Identification of Health Risks of Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease in China Using the Geographical Detector Technique
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. HFMD Data
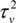 , as following equation [18,19].
, as following equation [18,19].

 and
and 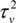 , respectively. In this model, we use gamma distribution as prior distribution of the hyper-parameters: 1/τv2 ~ Gamma(0.001, 0.001) and 1/τu2 ~ Gamma(0.5, 0.0005) [11]. The Hierarchical Bayesian model is conducted by MCMC simulation in WinBUGS 1.4, and the length of burn-in sequence is 5,000 [11]. The incidence of children is shown in Figure 1 (after adjustment by the Hierarchical Bayesian model).
, respectively. In this model, we use gamma distribution as prior distribution of the hyper-parameters: 1/τv2 ~ Gamma(0.001, 0.001) and 1/τu2 ~ Gamma(0.5, 0.0005) [11]. The Hierarchical Bayesian model is conducted by MCMC simulation in WinBUGS 1.4, and the length of burn-in sequence is 5,000 [11]. The incidence of children is shown in Figure 1 (after adjustment by the Hierarchical Bayesian model).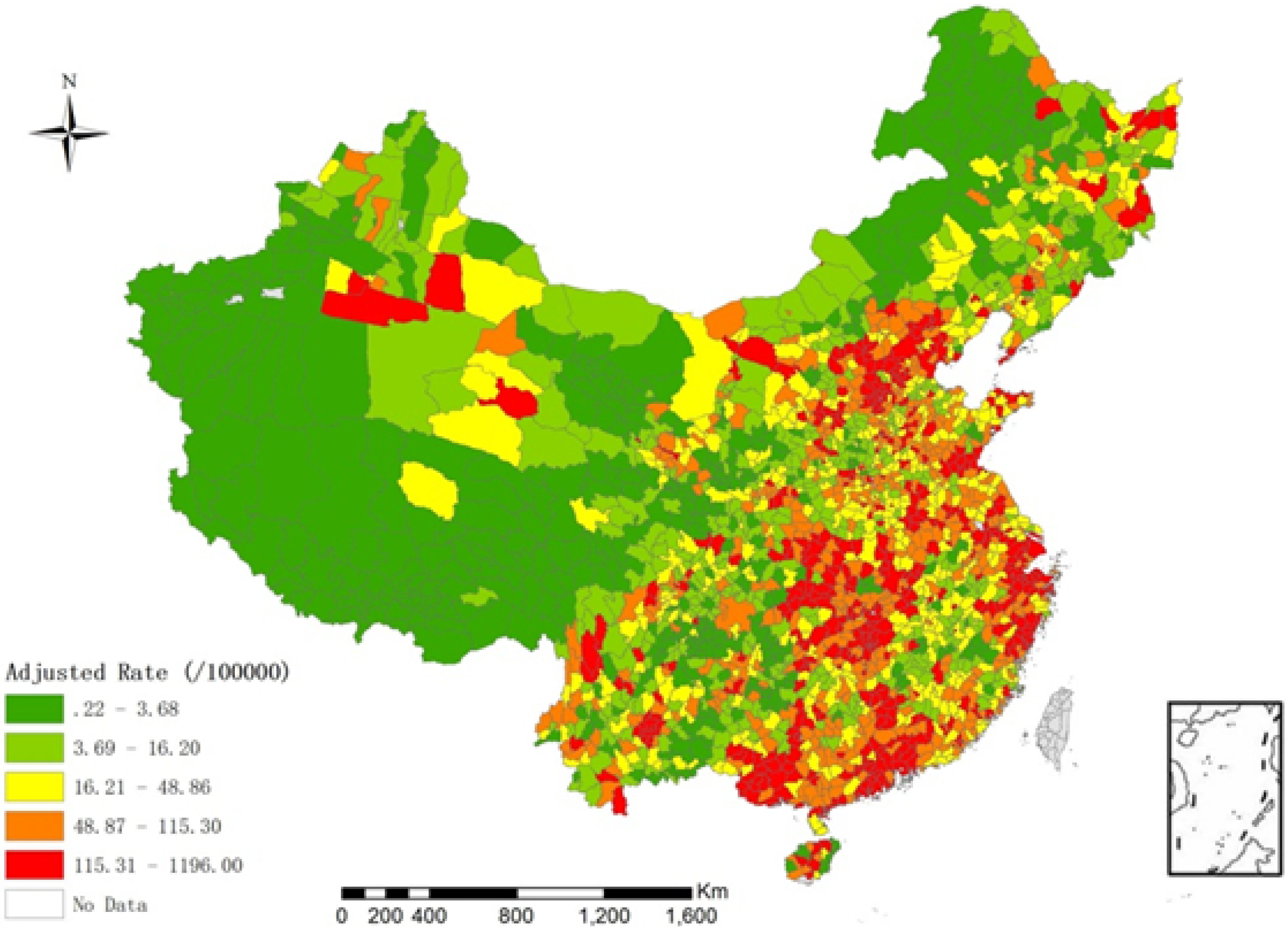
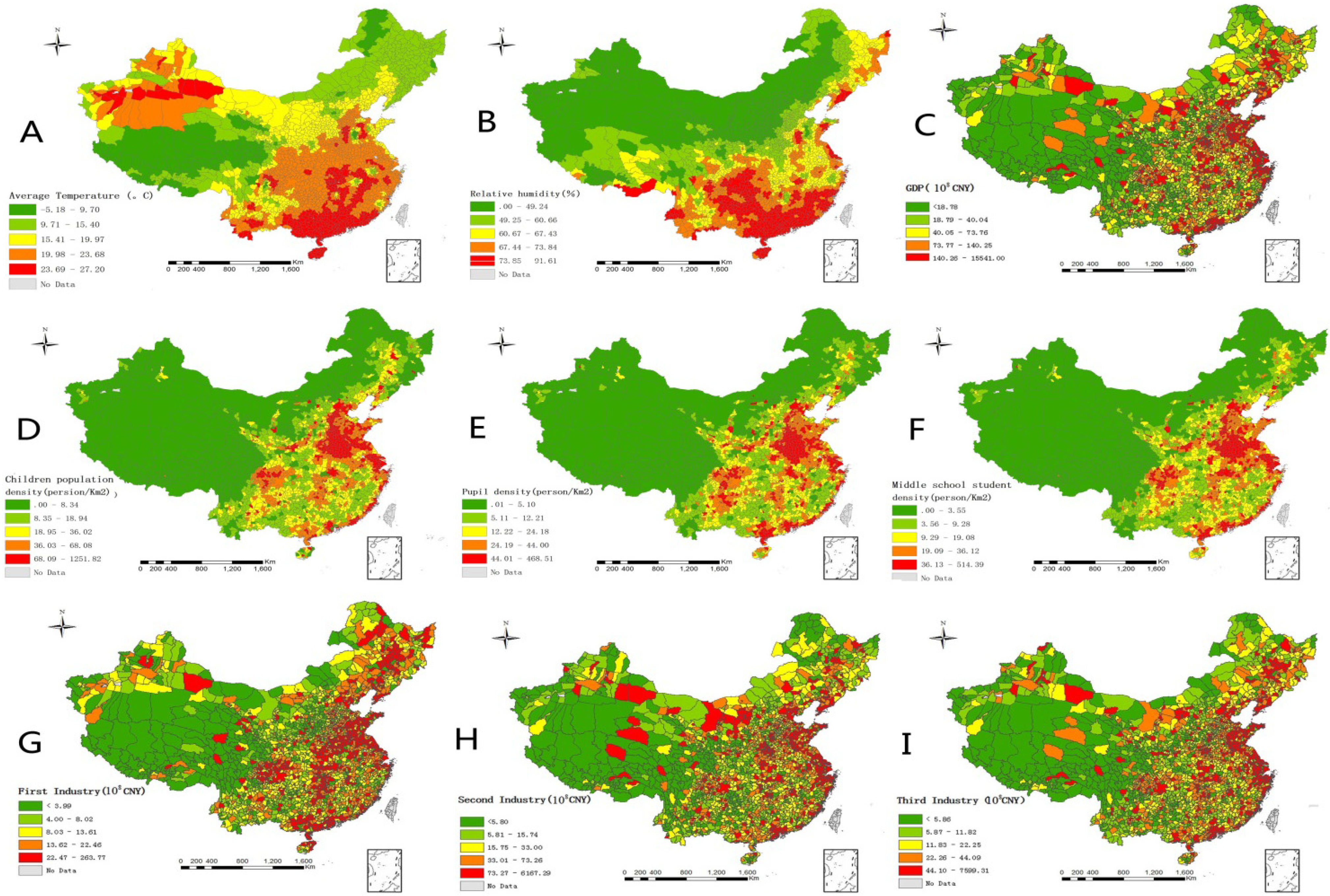
2.2. Determinants of HFMD and Their Proxies
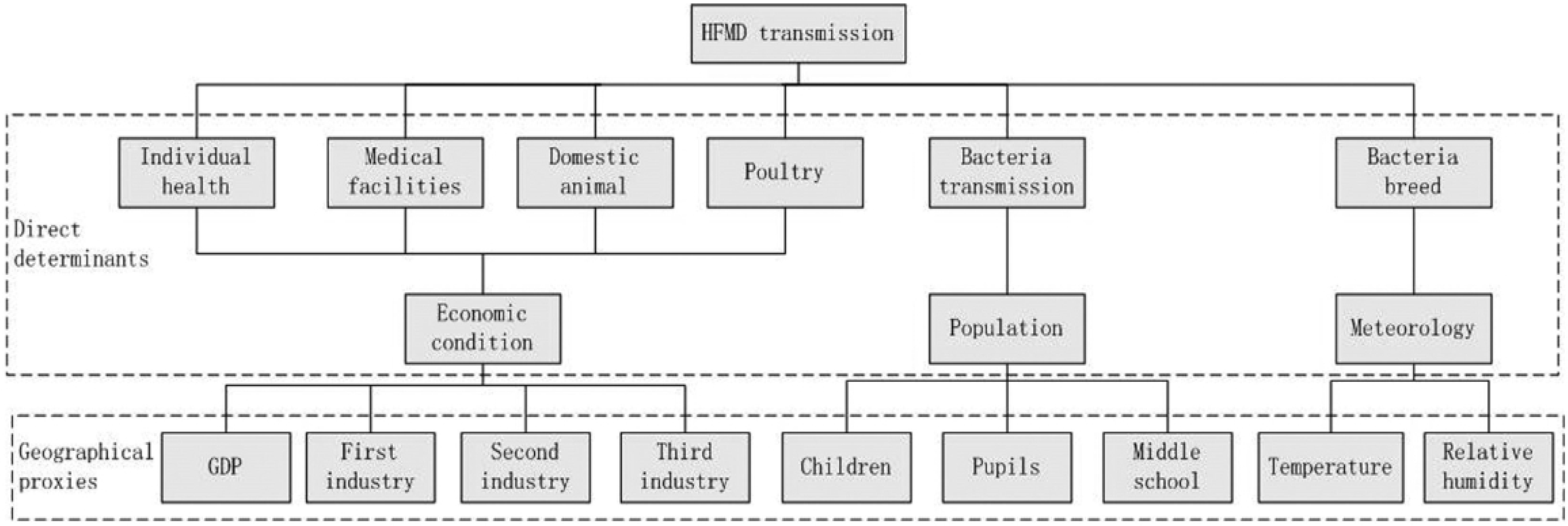
2.3. Geographical Detector
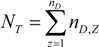 . The incidence of HFMD in every grid in the sub-region was defined as Hz,i (1 ≤ z ≤ nD, 1 ≤ i ≤ nD,Z).
. The incidence of HFMD in every grid in the sub-region was defined as Hz,i (1 ≤ z ≤ nD, 1 ≤ i ≤ nD,Z).

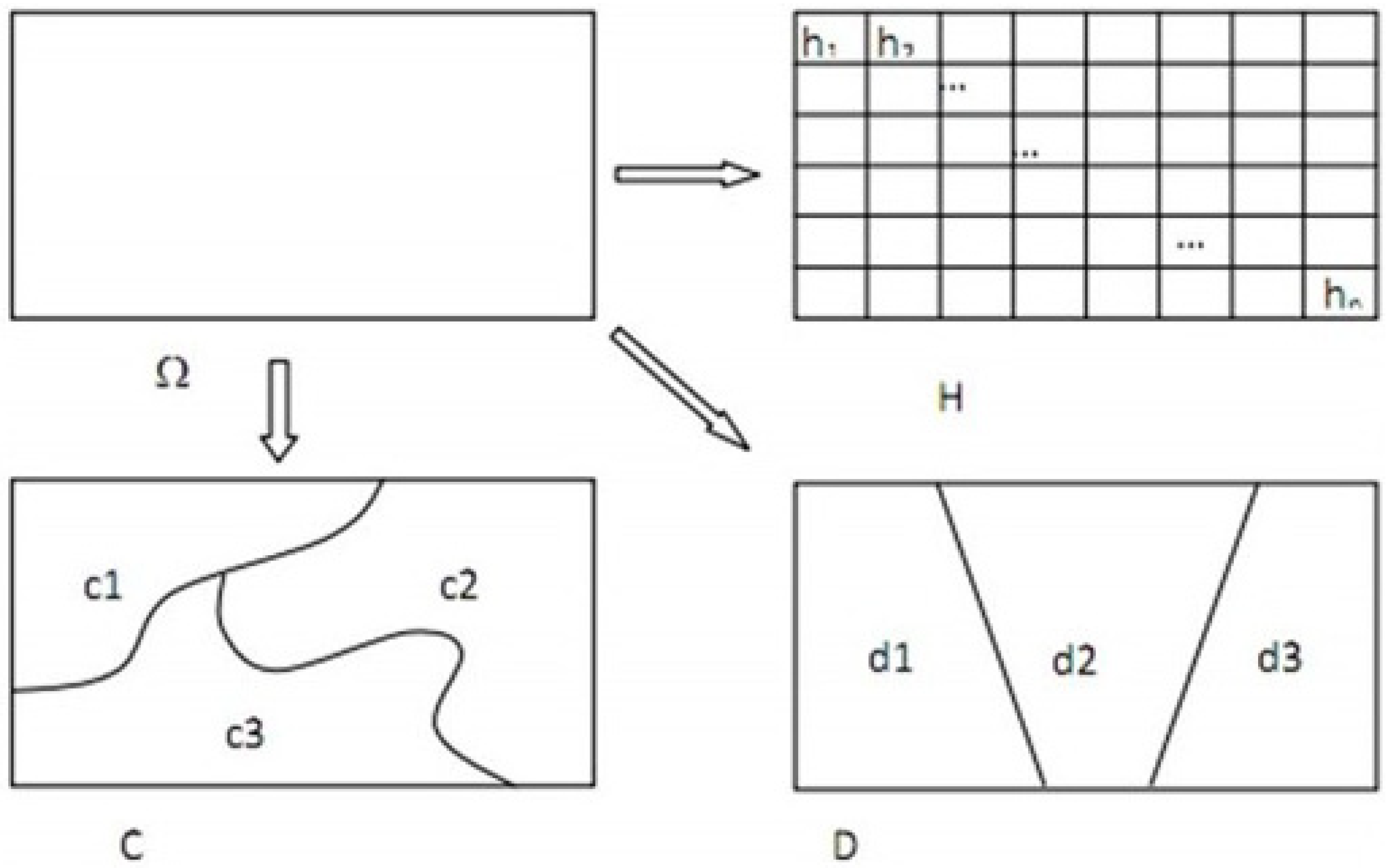
2.3.1. Risk Detector






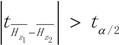 , we can then reject H0, denoting that the incidence of HFMD in these two sub-regions was significantly different; otherwise the difference between them may be caused by error.
, we can then reject H0, denoting that the incidence of HFMD in these two sub-regions was significantly different; otherwise the difference between them may be caused by error.2.3.2. Factor Detector

 . If the risk factor affected the incidence of HFMD completely, then the sample variance in each sub-region was equal to 0 [15], which means that
. If the risk factor affected the incidence of HFMD completely, then the sample variance in each sub-region was equal to 0 [15], which means that  was also equal to 0. We defined the power of determinant (PD) as:
was also equal to 0. We defined the power of determinant (PD) as:

 is close to 0, which means that this factor has the same distribution as the incidence of HFMD.
is close to 0, which means that this factor has the same distribution as the incidence of HFMD.2.3.3. Ecological Detector
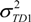 and
and 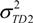 , respectively. The total number of grids divided by these risk factors is nT,D1 and nT,D2 respectively. To compare the differences between
, respectively. The total number of grids divided by these risk factors is nT,D1 and nT,D2 respectively. To compare the differences between 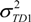 and
and 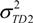 , the F test was used:
, the F test was used:

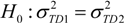 , the confidence level was calculated (generally α = 5%). If H0 was rejected under the confidence level α, this indicated that these two factors had a significant difference on the influence of HFMD.
, the confidence level was calculated (generally α = 5%). If H0 was rejected under the confidence level α, this indicated that these two factors had a significant difference on the influence of HFMD.2.3.4. Interactive Detector
3. Results
| Variables | Mean | Min | 25% | 50% | 75% | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Incidence (cases/105) | 76.1 | 0.2 | 5.3 | 29.5 | 94.2 | 1,196.0 |
| AT (℃) | 19.7 | −5.2 | 16.9 | 21.0 | 23.1 | 27.2 |
| Rainfall (mm) | 99.6 | 0.1 | 38.9 | 83.7 | 135.8 | 497.9 |
| RH (%) | 61.3 | 0.5 | 52.9 | 64.4 | 72.4 | 91.6 |
| PD0_9 (person/ km2) | 39.6 | 0.3 | 8.9 | 23.5 | 55.5 | 526.2 |
| PupD (person/ km2) | 29.1 | 0.1 | 6.9 | 17.7 | 37.9 | 468.5 |
| MSD (person/ km2) | 23.2 | 0.1 | 4.9 | 13.1 | 30.1 | 514.4 |
| GDP (108 CNY) | 153.6 | 0.8 | 22.9 | 55.1 | 115.4 | 15,541.0 |
| FirstIndustry (108 CNY) | 14.2 | 0.4 | 5.1 | 10.3 | 19.6 | 263.7 |
| SecondIndustry (108 CNY) | 74.5 | 1.5 | 8.0 | 23.1 | 58.9 | 6,167.3 |
| ThirdIndustry (108 CNY) | 57.2 | 0.6 | 7.2 | 16.5 | 35.1 | 7,599.3 |
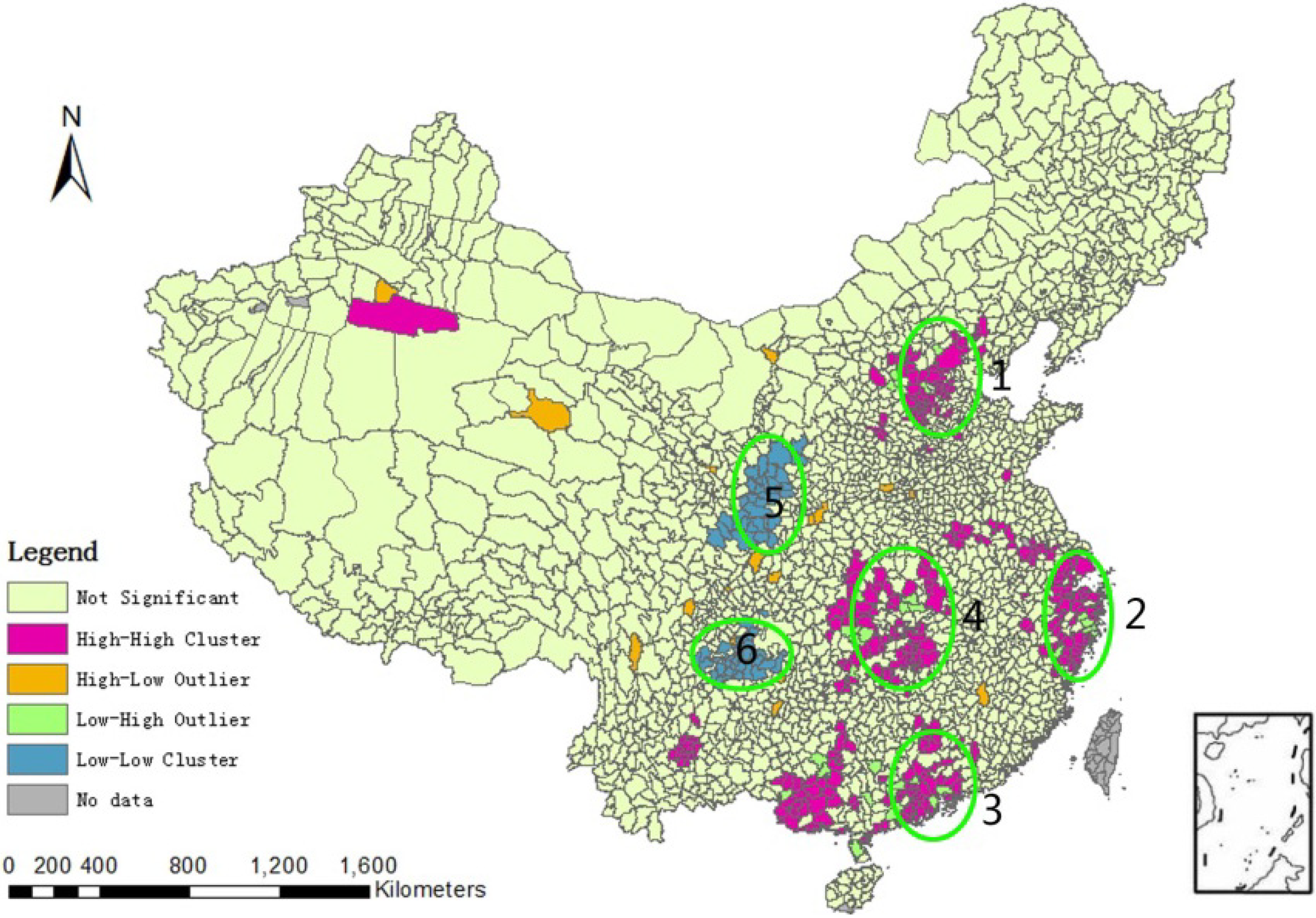
| Stratum | <7 | 7–13 | 13–16 | 16–18 | 18–22 | 22–24 | >24 |
| Incidence | 2.9 | 18.2 | 18.6 | 53.5 | 51.6 | 62.8 | 122.6 |
| Stratum | <0.5 | 0.5–2.5 | 2.5–6.7 | 6.7–26.3 | 26.3–65.8 | 65.8–105.8 | >105.8 |
| Incidence | 12.4 | 16.5 | 42.5 | 60.3 | 84.1 | 130.5 | 182.8 |
| Risk factors | AT | RH | GDP | FI | TI | PD0_9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RH | N | |||||
| GDP | Y | Y | ||||
| FI | N | N | Y | |||
| TI | Y | Y | N | Y | ||
| PD0_9 | Y | Y | N | Y | N | |
| MSD | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Risk factors | AT | RH | GDP | FI | TI | PD0_9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RH | 0.28 | |||||
| GDP | 0.31 | 0.28 | ||||
| FI | 0.17 | 0.16 | 0.24 | |||
| TI | 0.31 | 0.32 | 0.34 | 0.26 | ||
| PD0_9 | 0.31 | 0.33 | 0.35 | 0.30 | 0.42 | |
| MSD | 0.23 | 0.21 | 0.29 | 0.19 | 0.26 | 0.27 |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- China CDC 2009. Available online: http://www.cdcp.org.cn/editor/uploadfile/20090429174659788.ppt (accessed on 26 February 2014).
- Ang, L.W.; Koh, B.K.; Chan, K.P.; Chua, L.T.; James, L.; Goh, K.T. Epidemiology and control of hand, foot and mouth disease in Singapore, 2001–2007. Ann. Acad. Med. Singap. 2009, 38, 106–112. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Guo, Y.; Christakos, G.; Yang, W.; Liao, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Lai, S.; Chen, H. Hand, foot and mouth disease: Spatiotemporal transmission and climate. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2011, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatproedprai, S.; Theanboonlers, A.; Korkong, S.; Thongmee, C.; Wananukul, S.; Poovorawan, Y. Clinical and molecular characterization of hand-foot-and-mouth disease in Thailand, 2008–2009. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 63, 229–233. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, M.; Chen, E.-R.; Hsu, K.-H.; Twu, S.-J.; Chen, K.-T.; Tsai, S.-F.; Wang, J.-R.; Shih, S.-R. An epidemic of enterovirus71 infection in Taiwan. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 929–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podin, Y.; Gias, E.L.M.; Ong, F.; Leong, Y.-W.; Yee, S.-F.; Yusof, M.A.; Perera, D.; Teo, B.; Wee, T.-Y.; Ya, S.-C.; et al. Sentinel surveillance for human enterovirus 71 in Sarawak, Malaysia: Lessons from the first 7 years. BMC Public Health 2006, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, W.; Ren, J.; Tan, X.; Wang, Y.; Mao, N.; Xu, S.; Zhu, S.; Cui, A.; et al. An emerging recombinant human enterovirus 71 responsible for the 2008 outbreak of hand foot and mouth disease in Fuyang city of China. Virol J. 2010, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Feng, Z.; Yang, Y.; Self, S.; Gao, Y.; Longini, I.M.; Wakefield, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Chen, X.; et al. Hand, foot, and mouth disease in China: Patterns of spread and transmissibility during 2008–2009. Epidemiology 2011, 22, 781–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UK Communicable Disease Surveillance Centre. Hand, foot and mouth disease. Commun. Dis. Rep. 1980, 34, 3–4. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, E.; Lam, T.; Wong, C.; Chuang, S.K. Is hand, foot and mouth disease associated with meteorological parameters? Epidemiol. Infect. 2010, 138, 1779–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Jia, L.; Liao, Y.; Lai, S.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, D.; Yang, W. Determinants of the incidence of hand, foot and mouth disease in china using geographically weighted regression models. PLoS One 2012, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.D.; Zeng, D.J.; Wang, Q.Y.; Zheng, X.L.; Wang, F.Y. An epidemiological analysis of the Beijing 2008 hand-foot-mouth epidemic. Chin. Sci. Bulletin. 2010, 55, 1142–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.T. Analysis of HFMD epidemiology and risk factors in Hebei district of Tianjin from 2008 to 2009. Port Health Control. 2010, 15, 26–28. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, L.Y.; King, C.C.; Hsu, K.H.; Ning, H.C.; Tsao, K.C.; Li, C.C.; Huang, Y.C.; Shih, S.R.; Chiou, S.R.; Chen, P.Y. Risk factors of enterovirus 71 infection and associated hand, foot, and mouth disease/herpangina in children during an epi-demic in Taiwan. Pediatrics 2002, 109, e88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-F.; Li, X.-H.; Christakos, G.; Liao, Y.-L.; Zhang, T.; Gu, X.; Zheng, X.-Y. Geographical detectors-based health risk assessment and its application in the neural tube defects study of the Heshun Region, China. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 107–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Ren, D.; Zhu, J. Geographical detector-based risk assessment of the under-five mortality in the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake, China. PloS One 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.P. Regression Analysis with Dummy Variables. Understanding Regression Analysis; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Haining, R. Spatial Data Analysis: Theory and Practice; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Lawson, A.B.; Browne, W.J.; Rodeiro, C.L.V. Disease Mapping with WinBUGS and MLwiN; Wiley/John Wiley & Sons Inc: Chichester, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson, M.F. Interpolating mean rainfall using thin plate smoothing splines. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sys. 1995, 9, 385–403. [Google Scholar]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. China City Statistical Yearbooks-2009. China Statistics, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. China Statistical Yearbooks for Regional Economy-2009. China Statistics, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. China County Statistical Yearbooks-2009. China Statistics, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Grimmett, R.R.; Stirzaker, D.R. Probability and Random Processes; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, L.-Y.; Tsao, K.-C.; Hsia, S.-H.; Shih, S.-R.; Huang, C.-G.; Chan, W.-K.; Hsu, K.-H.; Fang, T.-Y.; Huang, Y.-C.; Lin, T.-Y. Transmission and clinical features of enterovirus 71 infections in household contacts in Taiwan. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2004, 291, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, F.-C.; Huang, H.-C.; Chi, C.-Y.; LIN, T.-L.; Liu, C.-C.; Jian, J.-W.; Hsu, L.-C.; Wu, H.-S.; Wang, H.-C.; Hsu, Y.-W.; et al. Epidemiological survey of enterovirus infections occurring in Taiwan between 2000 and 2005: Analysis of sentinel physician surveillance data. J. Med. Virol. 2007, 79, 1850–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.M.; Kang, K.; Wang, H.F.; Wang, Y.X.; Su, J. Analysis of HFMD s epidemic situation of 2009 in Henan province, forecast of HFMD prevalence trend, prevention and control strategy of 2010. Henan J. Prev. Med. 2010, 21, 161–169. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, X.F.; Huang, H.M.; Xie, M.; Zhang, J.Q.; Hu, J. Epidemiological analysis of hand-foot-mouth disease in Shanghai Yangpu District during 2005–2008. Chin. J. Dis. Control Prev. 2010, 14, 512–515. [Google Scholar]
- Better Support for Parents-Centre-Based Childcare to be of Good Quality and Accessible, while Remaining Affordable. Available online: http://www.ecda.gov.sg/PressReleases/Pages/Better-Support-For-Parents---Centre-Based-Child-Care-To-Be-Of-Good-Quality-And-Accessible-While-Remaining-Affordable.aspx. (accessed on 28 February 2014).
- Singapore Social Statistics In Brief 2004. Available online: http://unpan1.un.org/intradoc/groups/public/documents/APCITY/UNPAN024574.pdf. (accessed on 28 February 2014).
- Uterback, J.M.; Suarez, F.F. Innovation, competition, and industry structure. Res. Policy 1993, 22, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-F.; Xu, C.-D.; Tong, S.-L.; Chen, H.-Y.; Yang, W.-Z. Spatial dynamic patterns of hand-foot-mouth disease in the People’s Republic of China. Geospatial Health. 2013, 7, 381–390. [Google Scholar]
- Hii, Y.L.; Rocklov, J.; Ng, N. Short term effects of weather on hand, foot and mouth disease. PLoS One 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abad, F.X.; Pintó, R.M.; Bosch, A. Survival of enteric viruses on environmental fomites. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1994, 60, 3704–3710. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, F.; Ge, Y.; Wang, J. Optimal discretization for geographical detectors-based risk assessment. GISci. Remote Sens. 2013, 50, 78–92. [Google Scholar]
- Delmelle, E.; Kim, C.; Xiao, N.; Chen, W. Methods for space-time analysis and modeling: An overview. Int. J. Appl. Geospatial Res. 2013, 4, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, P.; Wakefield, J.; Best, N.; Briggs, D. Spatial Epidemiology: Methods and Applications; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Lawson, A.B.; Biggeri, A.; Bohning, D.; Lesaffre, E.; Viel, J.-F.; Bertollini, R. Disease Mapping and Risk Assessment for Public Health; Wiley/John Wiley & Sons Inc: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, J.; Wang, J.; Bo, Y.; Xu, C.; Hu, M.; Huang, D. Identification of Health Risks of Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease in China Using the Geographical Detector Technique. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 3407-3423. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph110303407
Huang J, Wang J, Bo Y, Xu C, Hu M, Huang D. Identification of Health Risks of Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease in China Using the Geographical Detector Technique. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2014; 11(3):3407-3423. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph110303407
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Jixia, Jinfeng Wang, Yanchen Bo, Chengdong Xu, Maogui Hu, and Dacang Huang. 2014. "Identification of Health Risks of Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease in China Using the Geographical Detector Technique" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 11, no. 3: 3407-3423. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph110303407
APA StyleHuang, J., Wang, J., Bo, Y., Xu, C., Hu, M., & Huang, D. (2014). Identification of Health Risks of Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease in China Using the Geographical Detector Technique. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 11(3), 3407-3423. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph110303407






