Seasonal Dynamics of Microcystis spp. and Their Toxigenicity as Assessed by qPCR in a Temperate Reservoir
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
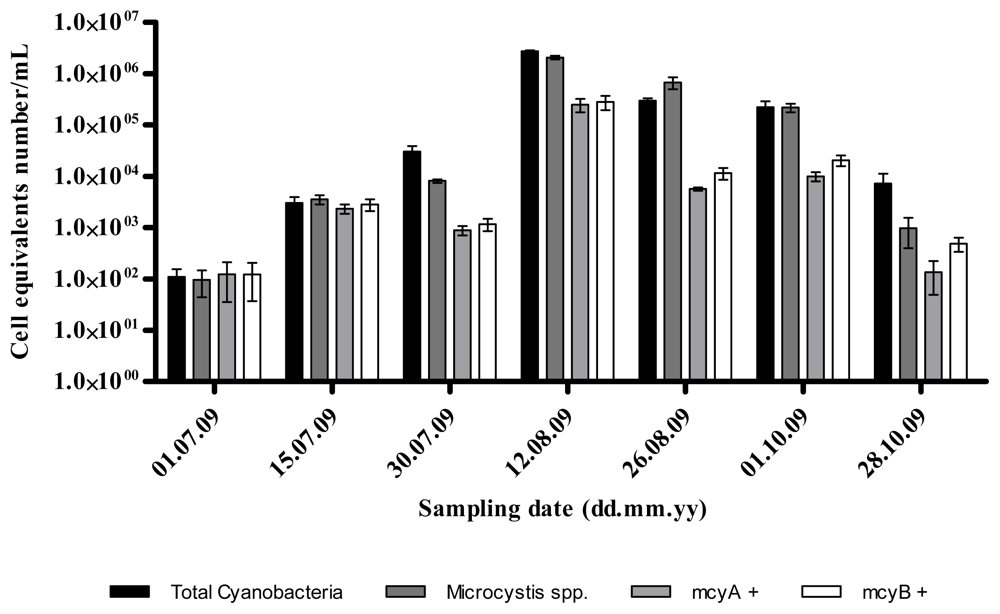
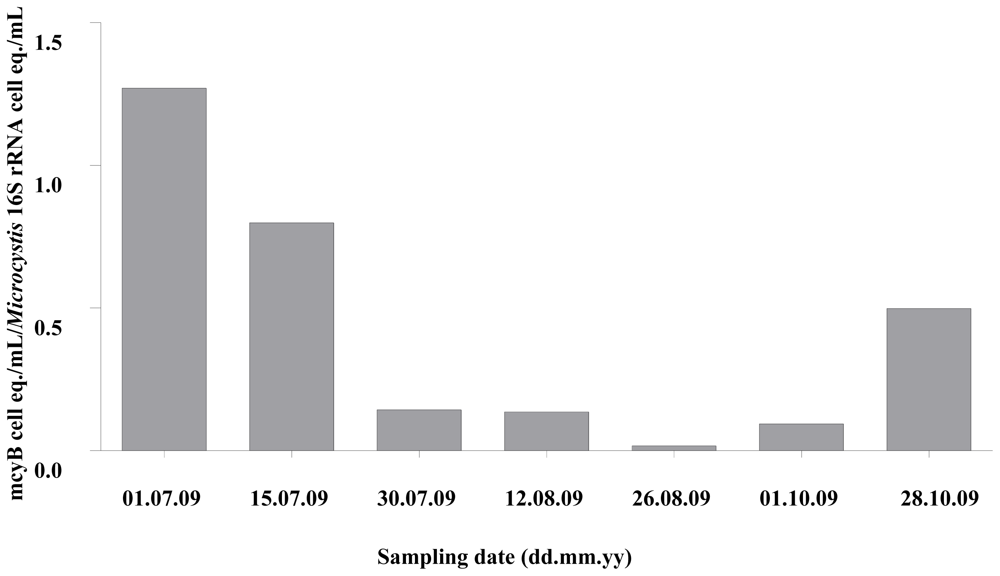
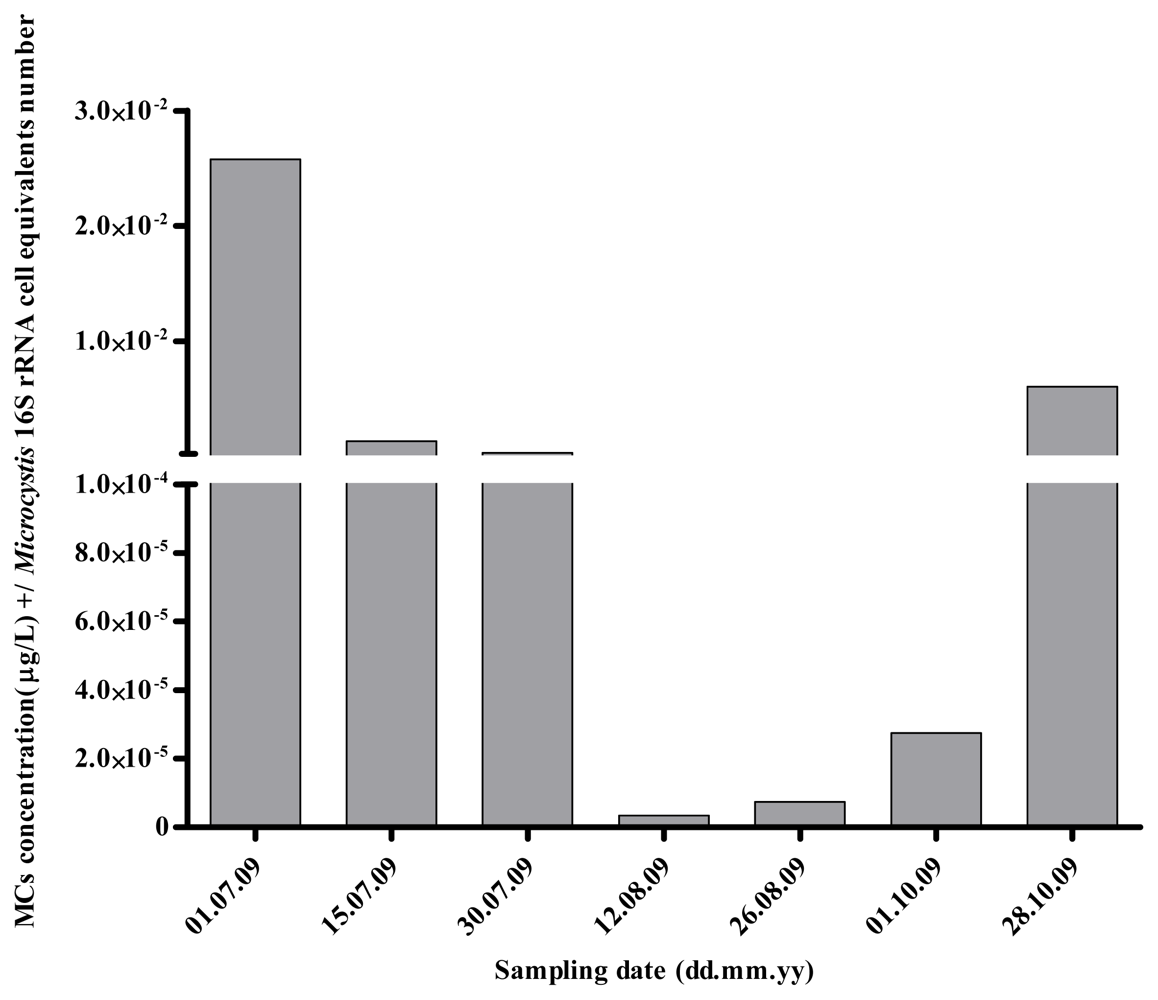
2.1. Quantitative Analysis of Microcystis spp. Community Composition by qPCR
2.2. Discussion
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Sample Collection and Analysis of Limnological Parameters
3.2. DNA Extraction and qPCR Reactions
3.3. Standard Curves Development
3.4. Quantification of MCs by ELISA
3.5. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
- Samples Availability: Available from the authors.
References
- Carpenter, SR; Caraco, NF; Correll, DL; Howarth, RW; Sharpley, AN; Smith, VH. Nonpoint pollution of surface waters with phosphorus and nitrogen. Ecol. Appl 1998, 8, 559–568. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, VH; Tilman, GD; Nekola, JC. Eutrophication: Impacts of excess nutrient inputs on freshwater, marine, and terrestrial ecosystems. Environ. Poll 1999, 100, 179–196. [Google Scholar]
- Kuiper-Goodman, T; Falconer, I; Fitzgerald, J. Human Health Aspects. In Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water: A Guide to Their Public Health Consequences, Monitoring and Management; Chorus, I, Bartram, J, Eds.; E & FN Spon: London, UK, 1999; pp. 113–153. [Google Scholar]
- Sivonen, K; Jones, G. Cyanobacterial Toxins. In Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water: A Guide to Their Public Health Consequences, Monitoring and Management; Chorus, I, Bartram, J, Eds.; E & FN Spoon: London, UK, 1999; pp. 55–71. [Google Scholar]
- Carmichael, WW; Falconer, IR. Diseases Related to Freshwater Blue Green Algal Toxins, and Control Measures. In Algal Toxins in Seafood and Drinking Water; Falconer, IR, Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1993; pp. 187–209. [Google Scholar]
- Carmichael, WW. The toxins of cyanobacteria. Sci. Am 1994, 270, 78–86. [Google Scholar]
- Vasconcelos, VM. Cyanobacterial toxins in Portugal: Effects on aquatic animals and risk for human health. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res 1999, 32, 249–254. [Google Scholar]
- Vasconcelos, VM; Sivonen, K; Evans, WR; Carmichael, WW; Namikoshi, M. Isolation and characterization of microcystins (heptapeptide hepatotoxins) from Portuguese strains of Microcystis aeruginosa Kutz. emed Elekin. Arch. Hydrobiol 1995, 134, 295–305. [Google Scholar]
- Vasconcelos, VM; Sivonen, K; Evans, WR; Carmichael, WW; Namikoshi, M. Microcystin (heptapeptide hepatotoxins) diversity in cyanobacterial blooms collected in Portuguese fresh waters. Water Res 1996, 30, 2377–2384. [Google Scholar]
- MacKintosh, C; Beattie, KA; Klumpp, S; Cohen, P; Codd, GA. Cyanobacterial MC-LR is a potent and specific inhibitor of protein phosphatases 1 and 2A from both mammals and higher plants. FEBS Lett 1990, 264, 187–192. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya, R; Sugendran, K; Dangi, RS; Rao, PV. Toxicity evaluation of freshwater cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa PCC 7806: II. Nephrotoxicity in rats. Biomed. Environ. Sci 1997, 10, 93–101. [Google Scholar]
- Falconer, IR. Tumor promotion and liver injury caused by oral consumption of cyanobacteria. Environ. Toxicol. Water Qual 1991, 6, 177–184. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, E; Kondo, F; Terao, K; Harada, K-I. Neoplastic nodular formation in mouse liver induced by repeated intraperitoneal injections of microcystin-LR. Toxicon 1997, 35, 1453–1457. [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich, D; Hoeger, S. Guidance values for microcystins in water and cyanobacterial supplement products (blue-green algal supplements): A reasonable or misguided approach? Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol 2005, 203, 273–289. [Google Scholar]
- Dittmann, E; Neilan, BA; Erhard, M; Von Döhren, H; Börner, T. Insertional mutagenesis of a peptide synthetase gene that is responsible for hepatotoxin production in the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa PCC 7806. Mol. Microbiol 1997, 26, 779–787. [Google Scholar]
- Neilan, BA; Dittmann, E; Rouhiainen, L; Bass, RA; Schaub, V; Sivonen, K; Börner, T. Nonribosomal peptide synthesis and toxigenicity of cyanobacteria. J. Bacteriol 1999, 181, 4089–4097. [Google Scholar]
- Nishizawa, T; Asayama, M; Fujii, K; Harada, KI; Shirai, M. Genetic analysis of the peptide synthetase genes for a cyclic heptapeptide microcystin in Microcystis spp. J Biochem 1999, 126, 520–529. [Google Scholar]
- Tillett, D; Dittmann, E; Erhard, M; von Döhren, H; Börner, T; Neilan, BA. Structural organization of microcystin biosynthesis in Microcystis aeruginosa PCC7806: An integrated peptide-polyketide synthetase system. Chem. Biol 2000, 7, 753–764. [Google Scholar]
- Harada, K. Laboratory Analysis of Cyanotoxins. In Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water: A Guide to Their Public Health Consequences, Monitoring, and Management; Chorus, I, Bartram, J, Eds.; E & FN Spon: London, UK, 1999; pp. 369–405. [Google Scholar]
- Sivonen, K. Emerging high throughput analyses of cyanobacterial toxins and toxic cyanobacteria. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol 2008, 619, 539–557. [Google Scholar]
- Nishizawa, T; Ueda, A; Asayama, M; Fujii, K; Harada, K-I; Ochi, K; Shirai, M. Polyketide synthase gene coupled to the peptide synthetase module involved in the biosynthesis of the cyclic heptapeptide microcystin. J. Biochem 2000, 127, 779–789. [Google Scholar]
- Hisbergues, M; Christiansen, G; Rouhiainen, L; Sivonen, K; Börner, T. PCR-based identification of microcystin-producing genotypes of different cyanobacterial genera. Arch. Microbiol 2003, 180, 402–410. [Google Scholar]
- Rantala, A; Rajaniemi-Wacklin, P; Lyra, C; Lepisto, L; Rintala, J; Mankiewicz-Boczek, J; Sivonen, K. Detection of microcystin-producing cyanobacteria in finnish lakes with genus-specific microcystin synthetase gene E (mcyE) PCR and associations with environmental factors. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 2006, 72, 6101–6110. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, M; Yoshida, T; Takashima, Y; Hosoda, N; Hiroishi, S. Dynamics of microcystin-producing and non-microcystin-producing Microcystis populations is correlated with nitrate concentration in a Japanese lake. FEMS Microbiol. Lett 2007, 266, 49–53. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, JH; Hidaka, T; Tsuno, H. Quantification of toxic Microcystis and evaluation of its dominance ratio in blooms using real-time PCR. Environ. Sci. Technol 2008, 43, 812–818. [Google Scholar]
- Rinta-Kanto, JM; Konopko, EA; DeBruyn, JM; Bourbonniere, RA; Boyer, GL; Wilhelm, SW. Lake Erie Microcystis: Relationship between microcystin production, dynamics of genotypes and environmental parameters in a large lake. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 665–673. [Google Scholar]
- Sabart, M; Pobel, D; Briand, E; Combourieu, B; Salencon, MJ; Humbert, JF; Latour, D. Spatiotemporal variations in microcystin concentrations and in the proportions of microcystin-producing cells in several Microcystis aeruginosa populations. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 2010, 76, 4750–4759. [Google Scholar]
- Vaitomaa, J; Rantala, A; Halinen, K; Rouhiainen, L; Tallberg, P; Mokelke, L; Sivonen, K. Quantitative real-time pcr for determination of microcystin synthetase E copy numbers for Microcystis and Anabaena in lakes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 2003, 69, 7289–7297. [Google Scholar]
- Kaebernick, M; Neilan, BA. Ecological and molecular investigations of cyanotoxin production. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol 2001, 35, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Chorus, I. Environmental Factors and MC Levels in Waterbodies. In Cyanotoxins: Occurrence, Causes, Consequences; Chorus, I, Ed.; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2001; pp. 159–177. [Google Scholar]
- Janse, I; Kardinaal, WEA; Agterveld, MK-V; Meima, M; Visser, PM; Zwart, G. Contrasting microcystin production and cyanobacterial population dynamics in two Planktothrix-dominated freshwater lakes. Environ. Microbiol 2005, 7, 1514–1524. [Google Scholar]
- Gobler, CJ; Davis, TW; Coyne, KJ; Boyer, GL. Interactive influences of nutrient loading, zooplankton grazing, and microcystin synthetase gene expression on cyanobacterial bloom dynamics in a eutrophic New York lake. Harmful Algae 2007, 6, 119–133. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, TW; Berry, DL; Boyer, GL; Gobler, CJ. The effects of temperature and nutrients on the growth and dynamics of toxic and nontoxic strains of Microcystis during cyanobacterial blooms. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 715–725. [Google Scholar]
- Kardinaal, WEA; Janse, I; Kamst-Van Agterveld, M; Meima, M; Snoek, J; Mur, LR; Huisman, J; Zwart, G; Visser, PM. Microcystis genotype succession in relation to microcystin concentrations in freshwater lakes. Aquat. Microb. Ecol 2007, 48, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Kardinaal, WEA; Tonk, L; Janse, I; Hol, S; Slot, P; Huisman, J; Visser, PM. Competition for light between toxic and nontoxic strains of the harmful cyanobacterium Microcystis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 2007, 73, 2939–2946. [Google Scholar]
- Welker, M; Šejnohová, L; Némethová, D; von Döhren, H; Jarkovský, J; Maršálek, B. Seasonal shifts in chemotype composition of Microcystis sp. communities in the pelagial and sediment of a shallow reservoir. Limnol. Oceanogr 2007, 52, 609–691. [Google Scholar]
- Oliva Teles, L; Pereira, E; Saker, M; Vasconcelos, V. Virtual experimentation on cyanobacterial bloom dynamics and its application to a temperate reservoir (Torrão, Portugal). Lakes Reserv. Res. Manag 2008, 13, 135–143. [Google Scholar]
- Kurmayer, R; Christiansen, G; Chorus, I. The abundance of microcystin-producing genotypes correlates positively with colony size in Microcystis sp. and determines its microcystin net production in lake wannsee. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 2003, 69, 787–795. [Google Scholar]
- Kurmayer, R; Kutzenberger, T. Application of real-time PCR for quantification of microcystin genotypes in a population of the toxic cyanobacterium Microcystis sp. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 2003, 69, 6723–6730. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, W; Liu, X; Tan, J; Li, D; Yang, H. Diversity and dynamics of microcystin—Producing cyanobacteria in China’s third largest lake, Lake Taihu. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 637–644. [Google Scholar]
- Ohtake, A; Shirai, M; Aida, T; Mori, N; Harada, KI; Matsuura, K; Suzuki, M; Nakano, M. Toxicity of Microcystis species isolated from natural blooms and purification of the toxin. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 1989, 55, 3202–3207. [Google Scholar]
- Shirai, M; Ohtake, A; Sano, T; Matsumoto, S; Sakamoto, T; Sato, A; Aida, T; Harada, KI; Shimada, T; Suzuki, M; et al. Toxicity and toxins of natural blooms and isolated strains of Microcystis spp. (cyanobacteria) and improved procedure for purification of cultures. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 1991, 57, 1241–1245. [Google Scholar]
- Vezie, C; Brient, L; Sivonen, K; Bertru, G; Lefeuvre, J-C; Salkinoja-Salonen, M. Variation of MC content of cyanobacterial bloom sand isolated strains in Lake Grand-Lieu (France). Microb. Ecol 1998, 35, 126–135. [Google Scholar]
- Rohrlack, T. Isolation and characterization of colony-forming Microcystis aeruginosa strains. In Cyanotoxins: Occurrences, Causes, Consequences; Chorus, I, Ed.; Springer Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2001; pp. 152–158. [Google Scholar]
- Briand, E; Escoffier, N; Straub, C; Sabart, M; Quiblier, C; Humbert, J-F. Spatiotemporal changes in the genetic diversity of a bloom-forming Microcystis aeruginosa (cyanobacteria) population. ISME J 2009, 3, 419–429. [Google Scholar]
- Nonneman, D; Zimba, PV. A PCR-based test to assess the potential for microcystin occurrence in channel catfish production ponds. J. Phycol 2002, 38, 230–233. [Google Scholar]
- Briand, E; Gugger, M; Francois, J-C; Bernard, C; Humbert, J-F; Quiblier, C. Temporal variations in the dynamics of potentially microcystin-producing strains in a bloom-forming Planktothrix agardhii (cyanobacterium) population. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 2008, 74, 3839–3848. [Google Scholar]
- Kardinaal, WEA; Visser, PM. Dynamics of Cyanobacterial Toxins: Sources of Variability in Microcystin Concentrations. In Harmful Cyanobacteria; Huisman, J, Matthijs, HCP, Visser, PM, Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2005; pp. 41–63. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, M; Yoshida, T; Kashima, A; Takashima, Y; Hosoda, N; Nagasaki, K; Hiroishi, S. Ecological dynamics of the toxic bloom-forming cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa and its cyanophages in freshwater. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 2008, 74, 3269–3273. [Google Scholar]
- Crosby, LD; Criddle, CS. Understanding bias in microbial community analysis techniques due to rrn operon copy number heterogeneity. BioTechniques 2003, 34, 790–802. [Google Scholar]
- Nübel, U; Garcia-Pichel, F; Muyzer, G. PCR primers to amplify 16S rRNA genes from cyanobacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 1997, 63, 3327–3332. [Google Scholar]
- Neilan, BA; Jacobs, D; Therese, DD; Blackall, LL; Hawkins, PR; Cox, PT; Goodman, AE. rRNA sequences and evolutionary relationships among toxic and nontoxic cyanobacteria of the genus Microcystis. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol 1997, 47, 693–697. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, FS; Huang, X; Wei, RD. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for microcystins in blue-green algal blooms. J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem 1990, 73, 451–456. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, J; Saker, M; Moreira, C; Welker, M; Fastner, J; Vasconcelos, V. Peptide diversity in strains of the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa isolated from Portuguese water supplies. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol 2009, 82, 951–961. [Google Scholar]


| Sampling date | 01.07.09 | 15.07.09 | 30.07.09 | 12.08.09 | 26.08.09 | 01.10.09 | 28.10.09 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 8.8 | 8.4 | 8.1 | 8.7 | 7.8 | 6.1 | 6.9 |
| Dissolved oxygen (mg/L) | - | 6.5 | 10.5 | - | 4.2 | 7.0 | 4.0 |
| Temperature (°C) | 26.1 | 25.1 | 25.2 | 27.0 | 25.3 | 22.8 | 20.5 |
| Conductivity (μS/Cm) | 60 | 63 | 65 | 67 | 74 | 118 | 155 |
| Target gene | Reference strain | Efficiency | Slope | Y-intercept | R2 | Melting temperature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cyanobacteria 16S rRNA | M. aeruginosa genomic DNA | 90.7 | −3.568 | 37.288 | 0.991 | 86.5–87.0 °C |
| Microcystis 16S rRNA | M. aeruginosa genomic DNA | 88.4 | −3.636 | 34.156 | 0.999 | 87.5–88.0 °C |
| Cyanobacterial mcyA | M. aeruginosa genomic DNA | 87.6 | −3.660 | 35.092 | 0.998 | 82.0–82.5 °C |
| Microcystis mcyB | M. aeruginosa genomic DNA | 88.3 | −3.637 | 34.862 | 1.000 | 81.5–82.0 °C |
| Spearman correlation values | pH | Dissolved oxygen (mg/L) | Temp. (°C) | Cond. (μS/Cm) | MC-LR (μg eq/L) | Cyanob. 16S rRNA | Microcystis 16S rRNA | Cyanob. mcyA | Microcystis mcyB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | |||||||||
| Dissolved oxygen (mg/L) | −0.31 | ||||||||
| Temperature (°C) | 0.79 | −0.26 | |||||||
| Conductivity (μS/Cm) | −0.86 | 0.14 | −0.57 | ||||||
| Microcystins μg/L | −0.43 | 0.20 | −0.11 | 0.71 | |||||
| Cyanobacterial 16S rRNA (cell number equivalent/mL) | −0.29 | 0.49 | 0.29 | 0.50 | 0.75 | ||||
| Microcystis16S rRNA (cell number equivalent/mL) | −0.18 | 0.60 | 0.36 | 0.32 | 0.68 | 0.96 | |||
| Cyanobacterial mcyA (cell number equivalent/mL) | −0.21 | 0.60 | 0.21 | 0.32 | 0.79 | 0.86 | 0.93 | ||
| Microcystis mcyB (cell number equivalent/mL) | −0.21 | 0.60 | 0.21 | 0.32 | 0.79 | 0.86 | 0.93 | 1.00 | |
| Target | Primer | Sequence (5′–3′) | Size (bp) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cyanobacteria 16S rRNA | Cya 359F Cya 781R | GGGGAATYTTCCGCAATGGG GACTACWGGGGTATCTAATCCCWTT | 446 | [16] |
| Microcystis 16S rRNA | Micr 184F Micr 431R | GCCGCRAGGTGAAAMCTAA AATCCAAARACCTTCCTCCC | 220 | [16] |
| mcyA All genera | mcyA CD1F mcyA CD1R | AAAATTAAAAGCCGTATCAAA AAAAGTGTTTTATTAGCGGCTCAT | 297 | [22] |
| mcyB Microcystis | mcyB 2959F mcyB 3278R | TGGGAAGATGTTCTTCAGGTATCCAA AGAGTGGAAACAATATGATAAGCTAC | 350 | [46] |
| PCR protocol | Primer pair | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial denaturation | Denaturation | Annealing | Extension | Number of cycles | |
| CYA 359F/781R | 5 min at 95 °C | 15 s at 95 °C | 15 s at 60 °C | 30 s at 72 °C | 50 |
| Micr 184F/381R | 5 min at 95 °C | 15 s at 95 °C | 30 s at 52 °C | 30 s at 72 °C | 40 |
| mcyA CD1F/CD1R | 5 min at 95 °C | 15 s at 95 °C | 30 s at 59 °C | 30 s at 72 °C | 40 |
| mcyB 2959F/3278R | 5 min at 95 °C | 15 s at 95 °C | 30 s at 59 °C | 30 s at 72 °C | 40 |
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Martins, A.; Moreira, C.; Vale, M.; Freitas, M.; Regueiras, A.; Antunes, A.; Vasconcelos, V. Seasonal Dynamics of Microcystis spp. and Their Toxigenicity as Assessed by qPCR in a Temperate Reservoir. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1715-1730. https://doi.org/10.3390/md9101715
Martins A, Moreira C, Vale M, Freitas M, Regueiras A, Antunes A, Vasconcelos V. Seasonal Dynamics of Microcystis spp. and Their Toxigenicity as Assessed by qPCR in a Temperate Reservoir. Marine Drugs. 2011; 9(10):1715-1730. https://doi.org/10.3390/md9101715
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartins, António, Cristiana Moreira, Micaela Vale, Marisa Freitas, Ana Regueiras, Agostinho Antunes, and Vitor Vasconcelos. 2011. "Seasonal Dynamics of Microcystis spp. and Their Toxigenicity as Assessed by qPCR in a Temperate Reservoir" Marine Drugs 9, no. 10: 1715-1730. https://doi.org/10.3390/md9101715
APA StyleMartins, A., Moreira, C., Vale, M., Freitas, M., Regueiras, A., Antunes, A., & Vasconcelos, V. (2011). Seasonal Dynamics of Microcystis spp. and Their Toxigenicity as Assessed by qPCR in a Temperate Reservoir. Marine Drugs, 9(10), 1715-1730. https://doi.org/10.3390/md9101715







