The Risk Factors Related to Voice Disorder in Teachers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
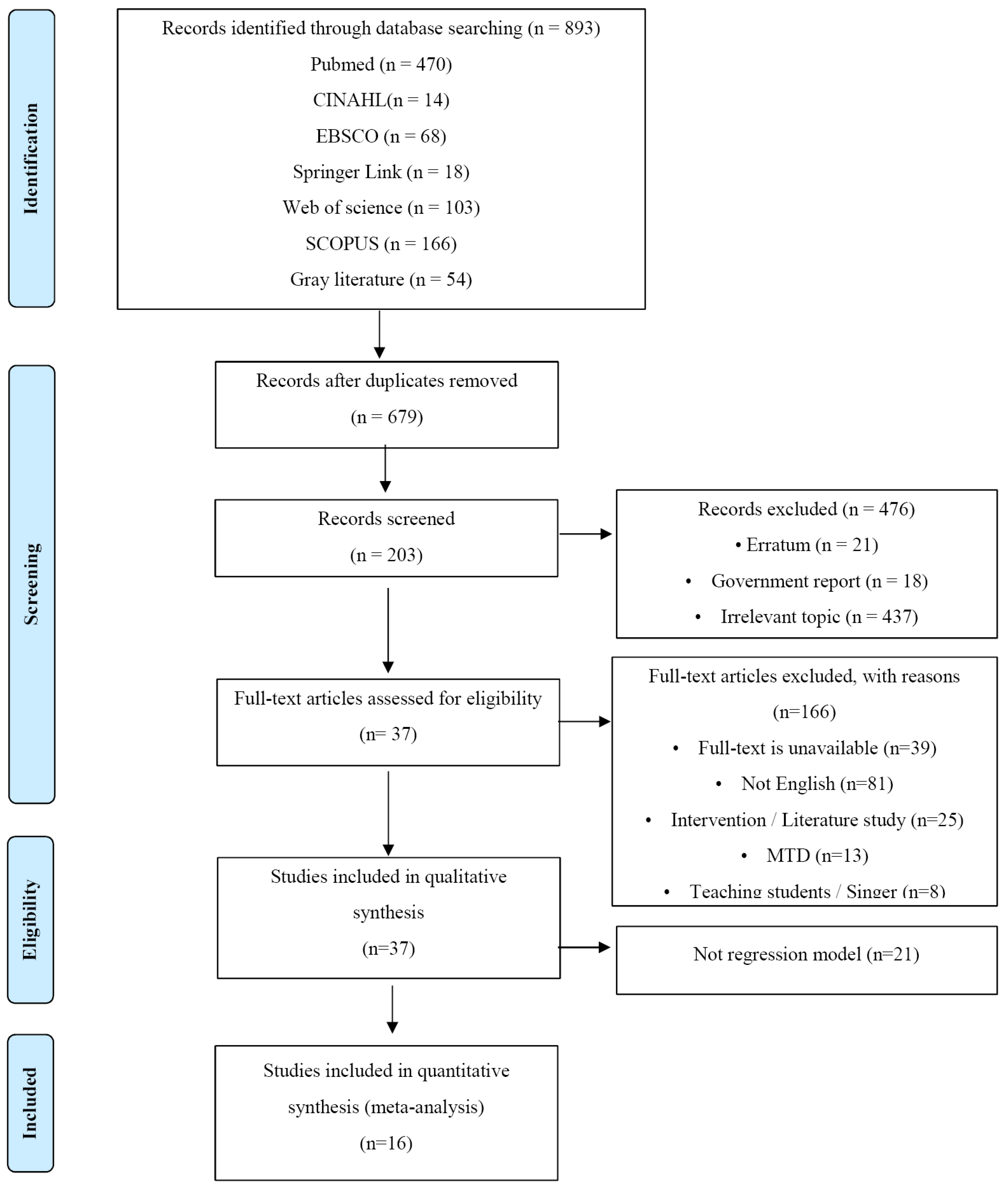
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Review
2.1.1. Pubmed
2.1.2. Web of Science
2.1.3. EBSCO (ASC, CINAHL, Medline)
2.2 Literature Selection Criteria
2.3 Quality Assessment
2.4 Meta-Analysis
2.4.1. Effect Size Estimation and Interpretation
2.4.2. Homogeneity Test
2.4.3. Publication Bias Test
3. Results
3.1. General Characteristics of Literature
3.2. Results of Quality Assessment
3.3. Definition of Voice Disorders
3.4. Health Level Assessment
3.5 Risk Factors of Teachers’ Voice Disorders
3.5.1. Sociodemographic Factors and Health Behaviors
3.5.2. Health Factors
3.5.3. Diseases Associated with Voice Disorders
3.5.4. Occupational Environment
3.5.5. Subjective Voice Problem Recognition
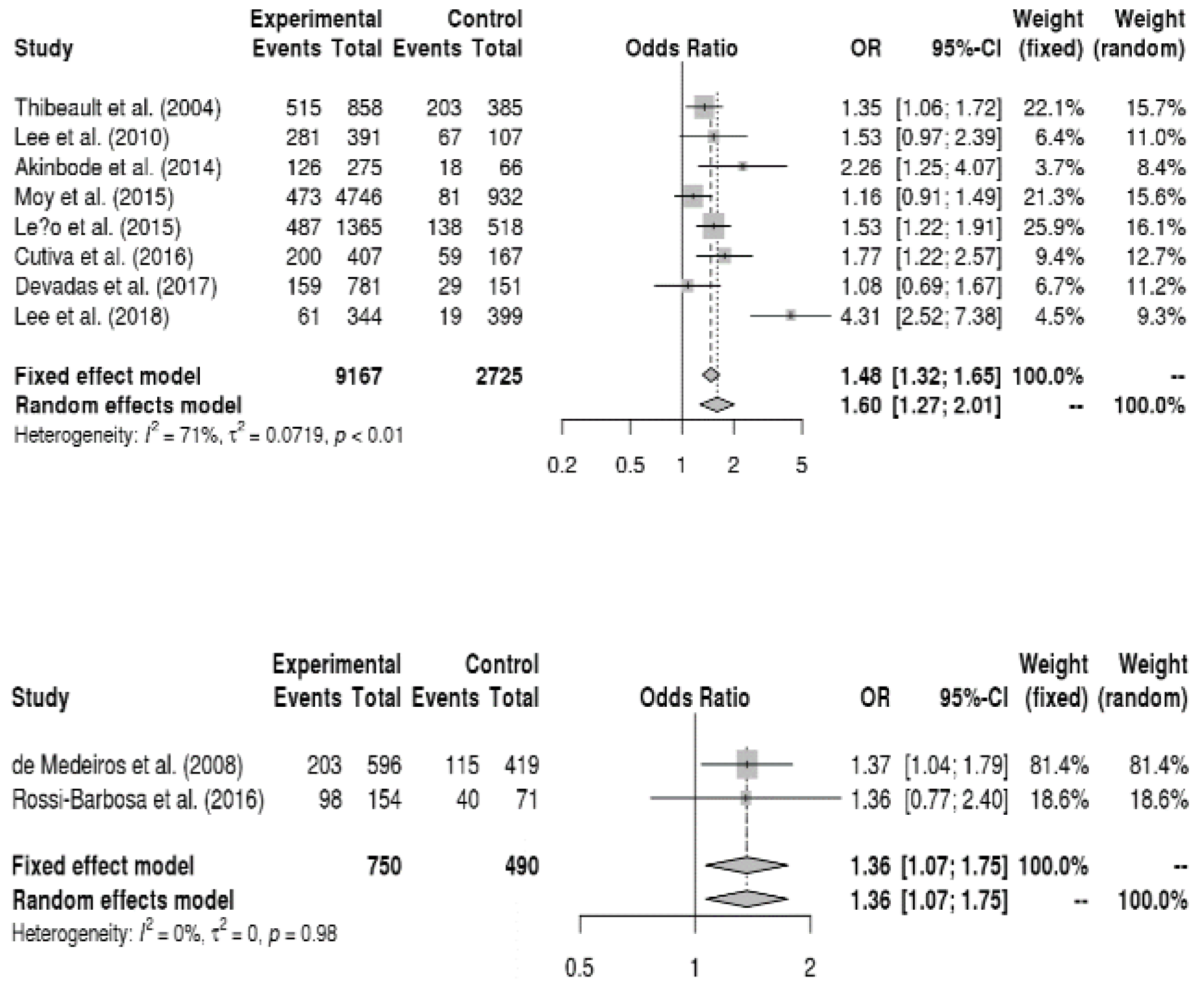
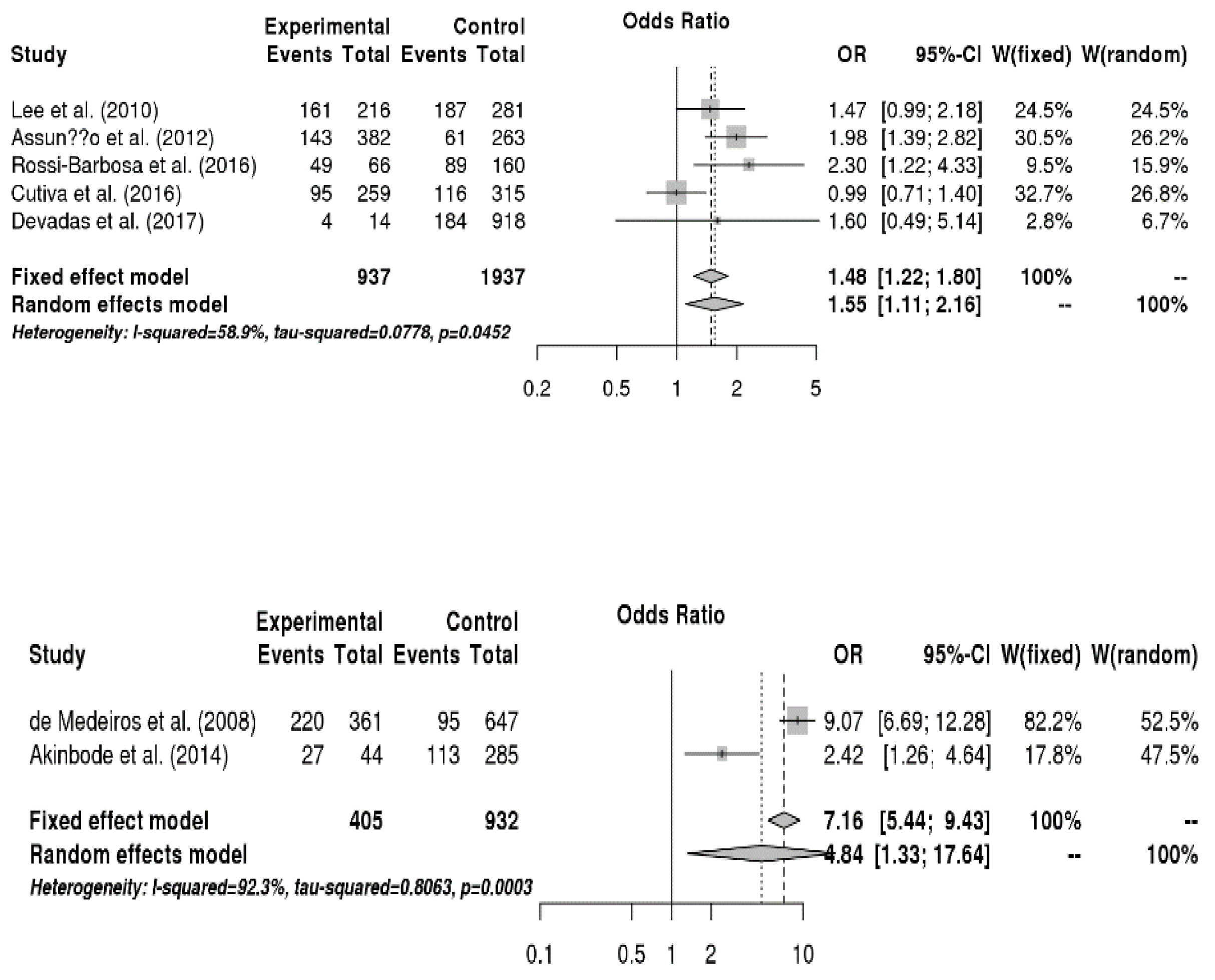
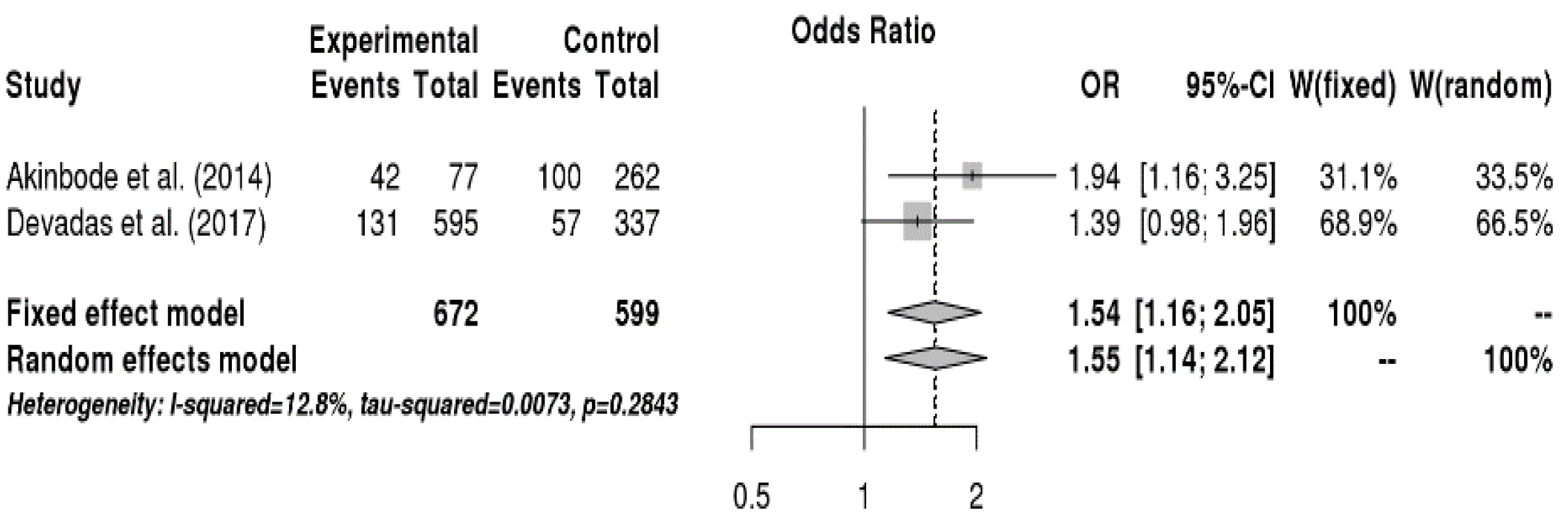
3.6. Meta-Analysis
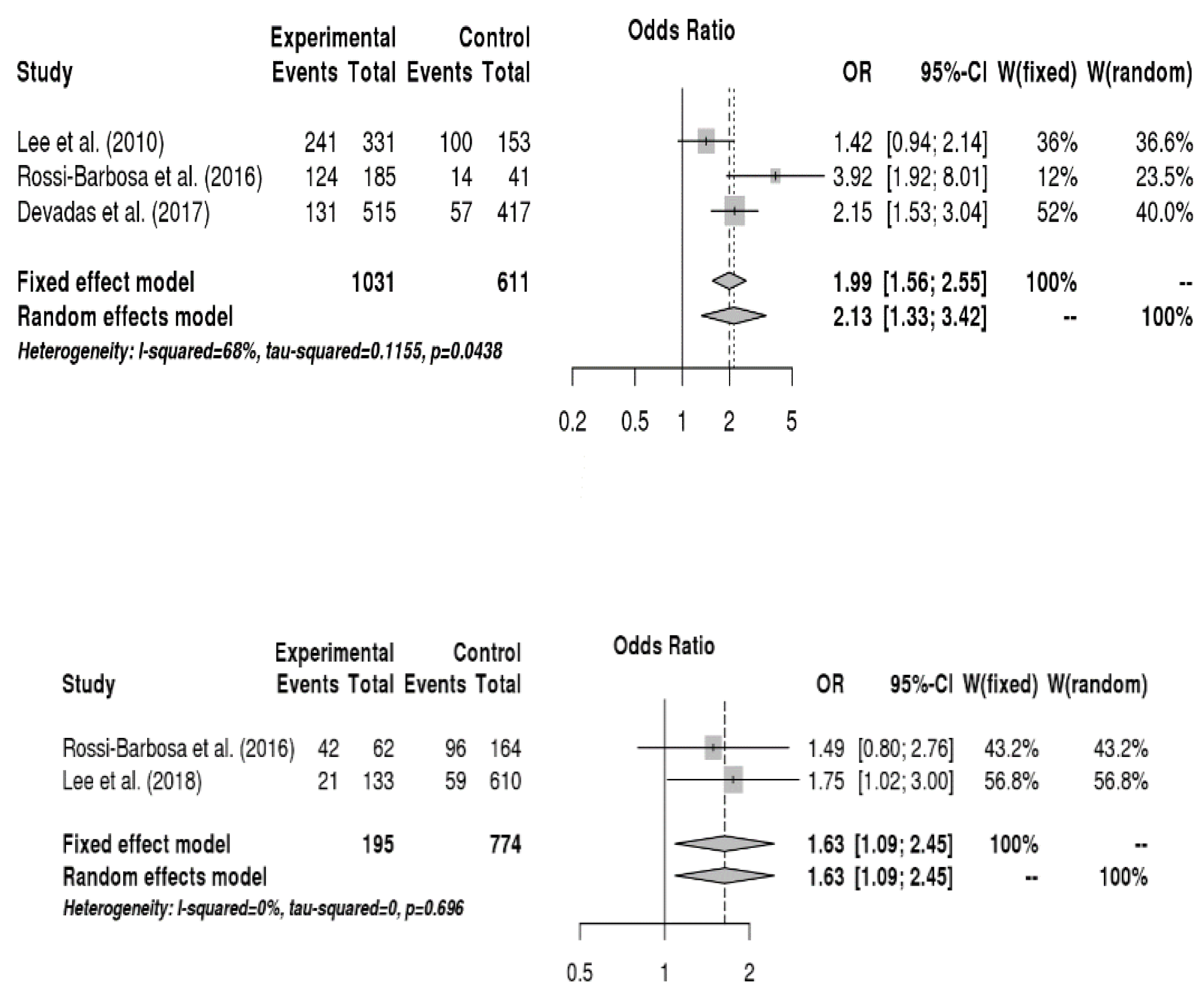
3.6.1. Relationship between Sociodemographic Factors and Voice Disorders
3.6.2. Relationship between Disease Factors and Voice Disorders
3.6.3. Relationship between Health Risk Behaviors and Voice Disorders
3.6.4. Relationship between Occupational Environment and Voice Disorders
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Titze, I.R.; Lemke, J.; Montequin, D. Populations in the US workforce who rely on voice as a primary tool of trade: A preliminary report. J. Voice 1997, 1, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifpanahi, S.; Izadi, F.; Jamshidi, A.A.; Torabinezhad, F.; Sarrafzadeh, J.; Sobhani-Rad, D.; anjuie, M. Prevalence of voice disorders and associated risk factors in teachers and nonteachers in Iran. J. Voice 2016, 30, 506-e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.Y.; Lao, X.Q.; Yu, I.T. A cross-sectional survey of voice disorders among primary school teachers in Hong Kong. J. Occup. Health 2010, 52, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moy, F.M.; Hoe, V.C.W.; Hairi, N.N.; Chu, A.H.Y.; Bulgiba, A.; Koh, D. Determinants and effects of voice disorders among secondary school teachers in Peninsular Malaysia using a Validated Malay Version of VHI-10. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leão, S.H.D.S.; Oates, J.M.; Purdy, S.C.; Scott, D.; Morton, R.P. Voice problems in New Zealand teachers: A national survey. J. Voice 2015, 29, 645-e1–. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alva, A.; Machado, M.; Bhojwani, K.; Sreedharan, S. Study of risk factors for development of voice disorders and its impact on the quality of life of school teachers in Mangalore, India. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2017, 11, MC01–MC05. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Brito Mota, A.F.; Giannini, S.P.P.; de Oliveira, I.B.; Paparelli, R.; Dornelas, R.; Ferreira, L.P. Voice disorder and burnout syndrome in Teachers. J. Voice 2018, 33, 581-e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannini, S.P.P.; de Oliveira, M.D.R.D.; Fischer, F.M.; Ghirardi, A.C.D.A.M.; Ferreira, L.P. Teachers’ voice disorders and loss of work ability: A case-control study. J. Voice 2015, 29, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sliwinska-Kowalska, M.; Niebudek-Bogusz, E.; Fiszer, M.; Los-Spychalska, T.; Kotylo, P.; Sznurowska-Przygocka, B.; Modrzewska, M. The prevalence and risk factors for occupational voice disorders in teachers. Folia. Phoniatr. Logop. 2006, 58, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdan, A.L.; Sibai, A.M.; Srour, Z.M.; Sabra, O.A.; Deeb, R.A. Voice disorders in teachers. The role of family physicians. Saudi Med. J. 2007, 28, 422–428. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, E.R.B.N.; Tavares, E.L.M.; Martins, R.H.G. Voice disorders in teachers: Clinical, videolaryngoscopical, and vocal aspects. J. Voice 2015, 29, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Medeiros, A.M.; Barreto, S.M.; Assunção, A.Á. Voice disorders (dysphonia) in public school female teachers working in Belo Horizonte: Prevalence and associated factors. J. Voice 2008, 22, 676–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.R.; Kim, H.R.; Lee, S. Effect of teacher’s working conditions on voice disorder in Korea: A nationwide survey. Ann. Occup. Environ. Med. 2018, 30, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Rocha, L.M.; de Lima Bach, S.; do Amaral, P.L.; Behlau, M.; de Mattos Souza, L.D. Risk factors for the incidence of perceived voice disorders in elementary and middle school teachers. J. Voice 2017, 31, 258-e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.H.; Chiang, S.C.; Chung, Y.M.; Hsiao, L.C.; Hsiao, T.Y. Risk factors and effects of voice problems for teachers. J. Voice 2010, 24, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akinbode, R.; Lam, K.B.H.; Ayres, J.G.; Sadhra, S. Voice disorders in Nigerian primary school teachers. Occup. Med. 2014, 64, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinite, B. Epidemiology of voice disorders in Latvian school teachers. J. Voice 2017, 31, 508-e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devadas, U.; Bellur, R.; Maruthy, S. Prevalence and risk factors of voice problems among primary school teachers in India. J. Voice 2017, 31, 117-e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi-Barbosa, L.A.R.; Barbosa, M.R.; Morais, R.M.; de Sousa, K.F.; Silveira, M.F.; Gama, A.C.C.; Caldeira, A.P. Self-reported acute and chronic voice disorders in teachers. J. Voice 2016, 30, 755-e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantor Cutiva, L.C.; Fajardo, A.; Burdorf, A. Associations between self-perceived voice disorders in teachers, perceptual assessment by speech-language pathologists, and instrumental analysis. Int. J. Speech Lang. Pathol. 2016, 18, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vertanen-Greis, H.; Löyttyniemi, E.; Uitti, J. Voice disorders are associated with stress among teachers: A cross-sectional study in Finland. J. Voice 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assunção, A.A.; Bassi, I.B.; de Medeiros, A.M.; de Souza Rodrigues, C.; Gama, A.C.C. Occupational and individual risk factors for dysphonia in teachers. Occup. Med. (Lond.) 2012, 62, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Rocha, L.M.; Behlau, M.; de Mattos Souza, L.D. Behavioral dysphonia and depression in elementary school teachers. J. Voice 2015, 29, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Alvear, R.M.B.; Barón, F.J.; Martínez-Arquero, A.G. School teachers’ vocal use, risk factors, and voice disorder prevalence: Guidelines to detect teachers with current voice problems. Folia. Phoniatr. Logop. 2011, 63, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutiva, L.C.C.; Vogel, I.; Burdorf, A. Voice disorders in teachers and their associations with work-related factors: A systematic review. J. Commun. Disord. 2013, 46, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattiske, J.A.; Oates, J.M.; Greenwood, K.M. Vocal problems among teachers: A review of prevalence, causes, prevention, and treatment. J. Voice 1998, 2, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, R.H.G.; Pereira, E.R.B.N.; Hidalgo, C.B.; Tavares, E.L.M. Voice disorders in teachers. A review. J. Voice 2014, 28, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kmet, L.M.; Lee, R.; Cook, L.S. Standard Quality Assessment Criteria for Evaluating Primary Research Papers from a Variety of Fields; Alberta Heritage Foundation for Medical Research: Edmonton, AB, Canada, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, Y.H.; Chee, D.Y.; Girdler, S.; Lee, H.C. Median nerve mobilization techniques in the treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome: A systematic review. J. Hand Ther. 2017, 30, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, L.; Packer, T.L.; Tang, S.H.; Girdler, S. Self-management education programs for age-related macular degeneration: A systematic review. Australas. J. Ageing 2008, 27, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibeault, S.L.; Merrill, R.M.; Roy, N.; Gray, S.D.; Smith, E.M. Occupational risk factors associated with voice disorders among teachers. Ann. Epidemiol. 2004, 14, 786–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, C.F.; Preciado, J.L. Vocal fold nodules. Risk factors in teachers. A case control study design. Acta Otorrinolaringol. Esp. 2003, 54, 253–260. [Google Scholar]
- Tavares, E.L.; Martins, R.H. Vocal evaluation in teachers with or without symptoms. J. Voice 2007, 21, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceballos, A.G.D.C.D.; Carvalho, F.M.; Araújo, T.M.D.; Reis, E.J.F.B.D. Auditory vocal analysis and factors associated with voice disorders among teachers. Rev. Bras. Epidemiol. 2011, 14, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, J.B.; Blair, J.C. The effect of classroom amplification on the signal-to-noise ratio in classrooms while class is in session. Lang. Speech Hear. Serv. Sch. 2008, 39, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindstrom, F.; Waye, K.P.; Södersten, M.; McAllister, A.; Ternström, S. Observations of the relationship between noise exposure and preschool teacher voice usage in day-care center environments. J. Voice 2011, 25, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boone, D.; McFarlane, S.C.; Von Berg, S.L.; Zraick, R.I. The Voice and Voice Therapy, 9th ed.; Pearson Education Inc.: Boston, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Crandell, C.C.; Smaldino, J.J. An update of classroom acoustics for children with hearing impairment. Volta Rev. 1994, 96, 291–306. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, W.J. An analysis of noise conditions in elementary schools located near airports and roads. Fam. Environ. Res. 2005, 43, 31–47. [Google Scholar]
- Byeon, H. Gender differences in risk factors of benign vocal fold disease in Korea: The fifth Korea National Health and Nutritional Examination Survey. Logop. Phoniatr. Vocology 2016, 41, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.M. Self-reported impact of dysphonia in a primary care population: An epidemiological study. Laryngoscope 2010, 120, 2022–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayres, J.G.; Gabbott, P.L.A. Vocal cord dysfunction and laryngeal hyperresponsiveness: A function of altered autonomic balance? Thorax 2002, 57, 284–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, C.M. Functional Dysphonia and Voice Therapy; Medbook: Seoul, Korea, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, N.; Merrill, R.M.; Gray, S.D.; Smith, E.M. Voice disorders in the general population: Prevalence, risk factors, and occupational impact. Laryngoscope 2005, 115, 1988–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byeon, H.; Lee, Y. Prevalence and risk factors of benign laryngeal lesions in the adult population. CSD 2010, 15, 648–656. [Google Scholar]

| Study | Items on Standard Quality Assessment Checklist | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | Total | |
| Thibeault et al. (2004) | + | + | + | + | - | N/A | N/A | + | ± | + | + | + | + | + | 21 |
| Sliwinska-Kowalska et al. (2006) | + | + | + | ± | - | N/A | N/A | + | ± | + | + | + | + | + | 20 |
| Hamdan et al. (2007) | + | + | ± | + | - | N/A | N/A | + | ± | + | + | + | + | + | 20 |
| de Medeiros et al. (2008) | + | + | + | + | + | N/A | N/A | + | ± | + | + | + | + | + | 23 |
| Lee et al. (2010) | + | + | + | + | + | N/A | N/A | + | + | + | + | ± | + | + | 23 |
| De Alvear et al. (2011) | + | + | + | ± | - | N/A | N/A | + | + | + | + | ± | + | + | 20 |
| Assunção et al. (2012) | + | + | ± | + | - | N/A | N/A | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 21 |
| Akinbode et al. (2014) | + | + | + | + | + | N/A | N/A | + | ± | + | + | + | + | + | 23 |
| Leão et al. (20015) | + | + | + | + | - | N/A | N/A | + | ± | + | + | + | + | + | 21 |
| da Rocha et al. (2015) | + | + | + | + | + | N/A | N/A | + | ± | + | + | ± | + | + | 22 |
| Moy et al. (2015) | + | + | + | + | + | N/A | N/A | + | ± | + | + | + | + | + | 23 |
| Cantor Cutiva et al. (2016) | + | + | + | + | - | N/A | N/A | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 22 |
| Rossi-Barbosa et al. (2016) | + | + | + | + | + | N/A | N/A | + | + | + | + | ± | + | + | 23 |
| Devadas et al. (2017) | + | + | + | + | + | N/A | N/A | + | ± | + | + | ± | + | + | 22 |
| da Rocha et al. (2017) | + | + | + | + | - | N/A | N/A | + | + | + | + | ± | + | + | 21 |
| Lee et al. (2018) | + | + | + | + | + | N/A | N/A | + | ± | + | + | + | + | + | 23 |
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Byeon, H. The Risk Factors Related to Voice Disorder in Teachers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3675. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16193675
Byeon H. The Risk Factors Related to Voice Disorder in Teachers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(19):3675. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16193675
Chicago/Turabian StyleByeon, Haewon. 2019. "The Risk Factors Related to Voice Disorder in Teachers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 19: 3675. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16193675
APA StyleByeon, H. (2019). The Risk Factors Related to Voice Disorder in Teachers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(19), 3675. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16193675




