Cyanobacterial Toxins as Allelochemicals with Potential Applications as Algaecides, Herbicides and Insecticides
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Raison D’Être of Cyanobacterial Toxins?
3. Chemical Defenses of Cyanobacteria Against Planktivores
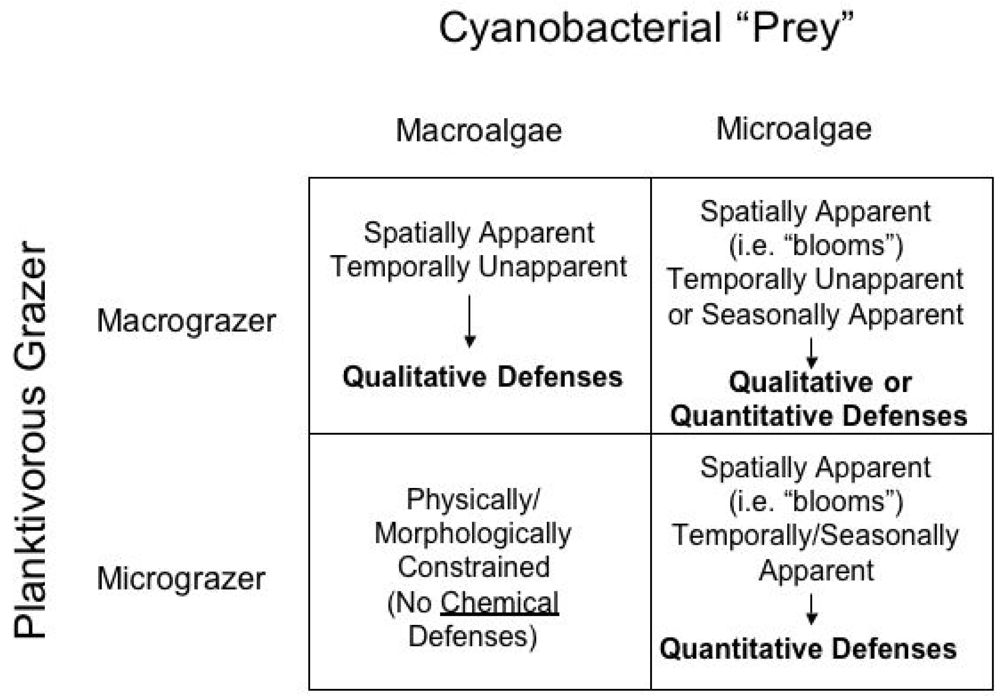
3.1 Apparency Theory
3.2. Apparency Theory and Chemical Ecology of Cyanobacteria
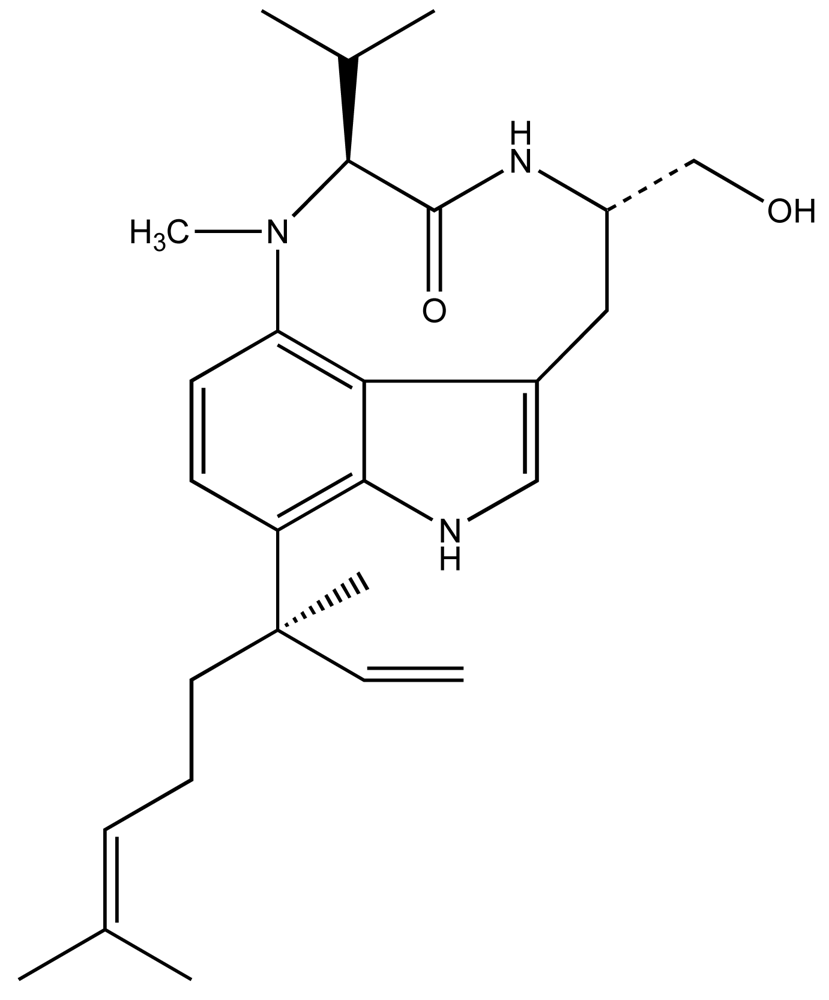
3.3. Macrograzer-Macroalgae Interactions: Qualitative Toxins of Lyngbya majuscula
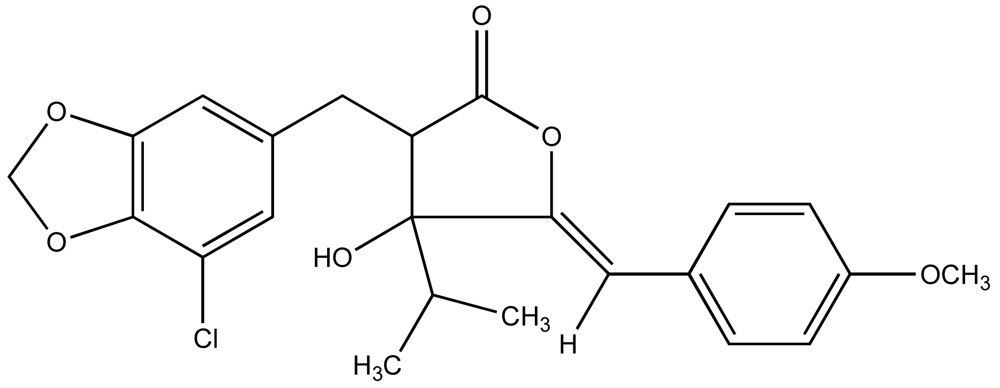
3.4. Micrograzer-Microalgae Interactions: Quantitative Defenses of Microcystis aerugunosa Against Daphnia
3.5. Macrograzer-Microalgae Interactions: Seasonal Apparency and Microcystins as Quantitative Defense Against Freshwater Fish
4. Allelopathic Compounds from Cyanobacteria
5. Potential Commercial Development of Insectides, Algaecides and Herbicides from Cyanobacteria
6. Allelopathic and Mosquito Larvicidal Compounds from Cyanobacteria in the Florida Everglades
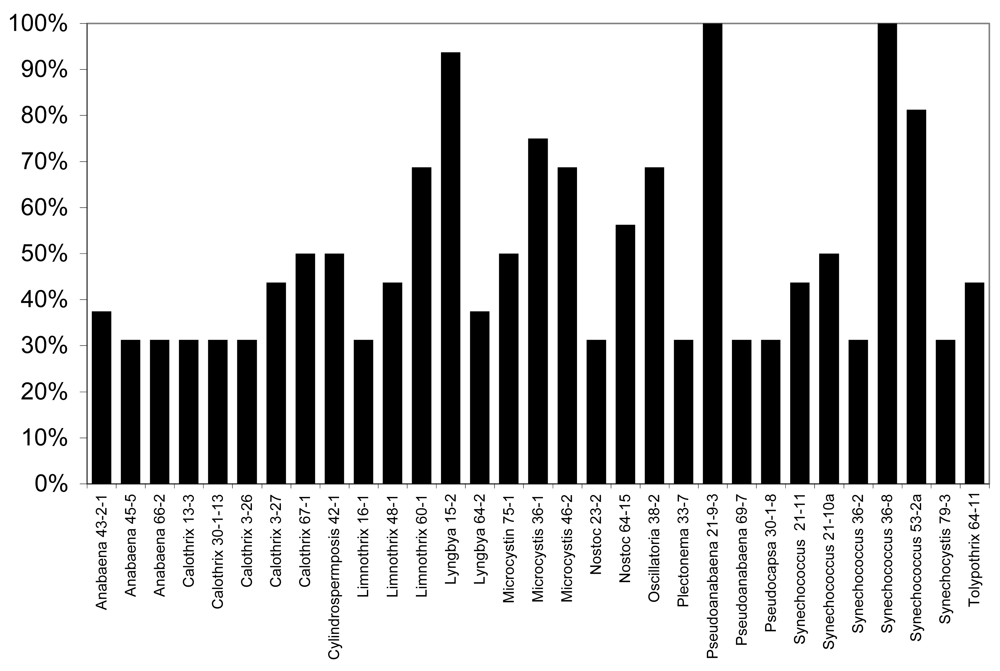
6.1. Antialgal Metabolites from Cyanobacteria and Allelopathy in the Florida Everglades
6.2. Mosquito Larvicidal Activity of Cyanobacterial Isolates
7. Conclusion
Acknowledgements
References
- Fraenkel, G. Raison D’Être of Secondary Plant Substances. Science 1959, 129, 1466–1470. [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich, PR; Raven, PH. Butterflies and Plants: A Study in Coevolution. Evolution 1964, 18, 586–608. [Google Scholar]
- Benson, JM. Cyanobacterial Toxins. Drugs 2008, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Gerwick, WH; Tan, LT; Sitachitta, N. Cordell, G, Ed.; The Alkaloids; Chemistry and Biology: Academic Press, 2001; Volume 57, pp. 75–117. [Google Scholar]
- Francis, G. Poisonous Australian Lake. Nature 1878, 18, 11–12. [Google Scholar]
- Chorus, J; Falconer, IR; Salas, HJ; Bartram, J. Health Risks Caused by Freshwater Cyanobacteria in Recreational Waters. J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev 2000, 3, 323–347. [Google Scholar]
- Hitzfield, BC; Höger, SJ; Dietrich, DR. Cyanobacterial Toxins: Removal During Drinking Water Treatment, and Human Risk Assessment. Environ Health Perspect 2000, 108(Suppl 1), 113–122. [Google Scholar]
- Duy, TN; Lam, PK; Shaw, GR; Connell, DW. Toxicology and Risk Assessment of Freshwater Cyanobacterial (Blue-Green Algal) Toxins in Water. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 2000, 163, 113–185. [Google Scholar]
- Azevedo, SM; Carmichael, WW; Jochimsen, EM; Rinehart, KL; Lau, S; Shaw, GR; Eaglesham, GK. Human Intoxication by Microcystins During Renal Dialysis Treatment in Caruaru, Brazil. Toxicology 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, PV; Gupta, N; Bhaskar, AS; Jayaraj, R. Toxins and Bioactive Compounds from Cyanobacteria and Their Implications on Human Health. J Environ Biol 2002, 23, 215–224. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, HU; Frank, C. Toxicity Assessment of Cyanobacterial Toxin Mixtures. Environ Toxicol 2002, 17, 395–399. [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths, DJ; Saker, ML. The Palm Island Mystery Disease 20 Years On: A Review of Research on the Cyanotoxin Cylindrospermopsin. Environ Toxicol 2003, 18, 78–93. [Google Scholar]
- Codd, GA; Morrison, LF; Metcalf, JS. Cyanobacterial Toxins: Risk Management for Health Protection. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 2005, 203, 264–272. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, I; Webb, PM; Schluter, PJ; Shaw, GR. Recreational and Occupational Field Exposure to Freshwater Cyanobacteria – A Review of Anecdotal and Case Reports, Epidemiological Studies and the Challenges for Epidemiologic Assessment. Environ Health 2006, 5, 6–19. [Google Scholar]
- Osborne, NJT; Webb, PM; Shaw, GR. The Toxins of Lyngbya majuscula and Their Human and Ecological Health Effects. Environ Int 2001, 27, 381–392. [Google Scholar]
- Feeney, P. Wallace, J, Mansell, R, Eds.; Plant Apparency and Chemical Defense. In Recent Advances in Phytochemistry; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1976; Volume 10, pp. 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Rhoades, DF; Cates, RG. Toward a General Theory of Plant Antiherbivore Chemistry. Recent Adv Phytochem 1976, 10, 168–213. [Google Scholar]
- Staley, JT. The Gas Vacuole: An Early Organelle of Prokaryote Motility? Origins Life 1980, 10, 111–116. [Google Scholar]
- Whitton, BA; Potts, M. The Ecology of Cyanobacteria: Their Diversity in Time and Space; Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Lampert, W. Laboratory Studies on Zooplankton-Cyanobacteria Interactions. N Z J Mar Freshwater Res 1987, 21, 483–490. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, T. Filtering Rates of Daphnia by Oscillatoria in Lake Washington. Limnol Oceanogr 1993, 18, 231–234. [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner, TWR; Hairston, NG, Jr; Howarth, RW. Feeding Rates and Filament Clipping by Crustacean Zooplankton Consuming Cyanobacteria. Int Ver Theor Angew Limnol Verh 1994, 25, 2375–2381. [Google Scholar]
- Epp, GT. Grazing on Filamentous Cyanobacteria by Daphnia pulicaria. Limnol Oceanogr 1996, 41, 560–567. [Google Scholar]
- DeMott, WR; Müller-Navrra, DC. The Importance of Highly Unsaturated Fatty Acids in Zooplankton Nutrition: Evidence from Experiments with Daphnia, a Cyanobacterium and Lipid Emulsions. Freshwater Biol 1997, 38, 649–664. [Google Scholar]
- Von Elert, E; Wolffrom, T. Supplementation of Cyanobacterial Food with Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Doe s Not Improve Growth of Daphnia. Limnol. Oceanogr 2001, 46, 1552–1558. [Google Scholar]
- Von Elert, E; Martin-Creuzburg, D; Le Coz, JR. Absence of Sterols Constrains Carbon Transfer Between Cyanobacteria and a Freshwater Herbivore (Daphnia galeata). Proc Royal Soc London 2003, 270, 1209–1214. [Google Scholar]
- Burja, AM; Banaigs, B; Abou-Mansour, E; Burgess, JG; Wright, PC. Marine Cyanobacteria – A Prolific Source of Natural Products. Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 9347–9377. [Google Scholar]
- Pittman, SJ; Pittman, KM. Short-Term Consequences of a Benthic Cyanobacterial Bloom (Lyngbya majuscula) for Fish and Penaeid Prawns in Moreton Bay (Queensland, Australia). Estuarine Coastal Shelf Sci 2005, 619–632. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, VJ; Arthur, KE; Ritson-Williams, R; Ross, C; Sharp, K. Chemical Defenses: From Compounds to Communities. Biol Bull 2007, 213, 226–251. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, VJ; Pennings, SC. Diet-Derived Chemical Defense in the Sea Hare Stylocheilus longicauda. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 1991, 151, 227–243. [Google Scholar]
- Pennings, SC; Weiss, AM; Paul, VJ. Secondary Metabolites of the Cyanobacterium Microcoleus lyngbyaceus and the Sea Hare Stylocheilus longicauda palatability and toxicity. Mar Biol 1996, 126, 735–743. [Google Scholar]
- Nagle, DG; Paul, VJ. Chemical Defense of a Marine Cyanobacterial Bloom. J Exp Biol Ecol 1998, 225, 29–38. [Google Scholar]
- Nagle, DG; Paul, VJ. Production of Secondary Metabolites by Filamentous Tropical Marine Cyanobacteria: Ecological Functions of the Compounds. J Phycol 1999, 35, 1412–1421. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, VJ; Cruz-Rivera, E; Thacker, RW. McClintock, J, Baker, W, Eds.; Chemical Mediation of Macroalgal-Herbivore Interactions: Ecological and Evolutionary Perspectives. In Marine Chemical Ecology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001; pp. 227–265. [Google Scholar]
- Capper, A; Cruz-Rivera, E; Paul, V; Tibbetts, I. Chemical Deterrence of a Marine Cyanobacterium Against Sympatric and Non-Sympatric Consumers. Hydrobiologia 2006, 553(1), 319–326. [Google Scholar]
- Capper, A; Tibbetts, IR; O’Neil, JM; Shaw, GR. Dietary Selectivity for the Toxic Cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula and Resultant Growth Rates in Two Species of Ophistobranch Mollusc. J Exp Biol Ecol 2006b, 331, 133–144. [Google Scholar]
- Capper, A; Tibbetts, IR; O’Neil, JM; Shaw, GR. Feeding Preference and Deterrence in Rabbitfish Siganus fuscescens for the Cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula in Moreton Bay, South-East Queensland, Australia. J Fish Biol 2006, 68(5), 1589–1609. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz-Rivera, E; Paul, VJ. Chemical Deterrence of a Cyanobacterial Metabolite Against Generalized and Specialized Grazers. J Chem Ecol 2007, 33, 213–217. [Google Scholar]
- Cardellina, J; Marner, FJ; Moore, RE. Seaweed Dermatitis: Structure of Lyngbyatoxin A. Science 1979, 204, 193–195. [Google Scholar]
- Nagle, DG; Paul, VJ; Roberts, MA. Ypoamide, a New Broadly Acting Feeding Deterrent from the Marine Cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula. Tetrah B edron Lett 1996, 37, 6263–6266. [Google Scholar]
- Arthur, KE; Limpus, CJ; Roelfsema, CM; Udy, JW; Shaw, GR. A Bloom of Lyngbya majuscula in Shoalwater Bay, Queensland, Australia: An Important Feeding Ground for the Green Turtle (Chelonia mydas). Harmful Algae 2006, 5, 251–265. [Google Scholar]
- Pennings, SC; Paul, VJ. Sequestration of Dietary Secondary Metabolites by Three Species of Sea Hares: Location, Specificity and Dynamics. Mar Biol 1993, 117, 535–546. [Google Scholar]
- Capper, A; Tibbetts, IR; O’Neil, JM; Shaw, GR. The Fate of Lyngbya majuscula Toxins in Three Potential Consumers. J Chem Ecol 2005, 31, 1595–1606. [Google Scholar]
- Pennings, SC; Paul, VJ; Dunbar, DC; Hamann, MT; Lumbang, WA; Novak, B; Jacobs, RS. Unpalatable Compounds in the Marine Gastropod Dolabella auricularia: Distribution and Effect of Diet. J Chem Ecol 1999, 25, 735–755. [Google Scholar]
- Pennings, SC; Nastisch, S; Paul, VJ. Vulnerability of Sea Hares to Fish Predators: Importance of Diet and Fish Species. Coral Reefs 2001, 20, 320–324. [Google Scholar]
- Nagai, H; Yasumoto, T; Hokama, Y. Aplysiatoxin and Debromoaplysiatoxin as the Causative Agents of Red Alga Gracilaria coronopifolia Poisoning in Hawaii. Toxicon 1996, 34, 753–761. [Google Scholar]
- Luesch, H; Harrigan, GG; Goetz, G; Horgen, FD. The Cyanobacterial Origin of Potent Anticancer Agents Originally Isolated from Sea Hares. Curr Med Chem 2002, 9, 1791–1806. [Google Scholar]
- Rohrlack, T; Christoffersen, K; Friberg-Jensen, U. Frequency of Inhibitors of Daphnid Trypsin in the Widely Distributed Cyanobacterial Genus Planktothrix. Environ Microbiol 2005, 7, 1667–1669. [Google Scholar]
- Lampert, W. Inhibitory and Toxic Effects of Blue-Green Algae on Daphnia. Int Rev Ges Hydrobiol 1981, 66, 285–298. [Google Scholar]
- Nizan, S; Dimentman, C; Shilo, M. Acute Toxic Effects of Cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa on Daphnia magna. Limnol Oceanogr 1986, 31, 497–502. [Google Scholar]
- Peñaloza, R; Rojas, M; Vila, I; Zambrano, F. Toxicity of a Soluble Peptide from Microcystis sp. to Zooplankton and Fish. Freshwater Biol 1991, 24, 233–240. [Google Scholar]
- Jungmann, D; Henning, M; Jüttner, F. Are the Same Compounds in Microcystis Responsible for Toxicity to Daphnia and Inhibition of its Filtering Rate? Int Rev Gesamten Hydrobiol 1991, 76, 47–56. [Google Scholar]
- Jungmann, D. Toxic Compounds Isolated from Microcystis PCC7806 That Are More Active Against Daphnia Than Two Microcystins. Limnol Oceanogr 1992, 1777–1783. [Google Scholar]
- Rohrlack, T; Dittman, E; Henning, M; Börner, T; Kohl, J. Role of Microcystins in Poisoning and Food Ingestion Inhibition of Daphnia galeata Caused by the Cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Appl Environ Micribol 1999, 65, 737–739. [Google Scholar]
- Kaebernick, M; Rohrlack, T; Christofferson, K; Neilan, BA. A Spontaneous Mutant of Microcystin Biosynthesis: Genetic Characterization and Effect on Daphnia. Environ Microbiol 2001, 3, 669–679. [Google Scholar]
- Rohrlack, T; Dittman, E; Borner, T; Christofferson, K. Effects of Cell-Bound Microcystins on Survival and Feeding of Daphnia spp. Appl Environ Microbiol 2001, 67, 3523–3529. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W; Song, L; Ou, D; Gan, N. Chronic Toxicity and Responses of Several Important Enzymes in Daphnia on Exposure to Sublethal Microcystin-LR. Environ Toxicol 2005, 20, 323–330. [Google Scholar]
- Sotero-Santos, RB; Souza e Silva, CR; Verani, NF; Nonaka, KO; Rocha, O. Toxicity of a Cyanobacteria Bloom in Barra Bonita Reservoir (Middle Tiete River, São Paulo, Brazil) . Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 2006, 64, 163–170. [Google Scholar]
- Okumura, DT; Sotero-Santos, RB; Takenaka, RA; Rocha, O. Evaluation of Cyanobacteria Toxicity in Tropical Reservoirs Using Crude Extracts Bioassay with Cladocerans. Ecotoxicol 2007, 16, 263–270. [Google Scholar]
- Dawson, RM. The Toxicology of Microcystins. Toxicon 1998, 36, 953–962. [Google Scholar]
- Dittman, E; Wiegand, C. Cyanobacterial Toxins – Occurrence, Biosynthesis and Impact on Human Affairs. Mol Nutr Food Res 2006, 50, 7–17. [Google Scholar]
- Dittmann, E; Neilan, BA; Erhard, M; von Döhren, H; Börner, T. Insertional Mutagenesis of a Peptide Synthetase Gene That is Responsible for Hepatotoxin Production in the Cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa PCC 7806. Mol Microbiol 1997, 26, 779–787. [Google Scholar]
- Dittman, E; Börner, T. Genetic Contributions to the Risk Assessment of Microcystins in the Environment. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 2005, 203, 192–200. [Google Scholar]
- Brautigan, DL. Flicking the Switches: Phosphorylation of Serine/Threonine Protein Phosphatases. Sem Cancer Biol 1995, 6, 211–217. [Google Scholar]
- Long, BM; Jones, GJ; Orr, PT. Cellular Microcystin Content in N-Limited Microcystis aeruginosa Can Be Predicted from Growth Rate. Appl Environ Microbiol 2001, 67, 278–283. [Google Scholar]
- Christofferson, K. Ecological Implication of Cyanobacterial Toxins in Aquatic Food Webs. Phycologia 1996, 35, 42–50. [Google Scholar]
- Blom, JF; Jüttner, F. High Crustacean Toxicity of Microcystin Congeners Does Not Correlate with High Protein Phosphatase Inhibitory Activity. Toxicon 2005, 46, 465–470. [Google Scholar]
- Lürling, M. Effects of Microcystin-Free and Microcystin-Containing Strains of the Cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa on Growth of the Grazer Daphnia magna. Environ Toxicol 2003, 18, 202–210. [Google Scholar]
- Jakobi, C; Rinehart, KL; Neuber, R; Mez, K; Weckesser, J. Cyanopeptolin SS, a Disulfated Depsipeptide from a Water Bloom in Leipzig (Germany): Structural Elucidation and Biological Activities. Phycologia 1996, 35, 111–116. [Google Scholar]
- Rohrlack, T; Christoffersen, K; Hansen, PE; Zhang, W; Czarnecki, O; Henning, M; Fastner, J; Erhard, M; Neilan, BA; Kaebernick, M. Isolation, Characterization and Quantitative Analysis of Microviridin J, a New Microcystis Metabolite Toxic to Daphnia. J Chem Ecol 2003, 29, 1757–1770. [Google Scholar]
- Rohrlack, T; Christofferson, K; Kaebernick, M; Neilan, BA. Microviridin J, a Cyanobacteria Protease Inhibitor that Causes a Lethal Molting Disruption in Daphnia. Appl Environ Microbiol 2004, 70, 5047–5050. [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal, MK; Bagchi, D; Bagchi, SN. Acute Inhibition of Protease and Suppression of Growth in Zooplankter, Moina macrocopa, by Microcystis Blooms Collected in Central India. Hydrobiologia 2001, 464, 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Czarnecki, O; Henning, M; Lippert, I; Welker, M. Identification of Peptide Metabolites of Microcystis (Cyanobacteria) That Inhibit Trypsin-Like Activity in Planktonic Herbivorous Daphnia (Cladocera). Environ Microbiol 2006, 8, 77–87. [Google Scholar]
- Peñaloza, R; Rojas, M; Vila, I; Zambrano, F. Toxicity of a Soluble Peptide from Microcystis sp. to Zooplankton and Fish. Freshwater Biol 1990, 24, 233–240. [Google Scholar]
- Hairston, NG, Jr; Lampert, W; Caceres, C; Holtmeier, C; Weider, L; Gaedke, U; Fischer, J; Fox, JA; Post, DM. Rapid Evolution Revealed by Dormant Eggs. Nature 1999, 401, 446. [Google Scholar]
- Hairston, NG; Holtmeier, CL; Lampert, W; Weider, LJ; Post, DM; Fischer, JM; Caceres, CE; Fox, JA; Gaedke, U. Natural Selection for Grazer Resistance to Toxic Cyanobacteria: Evolution of Phenotypic Plasticity? Evolution 2001, 55, 2203–2214. [Google Scholar]
- Gustaffson, S; Hansson, L-A. Development of Tolerance Against Toxic Cyanobacteria in Daphnia. Aquat Toxicol 2004, 38, 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson, S; Rengefors, KE; Hansson, L-A. Increased Consumer Fitness Following Transfer of Toxin Tolerance to Offspring via Maternal Effects. Ecology 2005, 86, 2561–2567. [Google Scholar]
- Sarnelle, O; Wilson, AE. Local Adaptation of Daphnia pulicaria to Toxic Cyanobacteria. Limnol Oceanogr 2005, 50, 1565–1571. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, AE; Hay, ME. A Direct Test of Cyanobacterial Chemical Defense: Variable Effects of Microcystin-Treated Food on Two Daphnia pulicaria Clones. Limnol Oceanogr 2007, 52, 1467–1479. [Google Scholar]
- Pflugmacher, S; Wiegand, C; Oberemm, A; Beattie, KA; Krause, E; Codd, GA; Steinberg, CEW. Identification of an Enzymatically-Formed Glutathione Conjugate of the Cyanobacterial Hepatotoxin Microcystin-LR. The First Step of Detoxication. Biochim Biophys Acta 1998, 1425, 527–533. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W; Song, L; Ou, D; Gan, N. Chronic Toxicity and Responses of Several Important Enzymes in Daphnia magna on Exposure to Sublethal Microcystin-LR. Environ Toxicol 2005, 20, 323–330. [Google Scholar]
- Adamovsky, O; Kopp, R; Hilscherova, K; Babica, P; Palikova, M; Paskova, V; Navratil, S; Marsalek, B; Blaha, L. Microcystin Kinetics (Bioaccumulation and Elimination) and Biochemical Response in Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio) and Silver Carp (Hypophtalmichthys molitrix) Exposed to Toxic Cyanobacterial Blooms. Environ Toxicol Chem 2007, 26, 2687–2693. [Google Scholar]
- Butler, LG. Hemingway, RW, Karchesy, JJ, Eds.; Chemistry and Significance of Condensed Tannins; Plenum Press: New York, 1989; pp. 391–402. [Google Scholar]
- Wynne-Edwards, KE. Evolutionary Biology of Plant Defenses Against Herbivory and Their Predictive Implications for Endocrine Disruptor Susceptibility in Vertebrates. Environ Health Perspect 2001, 109, 443–448. [Google Scholar]
- Andersen, RJ; Lu, HA; Chen, DZX; Holmes, CFB; Kent, ML; LeBlanc, M; Taylor, FJR; Williams, DE. Chemical and Biological Evidence Links Microcystins to Salmon “Netpen Liver Disease”. Toxicon 1993, 31, 1315–1323. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, MF; Harada, KI; Carmichael, WW; Fujiki, H. Toxic Microcystis; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, WJ; Dietrich, DR. Pathological and Biochemical Characterization of Microcystin-Induced Hepatopancreas and Kidney Damage in Carp (Cyprinus carpio). Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 2000, 164, 73–81. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P-J; Chien, M-S; Wu, F-J; Chou, H-N; Lee, S-J. Inhibition of Embryonic Development by Microcystin-LR in Zebrafish. Danio rerio Toxicon 2005, 45, 303–308. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X-Y; Wang, J; Liang, J-B; Liu, Y-D. Toxicity of Microcystins in the Isolated Hepatocytes of Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio). Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 2007, 67, 447–451. [Google Scholar]
- Oberemm, A; Fastner, J; Steinberg, CEW. Effects of Microcystin-LR and Cyanobacterial Crude Extracts on Embryo-Larval Development of Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Water Res 1997, 31, 2918–2921. [Google Scholar]
- Kirkpatrick, B; Fleming, LE; Squicciarini, D; Backer, LC; Clark, R; Abraham, W; Benson, J; Cheng, YS; Johnson, D; Pierce, R; Zaias, J; Bossart, GD; Baden, DG. Literature Review of Florida Red Tide: Implications for Human Health Effects. Harmful Algae 2004, 3, 99–115. [Google Scholar]
- Keating, KI. Allelopathic Influence on Blue-Green Bloom Sequence in a Eutrophic Lake. Science 1977, 196, 885–886. [Google Scholar]
- Vardi, A; Schatz, D; Beeri, K; Motro, U; Sukenik, A; Levine, A; Kaplan, A. Dinoflagellate-Cyanobacterium Communication May Determine the Composition of Phytoplankton Assemblage in a Mesotrophic Lake. Curr Biol 2002, 12, 1767–1772. [Google Scholar]
- Mason, CP; Edwards, KR; Carlson, RE; Pignatello, J; Gleason, FK; Wood, JM. Isolation of Chlorine-Containing Antibiotic from the Freshwater Cyanobacterium Scytonema hofmanni. Science 1982, 215, 400–402. [Google Scholar]
- Vepritskii, AA; Gromov, BV; Titota, NN; Mamkaeva, KA. Production of the Antibiotic-Algicide Cyanobacterin LU-2 by a Filamentous Cyanobacterium NostocSp. Mikrobiologiia 1991, 60, 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Gromov, BV; Vepritskii, AA; Titota, NN; Mamkayeva, KA; Alexandrova, OV. Production of the Antibiotic Cyanobacterin LU-1 by Nostoc linckia CALU 892. J Appl Phycol 1991, 3, 55–59. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, GD; Thanh Doan, N. Cyanobacterial Metabolites with Bioactivity Against Photosynthesis in Cyanobacteria, Algae and Higher Plants. J Appl Phycol 1999, 11, 337–344. [Google Scholar]
- Gleason, FK; Case, DE. Activity of the Natural Algicide, Cyanobacterin, on Angiosperms. Plant Physiol 1986, 80, 834–837. [Google Scholar]
- Flores, E; Wolk, CP. Production, by Filamentous, Nitrogen-Fixin Cyanobacteria, of a Bacteriocin and of Other Antibiotics That Killed Related Strains. Arch Microbiol 1986, 145, 215–219. [Google Scholar]
- Shlegel, I; Doan, NT; de Chazal, N; Smith, GD. Antibiotic Activity of Cyanobacterial Isolates from Australia and Asia Against Green Algae and Cyanobacteria. J Appl Phycol 1998, 10, 471–479. [Google Scholar]
- Rippka, R; Deruelles, J; Waterbury, JB; Herdman, M; Stanier, RY. Generic Assignments, Strain Histories, and Properties of Pure Cultures of Cyanobacteria. J Gen Microbiol 1979, 11, 1–61. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, A; Jüttner, F; Strasser, RJ. Action of the Allelochemical , Fischerellin A, on Photosystem II. Biochim Biophys Acta 1998, 1364, 326–336. [Google Scholar]
- Gantar, M; Berry, JP; Thomas, S; Wang, M; Perez, R; Rein, K. Allelopathic Activity Among Cyanobacteria and Microalgae Isolated from Florida Freshwater Habitats. FEMS Microbiol Lett 2008, 64, 55–64. [Google Scholar]
- Thahn Doan, N; Stewart, PR; Smith, GD. Inhibition of Bacterial RNA Polymerase by the Cyanobacterial Metabolites 12-Epi-Hapalindole E Isonitrile and Calothrixin A. FEMS Microbiol Lett 2001, 196, 135–139. [Google Scholar]
- Thanh, DN; Rickards, RW; Rothschild, JM; Smith, GD. Allelopathic Actions of the Alkaloid 12-Epi-Hapalindole E Isonitrile and Calothrixin A from Cyanobacteria of the Genera Fischerella and Calothrix. J Appl Phycol 2000, 12, 409–416. [Google Scholar]
- Rickards, RW; Rothschild, JM; Willis, AC; de Chazal, NM; Kirk, J; Kirk, K; Saliba, KJ; Smith, GD. Calothrixins A and B, Novel Pentacyclic Metabolites from Calothrix Cyanobacteria with Potent Activity Against Parasites and Human Cancer Cells. Tetrahedron 1999, 55, 13513–13520. [Google Scholar]
- Todorova, AK; Jüttner, F. Nostocyclamide: A New Macrocyclic, Thiazole-Containing Allelochemical from Nostoc sp. 31. J Org Chem 1995, 60, 7891–7895. [Google Scholar]
- Jüttner, F; Todorova, AK; Walch, N; von Philipsborn, W. Nostocyclamide M: A Cyanobacterial Cyclic Peptide with Allelopathic Activity from Nostoc 31. Phytochemistry 2001, 57, 613–619. [Google Scholar]
- Hirata, K; Nakagami, H; Takashimi, J; Muhmud, T; Kobayashi, M; In, Y; Ishida, T; Miyamoto, K. Novel violet pigment, nostocine, A, an extracellular metabolite from cyanobacterium Nostoc spongiaforme. Heterocycles 1996, 43, 1513–1519. [Google Scholar]
- Hirata, K; Yoshitomi, S; Dwi, S; Iwabe, O; Mahakhant, A; Polchai, J; Miyamoto, K. Bioactivities of Nostocine A Produced by a Freshwater Cyanobacterium Nostoc spongiaforme TISTR 8169. J Biosci Bioeng 2003, 95, 512–517. [Google Scholar]
- Becher, PG; Beuchat, J; Gademann, K; Jüttner, F. Nostocarboline: Isolation and Synthesis of a New Cholinesterase Inhibitor from Nostoc 78-12A. J Nat Prod 2005, 68, 1793–1795. [Google Scholar]
- Sedmark, B; Kosi, G. The Role of Microcystins in Heavy Cyanobacterial Bloom Formation. J Plankton Res 1998, 20, 691–708. [Google Scholar]
- Casanova, MT; Burch, MD; Brock, MA; Bond, PM. Does Toxic Microcystis aeruginosa Affect Aquatic Plant Establishment? Environ Toxicol 1999, 14, 97–109. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, J; Liebert, HP; Braune, W. Influence of Microcystin-RR on Growth and Photosynthetic Capacity of the Duckweed Lemna minor. Appl Bot Angew Bot 2000, 74, 100–105. [Google Scholar]
- Kearns, KD; Hunter, MD. Toxin-Producing Anabaena flos-aquae Induces Settling of Chlamydomonas reinhardii, a Competing Motile Alga. Microbiol Ecol 2001, 42, 80–86. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, DP; Tyagi, MB; Kumar, A; Thakur, JK; Kumar, A. Antialgal Activity of a Hepatotoxin-Producing Cyanobacterium, Microcystis aeruginosa. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 2001, 17, 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Pflugmacher, S. Possible Allelopathic Effects of Cyanotoxins, with Reference to Microsystin-LR, in Aquatic Ecosystems. Environ Toxicol 2002, 17, 407–413. [Google Scholar]
- Romanoska-Duda, Z; Tarczynska, M. The Influence of Microcystin-LR and Hepatotoxic Cyanobacterial Extract on the Water Plant Spirodela oligorrhiza. Environ Toxicol 2002, 17, 434–440. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, ZQ; Liu, YD; Li, DH. Physiological and Biochemical Analyses of Microcystin-RR Toxicity to the Cyanobacterium Synechococcus elongates. Environ Toxicol 2004, 19, 571–577. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, M-H; Kyong, H; Takamura, N. Reciprocal Allelopathic Responses Between Toxic Cyanobacteria (Microcystis aeruginosa) and Duckweed (Lemna japonica) . Toxicon 2007, 49, 727–733. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, ZA. Allelopathic Activity of Spirogyra sp.: Stimulating Bloom Formation and Toxin Production by Oscillatoria in Some Irrigation Canals, Egypt. J Plankton Res 2002, 24, 137–141. [Google Scholar]
- Ishida, K; Murakami, M. Kasumigamide, an Antialgal Peptide form the Cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. J Org Chem 2000, 65, 5898–5900. [Google Scholar]
- Wiegand, C; Peuthert, A; Pflugmacher, S; Carmeli, S. Effects of Microcin SF608 and Microcystin-LR, Two Cyanobacterial Compounds Produced by Microcystis sp., on Aquatic Organisms. Environ Toxicol 2002, 17, 400–406. [Google Scholar]
- Ikawa, M; Haney, JF; Sasner, JJ. Inhibition of Chlorella Growth by the Lipids of Cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Hydrobiologia 1996, 331, 167–170. [Google Scholar]
- Ikawa, M; Sasner, JJ; Haney, JF. Inhibition of Chlorella Growth by Degradation and Related Products of Linoleic and Linolenic Acids and the Possible Significance of Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Phytoplankton Ecology. Hydrobiologia 1997, 356, 143–148. [Google Scholar]
- Hagmann, L; Jüttner, F. Fischerellin A, a Novel Photosystem-II-Inhibiting Allelochemical of the Cyanobacterium Fischerella muscicola with Antifungal and Herbicidal Activity. Tetrahedron Lett 1996, 37, 6539–6542. [Google Scholar]
- Entzeroth, M; Mead, DJ; Patterson, ML; Moore, RE. A Herbicidal Fatty Acid Produced by Lyngbya aesturii. Phytochemistry 1985, 24, 2875–2876. [Google Scholar]
- Wium-Anderson, S; Anthoni, W; Christophersen, C; Houen, G. Allelopathic Effects on Phytoplankton by Substances from Aquatic Macrophytes. Oikos 1982, 39, 187–190. [Google Scholar]
- Nakai, S; Inoue, Y; Hosomi, M; Murakami, A. Growth Inhibition of Blue-Green Algae by Allelopathic Effects of Macrophytes. Water Sci Technol 1999, 39, 47–53. [Google Scholar]
- Körner, S; Nicklisch, A. Allelopathic Growth Inhibition of Selected Phytoplankton Species by Submerged Macrophytes. J Phycol 2002, 38, 862–871. [Google Scholar]
- Mulderij, G; Smolders, AJP; van Donk, E. Allelopathic Effect of the Aquatic Macrophytes, Stratiotes aloides, on Natural Phytoplankton. Freshwater Biol 2006, 51, 554–561. [Google Scholar]
- Babica, P; Blaha, L; Marsalek, B. Exploring the Natural Role of Microcystins – A Review of Effects on Photoautotrophic Organisms. J Phycol 2006, 42, 9–20. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, LT. Bioactive natural products from marine cyanobacteria for drug discovery. Phytochemistry 2007, 68, 954–979. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J; Shen, X; El Sayed, KA; Dunbar, DC; Perry, TL; Wilkins, SP; Hamann, MT. Marine Natural Products as Prototype Agrochemical Agents. J Agric Food Chem 2003, 51, 2246–2252. [Google Scholar]
- Berry, JP; Gantar, M; Gibbs, PDL; Schmale, MC. The Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Embryo as a Model System for Identification and Characterization of Developmental Toxins from Marine and Freshwater Microalgae. Comp Biochem Physiol Part C Pharmacol Toxicol 2007, 145, 61–72. [Google Scholar]
- Gubler, DJ. Resurgent Vector-Borne Diseases as a Global Health Problem. Emerging Infectious Diseases 1998, 4, 442–450. [Google Scholar]
- Sangthongpitag, K; Delaney, SF; Rogers, PL. Evaluation of four fresh-water unicellular cyanobacteria as potential hosts for mosquitocidal toxins. Biotechnol Lett 1996, 18, 175–180. [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez-Martinez, MG; Rodríguez, MH; Arrendondo-Jimenez, JI; Mendez-Sanchez, JD; Bond-Compean, JG; Gold-Morgan, M. Cianobacteria Associated with Anopheles albimanus (Dipter: Culcidae) Larval Habitats in Southern Mexico. J Med Entomol 2002, 39, 825–832. [Google Scholar]
- Kiviranta, J; Abdel-Hameed, A; Sivonen, K; Niemela, SI; Carlberg, G. Toxicity of Cyanobacteria to Mosquito Larvae – Screening of Active Compounds. Environ Toxicol Water Qual 1993, 8, 63–71. [Google Scholar]
- Nassar, MMI; Hafez, ST; Nagaty, IM; Khalaf, SAA. The insecticidal activity of cyanobacteria against four insects, two of medical importance and two agricultural pests with references to the action on albino mice. J Egypt Soc Parasitol 1999, 29, 939–949. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, DR; Thangavel, C; Kabilan, L; Suguna, S; Mani, TR; Shanmugasundaram, S. Larvicidal Properties of the Cyanobacterium Westiellopsis sp. Against Mosquito Vectors. Trans Royal Soc Trop Med Hyg 1999, 93, 232. [Google Scholar]
- Harada, K-I; Suomalainen, M; Uchida, H; Masul, H; Ohmura, K; Kiviranta, J; Niku-Paavola, M-L; Ikemoto, T. Insecticidal Compounds Against Mosquito Larvae from Oscillatoria agardhii Strain 27. Environ Toxicol 2000, 15, 114–119. [Google Scholar]
- Angsuthanasombat, C; Panyim, S. Biosynthesis of 130-Kilodalton Mosquito Larvicide in the Cyanobacterium Agmenellum quadruplicatum PR-6. Appl Environ Microbiol 1989, 55, 2428–2430. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, RC; Stevens, SE. Cloning and Expression of the cryIVD Gene of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. Israelensis in the Cyanobacterium Agmenellum quadruplicatum PR-6 and Its Resulting Larvicidal Activity. Appl Environ Microbiol 1992, 58, 1650–1655. [Google Scholar]
- Soltes-Rak, E; Kushner, DJ; Williams, DD; Coleman, JR. Factors Regulating cryIVB Expression in the Cyanobacterium Synechococcus PCC 7942. Mol Gen Genet 1995, 246, 301–308. [Google Scholar]
- Xiaoqiang, W; Vennison, SJ; Huirong, L; Ben-Dov, E; Zaritscky, A; Boussiba, S. Appl Environ Microbiol 1997, 63, 4971–4974.
- Manasherob, R; Ben-Dov, E; Xiaoqiang, W; Boussiba, S; Zaritsky, A. Protection from UV-B Damage of Mosquito Larvicidal Toxins from Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. isrealensis expressed in Anabaena PCC 7120. Curr Microbiol 2002, 45, 217–220. [Google Scholar]
- Khasdan, V; Ben-Dov, E; Manasherob, R; Boussiba, S; Karitsky, A. Mosquito Larvicidal Activity of Transgenic Anabaena PCC 7120 Expressing Toxins Genes from Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. Isrealensis FEMS Microbiol Lett 2003, 227, 189–195. [Google Scholar]
- Kucinska, J; Lonc, E; Rydzanicz, K. Trangenic Bioinsecticides Inimical to Parasites, but Imical to Environment. Wiad Parazytol 2003, 49, 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Berry, JP; Gantar, M; Gawley, RE; Wang, M; Rein, KS. Pharmacology and Toxicology of Pahayokolide A, a Bioactive Metabolite from a Freshwater Species of Lyngbya Isolated from the Florida Everglades. Comp Biochem Physiol Part C Pharmacol Toxicol 2004, 139, 231–238. [Google Scholar]
- Berry, JP; Gantar, M; Gawley, RE; Rein, KS. Steidinger, KA, Landsberg, JH, Tomas, CR, Vargo, GA, Eds.; Harmful Algae 2002. In Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission; Florida Institute of Oceanography and Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO, 2005; pp. 192–194. [Google Scholar]
- An, T; Krishnaswamy, T; Kumar, S; Wang, M; Liu, L; Lay, JO; Liyanage, R; Berry, J; Gantar, M; Marks, V; Gawley, RE; Rein, KS. Structures of Pahayokolides A and B, Cyclic Peptides from a Lyngbya sp. J Nat Prod 2007, 70, 730–735. [Google Scholar]

Share and Cite
Berry, J.P.; Gantar, M.; Perez, M.H.; Berry, G.; Noriega, F.G. Cyanobacterial Toxins as Allelochemicals with Potential Applications as Algaecides, Herbicides and Insecticides. Mar. Drugs 2008, 6, 117-146. https://doi.org/10.3390/md6020117
Berry JP, Gantar M, Perez MH, Berry G, Noriega FG. Cyanobacterial Toxins as Allelochemicals with Potential Applications as Algaecides, Herbicides and Insecticides. Marine Drugs. 2008; 6(2):117-146. https://doi.org/10.3390/md6020117
Chicago/Turabian StyleBerry, John P., Miroslav Gantar, Mario H. Perez, Gerald Berry, and Fernando G. Noriega. 2008. "Cyanobacterial Toxins as Allelochemicals with Potential Applications as Algaecides, Herbicides and Insecticides" Marine Drugs 6, no. 2: 117-146. https://doi.org/10.3390/md6020117
APA StyleBerry, J. P., Gantar, M., Perez, M. H., Berry, G., & Noriega, F. G. (2008). Cyanobacterial Toxins as Allelochemicals with Potential Applications as Algaecides, Herbicides and Insecticides. Marine Drugs, 6(2), 117-146. https://doi.org/10.3390/md6020117





