Impact of a Smart-Ring-Based Feedback System on the Quality of Chest Compressions in Adult Cardiac Arrest: A Randomized Preliminary Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
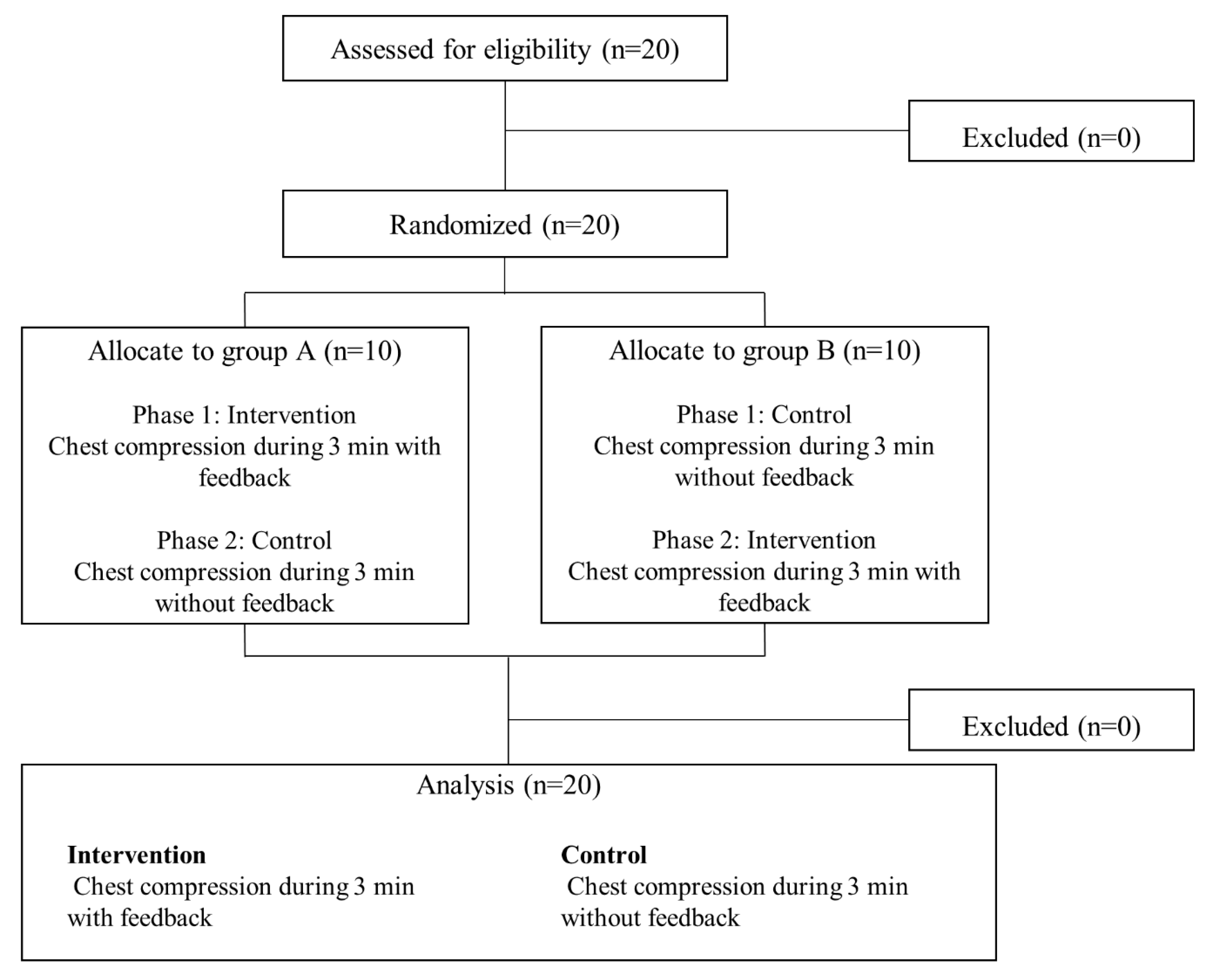
2.1. Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Equipment and Materials
2.4. Grouping and Experimental Conditions
2.5. Outcomes
2.6. Learnability and Usability of the Smart-Ring
- I would use this product frequently;
- I think the product is unnecessarily complex;
- I think the product is easy to use;
- I think I would need technical support to learn how to use this product;
- I think that the functions in the product are well-integrated;
- I think there was much inconsistency in the performance of the product;
- I imagine that most people would learn to use this product quickly;
- I find the product very uncomfortable to use;
- I feel confident using this product;
- I will need to learn many things before continuing to use the product.
- Positively worded domains = (score − 1);
- Negatively worded domains = (5 − score);
- After summing up the scores for the 10 domains, we multiplied by 2.5 = total SUS.
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Group Allocation and Participant Characteristics
3.2. Main Outcome
3.3. Results of the Learnability and Usability Evaluation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wong, C.X.; Brown, A.; Lau, D.H.; Chugh, S.S.; Albert, C.M.; Kalman, J.M.; Sanders, P. Epidemiology of Sudden Cardiac Death: Global and Regional Perspectives. Heart Lung Circ. 2019, 28, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehra, R. Global public health problem of sudden cardiac death. J. Electrocardiol. 2007, 40, S118–S122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ro, Y.S.; Shin, S.D.; Song, K.J.; Lee, E.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Ahn, K.O.; Chung, S.P.; Kim, Y.T.; Hong, S.O.; Choi, J.-A.; et al. A trend in epidemiology and outcomes of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest by urbanization level: A nationwide observational study from 2006 to 2010 in South Korea. Resuscitation 2013, 84, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, K.N.; Camp-Rogers, T.R.; Kotini-Shah, P.; Rios, M.D.; Gossip, M.R.; Moitra, V.K.; Haywood, K.L.; Dougherty, C.M.; Lubitz, S.A.; Rabinstein, A.A.; et al. Sudden Cardiac Arrest Survivorship: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2020, 141, e654–e685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchant, R.M.; Becker, L.B.; Abella, B.S.; Asch, D.A.; Groeneveld, P.W. Cost-effectiveness of therapeutic hypothermia after cardiac arrest. Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 2009, 2, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Panchal, A.R.; Bartos, J.A.; Cabañas, J.G.; Donnino, M.W.; Drennan, I.R.; Hirsch, K.G.; Kudenchuk, P.J.; Kurz, M.C.; Lavonas, E.J.; Morley, P.T.; et al. Part 3: Adult Basic and Advanced Life Support: 2020 American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care. Circulation 2020, 142, S366–S468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, J.; Meeks, R.; Edelson, D.; Gao, F.; Soar, J.; Perkins, G.D. The use of CPR feedback/prompt devices during training and CPR performance: A systematic review. Resuscitation 2009, 80, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkbright, S.; Finn, J.; Tohira, H.; Bremner, A.; Jacobs, I.; Celenza, A. Audiovisual feedback device use by health care professionals during CPR: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised and non-randomised trials. Resuscitation 2014, 85, 460–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semeraro, F.; Taggi, F.; Tammaro, G.; Imbriaco, G.; Marchetti, L.; Cerchiari, E.L. iCPR: A new application of high-quality cardiopulmonary resuscitation training. Resuscitation 2011, 82, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, T.K.; Wan, K.A.; Chan, J.C.K.; Lam, H.K.C.; Wong, Y.T.; Kan, P.G. New era of CPR: Application of i-technology in resuscitation. Hong Kong J. Emerg. Med. 2012, 19, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.S.; Kang, I.G.; Heo, S.J.; Chae, Y.S.; Kim, H.J.; Park, S.S.; Lee, M.J.; Jeong, W.J. A randomised, cross over study using a mannequin model to evaluate the effects on CPR quality of real-time audio-visual feedback provided by a smartphone application. Hong Kong J. Emerg. Med. 2014, 21, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, T.; Kitamura, T.; Nishiyama, C.; Murakami, Y.; Ando, M.; Kawamura, T.; Tasaki, O.; Kuwagata, Y.; Shimazu, T.; Iwami, T. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation support application on a smartphone–randomized controlled trial. Circ. J. 2015, 79, 1052–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eaton, G.; Renshaw, J.; Gregory, P.; Kilner, T. Can the British Heart Foundation PocketCPR application improve the performance of chest compressions during bystander resuscitation: A randomised crossover manikin study. Health Inform. J. 2018, 24, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, C.; Lee, J.; Oh, J.; Song, Y.; Chee, Y.; Lim, T.H.; Kang, H.; Shin, H. Effectiveness of feedback with a smartwatch for high-quality chest compressions during adult cardiac arrest: A randomized controlled simulation study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruenerbl, A.; Pirkl, G.; Monger, E.; Gobbi, M.; Lukowicz, P. Smart-watch life saver: Smart-watch interactive-feedback system for improving bystander CPR. In Proceedings of the 2015 ACM International Symposium on Wearable Computers, Osaka, Japan, 7–11 September 2015; pp. 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Song, Y.; Oh, J.; Chee, Y.; Ahn, C.; Shin, H.; Kang, H.; Lim, T.H. Smartwatch feedback device for high-quality chest compressions by a single rescuer during infant cardiac arrest: A randomized, controlled simulation study. Eur. J. Emerg. Med. 2019, 26, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Oh, J.; Chee, Y. A new chest compression depth feedback algorithm for high-quality CPR based on smartphone. Telemed. e-Health 2015, 21, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Chee, Y.; Oh, J.; Ahn, C.; Lim, T.H. Smartwatches as chest compression feedback devices: A feasibility study. Resuscitation 2016, 103, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Song, Y.; Lee, J.; Oh, J.; Lim, T.H.; Ahn, C.; Kim, I.Y. Development of smart ring-based chest compression depth feedback device for high quality chest compressions: A proof of concept study. Biosensors 2021, 11, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLellan, S.; Muddimer, A.; Peres, S.C. The effect of experience on System Usability Scale ratings. J. Usability Stud. 2012, 7, 56–67. [Google Scholar]
- Bangor, A.; Kortum, P.T.; Miller, J.T. An empirical evaluation of the system usability scale. Intl. J. Hum. Comput. Interact. 2008, 24, 574–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooke, J. Usability Evaluation in Industry; Taylor & Francis Ltd.: London, UK, 1996; pp. 4–7. [Google Scholar]
- An, M.; Kim, Y.; Cho, W.K. Effect of smart devices on the quality of CPR training: A systematic review. Resuscitation 2019, 144, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.S. Comparison of chest compression quality between the modified chest compression method with the use of smartphone application and the standardized traditional chest compression method during CPR. Technol. Health Care 2014, 22, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Lim, T.; Lee, Y.; Kim, W.; Cho, Y.; Kang, H. Assessment of chest compression depth obtained using the PocketCPR as an educational tool according to smartphone attachment site. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2016, 34, 2243–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topjian, A.A.; Raymond, T.T.; Atkins, D.; Chan, M.; Duff, J.P.; Joyner, B.L.; Lasa, J.J.; Lavonas, E.J.; Leve, A.; Mahgoub, M.; et al. Part 4: Pediatric Basic and Advanced Life Support: 2020 American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care. Circulation 2020, 142, S469–S523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
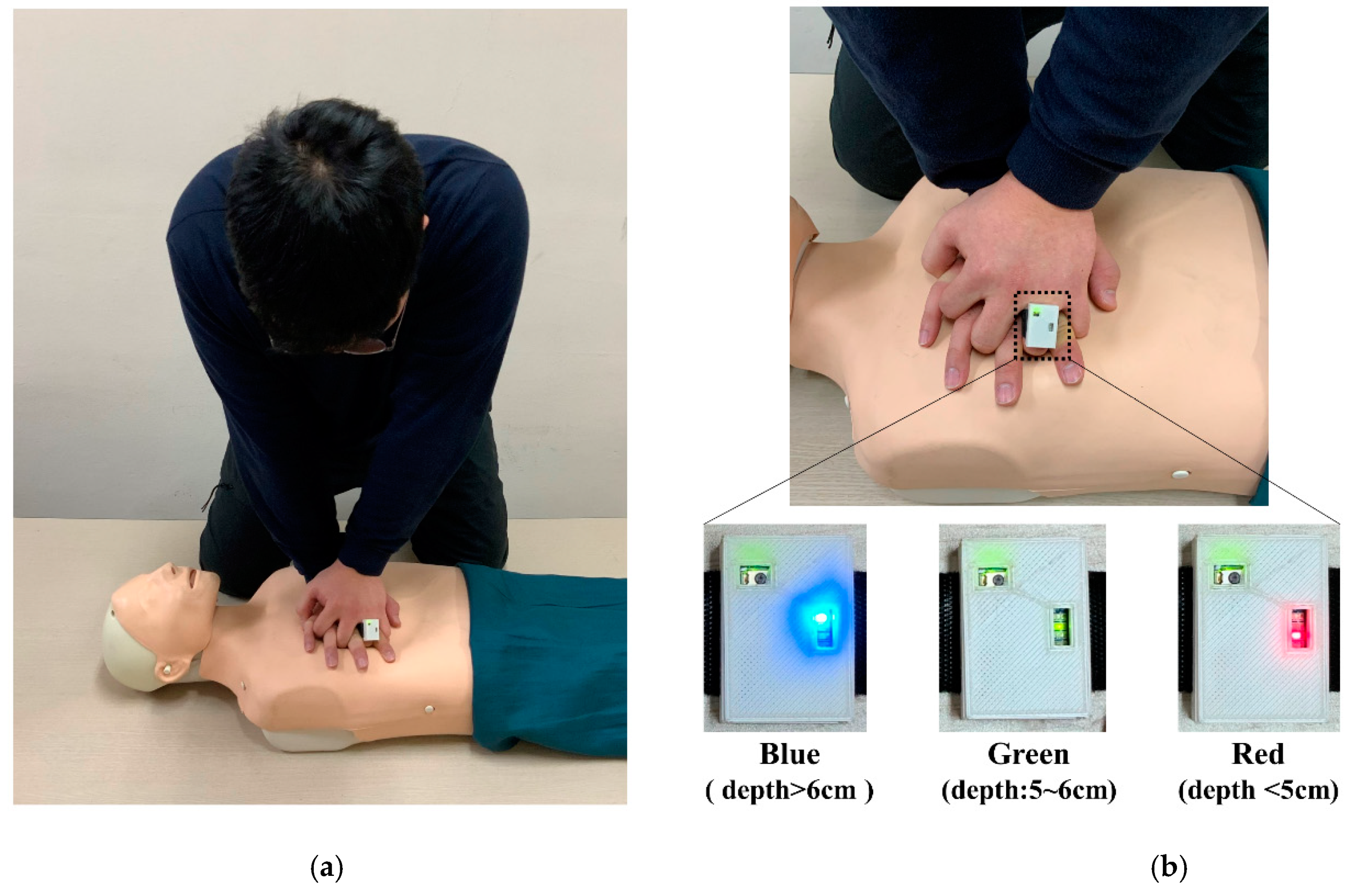
| Characteristics | Population | p-Value * | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male (n = 15) | Female (n = 5) | ||
| Age, years | 23 (21.5–24.5) | 21 (21–22) | 0.356 |
| Height, cm | 172.0 (170.0–176.0) | 162.0 (158.0–164.0) | 0.001 |
| Weight, kg | 72.0 (65.5–79.0) | 54.0 (53.0–55.0) | 0.001 |
| Body mass index | 24.1 (21.9–27.0) | 20.2 (20.0–21.6) | 0.019 |
| Number of CPR training sessions | 3 (2–3) | 3 (3–4) | 0.558 |
| Performance of CPR in real world | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | - |
| Outcome | Intervention (n = 20) | Control (n = 20) | p-Value * |
|---|---|---|---|
| CC depth, mm | 52.1 (46.3–54.8) | 47.1 (40.5–49.9) | 0.021 |
| Proportion of accurate-depth CCs, % | 88.7 (30.0–99.1) | 22.6 (0.0–58.5) | 0.033 |
| CC rate, counts/min | 99.6 (99.5–100.0) | 99.6 (99.6–99.8) | 0.616 |
| Proportion of complete chest decompression, % | 100 (99.7–100.0) | 100 (95.1-100) | 0.306 |
| Outcome | B | SE | VIF | p-Value ** |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| * CC depth, mm | ||||
| Sex, male | 8.88 | 2.21 | 1.33 | 0.019 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 0.93 | 0.30 | 1.33 | 0.003 |
| Feedback | 6.11 | 1.66 | 1.00 | <0.001 |
| Proportion of accurate-depth CCs, % | ||||
| Sex, male | 35.39 | 10.91 | 1.33 | <0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 5.60 | 1.47 | 1.33 | <0.001 |
| Feedback | 31.33 | 8.19 | 1.00 | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahn, C.; Lee, S.; Lee, J.; Oh, J.; Song, Y.; Kim, I.Y.; Kang, H. Impact of a Smart-Ring-Based Feedback System on the Quality of Chest Compressions in Adult Cardiac Arrest: A Randomized Preliminary Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5408. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18105408
Ahn C, Lee S, Lee J, Oh J, Song Y, Kim IY, Kang H. Impact of a Smart-Ring-Based Feedback System on the Quality of Chest Compressions in Adult Cardiac Arrest: A Randomized Preliminary Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(10):5408. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18105408
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhn, Chiwon, Seungjae Lee, Jongshill Lee, Jaehoon Oh, Yeongtak Song, In Young Kim, and Hyunggoo Kang. 2021. "Impact of a Smart-Ring-Based Feedback System on the Quality of Chest Compressions in Adult Cardiac Arrest: A Randomized Preliminary Study" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 10: 5408. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18105408
APA StyleAhn, C., Lee, S., Lee, J., Oh, J., Song, Y., Kim, I. Y., & Kang, H. (2021). Impact of a Smart-Ring-Based Feedback System on the Quality of Chest Compressions in Adult Cardiac Arrest: A Randomized Preliminary Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(10), 5408. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18105408








