Impact of a Culturally Tailored mHealth Medication Regimen Self-Management Program upon Blood Pressure among Hypertensive Hispanic Adults
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Protocol/Intervention/Groups
SMASH Intervention Group
2.4. Outcome Measures
3. Results
3.1. Resting Systolic Blood Pressure Level Changes
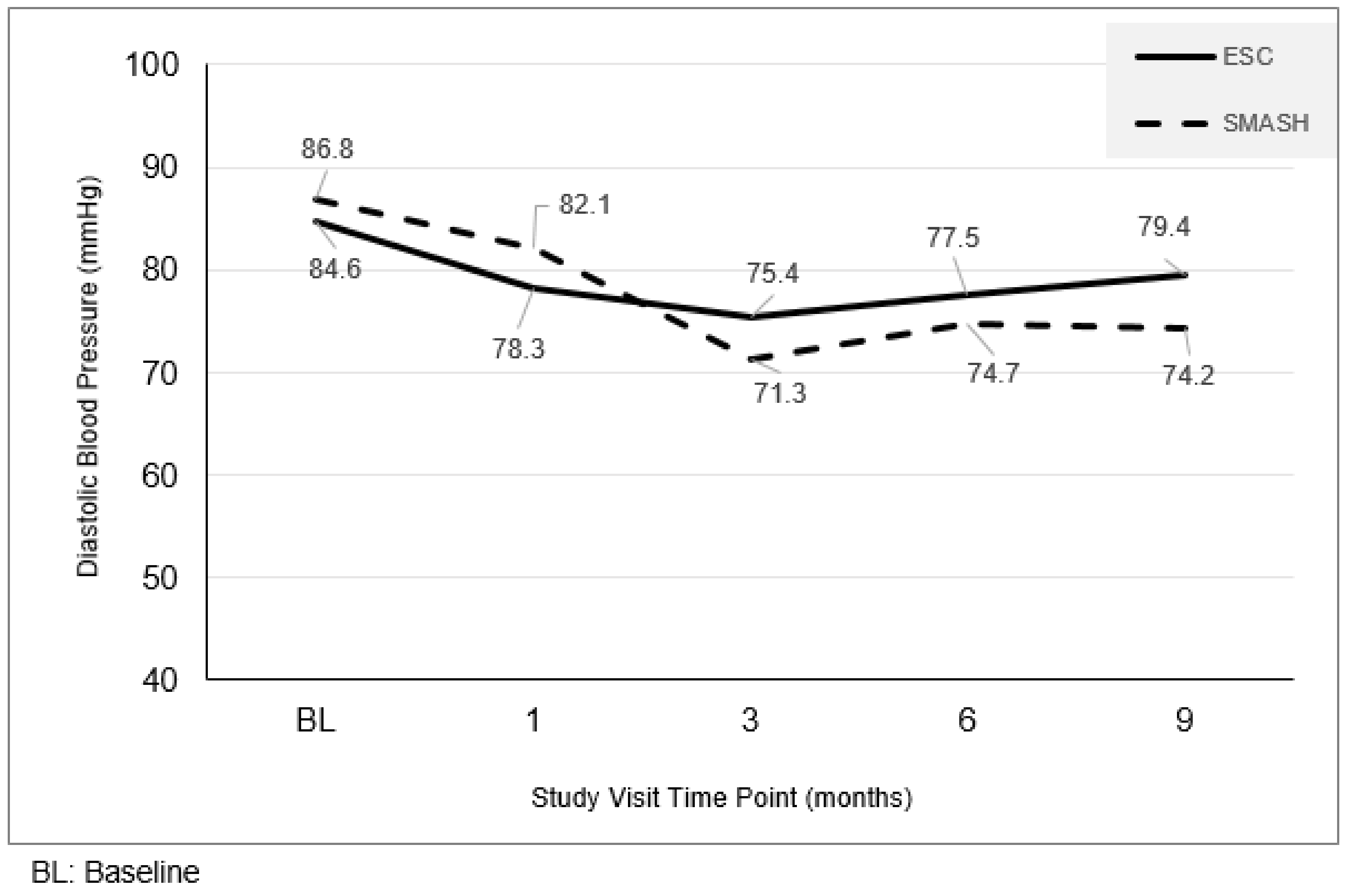
3.2. Resting Diastolic Blood Pressure Level Changes
3.3. The Seventh Joint National Committee (JNC7) Blood Pressure Control Changes
3.4. Medication and BP Self-Measurement Adherence
3.5. SMASH Satisfaction and Usability
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nwankwo, T.; Yoon, S.S.; Burt, V.; Gu, Q. Hypertension among adults in the united states: National health and nutrition examination survey, 2011–2012. NCHS Data Brief 2013, 133, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Egan, B.M.; Zhao, Y.; Axon, R.N. US trends in prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension, 1988-2008. JAMA 2010, 303, 2043–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keenan, N.L.; Rosendorf, K.A.; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Prevalence of hypertension and controlled hypertension–United States, 2005–2008. MMWR Surveill. Summ. 2011, 60, 94–97. [Google Scholar]
- Traylor, A.H.; Schmittdiel, J.A.; Uratsu, C.S.; Mangione, C.M.; Subramanian, U. Adherence to cardiovascular disease medications: Does patient-provider race/ethnicity and language concordance matter? J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2010, 25, 1172–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Chu, E.K.; Fang, J.; Wall, H.K.; Ayala, C. Nonadherence to antihypertensive medication among hypertensive adults in the united states horizontal line healthstyles, 2010. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2016, 18, 892–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, H.M.; Luo, R.; Hanlon, J.T.; Elting, L.S.; Suarez-Almazor, M.; Goodwin, J.S. Ethnic disparities in adherence to antihypertensive medications of medicare part d beneficiaries. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2012, 60, 1298–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, C.J.; Allison, M.; Daviglus, M.L.; Isasi, C.R.; Keller, C.; Leira, E.C.; Palaniappan, L.; Pina, I.L.; Ramirez, S.M.; Rodriguez, B.; et al. Status of cardiovascular disease and stroke in hispanics/latinos in the united states: A science advisory from the american heart association. Circulation 2014, 130, 593–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, R.; Bills, J.E.; Hecht, T.J.; Light, R.P. Role of home blood pressure monitoring in overcoming therapeutic inertia and improving hypertension control: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Hypertension 2011, 57, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glynn, L.G.; Murphy, A.W.; Smith, S.M.; Schroeder, K.; Fahey, T. Interventions used to improve control of blood pressure in patients with hypertension. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2010, 3, CD005182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappuccio, F.P.; Kerry, S.M.; Forbes, L.; Donald, A. Blood pressure control by home monitoring: Meta-analysis of randomised trials. BMJ 2004, 329, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloss, C.S.; Wineinger, N.E.; Peters, M.; Boeldt, D.L.; Ariniello, L.; Kim, J.Y.; Sheard, J.; Komatireddy, R.; Barrett, P.; Topol, E.J. A prospective randomized trial examining health care utilization in individuals using multiple smartphone-enabled biosensors. PeerJ 2016, 4, e1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Free, C.; Phillips, G.; Watson, L.; Galli, L.; Felix, L.; Edwards, P.; Patel, V.; Haines, A. The effectiveness of mobile-health technologies to improve health care service delivery processes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Med. 2013, 10, e1001363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinhubl, S.R.; Muse, E.D.; Topol, E.J. The emerging field of mobile health. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 283rv283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morawski, K.; Ghazinouri, R.; Krumme, A.; Lauffenburger, J.C.; Lu, Z.; Durfee, E.; Oley, L.; Lee, J.; Mohta, N.; Haff, N.; et al. Association of a smartphone application with medication adherence and blood pressure control: The medisafe-bp randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern. Med. 2018, 178, 802–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpp, K.G.; Troxel, A.B.; Mehta, S.J.; Norton, L.; Zhu, J.; Lim, R.; Wang, W.; Marcus, N.; Terwiesch, C.; Caldarella, K. Effect of electronic reminders, financial incentives, and social support on outcomes after myocardial infarction: The heartstrong randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern. Med. 2017, 177, 1093–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpp, K.G.; John, L.K.; Troxel, A.B.; Norton, L.; Fassbender, J.; Loewenstein, G. Financial incentive-based approaches for weight loss: A randomized trial. JAMA 2008, 300, 2631–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmel, S.E.; Troxel, A.B.; Loewenstein, G.; Brensinger, C.M.; Jaskowiak, J.; Doshi, J.A.; Laskin, M.; Volpp, K. Randomized trial of lottery-based incentives to improve warfarin adherence. Am. Heart J. 2012, 164, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deci, E.L.; Koestner, R.; Ryan, R.M. A meta-analytic review of experiments examining the effects of extrinsic rewards on intrinsic motivation. Psychol. Bull. 1999, 125, 627–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, J.; Ntoumanis, N.; Thogersen-Ntoumani, C.; Deci, E.; Ryan, R.; Duda, J.; Williams, G. Self-determination theory applied to healthy contexts: A meta-analysis. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 2012, 7, 325–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, R.M.; Kuhl, J.; Deci, E.L. Nature and autonomy: An organizational view of social and neurobiological aspects of self-regulation in behavior and development. Dev. Psychopathol. 1997, 9, 701–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, R.M.; Tobin, V.J.; Rollnick, S. Motivational interviewing and self-determination theory. J. Soc. Clin. Psychol. 2005, 24, 811–831. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, R.M.; Deci, E.L. Self-determination theory and the facilitation of intrinsic motivation, social development, and well-being. Am. Psychol. 2000, 55, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, R.; Deci, E. Facilitating health behaviour change and its maintenance: Interventions based on self-determination theory. Eur. Health Psychol. 2008, 10, 2–5. [Google Scholar]
- Sieverdes, J.; Gregoski, M.; Patel, S.; Williamson, D.; Brunner-Jackson, B.; Rundbaken, J.; Treiber, E.; Davidson, L.; Treiber, F. Medication and blood pressure mhealth self-management program with hispanic hypertensives: A proof of concept trial. Smart Homecare Technol. TeleHealth 2013, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, T.M.; McGillicuddy, J.; Mueller, M.; Brunner-Jackson, B.; Favella, A.; Anderson, A.; Torres, M.; Ruggiero, K.J.; Treiber, F.A. Evaluation of an mhealth medication regimen self-management program for african american and hispanic uncontrolled hypertensives. J. Pers. Med. 2015, 5, 389–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, M.; Williamson, D.; McCandless, R.; Mueller, M.; Gregoski, M.; Brunner-Jackson, B.; Treiber, E.; Davidson, L.; Treiber, F. Hispanic migrant farm workers’ attitudes toward mobile phone-based telehealth for management of chronic health conditions. J. Med. Internet Res. 2013, 15, e76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmunds, J.; Ntoumanis, N.; Duda, J.L. Testing a self-determination theory-based teaching style intervention in the exercise domain. Eur. J. Soc. Psychol. 2008, 38, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resnicow, K.; Davis, R.; Zhang, N.; Tolsma, D.; Alexander, G.; Wiese, C.; Cross, W.E., Jr.; Anderson, J.P.; Calvi, J.; Strecher, V. Tailoring a fruit and vegetable intervention on ethnic identity: Results of a randomized study. Health Psychol. 2009, 28, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resnicow, K.; McMaster, F. Motivational interviewing: Moving from why to how with autonomy support. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2012, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appel, L.J.; Champagne, C.M.; Harsha, D.W.; Cooper, L.S.; Obarzanek, E.; Elmer, P.J.; Stevens, V.J.; Vollmer, W.M.; Lin, P.H.; Svetkey, L.P.; et al. Effects of comprehensive lifestyle modification on blood pressure control: Main results of the premier clinical trial. JAMA 2003, 289, 2083–2093. [Google Scholar]
- Julius, S.; Nesbitt, S.D.; Egan, B.M.; Weber, M.A.; Michelson, E.L.; Kaciroti, N.; Black, H.R.; Grimm, R.H., Jr.; Messerli, F.H.; Oparil, S.; et al. Feasibility of treating prehypertension with an angiotensin-receptor blocker. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 1685–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morisky, D.E.; Ang, A.; Krousel-Wood, M.; Ward, H.J. Predictive validity of a medication adherence measure in an outpatient setting. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2008, 10, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakken, S.; Grullon-Figueroa, L.; Izquierdo, R.; Lee, N.J.; Morin, P.; Palmas, W.; Teresi, J.; Weinstock, R.S.; Shea, S.; Starren, J. Development, validation, and use of english and spanish versions of the telemedicine satisfaction and usefulness questionnaire. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2006, 13, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGillicuddy, J.W.; Taber, D.J.; Mueller, M.; Patel, S.; Baliga, P.K.; Chavin, K.D.; Sox, L.; Favela, A.P.; Brunner-Jackson, B.M.; Treiber, F.A. Sustainability of improvements in medication adherence through a mobile health intervention. Prog. Transplant. 2015, 25, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovbiagele, B.; Jenkins, C.; Patel, S.; Brunner-Jackson, B.; Anderson, A.; Saulson, R.; Treiber, F. Mobile health medication adherence and blood pressure control in recent stroke patients. J. Neurol. Sci. 2015, 358, 535–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGillicuddy, J.W.; Weiland, A.K.; Frenzel, R.M.; Mueller, M.; Brunner-Jackson, B.M.; Taber, D.J.; Baliga, P.K.; Treiber, F.A. Patient attitudes toward mobile phone-based health monitoring: Questionnaire study among kidney transplant recipients. J. Med. Internet Res. 2013, 15, e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, S.; Berkhouse, H.; Schooler, M.; Pu, W.; Sun, A.; Gong, E.; Yan, L.L. Effectiveness of mhealth interventions in improving medication adherence among people with hypertension: A systematic review. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2018, 20, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frias, J.; Virdi, N.; Raja, P.; Kim, Y.; Savage, G.; Osterberg, L. Effectiveness of digital medicines to improve clinical outcomes in patients with uncontrolled hypertension and type 2 diabetes: Prospective, open-label, cluster-randomized pilot clinical trial. J. Med. Internet Res. 2017, 19, e246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Free, C.; Phillips, G.; Galli, L.; Watson, L.; Felix, L.; Edwards, P.; Patel, V.; Haines, A. The effectiveness of mobile-health technology-based health behaviour change or disease management interventions for health care consumers: A systematic review. PLoS Med. 2013, 10, e1001362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamine, S.; Gerth-Guyette, E.; Faulx, D.; Green, B.B.; Ginsburg, A.S. Impact of mhealth chronic disease management on treatment adherence and patient outcomes: A systematic review. J. Med. Internet Res. 2015, 17, e52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karhula, T.; Vuorinen, A.-L.; Rääpysjärvi, K.; Pakanen, M.; Itkonen, P.; Tepponen, M.; Junno, U.-M.; Jokinen, T.; van Gils, M.; Lähteenmäki, J. Telemonitoring and mobile phone-based health coaching among finnish diabetic and heart disease patients: Randomized controlled trial. J. Med. Internet Res. 2015, 17, e153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Demographic | SMASH (n = 26) | ESC (n = 28) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (M+/- SD) | 44.4 ± 7.2 | 46.8 ± 8.1 | |
| Gender | Male | 29% | 38% |
| Female | 71% | 62% | |
| Marital Status | Single | 24% | 10% |
| Married/Living with Significant Other | 47% | 62% | |
| Separated/Divorced | 24% | 21% | |
| Widowed | 5% | 7% | |
| Education | High School or less | 71% | 72% |
| Partial/College Grad | 29% | 28% | |
| Income | $0–25,000 | 71% | 62% |
| $25–50,000 | 29% | 21% | |
| >$50,000 | 0% | 3% | |
| Not Reported | 0% | 14% | |
| Employment | Full/Part-Time | 41% | 69% |
| Retired/Disabled | 0% | 0% | |
| Unemployed | 59% | 31% |
| Controlled SBP | SMASH | ESC | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 0 | 0 | -- |
| Month 1 | 80.0 | 42.3 | 0.005 |
| Month 3 | 92.0 | 62.5 | 0.013 |
| Month 6 | 94.4 | 57.9 | 0.009 |
| Month 9 | 92.3 | 27.8 | 0.001 |
| Controlled DBP | SMASH | SC | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 61.5 | 64.2 | 0.838 |
| Month 1 | 100 | 88.5 | 0.083 |
| Month 3 | 100 | 91.7 | 0.145 |
| Month 6 | 100 | 94.7 | 0.337 |
| Enhanced Standard Care | SMASH | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study Visit | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | ∆ | p-Value |
| Baseline | 6.99 | 2.39 | 6.83 | 1.99 | 0.154 | 0.78 |
| 1 | 7.85 | 1.66 | 9.42 | 0.95 | 1.573 | <0.001 |
| 3 | 7.98 | 1.95 | 9.13 | 1.50 | 1.142 | 0.017 |
| 6 | 7.48 | 1.7 | 10.22 | 0.43 | 2.741 | <0.001 |
| 9 | 6.84 | 1.52 | 9.81 | 1.31 | 2.971 | <0.001 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chandler, J.; Sox, L.; Kellam, K.; Feder, L.; Nemeth, L.; Treiber, F. Impact of a Culturally Tailored mHealth Medication Regimen Self-Management Program upon Blood Pressure among Hypertensive Hispanic Adults. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1226. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16071226
Chandler J, Sox L, Kellam K, Feder L, Nemeth L, Treiber F. Impact of a Culturally Tailored mHealth Medication Regimen Self-Management Program upon Blood Pressure among Hypertensive Hispanic Adults. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(7):1226. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16071226
Chicago/Turabian StyleChandler, Jessica, Luke Sox, Kinsey Kellam, Lauren Feder, Lynne Nemeth, and Frank Treiber. 2019. "Impact of a Culturally Tailored mHealth Medication Regimen Self-Management Program upon Blood Pressure among Hypertensive Hispanic Adults" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 7: 1226. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16071226
APA StyleChandler, J., Sox, L., Kellam, K., Feder, L., Nemeth, L., & Treiber, F. (2019). Impact of a Culturally Tailored mHealth Medication Regimen Self-Management Program upon Blood Pressure among Hypertensive Hispanic Adults. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(7), 1226. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16071226






