Psoriasis Increases the Risk of Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss: A Longitudinal Follow Up Study Using a National Sample Cohort
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population and Data Collection
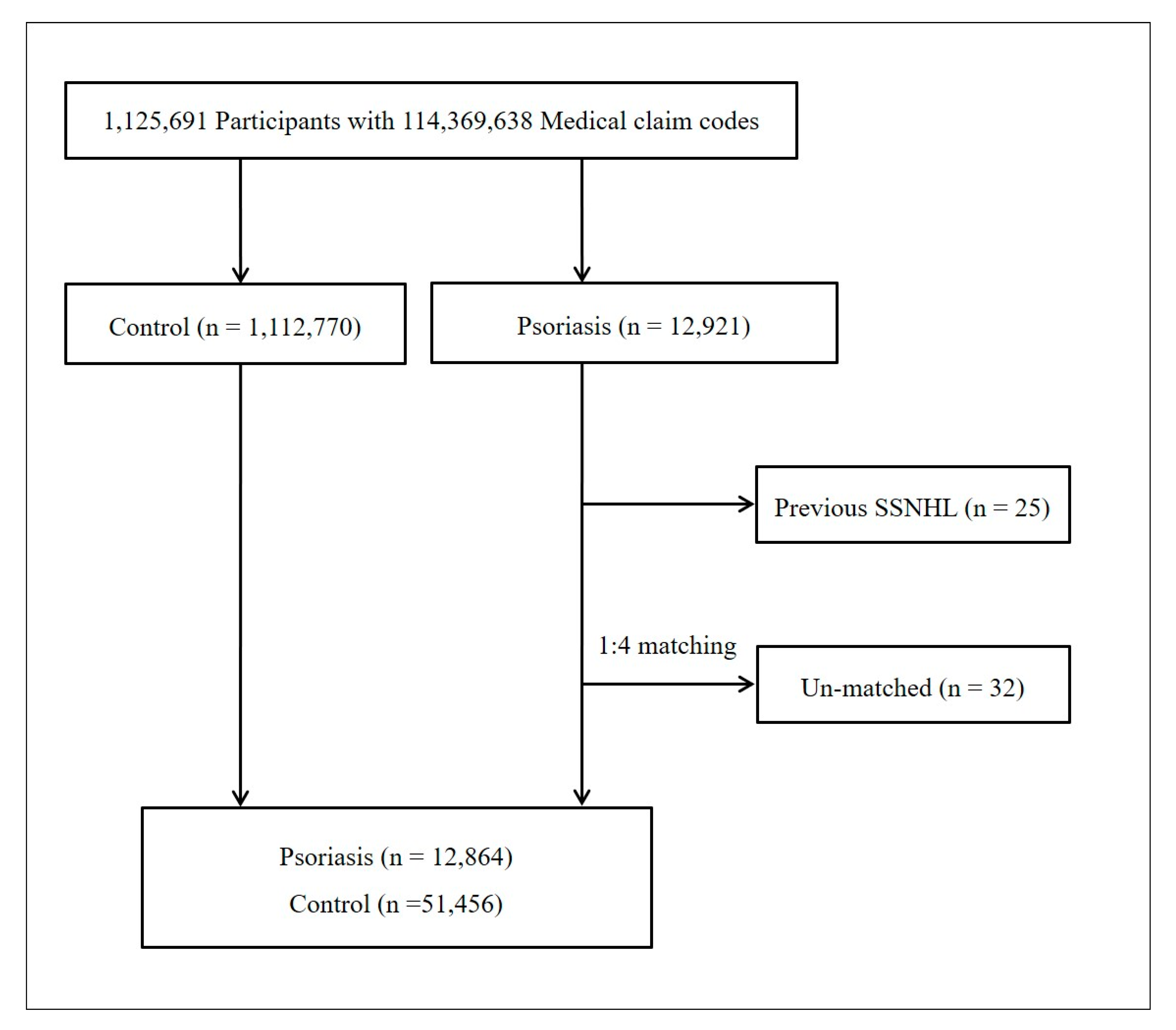
2.2. Participant Selection
2.3. Variables
2.4. Statistical Analyses
2.5. Availability of Data and Materials
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stachler, R.J.; Chandrasekhar, S.S.; Archer, S.M.; Rosenfeld, R.M.; Schwartz, S.R.; Barrs, D.M.; Brown, S.R.; Fife, T.D.; Ford, P.; Ganiats, T.G.; et al. Clinical practice guideline: Sudden hearing loss. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2012, 146 (Suppl. 3), S1–S35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosnier, I.; Stepanian, A.; Baron, G.; Bodenez, C.; Robier, A.; Meyer, B.; Fraysse, B.; Bertholon, P.; Defay, F.; Ameziane, N.; et al. Cardiovascular and thromboembolic risk factors in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A case-control study. Audiol. Neurootol. 2011, 16, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berrocal, J.R.; Ramírez-Camacho, R. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss: Supporting the immunologic theory. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2002, 111, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bovo, R.; Ciorba, A.; Martini, A. The diagnosis of autoimmune inner ear disease: Evidence and critical pitfalls. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2009, 266, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrup, C.; Luxon, L.M. Immune-mediated inner-ear disorders in neuro-otology. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2006, 19, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadoni, G.; Agostino, S.; Manna, R.; De Santis, A.; Fetoni, A.R.; Vulpiani, P.; Ottaviani, F. Clinical associations of serum antiendothelial cell antibodies in patients with sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Laryngoscope 2003, 113, 797–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, M.; Eliashar, R.; Ben-Yaakov, A.; Ulmansky, R.; Elidan, J. Prevalence and clinical significance of anticardiolipin, anti-beta2-glycoprotein-1, and anti-heat shock protein-70 autoantibodies in sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Audiol. Neurootol. 2008, 13, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Lin, S.W.; Weng, S.F.; Lin, Y.S. Risk of sudden sensorineural hearing loss in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: A population-based cohort study. Audiol. Neurootol. 2013, 18, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, Y.C.; Lin, Y.S.; Weng, S.F.; Lai, F.J. Risk of sudden sensorineural hearing loss in patients with psoriasis: A retrospective cohort study. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2015, 16, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Jung, A.R.; Kim, S.I.; Yeo, S.G. Refractory Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis Presenting as Facial Paralysis and Bilateral Sudden Deafness. J. Audiol. Otol. 2016, 20, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Saleem, M.D.; Feldman, S.R. Comorbidities in patients with psoriasis: The role of the dermatologist. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2017, 77, 191–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beringer, A.; Noack, M.; Miossec, P. IL-17 in Chronic Inflammation: From Discovery to Targeting. Trends Mol. Med. 2016, 22, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capo, A.; Di Nicola, M.; Auriemma, M.; Piaserico, S.; Cuccurullo, C.; Santilli, F.; Davi, G.; Amerio, P. Mean platelet volume variation after biologic therapy in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2014, 24, 133–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srikumar, S.; Deepak, M.K.; Basu, S.; Kumar, B.N. Sensorineural hearing loss associated with psoriatic arthritis. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2004, 118, 909–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, C.; Chiu, M.W. Psoriasis and comorbidities: Links and risks. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 7, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fiorentino, D.; Ho, V.; Lebwohl, M.G.; Leite, L.; Hopkins, L.; Galindo, C.; Goyal, K.; Langholff, W.; Fakharzadeh, S.; Srivastava, B.; et al. Risk of malignancy with systemic psoriasis treatment in the Psoriasis Longitudinal Assessment Registry. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2017, 77, 845–854.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chau, J.K.; Lin, J.R.; Atashband, S.; Irvine, R.A.; Westerberg, B.D. Systematic review of the evidence for the etiology of adult sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Laryngoscope 2010, 120, 1011–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahasitthiwat, V. A woman with sudden bilateral sensorineural hearing loss after treatment psoriasis with acitretin. J. Med. Assoc. Thail. 2005, 88 (Suppl. 1), S79–S81. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Lim, H.; Kong, I.G.; Kim, M.; Choi, H.G. Bidirectional association between gastroesophageal reflux disease and depression: Two different nested case-control studies using a national sample cohort. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Lim, J.S.; Kong, I.G.; Choi, H.G. Hearing impairment and the risk of neurodegenerative dementia: A longitudinal follow-up study using a national sample cohort. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Kong, I.G.; Oh, D.J.; Choi, H.G. Increased Risk of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo in Patients With a History of Sudden Sensory Neural Hearing Loss: A Longitudinal Follow-up Study Using a National Sample Cohort. Otol. Neurotol. 2019, 40, e135–e141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.Y.; Kong, I.G.; Oh, D.J.; Choi, H.G. Increased risk of sudden sensory neural hearing loss in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A longitudinal follow-up study using a national sample cohort. Clin. Rheumatol. 2019, 38, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Park, B.; Lim, H.; Kim, M.; Kong, I.G.; Choi, H.G. Gastroesophageal reflux disease increases the risk of chronic rhinosinusitis: A nested case-control study using a national sample cohort. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2019, 9, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.K.; Hong, S.M.; Park, I.S.; Choi, H.G. Association Between Migraine and Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Among Adults in South Korea. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2019, 145, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, H.; Li, B.; Couris, C.M.; Fushimi, K.; Graham, P.; Hider, P.; Januel, J.M.; Sundararajan, V. Updating and validating the Charlson comorbidity index and score for risk adjustment in hospital discharge abstracts using data from 6 countries. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 173, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutolo, M.; Sulli, A.; Straub, R.H. Estrogen metabolism and autoimmunity. Autoimmun. Rev. 2012, 11, A460–A464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisashi, K.; Komune, S.; Taira, T.; Uemura, T.; Sadoshima, S.; Tsuda, H. Anticardiolipin antibody-induced sudden profound sensorineural hearing loss. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 1993, 14, 275–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinz, J.C. From bench to bedside--translational research in psoriasis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2010, 24 (Suppl. 6), 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbach, S.; Croxford, A.L.; Oelze, M.; Schüler, R.; Minwegen, D.; Wegner, J.; Koukes, L.; Yogev, N.; Nikolaev, A.; Reißig, S.; et al. Interleukin 17 drives vascular inflammation, endothelial dysfunction, and arterial hypertension in psoriasis-like skin disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 2658–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyrrell, J.S.; Whinney, D.J.; Ukoumunne, O.C.; Fleming, L.E.; Osborne, N.J. Prevalence, associated factors, and comorbid conditions for Ménière’s disease. Ear Hear. 2014, 35, e162–e169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frejo, L.; Requena, T.; Okawa, S.; Gallego-Martinez, A.; Martinez-Bueno, M.; Aran, I.; Batuecas-Caletrio, A.; Benitez-Rosario, J.; Espinosa-Sanchez, J.M.; Fraile-Rodrigo, J.J.; et al. Regulation of Fn14 Receptor and NF-kappaB Underlies Inflammation in Meniere’s Disease. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, A.W.; Harskamp, C.T.; Ledo, L.; Rogers, J.H.; Armstrong, E.J. Coronary artery disease in patients with psoriasis referred for coronary angiography. Am. J. Cardiol. 2012, 109, 976–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidovici, B.B.; Sattar, N.; Prinz, J.; Puig, L.; Emery, P.; Barker, J.N.; van de Kerkhof, P.; Ståhle, M.; Nestle, F.O.; Girolomoni, G.; et al. Psoriasis and systemic inflammatory diseases: Potential mechanistic links between skin disease and co-morbid conditions. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2010, 130, 1785–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egeberg, A.; Mallbris, L.; Hilmar Gislason, G.; Skov, L.; Riis Hansen, P. Increased risk of migraine in patients with psoriasis: A Danish nationwide cohort study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2015, 73, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.C.; Kainz, V.; Burstein, R.; Levy, D. Tumor necrosis factor-α induces sensitization of meningeal nociceptors mediated via local COX and p38 MAP kinase actions. Pain 2011, 152, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, C.H.; Liu, C.J.; Fuh, J.L.; Shiao, A.S.; Chen, T.J.; Wang, S.J. Migraine is a risk factor for sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A nationwide population-based study. Cephalalgia 2013, 33, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, R.M.; Miller, A.; Scianna, J.M.; Stankiewicz, J.A. Chronic rhinosinusitis and psoriasis: Do mutually exclusive systemic Th1 and Th2 disease patterns exist? Acta Otolaryngol. 2007, 127, 780–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, J.J.; Wu, C.S.; Lin, H.C. Increased risk of psoriasis following chronic rhinosinusitis without nasal polyps: A population-based matched-cohort study. Br. J. Dermatol. 2013, 168, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wu, L.; Lu, C.; Wu, D. Analysis of miRNA-mRNA interaction network reveals gap junction beta 2 as a potential candidate gene involved in psoriatic hearing loss pathogenesis. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Press, E.R.; Shao, Q.; Kelly, J.J.; Chin, K.; Alaga, A.; Laird, D.W. Induction of cell death and gain-of-function properties of connexin26 mutants predict severity of skin disorders and hearing loss. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 9721–9732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Nicholson, B.J. The role of connexins in ear and skin physiology—Functional insights from disease-associated mutations. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1828, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | Total Participants | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Psoriasis (n, %) | Control (n, %) | p-Value | |
| Age (years old) | 1.000 | ||
| 0–4 | 127 (1.0) | 508 (1.0) | |
| 5–9 | 251 (2.0) | 1004 (2.0) | |
| 10–14 | 460 (3.6) | 1840 (3.6) | |
| 15–19 | 614 (4.8) | 2456 (4.8) | |
| 20–24 | 785 (6.1) | 3140 (6.1) | |
| 25–29 | 995 (7.7) | 3980 (7.7) | |
| 30–34 | 1138 (8.8) | 4552 (8.8) | |
| 35–39 | 1207 (9.4) | 4828 (9.4) | |
| 40–44 | 1235 (9.6) | 4940 (9.6) | |
| 45–49 | 1264 (9.8) | 5056 (9.8) | |
| 50–54 | 1179 (9.2) | 4716 (9.2) | |
| 55–59 | 937 (7.3) | 3748 (7.3) | |
| 60–64 | 807 (6.3) | 3228 (6.3) | |
| 65–69 | 715 (5.6) | 2860 (5.6) | |
| 70–74 | 583 (4.5) | 2332 (4.5) | |
| 75–79 | 317 (2.5) | 1268 (2.5) | |
| 80–84 | 167 (1.3) | 668 (1.3) | |
| 85+ | 83 (0.6) | 332 (0.6) | |
| Sex | 1.000 | ||
| Male | 7129 (55.4) | 28,516 (55.4) | |
| Female | 5735 (44.6) | 22,940 (44.6) | |
| Income | 1.000 | ||
| 1 (lowest) | 258 (2.0) | 1032 (2.0) | |
| 2 | 844 (6.6) | 3376 (6.6) | |
| 3 | 828 (6.4) | 3312 (6.4) | |
| 4 | 937 (7.3) | 3748 (7.3) | |
| 5 | 1066 (8.3) | 4264 (8.3) | |
| 6 | 1118 (8.7) | 4472 (8.7) | |
| 7 | 1294 (10.1) | 5176 (10.1) | |
| 8 | 1337 (10.4) | 5348 (10.4) | |
| 9 | 1540 (12.0) | 6160 (12.0) | |
| 10 | 1734 (13.5) | 6936 (13.5) | |
| 11 (highest) | 1908 (14.8) | 7632 (14.8) | |
| Charlson Comorbidity index | <0.001 * | ||
| 0 | 5674 (44.1) | 25,311 (49.2) | |
| 1 | 1553 (12.1) | 5990 (11.6) | |
| 2 | 1518 (11.8) | 5721 (11.1) | |
| 3 | 1231 (9.6) | 4373 (8.5) | |
| ≥4 | 2888 (22.5) | 10,061 (19.6) | |
| SSNHL | 69 (0.5) | 185 (0.4) | 0.004 * |
| Characteristics | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crude | p-Value | Adjusted †,‡ | p-Value | ||
| Psoriasis | 0.005 * | 0.010 * | |||
| Yes | 1.49 (1.13–1.97) | 1.44 (1.09–1.90) | |||
| No | 1.00 | 1.00 | |||
| Chaacteristics | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crude | p-Value | Adjusted †,‡ | p-Value | ||
| 0–29 years old, n = 16,160 | |||||
| Psoriasis | 0.381 | 0.471 | |||
| Yes | 1.47 (0.62–3.50) | 1.38 (0.57–3.29) | |||
| No | 1.00 | 1.00 | |||
| 30–59 years old, n = 34,800 | |||||
| Psoriasis | 0.011 * | 0.023 * | |||
| Yes | 1.57 (1.11–2.21) | 1.50 (1.06–2.12) | |||
| No | 1.00 | 1.00 | |||
| 60+ years old, n = 13,360 | |||||
| Psoriasis | 0.311 | 0.329 | |||
| Yes | 1.33 (0.77–2.30) | 1.32 (0.76–2.28) | |||
| No | 1.00 | 1.00 | |||
| Men, n = 35,645 | |||||
| Psoriasis | 0.003 * | 0.006 * | |||
| Yes | 1.77 (1.22–2.58) | 1.70 (1.17–2.49) | |||
| No | 1.00 | 1.00 | |||
| Women, n = 28,675 | |||||
| Psoriasis | 0.313 | 0.390 | |||
| Yes | 1.24 (0.82–1.86) | 1.20 (0.79–1.81) | |||
| No | 1.00 | 1.00 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, H.G.; Park, B.; Hong, S.M.; Park, I.-S.; Kim, S.K. Psoriasis Increases the Risk of Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss: A Longitudinal Follow Up Study Using a National Sample Cohort. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9310. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17249310
Choi HG, Park B, Hong SM, Park I-S, Kim SK. Psoriasis Increases the Risk of Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss: A Longitudinal Follow Up Study Using a National Sample Cohort. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(24):9310. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17249310
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Hyo Geun, Bumjung Park, Seok Min Hong, Il-Seok Park, and Sung Kyun Kim. 2020. "Psoriasis Increases the Risk of Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss: A Longitudinal Follow Up Study Using a National Sample Cohort" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 24: 9310. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17249310
APA StyleChoi, H. G., Park, B., Hong, S. M., Park, I.-S., & Kim, S. K. (2020). Psoriasis Increases the Risk of Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss: A Longitudinal Follow Up Study Using a National Sample Cohort. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(24), 9310. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17249310





