Microplastics Reduce Short-Term Effects of Environmental Contaminants. Part I: Effects of Bisphenol A on Freshwater Zooplankton Are Lower in Presence of Polyamide Particles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microplastic Material and Chemicals
2.2. Study Design
2.2.1. Sorption Characteristics and BPA Content of PA Particles
2.2.2. Pre-Exposure with Single Substances
2.3. Exposure Experiments with Mixtures of BPA and PA Particles
2.4. Statistical Analysis
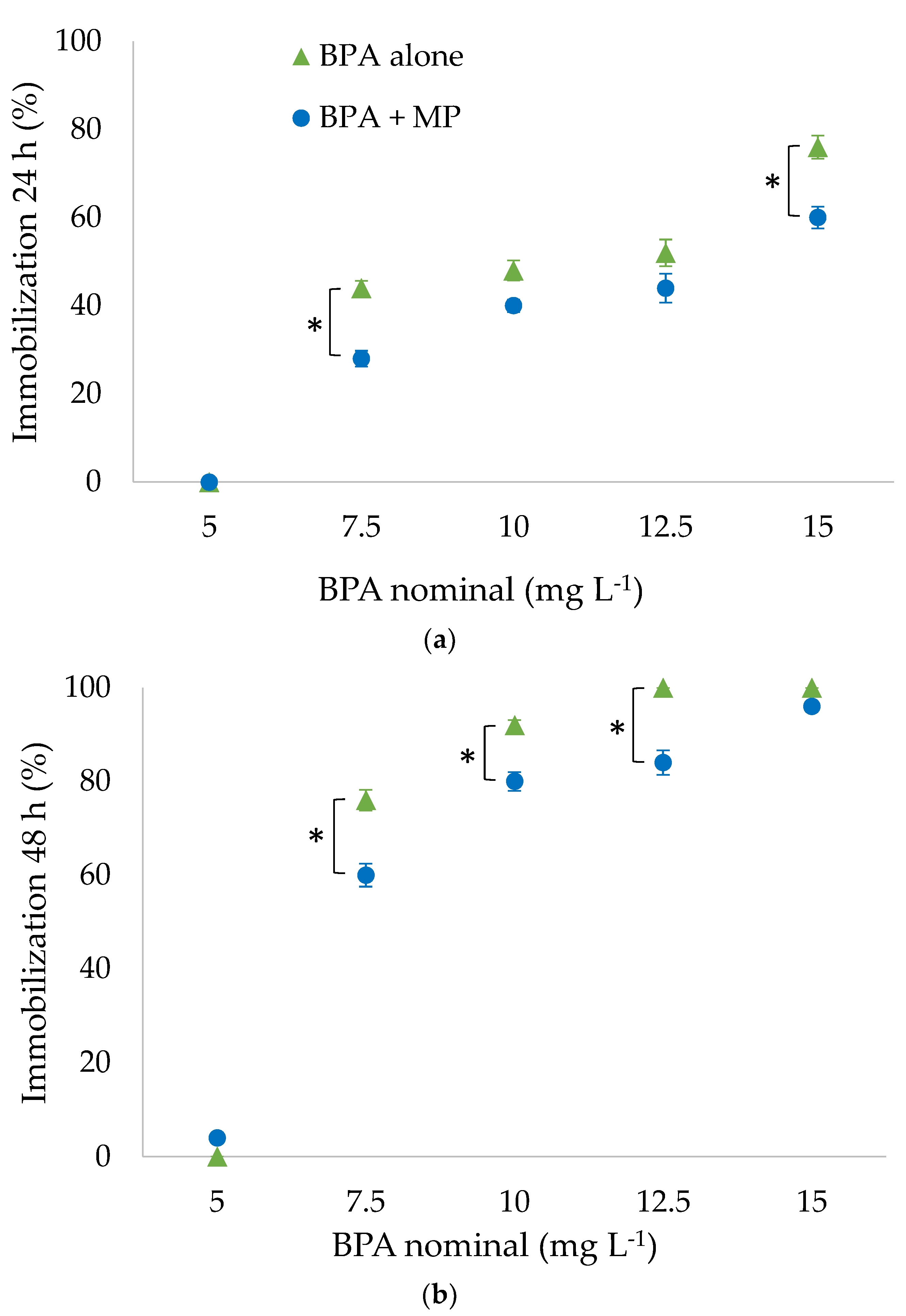
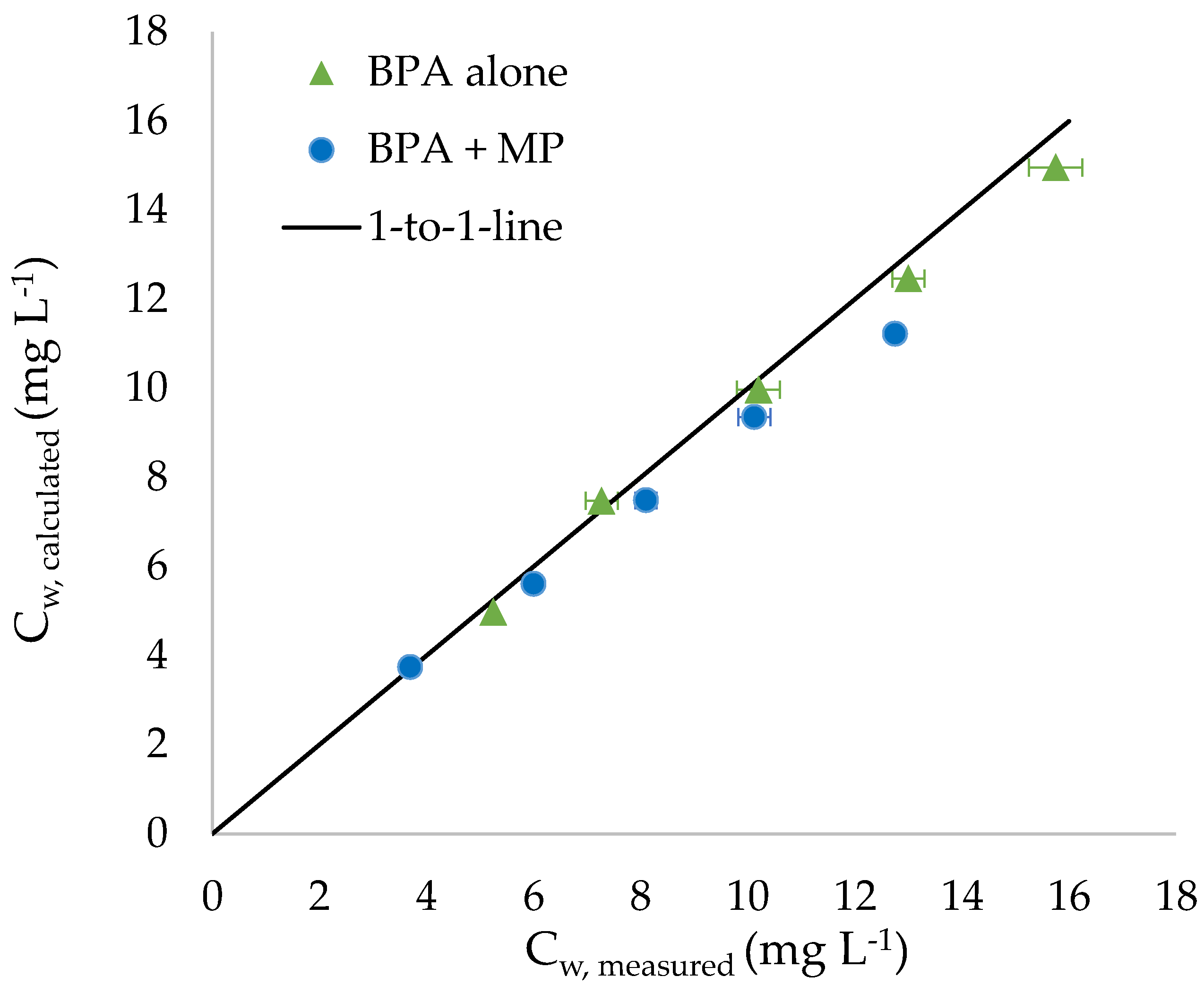
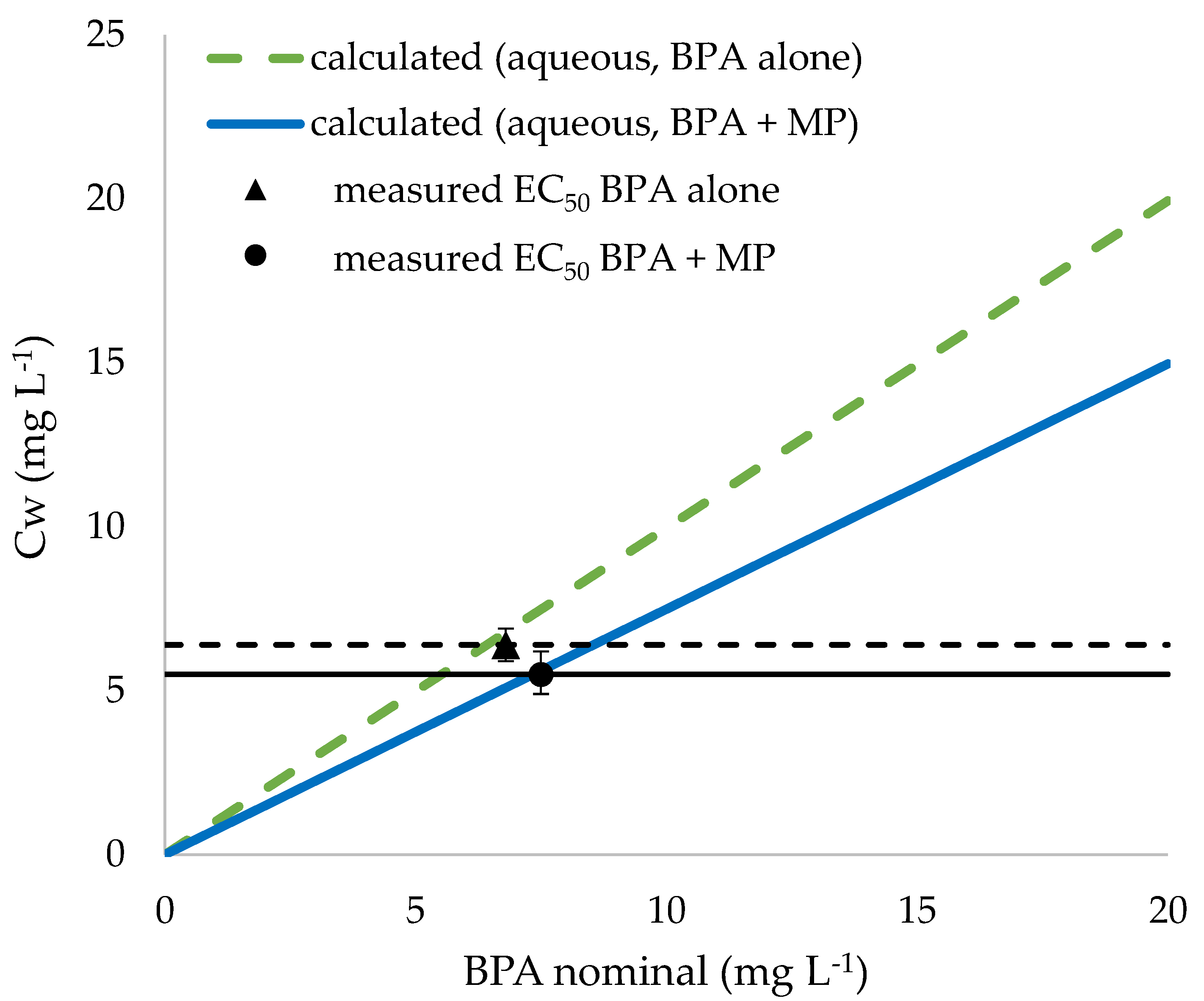
3. Results
Exposure Experiments with Mixtures of BPA and PA Particles
4. Discussion
4.1. Study Design with Predefined Conditions
4.2. Exposure Experiments with Mixtures of BPA and PA Particles
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moore, C.J. Synthetic polymers in the marine environment: A rapidly increasing, long-term threat. Environ. Res. 2008, 108, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eerkes-Medrano, D.; Thompson, R.C.; Aldridge, D.C. Microplastics in freshwater systems: A review of the emerging threats, identification of knowledge gaps and prioritisation of research needs. Water Res. 2015, 75, 63–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koelmans, A.A.; Bakir, A.; Burton, G.A.; Janssen, C.R. Microplastic as a vector for chemicals in the aquatic environment: Critical review and model-supported reinterpretation of empirical studies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 3315–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, A.T.; Simmons, S.L. Estuarine litter at the river/beach interface in the Bristol Channel, United Kingdom. J. Coast. Res. 1997, 13, 1159–1165. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, S.; Worch, E.; Knepper, T.P. Occurrence and spatial distribution of microplastics in river shore sediments of the Rhine-Main area in Germany. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 6070–6076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zbyszewski, M.; Corcoran, P.L. Distribution and degradation of fresh water plastic particles along the beaches of Lake Huron, Canada. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2011, 220, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.J.; Lattin, G.L.; Zellers, A.F. Quantity and type of plastic debris flowing from two urban rivers to coastal waters and beaches of Southern California. J. Integr. Coast. Zone Manag. 2011, 11, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure, F.; Demars, C.; Wieser, O.; Kunz, M.; de Alencastro, L.F. Plastic pollution in Swiss surface waters: Nature and concentrations, interaction with pollutants. Environ. Chem. 2015, 12, 582–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhof, H.K.; Laforsch, C.; Wiesheu, A.C.; Schmid, J.; Anger, P.M.; Niessner, R.; Ivleva, N.P. Pigments and plastic in limnetic ecosystems: A qualitative and quantitative study on microparticles of different size classes. Water Res. 2016, 98, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Free, C.M.; Jensen, O.P.; Mason, S.A.; Eriksen, M.; Williamson, N.J.; Boldgiv, B. High-levels of microplastic pollution in a large, remote, mountain lake. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 85, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yonkos, L.T.; Friedel, E.A.; Perez-Reyes, A.C.; Ghosal, S.; Arthur, C.D. Microplastics in four estuarine rivers in the Chesapeake Bay, U.S.A. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 14195–14202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCormick, A.R.; Hoellein, T.J.; London, M.G.; Hittie, J.; Scott, J.W.; Kelly, J.J. Microplastic in surface waters of urban rivers: Concentration, sources, and associated bacterial assemblages. Ecosphere 2016, 7, e01556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebreton, L.C.M.; van der Zwet, J.; Damsteeg, J.-W.; Slat, B.; Andrady, A.; Reisser, J. River plastic emissions to the world’s oceans. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Zhu, L.; Wang, T.; Li, D. Suspended microplastics in the surface water of the Yangtze Estuary System, China: First observations on occurrence, distribution. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 86, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, S.L.; Thompson, R.C.; Galloway, T.S. The physical impacts of microplastics on marine organisms: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 178, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziajahromi, S.; Kumar, A.; Neale, P.A.; Leusch, F.D.L. Impact of microplastic beads and fibers on waterflea (Ceriodaphnia dubia) survival, growth, and reproduction: Implications of single and mixture exposures. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 13397–13406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Au, S.Y.; Bruce, T.F.; Bridges, W.C.; Klaine, S.J. Responses of Hyalella azteca to acute and chronic microplastic exposures. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2015, 34, 2564–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jemec, A.; Horvat, P.; Kunej, U.; Bele, M.; Kržan, A. Uptake and effects of microplastic textile fibers on freshwater crustacean Daphnia magna. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehse, S.; Kloas, W.; Zarfl, C. Short-term exposure with high concentrations of pristine microplastic particles leads to immobilisation of Daphnia magna. Chemosphere 2016, 153, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjollema, S.B.; Redondo-Hasselerharm, P.; Leslie, H.A.; Kraak, M.H.S.; Vethaak, A.D. Do plastic particles affect microalgal photosynthesis and growth? Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 170, 259–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenkranz, P.; Chaudhry, Q.; Stone, V.; Fernandes, T.F. A comparison of nanoparticle and fine particle uptake by Daphnia magna. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2009, 28, 2142–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Huang, A.; Cao, S.; Sun, F.; Wang, L.; Guo, H.; Ji, R. Effects of nanoplastics and microplastics on toxicity, bioaccumulation, and environmental fate of phenanthrene in fresh water. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malaj, E.; von der Ohe, P.C.; Grote, M.; Kühne, R.; Mondy, C.P.; Usseglio-Polatera, P.; Brack, W.; Schäfer, R.B. Organic chemicals jeopardize the health of freshwater ecosystems on the continental scale. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 9549–9554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teuten, E.L.; Saquing, J.M.; Knappe, D.R.U.; Barlaz, M.A.; Jonsson, S.; Björn, A.; Rowland, S.J.; Thompson, R.C.; Galloway, T.S.; Yamashita, R.; et al. Transport and release of chemicals from plastics to the environment and to wildlife. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2027–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakir, A.; Rowland, S.J.; Thompson, R.C. Enhanced desorption of persistent organic pollutants from microplastics under simulated physiological conditions. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 185, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teuten, E.L.; Rowland, S.J.; Galloway, T.S.; Thompson, R.C. Potential for plastics to transport hydrophobic contaminants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 7759–7764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browne, M.A.; Niven, S.J.; Galloway, T.S.; Rowland, S.J.; Thompson, R.C. Microplastic moves pollutants and additives to worms, reducing functions linked to health and biodiversity. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, 2388–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heimeier, R.A.; Shi, Y.-B. Amphibian metamorphosis as a model for studying endocrine disruption on vertebrate development: Effect of bisphenol A on thyroid hormone action. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2010, 168, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, G.; Lutz, I.; Krüger, A.; Kloas, W. Bisphenol A induces feminization in Xenopus laevis tadpoles. Environ. Res. 2004, 94, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.-Y.; Ike, M.; Fujita, M. Acute toxicity, mutagenicity, and estrogenicity of bisphenol-A and other bisphenols. Environ. Toxicol. 2002, 17, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brotons, J.A.; Olea-Serrano, M.F.; Villalobos, M.; Pedraza, V.; Olea, N. Xenoestrogens released from lacquer coatings in food cans. Environ. Health Perspect. 1995, 103, 608–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wardrop, P.; Shimeta, J.; Nugegoda, D.; Morrison, P.D.; Miranda, A.; Tang, M.; Clarke, B.O. Chemical pollutants sorbed to igested microbeads from personal care products accumulate in fish. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 4037–4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karami, A.; Romano, N.; Galloway, T.; Hamzah, H. Virgin microplastics cause toxicity and modulate the impacts of phenanthrene on biomarker responses in African catfish (Clarias gariepinus). Environ. Res. 2016, 151, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochman, C.M.; Hoh, E.; Kurobe, T.; Teh, S.J. Ingested plastic transfers hazardous chemicals to fish and induces hepatic stress. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batel, A.; Linti, F.; Scherer, M.; Erdinger, L.; Braunbeck, T. Transfer of benzoapyrene from microplastics to Artemia nauplii and further to zebrafish via a trophic food web experiment: CYP1A induction and visual tracking of persistent organic pollutants. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 1656–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochman, C.M.; Parnis, J.M.; Browne, M.A.; Serrato, S.; Reiner, E.J.; Robson, M.; Young, T.; Diamond, M.L.; Teh, S.J. Direct and indirect effects of different types of microplastics on freshwater prey (Corbicula fluminea) and their predator (Acipenser transmontanus). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakir, A.; O’Connor, I.A.; Rowland, S.J.; Hendriks, A.J.; Thompson, R.C. Relative importance of microplastics as a pathway for the transfer of hydrophobic organic chemicals to marine life. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besseling, E.; Foekema, E.M.; van den Heuvel-Greve, M.J.; Koelmans, A.A. The effect of microplastic on the uptake of chemicals by the lugworm Arenicola marina (L.) under environmentally relevant exposure conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 8795–8804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koelmans, A.A.; Besseling, E.; Foekema, E.M. Leaching of plastic additives to marine organisms. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 187, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinteich, J.; Seidensticker, S.; Marggrader, N.; Zarfl, C. Microplastics reduce short-term effects of environmental pollutants. Part II: Polyethylene particles decrease the effect of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons on microorganisms. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. in press.
- Beckingham, B.; Ghosh, U. Differential bioavailability of polychlorinated biphenyls associated with environmental particles: Microplastic in comparison to wood, coal and biochar. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 220, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul-Pont, I.; Lacroix, C.; González Fernández, C.; Hégaret, H.; Lambert, C.; Le Goïc, N.; Frère, L.; Cassone, A.-L.; Sussarellu, R.; Fabioux, C.; et al. Exposure of marine mussels Mytilus spp. to polystyrene microplastics: Toxicity and influence on fluoranthene bioaccumulation. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 216, 724–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devriese, L.I.; de Witte, B.; Vethaak, A.D.; Hostens, K.; Leslie, H.A. Bioaccumulation of PCBs from microplastics in Norway lobster (Nephrops norvegicus): An experimental study. Chemosphere 2017, 186, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klüttgen, B.; Dülmer, U.; Engels, M.; Ratte, H. ADaM, an artificial freshwater for the culture of zooplankton. Water Res. 1994, 28, 743–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzenbach, R.P.; Gschwend, P.M.; Imboden, D.M. Environmental Organic Chemistry, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lampert, W. The dynamics of Daphnia magna in a shallow lake. Verh. Int. Ver. Theor. Angew. Limnol. 1991, 24, 795–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, P.A.; Rowan, M.; Webster, K.E.; Peters, R.H. Browsing and grazing by cladoceran filter feeders. Can. J. Zool. 1979, 57, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampert, W. Feeding and nutrition in Daphnia. Mem. Ist. Ital. Idrobiol 1987, 45, 143–192. [Google Scholar]
- Burns, C.W. The relationship between body size of filter-feeding Cladocera and the maximum size of particle ingested. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1968, 13, 675–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gophen, M.; Geller, W. Filter mesh size and food particle uptake by Daphnia. Oecologia 1984, 64, 408–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennan, S.J.; Brougham, C.A.; Roche, J.J.; Fogarty, A.M. Multi-generational effects of four selected environmental oestrogens on Daphnia magna. Chemosphere 2006, 64, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Organization for Economic Co-Operation and Development. OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 2; Test No. 202: Daphnia sp. Acute Immobilisation Test; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Veith, G.D.; Macek, K.J.; Petrocelli, S.R.; Carroll, J. An evaluation of using partition coefficients and water solubility to estimate bioconcentration factors for organic chemicals in fish. In Aquatic Toxicology; Eaton, J.G., Parrish, P.R., Hendricks, A.C., Eds.; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1980; pp. 116–129. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, F.R.; Syberg, K.; Shashoua, Y.; Bury, N.R. Influence of polyethylene microplastic beads on the uptake and localization of silver in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Pollut. 2015, 206, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochman, C.M.; Kurobe, T.; Flores, I.; Teh, S.J. Early warning signs of endocrine disruption in adult fish from the ingestion of polyethylene with and without sorbed chemical pollutants from the marine environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 493, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo, S.; Yuyama, M.; Takada, H. Desorption kinetics of hydrophobic organic contaminants from marine plastic pellets. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 74, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staples, C.A.; Dome, P.B.; Klecka, G.M.; Oblock, S.T.; Harris, L.R. A review of the environmental fate, effects, and exposures of Bisphenol A. Chemosphere 1998, 36, 2149–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Shim, W.J.; Kwon, J.-H. Sorption capacity of plastic debris for hydrophobic organic chemicals. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 470–471, 1545–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakir, A.; Rowland, S.J.; Thompson, R.C. Competitive sorption of persistent organic pollutants onto microplastics in the marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 2782–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sleight, V.A.; Bakir, A.; Thompson, R.C.; Henry, T.B. Assessment of microplastic-sorbed contaminant bioavailability through analysis of biomarker gene expression in larval zebrafish. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 116, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koelmans, A.A.; Besseling, E.; Wegner, A.; Foekema, E.M. Plastic as a carrier of POPs to aquatic organisms: A model analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 7812–7820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murtaugh, P.A. The influence of food concentration and feeding rate on the gut residence time of Daphnia. J. Plankton Res. 1985, 7, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuch, H.M.; Ballschmiter, K. Determination of endocrine-disrupting phenolic compounds and estrogens in surface and drinking water by HRGC-(NCI)-MS in the picogram per liter range. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 3201–3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Compartment | Mass Distribution of BPA (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| BPA alone | BPA + MP | |
| water | 99.72 | 74.85 |
| organisms | 0.28 | 0.21 |
| PA-particles | - | 24.94 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rehse, S.; Kloas, W.; Zarfl, C. Microplastics Reduce Short-Term Effects of Environmental Contaminants. Part I: Effects of Bisphenol A on Freshwater Zooplankton Are Lower in Presence of Polyamide Particles. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 280. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15020280
Rehse S, Kloas W, Zarfl C. Microplastics Reduce Short-Term Effects of Environmental Contaminants. Part I: Effects of Bisphenol A on Freshwater Zooplankton Are Lower in Presence of Polyamide Particles. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2018; 15(2):280. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15020280
Chicago/Turabian StyleRehse, Saskia, Werner Kloas, and Christiane Zarfl. 2018. "Microplastics Reduce Short-Term Effects of Environmental Contaminants. Part I: Effects of Bisphenol A on Freshwater Zooplankton Are Lower in Presence of Polyamide Particles" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 15, no. 2: 280. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15020280
APA StyleRehse, S., Kloas, W., & Zarfl, C. (2018). Microplastics Reduce Short-Term Effects of Environmental Contaminants. Part I: Effects of Bisphenol A on Freshwater Zooplankton Are Lower in Presence of Polyamide Particles. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(2), 280. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15020280




