Synchronization of Human Autonomic Nervous System Rhythms with Geomagnetic Activity in Human Subjects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods and Procedures
2.1. Participants
2.2. HRV Data Collection
2.3. HRV Measures
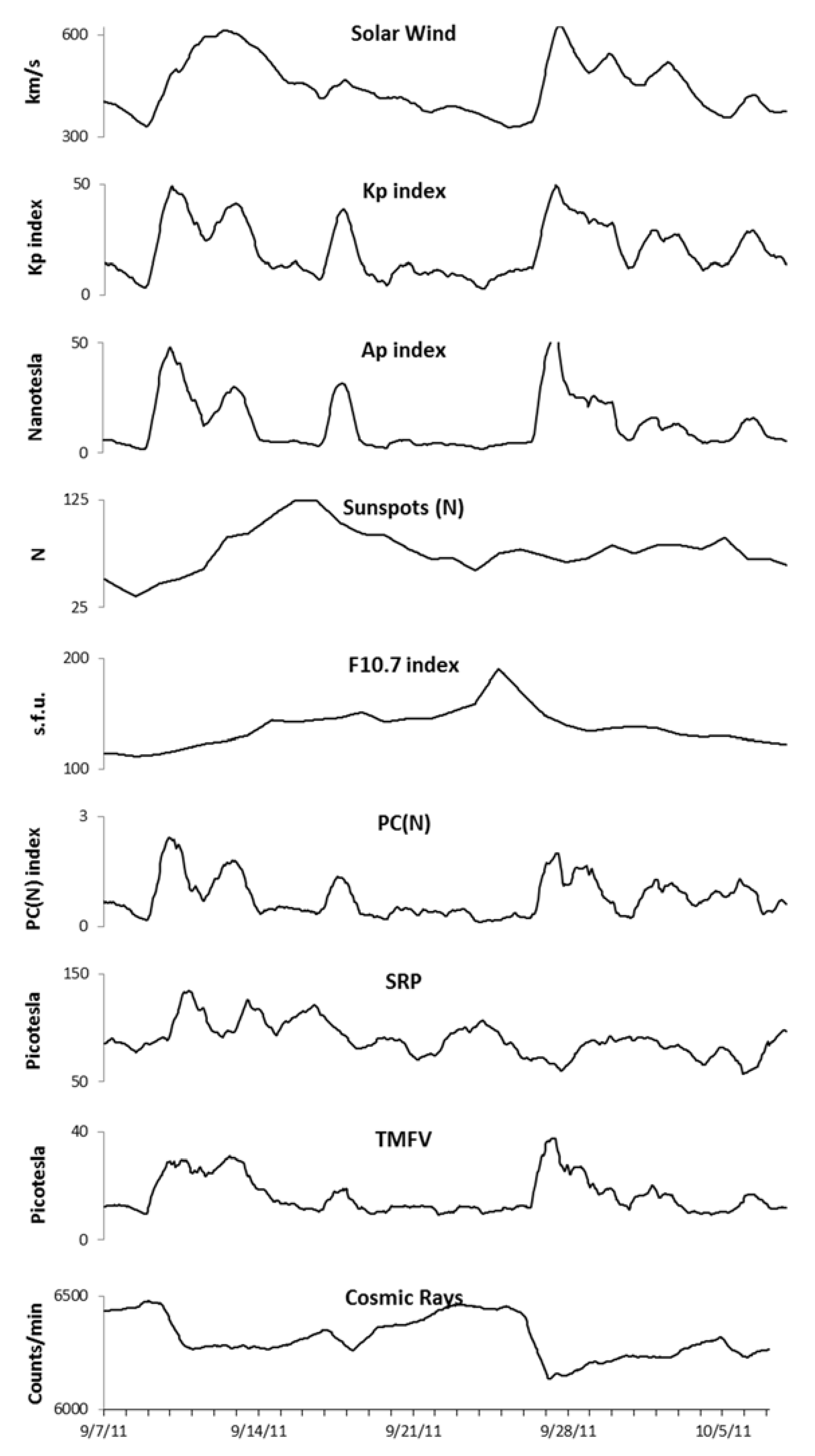
2.4. Environmental Measures
2.5. Statistical Analysis
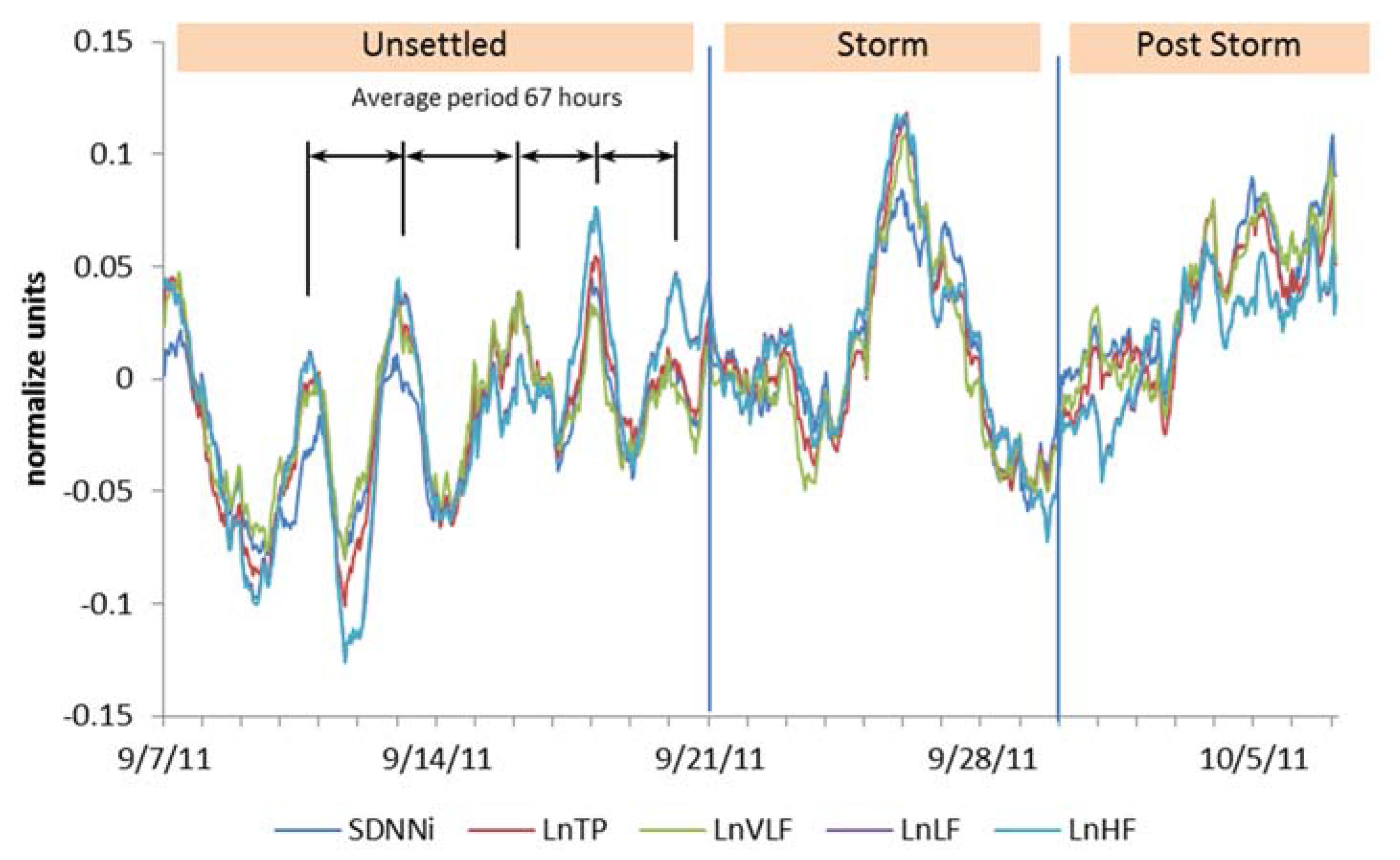
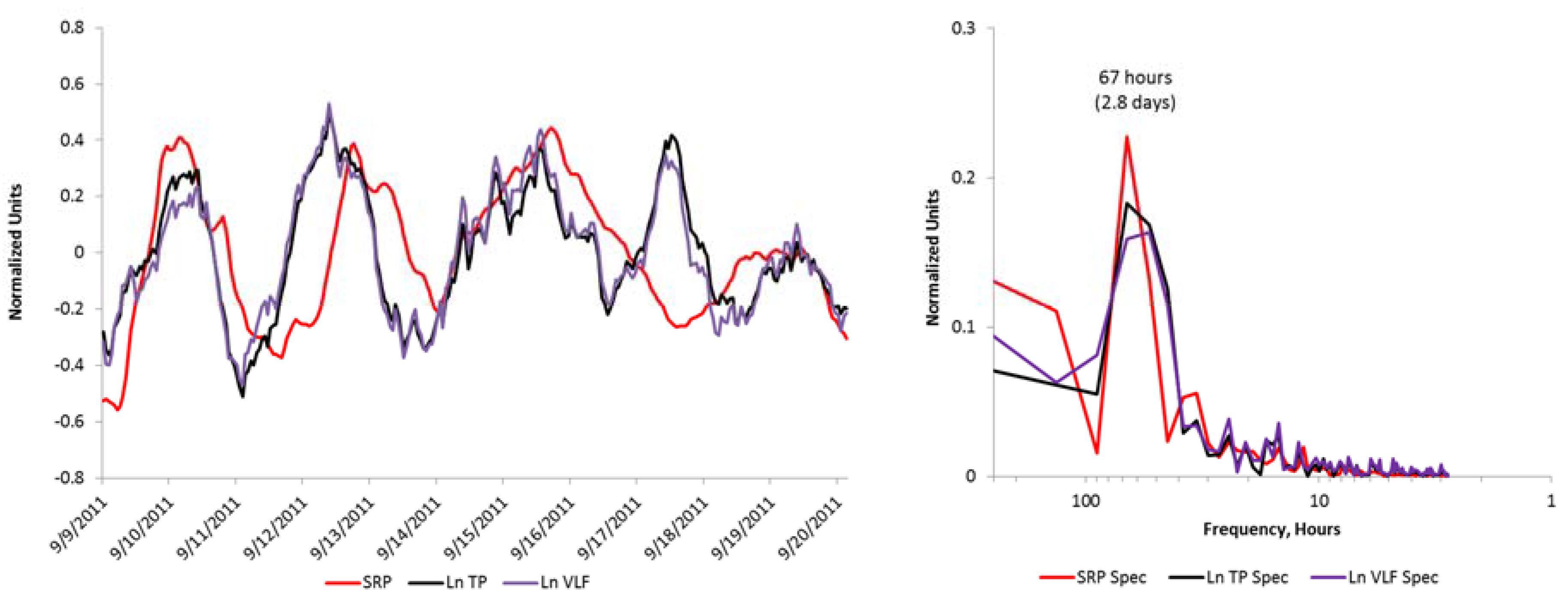
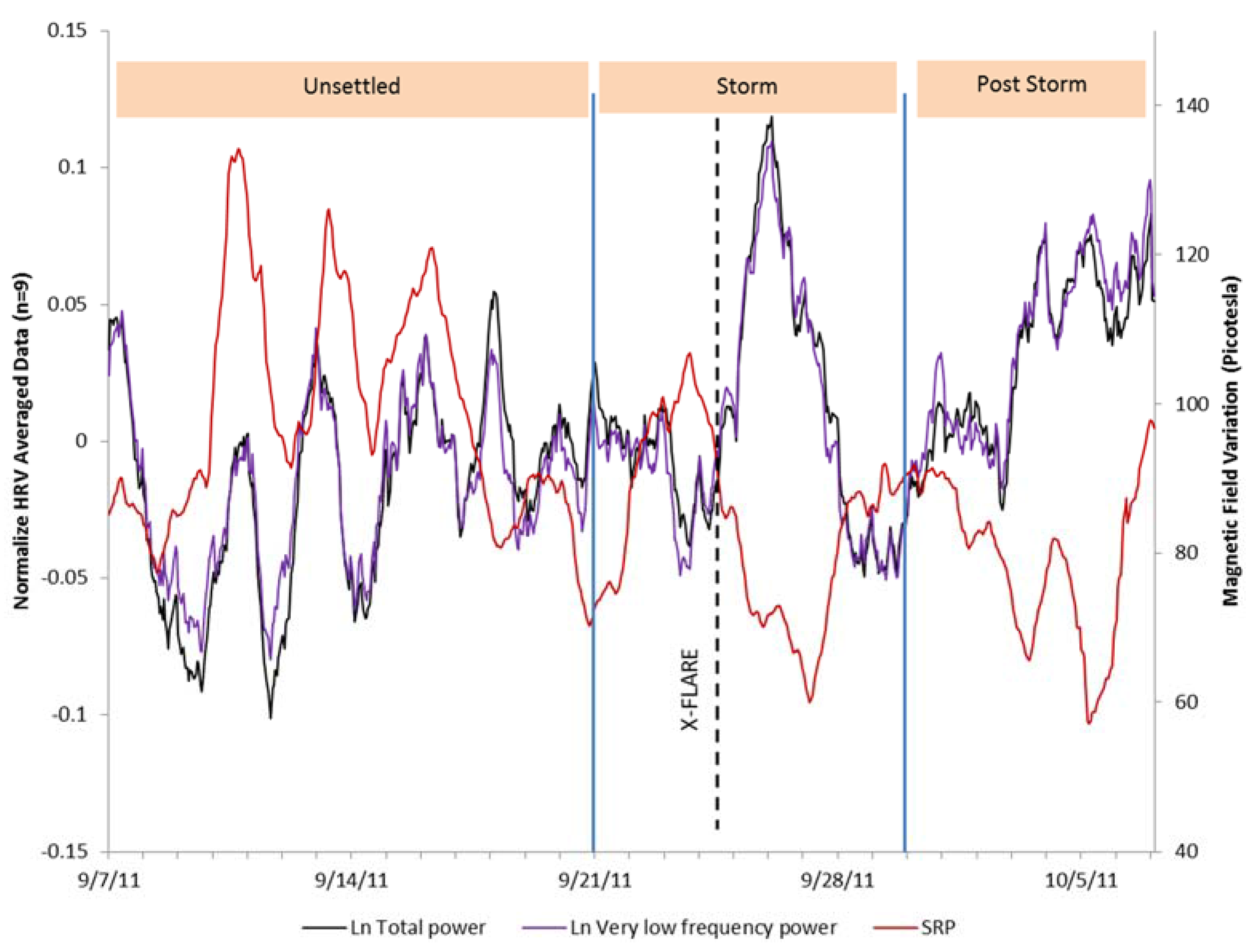
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANS | Autonomic nervous system |
| EEG | Electroencephalogram |
| HRV | Heart rate variability |
| HF | High frequency |
| LF | low frequency |
| LF/HF ratio | low frequency divided by high frequency power |
| VLF | very low frequency |
| SNDNi | SDNN index |
| TP | Total power |
| IBI | Inter-beat-interval |
| ULF | Ultra low frequency |
| Environmental related measures | |
| Pc | pulsations continuous |
| Pi | pulsations irregular |
| SR | Schumann resonance |
| SRP | Schumann resonance power |
| SWS | Solar wind speed |
| PC(N) | index polar cap north |
| CR | Cosmic rays |
| TMFV | Total magnetic field variance |
| CME | coronal mass ejection |
References
- Cornelissen, G.; Halberg, F.; Schwartkopff, O.; Delmore, P.; Katinas, G.; Hunter, D.; Tarquini, B.; Tarquini, R.; Perfetto, F.; Watanabe, Y.; et al. Chronomes, time structures, for chronobioengineering for “a full life”. Biomed. Instrum. Technol. 1999, 33, 152–187. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Doronin, V.N.; Parfentev, V.A.; Tleulin, S.Z.; Namvar, R.A.; Somsikov, V.M.; Drobzhev, V.I.; Chemeris, A.V. Effect of variations of the geomagnetic field and solar activity on human physiological indicators. Biofizika 1998, 43, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Halberg, F.; Cornelissen, G.; McCraty, R.; Al-Abdulgader, A.A. Time structures (chronomes) of the blood circulation, populations’ health, human affairs and space weather. World Heart J. 2011, 3, 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Khorseva, N. Using psychophysiological indices to estimate the effect of cosmophysical factors (review). Izv. Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 2013, 49, 839–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halberg, F.; Cornelissen, G.; Otsuka, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Katinas, G.S.; Burioka, N.; Delyukov, A.; Gorgo, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Weydahl, A.; et al. Cross-spectrally coherent ~10.5- and 21-year biological and physical cycles, magnetic storms and myocardial infarctions. Neuroendocrinology 2000, 21, 233–258. [Google Scholar]
- Khabarova, O.; Dimitrova, S. On the nature of people’s reaction to space weather and meteorological weather changes. Sun Geosph. 2009, 4, 60–71. [Google Scholar]
- Burch, J.B.; Reif, J.S.; Yost, M.G. Geomagnetic disturbances are associated with reduced nocturnal excretion of a melatonin metabolite in humans. Neurosci. Lett. 1999, 266, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapoport, S.I.; Malinovskaia, N.K.; Oraevskii, V.N.; Komarov, F.I.; Nosovskii, A.M.; Vetterberg, L. Effects of disturbances of natural magnetic field of the earth on melatonin production in patients with coronary heart disease. Klin. Med. (Mosk) 1997, 75, 24–26. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bergiannaki, J.-D.; Paparrigopoulos, T.J.; Stefanis, C.N. Seasonal pattern of melatonin excretion in humans: Relationship to day length variation rate and geomagnetic field fluctuations. Experientia 1996, 52, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherry, N. Schumann resonances, a plausible biophysical mechanism for the human health effects of solar/geomagnetic activity. Nat. Hazards 2002, 26, 279–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghione, S.; Mazzasalma, L.; Del Seppia, C.; Papi, F. Do geomagnetic disturbances of solar origin affect arterial blood pressure? J. Hum. Hypertens. 1998, 12, 749–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamer, J.R. Biological Entrainment of the Human Brain by Low Frequency Radiation; Northrop Space Laboratories: Hawthorne, CA, USA, 1965; pp. 65–199. [Google Scholar]
- Cernouss, S.; Vinogradov, A.; Vlassova, E. Geophysical hazard for human health in the circumpolar auroral belt: Evidence of a relationship between heart rate variation and electromagnetic disturbances. Nat. Hazards 2001, 23, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornélissen, G.; Halberg, F.; Breus, T.; Syutkina, E.V.; Baevsky, R.; Weydahl, A.; Watanabe, Y.; Otsuka, K.; Siegelova, J.; Fiser, B. Non-photic solar associations of heart rate variability and myocardial infarction. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2002, 64, 707–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villoresi, G.; Ptitsyna, N.G.; Tiasto, M.I.; Iucci, N. Myocardial infarct and geomagnetic disturbances: Analysis of data on morbidity and mortality. Biofizika 1998, 43, 623–632. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Malin, S.R.C.; Srivastava, B.J. Correlation between heart attacks and magnetic activity. Nature 1979, 277, 646–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoupel, E. Sudden cardiac deaths and ventricular extrasystoles on days of four levels of geomagnetic activity. J. Basic Physiol. Pharmacol. 1993, 4, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persinger, M.A. Sudden unexpected death in epileptics following sudden, intense, increases in geomagnetic activity: Prevalence of effect and potential mechanisms. Int. J. Biometeorol. 1995, 38, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knox, E.G.; Armstrong, E.; Lancashire, R.; Wall, M.; Hayes, R. Heart attacks and geomagnetic activity. Nature 1979, 281, 564–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannaropoulou, E.; Papailiou, M.; Mavromichalaki, H.; Gigolashvili, M.; Tvildiani, L.; Janashia, K.; Preka-Papadema, P.; Papadima, T. A study on the various types of arrhythmias in relation to the polarity reversal of the solar magnetic field. Nat. Hazards 2014, 70, 1575–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoupel, E.; Wittenberg, C.; Zabludowski, J.; Boner, G. Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring in patients with hypertension on days of high and low geomagnetic activity. J. Hum. Hypertens. 1995, 9, 293–294. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Caswell, J.M.; Carniello, T.N.; Murugan, N.J. Annual incidence of mortality related to hypertensive disease in Canada and associations with heliophysical parameters. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2016, 60, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lean, J. Evolution of the sun’s spectral irradiance since the maunder minimum. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2000, 27, 2425–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapping, K. Recent solar radio astronomy at centimeter wavelengths: The temporal variability of the 10.7-cm flux. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1987, 92, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babayev, E.; Crosby, N.; Obridko, V.; Rycroft, M. Potential effects of solar and geomagnetic variability on terrestrial biological systems. In Advances in Solar and Solar Terrsetrial Physics; Maris, G., Demetrescu, C., Eds.; Research Signpost: Kerala, India, 2012; pp. 329–376. [Google Scholar]
- McCraty, R.; Shaffer, F. Heart rate variability: New perspectives on physiological mechanisms, assessment of self-regulatory capacity, and health risk. Glob. Adv. Health Med. 2015, 4, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCraty, R.; Zayas, M. Cardiac coherence, self-regulation, autonomic stability, and psychosocial well-being. Front. Psychol. 2014, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginsberg, J.P.; Berry, M.E.; Powell, D.A. Cardiac coherence and PTSD in combat veterans. Altern. Ther. Health Med. 2010, 16, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thayer, J.F.; Hansen, A.L.; Saus-Rose, E.; Johnsen, B.H. Heart rate variability, prefrontal neural function, and cognitive performance: The neurovisceral integration perspective on self-regulation, adaptation, and health. Ann. Behav. Med. 2009, 37, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffer, F.; McCraty, R.; Zerr, C. A healthy heart is not a metronome: An integrative review of the heart’s anatomy and heart rate variability. Front. Psychol. 2014, 5, 1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, D.H.; Martin, G.J.; Magid, N.; Weiss, J.S.; Schaas, J.W.; Kehoe, R.; Zheutlin, T.; Fintel, D.J.; Hsieh, A.-M.; Lesch, M. Low heart rate variability and sudden cardiac death. J. Electrocardiol. 1988, 21, S46–S55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, H.; Venditti, F.J., Jr.; Manders, E.S.; Evans, J.C.; Larson, M.G.; Feldman, C.L.; Levy, D. Reduced heart rate variability and mortality risk in an elderly cohort. The Framingham heart study. Circulation 1994, 90, 878–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berntson, G.G.; Norman, G.J.; Hawkley, L.C.; Cacioppo, J.T. Cardiac autonomic balance versus cardiac regulatory capacity. Psychophysiology 2008, 45, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geisler, F.C.; Kubiak, T.; Siewert, K.; Weber, H. Cardiac vagal tone is associated with social engagement and self-regulation. Biol. Psychol. 2013, 93, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasermoaddeli, A.; Sekine, M.; Kagamimori, S. Association between sense of coherence and heart rate variability in healthy subjects. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2004, 9, 272–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zohar, A.; Cloninger, R.; McCraty, R. Personality and heart rate variability: Exploring pathways from personality to cardiac coherence and health. Open J. Soc. Sci. 2013, 1, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, Y.; Cornelissen, G.; Halberg, F.; Otsuka, K.; Ohkawa, S.I. Associations by signatures and coherences between the human circulation and helio- and geomagnetic activity. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2001, 55 (Suppl. S1), 76s–83s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrova, S.; Angelov, I.; Petrova, E. Solar and geomagnetic activity effects on heart rate variability. Nat. Hazards 2013, 69, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, K.; Cornelissen, G.; Weydahl, A.; Holmeslet, B.; Hansen, T.L.; Shinagawa, M.; Kubo, Y.; Nishimura, Y.; Omori, K.; Yano, S.; et al. Geomagnetic disturbance associated with decrease in heart rate variability in a subarctic area. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2001, 55 (Suppl. S1), 51s–56s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, K.; Ichimaru, Y.; Cornelissen, G.; Weydahl, A.; Holmeslet, B.; Schwartzkopff, O.; Halberg, F. Dynamic Analysis of Heart Rate Variability from 7-Day Holter Recordings Associated with Geomagnetic Activity in Subarctic Area; Computers in Cardiology 2000; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2000; pp. 453–456. [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka, K.; Yamanaka, T.; Cornelissen, G.; Breus, T.; Chibisov, S.; Baevsky, R.; Halberg, F.; Siegelova, J.; Fiser, B. Altered chronome of heart rate variability during span of high magnetic activity. Scr. Med. (Brno) 2000, 73, 111–116. [Google Scholar]
- Gmitrov, J.; Ohkubo, C. Geomagnetic field decreases cardiovascular variability. Electromagn. Magnetobiol. 1999, 18, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breus, T.K.; Baevskii, R.M.; Chernikova, A.G. Effects of geomagnetic disturbances on humans functional state in space flight. J. Biomed. Sci. Eng. 2012, 5, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baevsky, R.; Petrov, V.; Cornelissen, G.; Halberg, F.; Orth-Gomer, K.; Akerstedt, T.; Otsuka, K.; Breus, T.; Siegelova, J.; Dusek, J. Meta-analyzed heart rate variability, exposure to geomagnetic storms, and the risk of ischemic heart disease. Scr. Med. 1997, 70, 201–206. [Google Scholar]
- Oinuma, S.; Kubo, Y.; Otsuka, K.; Yamanaka, T.; Murakami, S.; Matsuoka, O.; Ohkawa, S.; Cornelissen, G.; Weydahl, A.; Holmeslet, B. Graded response of heart rate variability, associated with an alteration of geomagnetic activity in a subarctic area. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2002, 56, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, H.; Larson, M.G.; Venditti, F.J., Jr.; Manders, E.S.; Evans, J.C.; Feldman, C.L.; Levy, D. Impact of reduced heart rate variability on risk for cardiac events. The Framingham heart study. Circulation 1996, 94, 2850–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dmitreva, I.; Khabarova, O.; Obridko, V.; Ragulskaja, M.; Reznikov, A. Experimental confirmations of bioeffective effect of magnetic storms. Astron. Astrophys. Trans. 2000, 19, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khabarova, O. Investigation of the tchizhevsky-velhover effect. Biophysics 2004, 49, S60. [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrova, S.; Stoilova, I.; Cholakov, I. Influence of local geomagnetic storms on arterial blood pressure. Bioelectromagnetics 2004, 25, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samsonov, S.; Sokolov, V.; Strekalovskaya, A.; Petrova, P. On the Relationship of Cardiovascular Disease Exacerbation to Helio-Geophysical Disturbances. In Proceedings of the XXVII Annual Seminar (Physics of Auroral Phenomena), Apatity, Russian, 2004; pp. 134–137. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/S_Samsonov/publication/228907582_On_the_relationship_of_cardiovascular_disease_exacerbation_to_heliogeophysical_disturbances/links/0912f508f089a6118c000000.pdf (accessed on 3 July 2017).
- Azcárate, T.; Mendoza, B.; de la Peña, S.S.; Martínez, J. Temporal variation of the arterial pressure in healthy young people and its relation to geomagnetic activity in Mexico. Adv. Space Res. 2012, 50, 1310–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrova, S.; Mustafa, F.; Stoilova, I.; Babayev, E.; Kazimov, E. Possible influence of solar extreme events and related geomagnetic disturbances on human cardio-vascular state: Results of collaborative Bulgarian–Azerbaijani studies. Adv. Space Res. 2009, 43, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoupel, E.; Babayev, E.; Abramson, E.; Sulkes, J. Days of “zero” level geomagnetic activity accompanied by the high neutron activity and dynamics of some medical events—Antipodes to geomagnetic storms. Health 2013, 5, 855–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoupel, E.; Kalediene, R.; Petrauskiene, J.; Starkuviene, S.; Abramson, E.; Israelevich, P.; Sulkes, J. Twenty years study of solar, geomagnetic, cosmic ray activity links with monthly deaths number (n-850304). J. Biomed. Sci. Eng. 2011, 4, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southwood, D. Some features of field line resonances in the magnetosphere. Planet. Space Sci. 1974, 22, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heacock, R. Two subtypes of type pi micropulsations. J. Geophys. Res. 1967, 72, 3905–3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleimenova, N.; Kozyreva, O. Daytime quasiperiodic geomagnetic pulsations during the recovery phase of the strong magnetic storm of 15 May 2005. Geomagn. Aeron. 2007, 47, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenchenko, T.; Medvedeva, A.; Khorseva, N.; Breus, T. Synchronization of human heart-rate indicators and geomagnetic field variations in the frequency range of 0.5–3.0 mHz. Izv. Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 2014, 50, 736–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumann, W.; Konig, H. Uber die beobachtung von “atmospherics” bei geringsten frequenzen. Die Naturwiss. 1954, 41, 183–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König, H.L.; Krueger, A.P.; Lang, S.; Sönning, W. Biologic Effects of Environmental Electromagnetism; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pobachenko, S.V.; Kolesnik, A.G.; Borodin, A.S.; Kalyuzhin, V.V. The contigency of parameters of human encephalograms and Schumann resonance electromagnetic fields revealed in monitoring studies. Complex Syst. Biophys. 2006, 51, 480–483. [Google Scholar]
- Saroka, K.S.; Persinger, M.A. Quantitative evidence for direct effects between earth-ionosphere Schumann resonances and human cerebral cortical activity. Int. Lett. Chem. Phys. Astron. 2014, 20, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persinger, M.A.; Saroka, K.S. Human quantitative electroencephalographic and Schumann resonance exhibit real-time coherence of spectral power densities: Implications for interactive information processing. J. Signal Inf. Process. 2015, 6, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camm, A.J.; Malik, M.; Bigger, J.T.; Breithardt, G.; Cerutti, S.; Cohen, R.J.; Singer, D.H. Heart rate variability standards of measurement, physiological interpretation, and clinical use. Task force of the European society of cardiology and the North American society of pacing and electrophysiology. Circulation 1996, 93, 1043–1065. [Google Scholar]
- Malliani, A. Association of heart rate variability components with physiological regulatory mechanisms. In Heart Rate Variability; Malik, M., Camm, A.J., Eds.; Futura Publishing Company Inc.: Armonk, NY, USA, 1995; pp. 173–188. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, H.; Muller-Werdan, U.; Hoffmann, T.; Francis, D.P.; Piepoli, M.F.; Rauchhaus, M.; Prondzinsky, R.; Loppnow, H.; Buerke, M.; Hoyer, D.; et al. Autonomic dysfunction predicts mortality in patients with multiple organ dysfunction syndrome of different age groups. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 33, 1994–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadase, M.; Azuma, A.; Zen, K.; Asada, S.; Kawasaki, T.; Kamitani, T.; Kawasaki, S.; Sugihara, H.; Matsubara, H. Very low frequency power of heart rate variability is a powerful predictor of clinical prognosis in patients with congestive heart failure. Circ. J. Off. J. Jan. Circ. Soc. 2004, 68, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardi, L.; Valle, F.; Coco, M.; Calciati, A.; Sleight, P. Physical activity influences heart rate variability and very-low-frequency components in holter electrocardiograms. Cardiovasc. Res. 1996, 32, 234–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCraty, R.; Atkinson, M.; Tomasino, D.; Bradley, R.T. The coherent heart: Heart-brain interactions, psychophysiological coherence, and the emergence of system-wide order. Integral Rev. 2009, 5, 10–115. [Google Scholar]
- Novak, V.; Saul, J.P.; Eckberg, D.L. Task force report on heart rate variability. Circulation 1997, 96, 1056–1057. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McCraty, R.; Deyhle, A. The global coherence initiative: Investigating the dynamic relationship between people and earth’s energetic systems. In Bioelectromagnetic and Subtle Energy Medicine, 2nd ed.; Rosch, P.J., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Crooker, N.; Feynman, J.; Gosling, J. On the high correlation between long-term averages of solar wind speed and geomagnetic activity. J. Geophys. Res. 1977, 82, 1933–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathie, R.; Mann, I. A correlation between extended intervals of ULF wave power and storm-time geosynchronous relativistic electron flux enhancements. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2000, 27, 3261–3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, I.; Wibberenz, G.; Cane, H. The relationship between recurring cosmic ray depressions and corotating solar wind streams at ≤1 AU: IMP 8 and Helios 1 and 2 anticoincidence guard rate observations. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1996, 101, 13483–13496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPherron, R.L. Magnetic pulsations: Their sources and relation to solar wind and geomagnetic activity. Surv. Geophys. 2005, 26, 545–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabdulgader, A.; McCraty, R.; Atkinson, M.; Dobyns, Y.; Stolc, V.; Ragulskis, M. Long-term study of heart rate variability responses to changes in the solar and geomagnetic environment. Nat. Commun. 2017. in review. [Google Scholar]
- McCraty, R.; Deyhle, A.; Childre, D. The global coherence initiative: Creating a coherent planetary standing wave. Glob. Adv. Health Med. 2012, 1, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoupel, E.; Abramson, E.; Israelevich, P.; Sulkes, J.; Harell, D. Dynamics of serum c-reactive protein (CRP) level and cosmophysical activity. Eur. J. Int. Med. 2007, 18, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsutake, G.; Otsuka, K.; Hayakawa, M.; Sekiguchi, M.; Cornélissen, G.; Halberg, F. Does Schumann resonance affect our blood pressure? Biomed. Pharmacother. 2005, 59, S10–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saroka, K.S.; Vares, D.E.; Persinger, M.A. Similar spectral power densities within the Schumann resonance and a large population of quantitative electroencephalographic profiles: Supportive evidence for Koenig and pobachenko. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alabdulgader, A.; Maccraty, R.; Atkinson, M.; Vainoras, A.; Berškienė, K.; Mauricienė, V.; Navickas, Z.; Šmidtaitė, R.; Landauskas, M.; Daunoravičienė, A. Human heart rhythm sensitivity to earth local magnetic field fluctuations. J. Vibroeng. 2015, 17, 3271–3278. [Google Scholar]
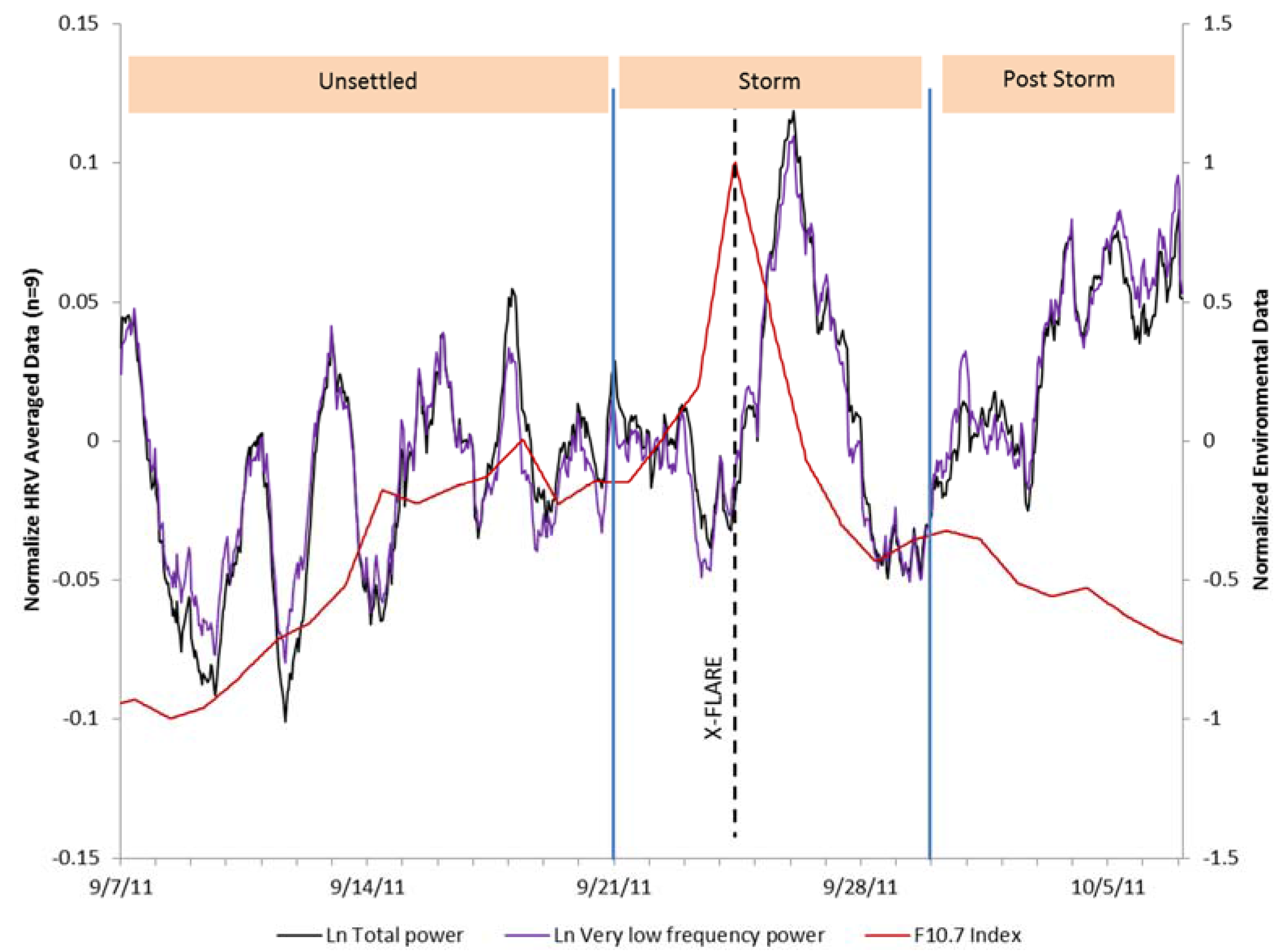
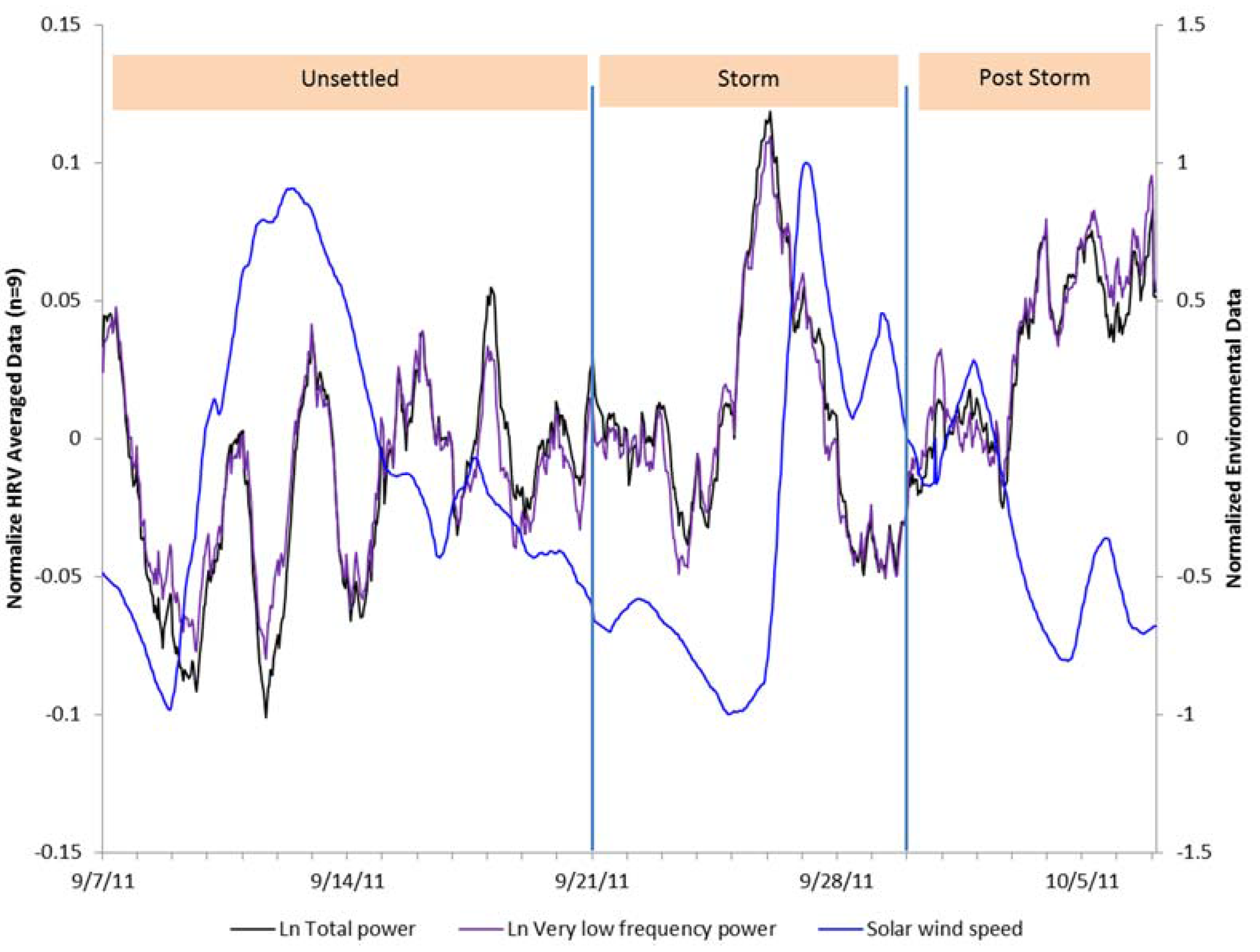
| IBI | SDNNi | ln TP | ln VLF | ln LF | ln HF | ln LF/HF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Excluding 1 | 0.99 | 0.95 | 0.94 | 0.93 | 0.94 | 0.92 | 0.94 |
| Excluding 2 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.97 |
| Excluding 3 | 0.96 | 0.87 | 0.95 | 0.92 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.98 |
| Excluding 4 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.94 | 0.93 | 0.96 | 0.99 | 0.98 |
| Excluding 5 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.94 | 0.95 | 0.94 | 0.96 | 0.96 |
| Excluding 6 | 0.93 | 0.99 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.93 | 0.97 | 0.98 |
| Excluding 7 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.97 | 0.97 |
| Excluding 8 | 0.95 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.97 |
| Excluding 9 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 0.97 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Mean IBI, ms | 1 | ||||||
| 2. SDNNi, ms | 0.52 *** | 1 | |||||
| 3. ln TP, ms2/Hz | 0.53 *** | 0.95 *** | 1 | ||||
| 4. ln VLF, ms2/Hz | 0.60 *** | 0.94 *** | 0.97 *** | 1 | |||
| 5. ln LF, ms2/Hz | 0.31 ** | 0.83 *** | 0.90 *** | 0.81 *** | 1 | ||
| 6. ln HF, ms2/Hz | 0.50 *** | 0.87 *** | 0.91 *** | 0.85 *** | 0.83 *** | 1 | |
| 7. ln LF/HF | −0.59 *** | −0.55 *** | −0.55 *** | −0.55 *** | −0.28 ** | −0.73 *** | 1 |
| Solar Wind | Kp Index | Ap Index | Sunspots | F10.7 | PC(N) | SRP | TMFV | Cosmic Rays | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solar wind speed, Km/s | 1 | ||||||||
| Kp Index | 0.73 *** | 1 | |||||||
| Ap Index, nT | 0.65 *** | 0.94 *** | 1 | ||||||
| Sunspots, n | 0.18 *** | −0.08 * | −0.13 *** | 1 | |||||
| F10.7, sfu | 0.04 | −0.15 *** | −0.09 ** | 0.33 *** | 1 | ||||
| PC(N) index | 0.54 *** | 0.90 *** | 0.87 *** | −0.16 *** | −0.33 *** | 1 | |||
| SRP, pT | 0.11 ** | −0.11 ** | −0.06 | 0.30 *** | −0.09 ** | −0.10 ** | 1 | ||
| TMFV, pT | 0.78 *** | 0.87 *** | 0.90 *** | −0.13 *** | −0.09 * | 0.78 *** | 0.08 * | 1 | |
| Cosmic Ray, counts/min | −0.72 *** | −0.54 *** | −0.42 *** | −0.24 *** | −0.04 | −0.35 *** | 0.13 *** | −0.45 *** | 1 |
| Unsettled Period | |||||||||
| Solar Wind | Kp Index | Ap Index | Sunspots | F10.7 Index | PC(N) | SRP | TMFV | Cosmic Rays | |
| IBI, ms | 0.38 *** | −0.15 ** | −0.32 *** | 0.25 *** | 0.09 | −0.18 ** | 0.28 *** | 0.02 | −0.39 *** |
| SDNNi, ms | −0.18 ** | −0.30 *** | −0.35 *** | 0.41 *** | 0.44 *** | −0.32 *** | −0.03 | −0.42 *** | −0.15 ** |
| ln TP, ms2/Hz | −0.08 | −0.14 ** | −0.21 *** | 0.38 *** | 0.42 *** | −0.19 *** | 0.10 | −0.28 *** | −0.23 *** |
| ln VLF, ms2/Hz | −0.02 | −0.10 | −0.17 ** | 0.34 *** | 0.28 *** | −0.12 * | 0.16 ** | −0.20 *** | −0.19 *** |
| ln LF, ms2/Hz | −0.19 *** | −0.14 ** | −0.18 ** | 0.24 *** | 0.41 *** | −0.19 *** | −0.04 | −0.31 *** | −0.12 * |
| ln HF, ms2/Hz | −0.17 ** | −0.13 * | −0.17 ** | 0.24 *** | 0.41 *** | −0.18 *** | −0.05 | −0.29 *** | −0.13 * |
| ln LF/HF | −0.33 *** | 0.15 ** | 0.30 *** | −0.54 *** | −0.54 *** | 0.26 *** | −0.07 | 0.16 ** | 0.58 *** |
| Storm Period | |||||||||
| Solar Wind | Kp Index | Ap Index | Sunspots | F10.7 Index | PC(N) | SRP | TMFV | Cosmic Rays | |
| IBI, ms | −0.30 *** | −0.15 * | −0.04 | −0.01 | 0.64 *** | −0.13 | 0.20 ** | −0.06 | 0.28 *** |
| SDNNi, ms | −0.03 | 0.12 | 0.24 *** | −0.06 | 0.21 ** | 0.15 * | −0.69 *** | 0.36 *** | 0.13 |
| ln TP, ms2/Hz | −0.09 | 0.11 | 0.22 ** | 0.06 | 0.13 * | 0.13 | −0.69 *** | 0.34 *** | 0.15 * |
| ln VLF, ms2/Hz | −0.08 | 0.14 * | 0.26 *** | 0.14 * | 0.18 ** | 0.15 * | −0.70 *** | 0.36 *** | 0.14 * |
| ln LF, ms2/Hz | −0.20 ** | 0.02 | 0.12 | -0.01 | 0.22 ** | 0.08 | −0.59 *** | 0.26 *** | 0.23 *** |
| ln HF, ms2/Hz | −0.20 ** | 0.02 | 0.13 | 0.00 | 0.23 *** | 0.08 | −0.59 *** | 0.27 *** | 0.23 *** |
| ln LF/HF | −0.40 *** | −0.23 *** | −0.24 *** | −0.23 *** | 0.43 *** | −0.10 | 0.21 ** | −0.18 ** | 0.26 *** |
| Post-Storm Period | |||||||||
| Solar Wind | Kp Index | Ap Index | Sunspots | F10.7 Index | PC(N) | SRP | TMFV | Cosmic Rays | |
| IBI, ms | −0.61 *** | 0.09 | −0.01 | −0.40 *** | −0.79 *** | 0.17 * | −0.68 *** | −0.22 ** | 0.53 *** |
| SDNNi, ms | −0.79 *** | −0.14 | −0.25 ** | −0.47 *** | −0.80 *** | 0.06 | −0.32 *** | −0.32 *** | 0.69 *** |
| ln TP, ms2/Hz | −0.80 *** | −0.14 | −0.25 *** | −0.30 *** | −0.77 *** | 0.15 * | −0.46 *** | −0.34 *** | 0.76 *** |
| ln VLF, ms2/Hz | −0.82 *** | −0.12 | −0.19 * | −0.46 *** | −0.80 *** | 0.05 | −0.44 *** | −0.30 *** | 0.67 *** |
| ln LF, ms2/Hz | −0.79 *** | −0.26*** | −0.37 *** | −0.31 *** | −0.87 *** | −0.06 | −0.51 *** | −0.58 *** | 0.63 *** |
| ln HF, ms2/Hz | −0.77 *** | −0.25*** | −0.37 *** | −0.30 *** | −0.87 *** | −0.05 | −0.51 *** | −0.58 *** | 0.62 *** |
| ln LF/HF | 0.42 *** | 0.24** | 0.21 ** | −0.08 | 0.10 | −0.13 | 0.46 *** | 0.25 ** | −0.63 *** |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
McCraty, R.; Atkinson, M.; Stolc, V.; Alabdulgader, A.A.; Vainoras, A.; Ragulskis, M. Synchronization of Human Autonomic Nervous System Rhythms with Geomagnetic Activity in Human Subjects. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 770. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14070770
McCraty R, Atkinson M, Stolc V, Alabdulgader AA, Vainoras A, Ragulskis M. Synchronization of Human Autonomic Nervous System Rhythms with Geomagnetic Activity in Human Subjects. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2017; 14(7):770. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14070770
Chicago/Turabian StyleMcCraty, Rollin, Mike Atkinson, Viktor Stolc, Abdullah A. Alabdulgader, Alfonsas Vainoras, and Minvydas Ragulskis. 2017. "Synchronization of Human Autonomic Nervous System Rhythms with Geomagnetic Activity in Human Subjects" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 14, no. 7: 770. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14070770
APA StyleMcCraty, R., Atkinson, M., Stolc, V., Alabdulgader, A. A., Vainoras, A., & Ragulskis, M. (2017). Synchronization of Human Autonomic Nervous System Rhythms with Geomagnetic Activity in Human Subjects. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 14(7), 770. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14070770










