Protective and Risk Factors in Exercise Addiction: A Series of Moderated Mediation Analyses
Abstract
1. Introduction
Objectives and Hypotheses
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants, Procedure, and Ethics
2.2. Measures
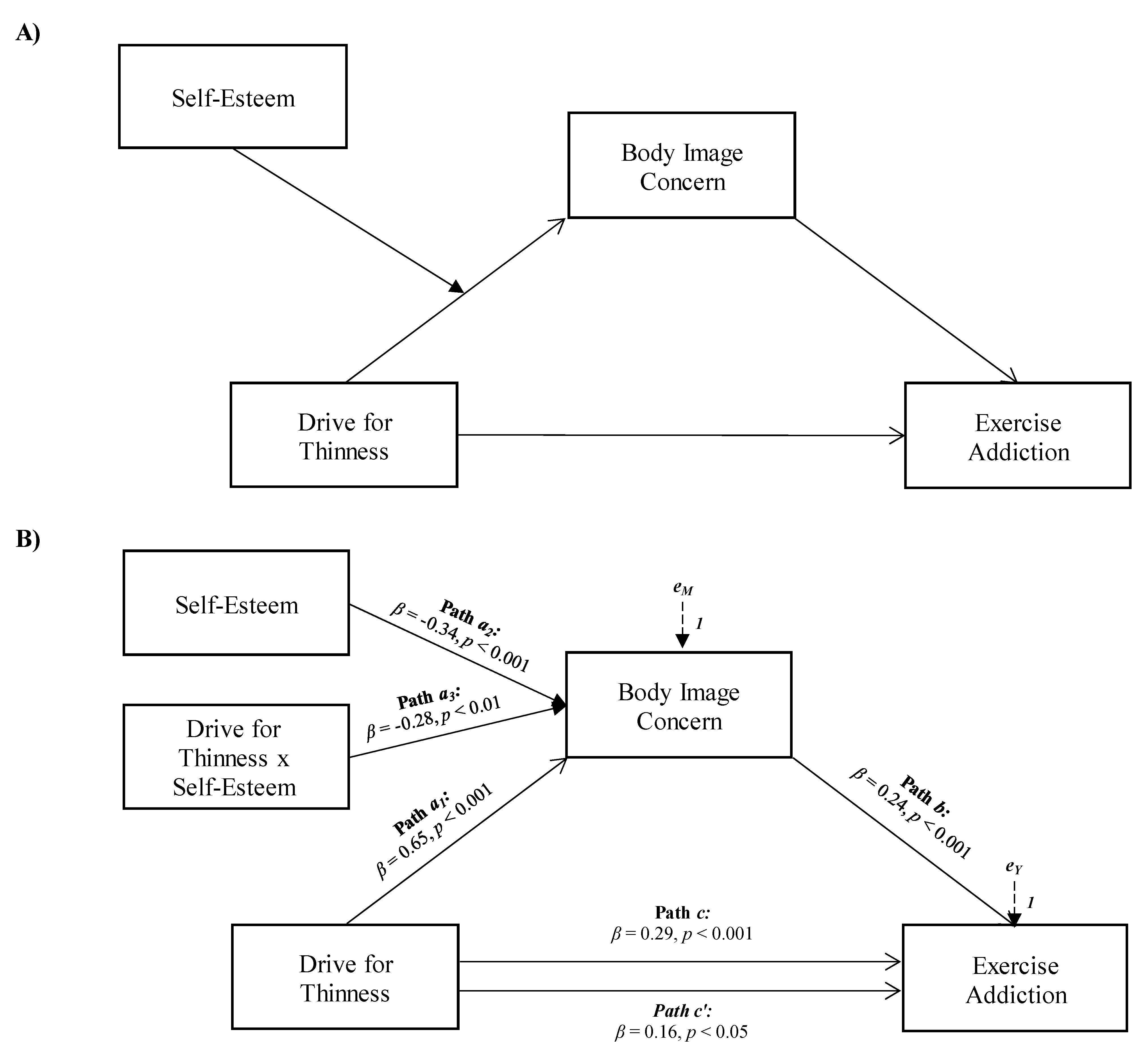
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Differences in the Levels of Exercise Addiction Based on the Risk of Eating Disorder
4.2. Drive for Thinness as Antecedent of Exercise Addiction
4.3. Bulimia as Antecedent of Exercise Addiction
4.4. Body Dissatisfaction as Antecedent of Exercise Addiction
4.5. A Focus on the Mediating Role of Body Image Concerns
4.6. A Focus on the Protective Role of Self-Esteem (the Moderator Variable)
4.7. Limitations and Suggestions for Future Research
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; American Psychiatry Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths, M.D. Behavioural addiction and substance addiction should be defined by their similarities not their dissimilarities. Addiction 2017, 112, 1718–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabo, A.; Griffiths, M.D.; de La Vega Marcos, R.; Mervó, B.; Demetrovics, Z. Methodological and conceptual limitations in exercise addiction research. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2015, 88, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brown, R.I.F. Some contributions of the study of gambling to the study of other addictions. In Gambling Behaviour and Problem Gambling; Eadington, W.R., Cornelius, J.A., Eds.; University of Nevada Press: Reno, NV, USA, 1993; pp. 241–272. [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths, M. Behavioural addiction: An issue for everybody? J. Workplace Learn. 1996, 8, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, M. Exercise addiction: A case study. Addict. Res. Theory 1997, 5, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, M.D. A ‘components’ model of addiction within a biopsychosocial framework. J. Subst. Use 2005, 10, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, A.; de la Vega, R.M.; Ruiz-Barquin, R.; Rivera, O. Exercise addiction in Spanish athletes: Investigation of the roles of gender, social context and level of involvement. J. Behav. Addict. 2013, 2, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terry, A.; Szabo, A.; Griffiths, M. The Exercise Addiction Inventory: A new brief screening tool. Addict. Res. Theory 2004, 12, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharmer, C.; Gorrell, S.; Schaumberg, K.; Anderson, D. Compulsive exercise or exercise dependence? Clarifying conceptualizations of exercise in the context of eating disorder pathology. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2020, 46, 101586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symons Downs, D.; MacIntyre, R.I.; Heron, K.E. Exercise addiction and dependence. In APA Handbook of Sport and Exercise Psychology; Anshel, M.H., Petruzzello, S.J., Labbe, E.E., Eds.; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2019; Volume 2, pp. 589–604. [Google Scholar]
- Dumitru, D.C.; Dumitru, T.; Maher, A.J. A systematic review of exercise addiction: Examining gender differences. J. Phys. Educ. Sport. 2018, 18, 1738–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berczik, K.; Szabó, A.; Griffiths, M.D.; Kurimay, T.; Kun, B.; Urbán, R.; Demetrovics, Z. Exercise addiction: Symptoms, diagnosis, epidemiology, and etiology. Subst. Use Misuse 2012, 47, 403–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landolfi, E. Exercise addiction. Sports Med. 2012, 43, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichtenstein, M.B.; Hinze, C.J.; Emborg, B.; Thomsen, F.; Hemmingsen, S.D. Compulsive exercise: Links, risks and challenges faced. Psychol. Res. Behav. Manag. 2017, 10, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aidman, E.V.; Woollard, S. The influence of self-reported exercise addiction on acute emotional and physiological responses to brief exercise deprivation. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2003, 4, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, A.; Griffiths, M.D.; Demetrovics, Z. Exercise addiction. In The Neuropathology of Drug Addictions and Substance Misuse; Preedy, V., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2016; Volume 3, pp. 984–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freimuth, M.; Moniz, S.; Kim, S.R. Clarifying exercise addiction: Differential diagnosis, co-occurring disorders, and phases of addiction. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2011, 8, 4069–4081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caretti, V.; La Barbera, D. Le Nuove Dipendenze: Diagnosi e Clinica; Carocci Editore: Rome, Italy, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Egorov, A.Y.; Szabo, A. The exercise paradox: An interactional model for a clearer conceptualization of exercise addiction. J. Behav. Addict. 2013, 2, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicilia, Á.; Alcaraz-Ibáñez, M.; Lirola, M.J.; Burgueño, R. Influence of goal contents on exercise addiction: Analysing the mediating effect of passion for exercise. J. Hum. Kinet. 2017, 59, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, B.; Karr, T.; Zunker, C.; Mitchell, J.; Thompson, R.; Sherman, R.; Crosby, R.D.; Cao, L.; Erickson, A.; Wonderlich, S.A. Primary and secondary exercise dependence in a community-based sample of road race runners. J. Sport. Exerc. Psychol. 2013, 35, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trott, M.; Jackson, S.E.; Firth, J.; Jacob, L.; Grabovac, I.; Mistry, A.; Stubbs, B.; Smith, L. A comparative meta-analysis of the prevalence of exercise addiction in adults with and without indicated eating disorders. Eat Weight Disord 2020, 26, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, A.; Griffiths, M.D.; Demetrovics, Z. Psychology and exercise. In Nutrition and Enhanced Sports Performance; Bacghi, D., Nair, S., Sen, C., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2019; pp. 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, B.J.; Hausenblas, H.A.; Freimuth, M. Exercise addiction and compulsive exercising: Relationship to eating disorders, substance use disorders, and addictive disorders. In Eating Disorders, Addictions and Substance Use Disorders: Research, Clinical and Treatment Perspectives; Brewerton, T., Baker Dennis, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 127–144. [Google Scholar]
- Garner, D.M.; Olmstead, M.P.; Polivy, J. Development and validation of a multidimensional eating disorder inventory for anorexia nervosa and bulimia. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 1983, 2, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannini, M.; Conti, C. Italian Adaptation of Eating Disorder Inventory-3: Referral Form (RF); Giunti O.S.: Florence, Italy, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenstein, M.B.; Christiansen, E.; Elklit, A.; Bilenberg, N.; Støving, R.K. Exercise addiction: A study of eating disorder symptoms, quality of life, personality traits and attachment styles. Psychiatry Res. 2014, 215, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lease, H.J.; Bond, M.J. Correspondence between alternate measures of maladaptive exercise, and their associations with disordered eating symptomatology. J. Behav. Addict. 2013, 2, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Maselli, M.; Gobbi, E.; Probst, M.; Carraro, A. Prevalence of primary and secondary exercise dependence and its correlation with drive for thinness in practitioners of different sports and physical activities. Int. J. Ment. Health Addict. 2019, 17, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackard, D.M.; Brehm, B.J.; Steffen, J.J. Exercise and eating disorders in college-aged women: Profiling excessive exercisers. Eat. Disord. 2002, 10, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortes, L.D.S.; Neves, C.M.; Filgueiras, J.F.; Almeida, S.S.; Ferreira, M.E.C. Body dissatisfaction, psychological commitment to exercise and eating behavior in young athletes from aesthetic sports. Rev. Bras. Cineantropometria Desempenho Hum. 2013, 15, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandi, S.; Clementi, C.; Guidi, J.; Benassi, M.; Tossani, E. Personality characteristics and psychological distress associated with primary exercise dependence: An exploratory study. Psychiatry Res. 2011, 189, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, A.; Demetrovics, Z.; Griffiths, M.D. Morbid exercise behavior: Addiction or psychological escape? In The Exercise Effect on Mental Health: Neurobiological Mechanisms; Budde, H., Wegner, M., Eds.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 277–311. [Google Scholar]
- Alcaraz-Ibáñez, M.; Paterna, A.; Sicilia, Á.; Griffiths, M.D. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on the Relationship between Body Dissatisfaction and Morbid Exercise Behaviour. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brudzynski, L.R.; Ebben, W. Body image as a motivator and barrier to exercise participation. Int. J. Exerc. Sci. 2010, 3, 14–24. [Google Scholar]
- Cash, T.F. Body image: Past, present, and future. Body Image 2004, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, D.A.; Bennett, A.S.; Schebendach, J.; Foltin, R.W.; Devlin, M.J.; Walsh, B.T. Exercise “addiction” in anorexia nervosa: Model development and pilot data. CNS Spectr. 2004, 9, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littleton, H.L.; Axsom, D.; Pury, C.L. Development of the Body Image Concern Inventory. Behav. Res. Ther. 2005, 43, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollei, I.; Schieber, K.; de Zwaan, M.; Svitak, M.; Martin, A. Body dysmorphic disorder and nonweight-related body image concerns in individuals with eating disorders. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2013, 46, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sicilia, A.; Alcaraz-Ibáñez, M.; Chiminazzo, J.G.C.; Fernandes, P.T. Latent profile analysis of exercise addiction symptoms in Brazilian adolescents: Association with health-related variables. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 273, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaydon, M.J.; Lindner, K.J. Eating disorders and exercise dependence in triathletes. Eat. Disord. 2002, 10, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, A.; Quattrone, D.; Scimeca, G.; Cicciarelli, C.; Romeo, V.M.; Pandolfo, G.; Zoccali, R.A.; Muscatello, M.R.A. Unraveling exercise addiction: The role of narcissism and self-esteem. J. Addict. 2014, 2014, 987841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, M. Rosenberg self-esteem scale (RSE). PsycTESTS Dataset 1965, 61, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Dea, J.A. Body image and self-esteem. In Encyclopedia of Body Image and Human Appearance; Cash, T.F., Ed.; Elsevier Academic Press: Norfolk, VA, USA, 2012; pp. 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankauskiene, R.; Baceviciene, M. Body image concerns and body weight overestimation do not promote healthy behaviour: Evidence from adolescents in Lithuania. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobera, I.J.; Ríos, P.B. Body image quality of life in eating disorders. Patient Prefer. Adherence 2011, 5, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, M.D.; Szabo, A.; Terry, R. The Exercise Addiction Inventory: A quick and easy screening tool for health practitioners. Br. J. Sports Med. 2005, 39, e30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gori, A.; Topino, E.; Griffiths, M. A screening tool for exercise addiction: The psychometric properties of the Italian Exercise Addiction Inventory. Int. J. Ment. Health Addict. 2021. under review. [Google Scholar]
- Garner, D.M. Eating Disorder Inventory-3 (EDI-3); Professional Manual; Psychological Assessment Resources: Odessa, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Luca, M.; Giannini, M.; Gori, A.; Littleton, H. Measuring dysmorphic concernsin Italy: Psychometric properties of the Italian Body Image Concern Inventory (I-BICI). Body Image 2011, 8, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prezza, M.; Trombaccia, F.R.; Armento, L. La scala dell’autostima di Rosenberg: Traduzione e validazione Italiana [The Rosenberg Self-Esteem Scale: Italian translation and validation]. Giunti Organ. Spec. 1997, 223, 35–44. [Google Scholar]
- Hayes, A.F. Introduction to Mediation, Moderation, and Conditional Process Analysis Second Edition: A Regression-Based Approach; Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wayne, S.J.; Lemmon, G.; Hoobler, J.M.; Cheung, G.W.; Wilson, M.S. The ripple effect: A spillover model of the detrimental impact of work–family conflict on job success. J. Organ. Behav. 2017, 38, 876–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, A. Exercise Addiction: A Symptom or a Disorder; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Shroff, H.; Reba, L.; Thornton, L.M.; Tozzi, F.; Klump, K.L.; Berrettini, W.H.; Brandt, H.; Crawford, S.; Crow, S.; Fichter, M.M.; et al. Features associated with excessive exercise in women with eating disorders. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2006, 39, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon Grima, J.S.; Estrada-Marcen, N.; Montero-Marin, J. Exercise addiction measure through the Exercise Addiction Inventory (EAI) and health in habitual exercisers. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Adicciones 2018, 31, 233–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solmi, M.; Veronese, N.; Correll, C.U.; Favaro, A.; Santonastaso, P.; Caregaro, L.; Vancampfort, D.; Luchini, C.; De Hert, M.; Stubbs, B. Bone mineral density, osteoporosis, and fractures among people with eating disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2016, 133, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fietz, M.; Touyz, S.; Hay, P. A risk profile of compulsive exercise in adolescents with an eating disorder: A systematic review. Adv. Eat. Disord. Theory Res. Pract. 2014, 2, 241–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taber, K.H.; Black, D.N.; Porrino, L.J.; Hurley, R.A. Neuroanatomy of dopamine: Reward and addiction. J. Neuropsychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2012, 24, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homan, K. Athletic-ideal and thin-ideal internalization as prospective predictors of body dissatisfaction, dieting, and compulsive exercise. Body Image 2010, 7, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, E.; Rushford, N.; Soon, S.; McDermott, C. Dysfunctional metacognition and drive for thinness in typical and atypical anorexia nervosa. J. Eat. Disord. 2015, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcaraz-Ibáñez, M.; Paterna, A.; Sicilia, Á.; Griffiths, M.D. Morbid exercise behaviour and eating disorders: A meta-analysis. J. Behav. Addict. 2020, 9, 206–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, A.S.; Thomas, J.J.; Greenberg, J.L.; Elliott, C.M.; Matheny, N.L.; Wilhelm, S. Anorexia nervosa and body dysmorphic disorder: A comparison of body image concerns and explicit and implicit attractiveness beliefs. Body Image 2015, 14, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendelson, B.K.; Mendelson, M.J.; White, D.R. Body-esteem scale for adolescents and adults. J. Pers. Assess. 2001, 76, 90–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adkins, E.C.; Keel, P.K. Does “excessive” or “compulsive” best describe exercise as a symptom of bulimia nervosa? Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2005, 38, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, C.; Taranis, L.; Goodwin, H.; Haycraft, E. Compulsive exercise and eating disorders. Eur. Eat. Disord. Rev. 2011, 19, 174–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, B.; Hausenblas, H.; Rossi, J. The moderating effect of gender on ideal-weight goals and exercise dependence symptoms. J. Behav. Addict. 2013, 2, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, M.; Parker, C.; Nielsen, A. What predicts drive for muscularity in college students? Eat. Behav. 2011, 12, 228–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, S.B.; Maguire, S.; Russell, J.; Touyz, S.W. The emotional regulatory features of bulimic episodes and compulsive exercise in muscle dysmorphia: A case report. Eur. Eat. Disord. Rev. 2012, 20, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrabosky, J.I.; Cash, T.F.; Veale, D.; Neziroglu, F.; Soll, E.A.; Garner, D.M.; Strachan-Kinser, M.; Bakke, B.; Clauss, L.J.; Phillips, K.A.; et al. Multidimensional body image comparisons among patients with eating disorders, body dysmorphic disorder, and clinical controls: A multisite study. Body Image 2009, 6, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corazza, O.; Simonato, P.; Demetrovics, Z.; Mooney, R.; van de Ven, K.; Roman-Urrestarazu, A.; Rácmolnár, L.; De Luca, I.; Cinosi, E.; Santacroce, R.; et al. The emergence of exercise addiction, body dysmorphic disorder, and other image-related psychopathological correlates in fitness settings: A cross sectional study. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harter, S. The Construction of the Self: Developmental and Sociocultural Foundations; Guilford Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Thoits, P.A. Self, identity, stress, and mental health. In Handbook of the Sociology of Mental Health; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 357–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chekroud, S.R.; Gueorguieva, R.; Zheutlin, A.B.; Paulus, M.; Krumholz, H.M.; Krystal, J.H.; Chekroud, A.M. Association between physical exercise and mental health in 1 · 2 million individuals in the USA between 2011 and 2015: A cross-sectional study. Lancet Psychiatry 2018, 5, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Characteristics | M ± SD | n | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 30.8 ± 11.98 | |||
| Sex | ||||
| Females | 228 | 71.47 | ||
| Males | 91 | 28.53 | ||
| Marital Status | ||||
| Single | 220 | 68.97 | ||
| Married | 42 | 13.17 | ||
| Cohabiting | 44 | 13.79 | ||
| Separated | 7 | 2.19 | ||
| Divorced | 5 | 1.57 | ||
| Widowed | 1 | 0.31 | ||
| Education | ||||
| Middle School diploma | 13 | 4.08 | ||
| High School diploma | 145 | 45.45 | ||
| University degree | 90 | 28.21 | ||
| Master’s degree | 45 | 14.11 | ||
| Post-lauream specialization | 26 | 8.15 | ||
| Occupation | ||||
| Student | 104 | 32.60 | ||
| Working student | 58 | 18.18 | ||
| Employee | 86 | 26.96 | ||
| Freelance | 19 | 5.96 | ||
| Entrepreneur | 17 | 5.33 | ||
| Trader | 8 | 2.51 | ||
| Artisan | 5 | 1.57 | ||
| Armed forces | 1 | 0.31 | ||
| Unemployed | 13 | 4.08 | ||
| Retired | 8 | 2.51 | ||
| Referral criteria (EDI-3-RF) | ||||
| A least one | 203 | 63.64 | ||
| None | 116 | 36.36 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. EAI | 1 | |||||
| 2. EDI (F1) | 0.292 ** | 1 | ||||
| 3. EDI (F2) | 0.150 ** | 0.631 ** | 1 | |||
| 4. EDI (F3) | 0.172 ** | 0.638 ** | 0.449 ** | 1 | ||
| 5. BICI | 0.328 ** | 0.565 ** | 0.269 ** | 0.573 ** | 1 | |
| 6. RSES | −0.203 ** | −0.396 ** | −0.230 ** | −0.465 ** | −0.631 ** | 1 |
| Antecedent | Total Effect [95% CI] | Direct Effect [95% CI] | Test of Highest Order Unconditional Interaction: | Bootstrapping 95% CI for the Moderation Effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drive for thinness | 0.130 *** [0.0826; 0.1765] | 0.069 * [0.0136; 0.1252] | ΔR2 = 0.010 F(1, 315) = 6.810, p < 0.01 | [−0.0418; −0.0043] |
| Bulimia | 0.089 ** [0.0239; 0.1530] | 0.039 [−0.0248; 0.1032] | ΔR2 = 0.019 F(1, 315) = 10.252, p < 0.01 | [−0.0676; −0.00129] |
| Body dissatisfaction | 0.095 ** [0.0350; 0.1533] | −0.013 [−0.0881; 0.0699] | ΔR2 = 0.016 F(1, 315) = 10.315, p < 0.01 | [−0.0641; −0.0138] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gori, A.; Topino, E.; Griffiths, M.D. Protective and Risk Factors in Exercise Addiction: A Series of Moderated Mediation Analyses. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9706. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18189706
Gori A, Topino E, Griffiths MD. Protective and Risk Factors in Exercise Addiction: A Series of Moderated Mediation Analyses. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(18):9706. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18189706
Chicago/Turabian StyleGori, Alessio, Eleonora Topino, and Mark D. Griffiths. 2021. "Protective and Risk Factors in Exercise Addiction: A Series of Moderated Mediation Analyses" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 18: 9706. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18189706
APA StyleGori, A., Topino, E., & Griffiths, M. D. (2021). Protective and Risk Factors in Exercise Addiction: A Series of Moderated Mediation Analyses. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(18), 9706. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18189706







