Turbinate Submucosal Reduction Operation Reduced Migraine Admission among Patients with Chronic Hypertrophic Rhinitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
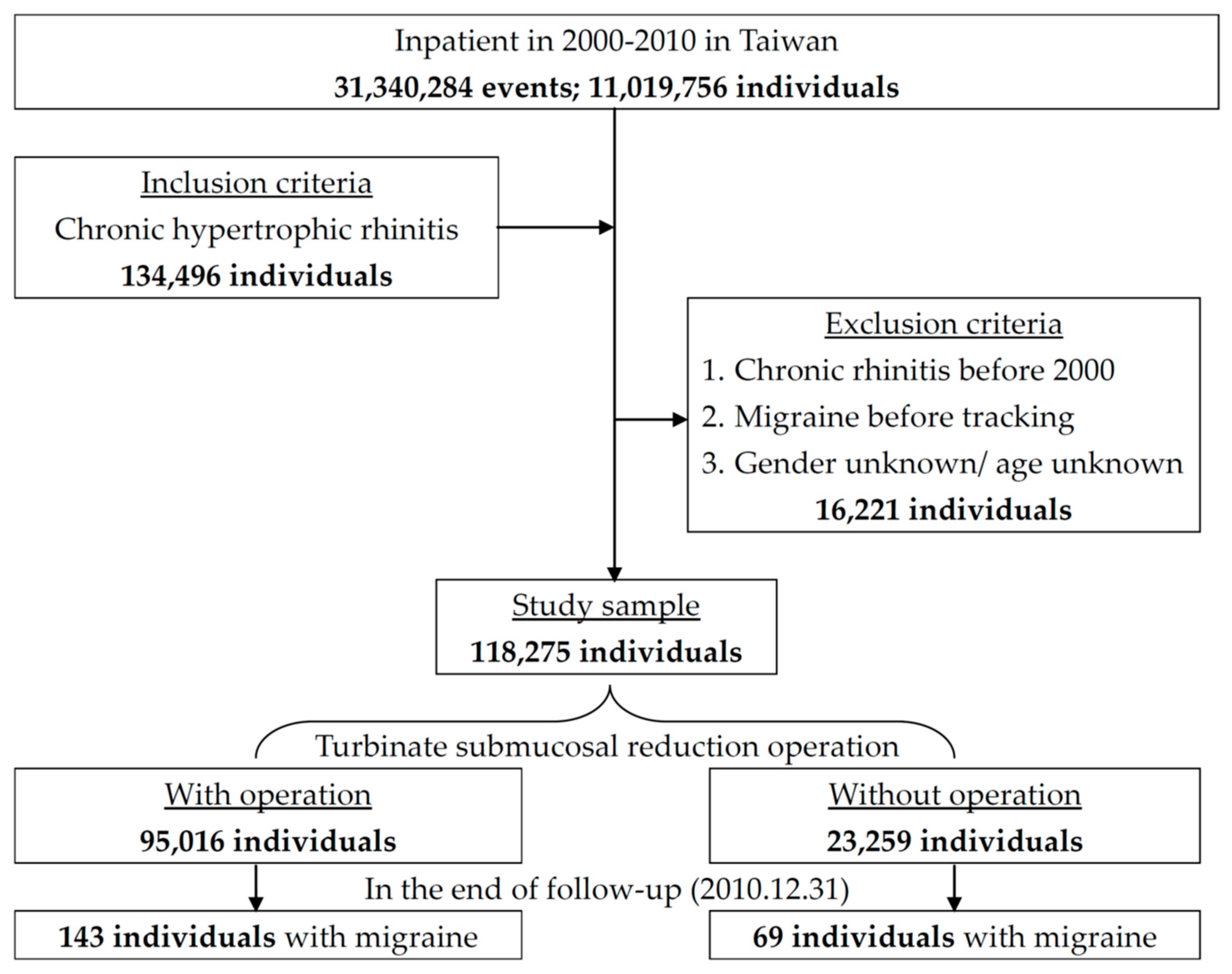
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, S.J.; Fuh, J.L.; Juang, K.D.; Lu, S.R. Rising prevalence of migraine in Taiwanese adolescents aged 13–15 years. Cephalalgia 2005, 25, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS). The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition (beta version). Cephalalgia 2013, 33, 629–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doretti, A.; Shestaritc, I.; Ungaro, D.; Lee, J.I.; Lymperopoulos, L.; Kokoti, L.; Guglielmetti, M.; Mitsikostas, D.D.; Lampl, C. School of Advanced Studies of the European Headache Federation (EHF-SAS). Headaches in the emergency department–A survey of patients’ characteristics, facts and needs. J. Headache Pain 2019, 20, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diener, H.C.; Solbach, K.; Holle, D.; Gaul, C. Integrated care for chronic migraine patients: Epidemiology, burden, diagnosis and treatment options. Clin. Med. 2015, 15, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derebery, J.; Meltzer, E.; Nathan, R.A.; Stang, P.E.; Campbell, U.B.; Corrao, M.; Stanford, R. Rhinitis symptoms and comorbidities in the United States: Burden of rhinitis in America survey. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2008, 139, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, V.T.; Fanning, K.M.; Serrano, D.; Buse, D.C.; Reed, M.L.; Bernstein, J.A.; Lipton, R.B. Chronic rhinitis and its association with headache frequency and disability in persons with migraine: Results of the American Migraine Prevalence and Prevention (AMPP) Study. Cephalalgia 2014, 34, 336–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rains, J.C.; Poceta, J.S. Sleep-related headaches. Neurol. Clin. 2012, 30, 1285–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, V.T.; Taylor, F.; Gebhardt, B.; Tomaszewski, M.; Ellison, J.S.; Martin, G.V.; Levin, L.; Al-Shaikh, E.; Nicolas, J.; Bernstein, J.A. Allergy and immunotherapy: Are they related to migraine headache? Headache 2011, 51, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buse, D.; Manack, A.; Serrano, D.; Turkel, C.; Lipton, R. Sociodemographic and comorbidity profiles of chronic migraine and episodic migraine sufferers. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2010, 81, 428–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.J.; Fuh, J.L.; Young, Y.H.; Lu, S.R.; Shia, B.C. Prevalence of migraine in Taipei, Taiwan: A population-based survey. Cephalalgia 2000, 20, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Health Insurance Research Database. Available online: http://nhird.nhri.org.tw/en/index.html (accessed on 1 June 2020).
- Welge-Lüssen, A.; Hauser, R.; Probst, R. 3-year follow-up after endonasal microscopic paranasal sinus surgery in migraine and cluster headache. Laryngorhinootologie 1996, 75, 392–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, Y.; Goadsby, P. The periaqueductal grey matter modulates trigeminovascular input: A role in migraine? Neuroscience 2001, 106, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsarava, Z.; Lehnerdt, G.; Duda, B.; Ellrich, J.; Diener, H.; Kaube, H. Sensitization of trigeminal nociception specific for migraine but not pain of sinusitis. Neurology 2002, 59, 1450–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryglas, A. Allergic rhinitis and chronic daily headaches: Is There a Link? Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2016, 16, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sabra, O.; Muhammad, A.M.; Al Zayer, M.; Altuwaijri, S. Frequency of migraine as a chief complaint in otolaryngology outpatient practice. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 173165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreiber, C.P.; Hutchinson, S.; Webster, C.J.; Ames, M.; Richardson, M.S.; Powers, C. Prevalence of migraine in patients with a history of self-reported or physician-diagnosed sinus headache. Arch Intern. Med. 2004, 164, 1769–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eross, E.; Dodick, D.; Eross, M. The sinus, allergy and migraine study (SAMS). Headache 2007, 47, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goadsby, P.J.; Hoskin, K.L. The distribution of trigeminovascular afferents in the nonhuman primate brain Macaca nemestrina: Ac-fos immunocytochemical study. J. Anat. 1997, 190, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciancarelli, I.; Tozzi-Ciancarelli, M.; Spacca, G.; Di Massimo, C.; Carolei, A. Relationship between biofeedback and oxidative stress in patients with chronic migraine. Cephalalgia 2007, 27, 1136–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, M.; Silverman, B.; Prifti, N.; Ying, W.; Persaud, Y.; Schneider, A. Prevalence of migraine headaches in patients with allergic rhinitis. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2006, 97, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayarathna, D.; Thenakoon, S.; Senananayaka, K.J. Migraine and neurological disorders comorbidity-consideration of sinus hypoxic nitric oxide theory for migraine. J. Neurol. Disord. 2014, 2, 1000175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bektas, H.; Karabulut, H.; Doganay, B.; Acar, B. Allergens might trigger migraine attacks. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2017, 117, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lateef, T.M.; Cui, L.; Nelson, K.B.; Nakamura, E.F.; Merikangas, K.R. Physical comorbidity of migraine and other headaches in US adolescents. J. Pediatr. 2012, 161, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patten, S.B. Long-term medical conditions and major depression in a Canadian population study at waves 1 and 2. J. Affect Disord. 2001, 63, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, A.C.; Staiger, T.; Sullivan, M. The efficacy of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors for the management of chronic pain. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 1997, 12, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penn, I.W.; Chuang, E.; Chuang, T.Y.; Lin, C.L.; Kao, C.H. Bidirectional association between migraine and fibromyalgia: Retrospective cohort analyses of two populations. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e026581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, V.T.; Fanning, K.M.; Serrano, D.; Buse, D.C.; Reed, M.L.; Lipton, R.B. Asthma is a risk factor for new onset chronic migraine: Results from the American migraine prevalence and prevention study. Headache 2016, 56, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, F.; Castillo, J.; Pardo, J.; Lema, M.; Noya, M. Catecholamine levels in plasma and CSF in migraine. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry. 1993, 56, 1119–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Aupiais, C.; Wanin, S.; Romanello, S.; Spiri, D.; Moretti, R.; Boizeau, P.; Massano, D.; Zuccotti, G.V.; Crichiutti, G.; Kanagarajah, L. Association between migraine and atopic siseases in childhood: A potential protective role of anti-allergic drugs. Headache 2017, 57, 612–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, C.I.; Lin, C.C.; Chen, W.H.; Wang, H.C.; Kao, C.H. Association between migraine and irritable bowel syndrome: A population-based retrospective cohort study. Eur. J. Neurol. 2014, 21, 1198–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Turbinate Submucosal Reduction Operation | Total | With | Without | p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | n | % | n | % | n | % | |
| 118,275 | 95,016 | 80.33 | 23,259 | 19.67 | |||
| Gender (Male) | 83,307 | 70.44 | 68,443 | 72.03 | 14,864 | 63.91 | <0.001 |
| Age (years) | 37.58 ± 14.28 | 35.56 ± 12.78 | 45.85 ± 16.87 | <0.001 | |||
| Age group (years) | <0.001 | ||||||
| <30 | 44,678 | 37.77 | 39,810 | 41.90 | 4868 | 20.93 | |
| 30–45 | 40,317 | 34.09 | 33,320 | 35.07 | 6997 | 30.08 | |
| ≥45 | 33,280 | 28.14 | 21,886 | 23.03 | 11,394 | 48.99 | |
| Diabetes mellitus | 2093 | 1.77 | 851 | 0.90 | 1242 | 5.34 | <0.001 |
| Hypertension | 4348 | 3.68 | 2159 | 2.27 | 2189 | 9.41 | <0.001 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 356 | 0.30 | 104 | 0.11 | 252 | 1.08 | <0.001 |
| Depression | 404 | 0.34 | 103 | 0.11 | 301 | 1.29 | <0.001 |
| Anxiety | 400 | 0.34 | 85 | 0.09 | 315 | 1.35 | <0.001 |
| Chronic fatigue syndrome | 2 | 0.00 | 1 | 0.00 | 1 | 0.00 | 0.355 |
| Fibromyalgia | 73 | 0.06 | 10 | 0.01 | 63 | 0.27 | <0.001 |
| Irritable bowel syndrome | 27 | 0.02 | 8 | 0.01 | 19 | 0.08 | <0.001 |
| Sleep disturbance | 6052 | 4.93 | 4457 | 4.48 | 1595 | 6.86 | <0.001 |
| Temporomandibular joint disorder | 12 | 0.01 | 2 | 0.00 | 10 | 0.04 | <0.001 |
| Dysmenorrhea | 4 | 0.00 | 1 | 0.00 | 3 | 0.01 | 0.026 |
| Asthma | 1804 | 1.53 | 352 | 0.37 | 1452 | 6.24 | <0.001 |
| Season | <0.001 | ||||||
| Spring (March–May) | 31,062 | 26.26 | 24,846 | 26.15 | 6216 | 26.73 | |
| Summer (June–August) | 30,437 | 25.73 | 24,789 | 26.09 | 5648 | 24.28 | |
| Autumn (September–November) | 27,952 | 23.63 | 22,340 | 23.51 | 5612 | 24.13 | |
| Winter (December–February) | 28,824 | 24.37 | 23,041 | 24.25 | 5783 | 24.86 | |
| Location | <0.001 | ||||||
| Northern Taiwan | 47,644 | 40.28 | 40,118 | 42.22 | 7526 | 32.36 | |
| Middle Taiwan | 34,757 | 29.39 | 26,919 | 28.33 | 7838 | 33.70 | |
| Southern Taiwan | 31,678 | 26.78 | 25,792 | 27.14 | 5886 | 25.31 | |
| Eastern Taiwan | 4070 | 3.44 | 2095 | 2.20 | 1975 | 8.49 | |
| Outlet islands | 126 | 0.11 | 92 | 0.10 | 34 | 0.15 | |
| Urbanization level | <0.001 | ||||||
| 1 (Highest) | 44,393 | 37.53 | 37,016 | 38.96 | 7377 | 31.72 | |
| 2 | 57,057 | 48.24 | 46,318 | 48.75 | 10,739 | 46.17 | |
| 3 | 5222 | 4.42 | 3549 | 3.74 | 1673 | 7.19 | |
| 4 (Lowest) | 11,603 | 9.81 | 8133 | 8.56 | 3470 | 14.92 | |
| Level of care | <0.001 | ||||||
| Medical center | 55,660 | 47.06 | 47,288 | 49.77 | 8372 | 35.99 | |
| Regional hospital | 51,281 | 43.36 | 38,961 | 41.00 | 12,320 | 52.97 | |
| Local hospital | 11,334 | 9.58 | 8767 | 9.23 | 2567 | 11.04 | |
| Insured premium (NT$) | <0.001 | ||||||
| <18,000 | 115,477 | 97.63 | 92,717 | 97.58 | 22,760 | 97.85 | |
| 18,000–34,999 | 1748 | 1.48 | 1399 | 1.47 | 349 | 1.50 | |
| 35,000+ | 1050 | 0.89 | 900 | 0.95 | 150 | 0.64 | |
| Variables | Crude HR | 95% CI | 95% CI | p | Adjusted HR | 95% CI | 95% CI | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turbinate Submucosal Reduction Operation | ||||||||
| 0.759 | 0.569 | 0.911 | 0.011 * | 0.858 | 0.633 | 0.962 | 0.022 * | |
| Gender | ||||||||
| Male | 0.521 | 0.398 | 0.682 | <0.001 * | 0.603 | 0.458 | 0.794 | <0.001 * |
| Female | Reference | Reference | ||||||
| Age (years) | ||||||||
| <30 | Reference | Reference | ||||||
| 30–45 | 1.569 | 1.018 | 2.501 | 0.041 * | 1.479 | 0.942 | 2.324 | 0.089 |
| ≥45 | 1.361 | 0.877 | 2.111 | 0.169 | 1.276 | 0.803 | 2.029 | 0.302 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 0.531 | 0.289 | 0.975 | 0.041 * | 0.479 | 0.255 | 0.9 | 0.022 * |
| Hypertension | 1.079 | 0.750 | 1.553 | 0.680 | 1.366 | 0.919 | 2.029 | 0.123 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 1.148 | 0.566 | 2.329 | 0.701 | 1.028 | 0.493 | 2.143 | 0.941 |
| Depression | 7.560 | 5.158 | 11.082 | <0.001 * | 4.348 | 2.826 | 6.69 | <0.001 * |
| Anxiety | 6.398 | 4.418 | 10.894 | <0.001 * | 3.750 | 2.267 | 6.203 | <0.001 * |
| Chronic fatigue syndrome | 10.813 | 1.515 | 77.160 | 0.018 * | 3.882 | 0.500 | 30.124 | 0.195 |
| Fibromyalgia | 13.303 | 8.538 | 27.070 | <0.001 * | 7.326 | 3.427 | 15.661 | <0.001 * |
| Irritable bowel syndrome | 6.849 | 1.682 | 27.881 | 0.007 * | 3.368 | 0.800 | 14.182 | 0.098 |
| Sleep disturbance | 2.568 | 1.465 | 4.503 | 0.001 * | 1.711 | 0.954 | 3.067 | 0.071 |
| Asthma | 2.226 | 1.270 | 3.901 | 0.005 * | 1.969 | 1.11 | 3.491 | 0.02 * |
| Season | ||||||||
| Spring (March–May) | Reference | Reference | ||||||
| Summer (June–August) | 0.957 | 0.637 | 1.439 | 0.834 | 0.941 | 0.626 | 1.416 | 0.772 |
| Autumn (September–November) | 1.097 | 0.748 | 1.609 | 0.636 | 1.042 | 0.709 | 1.532 | 0.832 |
| Winter (December–February) | 1.225 | 0.822 | 1.825 | 0.319 | 1.198 | 0.801 | 1.787 | 0.381 |
| Urbanization level | ||||||||
| 1 (Highest) | 0.765 | 0.494 | 1.185 | 0.231 | 0.970 | 0.603 | 1.560 | 0.900 |
| 2 | 1.139 | 0.776 | 1.674 | 0.507 | 1.409 | 0.941 | 2.111 | 0.096 |
| 3 | 0.940 | 0.525 | 1.683 | 0.835 | 1.037 | 0.578 | 1.863 | 0.902 |
| 4 (Lowest) | Reference | Reference | ||||||
| Level of care | ||||||||
| Medical center | 0.685 | 0.470 | 0.997 | 0.048 * | 0.672 | 0.445 | 1.015 | 0.059 |
| Regional hospital | 0.873 | 0.621 | 1.228 | 0.438 | 0.825 | 0.583 | 1.168 | 0.278 |
| Local hospital | Reference | Reference | ||||||
| Insured premium (NT$) | ||||||||
| <18,000 | Reference | Reference | ||||||
| 18,000–34,999 | 1.667 | 0.740 | 3.754 | 0.217 | 1.799 | 0.797 | 4.063 | 0.158 |
| 35,000+ | 0.691 | 0.097 | 4.927 | 0.712 | 0.695 | 0.125 | 6.399 | 0.912 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, C.-A.; Chang, Y.-H.; Cheng, C.-G.; Lin, H.-C.; Chung, C.-H.; Chien, W.-C. Turbinate Submucosal Reduction Operation Reduced Migraine Admission among Patients with Chronic Hypertrophic Rhinitis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5455. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17155455
Cheng C-A, Chang Y-H, Cheng C-G, Lin H-C, Chung C-H, Chien W-C. Turbinate Submucosal Reduction Operation Reduced Migraine Admission among Patients with Chronic Hypertrophic Rhinitis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(15):5455. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17155455
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Chun-An, Yin-Han Chang, Chun-Gu Cheng, Hung-Che Lin, Chi-Hsiang Chung, and Wu-Chien Chien. 2020. "Turbinate Submucosal Reduction Operation Reduced Migraine Admission among Patients with Chronic Hypertrophic Rhinitis" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 15: 5455. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17155455
APA StyleCheng, C.-A., Chang, Y.-H., Cheng, C.-G., Lin, H.-C., Chung, C.-H., & Chien, W.-C. (2020). Turbinate Submucosal Reduction Operation Reduced Migraine Admission among Patients with Chronic Hypertrophic Rhinitis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(15), 5455. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17155455





