Abstract
Adsorption by activated carbons (AC) is an effective option for phenolic wastewater treatment. Three commercial AC, including coal-derived granular activated carbons (GAC950), coal-derived powdered activated carbons (PAC800), and coconut shell-derived powdered activated carbons (PAC1000), were utilized as adsorbent to study its viability and efficiency for phenol removal from wastewater. Pseudo-first order, pseudo-second order, and the Weber–Morris kinetic models were used to find out the kinetic parameters and mechanism of adsorption process. Further, to describe the equilibrium isotherms, the experimental data were analyzed by the Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm models. According to the experimental results, AC presented a micro/mesoporous structure, and the removal of phenol by AC was affected by initial phenol concentration, contact time, pH, temperature, and humic acid (HA) concentration. The pseudo-second order kinetic and Langmuir models were found to fit the experimental data very well, and the maximum adsorption capacity was 169.91, 176.58, and 212.96 mg/g for GAC950, PAC800, and PAC1000, respectively, which was attributed to differences in their precursors and physical appearance. Finally, it was hard for phenol to be desorbed in a natural environment, which confirmed that commercial AC are effective adsorbents for phenol removal from effluent wastewater.
1. Introduction
Activated carbons (AC) are carbonaceous materials with large specific surface area, superior porosity, high physicochemical-stability, and excellent surface reactivity, extensively used for adsorption of several environmental contaminants, gas separation, heterogeneous catalysis, gas storage, and gas masks, among others [1]. The worldwide demand of AC reached 12,804,000 tons in 2015, and the research into AC has also had an important increase, yielding a production of 17,516 research papers from 1995 to 2016 [2]. Almost all carbon-rich precursors can be converted to AC through stabilization (if required), carbonization, and activation [3]. Selection of the raw material depends not only on the anticipated role of carbon-surface functionalities for given applications, but on the availability and low cost of raw material. In China, coal and coconut shell are the most common precursors for the largescale synthesis of commercial AC. Moreover, there are two most common physical forms, in which AC are used, these being granular active carbons (GAC) and powdered active carbons (PAC) [4]. Various commercial AC with different properties are manufactured for different applications.
Phenol is an organic compound found in wastewater disposed from many industries, such as refinery, petrochemical, coal processing, pharmaceutical, polymeric resin, and pesticide industries, among others [5,6]. Currently, phenol is produced at a rate of about 6 million ton/year worldwide, with a significantly increasing trend [7]. Excessive inhalation or exposure to phenol can cause coma, convulsions, cyanosis, and other adverse reactions [5,7]. Phenol has also been registered as a priority pollutant by the US Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA), with a permissible limit of 0.1 mg/L in wastewater and 1 ug/mL in water supplies [8]. Several technologies, including adsorption [9], oxidation [10], membrane separation [11], biodegradation [12], and ion exchange [13], have been proposed for treatment of the phenol wastewaters. Among them, adsorption by AC is the most widely used and most powerful technique for the elimination of phenol.
The adsorption capacity and mechanisms of phenol adsorption by AC could be influenced by the properties of AC, such as specific surface area, surface functional groups, pore size distribution, and other surface characteristics. For example, Lorenc-Grabowska et al. (2016) [14] reported that the main mechanism determining phenol adsorption was micropore filling within a pore size of 0.8-1.4 nm. Zhang et al. (2016) [9] found that phenol adsorption capacity improved in comparison with the raw sample, owing to the decrease of total oxygen-containing functional groups on the thermal modified AC samples. The properties of AC are not only strongly dependent on AC feedstocks, but also on physical appearance. Despite vast studies on factors that influence the process of phenol uptake, there are relatively few studies focusing on the comparison of adsorption mechanisms for commercial AC produced from different feedstocks and different physical appearance. Another important aspect is that once the activated carbon is exhausted, it must be carefully disposed as hazardous waste. Various technologies including thermal regeneration [15], chemical regeneration [16], bio-regeneration [4], and ultrasound [17] can be used for the desorption of phenols from AC. However, the release mechanism of phenol under natural conditions has not been fully understood up until now. Therefore, the objectives of our work are (1) to investigate impacts of feedstock and physical appearance on the properties of commercial AC, as well as their difference of adsorption capacity of phenol; (2) to optimize phenol adsorption condition, kinetic model, and isotherm model for commercial AC; and (3) to determine desorption characteristics of the three commercial AC under different release conditions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
The commercial activated carbons were collected from Sichuan Nan-Ke Activated Carbon Co., Ltd (Chengdu, China) and were classified as GAC950, PAC800, and PAC1000, where GAC and PAC represent granular active carbons and powdered activated carbons, respectively, and the last characters 950, 800, and 1,000 represent the iodine values of activated carbons. In addition, GAC950 and PAC800 were produced by coal, whereas PAC1000 was produced by coconut shell. All of the AC were washed thoroughly with deionized water and ethanol to remove any water-soluble impurities and then dried at 110 °C. Phenol, 4-aminoantipyrine, potassium ferricyanide, and other relevant solvents were purchased from Chengdu Ke-Long Chemical Regent Co. (Chengdu, China). All chemical reagents were analytical grade and used directly without further purification.
2.2. Physical and Chemical Characterization of AC
The surface morphologies of AC were observed by scanning electron microscope (SEM, Hitachi SU3500, Tokyo, Japan) after coating with gold for 30 s. The AC textural properties (specific surface area (As), average pore size, and total pore volume) were determined on the basis of nitrogen adsorption/desorption isotherms at 77 K, using a Micrometrics Gemini 2390 system. The specific surface area was determined with the standard Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) method and cumulative pore volumes by Barrett–Joyner–Halenda analysis. Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy (Tracer-100, Tokyo, Japan) was applied to determine the surface chemistry of the AC. All the samples and the dried KBr were ground at a mass ratio of 1:100, and the spectra were recorded from 400 to 4000 cm−1. The pHPZC (point of zero charge) of AC was determined by mixing 1 g of each AC with 20 mL of CO2-free deionized water, according to the procedure described by Moreno-Castilla et al. (2000) [18].
2.3. Phenol Adsorption on AC
Several key parameters, including the initial concentration (10–400 mg/L), contact time (0–400 min), pH (3–11), temperature (20–60 °C), and the concentration of humid acid (HA, 0–100 mg/L) were systematically taken into account to optimize the adsorption conditions. A total of 50 mg of AC and 80 mL of phenol solution were added to polyethylene tubes, which were placed onto a water bath oscillator at 150 r/min. Afterwards, the carbons were filtered and the concentration of phenol was analyzed by 4-aminoantipyrine spectrophotometric method. Phenol solution (1 mL) was taken in a clean dry colorimetric tube, then the volume was fixed to 50 mL with deionized water. The pH of solution was adjusted by adding 0.5 mL buffer solution (20% ammonia-ammonium chloride solution), and then 1 mL of 4-aminoantipyrine and 1 mL of potassium ferricyanide were added and mixed well. In this method, phenol reacts with 4-aminoantipyrine in the presence of potassium ferricyanide to form a colored antipyrine dye [19,20]. The colored sample was measured by UV-1100 UV-visible spectrophotometer (Shanghai Mapada Instrument Co. Ltd., Shanghai, China) at 510 nm. The assays were performed in replicate (n = 3) and blank tests were realized. The adsorption percentage (R, %) and the amount of phenols (qe, mg/g) on AC at equilibrium were calculated according to Equations (1) and (2):
where C0 (mg/L) and Ce (mg/L) are the initial and equilibrium concentrations of phenol, respectively; V (L) is the volume of the phenol solution; and m (g) is the amount of AC applied for adsorption.
2.3.1. Adsorption Kinetic Models
The kinetics of adsorption is an important characteristic to define the efficiency of adsorption. In order to investigate the mechanism of adsorption and kinetic parameters, sorption data was analyzed using pseudo-first order (Equation (3)), pseudo-second order (Equation (4)), and the Weber–Morris model (Equation (5)) [21]. Compared with the pseudo-first order and pseudo-second order kinetic models, the Weber–Morris model can generally identify the diffusion mechanism and rate controlling steps affecting the kinetics of adsorption. If an adsorption process is solely governed by intraparticle diffusion, the initial part of the Weber–Morris plot is a straight line passing through the origin. Otherwise, the intraparticle diffusion is not the only rate-controlling step but some degree of the boundary layer diffusion (or external mass transfer) also controls the adsorption [22].
where t (min) and qt (mg/g) are, respectively, the adsorption time and the amount of phenol adsorbed on AC at any time, t; qe,exp (mg/g) and qe (mg/g) are the amount of phenol adsorbed at experimental-equilibrium and calculated-equilibrium, respectively; k1 (min−1), k2 (g/mg/min), and k3 (mg/g/min1/2) are the rate constants of the pseudo-first order, pseudo-second order, and the Weber–Morris models, respectively.
2.3.2. Adsorption Equilibrium Models
The equilibrium adsorption data were fitted by Langmuir (Equation (6)) and Freundlich (Equation (7)) isotherm equations. The Langmuir isotherm is valid for monolayer adsorption onto a surface with a finite number of identical sites, and it is based on the assumption of adsorption homogeneity, such as equally available adsorption sites, monolayer surface coverage, and no interactions between adsorbed species. The Freundlich equation is an empirical relationship in which it is assumed that the non-ideal adsorption takes place on a heterogeneous surface with different adsorption energy and characters. It has been successfully applied for applications involving multilayer adsorption [23,24].
where qe (mg/g) is the amount of phenol adsorbed at equilibrium, Ce (mg/L) is the equilibrium concentration of phenol, qm (mg/g) is the maximum adsorption capacity, and KL (L/mg) is the Langmuir adsorption constant. KF (mg/g) and 1/n (unitless) are the Freundlich model constants related to adsorption capacity and adsorption intensity, respectively.
2.4. Phenol Desorption on AC
Desorption studies were conducted using various solution (deionized water/acid/alkali) and the equilibration time was 24 h. Nine samples of 50 mg each of AC saturated with phenol at initial concentration of 300 mg/L were prepared. Six AC samples were taken to be used at desorption experiment by NaOH (pH 12) and H2SO4 (pH 3) solution, whereas the other samples were taken in polyethylene tubes, including only deionized water to determine amount of desorbed phenol by shaker. After equilibrium, the phenol concentration in the solution was measured. The assays were performed in replicate (n = 3) and the release percentage (Rd) was calculated through the following equation:
where Cd (mg/L) is the concentration of phenol in release solution; Vd (L) is the volume of the release solution, and Vd = 0.08 in this work; m (g) is the amount of AC applied for release; and qe (mg/g) is the amount of phenol on AC at equilibrium.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of AC
Activated carbon is generally described as an amorphous form of graphite with a random structure of graphite plates, having highly porous structure with a range of cracks and crevices reaching molecular dimensions. As shown in Figure 1, GAC950 demonstrated a skeletal structure with pores, whereas PAC800 and PAC1000 had a uniform morphology. Further, the number of pores in PAC1000 were found to be more than that of PAC800, and these were also relatively larger in size. The presence of cavities in the AC structure is favorable for the adsorption process because they enable the penetration of phenol molecules into the adsorbent [25,26].
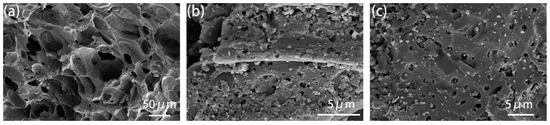
Figure 1.
Scanning electron microscope (SEM) images of (a) coal-derived granular activated carbons (GAC950), (b) coal-derived powdered activated carbons (PAC800), and (c) coconut shell-derived powdered activated carbons (PAC1000).
Physisorption with inert gas (N2) is one of the most common and effective ways to determine the specific surface area of porous materials. All the adsorption isotherms showed a mixture of type I and type IV isotherms. Thereafter, a hysteresis in the desorption of the N2 isotherm appeared. This result was consistent with the pore size distribution curve and demonstrated the microporosity to mesoporosity (1.5-50 nm) of AC (Figure 2) [27]. According to the nitrogen isotherms, GAC950, PAC800, and PAC1000 showed high surface areas of 700.57 m2/g, 542.33 m2/g, and 1025.02 m2/g, respectively. The average pore size defines the ability of the adsorbate molecules to penetrate inside the AC; only when the pores have a diameter larger than the effective molecular diameter of the adsorbate, the adsorbate molecules penetrate the adsorbent [28]. Phenol has an effective molecule diameter of 0.75 nm, and the average pore sizes presented by GAC950, PAC800, and PAC1000, were 2.22, 3.25, and 5.01 nm, respectively; all AC were suitable for phenol adsorption.
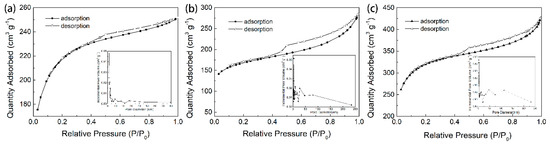
Figure 2.
Nitrogen adsorption-desorption isotherms and the Barrette–Joynere–Halenda desorption pore size distribution of (a) GAC950, (b) PAC800, and (c) PAC1000.
The functional groups on the AC (before adsorption and after adsorption) were measured by the FTIR spectroscopy, as depicted in Figure 3. The band at 3430 cm-1 referred to the O-H functional groups for all AC, and strong absorptions at around 1200 and 1500 cm-1 were observed, which might be assigned to C-H stretching of -CH3, -CH2 groups, and C=O stretching of quinone groups [8,25]. The presence of these oxygenated groups confers a negative charge density in AC surface. The phenol adsorption onto activated carbon occurred through the formation of a donor-acceptor complex between the electron donor groups (e.g., carbonyls) at the AC surface and the aromatic ring of the phenol that acts as the acceptor [14,29]. In addition, the hydroxyl adsorption band widened and a diffuse broad spectrum appeared after adsorption; which suggested that hydrogen bond also favor the phenol adsorption [30].
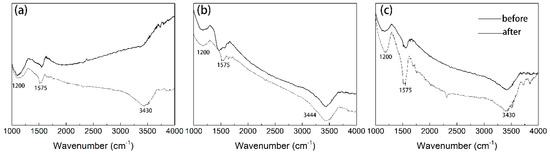
Figure 3.
FTIR spectra of (a) GAC950, (b) PAC800, and (c) PAC1000 before and after phenol adsorption.
3.2. Kinetics of Phenol Adsorption on AC
According to previous reports, qe of any adsorbent is highly dependent on the contact time with the adsorbate. The determination of equilibrium time of phenol adsorption was conducted at the initial phenol concentration range of 300 mg/L under neutral pH and temperature of 25 °C, and the experimental result is given in Figure 4. The rate of phenol adsorption was found to be very rapid during the initial 100 min. Thereafter, the adsorption capacity reached a plateau as the contact time increased further and exhibited adsorption at equilibrium after 180 min. This behavior can be explained because a large number of vacant surface sites are available for adsorption during the initial stage, and after a lapse of time, the remaining vacant surface sites are difficult to occupy due to repulsive forces between the solute molecules on the solid and bulk phases [31]. At equilibrium, the qe,exp of GAC950, PAC800, and PAC1000 were 169.91, 176.58, and 212.96 mg/g, respectively. It was also found that the removal of phenol by GAC950 was only slightly less than that by PAC800 at any contact time and that the removal of phenol by PAC800 was around 17% less than that by PAC1000.
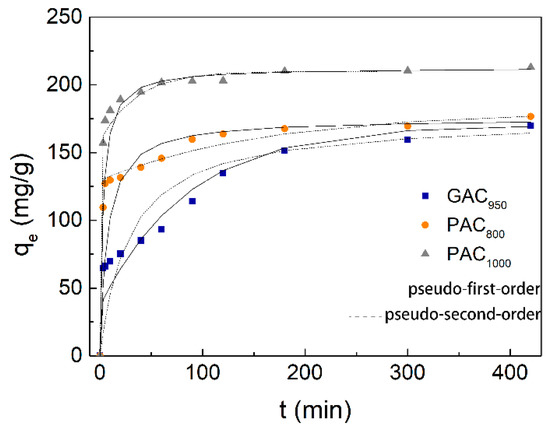
Figure 4.
Kinetic curves for phenol adsorption onto AC.
Pseudo-first order, pseudo-second order, and the Weber–Morris model kinetic parameters are represented in Table 1. The correlation coefficient for the pseudo-second order was higher than that of pseudo-first order kinetic model for both AC, and the calculated values of qe were extremely close to the experimental data (qe,exp), whereas the gap between calculated values and experimental data for pseudo-first-order model was more obvious. This indicated that the adsorption perfectly complied with pseudo-second order reaction and the adsorption of phenol appeared to be controlled by the chemisorption process simultaneously. In other words, the adsorption of phenol happened via surface exchange reactions until the surface functional sites were fully occupied; thereafter, phenol molecules diffused into the AC network for further interactions (such as inclusion complex, hydrogen bonding, hydrogen-phobic interactions) [32]. This result was consistent with the kinetics behavior of phenol adsorption on other AC samples [9,25]. On the other hand, the Weber–Morris plots were shown in Figure 5. The plots were not linear over the whole time range, implying that more than one process affected the adsorption, and the adsorption process contained both the surface adsorption and intraparticle diffusion. These behaviors can be explained due to the presence of micropores in the adsorbent.

Table 1.
Kinetic parameters for phenol adsorption onto AC.
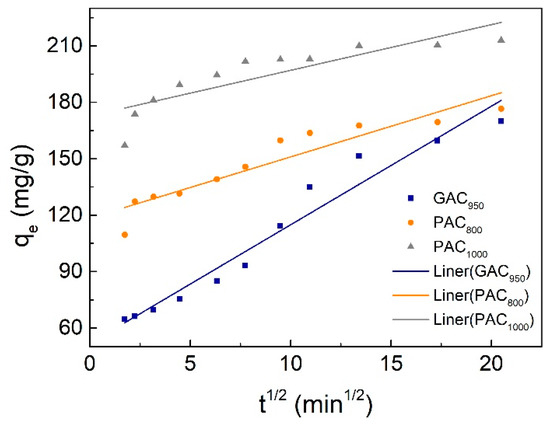
Figure 5.
Weber-Morris plot for phenol adsorption onto activated carbons (AC).
3.3. Isotherm of Phenol Adsorption on AC
We investigated the impact of initial phenol concentration (C0) by fixing adsorbent dose (50 mg) and contact time (≥420 min) under neutral pH and at ambient temperature (25 °C). As shown by the results in Figure 6, the amount of phenol adsorbed per unit weight of adsorbent increased with increasing C0. The C0 provided the necessary driving force to overcome the resistances to the mass transfer of phenol between aqueous and solid phases, and the increase in C0 also enhanced the interaction between phenol and AC [31]. Therefore, an increase in C0 of phenol enhanced the adsorption uptake of phenol. On the other hand, the adsorption efficiency (R%) of AC increased gradually at the beginning with increasing concentration of phenol. It decreased when the concentration increased further. This typical trend has been previously reported, and the reason can be mainly attributed to the saturated occupation of the adsorption sites of AC. In other words, at a lower concentration, the higher adsorption may be due to the presence of more available sites on the adsorbent than the number of phenol ions which are available in the solution. However, at higher concentrations, the number of phenol ions is relatively higher than available sites for adsorption [24]. The maximum adsorption percentage was determined at 30 mg/L as 69% for GAC950, 83% for PAC800, and 87% for PAC1000.
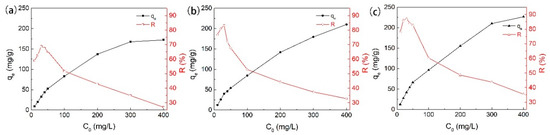
Figure 6.
Effects of the initial phenol concentrations on the adsorption on (a) GAC950, (b) PAC800, and (c) PAC1000.
The linear form of Langmuir and Freundlich isotherms of phenol on AC are shown in Figure 7 and the parameters of models are listed in Table 2. By comparing the coefficient of determination (R2), it can be concluded that the Langmuir model was more suitable to describe these sorption processes than the Freundlich model over the whole range of phenol concentrations; this indicated the homogeneous (monolayer) adsorption characteristics. In other words, AC had a uniform interfacial adsorption site for phenol [33]. PAC1000 had the highest adsorption capacity for phenol, and the maximum adsorption capacities calculated by the Langmuir isotherm were 246.31 mg/g. The next in line with a qmax of 232.02 mg/g was PAC800, and GAC950 was the lowest with an adsorption capacity of 214.13 mg/g. This can be explained by the fact that PAC1000 had the highest specific surface area and pore diffusion. Further, a possible explanation for the fact that the adsorption capacity of GAC950 was lower than PAC800 was the higher significance of pore diffusion and pore mouth closure in GAC [8,25].
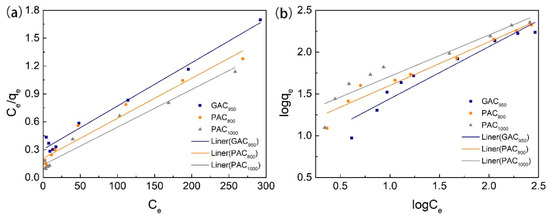
Figure 7.
Fitting curves of adsorption on phenol through the Langmuir (a) and Freundlich (b) models.

Table 2.
Equilibrium parameters for phenol adsorption onto AC.
3.4. The Effect of pH and Temperature on Phenol Adsorption
The pH of the solution is a critical parameter affecting the adsorption process because it affects the surface charge of the adsorbents as well as the degree of ionization and speciation of pollutants. It is a common observation that the surface adsorbs anions favorably at lower pH due to the presence of H+ ions, whereas the surface is active for the adsorption of cations at higher pH due to the deposition of OH− ions [34]. In this work, the effect of pH on the adsorption of phenol was investigated under five individual pH values of 3.0, 5.0, 7.0, 9.0, and 11.0. The initial concentration of phenol was 300 mg/L, the contact time was ≥420 min, and the adsorption temperature was controlled at 25 °C accordingly. As shown in Figure 8, the maximum adsorption was determined at pH 7 as 169.72 mg/g for GAC950 and 183.72 mg/g for PAC800. The maximum for PAC1000 was 200.96 mg/g at pH 5. The decrease in phenol adsorption as the pH dropped from 7(5) to 3 was mainly due to electrostatic repulsion. In detail, under acidic conditions, the pHPZC (point of zero charge) of AC (GAC950 7.4, PAC800 7.6, and PAC1000 5.7) were higher than the pH of solution, and there were many positive charges on the surface of AC. Further, the phenolic compounds were in the non-ionized forms, and the surface groups were either neutral or positively charged. The adsorption of water and phenol was competitive and the adsorbability of phenol was low. At pH >7(5), the decrease of phenol adsorption may have resulted from two reasons. First, the negative charges on the surface of AC increased with pH and phenol changed from molecular state to ionic state, which made the repulsion force between phenol ions and AC significant. Second, phenolate anions were more soluble in the aqueous solution, and stronger adsorbate–water bonds must be broken before adsorption can take place [7,20].
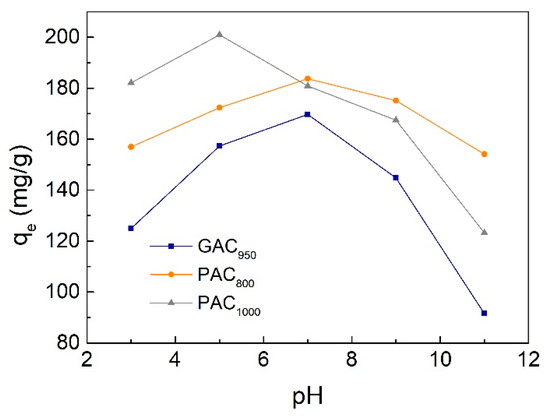
Figure 8.
Effect of initial pH value on phenol adsorption onto AC.
Temperature is another important parameter for removing phenol from wastewater, and it is desirable to obtain a high qe under room temperature without additional energy consumption. Figure 9 represents the experimental results of temperature effect on phenol adsorption within the range of 20–60 °C. The adsorption capacity of AC for phenol increased with the increase of temperature when the temperature was lower than 30 °C; however, when the temperature was higher than 30 °C, the adsorption capacity of AC decreased with the increase of temperature. At 30 °C, the qe values of GAC950, PAC800, and PAC1000, were 170.48, 182.77, and 200.49 mg/g, respectively. Because sorption is an exothermic process, it would be expected that an increase in temperature of the adsorbate–adsorbent system would result in decreased sorption capacity. However, if the adsorption process is controlled by the diffusion process (intraparticle transport-pore diffusion), the sorption capacity will show an increase with an increase in temperatures [31]. As has been shown earlier, the diffusion of adsorbate into pores of the sorbent was also a rate-controlling step. Therefore, the increase in sorption capacity with an increase in low temperature may be attributed to the diffusion process playing an important role. On the other hand, the active binding sites of AC were damaged and the binding forces between the phenol molecules and AC were weakened at a higher temperature; thus, the trend of desorption of phenol from the interface to the solution was increased [14,34].
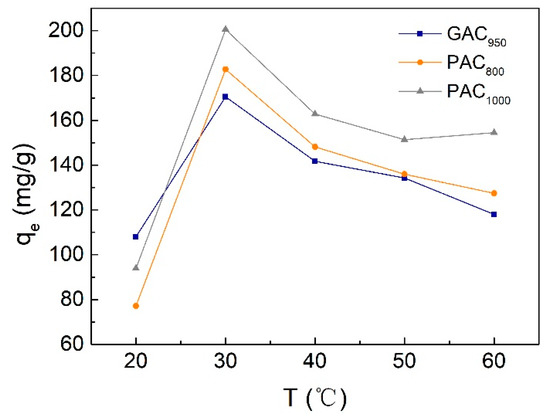
Figure 9.
Effect of temperature value on phenol adsorption onto AC.
3.5. The Effect of Humic Acid (HA) on Phenol Adsorption
The humic acid was combined with phenol to investigate the adsorption between humic acid (HA) and phenol for ACs in our work. As is shown in Figure 10, when the concentration of HA was 10 mg/L, qe decreased from 170.39 to 146.96 mg/g, 180.58 to 159.15 mg/g, and 210.01 to 186.87 mg/g for GAC950, PAC800, and PAC1000, respectively, with decrease rates of 13.75%, 11.87%, and 11.02%, respectively. Then, as the concentrations of HA increased, the qe value increased slowly; however, it was still lower than the qe without HA. The adsorption capacity of phenol on AC was decreased in the presence of HA because of competition by HA with phenol, either site competition or pore/interstice blockage [35]. In this case, the humic acid had an average molecular weight of 1716 ± 478 (by number) or 3303 ± 904 g/mol (by mass), whereas phenol had a molecular weight of 94 g/mol. It was unlikely that the humic acid would be capable of occupying the small pores energetically preferred by the phenol molecules. It was speculated that hydrophilic groups such as carboxyl group, hydroxyl group, and phenolic hydroxyl group in HA molecular structure were easy to unite with the oxygen-containing groups of AC, forming complex on the AC surface and thus blocking the adsorption site of AC [36]. Moreover, HA behaved as polyelectrolytes in solution and changed the surface charge of AC by making AC more negative, which increase adsorption of phenol reasonably. Some researchers have also concluded that the increased adsorption is due to desorption of poreblocking phenol [37].
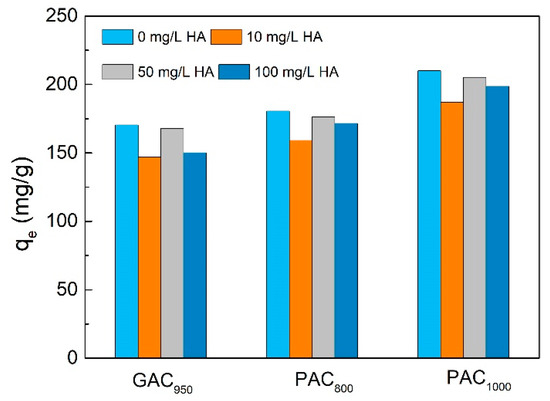
Figure 10.
Effect of humic acid (HA) concentration on phenol adsorption onto AC.
3.6. Desorption Study
Desorption studies help elucidate the mechanism of adsorption and recover the precious phenols, water, and adsorbent. Attempts were made to desorb phenol from the spent carbons using various solutions (deionized water/acid/alkali), and the results are shown in Figure 11. The release rate of AC in alkali was higher than that of acid and deionized water. This may be attributed to the formation of salt of phenol, which may have facilitated desorption of phenol from the carbon surfaces and weakened the interaction between phenol and AC [19]. Further, the desorption rates of phenol from PAC800 and PAC1000 in deionized water were 13% and 12%, respectively, whereas for GAC950 it was only 9%, which may have been caused by the small pore size of GAC950. Phenol has the high affinity of the compounds to AC, and it’s hard to desorption after it penetrates into the smaller pores of AC [38].
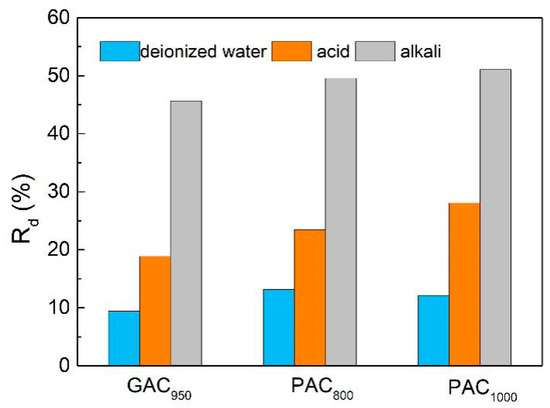
Figure 11.
The phenol release percentage of AC.
4. Conclusions
The results concluded that the feedstock and physical appearance had a great effect on the properties of commercial AC and that they would impact the capacity and mechanism of phenol adsorption on commercial AC. Although the surface area values of GAC950 were higher than PAC800, both adsorption rate and the adsorption capacity of GAC950 were found to be lower than PAC800. A possible explanation for this observation was the higher pore diffusion in PAC800. Compared with PAC800, PAC1000 was derived from coconut shell, possessing higher surface area and pore diffusion, and had the highest adsorption capacity for phenol. Additionally, the effects of several parameters, including the pH, temperature, initial phenol concentration, and contact time, were systematically investigated, and the desirable adsorption conditions, adsorption kinetics model, and equilibrium model for phenol were obtained. More importantly, the three commercial AC are suitable to be used for emergency treatment of phenol accidents because of their low desorption ratio in possible release conditions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.X. and H.S.; methodology, B.X. and J.Q.; software, B.X.; validation, B.X., S.W., and X.L.; formal analysis, B.X.; investigation, B.X., S.W., and X.L.; resources, J.Q. and W.C.; data curation, B.X.; writing—original draft preparation, B.X.; writing—review and editing, H.S.; visualization, B.X. and H.S.; supervision, H.S.; project administration, H.S.; funding acquisition, H.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key Technology R&D Program of China (2018YFC1900103).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sevilla, M.; Mokaya, R. Energy storage applications of activated carbons: Supercapacitors and hydrogen storage. Energy Env. Sci. 2014, 7, 1250–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-García, P. Activated carbon from lignocellulosics precursors: A review of the synthesis methods, characterization techniques and applications. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2018, 82, 1393–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz-Guillena, M.J.; Illán-Gómez, M.J.; Martin-Martinez, J.M.; Linares-solano, A.; Salinas-Martinez de Lecea, C. Activated carbons from Spanish coals. 1. Two-stage carbon dioxide activation. Energ. Fuel. 1992, 6, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Gamal, M.; Mousa, H.A.; El-Naas, M.H.; Zacharia, R.; Judd, S. Bio-regeneration of activated carbon: A comprehensive review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 197, 345–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmaruzzaman, M. Adsorption of phenolic compounds on low-cost adsorbents: A review. Adv. Colloid. Interf. Sci. 2008, 143, 48–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabrowski, A.; Podkoscielny, P.; Hubicki, Z.; Barczak, M. Adsorption of phenolic compounds by activated carbon-a critical review. Chemosphere 2005, 58, 1049–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busca, G.; Berardinelli, S.; Resini, C.; Arrighi, L. Technologies for the removal of phenol from fluid streams: A short review of recent developments. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 160, 265–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, J.; Wu, J.; Alsaedi, A.; Hayat, T.; Li, J. Insight into the mechanism of adsorption of phenol and resorcinol on activated carbons with different oxidation degrees. Colloid. Surf. A 2019, 563, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Huo, P.; Liu, W. Behavior of phenol adsorption on thermal modified activated carbon. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2016, 24, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Gao, Y.; Pang, S.Y.; Lu, X.T.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, J.; Wang, Q. Understanding the role of manganese dioxide in the oxidation of phenolic compounds by aqueous permanganate. Env. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Zhou, J.; Tan, Y.; Zhang, A.; Xia, Y.; Ji, L. Treatment of highly-concentrated phenol wastewater with an extractive membrane reactor using silicone rubber. Desalination 2006, 195, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.K.; Philip, L. Effect of cyanide on phenolics and aromatic hydrocarbons biodegradation under anaerobic and anoxic conditions. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 256, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caetano, M.; Valderrama, C.; Farran, A.; Cortina, J.L. Phenol removal from aqueous solution by adsorption and ion exchange mechanisms onto polymeric resins. J. Colloid. Interf. Sci. 2009, 338, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenc-Grabowska, E.; Diez, M.A.; Gryglewicz, G. Influence of pore size distribution on the adsorption of phenol on PET-based activated carbons. J. Colloid. Interf. Sci. 2016, 469, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevskaia, D.M.; Guerrero-Ruiz, A. Comparative study of the adsorption from aqueous solutions and the desorption of phenol and nonylphenol substrates on activated carbons. J. Colloid. Interf. Sci. 2001, 234, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinkus, K.; Reed, B.E.; Lin, W. NaOH regeneration of Pb and phenol-laden activated carbon. I. batch study results. Sep. Sci. Technol. 1997, 32, 2367–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juang, R.S.; Lin, S.H.; Cheng, C.H. Liquid-phase adsorption and desorption of phenol onto activated carbons with ultrasound. Ultras. Sonoch. 2006, 13, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Castilla, C.; López-Ramón, M.V.L.; Carrasco-Marín, F. Changes in surface chemistry of activated carbons by wet oxidation. Carbon 2000, 38, 1995–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkaya, B. Adsorption and desorption of phenol on activated carbon and a comparison of isotherm models. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 129, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LÜ, G.; Hao, J.; Liu, L.; Ma, H.; Fang, Q.; Wu, L.; Wei, M.; Zhang, Y. The Adsorption of Phenol by Lignite Activated Carbon. Chinese J. Chem. Eng. 2011, 19, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. A Comparison of Chemisorption Kinetic Models Applied to Pollutant Removal on Various Sorbents. Process Saf. Env. 1998, 76, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Song, X.; Liu, X.; Yang, L.; Pan, F.; Lv, J. Studies on the removal of tetracycline by multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 178, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, M.; Lv, Q. Influence of pyrolysis temperature on cadmium removal capacity and mechanism by maize straw and platanus leaves biochars. IJERPH 2019, 16, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhao, W.; Wang, X.; Shi, Y.; Fan, H.; Sun, H.; Tan, L. Facile synthesis of a triptycene-based porous organic polymer with a high efficiency and recyclable adsorption for organic dyes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lütke, S.F.; Igansi, A.V.; Pegoraro, L.; Dotto, G.L.; Pinto, L.A.A.; Cadaval, T.R.S. Preparation of activated carbon from black wattle bark waste and its application for phenol adsorption. J. Env. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tancredi, N.; Medero, N.; Moller, F.; Piriz, J.; Plada, C.; Cordero, T. Phenol adsorption onto powdered and granular activated carbon, prepared from Eucalyptus wood. J. Colloid. Interf. Sci. 2004, 279, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S.W. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, D.H.; Robinson, C.W. A microbial regeneration process for granular activated carbon—I. process modelling. Water Res. 1990, 24, 1209–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattson, J.A.; Mark, H.B.; Malbin, M.D.; Weber, W.J.; Crittenden, J.C. Surface chemistry of active carbon: Specific adsorption of phenols. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 1969, 31, 116–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, X.Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.Y.; Su, Y.Y.; Cai, L.Y.; Shu, Y.D. Adsorption model of phenol on activated carbon. Chinese J. Nonf. Metal. 2012, 22, 226–231. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, V.C.; Swamy, M.M.; Mall, I.D.; Prasad, B.; Mishra, I.M. Adsorptive removal of phenol by bagasse fly ash and activated carbon: Equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamics. Colloid. Surface. A. 2006, 272, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Wang, C.; Yan, Z.; Jiang, H.; Xu, H. Magnetic particles modification of coconut shell-derived activated carbon and biochar for effective removal of phenol from water. Chemosphere 2018, 211, 962–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yener, J.; Kopac, T.; Dogu, G.; Dogu, T. Dynamic analysis of sorption of Methylene Blue dye on granular and powdered activated carbon. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 144, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilic, M.; Apaydin-Varol, E.; Putun, A.E. Adsorptive removal of phenol from aqueous solutions on activated carbon prepared from tobacco residues: Equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 189, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, A.; Ormeci, B. Competitive effects of humic acid and wastewater on adsorption of Methylene Blue dye by activated carbon and non-imprinted polymers. J. Env. Sci. (China) 2018, 66, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Fitzgerald, M.; Khov, C.; Schafermeyer, A.; Kupferle, M.J.; Sorial, G.A. Elucidating the role of phenolic compounds in the effectiveness of DOM adsorption on novel tailored activated carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 262, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelekani, C.; Snoeyink, V.L. Competitive adsorption between atrazine and methylene blue on activated carbon: The importance of pore size distribution. Carbon 2000, 38, 1423–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, F.; Liu, C.; Li, G.G.; Liu, Y.F.; Li, Y.; Zhu, L.Y. Adsorption and Desorption of Dyes by Waste-Polymer-Derived Activated Carbons. Env. Sci. (Chinese) 2012, 33, 147–155. [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).