Evaluation of Immunomagnetic Separation for the Detection of Salmonella in Surface Waters by Polymerase Chain Reaction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
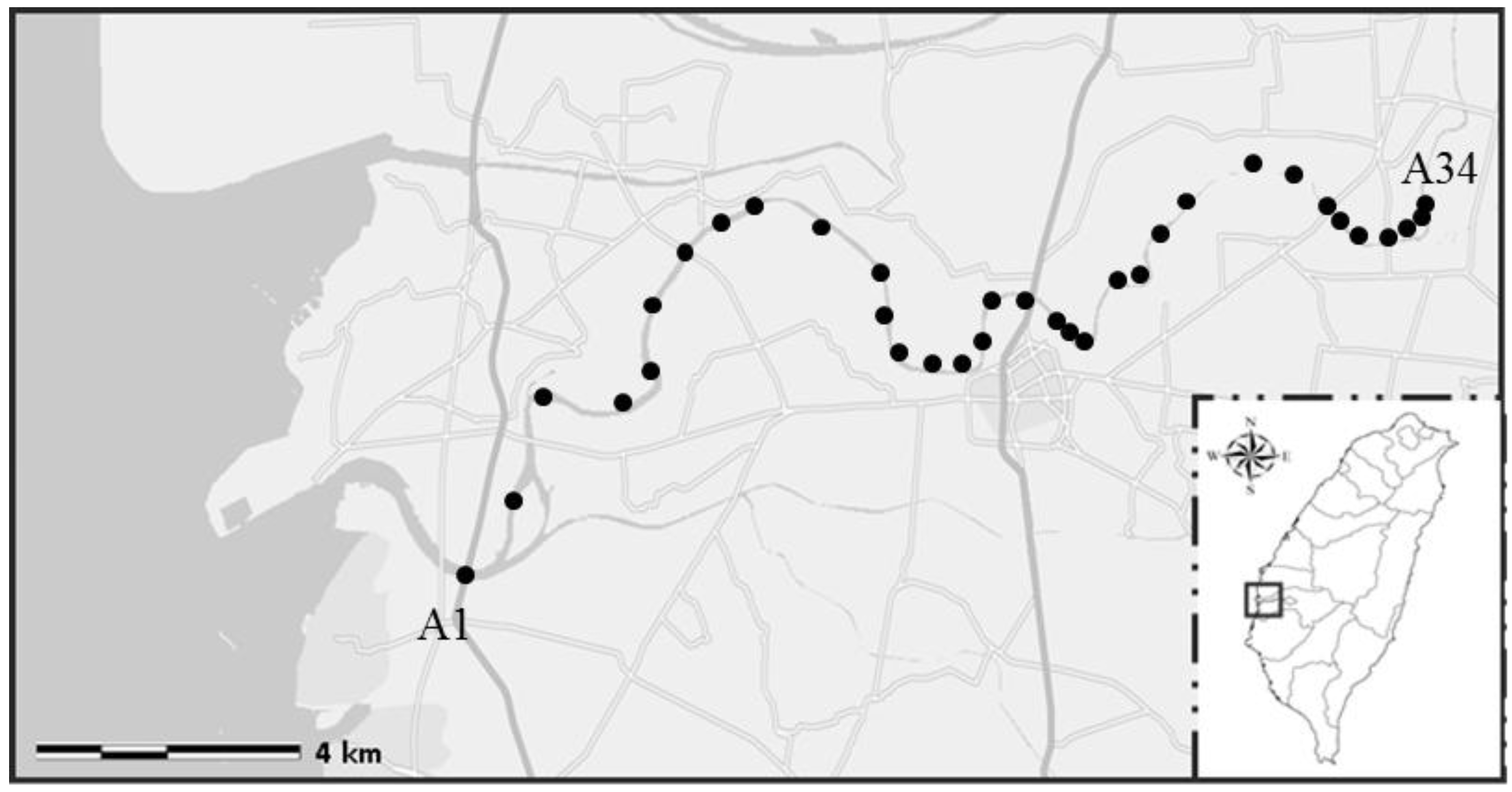
2.1. Sample Collection and Pre-Treatment
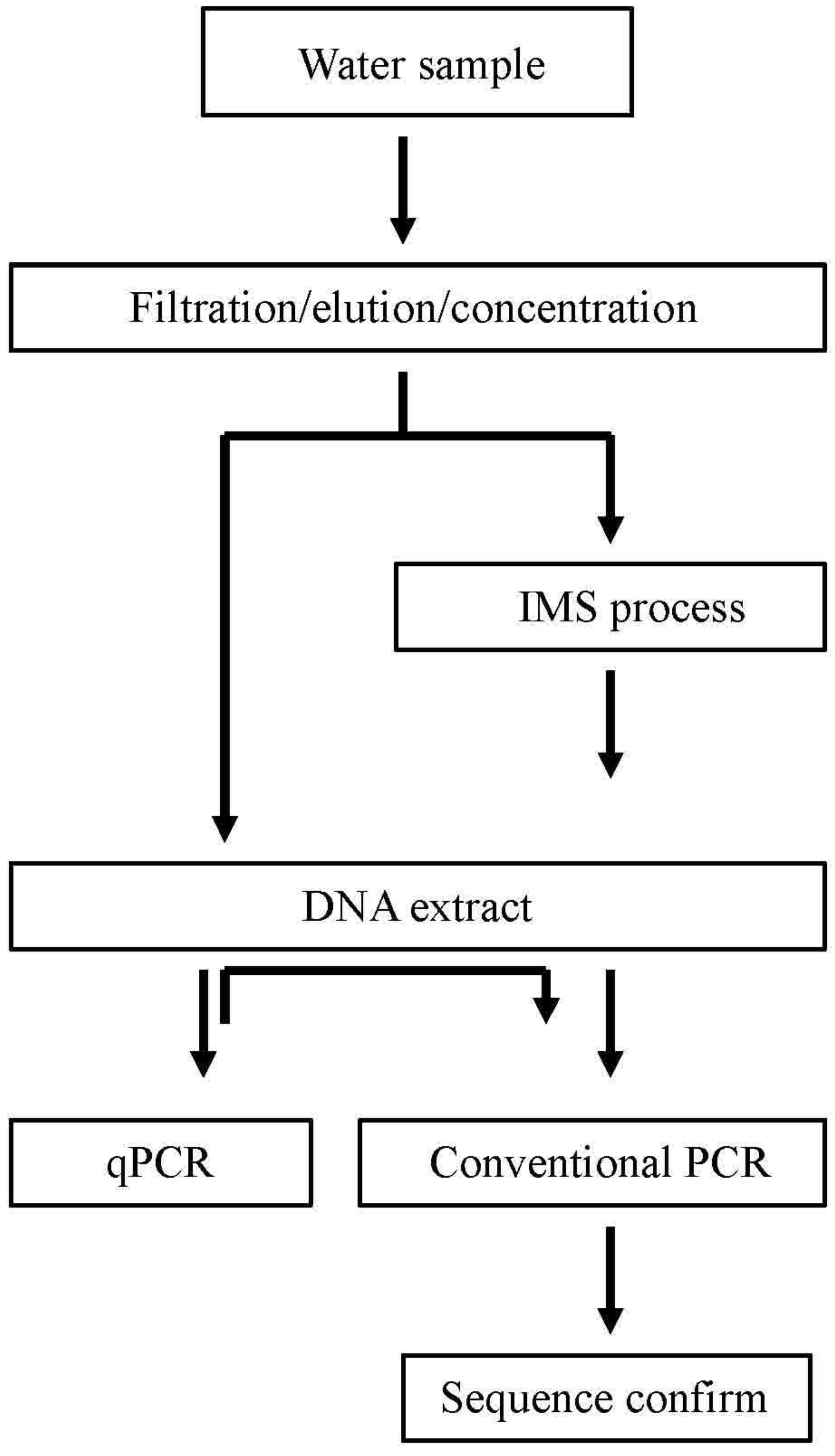
2.2. Immunomagnetic Separation (IMS) Procedure
2.3. PCR Analysis for Salmonella and Sequence Analysis
2.4. qPCR Analysis for Salmonella
2.5. Physical and Microbiological Parameter Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
| Sample No. * | Class of Water Quality | Salmonella Positive of Conventional PCR | Quantification of qPCR for Salmonella, CFU/100 mL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non IMS Procedure | IMS Procedure | |||
| A1 | C | N | P | 1.0 × 104 |
| A2 | C | P | P | 7.3 × 104 |
| A3 | C | N | N | 2.7 × 106 |
| A4 | C | N | P | 1.2 × 104 |
| A5 | C | N | P | 2.8 × 104 |
| A6 | C | N | P | 5.3 × 103 |
| A7 | C | P | P | ND |
| A8 | C | N | P | 7.1 × 103 |
| A9 | C | N | N | 1.7 × 104 |
| A10 | C | P | P | 2.1 × 104 |
| A11 | C | N | P | 4.7 × 103 |
| A12 | C | N | N | 7.6 × 103 |
| A13 | C | P | P | 1.1 × 104 |
| A14 | C | N | N | 1.7 × 104 |
| A15 | C | N | N | 1.9 × 104 |
| A16 | C | N | P | 1.2 × 103 |
| A17 | C | N | N | 8.6 × 103 |
| A18 | C | N | N | 1.1 × 104 |
| A19 | C | N | P | 5.2 × 103 |
| A20 | C | N | N | 2.0 × 104 |
| A21 | C | N | N | 1.8 × 104 |
| A22 | C | N | P | 1.9 × 104 |
| A23 | C | N | P | 1.2 × 104 |
| A24 | B | N | N | 3.1 × 103 |
| A25 | B | N | P | 1.0 × 104 |
| A26 | B | N | P | 5.5 × 104 |
| A27 | B | P | N | 2.0 × 104 |
| A28 | B | N | N | 3.4 × 104 |
| A29 | B | N | N | 8.1 × 104 |
| A30 | B | P | N | 1.1 × 104 |
| A31 | B | N | N | 7.9 × 103 |
| A32 | B | N | N | 1.9 × 104 |
| A33 | B | N | N | 4.6 × 103 |
| A34 | B | N | N | 2.4 × 102 |
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Medus, C.; Smith, K.E.; Bender, J.B.; Besser, J.M.; Hedberg, C.W. Salmonella outbreaks in restaurants in Minnesota, 1995 through 2003: Evaluation of the role of infected foodworkers. J. Food Prot. 2006, 69, 1870–1878. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hardnett, F.P.; Hoekstra, R.M.; Kennedy, M.; Charles, L.; Angulo, F.J. Epidemiologic issues in study design and data analysis related to FoodNet activities. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2004, 38, S121–S126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CDC. Salmonella. Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/salmonella/general/ (accessed on 15 September 2013).
- Wright, R.C. The survival patterns of selected faecal bacteria in tropical fresh waters. Epidemiol. Infect. 1989, 103, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baudart, J.; Lemarchand, K.; Brisabois, A.; Lebaron, P. Diversity of Salmonella strains isolated from the aquatic environment as determined by serotyping and amplification of the ribosomal DNA spacer regions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 1544–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- APHA. Standard Method for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 15th ed.; American Public Health Association and American Water Works Association and Water Environment Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Fung, D.Y. Predictions for rapid methods and automation in food microbiology. J. AOAC Int. 2002, 85, 1000–1002. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rossen, L.; Norskov, P.; Holmstrom, K.; Rasmussen, O.F. Inhibition of PCR by components of food samples, microbial diagnostic assays and DNA-extraction solutions. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1992, 17, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreader, C.A. Relief of amplification inhibition in PCR with bovine serum albumin or T4 gene 32 protein. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 1102–1106. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wilson, I.G. Inhibition and facilitation of nucleic acid amplification. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 3741–3751. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Burtscher, C.; Wuertz, S. Evaluation of the use of PCR and reverse transcriptase PCR for detection of pathogenic bacteria in biosolids from anaerobic digestors and aerobic composters. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 4618–4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kermekchiev, M.B.; Kirilova, L.I.; Vail, E.E.; Barnes, W.M. Mutants of Taq DNA polymerase resistant to PCR inhibitors allow DNA amplification from whole blood and crude soil samples. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matheson, C.D.; Gurney, C.; Esau, N.; Lehto, R. Assessing PCR inhibition from humic substances. Open Enzyme Inhib. J. 2010, 3, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCord, B.; Opel, K.; Funes, M.; Zoppis, S.; Jantz, L.M. An Investigation of the Effect of DNA Degradation and Inhibition on PCR Amplification of Single Source and Mixed Forensic Samples. Available online: http://www.ncjrs.gov/pdffiles1/nij/grants/236692.pdf (accessed on 31 Januray 2013).
- Kamble, K.D.; Kadu, S.S. Enhancement of DNase production from a moderate halophilic bacterium and studies on its phylogeny. Int. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 3, 1031–1037. [Google Scholar]
- Cudjoe, K.S.; Krona, R.; Olsen, E. IMS: A new selective enrichment technique for detection of Salmonella in foods. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1994, 23, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, C.H.; Ou, J.T. Rapid identification of Salmonella serovars in faeces by specific detection of virulence genes, invA and spvC, by an enrichment broth culture-multiplex PCR combination assay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1996, 34, 2619–2622. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yanez, M.A.; Carrasco-Serrano, C.; Barbera, V.M.; Catalan, V. Quantitative detection of Legionella pneumophila in water samples by immunomagnetic purification and real-time PCR amplification of the dotA gene. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 3433–3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conceicao, R.S.; Moreira, A.N.; Ramos, R.J.; Goularte, F.L.; Carvalhal, J.B.; Aleixo, J.A.G. Detection of salmonella sp in chicken cuts using immunomagnetic separation. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2008, 39, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamo-Castellvi, S.D.; Manning, A.; Rodriguez-Saona, L.E. Fourier-Transform infrared spectroscopy combined with immunomagnetic separation as a tool to discriminate Salmonella serovars. Analyst 2010, 135, 2987–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Water Resources Management and Policy Research Center. Available online: http://www.water.tku.edu.tw (accessed on 15 September 2014).
- Barbes, C.F.; Burton, D.R. Quantitation of DNA and RNA; Cold Spring Harbor Protocols: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2007; Volume 11, p. 47. [Google Scholar]
- Daum, L.K.; Barnes, W.J.; McAvin, J.C.; Neidert, M.S.; Cooper, L.A.; Huff, W.B.; Gaul, L.; Riggins, W.S.; Morris, S.; Salmen, A.; Lohman, K.L. Real-time PCR detection of Salmonella in suspect foods from a gastroenteritis outbreak in Kerr County, Texas. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 3050–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Chen, F.; Jiao, N. Genetic diversity and abundance of flavobacterial proteorhodopsin in China seas. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, S.; Yoshida, T.; Hosoda, N.; Honda, T.; Kuno, S.; Kamiji, R.; Hashimoto, R.; Sako, Y. Diurnal infection patterns and impact of Microcystis cyanophages in a Japanese pond. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 5805–5811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rompre, A.; Servais, P.; Baudart, J.; de-Roubin, M.R.; Laurent, P. Detection and enumeration of coliforms in drinking water: Current methods and emerging approaches. J. Microbiol. Methods 2002, 49, 31–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, I.R.; Ball, H.J.; Rowe, M.T. Isolation of Mycobacteriaum paratuberculosis from milk by immunomagnetic separation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 3153–3158. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gudnason, H.; Dufva, M.; Bang, D.D.; Wolff, A. Comparison of multiple DNA dyes for real-time PCR: Effects of dye concentration and sequence composition on DNA amplification and melting temperature. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Medici, D.; Croci, L.; Delibato, E.; di Pasquale, S.; Filetici, E.; Toti, L. Evaluation of DNA extraction methods for use in combination with SYBR Green I real-time PCR to detect Salmonella enterica serotype enteritidis in poultry. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 3456–3461. [Google Scholar]
- Favrin, S.J.; Jassim, S.A.; Griffiths, M.W. Development and optimization of a novel immunomagnetic separation-bacteriophage assay for detection of Salmonella enterica serovar enteritidis in broth. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercanoglu, B.; Griffiths, M.W. Combination of immunomagnetic separation with real-time PCR for rapid detection of Salmonella in milk, ground beef, and alfalfa sprouts. J. Food Prot. 2005, 68, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Notzon, A.; Helmuth, R.; Bauer, J. Evaluation of an immunomagnetic separation-real-time PCR assay for the rapid detection of Salmonella in meat. J. Food Prot. 2006, 69, 2896–2901. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Taban, B.M.; Ben, U.; Aytac, S.A. Rapid detection of Salmonella in milk by combined immunomagnetic separation-polymerase chain reaction assay. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 2382–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsu, C.-Y.; Hsu, B.-M.; Chang, T.-Y.; Hsu, T.-K.; Shen, S.-M.; Chiu, Y.-C.; Wang, H.-J.; Ji, W.-T.; Fan, C.-W.; Chen, J.-L. Evaluation of Immunomagnetic Separation for the Detection of Salmonella in Surface Waters by Polymerase Chain Reaction. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 9811-9821. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph110909811
Hsu C-Y, Hsu B-M, Chang T-Y, Hsu T-K, Shen S-M, Chiu Y-C, Wang H-J, Ji W-T, Fan C-W, Chen J-L. Evaluation of Immunomagnetic Separation for the Detection of Salmonella in Surface Waters by Polymerase Chain Reaction. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2014; 11(9):9811-9821. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph110909811
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsu, Chao-Yu, Bing-Mu Hsu, Tien-Yu Chang, Tsui-Kang Hsu, Shu-Min Shen, Yi-Chou Chiu, Hung-Jen Wang, Wen-Tsai Ji, Cheng-Wei Fan, and Jyh-Larng Chen. 2014. "Evaluation of Immunomagnetic Separation for the Detection of Salmonella in Surface Waters by Polymerase Chain Reaction" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 11, no. 9: 9811-9821. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph110909811
APA StyleHsu, C.-Y., Hsu, B.-M., Chang, T.-Y., Hsu, T.-K., Shen, S.-M., Chiu, Y.-C., Wang, H.-J., Ji, W.-T., Fan, C.-W., & Chen, J.-L. (2014). Evaluation of Immunomagnetic Separation for the Detection of Salmonella in Surface Waters by Polymerase Chain Reaction. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 11(9), 9811-9821. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph110909811





