Meta-Analysis on the Effects of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation on Naming of Elderly with Primary Progressive Aphasia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
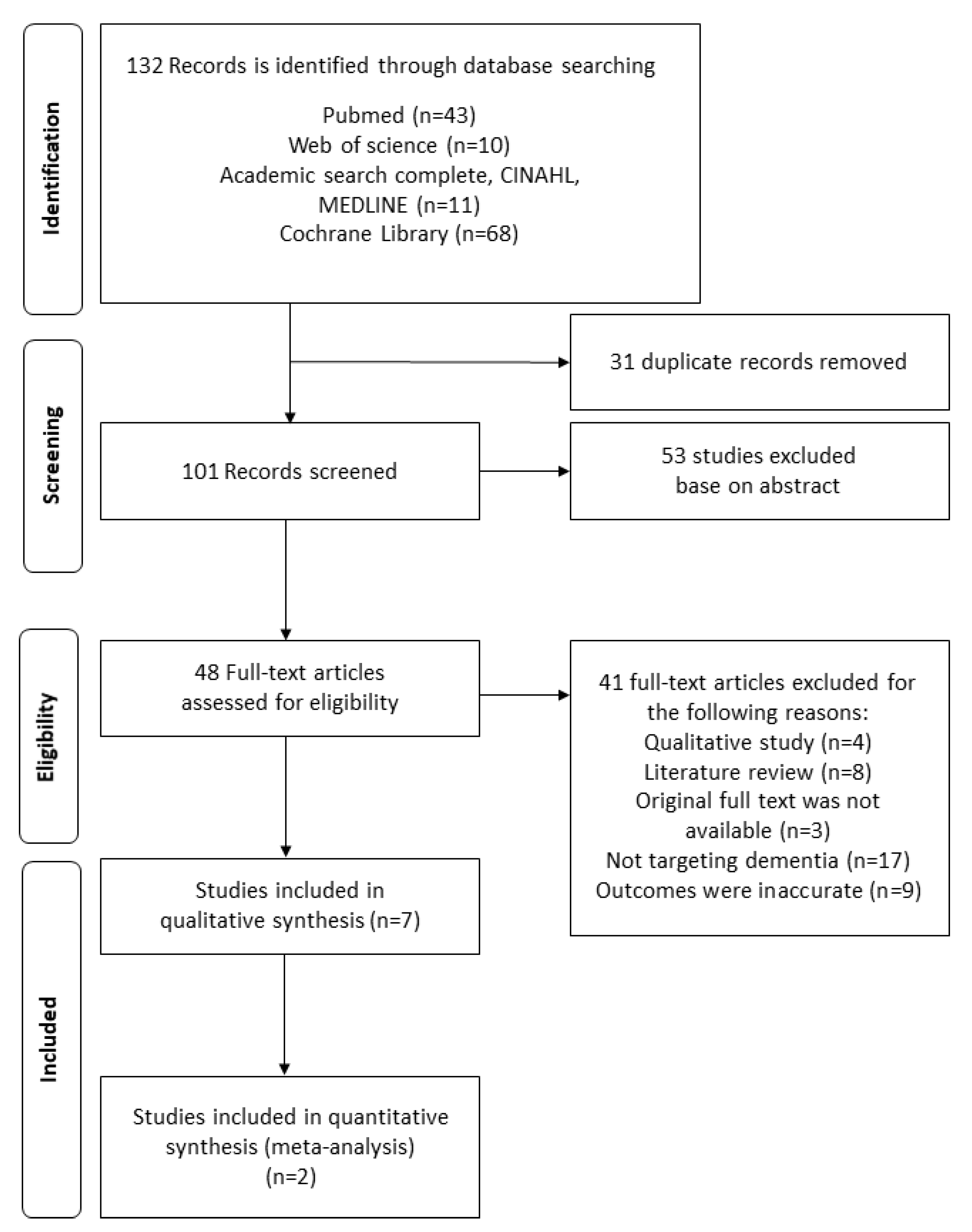
2.1. Literature Search
2.2. Literature Selection
2.3. Quality Assessment
2.4. Meta-Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Quality Assessment Results
3.2. Effects of tDCS on Improving the Naming Ability for PPA
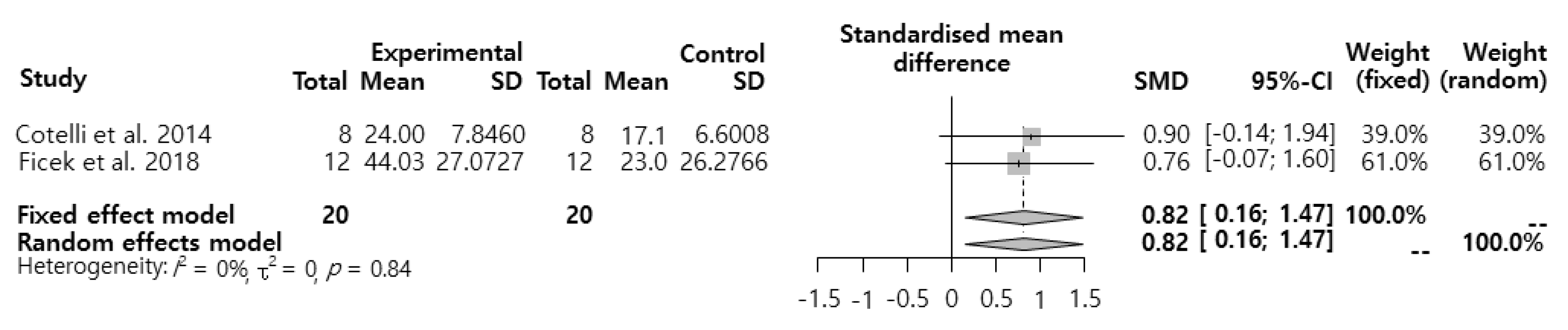
3.3. Meta-analysis for the Effects of tDCS Intervention on the Naming Performance of Patients with PPA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Laine, M.; Martin, N. Anomia: Theoretical and Clinical Aspects; Psychology Press: Hove, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Manning, L.; Warrington, E.K. Two routes to naming: A case study. Neuropsychologia 1996, 34, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glosser, G.; Donofrio, N. Differences between nouns and verbs after anterior temporal lobectomy. Neuropsychology 2001, 15, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, T.P. The reliability of cluster and switch scores for the Controlled Oral Word Association Test. Arch. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2003, 18, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laws, K.R.; Adlington, R.L.; Gale, T.M.; Moreno-Martínez, F.J.; Sartori, G. A meta-analytic review of category naming in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropsychologia 2007, 45, 2674–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klumpp, H.; Deldin, P. Review of brain functioning in depression for semantic processing and verbal fluency. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2010, 75, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppens, P. Aphasia and Related Neurogenic Communication Disorders; Jones & Bartlett Publishers: Burlington, VT, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jokel, R.; Graham, N.L.; Rochon, E.; Leonard, C. Word retrieval therapies in primary progressive aphasia. Aphasiology 2014, 28, 1038–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tak, S.; Hong, S.H. Face-name memory in Alzheimer’s disease. Geriatr. Nurs. 2014, 35, 290–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodges, J.R.; Erzinçlioğlu, S.; Patterson, K. Evolution of cognitive deficits and conversion to dementia in patients with mild cognitive impairment: A very-long-term follow-up study. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2006, 21, 380–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, A.; Gade, A.; Stokholm, J.; Waldemar, G. Semantic memory impairment in the earliest phases of Alzheimer’s disease. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2005, 19, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crinion, J.T. Transcranial direct current stimulation as a novel method for enhancing aphasia treatment effects. Eur. Psychol. 2016, 21, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helm-Estabrooks, N.; Albert, M.L. Manual of Aphasia and Aphasia Therapy; Pro-Ed Publishing: Austin, TX, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Bikson, M.; Grossman, P.; Thomas, C.; Zannou, A.L.; Jiang, J.; Adnan, T.; Mourdoukoutas, A.P.; Kronberg, G.; Truong, D.; Boggio, P.; et al. Safety of transcranial direct current stimulation: Evidence based update 2016. Brain Stimul. 2016, 9, 641–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, M.T.; Kasschau, M.; Dobbs, B.; Pawlak, N.; Pau, W.; Sherman, K.; Bikson, M.; Datta, A.; Charvet, L.E. Remotely supervised transcranial direct current stimulation: An update on safety and tolerability. J. Vis. Exp. 2017, 128, e56211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, L.; Koslowsky, M.; Lavidor, M. tDCS polarity effects in motor and cognitive domains: A meta-analytical review. Exp. Brain. Res. 2012, 216, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiozawa, P.; Fregni, F.; Benseñor, I.M.; Lotufo, P.A.; Berlim, M.T.; Daskalakis, J.Z.; Cordeiro, Q.; Brunoni, A.R. Transcranial direct current stimulation for major depression: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014, 17, 1443–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsner, B.; Kugler, J.; Pohl, M.; Mehrholz, J. Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) for improving aphasia in patients with aphasia after stroke. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horvath, J.C.; Forte, J.D.; Carter, O. Quantitative review finds no evidence of cognitive effects in healthy populations from single-session transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS). Brain Stimul. 2015, 8, 535–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 151, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kmet, L.M.; Lee, R.; Cook, L.S. Standard Quality Assessment Criteria for Evaluating Primary Research Papers from a Variety of Fields; Alberta Heritage Foundation for Medical Research: Edmonton, AB, Canada, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, L.; Packer, T.L.; Tang, S.H.; Girdler, S. Self-management education programs for age-related macular degeneration: A systematic review. Australas. J. Ageing 2008, 27, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, J.; Bauer, A.; Grossman, M.; Hamilton, R.H.; Coslett, H.B.; Reilly, J. Semantic feature training in combination with transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) for progressive anomia. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotelli, M.; Manenti, R.; Petesi, M.; Brambilla, M.; Cosseddu, M.; Zanetti, O.; Miniussi, C.; Padovani, A.; Borroni, B. Treatment of primary progressive aphasias by transcranial direct current stimulation combined with language training. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2014, 39, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficek, B.N.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Webster, K.T.; Desmond, J.E.; Hillis, A.E.; Frangakis, C.; Vasconcellos Faria, A.; Caffo, B.; Tsapkini, K. The effect of tDCS on functional connectivity in primary progressive aphasia. Neuroimage Clin. 2018, 19, 703–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsapkini, K.; Webster, K.T.; Ficek, B.N.; Desmond, J.E.; Onyike, C.U.; Rapp, B.; Frangakis, C.E.; Hillis, A.E. Electrical brain stimulation in different variants of primary progressive aphasia: A randomized clinical trial. Alzheimers Dement. 2018, 4, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsapkini, K.; Frangakis, C.; Gomez, Y.; Davis, C.; Hillis, A.E. Augmentation of spelling therapy with transcranial direct current stimulation in primary progressive aphasia: Preliminary results and challenges. Aphasiology 2014, 28, 1112–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConathey, E.M.; White, N.C.; Gervits, F.; Ash, S.; Coslett, H.; Grossman, M.; Hamilton, R.H. Baseline performance predicts tDCS-mediated improvements in language symptoms in primary progressive aphasia. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wu, D.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, M. Effects of transcranial direct current stimulation on language improvement and cortical activation in nonfluent variant primary progressive aphasia. Neurosci. Lett. 2013, 549, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohrer, J.D.; Knight, W.D.; Warren, J.E.; Fox, N.C.; Rossor, M.N.; Warren, J.D. Word-finding difficulty: A clinical analysis of the progressive aphasias. Brain 2008, 131, 8–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardiman, O.; Doherty, C.P.; Elamin, M.; Bede, P. Neurodegenerative Disorders; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Budd, M.A.; Kortte, K.; Cloutman, L.; Newhart, M.; Gottesman, R.F.; Davis, C.; Heidler-Gary, J.; Seay, M.W.; Hillis, A.E. The nature of naming errors in primary progressive aphasia versus acute post-stroke aphasia. Neuropsychology 2010, 24, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, L.F.; de Souza, I.C.; Vidor, L.P.; de Souza, A.; Deitos, A.; Volz, M.S.; Fregni, F.; Caumo, W.; Torres, I.L. Neurobiological effects of transcranial direct current stimulation: A review. Front. Psychiatry 2012, 3, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Lee, J. Application of transcranial direct current stimulation in psychiatry. J. Korean Neuropsychiatr. Assoc. 2016, 55, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Criteria | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study | ||||||||||||||||
| Wang, et al. 2013 [29] | + | + | ± | + | N/A | N/A | N/A | + | − | − | + | ± | ± | + | 15 | |
| Cotelli, et al. 2014b [24] | + | + | + | + | ± | + | + | + | ± | + | + | + | + | + | 26 | |
| Tsapkini, et al. 2014 [27] | + | + | ± | + | ± | − | + | + | ± | + | + | ± | + | + | 22 | |
| Hung, et al. 2017 [23] | + | + | ± | + | − | N/A | N/A | + | ± | + | ± | ± | + | + | 18 | |
| McConathey, et al. 2017 [28] | + | + | + | + | ± | − | + | + | ± | + | + | + | + | + | 24 | |
| Ficek, et al. 2018 [25] | + | + | ± | + | ± | + | + | + | + | + | + | ± | + | + | 25 | |
| Tsapkini, et al. 2018 [26] | + | + | ± | ± | ± | + | + | + | ± | ± | + | ± | + | + | 22 | |
| Study and Design | Participants | Intervention | Assessment | Outcomes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stimulated Region | tDCS | Sham tDCS | Session | ||||
| Ficek et al. (2018) [25] Blinding & Crossover & RCT Design | PPA (n = 24) tDCS (n = 12) : age = 65.2 ± 7.0 Sham (n = 12) : age = 69.1 ± 5.6 | Left inferior frontal gyrus | Anodal 2 mA 20 min | 30 s | 15 sessions (daily) | Letter accuracy (Written naming) | Both tDCS and sham groups improved the letter accuracy of trained words |
| Hung et al. (2017) [23] pre-post design | PPA (n = 4) & AD (n = 1) : age = 66.6±8.56) | Left temporoparietal region | Anodal 1.5 mA 20 min | 30 s | 10 sessions (2 weeks) | Naming : six semantic items (trained and untrained items) | After tDCS intervention, trained items were maintain longer than untrained items. |
| Cotelli et al. (2014b) [24] Blinding & RCT design | PPA (n = 16) AtDCS (n = 8) : age = 63.4 ± 6.8 Placebo tDCS (n = 8) : age = 70.4 ± 6.8 | Left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex | Anodal 2 mA 25 min | 10 s | 10 sessions (2 weeks) | Languistic abilities : Aachen Aphasia Tes (AAT) | Naming accuracy of the AtDCS group increased selectively during the pre–after intervention period. |
| McConathey et al. (2017) [28] Blinding & Crossover & RCT design | PPA (n = 15) : age = 68.71 ± 6.97 tDCS (n = 7, analysis n = 4), Sham (n = 8, analysis n = 3) | Left prefrontal region | Anodal 1.5 mA 20 min | 30 s | 10 sessions (2 weeks) | Sementic process : BNT, PPT, Category Fluency tests | Those with lower base scores have improved significantly since the actual tDCS compared to those with higher base scores. |
| Wang et al. (2013) [29] A1-B1-A2-B2 | PPA (n = 1) : age = 67 | Left posterior perisylvian region, left Broca’s area | B1–B2 Anodal 1.2 mA 20 min | A1–A2 30 s | 5 days (A1–A2) 5 days (B1–B2) | Psycolinguistic Assessment in Chinese Aphasia (PACA) | After the B1 intervention, the scores of the four PACA sub items increased significantly. |
| Tsapkini et al. (2014) [27] Blinding & Crossover & RCT design | PPA(n = 6) | Left inferior frontal gyrus | 1–2 mA 20 min | 30 s | 15 sessions | Number of correctly spelled word-prompts associated with each phoneme | Significant improvement has been maintained through the follow-up period under the tDCS. |
| Tsapkini et al. (2018) [26] Blinding & Crossover & RCT | PPA (n = 36) 1. tDCS (n = 20, crossover n = 15) 2. Sham (n = 16, crossover n = 15) | Left inferior frontal gyrus | 2 mA 20 min | 30 s | 15 sessions (5 sessions per week) | Letter accuracy : trained & untrained items | Trained items were significantly improved immediately after tDCS intervention. |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Byeon, H. Meta-Analysis on the Effects of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation on Naming of Elderly with Primary Progressive Aphasia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17031095
Byeon H. Meta-Analysis on the Effects of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation on Naming of Elderly with Primary Progressive Aphasia. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(3):1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17031095
Chicago/Turabian StyleByeon, Haewon. 2020. "Meta-Analysis on the Effects of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation on Naming of Elderly with Primary Progressive Aphasia" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 3: 1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17031095
APA StyleByeon, H. (2020). Meta-Analysis on the Effects of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation on Naming of Elderly with Primary Progressive Aphasia. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(3), 1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17031095





