Converging on Bladder Health through Design Thinking: From an Ecology of Influence to a Focused Set of Research Questions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
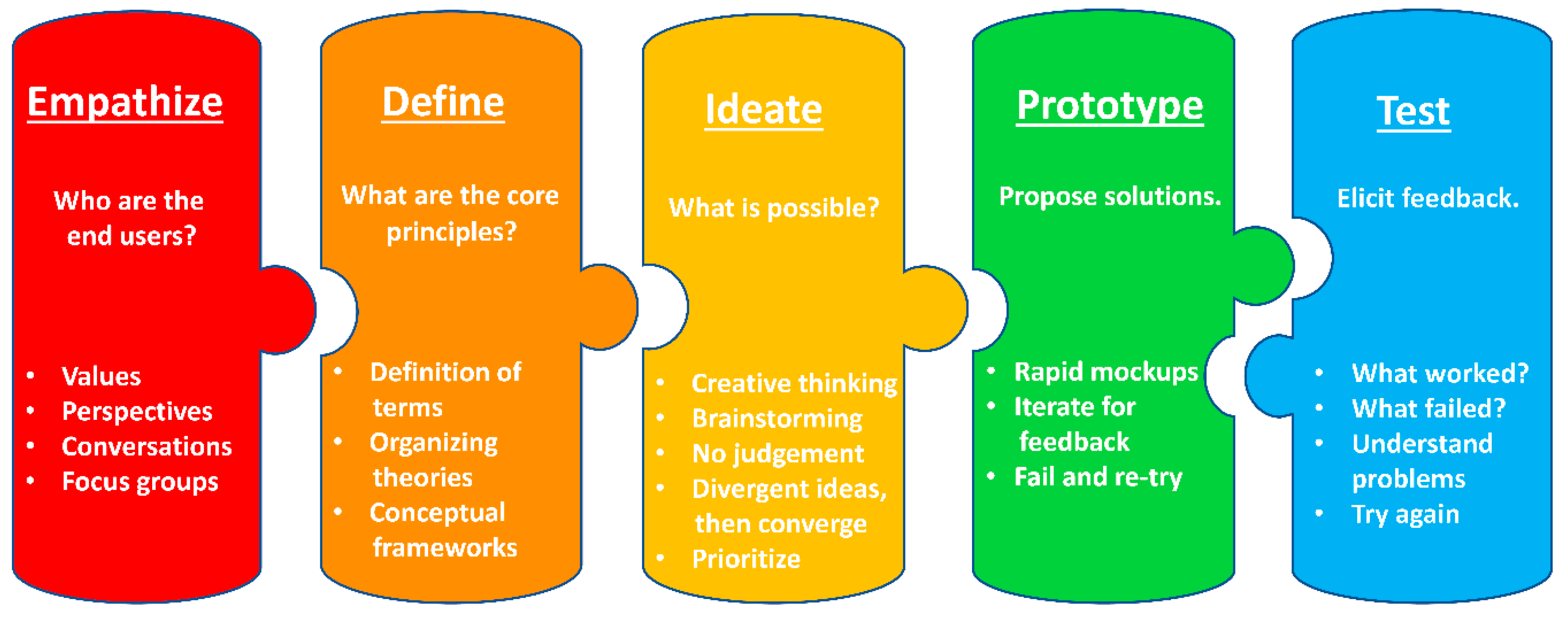
2.1. Overview of Design Thinking
2.2. Empathize
2.3. Define
2.4. Ideate
2.5. Prototype and Test
3. Discussion
3.1. Lessons Learned
3.2. Limitations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ghandour, L.; Minassian, V.; Al-Badr, A.; Ghaida, R.A.; Geagea, S.; Bazi, T. Prevalence and degree of bother of pelvic floor disorder symptoms among women from primary care and specialty clinics in Lebanon: An exploratory study. Int. Urogynecol. J. 2016, 28, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obioha, K.C.; Ugwu, E.O.; Obi, S.N.; Dim, C.C.; Oguanuo, T.C. Prevalence and predictors of urinary/anal incontinence after vaginal delivery: Prospective study of Nigerian women. Int. Urogynecol. J. 2015, 26, 1347–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumarsono, B.; Jong, J.J.; Wang, J.-Y.; Liao, L.; Lee, K.-S.; Yoo, T.K.; Liu, S.-P.; Chuang, Y. The prevalence of urinary incontinence in men and women aged 40 years or over in China, Taiwan and South Korea: A cross-sectional, prevalence-based study. LUTS Low. Urin. Tract Symptoms 2020, 23, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeleke, B.; Bell, R.J.; Billah, B.; Davis, S.R. Symptomatic pelvic floor disorders in community-dwelling older Australian women. Maturitas 2016, 85, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.; Xue, K.; Liu, Y.; Zhuo, L.; Tu, S.; Palmer, M.H. Toileting behaviors and factors associated with urinary incontinence in college-aged female students in China. Int. Urogynecol. J. 2019, 31, 961–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutcliffe, S.; Bavendam, T.; Cain, C.; Epperson, C.N.; Fitzgerald, C.M.; Gahagan, S.; Markland, A.D.; Shoham, D.A.; Smith, A.L.; Townsend, M.K.; et al. The spectrum of bladder health: The relationship between lower urinary tract symptoms and interference with activities. J. Women’s Health 2019, 28, 827–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coyne, K.S.; Sexton, C.C.; Thompson, C.L.; Milsom, I.; Irwin, D.; Kopp, Z.; Chapple, C.; Kaplan, S.; Tubaro, A.; Aiyer, L.P.; et al. The prevalence of lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) in the USA, the UK and Sweden: Results from the Epidemiology of LUTS (EpiLUTS) study. BJU Int. 2009, 104, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irwin, D.E.; Milsom, I.; Hunskaar, S.; Reilly, K.; Kopp, Z.; Herschorn, S.; Coyne, K.; Kelleher, C.; Hampel, C.; Artibani, W.; et al. Population-based survey of urinary incontinence, overactive bladder, and other lower urinary tract symptoms in five countries: Results of the EPIC study. Eur. Urol. 2006, 50, 1306–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NIDDK, RFA-DK-14-004: Prevention of Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms in Women. Available online: https://grants.nih.gov/grants/guide/rfa-files/RFA-DK-14-004.html2014 (accessed on 1 January 2020).
- Schmitz, K.H.; Bavendam, T.; Brady, S.S.; Brubaker, L.I.; Burgio, K.; Harlow, B.L.; James, A.; Lukacz, E.S.; Miller, J.M.; Newman, D.K.; et al. Is the juice worth the squeeze? Transdisciplinary team science in bladder health. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukacz, E.S.; Bavendam, T.G.; Berry, A.; Fok, C.S.; Gahagan, S.; Goode, P.S.; Hardacker, C.T.; Hebert-Beirne, J.; Lewis, C.E.; Lewis, J.; et al. A novel research definition of bladder health in women and girls: Implications for research and public health promotion. J. Women’s Health 2018, 27, 974–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brady, S.S.; Bavendam, T.G.; Berry, A.; Fok, C.S.; Gahagan, S.; Goode, P.S.; Hardacker, C.T.; Hebert-Beirne, J.; Lewis, C.E.; Lewis, J.; et al. The Prevention of Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (PLUS) in girls and women: Developing a conceptual framework for a prevention research agenda. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2018, 37, 2951–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, T. Change By Design: How Design Thinking Transforms Organizations and Inspires Innovation; HarperCollins: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 154–196. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, T.; Martin, R. Design for action. Harvard Business Review, 23 September 2015; 56–64. [Google Scholar]
- Kolko, J. Design thinking comes of age. Harvard Business Review, 23 September 2015; 66–71. [Google Scholar]
- Altman, M.; Huang, T.T.; Breland, J.Y. Design thinking in health care. Prev. Chronic Dis. 2018, 15, 180128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.T.K.; Aitken, J.; Ferris, E.; Cohen, N. Design thinking to improve implementation of public health interventions: An exploratory case study on enhancing park use. Des. Health 2018, 2, 236–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, J.P.; Fisher, T.R.; Trowbridge, M.; Bent, C. A design thinking framework for healthcare management and innovation. Healthcare 2016, 4, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vechakul, J.; Shrimali, B.P.; Sandhu, J.S. Human-centered design as an approach for place-based innovation in public health: A case study from Oakland, California. Matern. Child Health J. 2015, 19, 2552–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.M.; Palermo, A.-G.S. Community engagement in research: Frameworks for education and peer review. Am. J. Public Health 2010, 100, 1380–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolf, S.H.; Zimmerman, E.; Haley, A.; Krist, A.H. Authentic engagement of patients and communities can transform research, practice, and policy. Health Aff. 2016, 35, 590–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasso Plattner Institute of Design at Stanford, An Introduction to Design Thinking: Process Guide. Available online: https://s3-eu-west-1.amazonaws.com/ih-materials/uploads/Introduction-to-design-thinking.pdf (accessed on 15 May 2020).
- Low, L.K.; Williams, B.R.; Camenga, D.R.; Hebert-Beirne, J.; Brady, S.S.; Newman, D.K.; James, A.S.; Hardacker, C.T.; Nodora, J.; Linke, S.E.; et al. Prevention of lower urinary tract symptoms research consortium focus group study of habits, attitudes, realities, and experiences of bladder health. J. Adv. Nurs. 2019, 75, 3111–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liedtka, J. Why design thinking works. Harvard Business Review, 1 October 2018; 72–79. [Google Scholar]
- Lich, K.H.; Ginexi, E.M.; Osgood, N.D.; Mabry, P.L. A call to address complexity in prevention science research. Prev. Sci. 2012, 14, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishbein, D.H.; Ridenour, T.A.; Stahl, M.; Sussman, S. The full translational spectrum of prevention science: Facilitating the transfer of knowledge to practices and policies that prevent behavioral health problems. Transl. Behav. Med. 2016, 6, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, L.; Gauvin, L.; Raine, K.D. Ecological models revisited: Their uses and evolution in health promotion over two decades. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2011, 32, 307–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glass, T.; McAtee, M.J. Behavioral science at the crossroads in public health: Extending horizons, envisioning the future. Soc. Sci. Med. 2006, 62, 1650–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
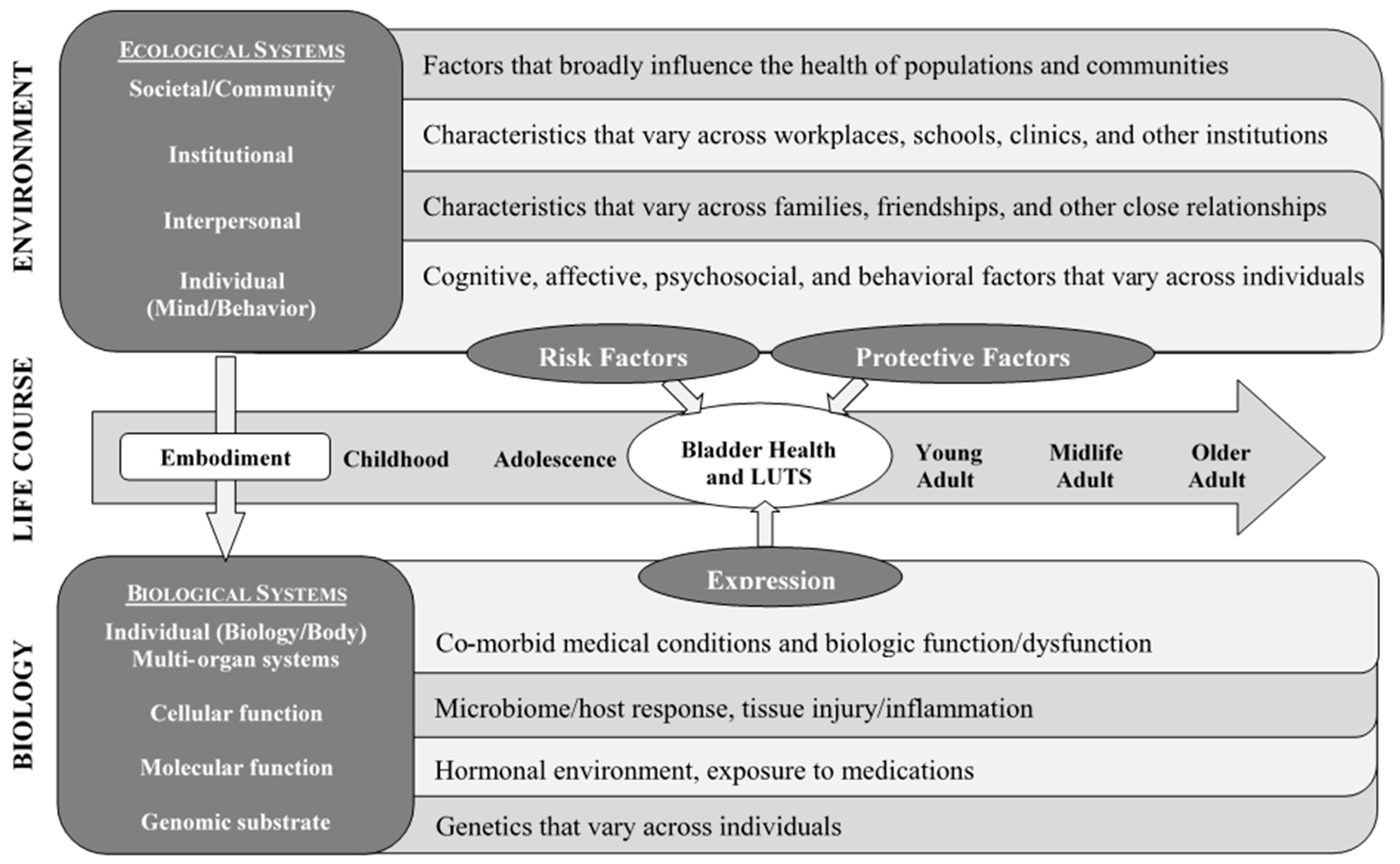
- Brady, S.S.; Berry, A.; Camenga, D.R.; Fitzgerald, C.M.; Gahagan, S.; Hardacker, C.T.; Harlow, B.L.; Hebert-Beirne, J.; Lacoursiere, D.Y.; Lewis, J.B.; et al. Applying concepts of life course theory and life course epidemiology to the study of bladder health and lower urinary tract symptoms among girls and women. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2020, 39, 1185–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, L.J.; Brown, T. (En)gendering racial disparities in health trajectories: A life course and intersectional analysis. SSM Popul. Health 2016, 2, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halfon, N.; Forrest, C.B. The emerging theoretical framework of life course health development. In Handbook of Life Course Health Development; Halfon, N., Forrest, C.B., Lerner, R.M., Faustman, E.M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 463–497. [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Shlomo, Y.; Mishra, G.; Kuh, D. Life course epidemiology. In Handbook of Epidemiology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 1521–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lich, K.H.; Ginexi, E.M.; Osgood, N.D.; Mabry, P.L. A call to address complexity in prevention science research. Prev. Sci. 2013, 14, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallis, J.; Owen, N. Ecological models of health behavior. In Health Behavior: Theory, Research, and Practice, 5th ed.; Jossey Bass: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2015; pp. 43–65. [Google Scholar]
- Brady, S.S.; Brubaker, L.; Fok, C.S.; Gahagan, S.; Lewis, C.E.; Lewis, J.; Lowder, J.L.; Nodora, J.; Stapleton, A.; Palmer, M.H.; et al. Development of conceptual models to guide public health research, practice, and policy: Synthesizing traditional and contemporary paradigms. Health Promot. Pr. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golden, S.D.; Earp, J. Social ecological approaches to individuals and their contexts: Twenty years of Health Education & Behavior health promotion interventions. Health Educ. Behav. 2012, 39, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaemi, S.N. The Rise and Fall of the Biopsychosocial Model: Reconciling Art and Science in Psychiatry; JHU Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2010; pp. 38–51. [Google Scholar]
- Solar, O.; Irwin, A.A. Conceptual Framework for Action on the Social Determinants of Health. Social Determinants of Health Discussion Paper 2 (Policy and Practice) 2010, World Health Organization. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/44489/9789241500852_eng.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2020).
- Kelley, T.; Littman, J. The Art of Innovation: Lessons in Creativity from IDEO, America’s Leading Design Firm; Random House: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt, G. Linkographic evidence for concurrent divergent and convergent thinking in creative design. Creat. Res. J. 2016, 28, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Scientific Considerations | 1. Does the research question involve a modifiable factor (i.e., does it inform prevention)?
|
| 2. If the research question relates to a modifiable factor, would the associated intervention be easy to implement/well-accepted? Low cost? | |
| 3. Does the research question inform groups more or less susceptible to the influence of a particular risk or protective factor (i.e., effect modification)? | |
| 4. Does the research question involve a risk or protective factor with a high prevalence (i.e., potential for high population attributable risk/impact)? | |
| 5. Does the research question have the potential for policy level impact? | |
| 6. Is the research question timely? | |
| 7. Does the research question relate to a risk/protective factor specific to bladder health (not general health)? | |
| 8. Does the research question help us understand women’s health, health behaviors, and health decision-making more broadly (i.e., does it have implications beyond bladder health?)? | |
| 9. Is the research question supported by a plausible mechanism (e.g., biological, psychological, etc.)? | |
| 10. Does the research question address a novel risk/protective factor? | |
| 11. Does the research question provide confirmatory data for a less well-established factor? | |
| 12. Does the research question provide confirmatory data for a more well-established factor? | |
| 13. Is the research question important enough that any result (positive, inverse, null) will move the field forward? | |
| 14. Could the research question push the field into new directions of inquiry or novel areas of research? | |
| 15. Is the research question well-positioned for the uniqueness of the consortium, or is it better suited to an individual research group or to existing data/ongoing studies? | |
| 16. Does the research exemplify transdisciplinary science? | |
| Practical Considerations | 17. Can the research question be addressed in a sample of the general population or does it require recruitment of a specific population? |
| 18. How many constructs are needed to answer the research question? | |
| 19. What is the degree of invasiveness of assessment of each construct (e.g., self-report, physical examination, recall/real-time assessment)? | |
| 20. What is the length of time/number of items needed to address each construct? | |
| 21. Do any of the necessary constructs contribute to answering more than one research question? | |
| 22. Does the research question overlap with multiple themes? | |
| 23. Will the research question provide preliminary data for additional grants/pilot projects? | |
Regarding the overall pool of research questions:
| |
| Dates | PLUS Consortium Activities | Proposed Revisions to Sequence or Timing | |
| Empathize | 7/15- | PLUS investigators bring diverse clinical/community experience | |
| 7/15- | Remote calls and in-person meetings with transdisciplinary investigators | ||
| 9/15- | Webinars share transdisciplinary knowledge and perspectives | ||
| 9/15 | Myers–Briggs type sharing | ||
| 7/17–4/18 | SHARE Qualitative Study | This activity would have been more helpful to begin earlier. It began during Prototyping and Testing, requiring revisiting of measures. A broad community engagement process early in this phase would have been preferable. | |
| Define | 7/15 | U.S. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases defines inclusion in PLUS | |
| 9/15–7/17 | PLUS develops research definition of bladder health | ||
| 7/15–9/15 | PLUS establishes conceptual framework | ||
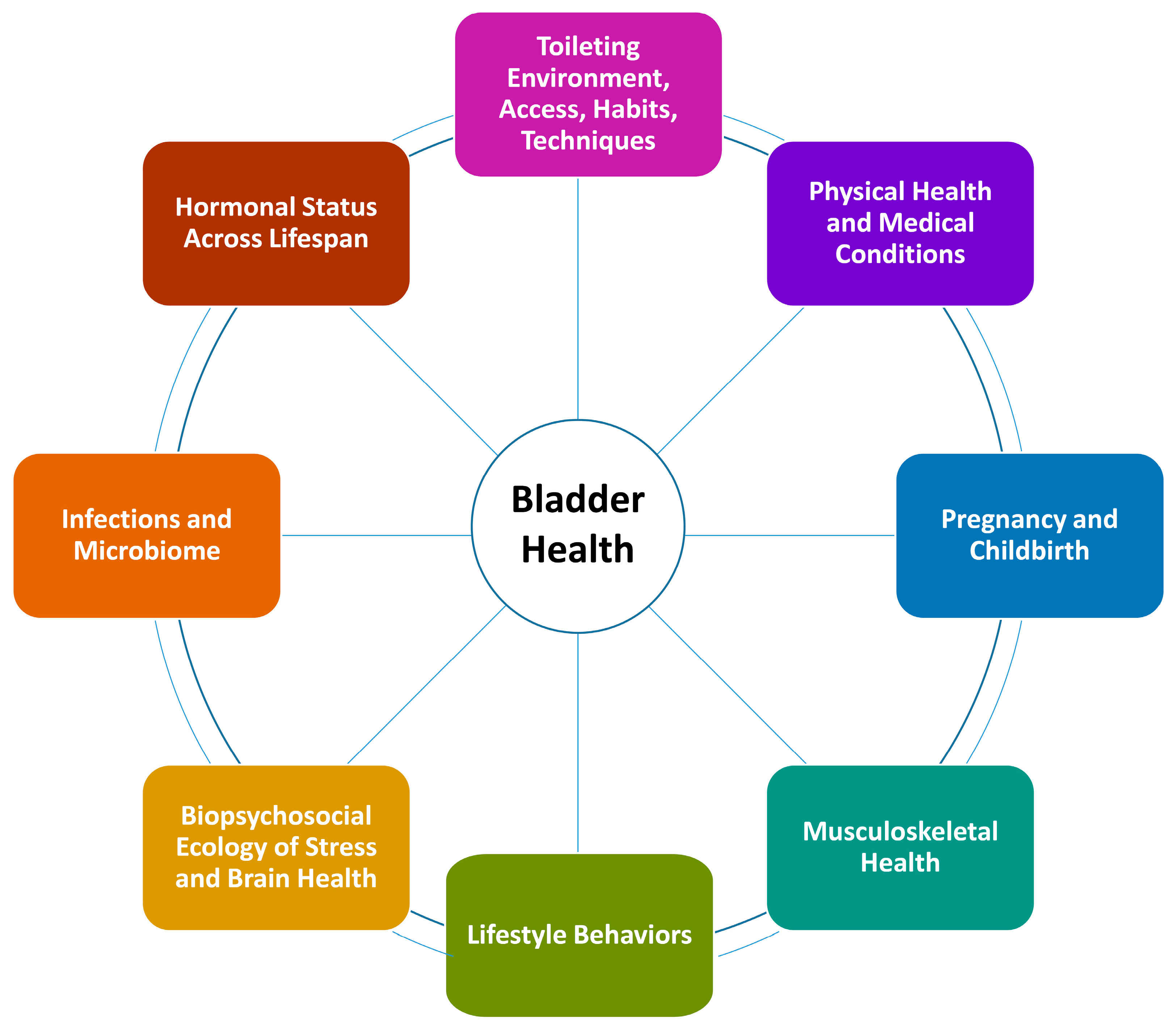
| Ideate | 9/16–10/16 | Terminology, Conceptual Frameworks and Models (TCFM) sub-committee generates list of candidate risk and protective factors | |
| 11/15 | Consortium participates in sticky notes ideation exercise: 600 factors identified | This could have preceded the TCFM generation of factors. | |
| 11/15–12/15 | TCFM refines list of factors | ||
| 1/16–2/16 | Members rank top 20 determinants; 44 prioritized factors across 8 themes | ||
| Prototype and Test | 1/17–7/17 | Individual and Environmental Work Groups develop measures for risk/protective factors | Consensus on a process to formulate research questions and measure of risk and protective factors at the Define stage would have prevented shifting directions. |
| 8/17–6/18 | Theme Teams develop research questions | Consensus on a plan to determine key covariates would have prevented investigators from trying to incorporate key covariates into questions to ensure their inclusion, leading to more novel questions. | |
| 10/17 and 11/17 | Theme Teams present research questions to entire consortium for comment | ||
| 11/17 | Study Design and Methodology Group (1) defines criteria to prioritize research questions and (2) gathers consortium feedback about which scientific and practical considerations are most important for prioritization | It would have been helpful at the Define stage for the PLUS Consortium to have determined the scientific and practical considerations of greatest importance to the consortium. These criteria could have been used to prioritize and select risk and protective factors and research questions of highest importance efficiently through a transparent and objective process. | |
| 4/18–2/19 | PLUS reviews 27 questions and generates and prioritizes missing questions in a similar manner | ||
| 2/19 | PLUS adopts 29 research questions for refinement and use in a national longitudinal observational study |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
B. Lewis, J.; S. Brady, S.; Sutcliffe, S.; L. Smith, A.; R. Mueller, E.; Rudser, K.; D. Markland, A.; Stapleton, A.; Gahagan, S.; Cunningham, S.D.; et al. Converging on Bladder Health through Design Thinking: From an Ecology of Influence to a Focused Set of Research Questions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4340. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17124340
B. Lewis J, S. Brady S, Sutcliffe S, L. Smith A, R. Mueller E, Rudser K, D. Markland A, Stapleton A, Gahagan S, Cunningham SD, et al. Converging on Bladder Health through Design Thinking: From an Ecology of Influence to a Focused Set of Research Questions. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(12):4340. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17124340
Chicago/Turabian StyleB. Lewis, Jessica, Sonya S. Brady, Siobhan Sutcliffe, Ariana L. Smith, Elizabeth R. Mueller, Kyle Rudser, Alayne D. Markland, Ann Stapleton, Sheila Gahagan, Shayna D. Cunningham, and et al. 2020. "Converging on Bladder Health through Design Thinking: From an Ecology of Influence to a Focused Set of Research Questions" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 12: 4340. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17124340
APA StyleB. Lewis, J., S. Brady, S., Sutcliffe, S., L. Smith, A., R. Mueller, E., Rudser, K., D. Markland, A., Stapleton, A., Gahagan, S., Cunningham, S. D., & Prevention of Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (PLUS) Research Consortium. (2020). Converging on Bladder Health through Design Thinking: From an Ecology of Influence to a Focused Set of Research Questions. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(12), 4340. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17124340





