klein-Weigel, P.; Ghods, M. Lipedema-Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2020, 117, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marshall, M.; Schwahn-Schreiber, C. Prävalenz des Lipödems bei berufstätigen Frauen in Deutschland. Phlebologie 2011, 40, 127–134. [Google Scholar]
- Forner-Cordero, I.; Szolnoky, G.; Forner-Cordero, A.; Kemény, L. Lipedema: An overview of its clinical manifestations, diagnosis and treatment of the disproportional fatty deposition syndrome-systematic review. Clin. Obes. 2012, 2, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langendoen, S.I.; Habbema, L.; Nijsten, T.E.C.; Neumann, H.A.M. Lipoedema: From clinical presentation to therapy. A review of the literature. Br. J. Dermatol. 2009, 161, 980–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fetzer, A.; Wise, C. Living with lipoedema: Reviewing different self-management techniques. Br. J. Community Nurs. 2015, 20, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Williams, A. Understanding the challenges of lipoedema. J. Community Nurs. 2018, 32, 34–41. [Google Scholar]
- Wold, L.E.; Hines, J.R.E.A.; Allen, E. V Lipedema of the legs: A syndrome characterized by fat legs and edema. Ann. Intern. Med. 1951, 34, 1243–1250. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Todd, M. Lipoedema: Presentation and management. Br. J. Community Nurs. 2010, 15, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Redondo Galán, C.; García Bascones, M.; Marquina Valero, M.A. Lipoedema: Symptoms, diagnosis and treatment. A literature review. Rehabilitacion 2018, 24, 325. [Google Scholar]
- Erbacher, G.; Bertsch, T. Lipoedema and Pain: What is the role of the psyche?—Results of a pilot study with 150 patients with Lipoedema. Phlebologie 2020, 49, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetzer, A. Specialist approaches to managing lipoedema. Br. J. Community Nurs. 2016, 21, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dudek, J.E.; Białaszek, W.; Ostaszewski, P. Quality of life in women with lipoedema: A contextual behavioral approach. Qual. Life Res. 2016, 25, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romeijn, J.R.M.; de Rooij, M.J.M.; Janssen, L.; Martens, H. Exploration of Patient Characteristics and Quality of Life in Patients with Lipoedema Using a Survey. Dermatol. Ther. 2018, 8, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bauer, A.-T.; von Lukowicz, D.; Lossagk, K.; Aitzetmueller, M.; Moog, P.; Cerny, M.; Erne, H.; Schmauss, D.; Duscher, D.; Machens, H.-G. New Insights on Lipedema: The Enigmatic Disease of the Peripheral Fat. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2019, 144, 1475–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira de Godoy, L.M.; Pereira de Godoy, H.J.; Pereira de Godoy Capeletto, P.; Guerreiro Godoy, M.F.; Pereira de Godoy, J.M. Lipedema and the Evolution to Lymphedema With the Progression of Obesity. Cureus 2020, 12, 142. [Google Scholar]
- Dudek, J.E.; Białaszek, W.; Gabriel, M. Quality of life, its factors, and sociodemographic characteristics of Polish women with lipedema. BMC Womens Health 2021, 21, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek, J.E.; Białaszek, W.; Ostaszewski, P.; Smidt, T. Depression and appearance-related distress in functioning with lipedema. Psychol. Health Med. 2018, 23, 846–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melander, C.; Juuso, P.; Olsson, M. Women’s experiences of living with lipedema. Health Care Women Int. 2021, 14, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, T.F.; Herbst, K.L. A Young Woman with Excessive Fat in Lower Extremities Develops Disordered Eating and Is Subsequently Diagnosed with Anorexia Nervosa, Lipedema, and Hypermobile Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome. Am. J. Case Rep. 2021, 22, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghods, M.; Georgiou, I.; Schmidt, J.; Kruppa, P. Disease progression and comorbidities in lipedema patients: A 10-year retrospective analysis. Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 33, e14534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemes, A.; Kormányos, Á.; Domsik, P.; Kalapos, A.; Gyenes, N.; Kemény, L.; Szolnoky, G. Are increased left ventricular strains compensatory effects in lipedema? Detailed analysis from the three-dimensional speckle-tracking echocardiographic MAGYAR-Path Study. J. Clin. Ultrasound 2020, 48, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbst, K.; Chava, Y.; Te, T.C.H.; Mirkovskaya, L.; Bharhagava, A. Lipedema Fat and Signs and Symptoms of Illness, Increase with Advancing Stage. Arch. Med. 2015, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Hardy, D.; Williams, A. Best practice guidelines for the management of lipoedema. Br. J. Community Nurs. 2017, 22, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torre, Y.S.-D.; Wadeea, R.; Rosas, V.; Herbst, K.L. Lipedema: Friend and foe. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 2018, 33, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipoedema, U.K. Lipoedema UK Big Survey 2014 Research Report. 2016. Available online: https://www.lipoedema.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2016/04/UK-Big-Surey-version-web.pdf (accessed on 18 June 2021).
- Grada, A.A.; Phillips, T.J. Lymphedema: Pathophysiology and clinical manifestations. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2017, 77, 1009–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwardat, N.; Di Renzo, L.; Alwardat, M.; Wsp., I. The effect of lipedema on health-related quality of life and psychological status: A narrative review of the literature. Eat. Weight Disord. Anorexia Bulim. Obes. 2020, 25, 851–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aksoy, H.; Karadag, A.S.; Wollina, U. Cause and management of lipedema-associated pain. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 34, e14364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Article Type | Focus | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Cross sectional study | ● Quality of life of people with lipoedema | [26] |
| ● Quality of life of people with lipoedema | [27] | |
| ● Quality of life of people with lipoedema | [23] | |
| ● Correlation between BMI and lymphoedema in people with lipoedema | [25] | |
| ● Lipoedema comorbidities | [24] | |
| Qualitative research | ● Subjective self-evaluation of the impact of lipoedema on health | [28] |
| Case study | ● Lipoedema and eating disorders | [29] |
| Pilot study | ● The connection between pain and psychological stress in people with lipoedema | [20] |
| Other study | ● Lipoedema comorbidities | [30] |
| ● Left atrial and ventricular abnormalities in people with lipoedema | [31] |
| Reference | Number of Subjects | Data not Available | Normal Body Weight (BMI = 18.5–24.9 kg/m2) | Overweight (BMI = 25–29.9 kg/m2) | Obesity (BMI > 30 kg/m2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [27] | n = 329 | n = 8 | 14 (4.3%) | 40 (14.4%) | 267 (81.3%) |
| [26] | n = 98 | n = 3 | 20 (20.4%) | 26 (26.5%) | 49 (50%) |
| [20] | n = 150 | n = 0 | 5 (3.3%) | 15 (10%) | 130 (86.7%) |
| [23] | n = 163 | n = 0 | 21 (12.9%) | 41 (25.2%) | 101 (61.9%) |
| Total | n = 729 | n = 11 | 60 (8.23%) | 122 (16.73%) | 547 (75.04%) |
| Comorbidity | Ghods M. [30] (n = 106) | Dudek J.E. [26] (n = 98) | Bauer A.T. [24] (n = 209) | Romejn J.R.M. [23] (n = 163) | Total (n = 576) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Allergy | 39 (36.8%) | - | 72 (34.4%) | - | 111 (19.27%) |
| Obesity | 39 (36.8%) | 49 (50%) | - | 81 | 161 (28%) |
| Sleep disorders | 27 (25.5%) | - | 45 (21.5%) | - | 72 (12.5%) |
| Hypothyroidism | 33 (31.1%) | 31 (31.6%) | 75 (35.9%) | 19 (11.65%) | 158 (27.5%) |
| Depression | 27 (25.5%) | 56 (57.14%) | 48 (23%) | - | 131 (22.74%) |
| Hypertension | 26 (24.5%) | 4 (4.1%) | 28 (13.4%) | - | 58 (10%) |
| Migraine | 24 (22.6%) | - | 47 (22.5%) | - | 71 (12.5%) |
| Skin disorders | 20 (18.8%) | - | - | - | 20 (3.5%) |
| Asthma | 19 (18%) | - | 27 (12.9%) | 8 (4.9%) | 54 (9.4%) |
| Bowel disorders | 11 (10.4%) | 4 (4.1%) | 27 (12.9%) | 8 (4.9%) | 50 (8.7%) |
| Rheumatic diseases | 9 (8.4%) | 20 (20.4%) | 7 (3.3%) | - | 36 (6.25%) |
| Dyslipidemia | 7 (6.6%) | - | 15 (7%) | - | 22 (3.8%) |
| Diabetes (type 1 and 2) | 5 (4.7%) | 13 (13.3%) | 5 | 9 (5.5%) | 32 (5.56%) |
| Polycystic Ovary Syndrome | 3 (2.8%) | 5 (5.1%) | 12 (5.7%) | - | 20 (3.5%) |
| Lymphoedema | - | 30 (30.6%) | - | 5 (3%) | 35 (6.2%) |
| Venous insufficiency | - | 20 (20.4%) | - | - | 20 (3.5%) |
| Fibromyalgia | - | 4 (4.1%) | - | 14 (8.5%) | 18 (3.2%) |
| Heart disease | - | - | - | 35 (21.47%) | 35 (6%) |
| Lack of comorbidities | 13 (12.3%) | 18 (18.4%) | 43 (20.6%) | 71 (43%) | 145 (25.17%) |
| Reference | Year | Number of Subjects | The Aim of the Study | Quality of Life Questionnaire | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [27] | 2018 | n = 329 | To investigate the relationship between depression and lowered self-esteem and the quality of life in people with lipoedema. | WHOQOL-BREF | Lower level of quality of life was associated with higher severity of symptoms, lower mobility, higher severity of depression, and lower self-esteem. |
| [26] | 2021 | n = 98 | Examination of factors related to the quality of life in people with lipoedema, presentation of the sociodemographic characteristics, and clinical symptoms among Polish women with lipoedema. | WHOQOL-BREF | A low level of quality of life was observed in the subjects. With more and more symptoms, the quality of life is lower. |
| [23] | 2018 | n = 163 | To investigate the characteristics of patients with lipoedema, quality of life, symptoms, and comorbidities. | RAND-36, EQ-5 D-3 L | The quality of life of people with lipoedema was significantly lower than the average quality of life in the Dutch population; people with comorbidities had a lower quality of life. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Czerwińska, M.; Ostrowska, P.; Hansdorfer-Korzon, R. Lipoedema as a Social Problem. A Scoping Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 10223. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph181910223
Czerwińska M, Ostrowska P, Hansdorfer-Korzon R. Lipoedema as a Social Problem. A Scoping Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(19):10223. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph181910223
Chicago/Turabian StyleCzerwińska, Monika, Paulina Ostrowska, and Rita Hansdorfer-Korzon. 2021. "Lipoedema as a Social Problem. A Scoping Review" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 19: 10223. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph181910223
APA StyleCzerwińska, M., Ostrowska, P., & Hansdorfer-Korzon, R. (2021). Lipoedema as a Social Problem. A Scoping Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(19), 10223. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph181910223






