Enantioselective Determination of Polycyclic Musks in River and Wastewater by GC/MS/MS
Abstract
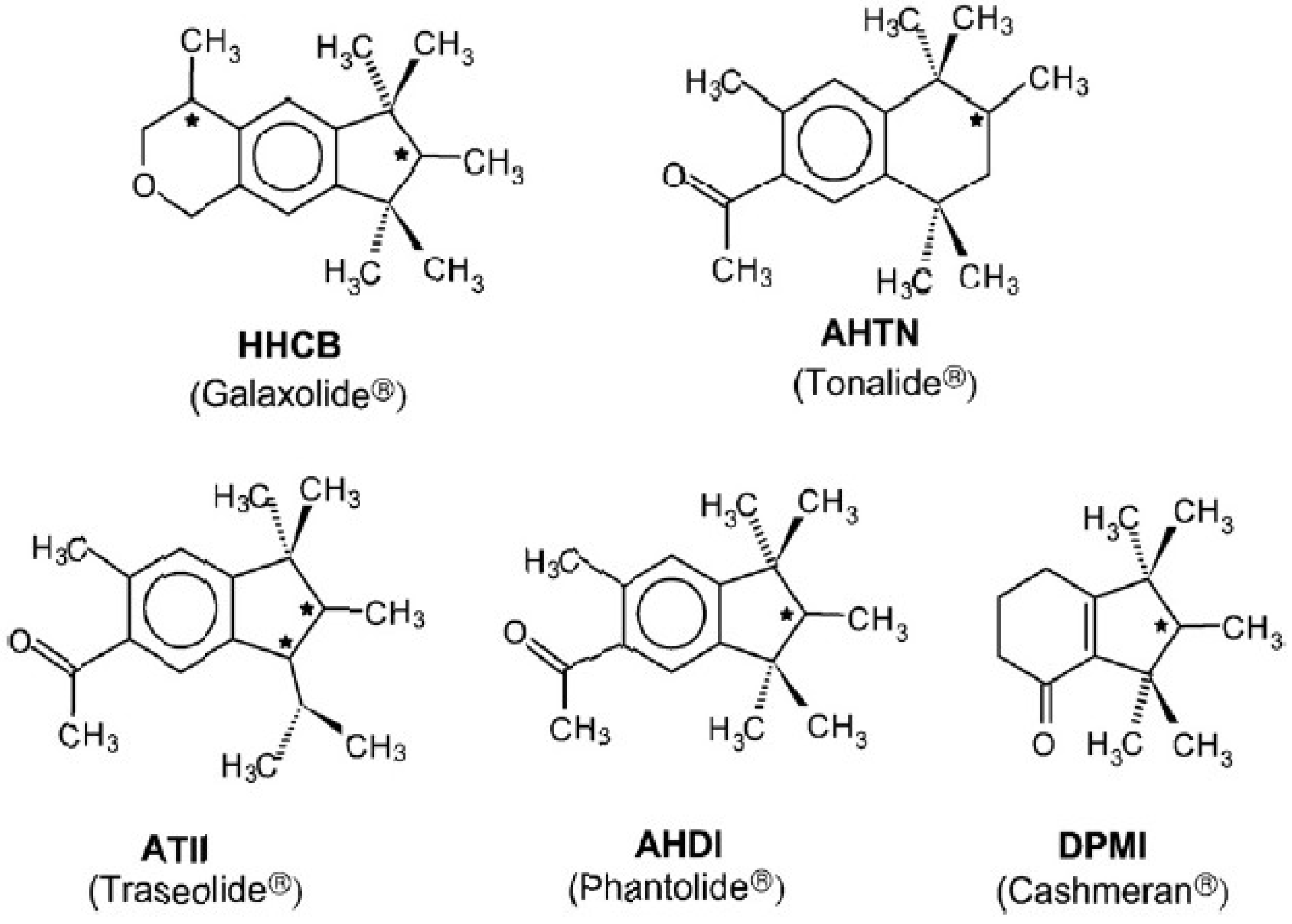
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Apparatus
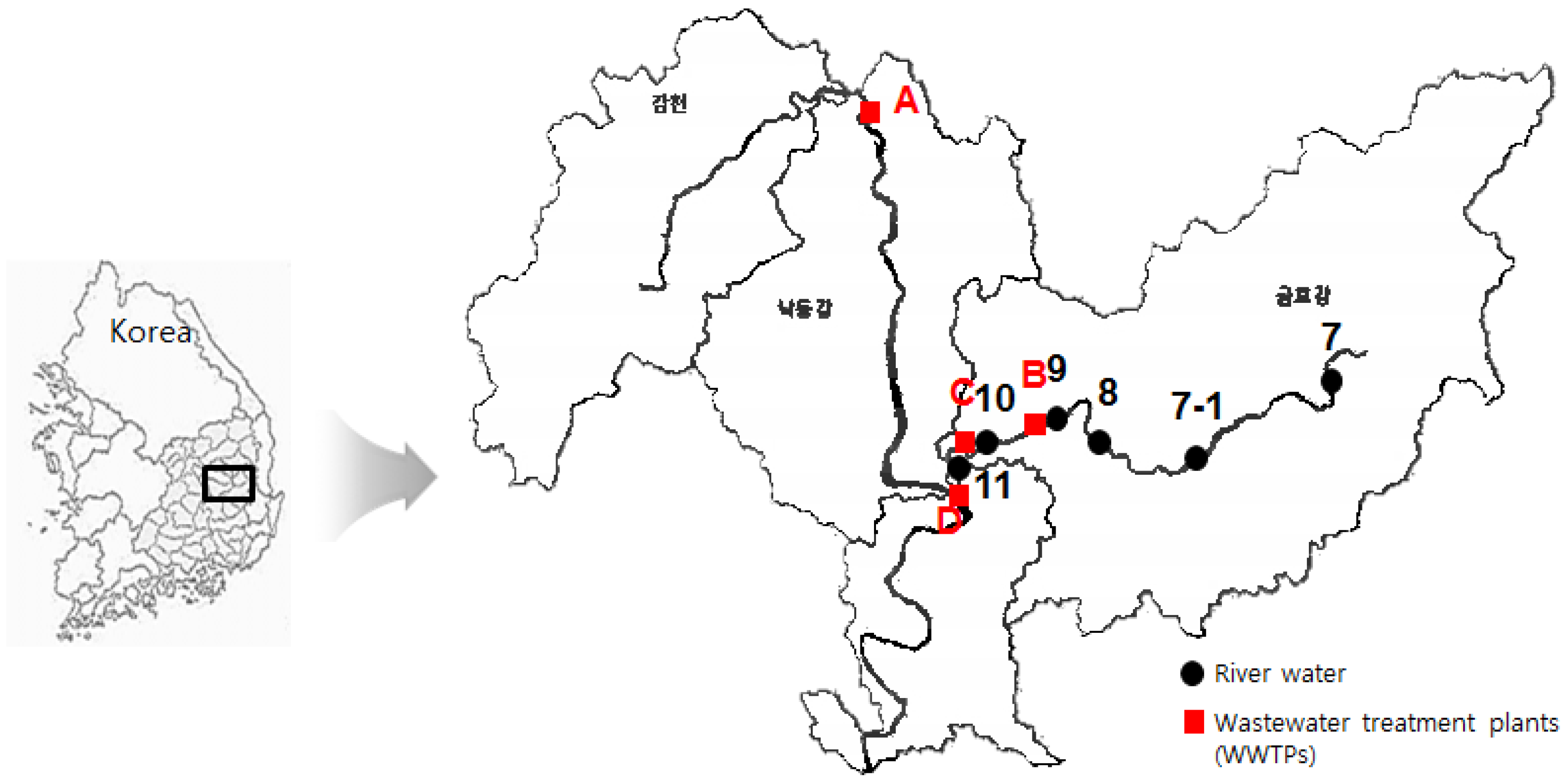
2.2. Characterization of Monitoring Sites and Sampling
2.3. Sample Preparation
2.4. Quantitative GC-MS-MS Analysis
2.5. Enantioselective GC-MS-MS Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
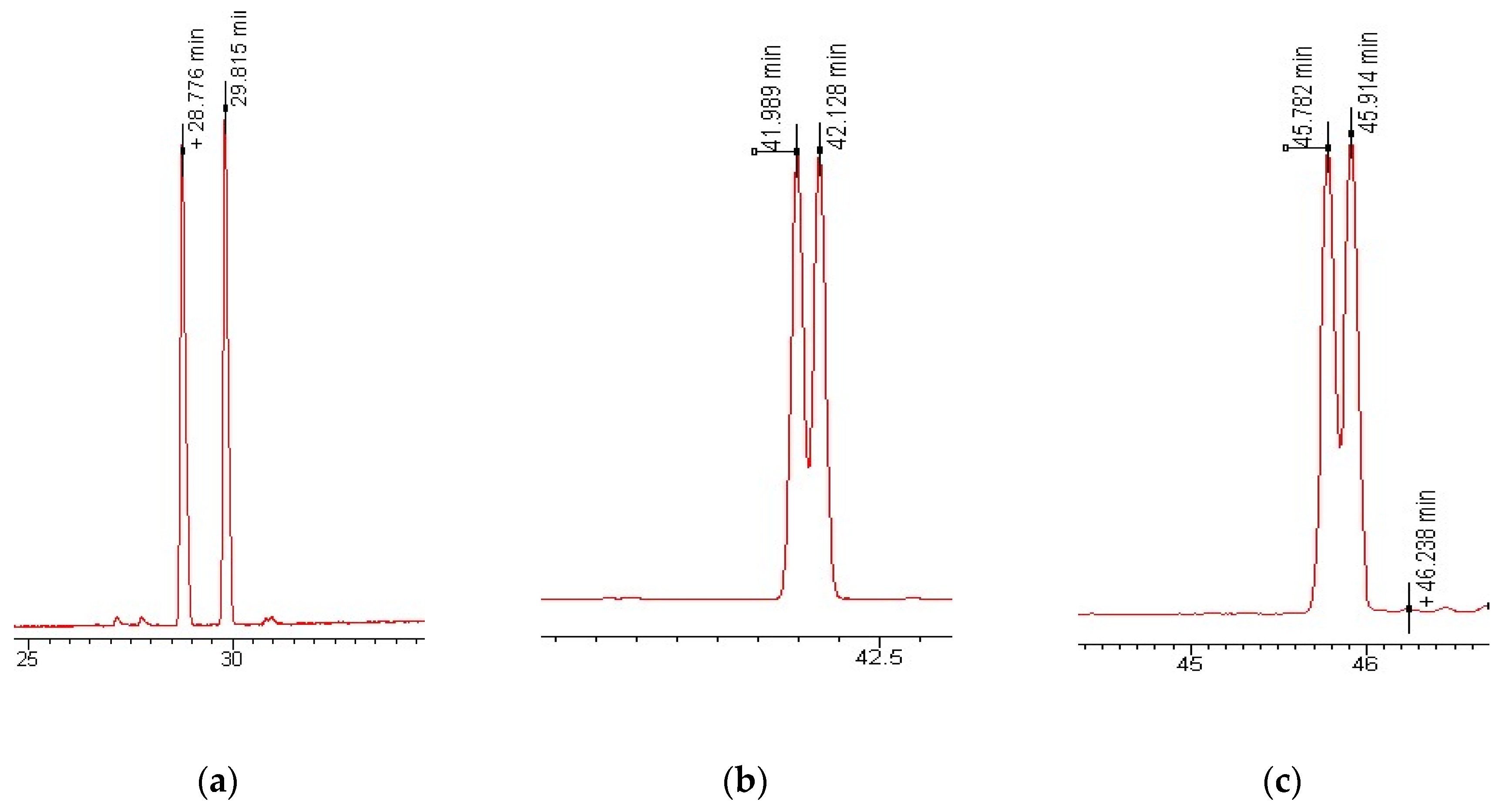
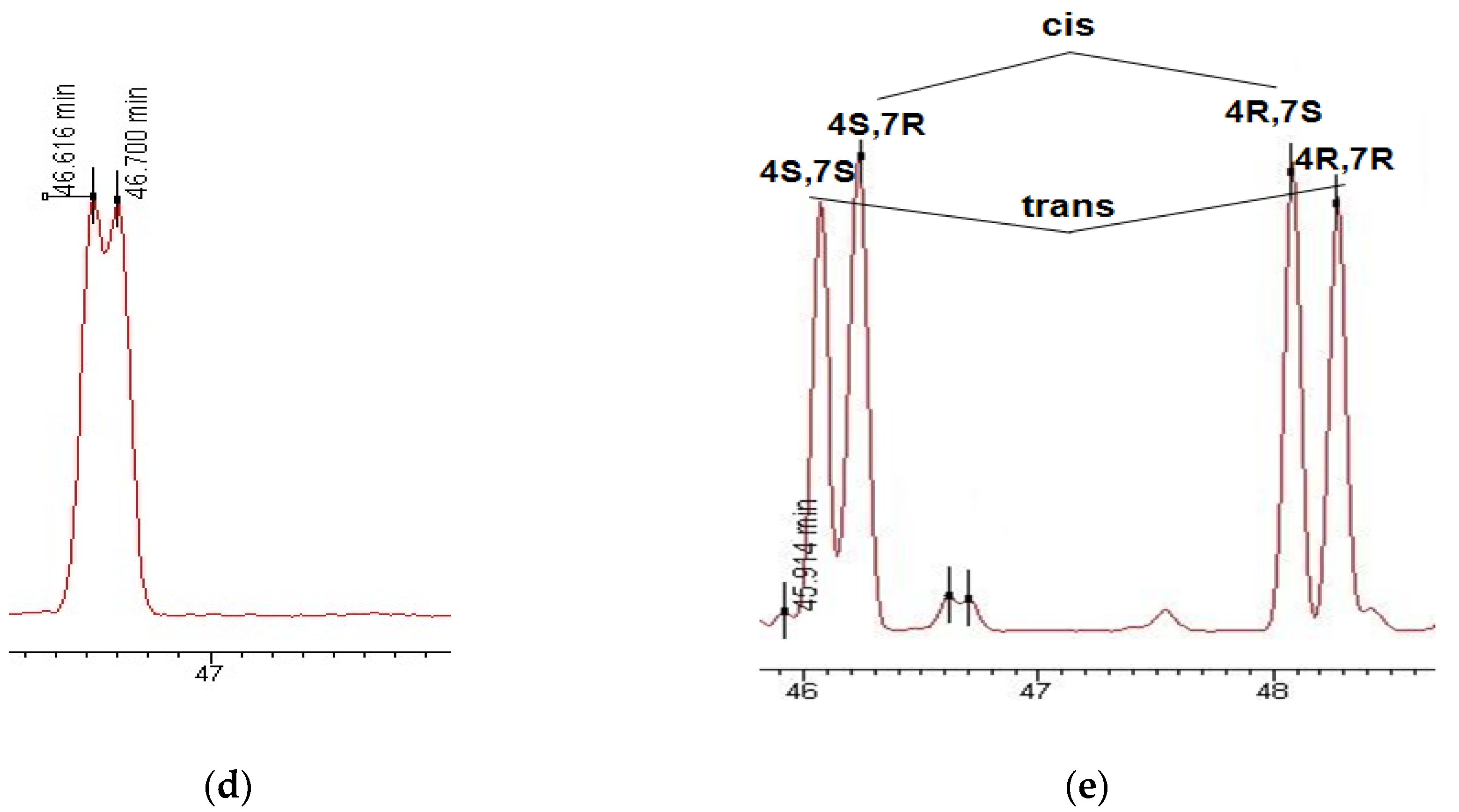
3.1. Enantioselective Analysis of Polycyclic Musks
3.2. Enantiomeric Ratios of Polycyclic Musks in River and Wastewater
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Q.; Tian, M.; Wang, M.; Shi, H.; Wang, M. Simultaneous enantioselective determination of triazole fungicide flutriafol in vegetables, fruits, wheat, soil, and water by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 2809–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Shi, H.; Gao, B.; Tian, M.; Hua, X.; Wang, M. Enantioseparation and determination of the chiral phenylpyrazole insecticide ethiprole in agricultural and environmental samples and its enantioselective degradation in soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 542, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Peng, Y.; Wang, L.; Luo, M.; Liu, X. Unequivocal enantiomeric identification and analysis of 10 chiral pesticides in fruit and vegetables by QuEChERS method combined with liquid chromatography-quadruple/linear ion trap mass spectrometry determination. Chirality 2015, 27, 958–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Gao, B.; Tian, M.; Shi, H.; Hua, X.; Wang, M. Enantioseparation and determination of triticonazole enantiomers in fruits, vegetables, and soil using efficient extraction and clean-up methods. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2016, 1009–1010, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, M.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, H.; Gao, B.; Hua, X.; Wang, M. Simultaneous determination of chiral pesticide flufiprole enantiomers in vegetables, fruits, and soil by high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 3499–3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Diao, J.; Di, S.; Zhou, Z. Bioaccumulation of isocarbophos enantiomers from laboratory-contaminated aquatic environment by tubificid worms. Chemosphere 2015, 124, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhuang, S.; Li, X.; Xu, M.; Lin, M.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, H. Enantioselective determination of acaricide etoxazole in orange pulp, peel, and whole orange by chiral liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2015, 38, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Song, B.; Ling, H.; Li, Z.; Li, M.; Hu, D. Enantiomeric separation of indoxacarb on an amylose-based chiral stationary phase and its application in study of indoxacarb degradation in water. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2014, 28, 1371–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, C.; Zhao, X.; Yang, P. GC-MS and HPLC-MS analysis of bioactive pharmaceuticals and personal-care products in environmental matrices. Trends Anal. Chem. 2007, 26, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallecillos, L.; Pocurull, E.; Borrull, F. A simple and automated method to determine macrocyclic musk fragrances in sewage sludge samples by headspace solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. 2013, 1314, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallecillos, L.; Borrull, F. Recent approaches for the determination of synthetic musk fragrances in environmental samples. Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 72, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallecillos, L.; Pocurull, E.; Borrull, F. Influence of pre-treatment process on matrix effect for the determination of musk fragrances in fish and mussel. Talanta 2015, 134, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiner, J.L.; Wong, C.M.; Arcaro, K.F.; Kannan, K. Synthetic musk fragrances in human milk from the United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 3815–3820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subedi, B.; Du, B.; Chambliss, C.K.; Koschorreck, J.; Rudel, H.; Quack, M.; Brooks, B.W.; Usenko, S. Occurrence of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in German fish tissue: A national study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 9047–9054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín, J.; Moder, M.; Gaudl, A.; Alonso, E.; Reemtsma, T. Multi-class method for biomonitoring of hair samples using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 8725–8734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatermann, R.; Biselli, S.; Huhnerfuss, H.; Rimkus, G.G.; Franke, S.; Hecker, M.; Kallenborn, R.; Karbe, L. Synthetic musks in the environment. Part 2: Enantioselective transformation of the polycyclic musk fragrances HHCB, AHTN, AHDI, and ATII in freshwater fish. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2002, 42, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berset, J.D.; Kupper, T.; Etter, R.; Tarradellas, J. Considerations about the enantioselective transformation of polycyclic musks in wastewater, treated wastewater and sewage sludge and analysis of their fate in a sequencing batch reactor plant. Chemosphere 2004, 57, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bester, K. Polycyclic musks in the Ruhr catchment area-transport, discharges of waste water, and transformations of HHCB, AHTN and HHCB-lactone. J. Environ. Monit. 2005, 7, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.-S.; Kim, U.-J.; Oh, J.-E.; Choi, M.; Hwan, D.-W. Comprehensive monitoring of synthetic musk compounds from freshwater to coastal environments in Korea: With consideration of ecological concerns and bioaccumulation. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 470–471, 1502–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schurig, V. Separation of enantiomers by gas chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2001, 906, 275–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schurig, V. Chiral separations using gas chromatography. Trends Anal. Chem. 2002, 21, 647–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.; Lee, C.; Heo, S.; Lee, J. Determination of personal care products in aquatic environmental samples by GC/MS. Anal. Sci. Technol. 2010, 23, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.; Lee, C.; Heo, S.; Lee, J. Occurrence of Synthetic musk compounds in surface and waste waters in Korea. J. Korean Soc. Environ. Eng. 2011, 33, 821–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| WWTPs a | Location | Treatment (m3/day) | Area Served (km2) | Population Served | Treatment Processes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Chilgok | 330,000 | 31.56 | 275,000 | Activated sludge |
| B | Daegu | 680,000 | 59.20 | 1,084,000 | |
| C | Daegu | 400,000 | 19.64 | 423,000 | |
| D | Daegu | 520,000 | 44.73 | 893,000 |
| Compounds | MRM a Ions | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Parent | Daughter 1 | Daughter 2 | |
| DPMI | 206 | 191 | 163 |
| AHDI | 244 | 229 | 187 |
| ATII | 258 | 215 | 173 |
| HHCB | 258 | 243 | 213 |
| AHTN | 258 | 243 | 187 |
| Compounds | Linearity a (r2) | LOD b (μg/L) | LOQ b (μg/L) | Accuracy c (%) | Precision c (RSD, %) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HHCB | 0.984 | 0.018 | 0.058 | 78.2 | 14.1 |
| AHTN | 0.980 | 0.024 | 0.076 | 75.2 | 17.0 |
| AHDI | 0.988 | 0.022 | 0.069 | 79.0 | 15.9 |
| DPMI | 0.991 | 0.025 | 0.079 | 85.2 | 13.3 |
| ATII | 0.989 | 0.034 | 0.107 | 80.6 | 11.9 |
| Sample | HHCB | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration (μg/L) | ER | ||||
| trans-HHCB | cis-HHCB | ||||
| River water | 7 | 1st | n.d a | - | - |
| 2nd | n.d | - | - | ||
| 7–1 | 1st | n.d | - | - | |
| 2nd | n.d | - | - | ||
| 8 | 1st | 0.277 | 0.95 | 1.03 | |
| 2nd | n.d | - | - | ||
| 9 | 1st | n.d | - | - | |
| 2nd | 0.280 | 1.09 | 0.95 | ||
| 10 | 1st | 0.280 | 0.86 | 1.02 | |
| 2nd | 0.342 | 0.97 | 1.10 | ||
| 11 | 1st | n.d | - | - | |
| 2nd | 0.319 | 0.96 | 1.07 | ||
| WWTPs | A | Influent | 0.785 | 0.94 | 1.04 |
| Effluent | 0.284 | 0.99 | 1.15 | ||
| B | Influent | 0.998 | 1.01 | 1.14 | |
| Effluent | 0.351 | 1.04 | 1.18 | ||
| C | Influent1 | 1.150 | 0.91 | 0.98 | |
| Influent2 | 2.016 | 0.98 | 1.02 | ||
| Effluent | 0.289 | 0.74 | 0.69 | ||
| D | Influent | 3.491 | 0.97 | 1.03 | |
| Effluent | 0.576 | 0.98 | 1.25 | ||
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, I.; Gopalan, A.-I.; Lee, K.-P. Enantioselective Determination of Polycyclic Musks in River and Wastewater by GC/MS/MS. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13030349
Lee I, Gopalan A-I, Lee K-P. Enantioselective Determination of Polycyclic Musks in River and Wastewater by GC/MS/MS. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2016; 13(3):349. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13030349
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Injung, Anantha-Iyengar Gopalan, and Kwang-Pill Lee. 2016. "Enantioselective Determination of Polycyclic Musks in River and Wastewater by GC/MS/MS" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 13, no. 3: 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13030349
APA StyleLee, I., Gopalan, A.-I., & Lee, K.-P. (2016). Enantioselective Determination of Polycyclic Musks in River and Wastewater by GC/MS/MS. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 13(3), 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13030349








