How Incivility and Academic Stress Influence Psychological Health among College Students: The Moderating Role of Gratitude
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants and Procedure
2.2. Measures
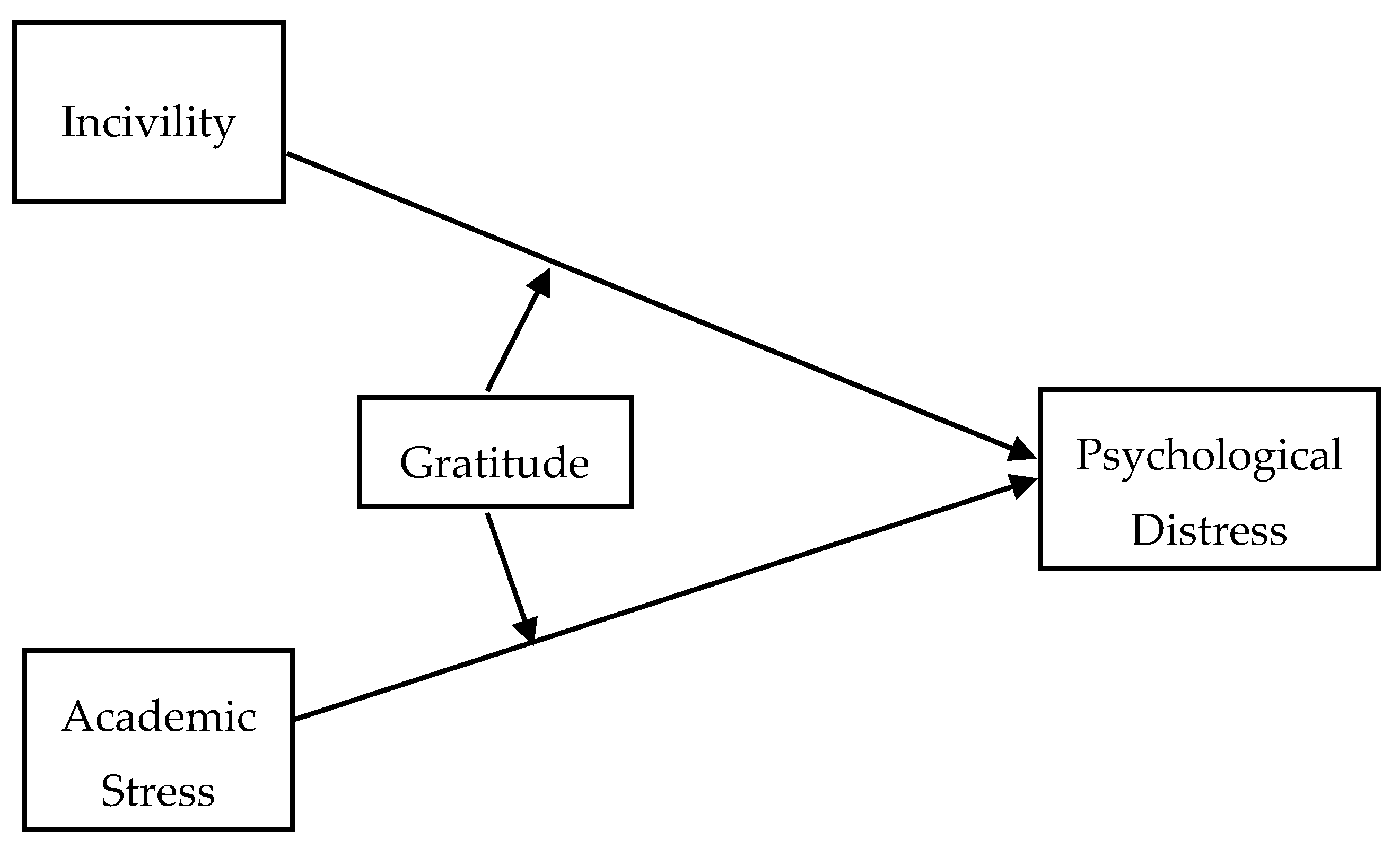
3. Methods
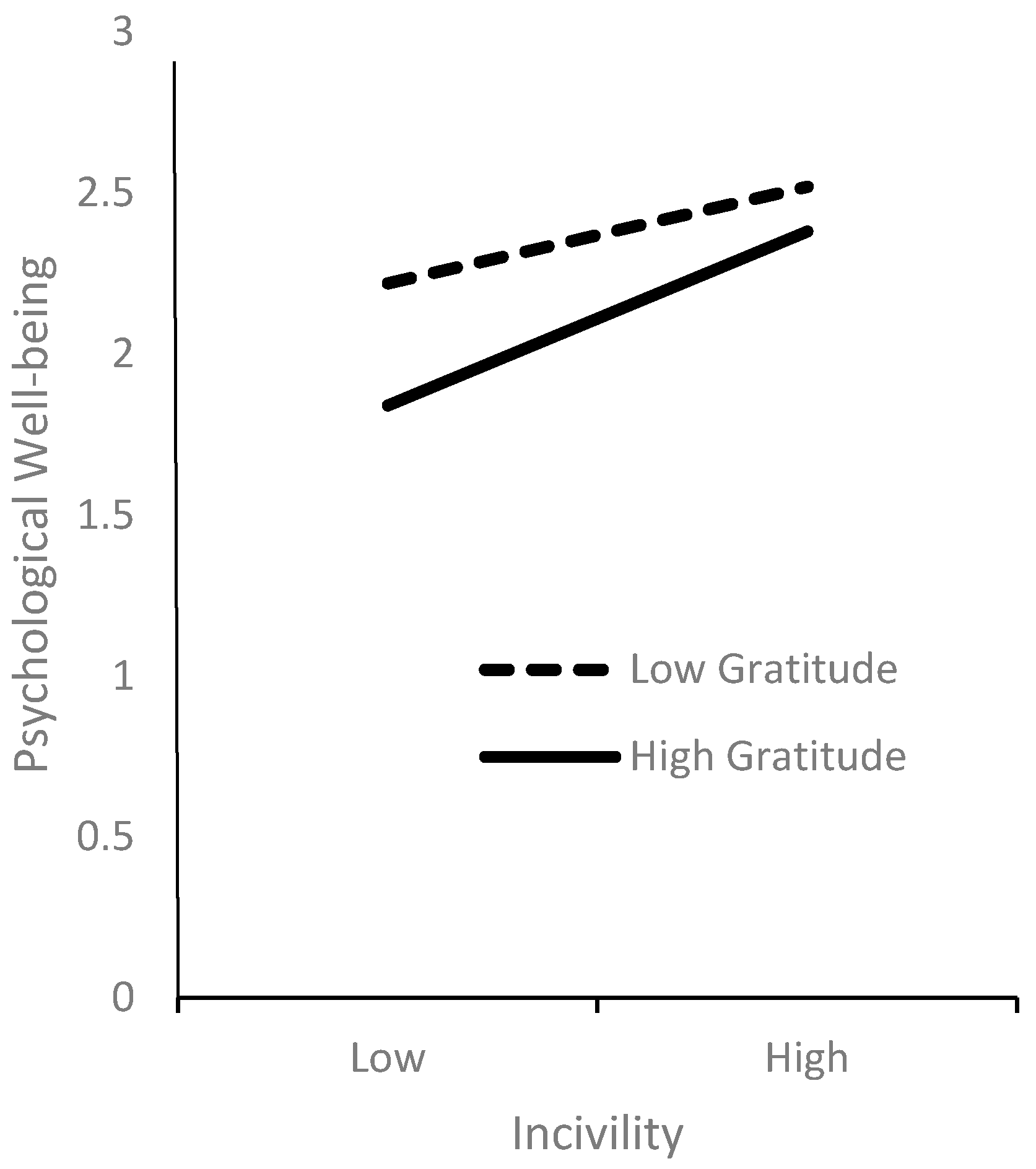
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Limitations
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- ul Haq, M.A.; Dar, I.S.; Aslam, M.; Mahmood, Q.K. Psychometric study of depression, anxiety and stress among university students. J. Public Health 2018, 26, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridner, S.H. Psychological distress: Concept analysis. J. Adv. Nurs. 2004, 45, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marquez, P.V.; Saxena, S. Making mental health a global priority. In Cerebrum: The Dana Forum on Brain Science; Dana Foundation: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 10–16. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Depression and Other Common Mental Disorders: Global Health Estimates; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/254610/WHO-MSD-MER-2017.2-eng.pdf (accessed on 5 March 2020).
- Bayram, N.; Bilgel, N. The prevalence and socio-demographic correlations of depression, anxiety and stress among a group of university students. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 2008, 43, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Ping, S.; Gao, W. Changes in undergraduate students’ Psychological well-being as they experience university life. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, S.; Anjum, A.; Uddin, M.E.; Rahman, M.A.; Hossain, M.F. Impacts of socio-cultural environment and lifestyle factors on the psychological health of university students in Bangladesh: A longitudinal study. J. Affect. Disord. 2019, 256, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massee, R. Qualitative and quantitative analyses of psycho-logical distress: Methodological complementarity and ontological incommensurability. Qual. Health Res. 2000, 10, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobfoll, S.E. Conservation of resources: A new attempt at conceptualizing stress. Am. Psychol. 1989, 44, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jue, F.U.; Benxian, Y.A.O.; Zhang, Y. Correlations among Work Stressors, Work Stress Responses, and Subjective Well-Being of Civil Servants: Empirical Evidence from China. Iran J. Public Health 2019, 48, 1059. [Google Scholar]
- LePine, J.A.; Podsakoff, N.P.; LePine, M.A. A meta-analytic test of the challenge stressor–hindrance stressor framework: An explanation for inconsistent relationships among stress and performance. Acad. Manag. J. 2005, 48, 764–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Qiu, S.; Dooley, L.M.; Ma, C. The Relationship between Challenge and Hindrance Stressors and Emotional Exhaustion: The Moderating Role of Perceived Servant Leadership. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudd, S.S.; Dumlao, J.; Erdmann-Sager, D.; Murray, D.; Phan, E.; Soukas, N.; Yokozuka, N. Stress at college: Effects on health habits, health status and self-esteem. Coll. Stud. J. 2000, 34, 217–227. [Google Scholar]
- Pedrelli, P.; Nyer, M.; Yeung, A.; Zulauf, C.; Wilens, T. College students: Mental health problems and treatment considerations. Acad. Psych. 2015, 39, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sliter, M.; Jex, S.; Wolford, K.; McInnerney, J. How rude! Emotional labor as a mediator between customer incivility and employee outcomes. J. Occup. Health Psychol. 2010, 15, 46–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, B.A. Incivility. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2000, 64, 445–450. [Google Scholar]
- Lane, S.D.; McCourt, H. Uncivil communication in everyday life: A response to Benson’s “The Rhetoric of Civility”. J. Contemp. Rhetor. 2013, 3, 17–29. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, K.A.; Walsh, M.M. Customer incivility and employee well-being: Testing the moderating effects of meaning, perspective taking and transformational leadership. Work Stress 2015, 29, 362–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Fritz, C.; Jex, S.M. Daily cyber incivility and distress: The moderating roles of resources at work and home. J. Manag. 2018, 44, 2535–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, K.; Jenkins, S.; Mallory, C.; Astroth, K.; Woith, W.; Jarvill, M. An Integrative Review Examining Student-to-Student Incivility and Effective Strategies to Address Incivility in Nursing Education. Nurs. Educ. 2020, 45, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmons, R.A.; Stern, R. Gratitude as a psychotherapeutic intervention. J. Clin. Psychol. 2013, 69, 846–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, J.L.; Chen, S.X.; Fung, H.H.; Bond, M.H.; Siu, N.Y.; Zhu, J.Y. Is gratitude always beneficial to interpersonal relationships? The interplay of grateful disposition, grateful mood, and grateful expression among married couples. Pers. Soc. Psychol. Bull. 2020, 46, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, B. An attributional theory of achievement motivation and emotion. Psychol. Rev. 1985, 92, 548–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emmons, R.A. Gratitude Works: A Twenty-One-Day Program for Creating Emotional Prosperity; Jossey-Bass: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Szcześniak, M.; Bielecka, G.; Bajkowska, I.; Czaprowska, A.; Madej, D. Religious/Spiritual Struggles and Life Satisfaction among Young Roman Catholics: The Mediating Role of Gratitude. Religions 2019, 10, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.S.; Bae, S.M. Gratitude Moderates the Mediating Effect of Deliberate Rumination on the Relationship between Intrusive Rumination and Posttraumatic Growth. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, P.J.J.; Gallegos, L.I.F.; Lira, C.J.; Vásquez, S.I.A. Perceived psychological well-Being among university students: A comparative study by gender. Eur. Sci. J. 2019, 15, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moksnes, U.K.; Lazarewicz, M. The association between stress, resilience, and emotional symptoms in Norwegian adolescents from 13 to 18 years old. J. Health Psychol. 2019, 24, 1093–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podsakoff, P.M.; MacKenzie, S.B.; Podsakoff, N.P. Sources of method bias in social science research and recommendations on how to control it. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2012, 63, 539–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortina, L.M.; Magley, V.J.; Williams, J.H.; Langhout, R.D. Incivility in the workplace: Incidence and impact. J. Occup. Health Psychol. 2001, 6, 64–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LePine, J.A.; LePine, M.A.; Jackson, C.L. Challenge and hindrance stress: Relationships with exhaustion, motivation to learn, and learning performance. J. Appl. Psychol. 2004, 89, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullough, M.E.; Emmons, R.A.; Tsang, J.A. The grateful disposition: A conceptual and empirical topography. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 2002, 82, 112–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, R.C.; Green, J.G.; Gruber, M.J.; Sampson, N.A.; Bromet, E.; Cuitan, M.; Furukawa, T.A.; Gureje, O.; Hinkov, H.; Hu, C.Y.; et al. Screening for serious mental illness in the general population with the K6 screening scale: Results from the WHO World Mental Health (WMH) survey initiative. Int. J. Methods Psychiatr. Res. 2010, 19, 4–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshki, M.; Ashtarian, H. Perceived health locus of control, self-esteem, and its relations to psychological well-being status in Iranian students. Iran J. Public Health 2010, 39, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yasmin, K.H.A.N.; Taghdisi, M.H.; Nourijelyani, K. Psychological Well-Being (PWB) of school adolescents aged 12–18 yr, its correlation with general levels of Physical Activity (PA) and socio-demographic factors in Gilgit, Pakistan. Iran J. Public Health 2015, 44, 804. [Google Scholar]
- Aiken, L.S.; West, S.G. Multiple Regression: Testing and Interpreting Interactions; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Abubakar, A.M. Linking work-family interference, workplace incivility, gender and psychological distress. J. Manag. Dev. 2018, 37, 226–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, P.C.; Woodward, K.; Stone, T.; Kolts, R.L. Gratitude and happiness: Development of a measure of gratitude, and relationships with subjective well-being. Soc. Behav. Pers. 2003, 31, 431–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, A.M.; Froh, J.J.; Geraghty, A.W.A. Gratitude and well-being: A review and theoretical integration. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2010, 30, 890–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolen-Hoeksema, S.; Parker, L.E.; Larson, J. Ruminative coping with depressed mood following loss. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 1994, 67, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froh, J.J.; Yurkewicz, C.; Kashdan, T.B. Gratitude and subjective well-being in early adolescence: Examining gender differences. J. Adolesc. 2009, 32, 633–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, A.K.; Musher-Eizenman, D.R.; Holub, S.C.; Dalrymple, J. What are children thankful for? An archival analysis of gratitude before and after the attacks of September 11. J. Appl. Dev. Psychol. 2004, 25, 541–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, N.; Emmons, R.A.; Ironson, G.; Hill, P.C. General feelings of gratitude, gratitude to god, and hemoglobin A1c: Exploring variations by gender. J. Posit. Psychol. 2017, 12, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, P.C.; Scheer, J.; Ovnicek, M.; Kolts, R. The debt of gratitude: Dissociating gratitude and indebtedness. Cogn. Emot. 2006, 20, 217–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlKandari, N. The level of student incivility: The need of a policy to regulate college student civility. Coll. Stud. J. 2011, 45, 257–268. [Google Scholar]
| Variable | M | SD | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Age | 2.14 | 1.12 | |||||||
| 2. Gender | 1.78 | 0.42 | −0.06 | ||||||
| 3. Income | 2.34 | 1.27 | 0.03 | −0.08 * | |||||
| 4. Incivility | 2.45 | 0.75 | 0.03 | −0.06 | −0.04 | ||||
| 5. Stress | 2.98 | 0.56 | 0.02 | 0.04 | −0.12 ** | 0.30 ** | |||
| 6. Gratitude | 3.89 | 0.63 | −0.07 * | 0.15 ** | 0.00 | −0.10 ** | −0.01 | ||
| 7. Psychological distress | 2.45 | 0.72 | 0.08 * | 0.01 | −0.04 | 0.37 ** | 0.52 ** | −0.20 ** |
| Model | χ2 | df | Δ χ2 | RMSEA | CFI | TLI | SRMR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Four-factor model IN, ST, GR, PS | 502.17 | 203 | 0.04 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.04 | |
| Three-factor model IN + ST, GR, PS | 2289.18 | 206 | 1787.01 ** | 0.11 | 0.73 | 0.70 | 0.12 |
| Two-factor model IN + ST + GR, PS | 3793.65 | 208 | 3291.48 ** | 0.14 | 0.54 | 0.48 | 0.16 |
| One factor model IN + ST + GR + PS | 4759.14 | 209 | 4256.97 ** | 0.16 | 0.41 | 0.35 | 0.16 |
| Psychological Distress | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 |
| Control Variables | |||
| Age | 0.09 ** (0.00) | 0.06 * (0.04) | 0.06 * (0.04) |
| Gender | 0.01 (0.58) | 0.04 (0.22) | 0.04 (0.27) |
| Income | −0.05 (0.15) | 0.02 (0.47) | 0.02 (0.49) |
| Predictors | |||
| Incivility | 0.22 ** (0.00) | 0.22 ** (0.00) | |
| Stress | 0.46 ** (0.00) | 0.46 ** (0.00) | |
| Gratitude | −0.18 ** (0.00) | −0.17 ** (0.00) | |
| Incivility × Gratitude | 0.07 * (0.02) | ||
| Stress × Gratitude | −0.05 (0.11) | ||
| Δ R2 | 0.01 ** (0.00) | 0.35 ** (0.00) | 0.01 * (0.02) |
| F | 2.82 * (0.03) | 83.11 ** (0.00) | 63.32 ** (0.00) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, N.; Qiu, S.; Alizadeh, A.; Wu, H. How Incivility and Academic Stress Influence Psychological Health among College Students: The Moderating Role of Gratitude. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3237. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17093237
Huang N, Qiu S, Alizadeh A, Wu H. How Incivility and Academic Stress Influence Psychological Health among College Students: The Moderating Role of Gratitude. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(9):3237. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17093237
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Naizhu, Shaoping Qiu, Amin Alizadeh, and Hongchao Wu. 2020. "How Incivility and Academic Stress Influence Psychological Health among College Students: The Moderating Role of Gratitude" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 9: 3237. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17093237
APA StyleHuang, N., Qiu, S., Alizadeh, A., & Wu, H. (2020). How Incivility and Academic Stress Influence Psychological Health among College Students: The Moderating Role of Gratitude. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(9), 3237. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17093237





