Effects of Augmented-Reality-Based Exercise on Muscle Parameters, Physical Performance, and Exercise Self-Efficacy for Older Adults
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
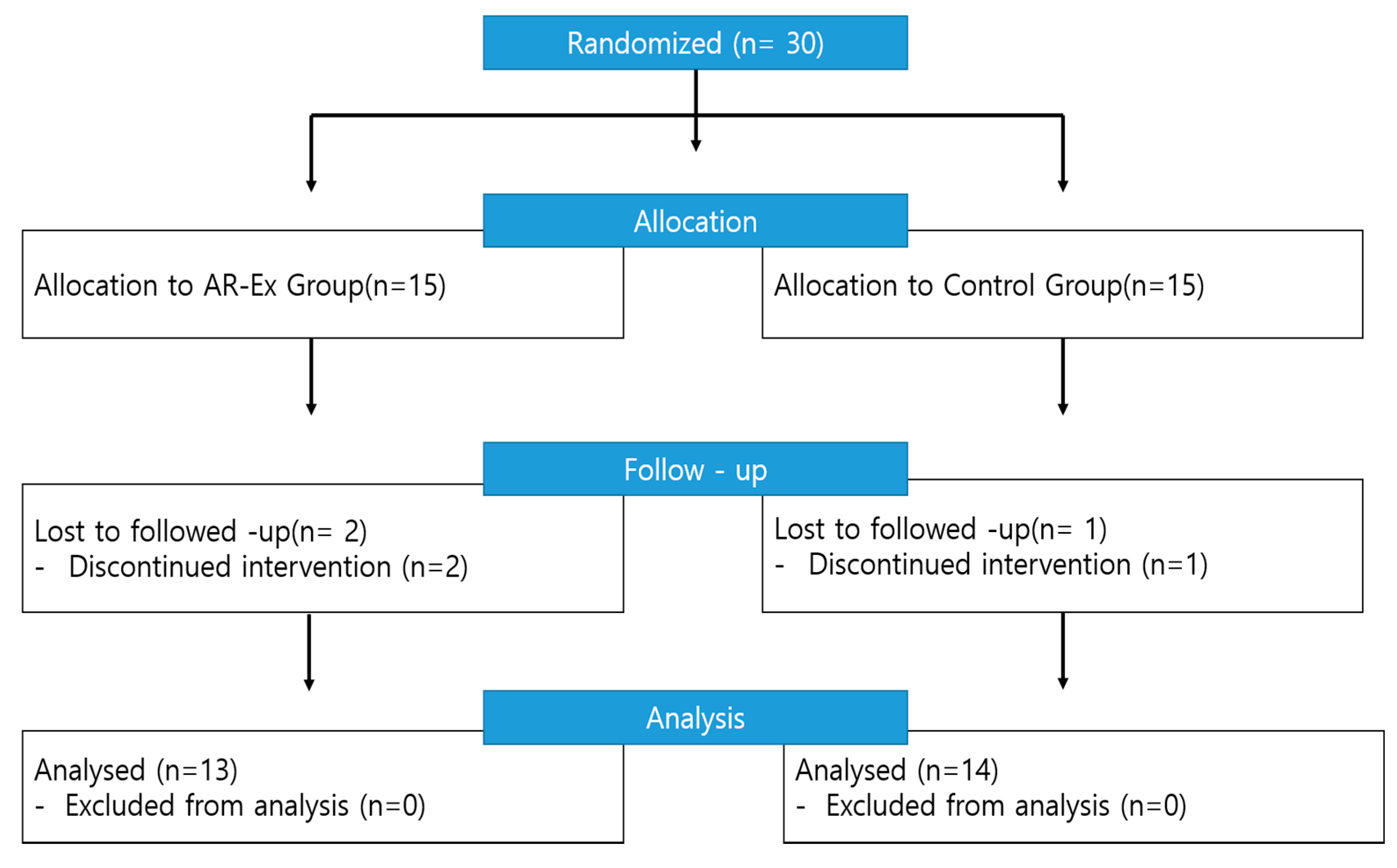
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Augmented-Reality-Based Muscle Reduction Prevention Exercise Program
2.3. Muscle Mass and Muscle Function
2.4. Assessment of Physical Performance: Senior Fitness Test (SFT)
2.5. Exercise Self-Efficacy Scale
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Korea National Statistical Office. Population Projections for Korea; Korea National Statistical Office: Daejeon, Korea, 2018.
- Anker, S.D.; Morley, J.E.; von Haehling, S. Welcome to the ICD-10 code for sarcopenia. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2016, 7, 512–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Baeyens, J.P.; Bauer, J.M.; Boirie, Y.; Cederholm, T.; Landi, F.; Martin, F.C.; Michel, J.P.; Rolland, Y.; Schneider, S.M.; et al. Sarcopenia: European consensus on definition and diagnosis: Report of the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People. Age Ageing 2010, 39, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, I.; Heymsfield, S.; Wang, Z.; Ross, R. Skeletal muscle mass and distribution in 468 men and women aged 18–88 year. J. Appl. Physiol. 2000, 89, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morley, J.E.; Malmstrom, T.K. Frailty, sarcopenia, and hormones. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2013, 42, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cederholm, T.; Morley, J.E. Sarcopenia: The new definitions. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2015, 18, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchonville, M.F.; Villareal, D.T. Sarcopenic Obesity—How Do We Treat It? Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2013, 20, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastone, A.C.; Ferriolli, E.; Teixeira, C.P.; Dias, J.M.D.; Dias, R.C. Aerobic Fitness and Habitual Physical Activity in Frail and Nonfrail Community—Dwelling Elderly. J. Phys. Act. Health 2015, 12, 1304–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McPhee, J.S.; French, D.P.; Jackson, D.; Nazroo, J.; Pendleton, N.; Degens, H. Physical activity in older age: Perspectives for healthy ageing and frailty. Biogerontology 2016, 17, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oesen, S.; Halper, B.; Hofmann, M.; Jandrasits, W.; Franzke, B.; Strasser, E.M.; Graf, A.; Tschan, H.; Bachl, N.; Quittan, M.; et al. Effects of elastic band resistance training and nutritional supplementation on physical performance of institutionalised elderly—A randomized controlled trial. Exp. Gerontol. 2015, 72, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maula, A.; LaFond, N.; Orton, E.; Iliffe, S.; Audsley, S.; Vedhara, K.; Kendrick, D. Use it or lose it: A qualitative study of the maintenance of physical activity in older adults. BMC Geriatr. 2019, 19, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Krevelen, D.W.F.; Poelman, R. A survey of augmented reality technologies, applications and limitations. Int. J. Virtual Real. 2010, 9, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueckert, F.; Goerz, M.; Ataian, M.; Tessmann, S.; Prokosch, H.U. Empowerment of patients and communication with health care professionals through an electronic health record. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2003, 70, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merians, A.S.; Jack, D.; Boian, R.; Tremaine, M.; Burdea, G.C.; Adamovich, S.V.; Recce, M.; Poizner, H. Virtual reality-augmented rehabilitation for patients following stroke. Phys. Ther. 2002, 82, 898–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holden, M.K. Virtual environments for motor rehabilitation: Review. Cyberpsychol. Behav. 2005, 8, 187–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flynn, S.; Palma, P.; Bender, A. Feasibility of using the SonyPlayStation 2 gaming platform for an individual poststroke: A casereport. J. Neurol. Phys. Ther. 2007, 31, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, P.L.; Rand, D.; Katz, N.; Kizony, R. Video capturevirtual reality as a flexible and effective rehabilitation tool. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2004, 1, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.J.; Go, B.G.; Park, S.J.; Song, H.S.; Kim, K.J. The development of physical fitness test battery and evaluation criteria of it for elderly Korean person. Korean J. Meas. Eval. Phys. Educ. Sport Sci. 2014, 16, 15–29. [Google Scholar]
- Marcus, B.H.; Selby, V.C.; Niaura, R.S.; Rossi, J.S. Self-efficacy and the stages of exercise behavior change. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 1992, 63, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner, R.N.; Koehler, K.M.; Gallagher, D.; Romero, L.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Ross, R.R.; Garry, P.J.; Lindeman, R.D. Epidemiology of sarcopenia among the elderly in New Mexico. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1998, 147, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.K.; Liu, L.K.; Woo, J.; Assantachai, P.; Auyeung, T.W.; Bahyah, K.S.; Chou, M.Y.; Chen, L.Y.; Hsu, P.S.; Krairit, O.; et al. Sarcopenia in Asia: Consensus report of the Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia. J. AMDA 2014, 15, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, Y.K.; Kim, S.S.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, H.J.; Park, J.J.; Cho, Y.S.; Joung, S.H.; Kim, J.R.; Kim, B.H.; et al. Combined Aerobic and Resistance Exercise Training Reduces Circulating Apolipoprotein J Levels and Improves Insulin Resistance in Postmenopausal Diabetic Women. DMJ 2020, 44, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.Y.; Cho, J.H. Effects of combined exercise on the skeletal muscle mass index and balance scale of elderly women with sarcopenia. Asian J. Kinesiol. 2015, 17, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottomley, J.M.; Lewis, C.B. Geriatric Rehabilitation: A Clinical Approch, 2nd ed.; Pearson Education: Oxford, UK, 2003; p. 331. [Google Scholar]
- Landi, F.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Liperoti, R.; Capoluongo, E.; Giovannini, S.; Onder, G.; Tosato, M.; Bernabei, R.; Russo, A. Sarcopenia and mortality risk in frail older persons aged 80 years and older: Results from ilSIRENTE study. Age Ageing 2013, 42, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, H.N.; Chung, E.J.; Lee, B.H. The Effects of augmented reality-based Otago Exercise on Balance, Gait, and Falls Efficacy of Elderly Women. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2013, 25, 797–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoever, K.; Heber, A.; Eichberg, S.; Brixius, K. Influences of Resistance Training on Physical Function in Older, Obese Men and Women with Sarcopenia. J. Geriatr. Phys. Ther. 2018, 41, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.Y.; Oak, J.S. Effects of 12 Weeks Aerobic exercise Training on Fitness, Body Composition, Skeletal Muscle Index and Blood Lipid Profiles in Obese Elderly Women. Korean J. Obes. 2013, 22, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherrington, C.; Whitney, J.C.; Lord, S.R.; Herbert, R.D.; Cumming, R.G.; Close, J.C. Effective exercise for the prevention of falls: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Geriatr. Soc. 2008, 56, 2234–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H. The roles and competence of senior sports leaders to ensure the successful implementation of senior sports programs. J. Sport Leis. Stud. 2009, 35, 661–676. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, D.D. Aging and sarcopeina. JMNI 2007, 7, 344–345. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, J.Y.; Kim, J.E.; Kim, S.W.; Kong, H.J. Effects of home-based tele-exercise on sarcopenia among community-dwelling elderly adults: Body composition and functional fitness. Exp. Gerontol. 2017, 87, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M Silva, F.; Petrica, J.; Serrano, J.; Paulo, R.; Ramalho, A.; Lucas, D.; Ferreira, J.P.; Duarte-Mendes, P. The Sedentary Time and Physical Activity Levels on Physical Fitness in the Elderly: A Comparative Cross-Sectional Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.N.; Lee, H.J.; Cho, H.S.; Kim, E.D.; Hwang, J.S. Replacing Self-Efficacy in Physical Activity: Unconscious Intervention of the AR Game, Pokémon GO. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saposnik, G.; Teasell, R.; Mamdani, M.; Hall, J.; McIlroy, W.; Cheung, D.; Thorpe, K.E.; Cohen, L.G.; Bayley, M. Effectiveness of virtual reality using Wii gaming technology in stroke rehabilitation: A pliot randomized clinical trial and proof of principle. Stroke 2010, 41, 1477–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tunur, T.; DeBlois, A.; Yates-Horton, E.; Rickford, K.; Columna, L.A. augmented reality-based dance intervention for individuals with Parkinson’s disease: A pilot study. Disabil. Health J. 2019, 31, 100848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, J.D.; Massey, A.P.; Devaneaux, C.A. Innovation in weight loss programs: A 3-dimensional virtual-world approach. J. Med. Int. Res. 2012, 14, e120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.H.; Park, S.B.; Jang, S.H. Effects of game-based virtual reality on health-related quality of life in chronic stroke patients: A randomized, controlled study. CBM 2015, 63, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreurs, K.; Quan-Haase, A.; Martin, K. Problematizing the digital literacy paradox in thecontext of older adults’ ICT use: Aging, mediadiscourse, and self-determination. Can. J. Commun. 2017, 42, 359–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristics | Categories | N = 27 | AR-EX. (n = 13) | Con. (n = 14) | t or x2 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | ||||
| Age (year) | 65–69 | 4 (14.8) | 2 (15.4) | 2 (14.3) | 0.038 | 0.845 |
| 70–74 | 15 (55.6) | 7 (53.8) | 8 (57.1) | |||
| 75–79 | 6 (22.2) | 3 (23.1) | 3 (21.4) | |||
| 80< | 2 (7.4) | 1 (7.7) | 1 (7.2) | |||
| M ± SD | 72.74 ± 3.64 | 72.77 ± 3.79 | 72.71 ± 3.64 | |||
| Living together | Yes | 7 (25.9) | 2 (15.4) | 5 (35.7) | 1.191 | 0.020 * |
| No | 20 (74.1) | 11 (84.6) | 9 (64.3) | |||
| Education level | None | 1 (3.7) | 1 (7.7) | 0 (0) | −1.262 | 0.536 |
| Elementary school | 5 (18.6) | 3 (23.1) | 2 (14.3) | |||
| Middle school | 8 (29.6) | 4 (30.8) | 4 (28.6) | |||
| ≥High school | 13 (48.1) | 5 (38.4) | 8 (57.1) | |||
| Religion | No | 8 (29.6) | 4 (30.8) | 4 (28.6) | 0.123 | 0.812 |
| Yes | 19 (70.4) | 9 (69.2) | 10 (71.4) | |||
| Current job | No | 16 (59.3) | 7 (53.8) | 9 (64.3) | −0.534 | 0.363 |
| Yes | 11 (40.7) | 6 (46.2) | 5 (35.7) | |||
| Current disease | No | 3 (11.1) | 1 (7.6) | 2 (14.3) | −0.422 | 0.552 |
| 1 | 10 (37.0) | 6 (46.2) | 4 (21.4) | |||
| ≥2 | 14 (51.9) | 6 (46.2) | 8 (64.3) | |||
| Body Mass Index (kg/m2) | ∼18< to <23 | 3 (11.1) | 2 (15.4) | 1 (7.1) | −0.120 | 0.522 |
| 23–25 | 6 (22.2) | 2 (15.4) | 4 (28.6) | |||
| ≥25 | 18 (66.7) | 9 (69.2) | 9 (64.3) | |||
| M ± SD | 27.78 ± 3.50 | 27.40 ± 3.46 | 28.13 ± 3.64 |
| Type | Program Types | Intensity (RPE)/Time | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Warm-up | Stretching | 7–9/5 min | |
| Workout | Upper body resistance exercise (5 min) | Shoulder Abduction 180° Shoulder Flexion 180° Shoulder External Rotation A 90° Trunk Lateral Bending 35° Trunk Flexion 80° | 9–11/5 min |
| Lower body resistance exercise (5 min) | Hip Abduction 45° Hip Flexion 90°, Knee Flexion 90° Sitting Knee Extension 0° | 9–11/5 min | |
| Aerobic exercise (5 min) | Walking in place, forward, sideways, backward Heel raises Knee lifts Leg curls Front lunges | 11–13/5 min | |
| Flexibility exercise (5 min) | Neck Trunk Whole Body | 9–11/5 min | |
| Cool-down | Upper body stretching Lower body stretching | 7–9/5 min | |
| Categories | Group | Pre- | Post- | ANOVA (p) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M ± SD | M ± SD | G | T | G × T | ||
| ASM (kg) | Exp. | 15.32 ± 1.81 | 15.76 ± 1.67 | 0.847 | 0.061 | 0.003 * |
| Con. | 15.72 ± 1.62 | 15.06 ± 1.42 | ||||
| SMI (kg/m2) | Exp. | 6.49 ± 0.67 | 6.69 ± 0.63 | 0.659 | 0.030 | 0.003 * |
| Con. | 6.71 ± 0.57 | 6.67 ± 0.53 | ||||
| Gait speed (m/s) | Exp. | 6.98 ± 0.97 | 6.76 ± 0.89 | 0.233 | 0.001 | 0.013 * |
| Con. | 7.27 ± 0.73 | 7.23 ± 0.75 | ||||
| Hand grip strength (kg) | Exp. | 22.55 ± 6.30 | 22.91 ± 6.16 | 0.906 | 0.205 | 0.109 |
| Con. | 22.41 ± 8.24 | 22.37 ± 8.37 | ||||
| Categories | Group | Pre- | Post- | ANOVA (p) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M ± SD | M ± SD | G | T | G × T | ||
| Chair stand test (number in 30 s) | Exp. | 20.92 ± 6.59 | 21.72 ± 5.48 | 0.795 | 0.221 | 0.033 * |
| Con. | 20.85 ± 5.77 | 20.62 ± 5.41 | ||||
| 2-min step test (2MST) | Exp. | 103.46 ± 7.78 | 106.00 ± 8.13 | 0.366 | 0.339 | 0.020 * |
| Con. | 102.42 ± 8.75 | 101.28 ± 8.43 | ||||
| Sit and reach test (cm) | Exp. | 7.84 ± 15.21 | 7.22 ± 14.34 | 0.546 | 0.492 | 0.052 |
| Con. | 10.67 ± 13.10 | 10.96 ± 13.24 | ||||
| Timed up-and-go test (TUG) | Exp. | 6.60 ± 1.39 | 6.96 ± 1.52 | 0.730 | 0.886 | 0.032 * |
| Con. | 6.75 ± 1.47 | 6.43 ± 1.47 | ||||
| Figure-of-eight walk test (F8W) (s) | Exp. | 25.19 ± 5.20 | 25.53 ± 5.25 | 0.432 | 0.319 | 0.081 |
| Con. | 24.66 ± 3.57 | 23.45 ± 3.24 | ||||
| Categories | Group | Pre- | Post- | ANOVA (p) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M ± SD | M±SD | G | T | G × T | ||
| Exercise self-efficacy | Exp. | 14.85 ± 2.67 | 16.38 ± 3.01 | 0.766 | 0.049 | 0.001 * |
| Con. | 14.93 ± 2.84 | 14.36 ± 2.53 | ||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeon, S.; Kim, J. Effects of Augmented-Reality-Based Exercise on Muscle Parameters, Physical Performance, and Exercise Self-Efficacy for Older Adults. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3260. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17093260
Jeon S, Kim J. Effects of Augmented-Reality-Based Exercise on Muscle Parameters, Physical Performance, and Exercise Self-Efficacy for Older Adults. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(9):3260. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17093260
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeon, Sangwan, and Jiyoun Kim. 2020. "Effects of Augmented-Reality-Based Exercise on Muscle Parameters, Physical Performance, and Exercise Self-Efficacy for Older Adults" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 9: 3260. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17093260
APA StyleJeon, S., & Kim, J. (2020). Effects of Augmented-Reality-Based Exercise on Muscle Parameters, Physical Performance, and Exercise Self-Efficacy for Older Adults. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(9), 3260. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17093260






