The Association between the Mental Health Nurse-to-Registered Nurse Ratio and Patient Outcomes in Psychiatric Inpatient Wards: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Nursing Skill Mix in Medical and Surgical Wards
1.2. Nursing Skill Mix and Patient Outcomes in Mental Health Settings
1.3. Why Is Admission to Hospital a Good Research Outcome?
1.4. Nursing Skill Mix on Mental Health Wards
1.5. Aims
1.6. Review Question
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
- Observational and experimental studies.
- Conducted in an acute-inpatient psychiatric unit.
- The manuscript was written in English.
- Involving patients aged 18 years or over.
- Reported registered mental health-to-registered nurse ratio as the measure of skill mix.
- Readmission to psychiatric inpatient care or referral to a mental health crisis team was a reported outcome.
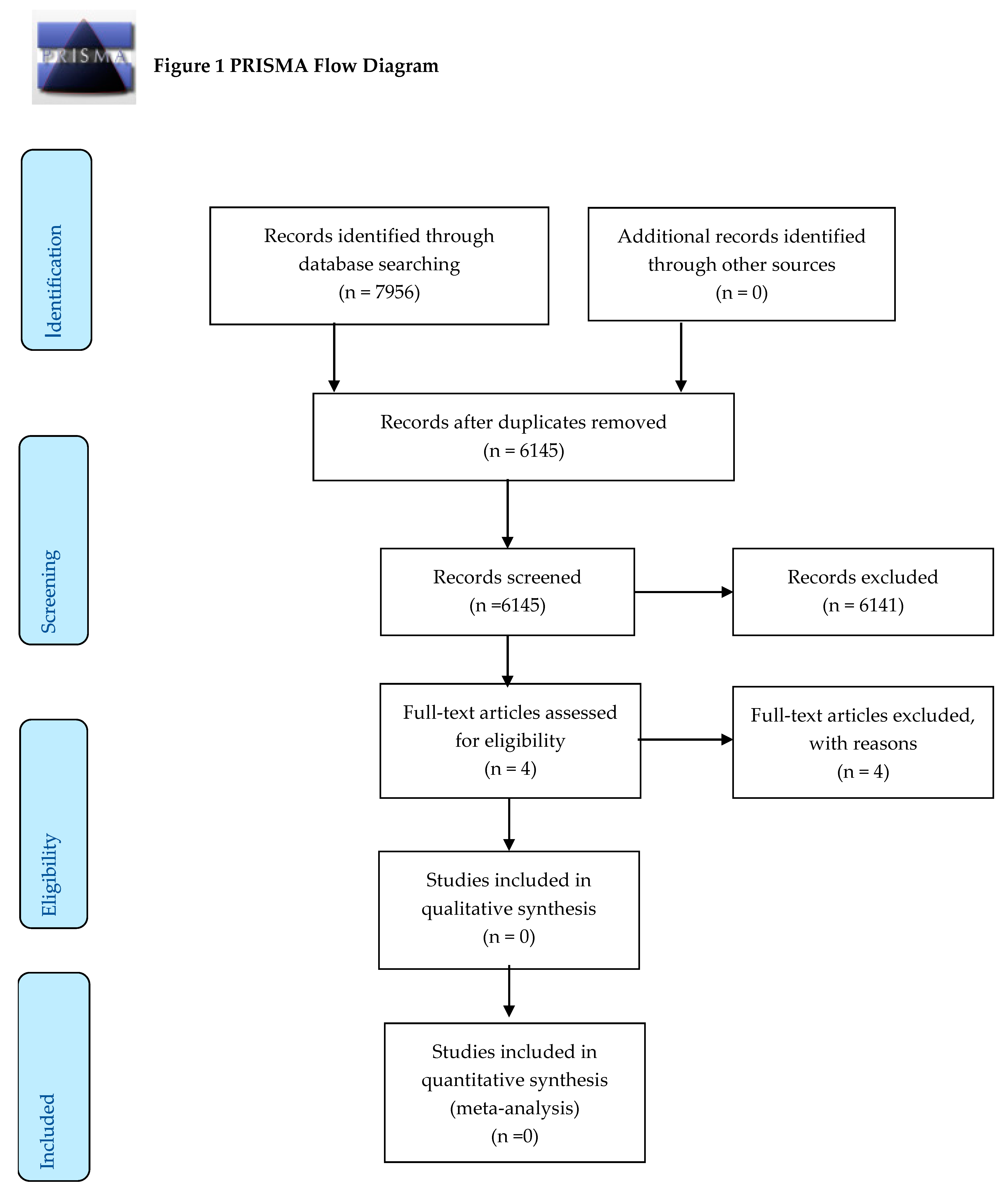
3. Results
Excluded Studies
4. Discussion
Review Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blegen, M.A.; Vaughn, T.E.; Goode, C.J. Nurse experience and education: Effect on quality of care. J. Nurs. Adm. 2001, 31, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiken, L.H.; Clarke, S.P.; Cheung, R.B.; Sloane, D.M.; Silber, J.H. Educational levels of hospital nurses and surgical patient mortality. JAMA 2003, 290, 1617–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasichay-Akkadechanunt, T.; Scalzi, C.C.; Jawad, A.F. The relationship between nurse staffing and patient outcomes. J. Nurs. Adm. 2003, 33, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estabrooks, C.A.; Midodzi, W.K.; Cummings, G.G.; Ricker, K.L.; Giovannetti, P. The Impact of Hospital Nursing Characteristics on 30-Day Mortality. Nurs. Res. 2005, 54, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutney-Lee, A.; Aiken, L.H. Effect of nurse staffing and education on the outcomes of surgical patients with comorbid serious mental illness. Psychiatr. Serv. 2008, 59, 1466–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sales, A.; Sharp, N.; Li, Y.-F.; Lowy, E.; Greiner, G.; Liu, C.-F.; Alt-White, A.; Rick, C.; Sochalski, J.; Mitchell, P.H.; et al. The association between nursing factors and patient mortality in the Veterans Health Administration: The view from the nursing unit level. Med. Care 2008, 46, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Heede, K.; Lesaffre, E.; Diya, L.; Vleugels, A.; Clarke, S.P.; Aiken, L.H.; Sermeus, W. The relationship between inpatient cardiac surgery mortality and nurse numbers and educational level: Analysis of administrative data. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2009, 46, 796–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucero, R.J.; Lake, E.T.; Aiken, L.H. Nursing care quality and adverse events in US hospitals. J. Clin. Nurs. 2010, 19, 2185–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sermeus, W.; Aiken, L.H.; Van den Heede, K.; Rafferty, A.M.; Griffiths, P.; Moreno-Casbas, M.T.; Busse, R.; Lindqvist, R.; Scott, A.P.; Bruyneel, L.; et al. Nurse forecasting in Europe (RN4CAST): Rationale, design and methodology. BMC Nurs. 2011, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiken, L.H.; Cimiotti, J.P.; Sloane, D.M.; Smith, H.L.; Flynn, L.; Neff, D.F. Effects of nurse staffing and nurse education on patient deaths in hospitals with different nurse work environments. J. Nurs. Adm. 2012, 42 (Suppl. 10), S10–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blegen, M.A.; Goode, C.J.; Park, S.H.; Vaughn, T.; Spetz, J. Baccalaureate education in nursing and patient outcomes. J. Nurs. Adm. 2013, 43, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutney-Lee, A.; Sloane, D.M.; Aiken, L.H. An increase in the number of nurses with baccalaureate degrees is linked to lower rates of postsurgery mortality. Health Aff. 2013, 32, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McHugh, M.D.; Kelly, L.A.; Smith, H.L.; Wu, E.S.; Vanak, J.M.; Aiken, L.H. Lower mortality in magnet hospitals. Med. Care 2013, 51, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, D.M.; Kutney-Lee, A.; McHugh, M.D.; Sloane, D.M.; Aiken, L.H. Impact of Critical Care Nursing on 30-Day Mortality of Mechanically Ventilated Older Adults. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 42, 1089–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yakusheva, O.; Lindrooth, R.; Weiss, M. Economic evaluation of the 80% baccalaureate nurse workforce recommendation: A patient-level analysis. Med. Care 2014, 52, 864–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiken, L.H.; Sloane, D.M.; Bruyneel, L.; Van den Heede, K.; Griffiths, P.; Busse, R.; Diomidous, M.; Kinnunen, J.; Kózka, M.; Lesaffre, E.; et al. Nurse staffing and education and hospital mortality in nine European countries: A retrospective observational study. Lancet 2014, 383, 1824–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; McHugh, M.D.; Aiken, L.H. Organization of Hospital Nursing and 30-Day Readmissions in Medicare Patients Undergoing Surgery. Med. Care 2015, 53, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, E.; Sloane, D.M.; Kim, E.-Y.; Kim, S.; Choi, M.; Yoo, I.Y.; Lee, H.S.; Aiken, L.H. Effects of nurse staffing, work environments, and education on patient mortality: An observational study. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2015, 52, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkantaras, I.; Mahfoud, Z.R.; Foreman, B.; Thompson, D.R.; Cannaby, A.-M.; Deshpande, D.H.; Watson, R.; Topping, A.; Gray, R. The effect of Nurse GraduaTeness on patient mortality: A cross sectional survey (the NuGaT study). J. Adv. Nurs. 2016, 72, 3034–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiken, L.H.; Sloane, D.; Griffiths, P.; Rafferty, A.M.; Bruyneel, L.; McHugh, M.; Maier, C.B.; Moreno-Casbas, M.T.; Ball, J.E.; Ausserhofer, D.; et al. Nursing skill mix in European hospitals: Cross-sectional study of the association with mortality, patient ratings, and quality of care. BMJ Qual. Saf. 2016, 26, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, J.E.; Bruyneel, L.; Aiken, L.H.; Sermeus, W.; Sloane, D.M.; Rafferty, A.M.; Lindqvist, R.; Tishelman, C.; Griffiths, P. RN4Cast Consortium Post-operative mortality, missed care and nurse staffing in nine countries: A cross-sectional study. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2018, 78, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, W.R.; Forrest, W.H., Jr.; Brown, B.W., Jr. Hospital structure and postoperative mortality and morbidity. In Organizational Research in Hospitals; Shortell, S.M., Brown, M., Eds.; Blue Cross Association: Chicago, IL, USA, 1976; pp. 72–89. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, L.M.; Doran, D.; Pink, G.H. Nurse staffing models, nursing hours, and patient safety outcomes. J. Nurs. Adm. 2004, 34, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowe, M.; Carlyle, D. Deconstructing risk assessment and management in mental health nursing. J. Adv. Nurs. 2003, 43, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pangman, V.C.; Sloan, J.; Guse, L. An examination of psychometric properties of the Mini-Mental State Examination and the Standardized Mini-Mental State Examination: Implications for clinical practice. Appl. Nurs. Res. ANR 2000, 13, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uppendahl, J.R.; Alozkan-Sever, C.; Cuijpers, P.; de Vries, R.; Sijbrandij, M. Psychological and Psychosocial Interventions for PTSD, Depression and Anxiety Among Children and Adolescents in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leach, M.J.; Jones, M.; Bressington, D.; Jones, A.; Nolan, F.; Muyambi, K.; Gillam, M.; Gray, R. The association between community mental health nursing and hospital admissions for people with serious mental illness: A systematic review. Syst. Rev. 2020, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staggs, V.S. Nurse staffing, RN mix, and assault rates on psychiatric units. Res. Nurs. Health 2012, 36, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowers, L.; Allan, T.; Simpson, A.; Nijman, H.; Warren, J. Adverse incidents, patient flow and nursing workforce variables on acute psychiatric wards: The Tompkins Acute Ward Study. Int. J. Soc. Psychiatry 2007, 53, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melvin, M.; Hall, P.; Bienek, E. Redesigning acute mental health services: An audit into the quality of inpatient care before and after service redesign in Grampian. J. Psychiatr. Ment. Health Nurs. 2005, 12, 733–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, K.R.; Lu, R.B.; Mao, W.C. Factors relevant to patient assaultive behavior and assault in acute inpatient psychiatric units in Taiwan. Arch. Psychiatr. Nurs. 2002, 16, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, G.; Dassen, T.; Moorer, P. The Perception of Aggression. Scand. J. Caring Sci. 1997, 11, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, D.W.; Ghose, S.; Williams, E.; Brown, K.; Khan, F. Evaluating psychiatric readmissions in the emergency department of a large public hospital. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2018, 14, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howes, O.D.; Vergunst, F.; Gee, S.; McGuire, P.; Kapur, S.; Taylor, D. Adherence to treatment guidelines in clinical practice: Study of antipsychotic treatment prior to clozapine initiation. Br. J. Psychiatry 2012, 201, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, J.; Dahm, M.; Lublin, H.; Taylor, D.M. Psychiatrists’ attitude towards and knowledge of clozapine treatment. J. Psychopharmacol. 2009, 24, 965–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, G.R.; Scott, J.E. Medication compliance and health education among outpatients with chronic mental disorders. Med. Care 1990, 28, 1181–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowie, C.R.; Depp, C.A.; McGrath, J.; Wolyniec, P.; Mausbach, B.T.; Thornquist, M.H.; Luke, J.; Patterson, T.L.; Harvey, P.D.; Pulver, A.E. Prediction of real-world functional disability in chronic mental disorders: A comparison of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Am. J. Psychiatry 2010, 167, 1116–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schennach, R.; Obermeier, M.; Meyer, S.; Jäger, M.; Schmauss, M.; Laux, G.; Pfeiffer, H.; Naber, D.; Schmidt, L.G.; Gaebel, W.; et al. Predictors of relapse in the year after hospital discharge among patients with schizophrenia. Psychiatr. Serv. 2012, 63, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieke, K.; McGeary, C.; Schmid, K.K.; Watanabe-Galloway, S. Risk Factors for Inpatient Psychiatric Readmission: Are There Gender Differences? Community Ment. Health J. 2015, 52, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, N.; Sethi, F. The ‘revolving door’: A study of factors involved in readmissions to a women’s psychiatric intensive care unit. J. Psychiatr. Intensive Care 2017, 13, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumball-Smith, J.; Hider, P. The validity of readmission rate as a marker of the quality of hospital care, and a recommendation for its definition. N. Z. Med. J. 2009, 122, 63–70. [Google Scholar]
- Barnett, R.; Lauer, G. Urban deprivation and public hospital admissions in Christchurch, New Zealand, 1990-1997. Health Soc. Care Community 2003, 11, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilkenny, M.; Dewey, H.M.; Sundararajan, V.; Andrew, N.E.; Lannin, N.A.; Anderson, C.; Donnan, G.; Cadilhac, D.A. Readmissions after stroke: Linked data from the Australian Stroke Clinical Registry and hospital databases. Med. J. Aust. 2015, 203, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Askren-Gonzalez, A.; Frater, J. Case management programs for hospital readmission prevention. Prof. Case Manag. 2012, 17, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerson, L.D.; Rose, L.E. Needs of persons with serious mental illness following discharge from inpatient treatment: Patient and family views. Arch. Psychiatr. Nurs. 2012, 26, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ascher-Svanum, H.; Zhu, B.; Faries, D.E.; Salkever, D.; Slade, E.P.; Peng, X.; Conley, R.R. The cost of relapse and the predictors of relapse in the treatment of schizophrenia. BMC Psychiatry 2010, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Europe Occupational Health Nursing Curriculum, WHO European Strategy for Continuing Education for Nurses and Midwives 2003; WHO: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Blythe, J.; White, J. Role of the mental health nurse towards physical health care in serious mental illness: An integrative review of 10 years of UK Literature. Int. J. Ment. Health Nurs. 2012, 21, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, R.; Brown, E. What does mental health nursing contribute to improving the physical health of service users with severe mental illness? A thematic analysis. Int. J. Ment. Health Nurs. 2016, 26, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyo, N.; Jones, M.; Gilbert, S.; Romero, L.; Gray, R. The association between mental health nurse to registered nurse ratio and patient outcomes in psychiatric inpatient wards: Protocol for a systematic review. J. Psychiatr. Ment. Health Nurs. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Shamseer, L.; Clarke, M.; Ghersi, D.; Liberati, A.; Petticrew, M.; Shekelle, P.; Stewart, L.A. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst. Rev. 2015, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkader, M.; Macmillan, J.F. The effect of a nurses’ industrial action on psychiatric hospital admissions. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 1990, 25, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.T.; Kim, S.J.; Jang, S.I.; Hahm, M.-I.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Park, E.C. The outcomes of psychiatric inpatients by proportion of experienced psychiatrists and nurse staffing in hospital: New findings on improving the quality of mental health care in South Korea. Psychiatry Res. 2015, 229, 880–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lacy, L.; Maddox, P.J. The Influence of Nursing Staff Numbers and Skill Mix on Seclusion and Restraint Use in Public Psychiatric Hospitals. Ph.D. Thesis, George Mason University, Fairfax, VA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Bowers, L.; Crowder, M. Nursing staff numbers and their relationship to conflict and containment rates on psychiatric wards—A cross sectional time series poisson regression study. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2012, 49, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowers, L.; Douzenis, A.; Galeazzi, G.M.; Forghieri, M.; Tsopelas, C.; Simpson, A.; Allan, T. Disruptive and dangerous behaviour by patients on acute psychiatric wards in three European centres. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 2005, 40, 822–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowers, L.; Brennan, G.; Flood, C.; Lipang, M.; Oladapo, P. Preliminary outcomes of a trial to reduce conflict and containment on acute psychiatric wards: City Nurses. J. Psychiatr. Ment. Health Nurs. 2006, 13, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lion, J.R.; Synder, W.; Merrill, G.L. Underreporting of assaults on staff in a state hospital. Hosp. Community Psychiatry 1981, 32, 497–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, C.; Tarantello, C.; Jones, M.P.; Tennant, C. Violence and Aggression in Psychiatric Units. Psychiatr. Serv. 1998, 49, 1452–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogarth, K.M.; Beattie, J.; Morphet, J. Nurses’ attitudes towards the reporting of violence in the emergency department. Australas. Emerg. Nurs. J. 2016, 19, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaffe, J.; Montgomery, P.; Hopewell, S.; Shepard, L.D. Empty Reviews: A Description and Consideration of Cochrane Systematic Reviews with No Included Studies. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, A.; Edwards, N.; Fleiszer, A. Empty systematic reviews: Hidden perils and lessons learned. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2007, 60, 595–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, M.J.; Booth, A. A typology of reviews: An analysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies. Health Inf. Libr. J. 2009, 26, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, N.; Kingdon, D.; Pelton, J.; Mehta, R.; Turkington, D. Effectiveness of brief cognitive-behavioral therapy for schizophrenia delivered by mental health nurses: Relapse and recovery at 24 months. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2009, 70, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiltse Nicely, K.L.; Sloane, U.M.; Aiken, L.H. Lower mortality for abdominal aortic aneurysm repair in high-volume hospitals is contingent upon nurse staffing. Health Serv. Res. 2012, 48, 972–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenzie, J.E.; Brennan, S.E.; Ryan, R.E.; Thomson, H.J.; Johnston, R.V.; Thomas, J. Chapter 3: Defining the criteria for including studies and how they will be grouped for the synthesis. In Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 6.0; Higgins, J.P.T., Thomas, J., Chandler, J., Cumpston, M., Li, T., Page, M.J., Welch, V.A., Eds.; updated July 2019; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2019; Available online: www.training.cochrane.org/handbook (accessed on 12 April 2020).
| Search Strategy: | |
|---|---|
| # | Searches |
| 1 | exp Hospitals, Psychiatric/ |
| 2 | exp Mental Disorders/ |
| 3 | exp Psychiatric Department, Hospital/ |
| 4 | exp Mental Health/ |
| 5 | (acute mental unit * or psychiatric inpatient care or psychiatric ward * or mental ward * or mental health unit *).mp. |
| 6 | (psychiatric service * or mental health care or psychiatric care or mental health care).mp. |
| 7 | (mental health hospital or psychiatric institution * or mental health institution * or mental health setting * or psychiatric setting * or psychiatric hospital *).mp. |
| 8 | (mental health inpatient or psych * inpatient * or psych * patient * or mentally ill patient * or mental patient or mental health patient *).mp. |
| 9 | 1 or 2 or 3 or 4 or 5 or 6 or 7 or 8 |
| 10 | (nurse patient ratio * or nursing staffing ratio * or nursing skill ratio * or nursing skill mix * or hours per patient day or nurse per patient day or full time equivalent or nurs * staff * or nurs * schedul * or task allocation * or delegation).mp. |
| 11 | (nursing staff numbers or staff mix or staffing levels).mp. |
| 12 | (educational preparation or education level or nursing care or grade mix or nurs * staff mix * or nursing grade * or care hours per patient *).mp. |
| 13 | exp Nursing Staff, Hospital/or Nursing/ |
| 14 | 11 or 12 or 13 |
| 15 | exp Psychiatric Nursing/ |
| 16 | (mental health registered nurs * or mental health nurs * or psych * nurs *).mp. |
| 17 | 15 or 16 |
| 18 | 9 and 14 and 17 |
| 19 | limit 18 to English language |
| Author | Setting | Design | Exposure | Measure of Exposure | Outcome | Results | Reason for Exclusion |
| Han et al., 2015 [53] | South Korea | Observational study | Psychiatrists and nurse staffing | Number of nurses Proportion of experienced psychiatrists | Readmission within 30 days of discharge | The odds of readmission were 5% lower for every 10 extra nurses per hospital. | Wrong exposure |
| Abdelkader et al., 1990 [52] | England | Comparison study | Nurses’ industrial action | Six-month period during the industrial action in 1982 | Admission | In 1982, there was a reduction in the total number of admissions by 30% compared to 1981. | Wrong exposure |
| Bowers et al., 2012 [55] | England | Time series analysis | Nursing staff numbers | Numbers of nursing staff on duty | Conflict and containment incidents | An increase in qualified nurses working on a ward was associated with a subsequent increase in conflict and containment incidents. | Wrong exposure and outcome |
| De Lacy et al., 2006 [54] | United States | Descriptive correlational research | Nursing staff numbers and skill mix | Nursing care staffing Nursing staff numbers Nursing skill mix Full-time equivalents | Seclusion and restraint use | An increased proportion of registered nurses was associated with a decrease in seclusion- and restraint-use measures. | Wrong exposure and outcome |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moyo, N.; Jones, M.; Kushemererwa, D.; Pantha, S.; Gilbert, S.; Romero, L.; Gray, R. The Association between the Mental Health Nurse-to-Registered Nurse Ratio and Patient Outcomes in Psychiatric Inpatient Wards: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6890. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17186890
Moyo N, Jones M, Kushemererwa D, Pantha S, Gilbert S, Romero L, Gray R. The Association between the Mental Health Nurse-to-Registered Nurse Ratio and Patient Outcomes in Psychiatric Inpatient Wards: A Systematic Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(18):6890. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17186890
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoyo, Nompilo, Martin Jones, Diana Kushemererwa, Sandesh Pantha, Sue Gilbert, Lorena Romero, and Richard Gray. 2020. "The Association between the Mental Health Nurse-to-Registered Nurse Ratio and Patient Outcomes in Psychiatric Inpatient Wards: A Systematic Review" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 18: 6890. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17186890
APA StyleMoyo, N., Jones, M., Kushemererwa, D., Pantha, S., Gilbert, S., Romero, L., & Gray, R. (2020). The Association between the Mental Health Nurse-to-Registered Nurse Ratio and Patient Outcomes in Psychiatric Inpatient Wards: A Systematic Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(18), 6890. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17186890







