Nicotine Component of Cigarette Smoke Extract (CSE) Decreases the Cytotoxicity of CSE in BEAS-2B Cells Stably Expressing Human Cytochrome P450 2A13
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cigarettes, Chemical and Reagents
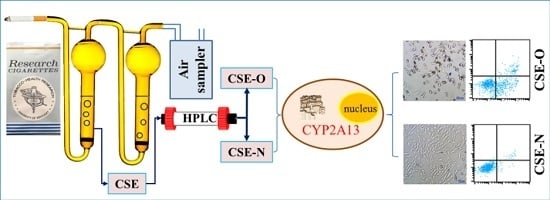
2.2. Preparation of CSE and Separation of Nicotine from CSE
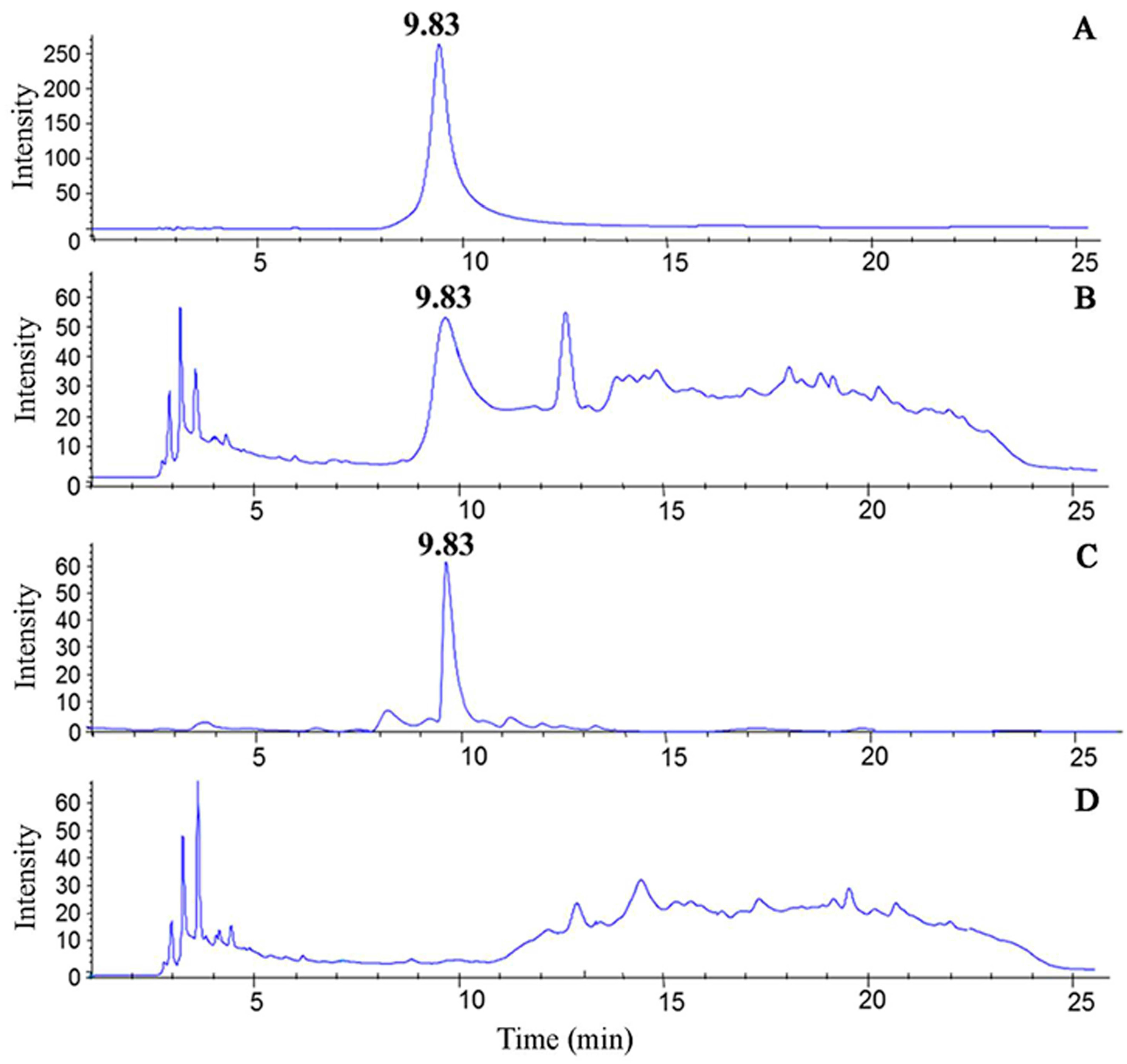
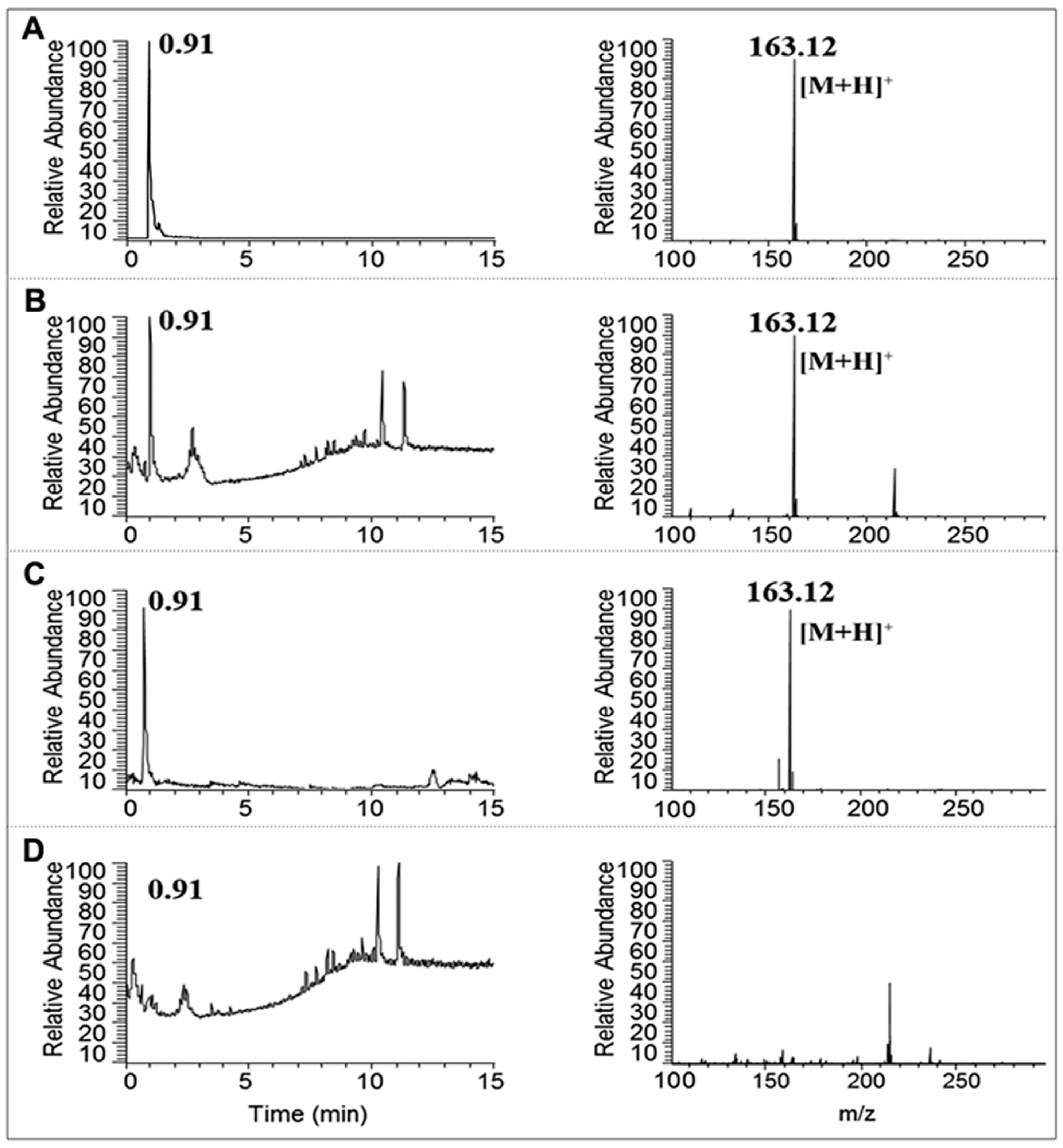
2.3. Identification of Nicotine by UPLC-MS/MS
2.4. Cell Viability Assay
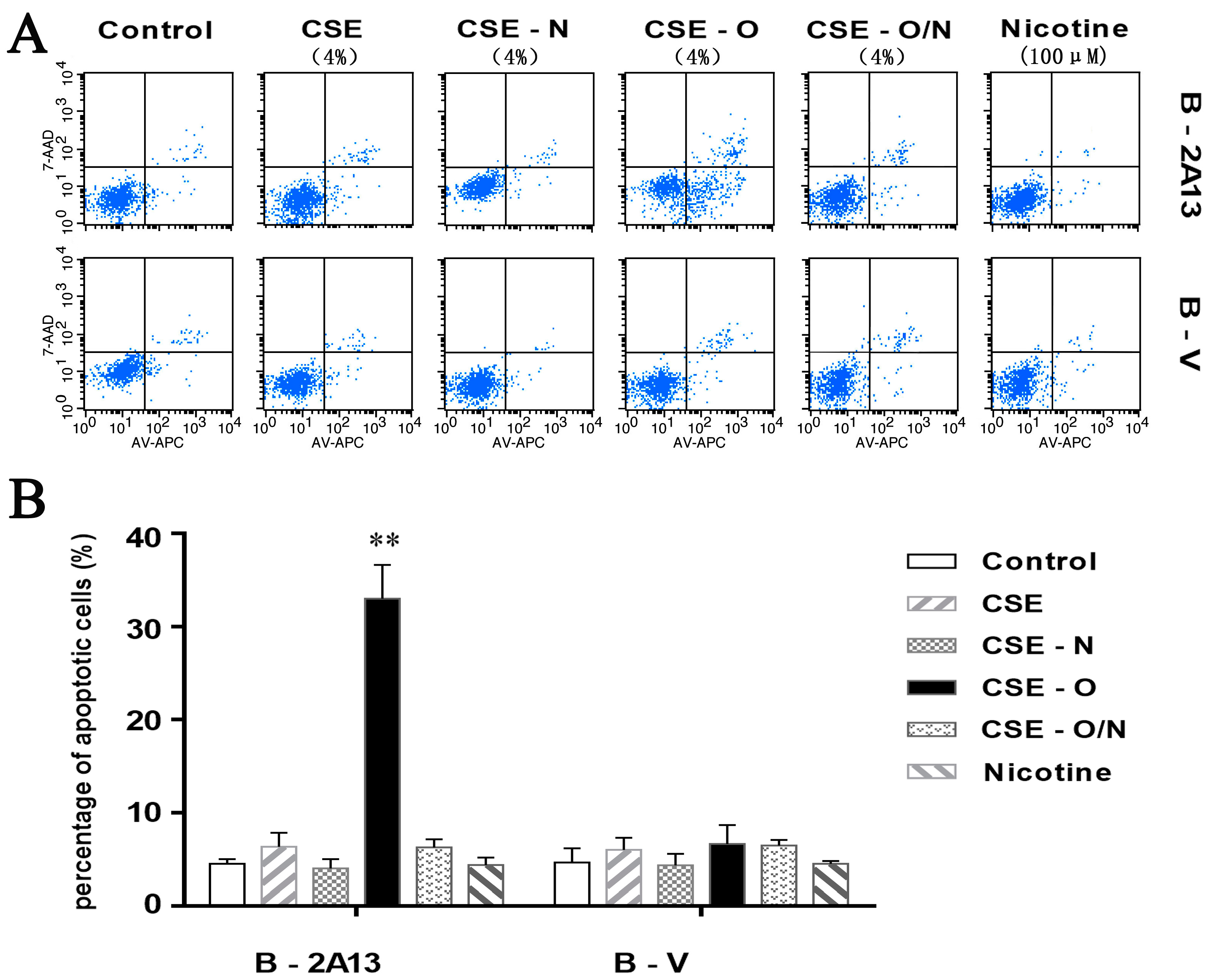
2.5. Cell Apoptosis Analysis
2.6. Determination of the Expression of Apoptosis-Related Proteins in Cells
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Separation and Identification of Nicotine in CSE
3.2. Effects of Nicotine on CSE-Induced Cytotoxicity in B-2A13 Cells
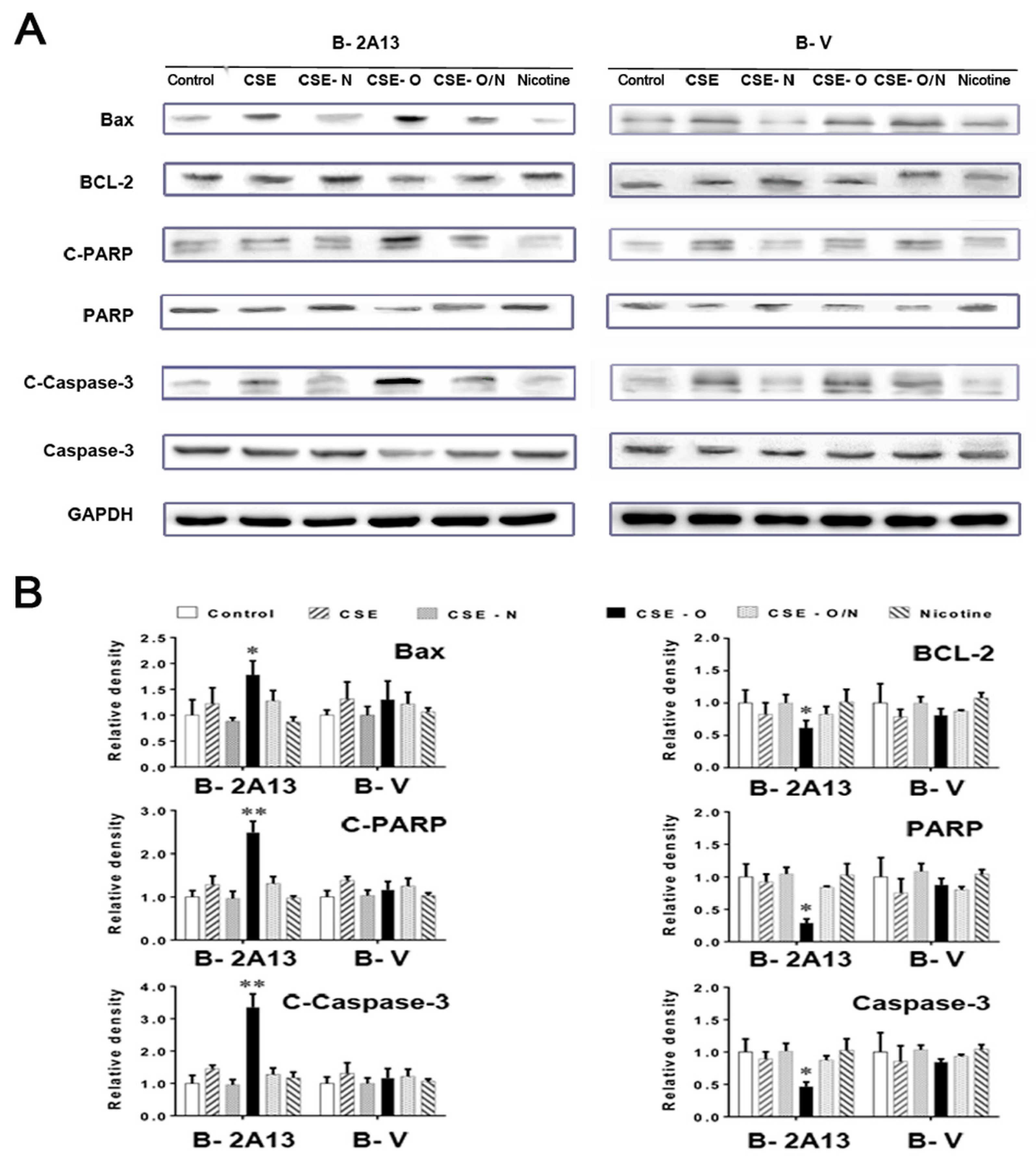
3.3. Effects of Nicotine on CSE-Induced Apoptosis and Expression of Related Proteins in B-2A13 Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CSE | Cigarette smoke extract |
| CYP | Cytochrome P450 |
| CYP2A13 | Cytochrome P450 2A13 |
| NNK | 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone |
| 3-MI | 3-methylindole |
| AFB1 | Aflatoxin B1 |
| BEAS-2B | Immortalized human bronchial epithelial (cells) |
| B-2A13 | BEAS-2B cells stably expressing CYP2A13 |
| HPLC | high-performance liquid chromatography |
| UPLC-MS/MS | Ultra-performance liquid chromatography tandem mass-spectrometry |
| C-PARP | Cleaved Poly (Adenosine Diphosphate-Ribose) Polymerase |
| PARP | Poly (Adenosine Diphosphate-Ribose) Polymerase |
| Bcl-2 | B cell lymphoma-2 |
| Bax | Bcl-2 Associated X Protein |
References
- Bilano, V.; Gilmour, S.; Moffiet, T. Global trends and projections for tobacco use, 1990–2025: An analysis of smoking indicators from the WHO Comprehensive Information Systems for Tobacco Control. Lancet 2015, 385, 966–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Peto, R.; Zhou, M.; Iona, A.; Smith, M.; Yang, L.; Guo, Y.; Chen, Y.; Bian, Z.; Lancaster, G.; et al. Contrasting male and female trends in tobacco-attributed mortality in China: Evidence from successive nationwide prospective cohort studies. Lancet 2015, 386, 1447–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koplan, J.; Eriksen, M. Smoking cessation for Chinese men and prevention for women. Lancet 2015, 386, 1422–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartlander, B.; Pratt, A. Tobacco in China: Taming the smoking dragon. Lancet 2015, 385, 2123–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, S.; Theodorou, I.G.; Zambianchi, M.; Chen, S.; Gow, A.; Schwander, S.; Zhang, J.J.; Chung, K.F.; Shaffer, M.S.; Ryan, M.P.; et al. Silver nanowire interactions with primary human alveolar type-II epithelial cell secretions: Contrasting bioreactivity with human alveolar type-I and type-II epithelial cells. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 10398–10409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talhout, R.; Schulz, T.; Florek, E.; van Benthem, J.; Wester, P.; Opperhuizen, A. Hazardous compounds in tobacco smoke. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2011, 8, 613–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, G.; Li, J.; Zheng, M.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, J.; Li, W. Nnk, a tobacco-specific carcinogen, inhibits the expression of lysyl oxidase, a tumor suppressor. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 12, 64–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leon, M.E.; Peruga, A.; McNeill, A.; Kralikova, E.; Guha, N.; Minozzi, S.; Espina, C.; Schuz, J. European Code against Cancer, 4th edition: Tobacco and cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. 2015, S20–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan-Yeung, M.; Dimich-Ward, H. Respiratory health effects of exposure to environmental tobacco smoke. Respirology 2003, 8, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Megaraj, V.; Wei, Y.; Ding, X. Identification of cytochrome P450 enzymes critical for lung tumorigenesis by the tobacco-specific carcinogen 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone (NNK): Insights from a novel Cyp2abfgs-null mouse. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 2584–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyama, T.; Uramoto, H.; Kagawa, N.; Yoshimatsu, T.; Osaki, T.; Nakanishi, R.; Nagaya, H.; Kaneko, K.; Muto, M.; Kawamoto, T.; et al. Cytochrome P450 in non-small cell lung cancer related to exogenous chemical metabolism. Front. Biosci. 2012, 4, 1539–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.R.; Thomas, P.E.; Lu, G.; Reuhl, K.R.; Yang, G.Y.; Wang, L.D.; Wang, S.L.; Yang, C.S.; He, X.Y.; Hong, J.Y. Cyp2a13 in human respiratory tissues and lung cancers: An immunohistochemical study with a new peptide-specific antibody. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2006, 34, 1672–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Tan, W.; Hao, B.; Miao, X.; Zhou, G.; He, F.; Lin, D. Substantial reduction in risk of lung adenocarcinoma associated with genetic polymorphism in Cyp2A13, the most active cytochrome P450 for the metabolic activation of tobacco-specific carcinogen NNK. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 8057–8061. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- D’Agostino, J.; Zhang, X.L.; Wu, H.; Ling, G.Y.; Wang, S.P.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Liu, F.C.; Ding, X.X. Characterization of Cyp2A13*2, a variant cytochrome P450 allele previously found to be associated with decreased incidences of lung adenocarcinoma in smokers. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2008, 36, 2316–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, C.; Wang, J.C.; Kou, X.C.; Chen, X.B.; Qin, Z.Y.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, C.; Xu, J.B.; Tan, W.; Jin, L.; et al. Pulmonary expression of Cyp2A13 and ABCB1 is regulated by FOXA2, and their genetic interaction is associated with lung cancer. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 1986–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Megaraj, V.; Zhou, X.; Xie, F.; Liu, Z.; Yang, W.; Ding, X. Role of Cyp2A13 in the bioactivation and lung tumorigenicity of the tobacco-specific lung procarcinogen 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone: In vivo studies using a Cyp2A13-humanized mouse model. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalas, J.R.; Hecht, S.S.; Murphy, S.E. Cytochrome P450 enzymes as catalysts of metabolism of 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone, a tobacco specific carcinogen. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2005, 18, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimada, T.; Takenaka, S.; Murayama, N.; Kramlinger, V.M.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, D.; Liu, J.; Foroozesh, M.K.; Yamazaki, H.; Guengerich, F.P.; et al. Oxidation of pyrene, 1-hydroxypyrene, 1-nitropyrene and 1-acetylpyrene by human cytochrome P450 2A13. Xenobiotica 2016, 46, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohgaki, H.; Kusama, K.; Matsukura, N.; Morino, K.; Hasegawa, H.; Sato, S.; Takayama, S.; Sugimura, T. Carcinogenicity in mice of a mutagenic compound, 2-amino-3-methylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoline, from broiled sardine, cooked beef and beef extract. Carcinogenesis 1984, 5, 921–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benowitz, N.L.; Hukkanen, J.; Jacob, P., III. Nicotine Chemistry, Metabolism, Kinetics and Biomarkers. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2009, 29–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, S.E.; Raulinaitis, V.; Brown, K.M. Nicotine 5’-oxidation and methyl oxidation by P450 2A enzymes. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2005, 33, 1166–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.J.; Lu, H.Y.; Li, Z.Y.; Bian, Q.; Qiu, L.L.; Li, Z.; Liu, Q.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, S.L. Cytochrome P450 2A13 mediates aflatoxin B1-induced cytotoxicity and apoptosis in human bronchial epithelial cells. Toxicology 2012, 300, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Weymarn, L.B.; Brown, K.M.; Murphy, S.E. Inactivation of CYP2A6 and CYP2A13 during Nicotine Metabolism. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006, 316, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comer, D.M.; Elborn, J.S.; Ennis, M. Inflammatory and cytotoxic effects of acrolein, nicotine, acetylaldehyde and cigarette smoke extract on human nasal epithelial cells. BMC Pulm. Med. 2014, 14, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, M.; Earla, R.; Shah, A.; Earla, R.L.; Gupte, R.; Mitra, A.K.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, S. A LC-MS/MS Method for Concurrent Determination of Nicotine Metabolites and Role of CYP2A6 in Nicotine Metabolism in U937 Macrophages: Implications in Oxidative Stress in HIV + Smokers. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2012, 7, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Lu, H.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, X.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, S.L. Cytochrome P450 2A13 is an efficient enzyme in metabolic activation of aflatoxin G1 in human bronchial epithelial cells. Arch. Toxicol. 2013, 87, 1697–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Weymarn, L.B.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Ding, X.; Hollenberg, P.F. Effects of 8-methoxypsoralen on cytochrome P450 2A13. Carcinogenesis 2005, 26, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noya, Y.; Seki, K.; Asano, H.; Mai, Y.; Horinouchi, T.; Higashi, T.; Terada, K.; Hatate, C.; Hoshi, A.; Nepal, P.; et al. Identification of stable cytotoxic factors in the gas phase extract of cigarette smoke and pharmacological characterization of their cytotoxicity. Toxicology 2013, 314, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asano, H.; Horinouchi, T.; Mai, Y.; Sawada, O.; Fujii, S.; Nishiya, T.; Minami, M.; Katayama, T.; Iwanaga, T.; Terada, K.; et al. Nicotine- and tar-free cigarette smoke induces cell damage through reactive oxygen species newly generated by PKC-dependent activation of NADPH oxidase. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 118, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Mei, Q.; Wan, X.; Que, H.; Li, L.; Wan, D. Determination of rutin and isoquercetin contents in Hibisci mutabilis folium in different collection periods by HPLC. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2015, 53, 1680–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimada, T.; Murayama, N.; Yamazaki, H.; Tanaka, K.; Takenaka, S.; Komori, M.; Kim, D.; Guengerich, F.P. Metabolic activation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and aryl and heterocyclic amines by human cytochromes P450 2A13 and 2A6. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2013, 26, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pouli, A.E.; Hatzinikolaou, D.G.; Piperi, C.; Stavridou, A.; Psallidopoulos, M.C.; Stavrides, J.C. The cytotoxic effect of volatile organic compounds of the gas phase of cigarette smoke on lung epithelial cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2003, 34, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, P.; Fofaria, N.; Prasad, S.; Sajja, R.K.; Weksler, B.; Couraud, P.O.; Romero, I.A.; Cucullo, L. Oxidative and pro-inflammatory impact of regular and denicotinized cigarettes on blood brain barrier endothelial cells: Is smoking reduced or nicotine-free products really safe? BMC Neurosci. 2014, 15, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeVore, N.M.; Scott, E.E. Nicotine and 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone binding and access channel in human cytochrome P450 2A6 and 2A13 enzymes. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 26576–26585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Megaraj, V.; Li, L.; Sell, S.; Hu, J.; Ding, X. Suppression of pulmonary cyp2a13 expression by carcinogen-induced lung tumorigenesis in a Cyp2A13-humanized mouse model. Drug Metab. Dispos. Biol. Fate Chem. 2015, 43, 698–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, K.; Li, L.; Liu, Z.; Hartog, M.; Kluetzman, K.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Ding, X. Generation and characterization of a novel Cyp2A13—Transgenic mouse model. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2014, 42, 1341–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Vleet, T.R.; Bombick, D.W.; Coulombe, R.A., Jr. Inhibition of human cytochrome P450 2E1 by nicotine, cotinine, and aqueous cigarette tar extract in vitro. Toxicol. Sci. 2001, 64, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yano, J.K.; Denton, T.T.; Cerny, M.A.; Zhang, X.; Johnson, E.F.; Cashman, J.R. Synthetic inhibitors of cytochrome P-450 2A6: Inhibitory activity, difference spectra, mechanism of inhibition, and protein cocrystallization. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 6987–7001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naserzadeh, P.; Hosseini, M.J.; Mohamadzadeh Asl, B.; Pourahmad, J. Toxicity mechanisms of cigarette smoke on mouse fetus mitochondria. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2015, 14, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Song, W.; Liu, C.; Chen, S.; Hua, J. Rapamycin inhibits acrolein-induced apoptosis by alleviating ROS-driven mitochondrial dysfunction in male germ cells. Cell Prolif. 2014, 47, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.A.; Yang, F.; Cole, G.M.; Chan, S.O. Inhibition of caspase-3-like activity reduces glutamate induced cell death in adult rat retina. Brain Res. 2001, 904, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.D.; Sandler, A.B. The epidemiology of lung cancer. Cancer Treat. Res. 2001, 105, 31–52. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Weems, J.M.; Lamb, J.G.; D’Agostino, J.; Ding, X.; Yost, G.S. Potent mutagenicity of 3-methylindole requires pulmonary cytochrome P450-mediated bioactivation: A comparison to the prototype cigarette smoke mutagens B(a)P and NNK. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2010, 23, 1682–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ji, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, N.; Wang, C.; Xia, R.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, S.-L. Nicotine Component of Cigarette Smoke Extract (CSE) Decreases the Cytotoxicity of CSE in BEAS-2B Cells Stably Expressing Human Cytochrome P450 2A13. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1221. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14101221
Ji M, Zhang Y, Li N, Wang C, Xia R, Zhang Z, Wang S-L. Nicotine Component of Cigarette Smoke Extract (CSE) Decreases the Cytotoxicity of CSE in BEAS-2B Cells Stably Expressing Human Cytochrome P450 2A13. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2017; 14(10):1221. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14101221
Chicago/Turabian StyleJi, Minghui, Yudong Zhang, Na Li, Chao Wang, Rong Xia, Zhan Zhang, and Shou-Lin Wang. 2017. "Nicotine Component of Cigarette Smoke Extract (CSE) Decreases the Cytotoxicity of CSE in BEAS-2B Cells Stably Expressing Human Cytochrome P450 2A13" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 14, no. 10: 1221. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14101221
APA StyleJi, M., Zhang, Y., Li, N., Wang, C., Xia, R., Zhang, Z., & Wang, S.-L. (2017). Nicotine Component of Cigarette Smoke Extract (CSE) Decreases the Cytotoxicity of CSE in BEAS-2B Cells Stably Expressing Human Cytochrome P450 2A13. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 14(10), 1221. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14101221