Abstract
Currently, adipose tissue is considered an endocrine organ that produces hormone-active substances, including leptin, which can play a key role in thermoregulation processes. Therefore, we performed a meta-analysis to investigate the influence of the climatic environment on leptin levels. A systematic literature search in the databases was carried out on 10 January 2020. Finally, 22 eligible articles were included in the current meta-analysis and a total of 13,320 participants were covered in the final analysis. It was shown that males of the “North” subgroup demonstrated significantly higher levels of leptin (10.02 ng/mL; CI: 7.92–12.13) than males of the “South” subgroup (4.9 ng/mL; CI: 3.71–6.25) (p = 0.0001). On the contrary, in the female group, a similar pattern was not detected (p = 0.91). Apparently, in order to maintain body temperature, higher leptin levels are required. The results of the study indicate that such effects are most pronounced in males and to a smaller extent in females, apparently due to a relatively high initial concentration of leptin in females. The correlation between leptin levels and climatic environment data support the hypothesis of leptin-mediated thermoregulation as an adaptive mechanism to cold climates.
1. Introduction
The indigenous people living in circumpolar regions have certain anatomical and physiological adaptations to protect the body from prolonged exposure to cold [1,2,3]. In response to chronic cold exposure, the rate of energy expenditure must increase to generate the additional heat needed to avert a drop in body temperature. One of the main mechanisms of increasing heat production in the body is nonshivering thermogenesis. This is mainly due to the metabolism in brown adipose tissue (BAT). Although BAT was initially considered to be present only in infants, it is now established that substantial BAT depots can be detected in the supraspinal, supraclavicular, pericardial and neck regions of adult humans [4,5,6,7,8,9]. In 2015, BAT in adults living in the cold climatic conditions of Eastern Siberia (Sakha Republic, Russia) was found. The BAT was detected in samples of adipose tissue from paraaortic, perirenal, subclavian, and parathyroid areas [10]. In BAT, nonshivering thermogenesis is mediated primarily by the uncoupling protein 1 (UCP1). This protein uncouples fatty acid oxidation from adenosine triphosphate production, leading to a futile metabolic process that results in increased heat production [11]. According to Efremova et al. [12], it was found that a constant part of the mediastinal and perirenal fat (up to about 40%) in adult residents of Eastern Siberia had a morphology typical of brown adipocytes and that a relevant percentage of it (up to about 30%) expressed the functional marker of UCP1 [12]. Many studies have shown that prolonged exposure to cold temperatures results in white-to-brown adipocyte transdifferentiation (browning) [13,14,15,16]. The process of browning is currently being studied by many researchers around the world [15,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28]. One of the most relevant in this sphere is the study of hormonal activities in browning processes. Leptin was the first adipokine to be discovered [28]. In humans, leptin is the product of the LEP gene that is located on chromosome 7 [29]. Leptin plays an important role in regulating energy homeostasis, but it can also affect some other physiological processes [30,31,32,33]. It was found that leptin can increase the expression of UCP1 [34,35], and stimulate the oxidation of fatty acids [36,37]. Leptin-deficient ob/ob mice are characterized not only by hyperphagia and obesity but also mild hypothermia; such mice will not survive a prolonged cold exposure [38]. Subsequently, it was found that the administration of exogenous leptin can optimize the body temperature in ob/ob mice [39], which suggests the direct involvement of leptin in thermoregulation. The available data suggest that leptin is involved in thermoregulation and possibly in adaptation to cold climates. Therefore, the present systematic review and meta-analysis were performed to summarize the results of original articles into a quantitative estimation of the correlation between leptin levels and climatic environment.
2. Materials and Methods
The present study was conducted following the Preferred Reporting Items of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses statement [40].
2.1. Search Strategy
PubMed-Medline databases were searched by using the following search terms in titles and abstracts: (“leptin”[MeSH Terms] OR “leptin”[All Fields]) AND (“body mass index”[MeSH Terms] OR (“body”[All Fields] AND “mass”[All Fields] AND “index”[All Fields]) OR “body mass index”[All Fields] OR (“body”[All Fields] AND “mass”[All Fields] AND “index”[All Fields] AND “bmi”[All Fields]) OR “body mass index bmi”[All Fields]). The literature was searched from inception to 10 January 2020.
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
The inclusion criteria for the studies were as follows: (1) the studies were case-controlled, cross-sectional, prospective, or clinical trials; (2) the studies examined serum or plasma leptin levels; (3) blood leptin levels should be measured using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) or radioimmunoassay (RIA), as these two methods are highly sensitive and specific; (4) leptin level unit is ng/mL; (5) the studies used mean values and standard deviations with a confidence interval (95%).
The exclusion criteria of studies were: (1) uncontrolled trials; (2) lack of sufficient information on baseline or follow-up leptin concentrations; (3) duplicated study.
2.3. Data Extraction
Eligible studies were reviewed, and the following data were abstracted: (1) author’s name; (2) year of publication; (3) country where the study was performed; (4) group size; (5) mean age or age range; (6) gender; (7) body mass index; (8) leptin levels; (9) blood leptin levels measurement method.
2.4. Quality Control
The methodological quality of the included studies was evaluated by the Newcastle-Ottawa scale. A total of nine items were involved in this form. The high-quality study was defined as a study with ≥7 awarded stars.
2.5. Data Analysis
Meta-analysis was conducted using RevMan 5.3 (The Cochrane Collaboration). The difference in blood leptin levels in individuals with elevated leptin and control groups was estimated by calculating the mean difference (MD). If the χ2 value was less than 0.10 and I2 exceeded 50%, then we considered there to be substantial heterogeneity and a random-effect model was applied to pool the data.
2.6. Climatic Environment
We divided data of included original articles by the climatic environment into “North” and “South” subgroups. The division into “North” and “South” was made according to the approximate border (40–45° N) of the transition from the subtropical climate zone to the temperate climate zone (Figure 1).
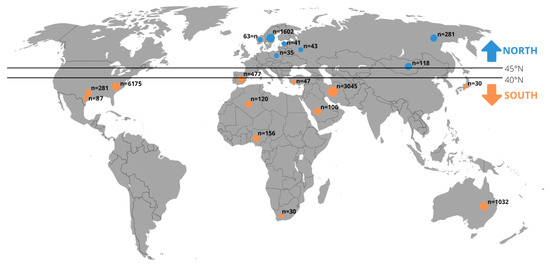
Figure 1.
The 13,320 individuals divided into the “North” and “South” subgroups included in the meta-analysis (detailed description about the literature search and eligible studies can be found in the results in Section 3.1).
2.7. Limitations of Meta-Analysis
There are certain limitations to our study. First, some heterogeneity may lead to reduced statistical power. Second, because sufficient data in primary studies are lacking, we were unable to perform further analyses to investigate other factors, such as a body fat mass, age, smoking, physical activity, diet, which may have affected our results.
2.8. Ethics Statement
This study was approved by the local Biomedical Ethics Committee of Yakut Scientific Center of Complex Medical Problems, Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, Yakutsk, Russia (Yakutsk, Protocol No. 16, 13 December 2014).
3. Results
3.1. Literature search and Eligible Studies
The search of the literature yielded 3827 relevant articles from PubMed. Then, the abstracts of these articles were reviewed to assess their eligibility. Following this assessment, 3608 articles did not meet the inclusion criteria, hence they were excluded. Furthermore, full texts of the 219 articles were reviewed and this resulted in the exclusion of 197 articles. In the end, 22 eligible articles met the inclusion criteria and were included in the final meta-analysis (Figure 2) [41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62].
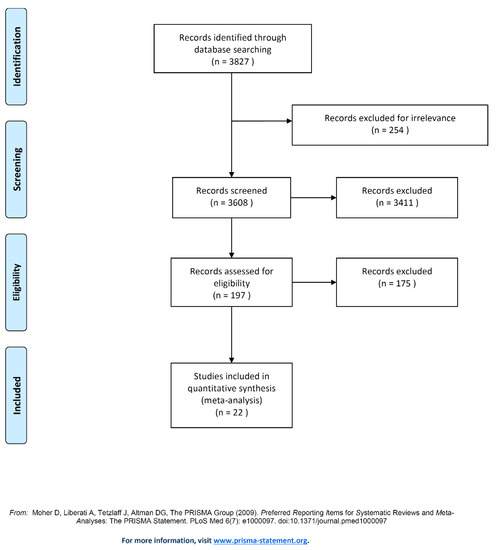
Figure 2.
Flow chart of study selection. Note: Presentation of the process by which relevant studies were retrieved from the databases, assessed, and selected, or excluded. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses (PRISMA) diagram for the study search [40].
3.2. Characteristics of the Articles
The final analysis included a total of 13,320 participants with sample sizes ranging from 15 to 1507 in the individual studies. These studies were published between 1994 and 2020. The age of the participants ranged from 20 to over 80 years. The detailed characteristics of these studies are summarized in Table 1. The control group included 9390 individuals (3840 females, 5550 males) with normal body weight (18.5–24.99 kg/m2). The group with elevated leptin levels included 3930 individuals (1933 females, 1997 males) with excess body weight and obesity (25–35 kg/m2). The data were divided into two subgroups (“North” and “South”), according to the geographical zones of the research sites.

Table 1.
Characteristics of the individual studies included in this meta-analysis.
3.3. The Leptin Levels Depending on Climatic Conditions
Figure 3 presents a forest plot for the MD constructed from a random-effects model of the leptin levels between elevated leptin subjects and controls in the 22 eligible studies. In Figure 3a, in males’ subgroup, the point estimate (black diamond’s) does not intersect with the point estimate of the averaged studies (dotted line), which indicates that there are statistically significant differences. For females, the point estimate (black diamond’s) of the “North” and “South” groups intersect with the point estimate of the averaged studies (dotted line), which indicates that there are no significant differences (Figure 3b). Thus, analysis of subgroups by leptin levels depending on the climatic environment revealed statistically significant differences among the males of the “North” subgroup, where the average leptin level (10.02 ng/mL; CI: 7.92–12.13) was twice as high compared to the “South” subgroup (4.98 ng/mL; CI: 3.71–6.25) (p = 0.0001) (Figure 3a). However, no statistically significant differences were found in the females (p = 0.91) (Figure 3b).
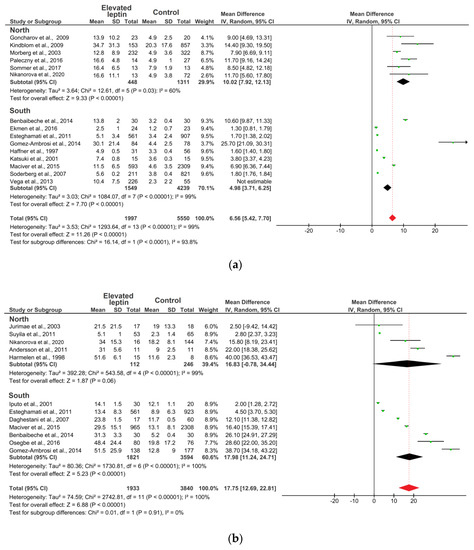
Figure 3.
Forest plot of meta-analysis: Mean difference in the circulating level of leptin in subjects with elevated leptin and controls: (a) males; (b) females. Note: Mean—average value; SD—standard deviation; Dotted line—the point estimate of the averaged studies; Black diamond—the point estimation; Red diamond—the average point estimation.
4. Discussion
For the first time, using published data, the meta-analysis was carried out to assess the influence of climatic conditions on the levels of leptin circulating in the blood of 13,320 individuals. The obtained results showed significant differences in leptin levels between “northern” and “southern” males, indicating the involvement of leptin in the key processes of thermoregulation and possibly in the mechanisms of human adaptation to cold environment. It is known that the mechanism of the regulation of thermoregulation and browning by leptin is associated with neurons of pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) in the arcuate nucleus [50,51,52,53]. Through the mechanism of leptin-dependent neuro-adipose linkage of nonshivering thermogenesis in BAT (Figure 4), leptin and its receptors in the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus increase the activity of POMC neurons, triggering the production and release of α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone. This hormone activates melanocortin-3 and 4 receptors, which increases the activity of the sympathetic nervous system and leads to an increased expression of uncoupling protein UCP1 in BAT [31,63]. In the BAT, noradrenaline is released as a response to signals from the hypothalamus which is activated by cold receptors in the skin. Furthermore, in the outer membrane of the brown fat cells, noradrenaline activates—via β-adrenalgenic receptors—adenylate cyclase in the cytosol of these cells to form cAMP. Via a protein kinase cascade, cAMP activates triglyceride lipase so that free fatty acids are formed. The released free fatty acids react with UCP1 and overcome UCP1 inhibition, wherein all the energy from the combustion of the substrate (food) is directly released as heat [64,65,66].
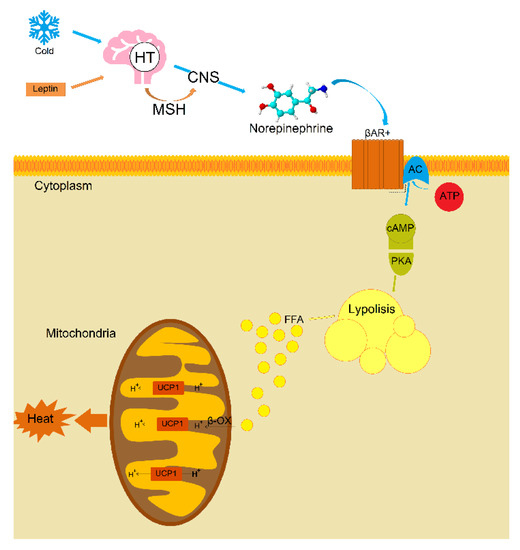
Figure 4.
Possible mechanism of leptin-dependent neuro-fatty linkage of nonshivering thermogenesis in brown adipose tissue (The figure adapted from the articles: [64,65,67]). Note: HP—hypothalamus, MSH—α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone, CNS—sympathetic nervous system, βAR—β-adrenaline receptors, AC—adenylate cyclase, ATP—adenosine triphosphate, cAMP—cyclic adenosine monophosphate, PKA—protein kinase A, FFA—free fatty acids, β-OX—β-oxidation.
The involvement of leptin in thermoregulation and energy homeostasis was also previously shown [38,39,68,69]. A study by Farooqi et al. [70] found that people with congenital leptin deficiency have mild hypothermia and low energy expenditure [70]. The body temperature and energy expenditure in these individuals were normalized with the introduction of exogenous leptin [70]. It can be assumed that, under the influence of low temperatures on the body, relatively high levels of leptin in the blood prevent a decrease in energy expenditure and body temperature, which, in turn, can be an adaptogenic mechanism to the effects of cold. The results of our study indicate that such effects are most pronounced in males and to a smaller extent in females, since it is known that females have a relatively high initial concentration of this adipokine in the blood due to their physiological features [70]. It was also previously suggested that women have relatively high levels of leptin due to a lower sensitivity to leptin in the central nervous system [71], as was shown in most obese humans having a leptin resistance [72]. The obtained results of the impact of the climatic environment on leptin levels suggest a possible leptin-dependent neuro-adipose connection between nonshivering thermogenesis and browning in people living in a cold climatic environment.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we showed a correlation between leptin levels and climatic environment data supporting the hypothesis of leptin-mediated thermoregulation as an adaptive mechanism to cold climates.
Author Contributions
Conceived and designed the meta-analysis, manuscript writing: A.A.N. and N.A.B. The collected data: S.S.N. and V.G.P. Analyzed the data: A.V.S., G.P.R. and S.S.K. Revision and approved the final version of manuscript: N.N.S., T.E.B., J.Ø.O. and S.A.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation (basic part of funding to M.K. Ammosov North-Eastern Federal University) and Russian Foundation for Basic Research (grants #18-05-600035_Arctika, #19-34-60023_Perspektiva).
Acknowledgments
We are thankful to all the authors whose articles contributed indispensable data for this systematic review and meta-analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Shephard, R.J. Health Consequences of ‘Modernization’: Evidence from Circumpolar Peoples, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Pääkkönen, T.; Leppäluoto, J. Cold Exposure and Hormonal Secretion: A Review. Int. J. Circumpolar Health 2002, 61, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjerregaard, P.; Dewailly, E.; Young, T.K.; Blanchet, C.; Hegele, R.A.; Ebbesson, S.E.O.; Risica, P.M.; Mulvad, G. Blood Pressure among the Inuit (Eskimo) Populations in the Arctic. Scand. J. Public Health 2003, 31, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedergaard, J.; Bengtsson, T.; Cannon, B. Unexpected Evidence for Active Brown Adipose Tissue in Adult Humans. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 293, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cypess, A.M.; Lehman, S.; Williams, G.; Tal, I.; Rodman, D.; Goldfine, A.B.; Kuo, F.C.; Palmer, E.L.; Tseng, Y.-H.; Doria, A.; et al. Identification and Importance of Brown Adipose Tissue in Adult Humans. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 1509–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Marken Lichtenbelt, W.D.; Vanhommerig, J.W.; Smulders, N.M.; Drossaerts, J.M.A.F.L.; Kemerink, G.J.; Bouvy, N.D.; Schrauwen, P.; Teule, G.J.J. Cold-Activated Brown Adipose Tissue in Healthy Men. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 1500–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virtanen, K.A.; Lidell, M.E.; Orava, J.; Heglind, M.; Westergren, R.; Niemi, T.; Taittonen, M.; Laine, J.; Savisto, N.-J.; Enerbäck, S.; et al. Functional Brown Adipose Tissue in Healthy Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 1518–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirbolooki, M.R.; Constantinescu, C.C.; Pan, M.-L.; Mukherjee, J. Quantitative Assessment of Brown Adipose Tissue Metabolic Activity and Volume Using 18F-FDG PET/CT and Β3-Adrenergic Receptor Activation. EJNMMI Res. 2011, 1, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orava, J.; Nuutila, P.; Lidell, M.E.; Oikonen, V.; Noponen, T.; Viljanen, T.; Scheinin, M.; Taittonen, M.; Niemi, T.; Enerbäck, S.; et al. Different Metabolic Responses of Human Brown Adipose Tissue to Activation by Cold and Insulin. Cell Metab. 2011, 14, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomskiy, M.I.; Chinti, S.; Tikhonov, D.G.; Loskutova, K.S.; Isakov, E.A. Brown Adipose Tissue and Extremely Cold Climate. Yakut Med. J. 2015, 49, 102–107. [Google Scholar]
- Cannon, B.; Nedergaard, J. Brown Adipose Tissue: Function and Physiological Significance. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 277–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efremova, A.; Senzacqua, M.; Venema, W.; Isakov, E.; Di Vincenzo, A.; Zingaretti, M.C.; Protasoni, M.; Thomski, M.; Giordano, A.; Cinti, S. A Large Proportion of Mediastinal and Perirenal Visceral Fat of Siberian Adult People Is Formed by UCP1 Immunoreactive Multilocular and Paucilocular Adipocytes. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kajimura, S.; Seale, P.; Kubota, K.; Lunsford, E.; Frangioni, J.V.; Gygi, S.P.; Spiegelman, B.M. Initiation of Myoblast/Brown Fat Switch through a PRDM16-C/EBP-β Transcriptional Complex. Nature 2009, 460, 1154–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrovic, N.; Walden, T.B.; Shabalina, I.G.; Timmons, J.A.; Cannon, B.; Nedergaard, J. Chronic Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor γ (PPARγ) Activation of Epididymally Derived White Adipocyte Cultures Reveals a Population of Thermogenically Competent, UCP1-Containing Adipocytes Molecularly Distinct from Classic Brown Adipocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 7153–7164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wahl, R. Responses of the Insulin Signaling Pathways in the Brown Adipose Tissue of Rats Following Cold Exposure. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cypess, A.M.; Haft, C.R.; Laughlin, M.R.; Hu, H.H. Brown Fat in Humans: Consensus Points and Experimental Guidelines. Cell Metab. 2014, 20, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonet, M.L.; Oliver, P.; Palou, A. Pharmacological and Nutritional Agents Promoting Browning of White Adipose Tissue. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids. 2013, 1831, 969–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez-Zamorano, N.; Fabbiano, S.; Chevalier, C.; Stojanović, O.; Colin, D.J.; Stevanović, A.; Veyrat-Durebex, C.; Tarallo, V.; Rigo, D.; Germain, S.; et al. Microbiota Depletion Promotes Browning of White Adipose Tissue and Reduces Obesity. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 1497–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; Fang, X.; Li, X.; Zhao, D.; Mo, F.; Jiang, G.; Yu, N.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Fu, M.; et al. Ginsenoside Rb1 Promotes Browning through Regulation of PPARγ in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 466, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahuri-Arisoylu, M.; Brody, L.P.; Parkinson, J.R.; Parkes, H.; Navaratnam, N.; Miller, A.D.; Thomas, E.L.; Frost, G.; Bell, J.D. Reprogramming of Hepatic Fat Accumulation and “browning” of Adipose Tissue by the Short-Chain Fatty Acid Acetate. Int. J. Obes. 2016, 40, 955–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargut, T.C.L.; Souza-Mello, V.; Aguila, M.B.; Mandarim-de-Lacerda, C.A. Browning of White Adipose Tissue: Lessons from Experimental Models. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 2017, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Sánchez, N.; Moreno-Navarrete, J.M.; Contreras, C.; Rial-Pensado, E.; Fernø, J.; Nogueiras, R.; Diéguez, C.; Fernández-Real, J.-M.; López, M. Thyroid Hormones Induce Browning of White Fat. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 232, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.-S.; Kim, E.-S.; Jung, J.-E.; Marciano, D.P.; Jo, A.; Koo, J.Y.; Choi, S.Y.; Yang, Y.R.; Jang, H.-J.; Kim, E.-K.; et al. PPARγ Antagonist Gleevec Improves Insulin Sensitivity and Promotes the Browning of White Adipose Tissue. Diabetes 2016, 65, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, K.; Ma, Y.; Qin, C.; Dong, C.; Jin, P.; Wu, Y.; Xiong, X.; Li, N.; Hu, C.; et al. Resveratrol Derivative BTM-0512 Mitigates Obesity by Promoting Beige Remodeling of Subcutaneous Preadipocytes. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2017, 49, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Wu, J.-Z.; Shen, J.; Chen, L.; He, T.; Jin, M.; Liu, H. Pentamethylquercetin Induces Adipose Browning and Exerts Beneficial Effects in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes and High-Fat Diet-Fed Mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.G.; Parks, J.S.; Kang, H.W. Quercetin, a Functional Compound of Onion Peel, Remodels White Adipocytes to Brown-like Adipocytes. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2017, 42, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Navarrete, J.M.; Serino, M.; Blasco-Baque, V.; Azalbert, V.; Barton, R.H.; Cardellini, M.; Latorre, J.; Ortega, F.; Sabater-Masdeu, M.; Burcelin, R.; et al. Gut Microbiota Interacts with Markers of Adipose Tissue Browning, Insulin Action and Plasma Acetate in Morbid Obesity. Mol. Nutr. Food. Res. 2018, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Proenca, R.; Maffei, M.; Barone, M.; Leopold, L.; Friedman, J.M. Positional Cloning of the Mouse Obese Gene and Its Human Homologue. Nature. 1994, 372, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, E.D.; Maffei, M.; Braden, V.V.; Proenca, R.; DeSilva, U.; Zhang, Y.; Chua, S.C.; Leibel, R.L.; Weissenbach, J.; Friedman, J.M. The Human Obese (OB) Gene: RNA Expression Pattern and Mapping on the Physical, Cytogenetic, and Genetic Maps of Chromosome 7. Genome Res. 1995, 5, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahima, R.S.; Bjorbaek, C.; Osei, S.; Flier, J.S. Regulation of Neuronal and Glial Proteins by Leptin: Implications for Brain Development*. Endocrinology 1999, 140, 2755–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowley, M.A.; Smart, J.L.; Rubinstein, M.; Cerdán, M.G.; Diano, S.; Horvath, T.L.; Cone, R.D.; Low, M.J. Leptin Activates Anorexigenic POMC Neurons through a Neural Network in the Arcuate Nucleus. Nature 2001, 411, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baicy, K.; London, E.D.; Monterosso, J.; Wong, M.-L.; Delibasi, T.; Sharma, A.; Licinio, J. Leptin Replacement Alters Brain Response to Food Cues in Genetically Leptin-Deficient Adults. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 18276–18279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garfield, A.S.; Patterson, C.; Skora, S.; Gribble, F.M.; Reimann, F.; Evans, M.L.; Myers, M.G.; Heisler, L.K. Neurochemical Characterization of Body Weight-Regulating Leptin Receptor Neurons in the Nucleus of the Solitary Tract. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 4600–4607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haynes, W.G.; Morgan, D.A.; Walsh, S.A.; Mark, A.L.; Sivitz, W.I. Receptor-Mediated Regional Sympathetic Nerve Activation by Leptin. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 100, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarpace, P.J.; Matheny, M.; Pollock, B.H.; Tumer, N. Leptin Increases Uncoupling Protein Expression and Energy Expenditure. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 1997, 273, E226–E230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Yu, X.; Gonzales, F.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Wang, M.Y.; Richardson, C.; Witters, L.A.; Unger, R.H. PPARα is necessary for the lipopenic action of hyperleptinemia on white adipose and liver tissue. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 11848–11853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minokoshi, Y.; Kim, Y.-B.; Peroni, O.D.; Fryer, L.G.D.; Müller, C.; Carling, D.; Kahn, B.B. Leptin Stimulates Fatty-Acid Oxidation by Activating AMP-Activated Protein Kinase. Nature 2002, 415, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halaas, J.; Gajiwala, K.; Maffei, M.; Cohen, S.; Chait, B.; Rabinowitz, D.; Lallone, R.; Burley, S.; Friedman, J. Weight-Reducing Effects of the Plasma Protein Encoded by the Obese Gene. Science 1995, 269, 543–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havel, P.J.; Kasim-karakas, S.; Dubuc, G.R.; Muller, W.; Phinney, S.D. Gender Differences in Plasma Leptin Concentrations. Nat. Med. 1996, 2, 949–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; PRISMA Group. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haffner, S.; Miettinen, H.; Mykkänen, L.; Karhapää, P.; Rainwater, D.; Laakso, M. Leptin Concentrations and Insulin Sensitivity in Normoglycemic Men. Int. J. Obes. 1997, 21, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Van Harmelen, V.; Reynisdottir, S.; Eriksson, P.; Thorne, A.; Hoffstedt, J.; Lonnqvist, F.; Arner, P. Leptin Secretion from Subcutaneous and Visceral Adipose Tissue in Women. Diabetes 1998, 47, 913–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsuki, A.; Sumida, Y.; Gabazza, E.C.; Murashima, S.; Tanaka, T.; Furuta, M.; Araki-Sasaki, R.; Hori, Y.; Nakatani, K.; Yano, Y.; et al. Plasma Levels of Agouti-Related Protein Are Increased in Obese Men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 1921–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iputo, J.E.; Robinson, D.; Mguni, M. Serum Leptin Concentration in a Rural African Population. E. Afr. Med. J. 2001, 78, 484–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jürimäe, T.; Sudi, K.; Jürimäe, J.; Payerl, D.; Rüütel, K. Relationships between Plasma Leptin Levels and Body Composition Parameters Measured by Different Methods in Postmenopausal Women: Leptin Level and Body Composition in Women. Am. J. Hum. Biol. 2003, 15, 628–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morberg, C.M.; Tetens, I.; Black, E.; Toubro, S.; Soerensen, T.I.A.; Pedersen, O.; Astrup, A. Leptin and Bone Mineral Density: A Cross-Sectional Study in Obese and Nonobese Men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 5795–5800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daghestani, M.H.; Ozand, P.T.; Al-Himadi, A.R.; Al-Odaib, A.N. Hormonal Levels of Leptin, Insulin, Ghrelin, and Neuropeptide Y in Lean, Overweight, and Obese Saudi Females. Saudi Med. J. 2007, 28, 1191–1197. [Google Scholar]
- Söderberg, S.; Zimmet, P.; Tuomilehto, J.; Chitson, P.; Gareeboo, H.; Alberti, K.G.M.M.; Shaw, J.E. Leptin Predicts the Development of Diabetes in Mauritian Men, but Not Women: A Population–Based Study. Int. J. Obes. 2007, 31, 1126–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncharov, N.P.; Katsya, G.V.; Chagina, N.A.; Gooren, L.J. Testosterone and Obesity in Men under the Age of 40 Years. Andrologia 2009, 41, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kindblom, J.M.; Ohlsson, C.; Ljunggren, Ö.; Karlsson, M.K.; Tivesten, Å.; Smith, U.; Mellström, D. Plasma Osteocalcin Is Inversely Related to Fat Mass and Plasma Glucose in Elderly Swedish Men. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2009, 24, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteghamati, A.; Noshad, S.; Khalilzadeh, O.; Morteza, A.; Nazeri, A.; Meysamie, A.; Esteghamati, A.; Nakhjavani, M. Contribution of Serum Leptin to Metabolic Syndrome in Obese and Nonobese Subjects. Arch. Med. Res. 2011, 42, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, J.; Karpe, F.; Sjöström, L.-G.; Riklund, K.; Söderberg, S.; Olsson, T. Association of Adipose Tissue Blood Flow with Fat Depot Sizes and Adipokines in Women. Int. J. Obes. 2012, 36, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suyila, Q.; Cui, H.; Yang, L.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, R.; Su, X. Serum Leptin Concentrations in Mongolian Women. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2013, 7, e75–e80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, G.L.; Grundy, S.M. Metabolic Risk Susceptibility in Men is Partially Related to Adiponectin/Leptin Ratio. J. Obes. 2013, 2013, 409679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benbaibeche, H.; Haffaf, E.M.; Kacimi, G.; Oudjit, B.; Koceir, E. Pathophysiological Characterization of Metabolic Syndrome in Overweight, Obese and Type 2 Diabetic Algerian Subjects: Interest of Adipokines as Dysmetabolic Biomarkers. Ann. Biol. Clin. 2014, 72, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Ambrosi, J.; Catalán, V.; Rodríguez, A.; Andrada, P.; Ramírez, B.; Ibáñez, P.; Vila, N.; Romero, S.; Margall, M.A.; Gil, M.J.; et al. Increased Cardiometabolic Risk Factors and Inflammation in Adipose Tissue in Obese Subjects Classified as Metabolically Healthy. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 2813–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekmen, N.; Helvaci, A.; Gunaldi, M.; Sasani, H.; Yildirmak, S.T. Leptin as an Important Link between Obesity and Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Men with Acute Myocardial Infarction. Indian Heart J. 2016, 68, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacIver, N.J.; Thomas, S.M.; Green, C.L.; Worley, G. Increased Leptin Levels Correlate with Thyroid Autoantibodies in Nonobese Males. Clin. Endocrinol. 2016, 85, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osegbe, I.; Okpara, H.; Azinge, E. Relationship between Serum Leptin and Insulin Resistance among Obese Nigerian Women. Ann. Afr. Med. 2016, 15, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paleczny, B.; Siennicka, A.; Zacharski, M.; Jankowska, E.A.; Ponikowska, B.; Ponikowski, P. Increased Body Fat Is Associated with Potentiation of Blood Pressure Response to Hypoxia in Healthy Men: Relations with Insulin and Leptin. Clin. Auton. Res. 2016, 26, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, C.; Lee, S.; Gulseth, H.L.; Jensen, J.; Drevon, C.A.; Birkeland, K.I. Soluble Leptin Receptor Predicts Insulin Sensitivity and Correlates With Upregulation of Metabolic Pathways in Men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 1024–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikanorova, A.A.; Barashkov, N.A.; Nahodkin, S.S.; Pshennikova, V.G.; Solov’ev, A.V.; Romanov, G.P.; Kuz’mina, S.S.; Sazonov, N.N.; Fedorova, S.A. Analiz urovnja leptina u jakutov (vostochnaja sibir) i ego rol’ v adaptacii k holodnomu klimatu [Analysis of the leptin levelsin the yakuts (eastern siberia) and its role in adaptation to the cold climate]. Vopr. Biol. Med. Farm. Him. [Quest. Biol. Med Pharm. Chem.] 2020, 23, 9–15. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Commins, S.P.; Watson, P.M.; Levin, N.; Beiler, R.J.; Gettys, T.W. Central Leptin Regulates the UCP1 and Ob Genes in Brown and White Adipose Tissue via Different Beta-Adrenoceptor Subtypes. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 33059–33067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingenberg, M. Mechanism and Evolution of the Uncoupling Protein of Brown Adipose Tissue. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1990, 15, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skulachev, V.P. Anion Carriers in Fatty Acid-Mediated Physiological Uncoupling. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 1999, 31, 431–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, S.F.; Madden, C.J.; Tupone, D. Central Neural Regulation of Brown Adipose Tissue Thermogenesis and Energy Expenditure. Cell Metab. 2014, 19, 741–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaus, S.; Casteilla, L.; Bouillaud, F.; Ricquier, D. The Uncoupling Protein UCP: A Membraneous Mitochondrial Ion Carrier Exclusively Expressed in Brown Adipose Tissue. Int. J. Biochem. 1991, 23, 791–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelleymounter, M.A.; Cullen, M.J.; Baker, M.B.; Hecht, R.; Winters, D.; Boone, T.; Collins, F. Effects of the Obese Gene Product on Body Weight Regulation in Ob/Ob Mice. Science 1995, 269, 540–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, S.; Kuhn, C.M.; Petro, A.E.; Swick, A.G.; Chrunyk, B.A.; Surwit, R.S. Role of Leptin in Fat Regulation. Nature 1996, 380, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooqi, I.S.; Jebb, S.A.; Langmack, G.; Lawrence, E.; Cheetham, C.H.; Prentice, A.M.; Hughes, I.A.; McCamish, M.A.; O’Rahilly, S. Effects of Recombinant Leptin Therapy in a Child with Congenital Leptin Deficiency. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 879–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licinio, J.; Negrão, A.B.; Mantzoros, C.; Kaklamani, V.; Wong, M.-L.; Bongiorno, P.B.; Negro, P.P.; Mulla, A.; Veldhuis, J.D.; Cearnal, L.; et al. Sex Differences in Circulating Human Leptin Pulse Amplitude: Clinical Implications. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1998, 83, 4140–4147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Considine, R.V.; Sinha, M.K.; Heiman, M.L.; Kriauciunas, A.; Stephens, T.W.; Nyce, M.R.; Ohannesian, J.P.; Marco, C.C.; McKee, L.J.; Bauer, T.L. Serum Immunoreactive-Leptin Concentrations in Normal-Weight and Obese Humans. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 334, 292–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).