Abstract
PM2.5 pollution has become a severe problem in China due to rapid industrialization and high energy consumption. It can cause increases in the incidence of various respiratory diseases and resident mortality rates, as well as increase in the energy consumption in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems due to the need for air purification. This paper reviews and studies the sources of indoor and outdoor PM2.5, the impact of PM2.5 pollution on atmospheric visibility, occupational health, and occupants’ behaviors. This paper also presents current pollution status in China, the relationship between indoor and outdoor PM2.5, and control of indoor PM2.5, and finally presents analysis and suggestions for future research.
1. Introduction
In recent years, hazy weather caused by multiple pollutants, with PM10 (cutoff sizes ≤ 10 µm, inhalable particles) and PM2.5 (cutoff sizes ≤ 2.5 µm, particles that can enter the lungs) as the main pollutants, has affected large areas of China, lasting for a long time. It has a significant regional characteristic, which is shown in Figure 1 [1]. According to the data collected from the air quality monitoring stations in 338 big cities in China, the range of annual average concentrations of PM2.5 in 2015 in the 388 cities was 11–125 μg·m−3 with an average value of 50 μg·m−3. PM2.5 was the primary pollutant for 66.8% of the severely polluted days. In 2016, the average annual concentration of PM2.5 was 12–158 μg·m−3, with an average value of 47 μg·m−3, and PM2.5 was the main pollutant for more than 80.3% of the days with severe pollution [2,3]. PM2.5 has thus become the primary pollutant of atmospheric particulate pollution in China [4]. Compared with the coarser particles, PM2.5 is smaller in size, larger in surface area, and more easily transported, which implies more toxicity and harmful substances that can penetrate deep into the human body. PM2.5 can stay in the atmosphere for a long time and travel for a long distance. Therefore, it has a greater impact on human health and the quality of the atmospheric environment. It has always been a hot topic in various related research fields around the world.
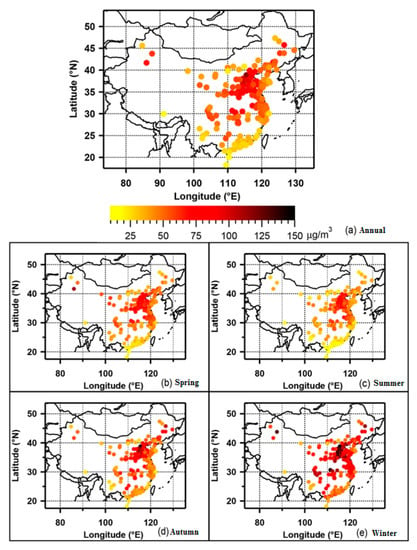
Figure 1.
Spatial and temporal distribution of PM2.5 in Chinese cities [5].
Since the 1980s, the USA and some European countries have conducted extensive studies on PM2.5, which are mainly related to the spatial and temporal distribution of PM2.5 concentrations, emission inventory, emission characteristics, source analysis and impact of PM2.5 on atmospheric visibility and human health [6]. In 1997, USA took the lead in establishing environmental air quality standards for PM2.5 and specified that the high limit of annual average PM2.5 concentration is 15 μg·m−3, and the 24 h concentration limit is 65 μg·m−3.
Two revisions have been made since then. Other countries (organizations) have also set PM2.5 concentration limits of their own (see Table 1). In China, it was not until in 2012 when the current ambient air quality standard was established and the concentration limit of PM2.5 was incorporated into the standard. The standard adopts the maximum limits set by the World Health Organization (WHO), i.e., the annual average concentration limit is 15 μg·m−3, and the 24-h concentration limit is 35 μg·m−3. However, it was not enforced nationwide until 2016. According to the latest PM2.5 concentration data published by WHO on 17 April 2016, the annual average PM2.5 concentration among 210 cities in China was in the range of 11–128 μg·m−3 [7]. It is noted that only 1.4% of the cities were able to meet the first level standard in China. The histogram distribution of PM2.5 concentrations is shown in Figure 2 [7]. It can be concluded that the problem of PM2.5 pollution in China is very serious and it is urgent to take action to control PM2.5 emission without delay.

Table 1.
Implementation time table for each country/organization on PM2.5 concentration limit.
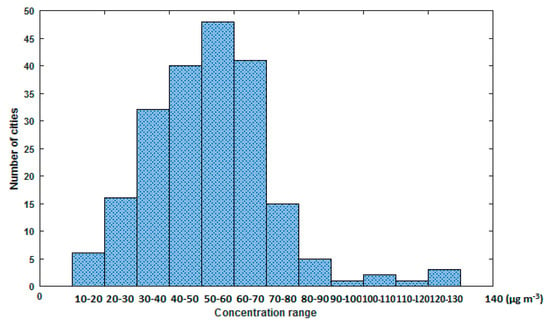
Figure 2.
Histogram distribution of PM2.5 concentration [7].
Due to the lack of long-term and large-scale monitoring data, compared with developed countries, research on PM2.5 in China started late and can be divided into three stages. The first stage was before 2004, and at the time the research on PM2.5 was of small scale and tentative. The studies were conducted mainly in major cities such as Beijing, Guangzhou, Nanjing and Shanghai. There were few studies on small and medium-sized cities, but only simple statistical and principle analysis on the data had been carried out [8,9,10,11,12,13,14]. For example, Wu et al. [16] conducted two-year data monitoring on PM2.5 concentration in Guangzhou, Wuhan, Lanzhou and Chongqing, and found that the PM2.5 concentration in the atmosphere generally exceeded 2–8 times of the limit set by the U.S. standard. Wang et al. [17] collected and analyzed nearly 10-year PM2.5 concentration data in urban and clean areas in China, and concluded that PM2.5 pollution is heavy in most parts of China. At the same time, He et al. [18] also collected PM2.5 concentration data from July 1997 to September 2000 in the city center and urban area in Beijing. It was shown that the seasonal variation of PM2.5 concentration was remarkable, with the highest in winter and the lowest in summer. Yang et al. [19] set up PM2.5 sampling points in Chegongzhuang and Tsinghua University in Beijing and started to discuss on the chemical composition characteristics of PM2.5. Huang et al. [20] collected 50 samples in five typical urban function areas of Nanjing in winter, spring and autumn and analyzed the PM2.5 pollution level. Wang et al. [21] studied the PM2.5 concentration in spring in Nanjing. Yang et al. [22] started to consider the source of PM2.5 in the atmosphere in Beijing.
The second stage is from 2004 to 2011. Although the research areas on PM2.5 gradually expanded, overall the research was still relatively straightforward, which were mainly related to the toxic effects of PM2.5 on cells [23,24,25,26,27,28], source analysis [29,30,31,32,33,34], and chemical composition analysis [35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42], etc. The third stage is from 2012 till now, due to the establishment of China’s PM2.5 air quality standards and gradual developments of nationwide PM2.5 observation stations, the number of researches on PM2.5 have increased exponentially. Since then, more and more disciplines have become involved in the study on PM2.5, but overall the research still lags behind, compared with developed countries. This paper aims at studying the advances in PM2.5 on research in China in recent years from the following four aspects: the sources of PM2.5, the influence of PM2.5, the correlation of indoor and outdoor PM2.5 concentration and the control of PM2.5, and trying to explore new insights for the scholars of future research.
2. Sources of PM2.5
2.1. Sources of PM2.5 in Urban Atmosphere
The sources of PM2.5 in urban atmosphere are very complicated. They can mainly be categorized into primary and secondary sources, of which primary sources refer to the direct emissions of various sources such as combustion sources. The secondary sources come from particles generated from the chemical processes in the atmosphere that oxidize the original gaseous components, such as sulfates and so on [43]. Currently, there are three methods, which are mostly often used to analyze the sources of atmospheric particulate matters, which are source inventory method, source model (dispersion model) method and receptor model method. The receptor model method is the most commonly used method for source analysis of PM2.5 in China [44]. The receptor model includes chemical mass balance method (CMB), positive matrix factorization (PMF) method, factor analysis (FA) method, principal component analysis (PCA) method, multi-linear engine (ME2) method and UNMIX method (UNMIX is a principal component method, but is based on geometrical analysis of the measurement dataset) [45]. Table 2 summarized the researches that have been conducted by the Chinese scholars on PM2.5 sources analysis. Some scholars also integrated these basic models with other methods for PM2.5 source apportionment analysis. For example, Wang et al. [46] used PMF model to derive PM2.5 contribution sources, and then used backward trajectory model to identify four potential directions to identify PM2.5 contribution sources, which shows that there was a clear difference in the distribution rates among all the different sources at different directions.

Table 2.
Modeling methods and analysis on sources of PM2.5.
Shi et al. [70] employed a chemical mass balance gas constraint-Iteration (CMBGC-Iteration) method for source appointment analysis in Tianjin. The outcomes from this method were compared with the ensemble-average outcomes of CMB, CMB-Iteration, CMB-GC, PMF, WALSPMF (Weighted Alternating Least Squares Positive Matrix Factorization), and NCAPCA (Non-negative Constrained Absolutely Principle Analysis), and it was found that they were comparable. From Table 2, it can be found that the sampling time of most scholars is periodical, although sometimes with very long time span, the sampling work was done only in typical months of each season, or even a few days in a typical month. Although there are contingency and uncertainty with the measurements, it can still reflect the contribution source categories of PM2.5 to some extent. Meanwhile, it is observed that the contribution rates of different sources to PM2.5 from different scholars vary greatly, and there are obvious differences, even for the same city. It could due to the differences in the sampling time of the study, contribution categories, regions, climate, energy structure, atmospheric environment, etc.
2.2. Sources of Indoor PM2.5
Sources of indoor PM2.5 can be divided into outdoor sources and indoor sources (see Figure 3). There is a time lag for the impact of outdoor PM2.5 concentration on the indoor PM2.5 to take effect. The indoor pollution sources are usually generated transiently and intermittently, resulting in large fluctuations in the concentration of indoor particulates [74].
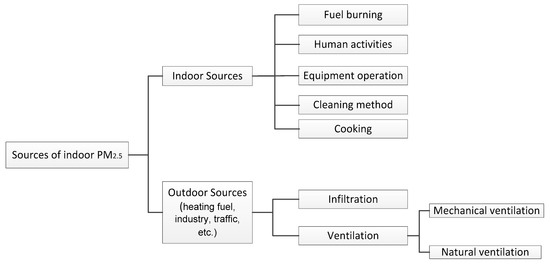
Figure 3.
Sources of indoor PM2.5.
2.2.1. Outdoor Sources
The outdoor sources come from heating fuel, industry, traffic, etc. [34,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73], due to the rapid industrialization, high energy consumption and large proportion of coal (60–70%) in the structure of energy sources in China. It has been acknowledged that there is close correlation between indoor and outdoor PM2.5 concentration levels, and outdoor PM2.5 is the main source of indoor PM2.5 pollution [75,76,77]. Wang et al. [78] showed that there was a significant correlation between indoor and outdoor concentrations of PM2.5 for rooms with normal airtightness and no air conditioning filter system. The indoor/outdoor (I/O) PM2.5 concentration ratio was up to 0.867. The correlation will be more obvious when the outdoor pollution level increases. Ji and Zhao [79] presented that 54–63% of indoor PM2.5 came from outdoors when the windows were closed, and it increased to as high as 92% when the windows were open. Han et al. [75] concluded that indoor PM2.5 concentration is significantly correlated with outdoor PM2.5 concentration but with 1 to 2 h delay, and the differences in the time lag effect are due to differences in environmental meteorological conditions such as outdoor air temperature, humidity ratio and wind direction.
2.2.2. Indoor Sources
There are many different types of indoor PM2.5 sources, which mainly come from fuel combustion, human activities, equipment operation, cleaning, and cooking. Indoor combustion of fuels such as coal, natural gas, alcohol, and mosquito coils can lead to the rapid increase of indoor PM2.5 concentration. Zhang and Duan [80] showed that burning a mosquito coil ring could release 626 μg·m−3 of PM2.5, which is 8.3 times the concentration limit allowed for the residential environment. Li et al. [81] concluded that PM2.5 concentration in households using coal to cook was significantly higher than those using gas or electricity, and if coal is switched to gas or electricity, the PM2.5 concentration in the kitchen could be reduced by 40–70%. Zhou et al. [82] indicated that human activities such as walking, dressing and cleaning could result in increased indoor PM2.5 concentration by 33%. Gui et al. [83] conducted experiments on dry-sweeping, wet-sweeping and air-dry sweeping in an office. The average indoor PM2.5 concentrations before cleaning were 47.3 μg·m−3, 40.6 μg·m−3 and 39.4 μg·m−3, respectively. The average indoor PM2.5 concentrations were 109.7 μg·m−3, 97.5 μg·m−3 and 43.3 μg·m−3 after cleaning. The average PM2.5 concentrations were increased by 2.3 times, 2.3 times and 1.1 times, respectively. Therefore, it is recommended to use wet sweeping under ventilated condition as much as possible. Sun et al. [84] found that the printer also plays a role in contributing to indoor PM2.5 concentration, and that PM2.5 released by printers with different performances was quite different. Zhang et al. [85] advised that different cooking habits, cooking methods, raw materials and even seasoning strongly influence the composition of particulate matters.
2.3. PM2.5 Reginal Variations
PM2.5 pollution has significant regional characteristics. The pollution conditions within or between regions is interrelated. PM2.5 pollution in one region is affected not only by local pollution sources but also outside regions to different levels of extent. A large number of studies have shown that PM2.5 pollution has regional transmission characteristics [86,87,88,89,90]. For example, the study from Xue et al. [86] showed that about 22%, 37%, 28%, and 14% of the annual average PM2.5 concentration in Jin-Jin-Ji, the Yangtze River Delta, Pearl River Delta and Chengdu-Chongqing city group were contributed by outside region, respectively. The contribution of PM2.5 concentration from outside region for Hainan, Shanghai, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Jilin and Jiangxi were all higher than 45%. For Beijing, Tianjin and Shijiazhuang, the outside contributions accounted for 37%, 42% and 33%, respectively. At the same time, some scholars also found that the degree of PM2.5 pollution in the same region gradually weakened from the urban center to the suburbs [91,92,93,94]. Zhang et al. [92] analyzed PM2.5 concentration data from 13 monitoring sites in Xi’an from 1 January to 26 April 2013, and found that the PM2.5 concentration in this area decreased from west to east, which is consistent with the characteristics of altitude and wind direction. Analysis from Zhao et al. [93] on the characteristics of PM2.5 and PM10 pollution in Beijing showed that the concentrations of PM gradually increased from the northern mountain region to the southern plain areas. In the central urban area, the concentrations were higher in the western part than those in the eastern part. There were some differences on the PM2.5 concentration levels between urban and rural areas in some cases. Wang et al. [95] indicated that although there were differences in the degree of PM2.5 pollution between the urban and suburbs areas, their variation trends were basically the same, which means that the degree of pollution in the suburbs area was affected to some extent by the high PM2.5 concentration in the city center.
2.4. Impact of Meteological Factors on PM2.5 Variations
Meteorological factors can significantly affect PM2.5 mass concentration, which can help to reduce or aggravate the urban air pollution. Song et al. [96] found that during high temperature weather in summer, although PM2.5 mass concentration was 2 to 3 times higher than that of low temperature period, the high temperature weather was still helpful to the diffusion of pollutants. Zheng et al. [97] also indicated that the effect of rainfall on the removal of particulate matter was obvious. The average PM2.5 concentration decreased by 56.3% following the rainfall, and PM2.5 mass concentration was less than 60 μg·m−3 within 72 h after the rainfall. Within 1 h after the rainfall, the PM2.5 concentration level stayed almost unchanged, and it kept declining within the next 12 h. Jiang and Li [98] showed that there was a negative correlation between PM2.5 mass concentration and precipitation. Large mixed layer thickness and unstable atmospheric layer junction help to the reduction of PM2.5 mass concentration. In Nanjing, the PM2.5 mass concentration was relatively low under northeast and southwest wind conditions, and it also had a negative correlation with the wind speed. High humidity did not help with the reduction of PM2.5 mass concentration but would affect the visibility. Humidity ratio of 60–70% is a turning zone for PM2.5 pollution. Some other scholars also showed that wind speed, wind direction, atmospheric stability, air humidity, rainfall, etc. also have significant impacts on the diffusion, dilution, agglomeration and retention of PM2.5 [99,100,101,102]. In addition, the meteorological factors that are mainly related to PM2.5 concentrations in different cities also vary due to the differences in emission intensity and diffusion conditions of pollutants. Zhang et al. [103] found that the meteorological factors related to PM2.5 concentration during winter in Shijiazhuang were relative humidity and average wind speed; the main meteorological factors related to PM2.5 concentration in Xi’an were relative humidity, average wind speed and maximum sustained wind speed; the ones in Beijing are relative humidity, average daily temperature, average wind speed, maximum sustained wind speed and minimum temperature; the ones in Taiyuan were daily average temperature, relative humidity, average wind speed, maximum and minimum temperature, and maximum sustained wind speed; and the ones in Guangzhou were relative humidity, average wind speed, maximum temperature and rainfall.
3. Various Impacts of PM2.5 Pollution
3.1. Impacts on Atmospheric Visibility
Visibility refers to the maximum distance that a person with normal eyesight can see clearly the contour of the target under the prevailing weather conditions, and it is an indicator on the transparency of the atmosphere. Some scholars pointed out that in recent years the atmospheric visibility in China has reduced sharply, which is closely related to the increase of the concentration of fine particulate matter (PM2.5) in the atmosphere [104,105]. Low-visibility weather has a significant impact on traffic, health, ecological landscape, etc. Visibility is also the most direct indicator of a city’s air quality [106]. At present, the study on the relationship between PM2.5 and atmospheric visibility mainly focuses on the statistical relationship among atmospheric visibility, PM2.5 concentration and meteorological factors. The results show that there is an obviously negative correlation between atmospheric visibility and PM2.5 mass concentration [107]. Some meteorological parameters such as relative humidity [106,108,109] also affect the relationship between PM2.5 and atmospheric visibility. For example, Hao et al. [108] pointed out that when the relative humidity was ≤19%, there was an obvious logarithmic relationship between PM2.5 mass concentration and atmospheric visibility; when the relative humidity was 20–29%, the relationship became exponential; and when the relative humidity was ≥30%, power relationship became obvious. However, Wang et al. [110] presented different viewpoints. They suggested that PM2.5 mass concentration is not related to atmospheric visibility. The reason why PM2.5 can affect the visibility is due to the difference in the chemical composition of PM2.5 in different seasons as well as difference in meteorological conditions.
3.2. Impacts on Regional Climate
The energy balance of the Earth-atmosphere system determines the state of the climate. In general, the energy balance of the Earth-atmosphere system is in dynamic equilibrium. However, if the balance is disturbed or destroyed, it causes the Earth climate to change [111]. There are direct and indirect impacts of PM2.5 on the climate. For the direct impact, the PM2.5 affects the earth-atmosphere radiation budget by scattering and absorption of solar radiation and ground longwave radiation. At the same time, PM2.5 can block the solar beams from reaching the Earth’s surface, and increase the optical density of the visible light, thus cutting down the solar energy that reaches the Earth’s surface. As a result, the ground temperature goes down and the temperature at high altitude rises. Zhang et al. [112] found that the aerosol optical depth (AOD) at 500 nm in North China reaches 0.60–1.00 during the pollution period, where the fine-mode particles contribute more than 90% to the aerosol extinction characteristics and the single-scattering albedo of the aerosol is lower than 0.88. Hu and Liu [113] pointed out that there is a negative correlation between PM2.5 concentration and total surface radiation. Especially at noon, the correlation coefficient can reach −0.62. In addition, in September and December, it was found that an increase of 1 μg·m−3 in PM2.5 concentration would cause a decrease in total radiation of 1.8 W/m2 and 0.5 W/m2, a drop of ground surface temperature by 0.11 °C and 0.02 °C, and a drop of air temperature by 0.03 °C and 0.01 °C. Wu et al. [114] studied the impact of PM2.5 on the urban heat island (UHI) and found that higher PM2.5 concentrations leads to lower UHI intensity, especially during the daytime and the UHI can be reduced by up to 1 K.
The changes in the concentration of particulate matter can affect the formation processes of cloud and rainfall, and indirectly affect climate change. In the formation of rain, it is necessary to have a nucleus of condensation in order to form raindrops from water vapor. Other than salt in the seawater, the sources of nucleus of condensation come from PM2.5. If there are too many particles, they may “eat away water”, so that the raindrops in the sky are not growing, then, drizzle and clear weather days will become less than before. On the other hand, the existence of PM2.5 might help to increase the number of condensation nuclei, so that possibility of rainfall will increase, and extreme rainstorm can even be produced. Therefore, in areas with heavy precipitation, PM2.5 may encourage precipitation and bring more rainfall; while in areas with little precipitation, it may help to reduce rainfall. Simulation from Gui et al. [115] showed that the increase of aerosol particulates in different regions of China resulted in decreased air temperatures at the height under 2 m, decreased humidity ratio and precipitation in most parts of eastern China. Yao et al. [116] studied air pollution in the Jing-Jin-Ji region and its impact on evapotranspiration (ET). They suggested that PM2.5 concentration has a significant negative effect on ET in most cities and that amount of water for agricultural irrigation could be reduced at high PM2.5 concentrations. In addition, PM2.5 can also aggravate or mitigate the acidification of rainwater in the pollution area, depending on the major components of the ions contained in PM2.5. Li and Zhang [117] sampled and analyzed data on precipitation and PM2.5 in Xi’an in 2011, and found that PM2.5 in Xi’an is acidic, which is in consistent with the pH value of the precipitation.
3.3. Impact on Human Health
As early as in the 1980s, a large number of epidemiological studies abroad have shown that PM2.5 has obvious side effects on human health [118,119,120,121]. The studies in China on the relationship between PM2.5 and human health also fully proved that PM2.5 can cause increases in the incidence of pulmonary heart disease [122], respiratory disease [123], cardiovascular disease [124], cancer [125,126] and other diseases, and even the death risk [127,128,129]. Long-term exposure to ambient PM2.5 might be an important risk factor of hypertension and is responsible for significant hypertension burden in adults in China [130,131], and it leads to reduced lung function [132,133]. PM2.5 is a risk factor for asthma [134,135], and it was related to the onset of children cough variant asthma by reducing immune regulation and ventilatory function [136]. PM2.5 exposures might affect reproductive health. Significantly decreased fertility rates by 2.0% per 10 μg·m−3 increment of PM2.5 were observed in [137]. Wu et al. [138] found that ambient PM exposure during sperm development adversely affects semen quality, in particular sperm concentration and count. However, Zhou et al. [139] argued that air PM10 and PM10–2.5 (2.5 ≤ cut sizes ≤ 10 µm) exposures, not PM2.5, are risk factors of semen quality. In addition, the indoor PM2.5 exposure levels were positively associated with skin aging manifestation, including score of pigment spots on forehead and wrinkle on upper lip [140]. PM2.5 may lead to induced DNA damage and cell cycle arrest in lung tumorigenesis [141]. Repeated exposure to PM2.5 induces vascular inflammation [142]. Measles incidence was found to be associated with exposure to ambient PM2.5 [143]. Significant associations between PM2.5 and acute coronary syndrome (ACS) have also been found in most studies [144]. PM2.5 may induce oxidative stress and inflammatory responses in human nasal epithelial cells, thereby leading to nasal inflammatory diseases [145]. Ambient PM2.5 concentrations were significantly associated with influenza-like-illness risk [146].
PM2.5 is associated with mortality. There are papers and reports on PM2.5 sources and associated mortality in China as part of the Global Burden of Disease (GBD). It was estimated that the global premature mortality by PM2.5 was at 3.15 million/year in 2010 with China being the leading country with about 1.33 million [147]. Lin et al. [148] found significant associations between PM2.5 daily exceedance concentration hours (DECH) and cardiovascular mortality (3.0–5.02% increase in mortality rate per 500 μg·m−3 increase in PM2.5). Health burden study by Song et al. [127] suggested that PM2.5 in 2015 contributed as much as 40.3% to total stroke deaths, 33.1% to acute lower respiratory infection (ALRI, <5 years) deaths, 26.8% to ischemic heart disease (IHD) deaths, 23.9% to lung cancer (LC) deaths, 18.7% to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) deaths, 30.2% to total deaths combining IHD, stroke, COPD, and LC, 15.5% to all cause deaths. Electronic hospitalization summary reports derived from 26 major cities in China between 1 January 2014 and 31 December 2015 showed that PM2.5 had a negative impact on incidence of delirium, which is an independent risk factor for morbidity and mortality among older surgical adults [149]. The non-accidental mortality rate increases with exposure to extreme weather condition, especially hot dry synoptic weather types (SWT) and warm humid [150]. The effects of ambient air pollution and temperature triggered out-of-hospital coronary deaths (OHCDs) in China [151]. It was found that there is a spatial correlation between the mortality of respiratory diseases in Chinese provinces, corresponding to the spatial effect of PM2.5 pollutions [152].
Some scholars have conducted studies on specific groups of people. For example, Li et al. [153] studied the relationship between pregnant women’s exposure to PM2.5 and the birth weight of newborns. Cheng et al. [154] pointed out that exposure of pregnant women in the third trimester, especially half a month before delivery, to high concentrations of PM2.5, will lead to an increased risk of preterm birth. It might also be associated with low birth weight (LBW) and small for gestational age (SGA) [155]. Chen et al. [156] showed that the allergenicity in children is potentially related to the indoor PM2.5 component and its content by comparing the toxicity of cells of allergic and non-allergic children exposed to indoor PM2.5. Tu [157] pointed out there is an impact of PM2.5 in Nanchang on the increase in outpatient pediatric respiratory disease outbreaks, with a maximum cumulative lag effect of 5 days. A 10 μg·m−3 increase of PM2.5 concentration in the atmosphere resulted in 0.43% increase of respiratory disease outpatient visits. Ouyang et al. [158] found that the PM2.5 concentrations are positively correlated with pneumonia hospitalization number of children, and their effect on boys is more obvious than that in the girls. PM2.5 was independently associated with the risk of intensive care unit admission due to pneumonia (ICUp), and the maximum effect occurred at 3 to 4 days after exposure [159]. There were positive correlation between high concentrations of PM2.5 and increasing daily emergency room visits [160]. In addition, PM2.5 might also affect people’s mental health. When exposed in haze weather for a long time, people could easily become depressed; in severe cases depression might also be induced. Study from Jia et al. [161] indicated that PM2.5 exposure might negatively affect mood regulation and increase the risk of mental disorder.
3.4. Impact on Human Behavior
PM2.5 is considered to be the “culprit” that causes hazy weather. It is harmful to people’s health and at the same time has affected all aspects of people’s living conditions. First of all, to cope with the frequent smog weather, people pay more and more attention to the prevention of PM2.5 inhalation. Wearing an anti-haze mask has become a popular habit in China. Gu and Xie [162] pointed out that in haze weather residents would go out with anti-haze masks and would selectively adjust their outdoor activities or change their ways of transportation depending on the outside air conditions. Residents will change their window opening behavior, such as window opening time and size to prevent PM2.5 penetration into the room [163,164]. Of course, turning on anti-haze air conditioners is also a preferred option due to their ability to reduce the PM2.5 concentration while maintaining high level of indoor thermal comfort [165]. In addition, the hazy weather is disruptive to the effects of many scenic landscapes, and therefore many tourists will change their travel decisions during hazy weather [166].
4. Indoor and Outdoor PM2.5 Relationship
4.1. Current Indoor PM2.5 Pollution Status
According to a survey on the life style of the residents, people in China spent 85% of their time indoors, of which 50% of their time was spent inside the buildings. In particular, the elderly spent 90% of their time indoors, of which 76% of their time was in the residential buildings [167]. Therefore, an indoor environment with an acceptable indoor PM2.5 mass concentration level is an essential prerequisite for healthy living of the residents. At present, there are not many researches on indoor PM2.5 pollution in China. However, it can be concluded that existing PM2.5 pollution in China is very serious (Table 3). Compared with the daily average limit of PM2.5 level of 35 μg·m−3 based on China’s latest ambient air quality standard, the PM2.5 concentration level in almost all of the buildings in the cities studied in Table 3 exceed the limit. In some heavily polluted public spaces, the PM2.5 concentration can exceed the limit by more than five times.

Table 3.
Current status of indoor PM2.5 pollution.
4.2. Ease of Indoor Environment Contaminated by Outdoor PM2.5
Some researchers have suggested that outdoor PM2.5 can enter the room through three ways, including natural ventilation, mechanical ventilation and infiltration [168]. For natural ventilation, the outdoor PM2.5 was driven by wind pressure and thermal pressure into the interior of the building, and often there is no filter to remove the particle matters. For buildings with central air conditioning system, the fresh air was introduced by mechanical ventilation and go through air filters, however, the filters cannot removed all the particle matters and hence the PM2.5 can enter the interior environment. The infiltration is related to air tightness. Due to the existence of cracks in the building envelope, the outdoor PM2.5 will penetrate through the crack even when the doors and windows are fully closed. It is very important to evaluate how easily the indoor environment can be contaminated by outdoor PM2.5. Currently, the indoor and outdoor particle concentration ratio (I/O ratio) and penetration coefficient are considered as two important parameters to be used for evaluation.
4.2.1. I/O Ratio
Most of the studies on I/O ratios were carried out based on field data measurement under natural ventilation or infiltration (see Table 4). From Table 4, it is found that the I/O ratios obtained by different researchers vary greatly. It could be due to the differences in the outdoor pollution level, outdoor weather conditions (outdoor wind speed, wind direction, temperature, humidity ratio, etc.), indoor sources of pollution, the conditions of the building envelope itself (the airtightness of the outer windows, the degree of sealing performance of the outer window with the wall, cracks over the wall, etc.), and the air changes per hour (ACH) [76,82,169,170,171,172,173,174,175]. Lin et al. [173] explored the difference of PM2.5 pollution in Wuhan and Guangzhou. Strong seasonal variation patterns were found, and PM2.5 pollution in Wuhan was more serious than that in Guangzhou. Through sampling data analysis, Zhou [174] found significant negative correlation among PM2.5 mass concentration, temperature, and wind speed. Significant positive correlation between PM2.5 mass concentration and relative humidity, and relatively weak relationship between PM2.5 mass concentration and atmospheric pressure were found. Wang et al. [175] found the indoor PM2.5 concentrations were affected by the outdoor PM2.5 concentration and the degree of air tightness of the outer windows. Under the same outdoor PM2.5 concentration, the outer windows with higher air-tightness were less prone to be affected by the outdoor PM2.5.

Table 4.
I/O (indoor/outdoor) ratio under different ventilation modes.
4.2.2. Penetration Coefficient
Through surveys on people’s window opening behavior, it is found that 60% of the people select to close the window under haze weather condition to prevent the outdoor PM2.5 from entering the indoor environment [185]. In the case of closing the doors and windows, study on the penetration of PM2.5 through the envelope cracks becomes particularly important. Some researches advised that the outdoor PM2.5 entering the building envelope through the cracks is the process of “penetration” [168,185,186,187], where “penetration coefficient” is the decisive factor to evaluate the rate of PM2.5 entering the indoor. Many foreign scholars obtained the penetration coefficients of fine particles through experimental measurements [187,188,189], e.g., Thatcher et al. [188] found that the penetration coefficient is larger for smaller fine particles. Some scholars in China have also conducted researches on determining the penetration coefficient. Their studies mainly focus on some influencing factors that affect the penetration coefficient of fine particles, such as the height of the crack [190], the roughness of the inner surface of the crack [191,192], the indoor/outdoor pressure difference [192], crack geometry [193], ACH [194] and so on. Due to the limitations of available devices and testing conditions, only a small number of studies in China currently focus on studying the penetration coefficient of PM2.5 alone. Based on previous studies, Li [185] discussed on the outer window penetration coefficient of PM2.5 is affected by multiple factors, including particle size, indoor/outdoor pressure difference, air exchange rate, and geometry and surface roughness of cracks in the building envelopes.
5. Indoor PM2.5 Control
5.1. Air Filter and Air Conditioner Combination
Since the outdoor PM2.5 pollution cannot be gotten rid of in the short run, it is important to control the indoor PM2.5 pollution level to reduce its impact on occupants’ health. Some researches focused on selection of certain combination of air filters. For example, Cao et al. [195] developed indoor PM2.5 pollution control model under mechanical ventilation, and advised on how to select certain combination of air filters with different particulate removal efficiencies for a central AC system. Tu et al. [196] conducted test on filter efficiency based on particle sizing and counting method and PM2.5 weight filtration method for multiple air filters of different materials and different particle removal efficiencies under the same experimental conditions. The relationship between these two filtration efficiencies provides a preliminary basis for the selection of PM2.5 air filter for indoor air conditioning and ventilation system. Wang [197] studied the filtration performance of different grades of PM2.5 filters and proposed suitable filter combination schemes based on the PM2.5 pollution status in different regions. Comprehensive evaluations on the performance of different filter combination schemes were conducted, which could be used as references for the design of primary air conditioning system. Based on the principle of mass conservation, Lv [198] developed an indoor PM2.5 concentration model of the primary return air-conditioning system and studied the impact of the changes of the filtration efficiency and the fresh air flow rate on the indoor PM2.5 concentration, when the filters are installed in the primary air section, return air section and supply air section, respectively. The results from these researches can only be used for the primary air supply of the central air-conditioning system. It is worth mentioning that split air conditioner systems are installed in most of the residential buildings in China for indoor environment control. The split system is a ductless system. It has an outdoor unit and an indoor unit, where the inside (evaporative) heat exchanger is separated from the outside (condensing unit) heat exchanger. No fresh air systems are equipped. In general, the measures taken by the residents in China to deal with outdoor PM2.5 pollution are to fully close the doors and windows. Hence, no fresh air can be treated by air filters and PM2.5 can still penetrate through the cracks. It is far from enough to fight with PM2.5 pollution by simply closing the doors and windows, so how to maintain a healthy indoor environment for buildings with split air conditioning system remains a problem to be solved in China.
5.2. Development of New Material for Air Filters
Some researchers dedicated to the development of new filter materials. For example, Zhao et al. [199] reported that high efficiency and low resistance air purification materials made by electrospun polyvinylidene fluoride fiber (PVDF) doping with negative ion powders (NIPs) can have purification efficiency of up to 99.9%. Zhang et al. [200] utilized high-thermal-stability polyimide nanofibers to develop a highly effective polyimide nanofiber air filter. The efficiency of the filter to remove PM2.5 from automobile exhaust at high temperatures can reach 99.5%. Li et al. [201] developed a reusable polyethersulfone hollow fiber membrane with high permeability using single-dry-jet wet-spinning technology. These filter materials have a high PM2.5 capturing capacity, and if they can be widely used in air conditioning system, the burden to remove the indoor PM2.5 will be greatly alleviated. However, due to the high initial investment cost, it is unrealistic to widely adopt this kind of filters in China.
Other researchers developed filters that can be attached to the window to allow air to flow through to reduce the filtering cost. For example, Liu et al. [202] introduced a polyacrylonitrile transparent filter that captures the PM through controlling the surface chemistry and microstructure of the air filters. It allows natural, passive ventilation to pass through the window and can achieve removal efficiency of up to 98.69% at transmittance of ~77% in haze weather. Zhao et al. [203] reported slip-effect functional nanofibrous membranes with purification efficiency of 99.09% and transmittance of 77% with low air resistance of 29.5 Pa. Khalid et al. [204] reported a blow-spinning technique for large scale coating of nanofiber transparent air filter on window screen which achieved standard PM2.5 removal efficiency of >99% with 80% optical transparency. However, the study from Shi et al. [205] found that the mean value of harmonic average air exchange rate when the windows are open is far below the national standard. Therefore, more measures are needed to be taken to further reduce the filter resistance to enhance natural ventilation.
5.3. Anti-Haze Room Air Conditioners Available in the Market
Frequent episodes of hazy weather remind the residents of the importance and urgency to improve air quality, and it has become a driving force for the traditional air-conditioners to be upgraded with PM2.5 purification functiond. Table 5 lists some of the popular AC products from different air conditioner companies with PM2.5 purification function, which come from Midea, Haier, Panasonic, Gree and KELON. For example, the air conditioner (AC) products of Midea utilize a washable PM2.5 purification module with an electronic generator to create an electric field in the dust collection device to captured charged particles, which effectively removes PM2.5. The air conditioning products of Haier use visualization function to capture PM2.5. Each AC unit is equipped with a 5-color indicator. When indoor PM2.5 level exceeds the high limit, the indicator turns red and urge the occupants to turn on the PM2.5 removal function, and it becomes blue when the indoor PM2.5 level is back to normal. Panasonic air conditioners release negatively charged “nanoe-G” to be absorbed by PM2.5 in the air, through which PM2.5 is negatively charged and collected by electric field with high efficiency. The air conditioning products of Kelon use “three processes” (stripping technology, packaging technology and melting technology) for PM2.5 purification. The air-conditioners listed are residential models, effective in room size of 10–50 m2 (2650–7200 W).

Table 5.
Air conditioner with efficient PM2.5 purification function.
6. Conclusions
The problem of PM2.5 pollution in China is severe. It has seriously threatened the health of the residents. As compared with the developed countries, studies on PM2.5 in China are still lagging behind. However, with the establishment of air quality standards for PM2.5 in recent years and development of PM2.5 monitoring stations nationwide in China, research on PM2.5 in China has gradually been enhanced. The studies on PM2.5 have increased exponentially, and more and more disciplines have got involved in the study on PM2.5, which are mainly related to PM2.5 source analysis, the impact of PM2.5 on human health, relationship between indoor and outdoor PM2.5 pollution levels and indoor PM2.5 control. It is worth mentioning that there are several measurement methods and small differences in the measurement results of PM2.5 concentration might be found. Most of the researches on I/O ratio and percentage of outdoor source contributions were based on the weighting method, which is a direct and reliable method. Generally speaking, the studies discussed throughout the paper will not be greatly affected with different measurement methods in various researches. There are still many shortcomings with current researches. For example, some studies only collected data in the typical month of the season or even a few days in a typical month. Although the data could be representative, they may also be incidental. Nowadays, depression, autism and other psychological diseases frequently occur, however, little research of PM2.5 impact on mental health can be found in China. Most of the researches on the indoor and outdoor pollution correlations are conducted only for a specific building, i.e., under specific physical and meteorological condition [75,76,77,78,79], for example, in a residential apartment [75], or in an office building [76]. Although many useful results have been obtained from these studies, they depend largely on the experimental conditions at the time when data were collected and cannot be applied to more general situations. In addition, although the environmental monitoring network of PM2.5 in the outdoor atmosphere is already established in China, the establishment of monitoring network on indoor air PM2.5, which is more closely related to human health, is still lagging behind. It may be due to the facts that the indoor PM2.5 pollution concentration limit is not clear in China. At the same time, the cost of creating household monitoring network is high, and it is difficult to carry out long time, standardized, PM2.5 monitoring and data collection indoor.
Acknowledgments
Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province under grant [2017CFB602] and Hunan Provincial Department of housing and urban rural development under grant [KY2016063].
Author Contributions
Yaolin Lin contributed to the conception and organization of the study. Yaolin Lin, Jiale Zou, Wei Yang and Chun-Qing Li wrote the manuscript. All the authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, P. Spatial distribution of haze pollution and its influencing factors. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2017, 27, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China. Bulletin on Environmental Conditions in China in 2015. Available online: http://www.mep.gov.cn/hjzl/zghjzkgb/lnzghjzkgb/201606/P020160602333160471955.pdf (accessed on 19 December 2017).
- Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China. Bulletin on Environmental Conditions in China in 2016. Available online: http://www.mep.gov.cn/hjzl/zghjzkgb/lnzghjzkgb/201706/P020170605833655914077.pdf (accessed on 19 December 2017).
- Liang, Z.; Ma, M.; Du, G. Comparison of characteristics and trend analysis of atmospheric pollution in Beijing–Tainji–Shijiazhuang during 2003–2012. Environ. Eng. 2014, 12, 76–81. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Cao, F. Fine particulate matter (PM2.5) in China at a city level. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Ma, Y.; He, K. Research on General Situation of PM2.5. World Environ. 2000, 4, 32–35. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. WHO’s Urban Ambient Air Pollution Database 2016. Available online: http://www.who.int/phe/health_topics/outdoorair/databases/who-aap-database-may2016.xlsx (accessed on 10 December 2017).
- US EPA. National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS). Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-02/documents/criteria.pdf (accessed on 24 December 2017).
- Australian Government, Department of the Environment and Energy. Ambient Air Quality Standards. Available online: http://www.environment.gov.au/protection/air-quality/air-quality-standards (accessed on 24 December 2017).
- WHO. WHO Air Quality Guidelines for Particulate Matter, Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide and Sulfur Dioxide. Available online: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/69477/1/WHO_SDE_PHE_OEH_06.02_eng.pdf (accessed on 24 December 2017).
- European Commission. Air Quality Standards. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/environment/air/quality/standards.htm (accessed on 24 December 2017).
- National Environment Agency. Air Quality and Targets. Available online: http://www.nea.gov.sg/anti-pollution-radiation-protection/air-pollution-control/air-quality-and-targets (accessed on 24 December 2017).
- Ministry of the Environment, Government of Japan. Environmental Quality Standards in Japan—Air Quality. Available online: http://www.env.go.jp/en/air/aq/aq.html (accessed on 24 December 2017).
- Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change, Government of India. National Ambient Air Quality Standards Central Pollution Control Board Notification. Available online: http://www.moef.nic.in/sites/default/files/notification/Recved%20national.pdf (accessed on 24 December 2017).
- Department of Science, Technology and Standards, Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China. Ambient Air Quality Standards. Available online: http://kjs.mep.gov.cn/hjbhbz/bzwb/dqhjbh/dqhjzlbz/201203/W020120410330232398521.pdf (accessed on 24 December 2017).
- Wu, G.; Hu, W.; Teng, E.; Wei, F. PM2.5 and PM10 pollution level in the four cities in China. China Environ. Sci. 1999, 2, 133–137. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Tang, D.; Liu, H.; Yue, X.; Pang, Z.; Ding, Y. Research on Current Pollution Status and Pollution Characteristics of PM2.5 in China. Res. Environ. Sci. 2000, 13, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Yang, F.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yao, X.; Chan, C.K.; Cadle, S.; Chan, T.; Mulawa, P. The characteristics of PM2.5 in Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 4959–4970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; He, K.; Ma, Y. Chemical characteristics of PM2.5 species in Beijing ambient air. J. Tsinghua Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2002, 42, 1605–1608. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Wang, G.; Wang, H.; Gao, S.; Wang, L. Pollution level of the airborne particulate matter (PM10, PM2.5) in Nanjing City. China Environ. Sci. 2002, 22, 334–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, G.; Gao, S.; Wang, L. Characteristics of atmospheric particulate pollution in spring in Nanjing City. China Environ. Sci. 2003, 23, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; He, K.; Ma, Y.; Chen, X.; Cadle, S.H.; Chan, T.; Mulawa, P.A. Characteristics and Sources of Trace Elements in Ambient PM2.5 in Beijing. Environ. Sci. 2003, 24, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, Z.; Song, W.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y. Study on mouse pulmonary acute injury induced by air-borne PM2.5. J. Hyg. Res. 2004, 33, 264–266. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, C.; Song, W.; Shi, Y. Study on the oxidative injury of the vascular endothelial cell affected by PM2.5. J. Hyg. Res. 2005, 34, 169–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.H.; Wang, Q.; Xu, D.Q. Immunological effect of PM2.5 on cytokine production in female Wistar rats. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2008, 21, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, X. Pollution Status and Cytotoxicity of PM2.5 in Hangzhou City. J. Environ. Health 2009, 2, 147–148. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, C.; Li, S.; Shang, D.; Zhu, X.; Chen, D.; Wang, R. Pathologic changes in trachea of rats exposed to PM2.5 artificial air pollution. Chin. J. Public Health 2011, 12, 1579–1581. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, C. Study on Toxic Effects of PM2.5 on Cardiovascular System. Ph.D. Thesis, Fudan University, Shanghai, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Dan, M.; Zhuang, G.; Li, X.; Tao, H.; Zhuang, Y. The characteristics of carbonaceous species and their sources in PM2.5 in Beijing. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 3343–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Salmon, L.G.; Schauer, J.J.; Zeng, L.; Kiang, C.S.; Zhang, Y.; Cass, G.R. Seasonal trends in PM2.5 source contributions in Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 3967–3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhuang, G.; Zhang, X.; Huang, K.; Xu, C.; Tang, A.; Chen, J.; An, Z. The ion chemistry, seasonal cycle, and sources of PM2.5 and TSP aerosol in Shanghai. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 2935–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Tang, X.; Xie, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zeng, L.; Lu, S. Source apportionment of PM2.5 in Beijing in 2004. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 146, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Sun, J. Source analysis of PM2.5 in Wuhan area. J. Liaoning Tech. Univ. Sci. Ed. 2009, 28, 125–127. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, W. Study on source apportionment of PM10 and PM2.5 in ambient air of Ningbo. Res. Environ. Sci. 2011, 33, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Duan, F.; He, K. PM2.5 speciation sampling and analysis methods. Environ. Monit. China 2004, 20, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.M.; Ye, B.M.; He, K.B.; Ma, Y.L.; Cadle, S.H.; Chan, T.; Mulawa, P.A. Characterization of Atmospheric Mineral Components of PM2.5 in Beijing and Shanghai, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 343, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.L.; Zhuang, G.S.; Tang, A.H.; Wang, Y.; An, Z.S. Chemical characteristics of PM2.5 and PM10 in haze-fog episodes in Beijing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 3148–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lain, S.C.; Zou, S.C.; Cao, J.J.; Lee, S.C.; Ho, K.F. Characterizing ionic species in PM2.5 and PM10 in four Pearl River Delta cities, South China. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 19, 939–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J. Chemical characteristics of PM2.5 during a typical haze episode in Guangzhou. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 21, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Yin, Y.; Wei, Y.; Yang, W. Characteristics of carbonaceous aerosols in PM2.5 in Nanjing. China Environ. Sci. 2010, 8, 1015–1020. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T. Chemical Compositions and Source Apportionment of PM2.5 in Changsha. Master’s Thesis, Central South University, Changsha, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, J.; Bai, Z.; Li, W.; Wu, L.; Liu, A.; Dong, H.; Xie, Y. Chemical composition of PM2.5 during winter in Tianjin, China. Particuology 2011, 3, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yun, H.; Guan, Z.; Li, X.; He, L.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, M. Source apportionment and secondary organic aerosol estimation of PM2.5 in an urban atmosphere in China. Sci. Sin. Terrae 2014, 44, 723–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Tang, Q.; Peng, J.; Wang, E.; Wang, S.; Cha, F. Study on Characterization and Source Apportionment of Atmospheric Particulate Matter in China. Environ. Sustain. Dev. 2011, 5, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, C. Review of PM2.5 Source Apportionment Methods in China. J. Peking Univ. Sci. Ed. 2014, 50, 1141–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yun, H.; Gong, Z.; Li, X.; He, L.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, M. Air pollution characteristic and variation trend of Central Triangle urban agglomeration from 2005 to 2014. Sci. Sin. Terrae 2014, 44, 723–734. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Bi, X.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Lv, A. Pollution characteristics and source apportionment of PM2.5 during heavy pollution process in Urumchi City. Res. Environ. Sci. 2014, 27, 113–119. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, X.; Chu, Y.; Yang, W.; Ren, L.; Bai, Z. Characterization of chemical composition mass balance and source appointment of ambient PM2.5 in Xinzhou city. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2017, 11, 4660–4668. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Z.; Bi, X.; Feng, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Fu, X.; Wen, Y. Source Apportionment of Ambient PM10 and PM2.5 in Urban Area of Ningbo City. Environ. Sci. Res. 2012, 25, 549–555. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, M. Tianjin Ambient Air PM2.5 Source Apportionment. Master’s Thesis, Nankai University, Tianjin, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, L.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, X.; Yang, W.; Yin, B.; Bai, Z.; Ji, Y. Source Apportionment of PM10 and PM2.5 in Urban Areas of Chongqing. Environ. Sci. Res. 2014, 27, 1387–1394. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Lian, Y.; Chen, T.; Liu, B.; Sun, F.; Cheng, G.; Su, J.; Zhang, D. Source apportionment of PM2.5 in Beijing by the chemical mass balance. Acta Sci. Circumst. 2015, 35, 2693–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Y.; Zhao, X.; Xu, X.; Gao, H.; Li, T.; Ding, M.; Liu, Y.; Han, B.; Bai, Z. Source Apportionment of PM2.5 in Xining by the Chemical Mass Balance. Environ. Monit. China 2016, 32, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Yu, H.; Hu, J.; Chai, F. Analysis of Source of PM2.5 in Xingtai Using Chemical Mass model. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2017, 33, 1075–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Wang, Z.; Feng, J.; Chen, H.; Zhang, F.; Liu, J. Carbonaceous species composition and source apportionment of PM2.5 in urban atmosphere of Wuhan. Ecol. Environ. 2012, 21, 1574–1579. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Tao, J.; Xie, S.; Zhou, L.; Song, D.; Zhang, P.; Cao, J.; Luo, L. Seasonal variations and source apportionment of PM2.5 at urban area of Chengdu. J. Environ. Sci. Circumst. 2013, 33, 2947–2952. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, Q.; Cui, H. PM2.5 source apportionment at suburb of Shanghai in winter based on real time monitoring. J. Nanjing Univ. Sci. Ed. 2015, 51, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Z.; Wang, X.; Tian, C.; Chen, Y.; Lin, Q.; Ji, L.; Zhi, G.; Li, J.; Zhang, G. Source apportionment of PM2.5 at a regional background site in North China using PMF linked with radiocarbon analysis: Insight into the contribution of biomass burning. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 11249–11265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, X.; Duan, J.; Li, Y.; Hu, J.; He, K. Chemical characteristics and source apportionment of PM2.5 in Lanzhou, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601–602, 1743–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Xie, S.D.; Luo, B.; Zhai, C.Z. Particulate pollution in urban Chongqing of southwest China: Historical trends of variation, chemical characteristics and source apportionment. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584–585, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, L.; Yang, L.; Yuan, Q.; Yan, C.; Dong, C.; Meng, C.; Sui, X.; Yang, F.; Lu, Y.; Wang, W. Sources apportionment of PM2.5 in a background site in the North China Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 590–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Lin, T.; Feng, J.; Fu, H.; Guo, Z. Source apportionment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in PM2.5 using positive matrix factorization modeling in Shanghai, China. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2015, 17, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J. Chemical Composition Characteristics and Source Apportionment of PM2.5 in Zhengzhou. Ph.D. Thesis, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Q.; Xu, L.; Wang, C. Pollution characteristics and source apportionment of PM2.5 from Qinshan District in Wuhan during the winter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 38, 159–164. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Du, P.; Guang, Q.; Feng, X.; Xu, D.; Lin, S. Application of ICP-MS and ICP-AES for Studying on Source Apportionment of PM2.5 during Haze Weather in Urban Beijing. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2015, 35, 1724–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Wang, L.; Ma, S.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, C.; Zheng, A. Spatial and temporal distribution and source analysis of components in PM2.5, Handan. Environ. Chem. 2017, 36, 1932–1940. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, C.; Wang, L.; Su, J.; Yang, J.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, F.; Ma, S. Chemical compositions and source apportionment of PM2.5 in Handan City, Hebei Province. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 39, 57–64. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, H.; Chen, W.; Dai, W.; Liu, H.; Wang, X.; He, K. Source apportionment of PM2.5 in Guangzhou combining observation data analysis and chemical transport model simulation. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 116, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Bi, X.; Liu, B.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, Q. Source Directional Apportionment of PM2.5 in Heze City. Environ. Sci. Res. 2017, 30, 1849–1858. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, G.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Tian, Y.; Wen, J.; Shi, X.; Feng, Y.; Ivey, C.E.; Russell, A.G. Source apportionment for fine particulate matter in a Chinese city using an improved gas-constrained method and comparison with multiple receptor models. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 233, 1058–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, X.; Ying, Q.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Hu, J.; Tang, Y.; Chen, X. Source apportionment of PM2.5 for 25 Chinese provincial capitals and municipalities using a source-oriented Community Multiscale Air Quality model. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Zhang, G.; Xiao, C.; Huang, D.; Yuan, G.; Yao, Y.; Wang, X.; Hua, L.; Wang, P.; Ni, B. Source Apportionment of PM2.5 in Xinzhen Beijing Using PIXE and XRF. At. Energy Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 1325–1330. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J. Establishment and application of pollutant Inventory-Chemical Mass Balance (I-CMB) model for source apportionment of PM2.5. Trans. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 38, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Yuan, D.; Zhao, Z. Residential indoor PM2.5 sources, concentration and influencing factors in China. J. Environ. Health 2015, 32, 825–829. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.; Qi, M.; Chen, Y.; Shen, H.; Liu, J.; Huang, Y.; Chen, H.; Liu, W.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; et al. Influences of ambient air PM2.5 concentration and meteorological condition on the indoor PM2.5 concentrations in a residential apartment in Beijing using a new approach. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 205, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Chen, C.; Wang, P.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Q.; Lu, B.; Cao, G.; Meng, C.; Wang, L.; et al. Characteristics of Change of PM2.5 Mass Concentration Indoors and Outdoors in an Office Building in Beijing in Summer and Winter. Build. Sci. 2015, 31, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, T.; Yao, W.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, Z. Influencing Factors of Outdoor PM2.5 Mass Concentration and Indoor Control Measures. Gas Heat 2016, 36, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Meng, D.; Li, X.; Tan, J. Indoor-outdoor relationships of PM2.5 in four residential dwellings in winter in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 215, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, W.; Zhao, B. Contribution of outdoor-originating particles, indoor-emitted particles and indoor secondary organic aerosol (SOA) to residential indoor PM2.5 concentration: A model-based estimation. Build. Environ. 2015, 90, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Duan, Y. Ditermination the PM2.5 concentration in the room of Liting mosquito-repellent incense and cigarette. Inn. Mong. Environ. Sci. 2013, 25, 184–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Cao, S.; Fan, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhao, X.; Leaderer, B.P.; Shen, G.; Zhang, Y. Duan, X. Household concentrations and personal exposure of PM2.5 among urban residents using different cooking fuels. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 548–549, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, J.; Zuo, J.; Chen, G.; Xu, L.; Rameezdeen, R. Indoor PM2.5 concentrations in residential buildings during a severely polluted winter: A case study in Tian, China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 64, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, F.; Ye, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, H. Influences of sweeping on the Concentration of Particulate Matter in the indoor air. J. Anhui Univ. Technol. Nat. Sci. 2013, 30, 250–254. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Lin, Z.; Mao, H. PM2.5 Emission from Laser Printers in an Environmental Chamber. Build. Energy Environ. 2016, 35, 44–48. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, N.; Han, B.; He, F.; Xu, J.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, Y.; Bai, Z. Chemical characteristic of PM2.5 emission and inhalational carcinogenic risk of domestic Chinese cooking. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 227, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, W.; Fu, F.; Wang, J.; Tang, G.; Lei, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y. Numerical study on the characteristics of regional transport of PM2.5 in China. China Environ. Sci. 2014, 34, 1361–1368. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.; Fung, J.C.H.; Yao, T.; Lau, A.K.H. A study of control policy in the Pearl River Delta region by using the particulate matter source apportionment method. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 76, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, W.; Li, J.F.; Wang, X.S.; Zhang, Y.H. Numerical modeling on the impact of long-range transport of air pollutants on the regional air quality in the Pearl River Delta. Acta Sci. Circumst. 2015, 35, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.Y.; Fan, S.J.; Deng, X.J.; Zhang, X.B.; Deng, T.; Li, T. Study on the regional transported effect of PM2.5 in Guangzhou area. J. Univ. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2014, 31, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xue, W.; Lei, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, W. Regional Transport Matrix Study of PM2.5 in Jingjinji Region, 2015. Environ. Sci. 2017, 38, 4897–4904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Chen, T.; Zhang, D.; Sun, F.; Pan, L. Spatial-temporal characteristics of PM2.5 in Beijing in 2013. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2015, 70, 110–120. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, J.; Bao, Y.; Li, J.; Yu, C. Study on the temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of PM2.5 in Xi’an city. Air Pollut. Control 2016, 34, 87–90. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.X.; Wang, Y.Q.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhang, H.L.; Zhao, B. Temporal and Spatial Distribution of PM2.5 and PM10 Pollution Status and the Correlation of Particulate Matters and Meteorological Factors During Winter and Spring in Beijing. Environ. Sci. 2014, 2, 418–427. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Z.; Wang, J. Pollution Characteristics and Determinants of Atmospheric Particulate Matter and Its Determinants in Guiyang. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Sunyatseni 2015, 54, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, S.; Guo, Z.; Han, Z.; Gong, X.; Li, Y. Study on the Variation Characteristics of SO2, PM10, and PM2.5 Concentrations in the Urban and Surburban Areas during Winter in Taiyuan. Environ. Sustain. Dev. 2014, 39, 190–193. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Tang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, M.; Fang, C.; Zeng, L.; Wang, W. Effects on Fine Particles by the Continued High Temperature Weather in Beijing. Environ. Sci. 2002, 23, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Zhao, W.; Yan, X.; Zhao, W.; Xiong, Q. Spatial and temporal variation of PM2.5 in Beijing city after rain. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2014, 23, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Li, C. Relationship of the Diffusion of PM2.5 and Meteorological Conditions in Nanjing Urban Area. Adm. Tech. Environ. Monit. 2016, 28, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.X.; Yin, Y.; Yang, W.F.; Rui, D.M.; Hang, W.Q. Analysis of the Pollution Characteristics & Influence Factors of PM2.5 in Nanjing Area. Environ. Sci. Manag. 2009, 34, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; He, J.; Lu, X.W.; She, J.F.; Guan, Z.Q. Spatial and Temporal Variations of PM2.5 and Its Relation to Meteorological Factors in the Urban Area of Nanjing, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, M.; Hu, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, H.; Qiu, F. Temporal and spatial distribution of PM2.5 concentration and the correlation of PM2.5 and meteorological factors in Kunming City. J. Yunnan Univ. 2016, 38, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.C.; Wu, Z.B.; Zhou, J.B.; Bao, J. Relationship between PM2.5 concentration and meteorological elements at Shangdianzi station of Beijing. J. Meteorol. Environ. 2015, 31, 99–104. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.P.; Han, L.J.; Zhou, W.Q.; Zheng, X.X. Relationships between fine particulate matter (PM2.5) and meteorological factors in winter at typical Chinese cities. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2016, 36, 7897–7907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Liu, Q.; Lian, Y.; Bi, X.; Li, F.; Tan, H.; Liao, B.; Chen, H. Hazy weather formation and visibility deterioration resulted from fine particulate (PM2.5) pollutions in Guangdong and Hong Kong. J. Environ. Sci. Circumst. 2012, 32, 2660–2669. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.; Zhao, X.; Meng, W.; Meng, Y.; He, D.; Liu, Y. Comparison of Influence of Fog and Haze on Visibility in Beijing. Environ. Sci. Res. 2012, 25, 1208–1214. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Shi, C.; Wu, B.; Yang, Y. Quantified Relationships among the Visibility, Relative Humidity and PM2.5 Mass Concentration in Hefei City. Ecol. Environ. 2017, 26, 1001–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Han, X.; Cai, Z.; Zhang, M. Study on characteristic of aerosol extinction at Tianjin City in Spring. China Environ. Sci. 2012, 32, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Zhang, G.; Yang, Y. The characteristics of atmospheric visibility and influencing factors. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2017, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Qiu, S.S.; Shang, J.; Wilfrid, O.M.F.; Liu, X.G.; Tian, H.Z.; Boman, J. Impact of Relative Humidity and Water Soluble Constituents of PM2.5 on Visibility Impairment in Beijing, China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2014, 14, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.L.; Zhang, Y.H.; Shao, M.; Liu, X.L.; Zeng, L.M.; Cheng, C.L.; Xu, X.F. Quantitative relationship between visibility and mass concentration of PM2.5 in Beijing. J. Environ. Sci. 2006, 3, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.D.; Gao, Q.X.; Zhang, S.H.; Chen, D.S.; Du, W.P.; Fu, J.F.; Bai, H.M. Research review of impacts and feedback of air pollution on climate change. Res. Environ. Sci. 2012, 25, 974–980. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Xia, X.; Che, H.; Tang, J.; Tang, Y.; Meng, W.; Dong, P. Observation Study on Aerosol Optical Properties and Radiative Forcing Using the Ground-based and Satellite Remote Sensing at Background Station during the Regional Pollution Episodes. Environ. Sci. 2014, 35, 2439–2448. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, S.L.; Liu, H.N. Effects of PM2.5 on the urban radiation and air temperature in Hefei. J. Meteorol. Sci. 2017, 1, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, T.; Riemer, N.; Chen, P.; Li, M.; Li, S. Urban heat island impacted by fine particles in Nanjing, China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Qian, Z.; He, H.; Zeng, X. Numerical study of indirect aerosols effect on regional climate over eastern China. J. Nanjing Univ. Nat. Sci. 2014, 50, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L. Causative impact of air pollution on evapotranspiration in the North China Plain. Environ. Res. 2017, 158, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Zhang, C. Analysis on the Relationship between PM2.5 and the Precipitation in Xi’an. Environ. Monit. China 2013, 29, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbey, D.E.; Ostro, B.E.; Petersen, F.; Burchette, R.J. Chronic respiratory symptoms associated with estimated long-term ambient concentrations of fine particulates less than 2.5 microns in aerodynamic diameter (PM2.5) and other air pollutants. J. Expo. Anal. Environ. Epidemiol. 1995, 5, 137–196. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Churg, A.; Brauer, M. Human lung parenchyma retains PM2.5. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1997, 155, 2109–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pope, C.A., III; Dockey, D.W. Heath effects of fine particulate air pollution: Lines that connect. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2006, 56, 709–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.H.; Kabir, E.; Kabir, S. A review on the human health impact of airborne particulate matter. Environ. Int. 2015, 74, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Geng, H.; Qiu, Y.; Tong, G.; Han, J.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, J. Relationship between PM2.5 exposure and pulmonary function in different working environments. J. Environ. Health 2013, 30, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, Y.; Xu, Y.; Shi, M.; Lian, Y. The impact of PM2.5 on the human respiratory system. J. Thorac. Dis. 2016, 8, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Huang, Z.; Shu, Z.; Yuan, H. Ambient PM2.5 during pregnancy and risk on preterm birth. Chin. J. Cardiol. 2014, 44, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, H.L.; Hsu, S.W.; Chang, Y.C.; Chan, T.C.; Tsou, H.C.; Chang, Y.C.; Chiang, P.H. Spatial Analysis of Ambient PM2.5 Exposure and Bladder Cancer Mortality in Taiwan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Yuan, F.; Chen, E.; Chen, L. Analysis of the relationship between PM2.5 and lung cancer based on protein-protein interactions. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen 2016, 19, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; He, J.; Wu, L.; Jin, T.; Chen, X.; Li, R.; Ren, P.; Zhang, L.; Mao, H. Heath burden attributable to ambient PM2.5 in China. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 575–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Zhu, J.; Li, W.; Xu, D.; Liu, J. Estimation of the PM2.5 health effects in China during 2000–2011. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 224, 10695–10707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, T.; Dong, H.; Yang, T.; Jian, Q.; Hu, G.; Feng, W.; Lv, J.; Lin, H. Association between PM2.5 air pollution and daily resident mortality in Guangzhou urban area in winter. J. Environ. Health 2015, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Guo, C.; Lau, A.K.H.; Chan, T.C.; Chuang, Y.C.; Lin, C.; Jiang, W.K.; Yeoh, E.K.; Tam, T.; Woo, K.S.; et al. Long-Term Exposure to Fine Particulate Matter, Blood Pressure, and Incident Hypertension in Taiwanese Adults. Environ. Health Perspect. 2018, 126, 017008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Guo, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Di, Q.; Liu, T.; Xiao, J.; Li, X.; Zeng, W.; Cummings-Vaughn, L.A.; Howard, S.W.; et al. Long-Term Effects of Ambient PM2.5 on Hypertension and Blood Pressure and Attributable Risk Among Older Chinese Adults. Hypertension 2017, 69, 806–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.; Hou, J.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, R.; Yin, W.; Huang, C.; Zhu, X.; Chen, W.; Yuan, J. Estimated individual inhaled dose of fine particles and indicators of lung function: A pilot study among Chinese young adults. Environ Pollut. 2018, 235, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, B.F.; Chen, Y.H.; Lin, Y.T.; Wu, X.T.; Leo Lee, Y. Relationship between exposure to fine particulates and ozone and reduced lung function in children. Environ. Res. 2015, 137, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Wong, G.W.; Li, J. Environmental Exposure and Genetic Predisposition as Risk Factors for Asthma in China. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2016, 8, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Wu, B.; Wang, Y.; He, H.; Lin, Z.; Tan, J.; Yang, L.; Kamp, D.W.; Zhou, X.; Tang, J.; et al. Particulate matter 2.5 induces autophagy via inhibition of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin kinase signaling pathway in human bronchial epithelial cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 1914–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Liu, Y.; Xue, Y.; Yang, L.Y.; Song, G.D.; Zhao, L. Correlational study on atmospheric concentrations of fine particulate matter and children cough variant asthma. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 20, 2650–2654. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xue, T.; Zhang, Q. Associating ambient exposure to fine particles and human fertility rates in China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Jin, L.; Shi, T.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, T.; Bao, W.; Xiang, H.; Zuo, Y.; Li, G.; et al. Association between ambient particulate matter exposure and semen quality in Wuhan, China. Environ. Int. 2017, 98, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, N.; Jiang, C.; Chen, Q.; Yang, H.; Wang, X.; Zou, P.; Sun, L.; Liu, J.; Li, L.; Huang, L.; et al. Exposures to Atmospheric PM10 and PM10–2.5 Affect Male Semen Quality: Results of MARHCS Study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 1571–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, A.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Hüls, A.; Vierkötter, A.; Yuan, Z.; Cai, J.; Zhang, J.; Gao, W.; Li, J.; et al. Indoor PM2.5 exposure affects skin aging manifestation in a Chinese population. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Shi, Y.; Asweto, C.O.; Feng, L.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, H.; Duan, J.; Sun, Z. Fine particle matters induce DNA damage and G2/M cell cycle arrest in human bronchial epithelial BEAS-2B cells. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 25071–25081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Wu, X.; Hu, J.; Dai, G.; Rong, A.; Guo, G. PM2.5 exposure decreases viability, migration and angiogenesis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells and human microvascular endothelial cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 2425–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Zhang, W.; Li, S.; Williams, G.; Liu, C.; Morgan, G.G.; Jaakkola, J.J.K.; Guo, Y. Is short-term exposure to ambient fine particles associated with measles incidence in China? A multi-city study. Environ. Res. 2017, 156, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, K.Q.; Yang, Y.K.; Zhou, X.L. Potential Harmful Effects of PM2.5 on Occurrence and Progression of Acute Coronary Syndrome: Epidemiology, Mechanisms, and Prevention Measures. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Z.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, R.; Xu, J.; Dong, W.; Zhuang, G.; Deng, C. Airborne Fine Particulate Matter Induces Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Human Nasal Epithelial Cells. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2016, 239, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, C.; Li, J.; Sun, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q. Impact of ambient fine particulate matter (PM2.5) exposure on the risk of influenza-like-illness: A time-series analysis in Beijing, China. Environ. Health 2016, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannadaki, D.; Lelieveld, J.; Pozzer, A. Implementing the U.S. air quality standard for PM2.5 worldwide can prevent millions of premature deaths per year. Environ. Health 2016, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Wang, X.; Qian, Z.M.; Guo, S.; Yao, Z.; Vaughn, M.G.; Dong, G.; Liu, T.; Xiao, J.; Li, X.; et al. Daily exceedance concentration hours: A novel indicator to measure acute cardiovascular effects of PM2.5 in six Chinese subtropical cities. Environ. Int. 2017, 111, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, L.; Li, Y.; Gan, C. Effect of short-term exposure to ambient air particulate matter on incidence of delirium in a surgical population. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, X.; Fang, B.; Wang, C.; Xia, T.; Bottai, M.; Fang, F.; Cao, Y. Relationship between fine particulate matter, weather condition and daily non-accidental mortality in Shanghai, China: A Bayesian approach. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, J.; Chen, R.; Meng, X.; Yang, C.; Zhao, Z.; Kan, H. Ambient air pollution, temperature and out-of-hospital coronary deaths in Shanghai, China. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 203, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Q.; Liang, Y.; Niu, X. China’s Air Quality and Respiratory Disease Mortality Based on the Spatial Panel Model. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Lu, F.; Liu, Y.; Chen, C. Association between maternal exposure to fine particulate matter and low birth weight: A meta analysis. J. Environ. Health 2017, 34, 38. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Feng, Y.; Duan, X.; Zhao, N.; Wang, J.; Li, C.; Guo, P.; Xie, B.; Zhang, F. Ambient PM2.5 during pregnancy and risk on preterm birth. Chin. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 37, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yao, C.; Che, Z.; Cao, J. Maternal exposure to fine particulate matter (PM2.5) and pregnancy outcomes: A meta-analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 3383–3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wu, Y.; Jiao, M.; Yang, X.; Ma, P.; Yuan, B. Comparison of the cytotoxicity of the indoor PM2.5 from allergic or from non-allergic children’s homes: An in vitro study. J. Environ. Sci. Circumst. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, H. The Characteristics of PM2.5 and the Relationship between PM2.5 and Children Health in Urban Areas in Nanchang. Master’s Thesis, Nanchang University, Nanchang, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, F.; Liu, S.; Mao, J.; Zheng, Q.; Ma, T.; Hu, M. Relationship between air pollution and the number of pneumonia hospitalization in a children’s hospital in Changsha. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 2017, 42, 1417–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Hong, Y.; Liu, N. Association of ambient Particulate matter 2.5 with intensive care unit admission due to pneumonia: A distributed lag non-linear model. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, G.; Jin, X.; Mu, J.; Pan, J.; Liang, F.; Tian, L.; Chen, S.; Guo, Q.; Dong, W.; et al. Study of relationship between atmospheric fine particulate matter concentration and one grade a tertiary hospital emergency room visits during 2012 and 2013 in Beijing. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi 2016, 50, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Z.; Wei, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, L.; Liu, H.; Guo, C.; Zhang, L.; Li, N.; Guo, S.; Qian, Y.; et al. Exposure to Ambient Air Particles Increases the Risk of Mental Disorder: Findings from a Natural Experiment in Beijing. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.; Xie, H. Investigation on Risk Cognition and Responding Behavior towards Haze of Nanjing Residents. Environ. Sci. Manag. 2015, 40, 178–187. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, S.; Zhao, B. Occupants’ interaction with windows in 8 residential apartments in Beijing and Nanjing, China. Build. Simul. 2015, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, S.; Xu, C.; Wei, S.; MHassan, T.; Xie, L.; Xiong, Y.; de Wilde, P. Research on the Occupant Window Opening Behavior in an Office Building in Beijing. Build. Sci. 2015, 31, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L. Healthy Air Supply-Smart Sensing Technology Leading New Direction of Air Conditioning into the Cold 2018. Househ. Appl. 2017, 9, 82–83. [Google Scholar]
- Nan, Y.; Sun, J. Effects of Haze on the Tourist Decision-Making. J. Guangzhou Univ. Soc. Sci. Ed. 2015, 10, 35–41. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J. Study on Healthy Risk Assessment & Simulation on Residential Indoor Environmental Based on Stochastic Theory. Ph.D. Thesis, Hunan University, Changsha, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Zhao, B. Review of relationship between indoor and outdoor particles: I/O ratio, infiltration factor and penetration factor. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, T. Residential indoor exposures of PM2.5 and relationship between indoor and outdoor PM2.5 in winter in Beijing. J. Environ. Health 2016, 4, 268–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Qian, H.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, H. Analysis of indoor and outdoor PM2.5 mass concentration and influencing factors of a kindergarten in Nanjing. Heat. Vent. Air Cond. 2012, 46, 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, W.; Fan, Y.; Huang, Y.; Li, L. The Characteristic of Indoor and Outdoor PM10, PM2.5, PM1.0 Pollution of Natural Ventilation. Contam. Control Air-Cond. Technol. 2015, 3, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, L. Dynamic Characteristics in Air Infiltration Rate with Respect to Atmospheric PM2.5 Pollution. J. Beijing Univ. Technol. 2017, 2, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Liao, Q.; Huang, F. Investigation on the Influencing Factors of PM2.5 Concentration. In Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of Chinese Society for Environmental Sciences, Haikou, China, 13–14 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L. Research on Affecting Factors of PM2.5. Contam. Control Air-Cond. Technol. 2017, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, G.; Meng, C.; Zhao, L.; Wang, J.; Wangm, X. Penetration of outdoor fine particulate matter (PM2.5) through building envelope and passive control methods. Heat. Vent. Air Cond. 2015, 12, 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Wang, Q.; Li, N.; Chang, J.; Lin, X.; Xu, D. Investigation of indoor fine particles in public places and influencing factors. J. Environ. Health 2014, 11, 993–996. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Cao, J.; Chen, F.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, Y. Characteristics of air pollution in various indoor public places. Chin. J. Public Health 2016, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Cao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, N.; Dong, T.; Zhao, X.; Li, T.; Duan, X.; Zhang, W. Preliminary study on indoor PM2.5 pollution levels of residents in Lanzhou during heating period. J. Environ. Health 2014, 3, 232–234. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Cui, L.; Zhou, L.; Wu, J.; Zhang, X.; Ding, Z.; Chen, X.; Ji, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, T.; et al. Investigation of indoor PM2.5 and PM1.0 in some houses in Nanjing. J. Environ. Health 2013, 10, 900. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Yu, S.; Liu, G.; Huang, G.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Z. Indoor Air Concentrations of PM2.5 in Hospitals in Shenzhen. J. Environ. Health 2012, 4, 330–331. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Wang, G.; Zheng, W.; Yang, Y.; Pan, Y. Hygienic survey about indoor PM2.5 and air nicotine in main public places in Tianjin. J. Environ. Health 2014, 31, 787–789. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, F.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, R.; Huang, L.; Li, R.; Zhang, G.; Guo, Q. Indoor PM2.5 pollution level and influencing factors in public places in Beijing in winter. J. Environ. Health 2014, 31, 262–263. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Yu, S.; Song, M. Study on the Pollution Level of Formaldehyde and PM2.5 in Indoor Environment of Furniture and Clothing Markets. Build. Sci. 2016, 32, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Fan, Y.; Yang, S.; Wu, J.; Li, Z.; Chen, H. Investigation of indoor air PM2.5 concentration in public places in Nanchang. J. Hyg. Res. 2014, 1, 146–148. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G. Study on the PM2.5 Penetration through Exterior Windows under Different Conditions and Control Methods. Ph.D. Thesis, China Academy of Building Research, Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, J. Penetration of particle through building envelope and its influence factor. Build. Sci. 2015, 31, 72–76. [Google Scholar]
- Tung, T.C.W.; Chao, C.Y.H.; John, B. A methodology to investigate the particulate penetration coefficient through building shell. Atmos. Environ. 1993, 33, 881–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thatcher, T.L.; Lunden, M.M.; Revzan, K.L.; Sextro, R.G.; Brown, N.J. A concentration rebound method for measuring particle penetration and deposition in the indoor environment. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 847–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, A.C.K.; Fung, J.L.S.; Li, M.; Leung, K.Y. Penetration of fine particles through rough cracks. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 60, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.L.; Nazaroff, W.W. Modeling pollutant penetration across building envelopes. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 4451–4462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Zhang, G.; Lin, Y.; Yu, J.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Q. Mathematical model of particle penetration through smooth/rough building envelop leakages. Build. Environ. 2009, 44, 1144–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Zhang, G.; Yu, J. Mathematical Simulation of Particle Penetration through Smooth and Rough Building Envelop Leakage. J. Hunan Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2008, 35, 12–15. [Google Scholar]
- Li, A.; Ren, T.; Yang, C.; Lv, W.; Zhangm, F. Study on particle penetration through straight, L, Z and wedge-shaped cracks in buildings. Build. Environ. 2017, 114, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Wang, X. Correlation study on air change rate and particle penetration coefficient through building envelope. Heat. Vent. Air Cond. 2016, 46, 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, G.; Xie, H.; Zhao, S. Strategic Research of Pollution Control of Indoor PM2.5 in Public Buildings. Build. Sci. 2015, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Tu, G. Study on particulate matter (PM2.5) filtration efficiency of ventilating air filters. Heat. Vent. Air Cond. 2016, 46, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X. The PM2.5 Filtration Performance and Comprehensive Assessment of Air Filter Used in Fresh Air Unit. Ph.D. Thesis, Chongqing University, Chongqing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.; Xu, X. Primary return air system PM2.5 control strategy. J. Environ. Eng. 2016, 10, 7141–7146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Hua, T.; Jiang, P.; Yin, X.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Low-Resistance Dual-Purpose Air Filter Releasing Negative Ions and Effectively Capturing PM2.5. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 12054–12063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, C.; Hsu, P.C.; Zhang, C.; Liu, N.; Lee, H.R.; Lu, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Chu, S.; Cui, Y. Nanofiber Air Filters with High-Temperature Stability for Efficient PM2.5 Removal from the Pollution Sources. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 3642–3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Feng, Y.; Wang, K.; Yong, W.F.; Yu, L.; Chung, T.S. Novel Hollow Fiber Air Filters for the Removal of Ultrafine Particles in PM2.5 with Repetitive Usage Capability. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 10041–10049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Hsu, P.C.; Lee, H.W.; Ye, M.; Zheng, G.; Liu, N.; Li, W.; Cui, Y. Transparent air filter for high-efficiency PM2.5 capture. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, S.; Yin, X.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Slip-Effect Functional Air Filter for Efficient Purification of PM2.5. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalid, B.; Bai, X.; Wei, H.; Huang, Y.; Wu, H.; Cui, Y. Direct Blow-Spinning of Nanofibers on a Window Screen for Highly Efficient PM2.5 Removal. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 1140–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, S.; Bian, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, C. A method for assessing the performance of nanofiber films coated on window screens in reducing residential exposures to PM2.5 of outdoor origin in Beijing. Indoor Air 2017, 27, 1190–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).