Effects of Di-(2-ethylhexyl) Phthalate on Lipid Metabolism by the JAK/STAT Pathway in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparations and Animals
2.2. Tissue Collection
2.3. Detection of Lipid and Hormone in Serum
2.4. RNA Extraction and RT-PCR Analysis
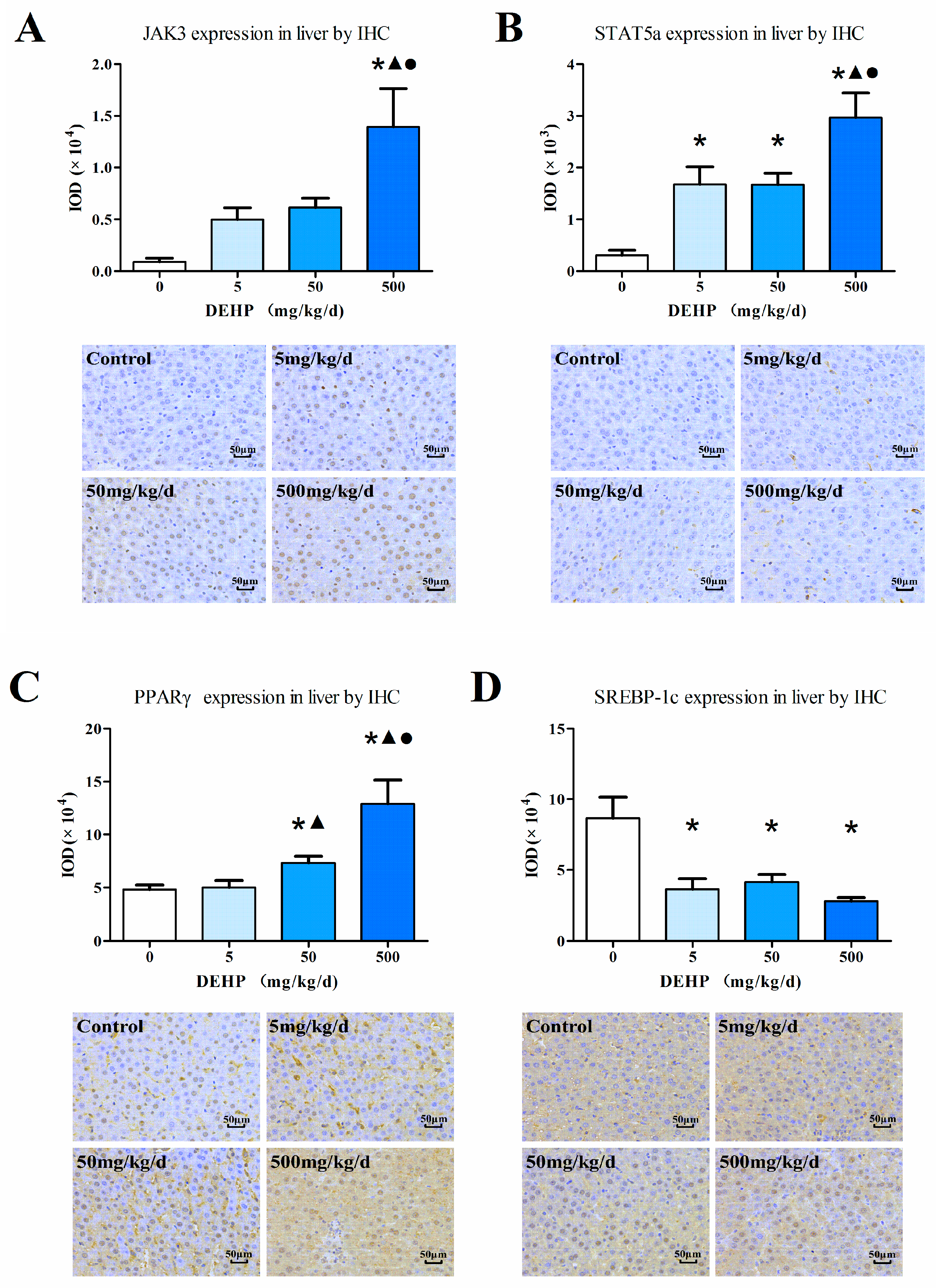
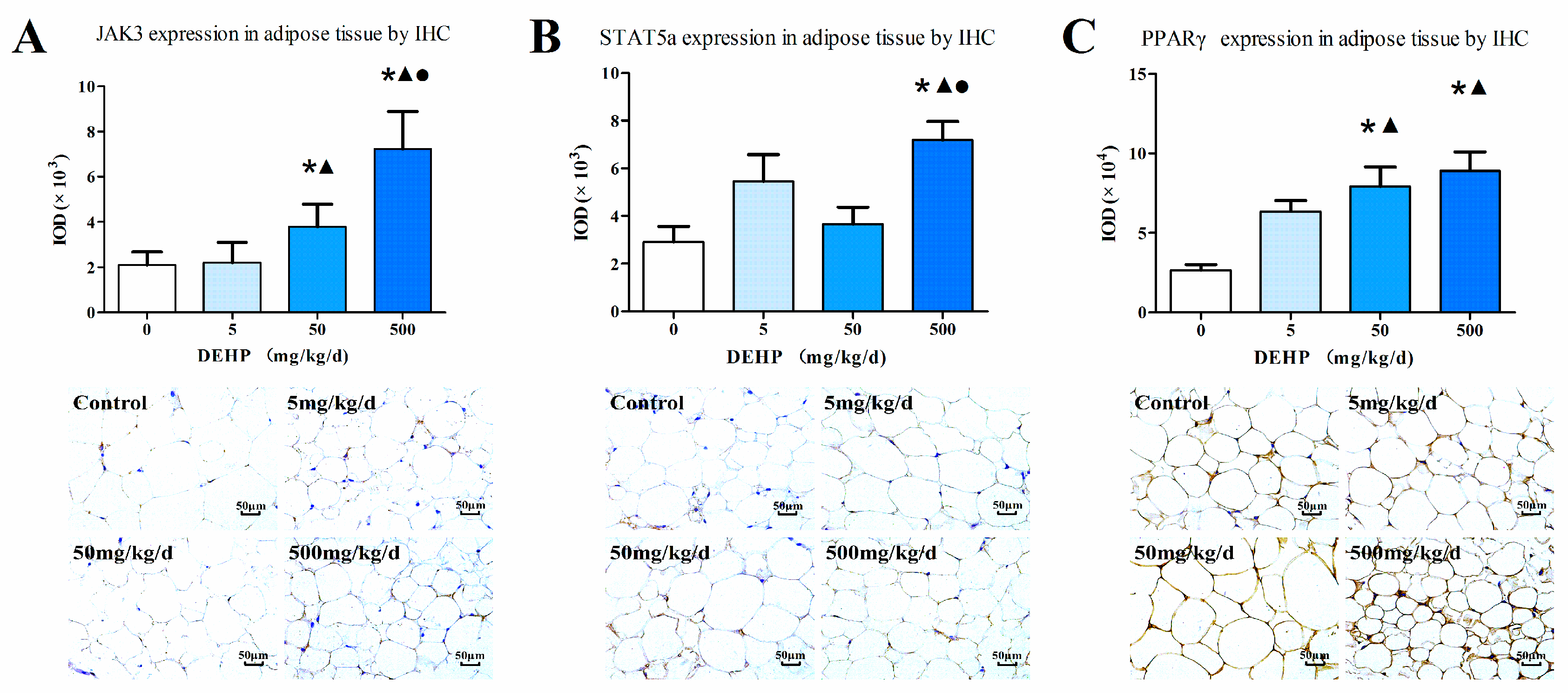
2.5. Immunohistochemistry
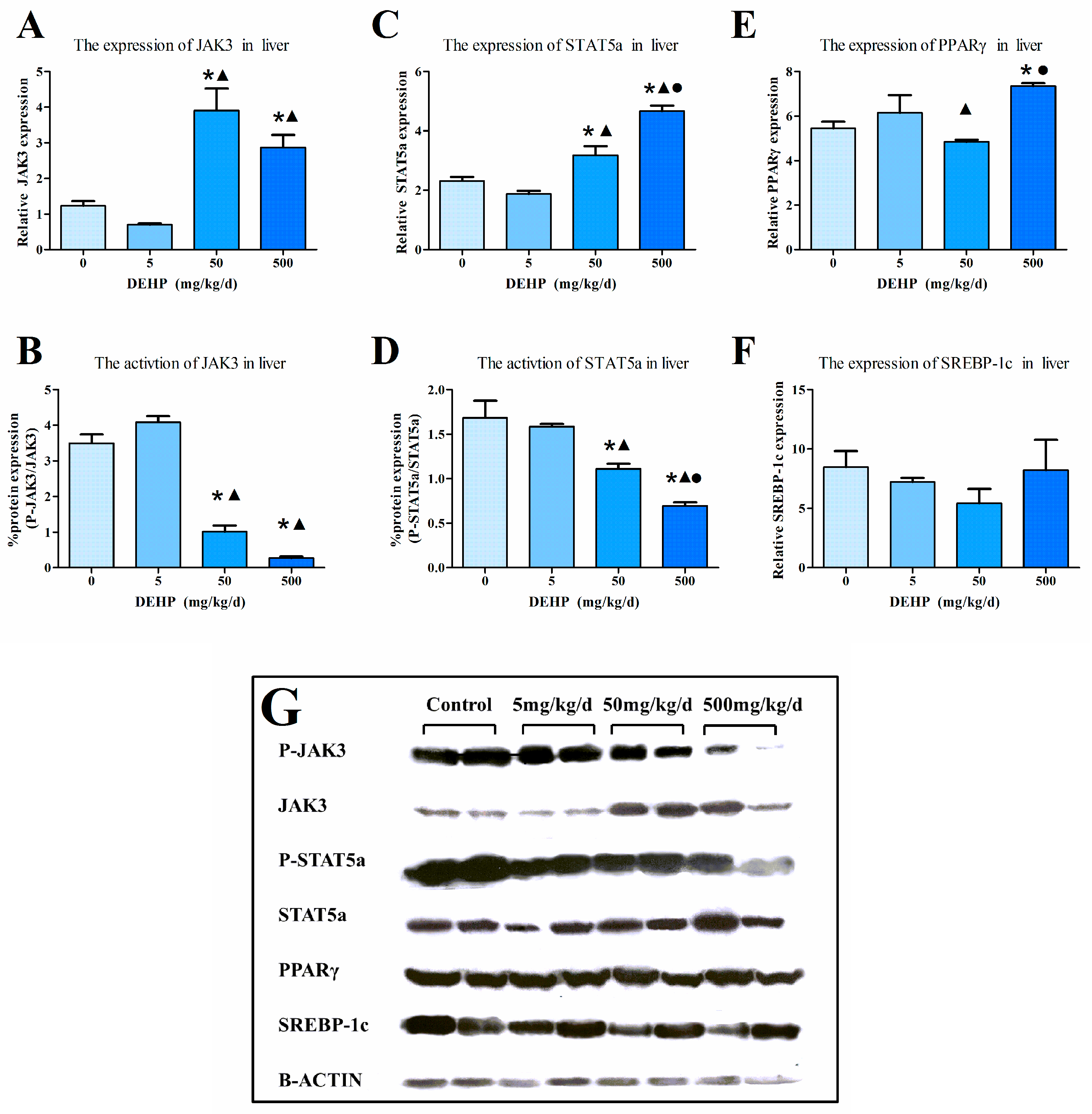
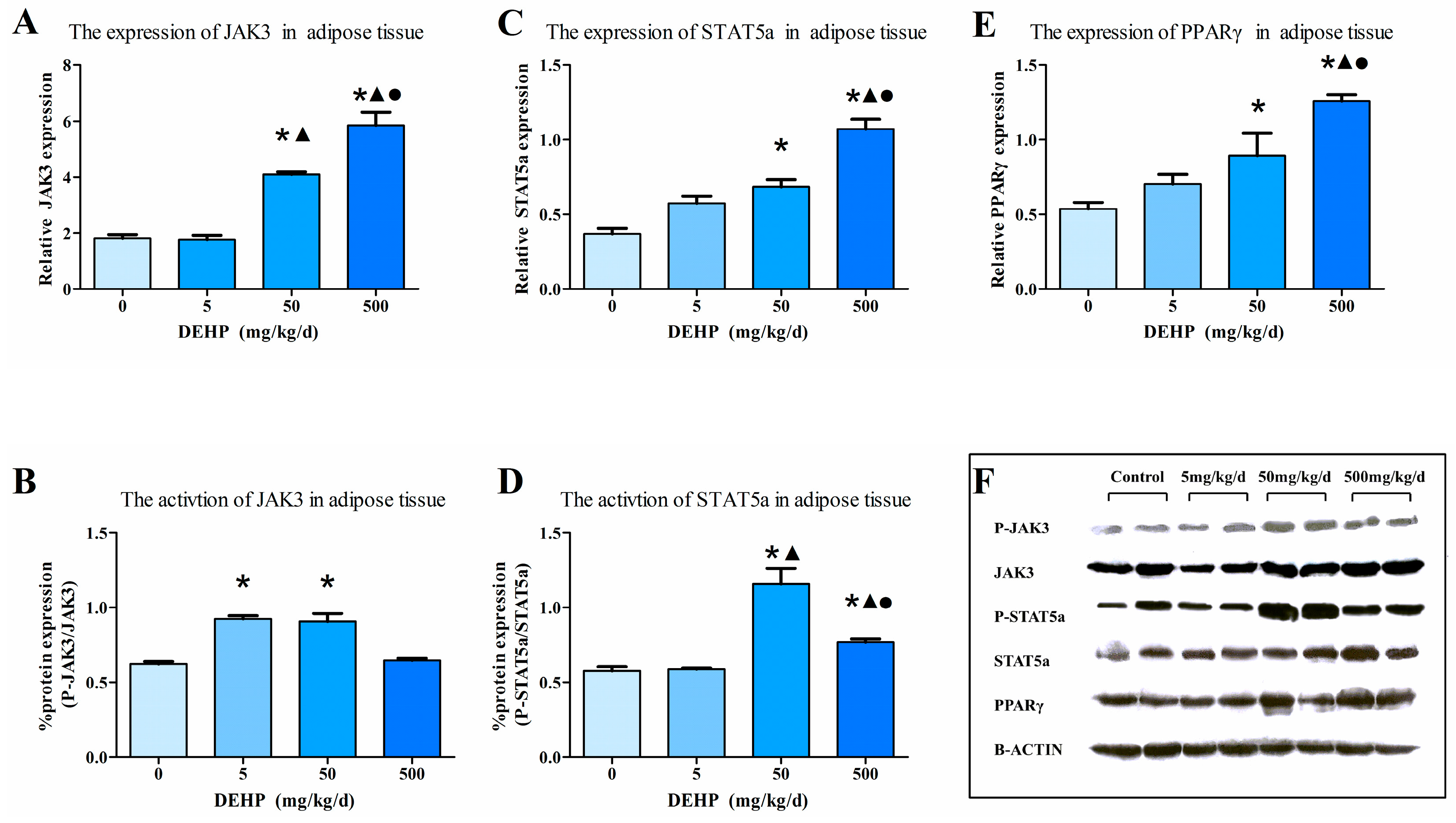
2.6. Western Blot
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
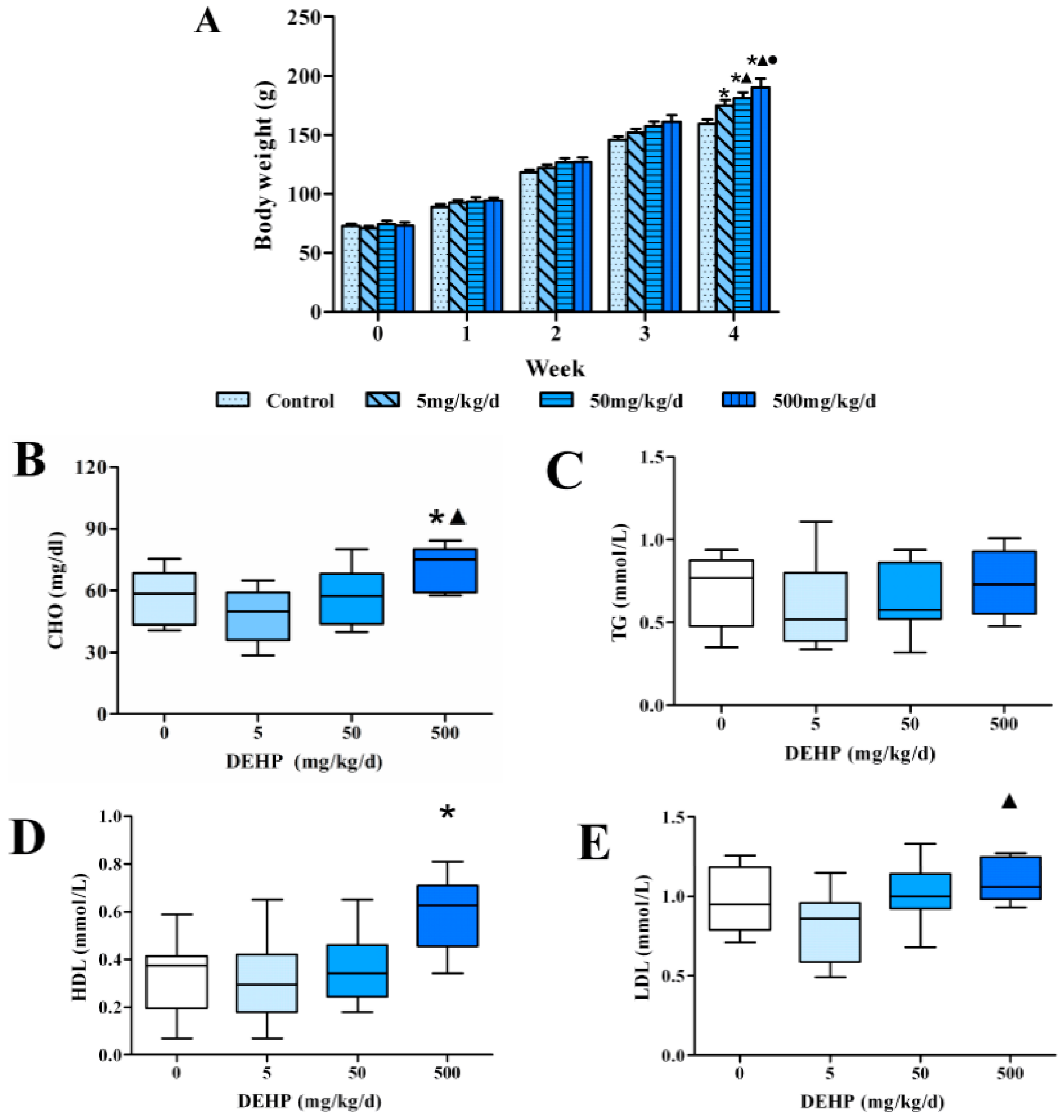
3.1. Effects of 4 Weeks of Dietary Exposure to DEHP on Body Weight in Rats
3.2. Effect of DEHP on Serum Lipid Levels in Rats
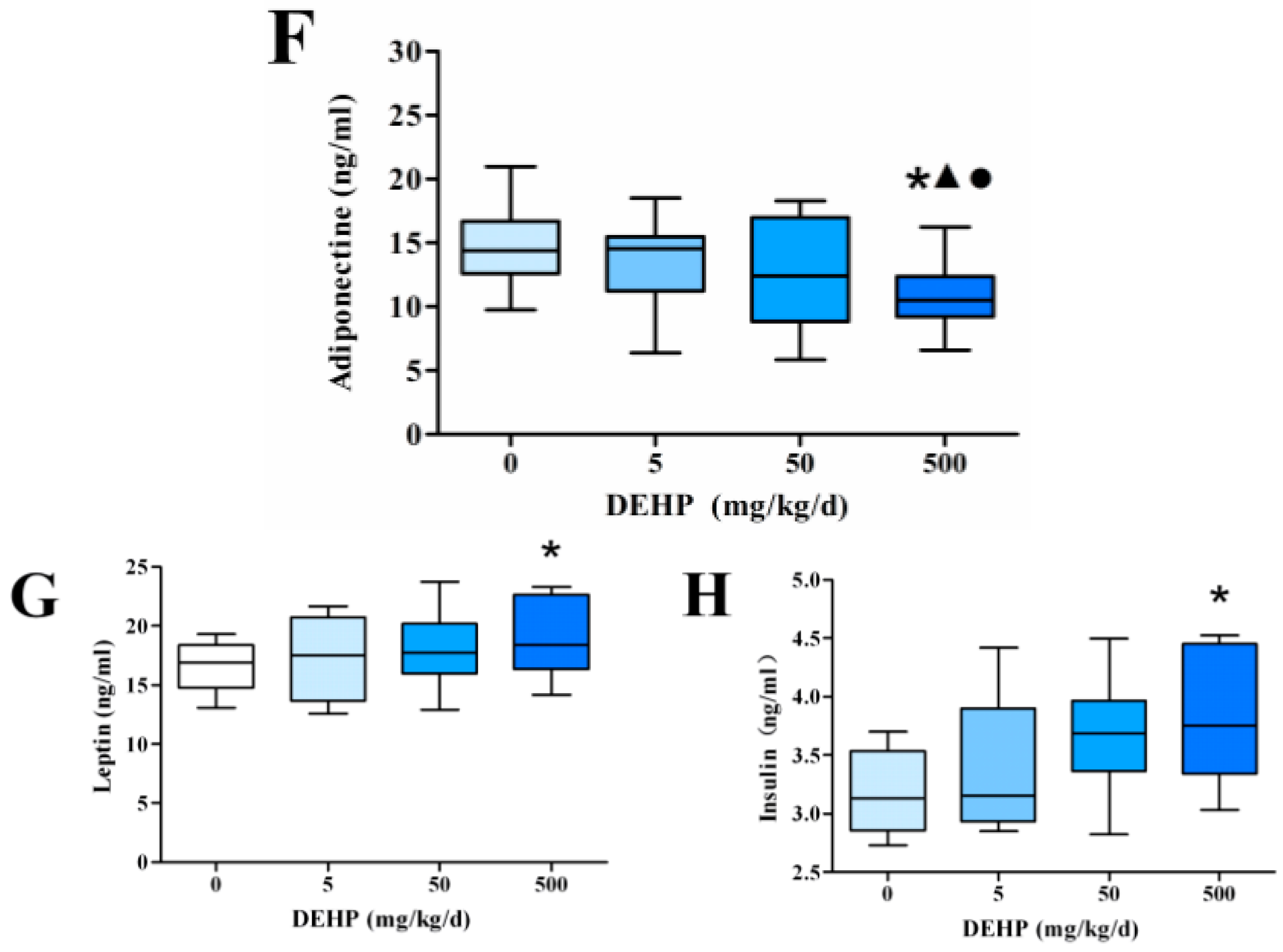
3.3. Effect of DEHP on Serum Lipid Metabolism Related Hormone Levels in Rats
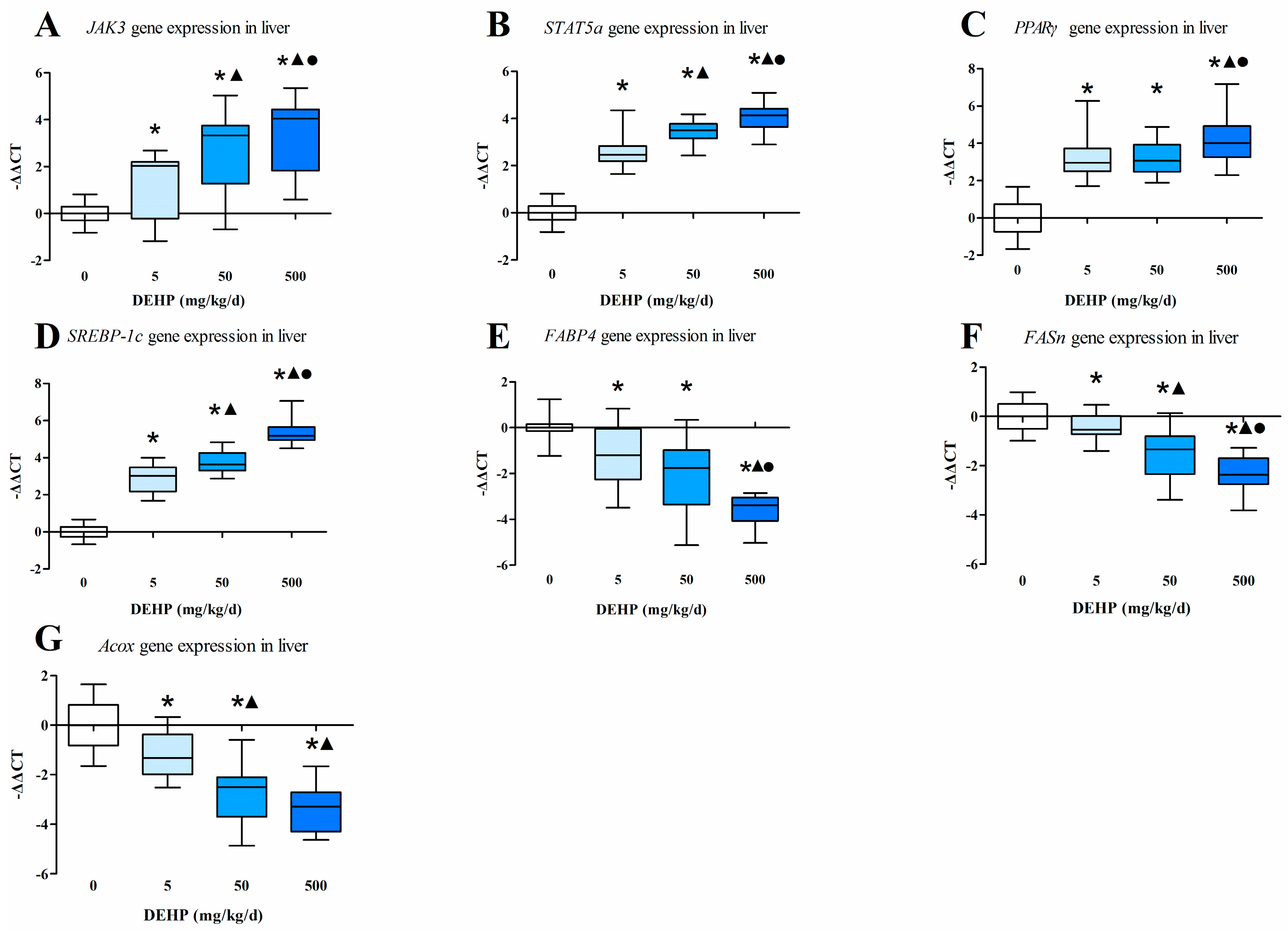
3.4. Gene Expression Analysis in the Liver
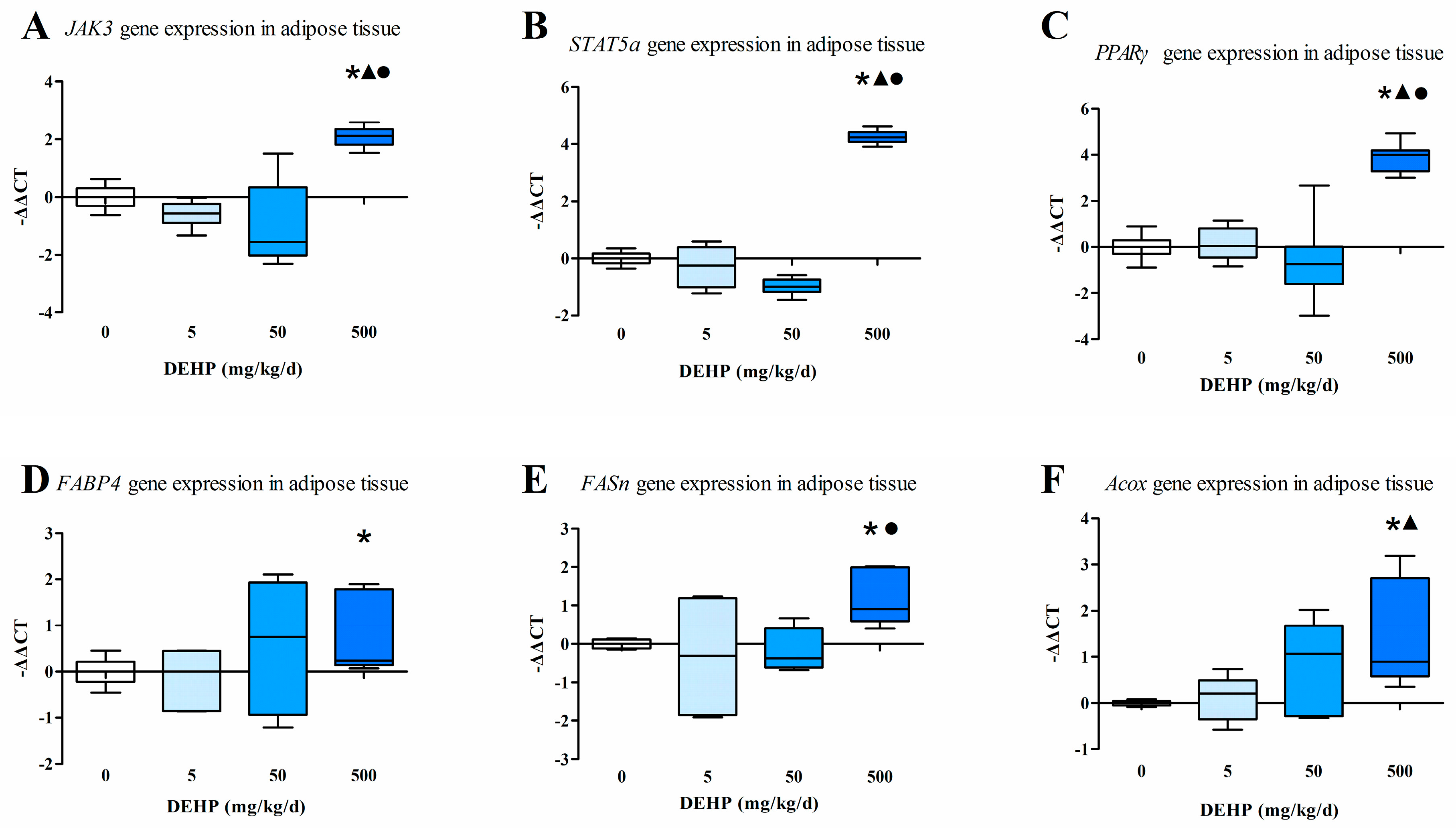
3.5. Gene Expression Analysis in Fat Tissue
3.6. Protein Expression in the Liver
3.7. Protein Expression in Fat Tissue
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DEHP | di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate |
| MEHP | Mono-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate |
| JAK | Janus Kinase |
| STAT | Signal transducers and activators of transcription |
| PPARγ | peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ |
| SREBP | sterol regulatory element binding proteins |
| TG | triglycerides |
| HDL | high density lipoprotein |
| LDL | low density lipoprotein |
| CHO | total cholesterol |
| FABP4 | fatty acid binding protein fatty 4 |
| FASn | fatty acid synthetase |
| Acox | acyl CoA oxidase |
| NOAEL | no observed adverse effect level |
| IHC | immunohistochemistry. |
References
- Klingmuller, D.; Allera, A. Endocrine disruptors: Hormone-active chemicals from the environment: A risk to humans? Dtsch. Med. Wochenschr. 2011, 136, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lyche, J.L.; Gutleb, A.C.; Bergman, A.; Eriksen, G.S.; Murk, A.J.; Ropstad, E.; Saunders, M.; Skaare, J.U. Reproductive and developmental toxicity of phthalates. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B Crit. Rev. 2009, 12, 225–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heudorf, U.; Mersch-Sundermann, V.; Angerer, J. Phthalates: Toxicology and exposure. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2007, 210, 623–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakashima, R.; Hayashi, Y.; Md, K.; Jia, X.; Wang, D.; Naito, H.; Ito, Y.; Kamijima, M.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Nakajima, T. Exposure to dehp decreased four fatty acid levels in plasma of prepartum mice. Toxicology 2013, 309, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, J.S.; Schaedlich, K.; Fiandanese, N.; Pocar, P.; Fischer, B. Effects of di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) on female fertility and adipogenesis in C3H/N mice. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 1123–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinelli, M.I.; Mocchiutti, N.O.; Bernal, C.A. Effect of di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) on lipolysis and lipoprotein lipase activities in adipose tissue of rats. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2010, 29, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauser, R.; Calafat, A.M. Phthalates and human health. Occup. Environ. Med. 2005, 62, 806–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.W.; Lin, C.L.; Tsai, Y.A.; Chang, C.H.; Liao, K.W.; Yu, C.J.; Yang, W.; Lee, M.J.; Huang, P.C.; Sun, C.W.; et al. The effects of phthalate and nonylphenol exposure on body size and secondary sexual characteristics during puberty. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2015, 218, 603–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Park, M.J. Phthalate exposure and childhood obesity. Ann. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 19, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bility, M.T.; Thompson, J.T.; McKee, R.H.; David, R.M.; Butala, J.H.; Vanden Heuvel, J.P.; Peters, J.M. Activation of mouse and human peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARS) by phthalate monoesters. Toxicol. Sci. 2004, 82, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, C.; Cheng, X.; Xia, H.; Ma, X. The endocrine disruptor mono-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate promotes adipocyte differentiation and induces obesity in mice. Biosci. Rep. 2012, 32, 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desvergne, B.; Feige, J.N.; Casals-Casas, C. Ppar-mediated activity of phthalates: A link to the obesity epidemic? Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2009, 304, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, S.Y.; Luk, C.T.; Brunt, J.J.; Sivasubramaniyam, T.; Lu, S.Y.; Schroer, S.A.; Woo, M. Adipocyte-specific deficiency of janus kinase (JAK) 2 in mice impairs lipolysis and increases body weight, and leads to insulin resistance with ageing. Diabetologia 2014, 57, 1016–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Yin, C.; Wang, S.; Xiao, Y. Jak-stat in lipid metabolism of adipocytes. JAKSTAT 2013, 2, e27203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodcock, K.J.; Kierdorf, K.; Pouchelon, C.A.; Vivancos, V.; Dionne, M.S.; Geissmann, F. Macrophage-derived upd3 cytokine causes impaired glucose homeostasis and reduced lifespan in drosophila fed a lipid-rich diet. Immunity 2015, 42, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavlock, R.; Boekelheide, K.; Chapin, R.; Cunningham, M.; Faustman, E.; Foster, P.; Golub, M.; Henderson, R.; Hinberg, I.; Little, R.; et al. Ntp center for the evaluation of risks to human reproduction: Phthalates expert panel report on the reproductive and developmental toxicity of di-n-octyl phthalate. Reprod. Toxicol. 2002, 16, 721–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vom Saal, F.S.; Nagel, S.C.; Coe, B.L.; Angle, B.M.; Taylor, J.A. The estrogenic endocrine disrupting chemical bisphenol a (BPA) and obesity. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2012, 354, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biemann, R.; Navarrete Santos, A.; Navarrete Santos, A.; Riemann, D.; Knelangen, J.; Bluher, M.; Koch, H.; Fischer, B. Endocrine disrupting chemicals affect the adipogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells in distinct ontogenetic windows. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 417, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buser, M.C.; Murray, H.E.; Scinicariello, F. Age and sex differences in childhood and adulthood obesity association with phthalates: Analyses of nhanes 2007–2010. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2014, 217, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha-Zavaleta, L.; Huitron, C.; Caceres-Cortes, J.R.; Alvarado-Moreno, J.A.; Valle-Mendiola, A.; Soto-Cruz, I.; Weiss-Steider, B.; Rangel-Corona, R. Interleukin-2 (IL-2) receptor-betagamma signalling is activated by C-KIT in the absence of IL-2, or by exogenous IL-2 via JAK3/STAT5 in human papillomavirus-associated cervical cancer. Cell Signal. 2004, 16, 1239–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalcanti, E.; Gigante, M.; Mancini, V.; Battaglia, M.; Ditonno, P.; Capobianco, C.; Cincione, R.I.; Selvaggi, F.P.; Herr, W.; Storkus, W.J.; et al. JAK3/STAT5/6 pathway alterations are associated with immune deviation in cd8 t cells in renal cell carcinoma patients. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2010, 2010, 935764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, J.A.; Cheng, H.; Nagy, Z.S.; Frost, J.A.; Kirken, R.A. Protein phosphatase 2a regulates interleukin-2 receptor complex formation and JAK3/STAT5 activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 3582–3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, A.J.; Stephens, J.M. The role of jak-stat signaling in adipose tissue function. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1842, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGillicuddy, F.C.; Chiquoine, E.H.; Hinkle, C.C.; Kim, R.J.; Shah, R.; Roche, H.M.; Smyth, E.M.; Reilly, M.P. Interferon gamma attenuates insulin signaling, lipid storage, and differentiation in human adipocytes via activation of the JAK/STAT pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 31936–31944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; He, M.; Chen, T.; Liu, Y.; Tian, Y.L.; Wu, Y.L.; Zhao, Y.; Shen, Y.; Yuan, Z.Y. Multiple roles of socs proteins: Differential expression of socs1 and socs3 in atherosclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 31, 1066–1074. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mishra, J.; Verma, R.K.; Alpini, G.; Meng, F.; Kumar, N. Role of janus kinase 3 in predisposition to obesity-associated metabolic syndrome. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 29301–29312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stark, G.R.; Darnell, J.E., Jr. The JAK-STAT pathway at twenty. Immunity 2012, 36, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barclay, J.L.; Nelson, C.N.; Ishikawa, M.; Murray, L.A.; Kerr, L.M.; McPhee, T.R.; Powell, E.E.; Waters, M.J. GH-dependent STAT5 signaling plays an important role in hepatic lipid metabolism. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.; Atlas, E. Bisphenol S- and bisphenol A-induced adipogenesis of murine preadipocytes occurs through direct peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma activation. Int J. Obes. (Lond.) 2016, 40, 1566–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chawla, A.; Schwarz, E.J.; Dimaculangan, D.D.; Lazar, M.A. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) gamma: Adipose-predominant expression and induction early in adipocyte differentiation. Endocrinology 1994, 135, 798–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meirhaeghe, A.; Fajas, L.; Gouilleux, F.; Cottel, D.; Helbecque, N.; Auwerx, J.; Amouyel, P. A functional polymorphism in a STAT5B site of the human PPAR gamma 3 gene promoter affects height and lipid metabolism in a french population. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2003, 23, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoonjans, K.; Peinado-Onsurbe, J.; Lefebvre, A.M.; Heyman, R.A.; Briggs, M.; Deeb, S.; Staels, B.; Auwerx, J. PPARalpha and PPARgamma activators direct a distinct tissue-specific transcriptional response via a PPRE in the lipoprotein lipase gene. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 5336–5348. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Linehan, C.; Gupta, S.; Samali, A.; O’Connor, L. Bisphenol A-mediated suppression of LPL gene expression inhibits triglyceride accumulation during adipogenic differentiation of human adult stem cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mynatt, R.L.; Stephens, J.M. Agouti regulates adipocyte transcription factors. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2001, 280, C954–C961. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.B.; Spiegelman, B.M. ADD1/SREBP1 promotes adipocyte differentiation and gene expression linked to fatty acid metabolism. Genes Dev. 1996, 10, 1096–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.B.; Wright, H.M.; Wright, M.; Spiegelman, B.M. ADD1/SREBP1 activates ppargamma through the production of endogenous ligand. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 4333–4337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, A.J.; Stephens, J.M. Emerging roles of JAK-STAT signaling pathways in adipocytes. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 22, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, C.; Cheng, X.; Guo, J.; Xia, H.; Ma, X. Perinatal exposure to diethyl-hexyl-phthalate induces obesity in mice. Front. Biosci. (Elite Ed.) 2013, 5, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladyman, S.R.; Grattan, D.R. JAK-STAT and feeding. JAKSTAT 2013, 2, e23675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.S.; Lu, Y.J.; Chang, H.H.; Hsu, S.H.; Kuo, P.H.; Shieh, C.C.; Yao, W.J.; Hsu, M.C.; Young, K.C.; Lin, W.Y.; et al. Role of adiponectin gene variants, adipokines and hydrometry-based percent body fat in metabolically healthy and abnormal obesity. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trujillo, M.E.; Scherer, P.E. Adiponectin—Journey from an adipocyte secretory protein to biomarker of the metabolic syndrome. J. Intern. Med. 2005, 257, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karavia, E.A.; Papachristou, N.I.; Sakellaropoulos, G.C.; Xepapadaki, E.; Papamichail, E.; Petropoulou, P.I.; Papakosta, E.P.; Constantinou, C.; Habeos, I.; Papachristou, D.J.; et al. Scavenger receptor class B type I regulates plasma apolipoprotein E levels and dietary lipid deposition to the liver. Biochemistry 2015, 54, 5605–5616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene | Sequence 5′-3′ | Sequence 3′-5′ |
|---|---|---|
| JAK3 | AGTGAGGCGCATGTGAAGATTG | CCGAAGCTCCACACGTCAGA |
| STAT5a | GTGCCCTCAGGCTCACTACAAC | CCACATGCCTGGCAACATC |
| PPARγ | GGAGCCTAAGTTTGAGTTTGCTGTG | TGCAGCAGGTTGTCTTGGATG |
| SREBP-1c | CCCTGCGAAGTGCTCACAA | GCGTTTCTACCACTTCAGGTTTCA |
| FABP4 | CCTTTGTGGGGACCTGGAAA | TGACCGGATGACGACCAAGT |
| FASn | TGGTCACAGACGATGACAGGA | AGGCGTCGAACTTGGACAGA |
| Acox1 | ATTGGCACCTACGCCCAGAC | CCAGGCCACCACTTAATGGAA |
| β-actin | CCCATTGAACACGGCATTG | GGTACGACCAGAGGCATACA |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jia, Y.; Liu, T.; Zhou, L.; Zhu, J.; Wu, J.; Sun, D.; Xu, J.; Wang, Q.; Chen, H.; Xu, F.; et al. Effects of Di-(2-ethylhexyl) Phthalate on Lipid Metabolism by the JAK/STAT Pathway in Rats. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13111085
Jia Y, Liu T, Zhou L, Zhu J, Wu J, Sun D, Xu J, Wang Q, Chen H, Xu F, et al. Effects of Di-(2-ethylhexyl) Phthalate on Lipid Metabolism by the JAK/STAT Pathway in Rats. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2016; 13(11):1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13111085
Chicago/Turabian StyleJia, Yiyang, Te Liu, Liting Zhou, Jian Zhu, Juan Wu, Di Sun, Jin Xu, Qi Wang, Huaiji Chen, Feng Xu, and et al. 2016. "Effects of Di-(2-ethylhexyl) Phthalate on Lipid Metabolism by the JAK/STAT Pathway in Rats" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 13, no. 11: 1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13111085
APA StyleJia, Y., Liu, T., Zhou, L., Zhu, J., Wu, J., Sun, D., Xu, J., Wang, Q., Chen, H., Xu, F., Zhang, Y., Zhang, T., Liu, H., & Ye, L. (2016). Effects of Di-(2-ethylhexyl) Phthalate on Lipid Metabolism by the JAK/STAT Pathway in Rats. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 13(11), 1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13111085





