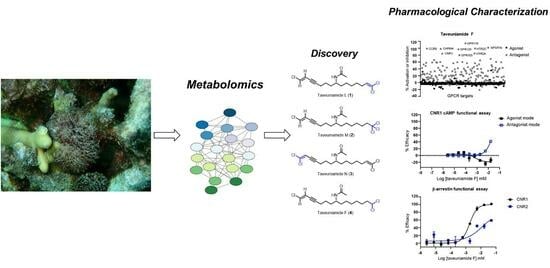
Chlorinated Enyne Fatty Acid Amides from a Marine Cyanobacterium: Discovery of Taveuniamides L-M and Pharmacological Characterization of Taveuniamide F as a GPCR Antagonist with CNR1 Selectivity
Abstract
1. Introduction
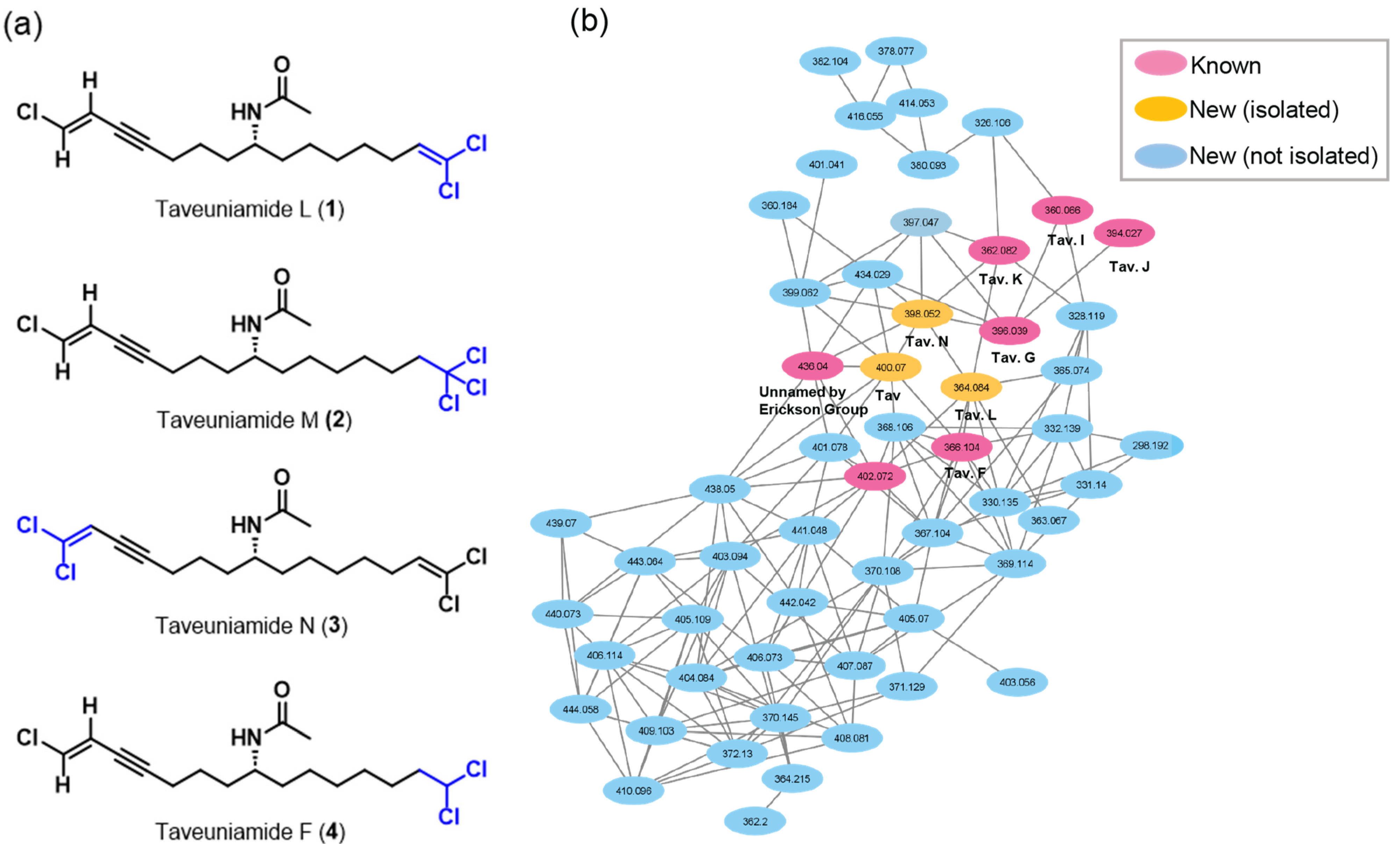
2. Results and Discussions
2.1. Isolation
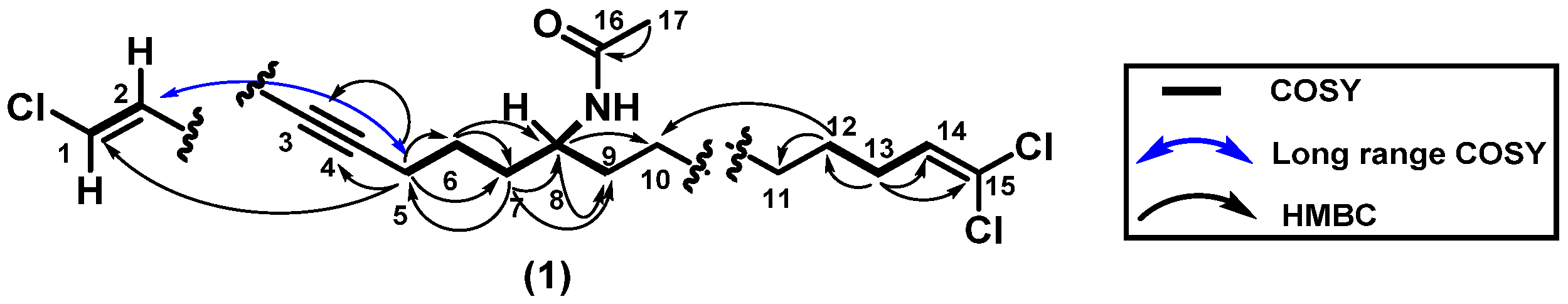
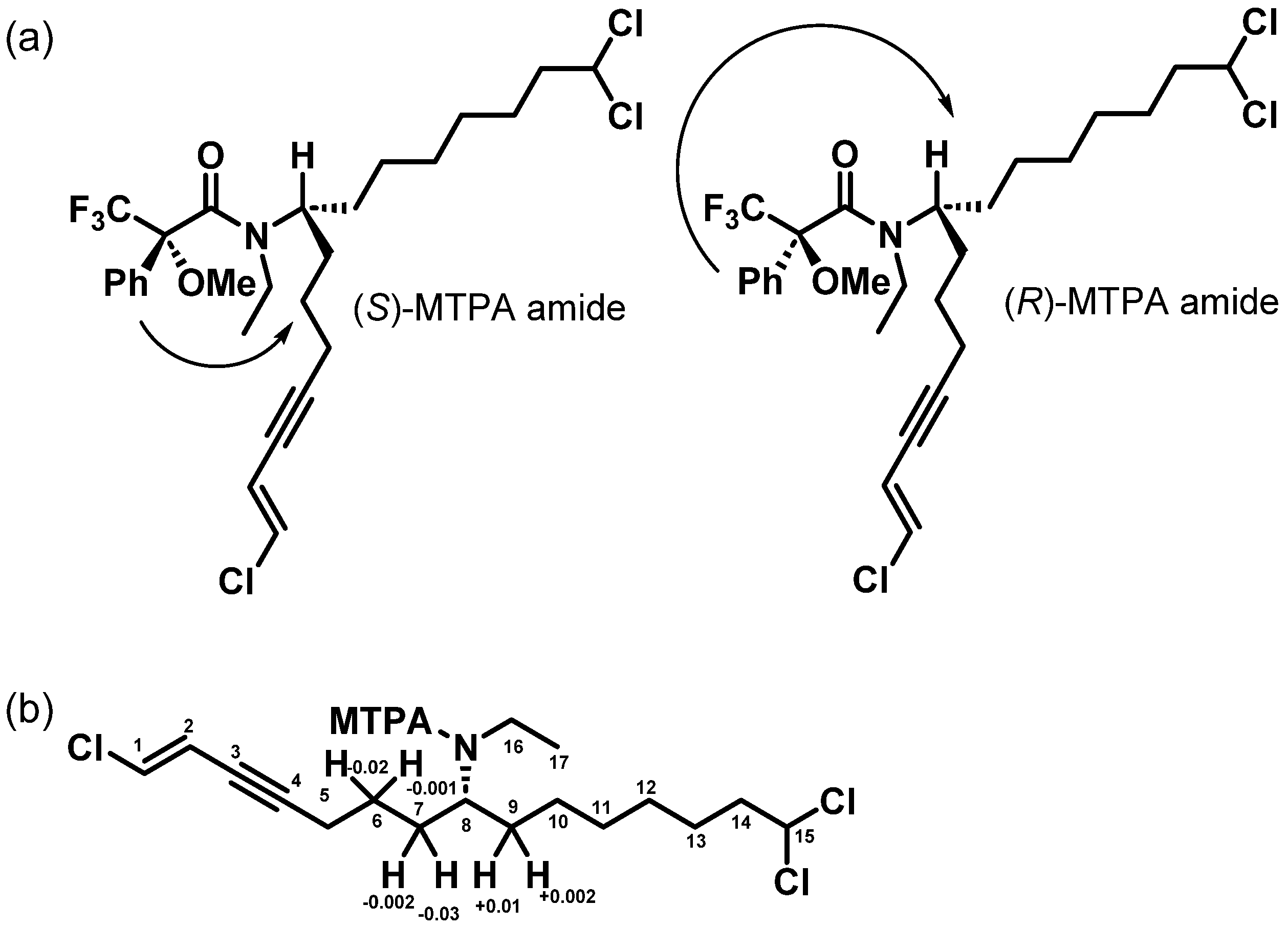
2.2. Structure Elucidation
2.3. Biological Characterization
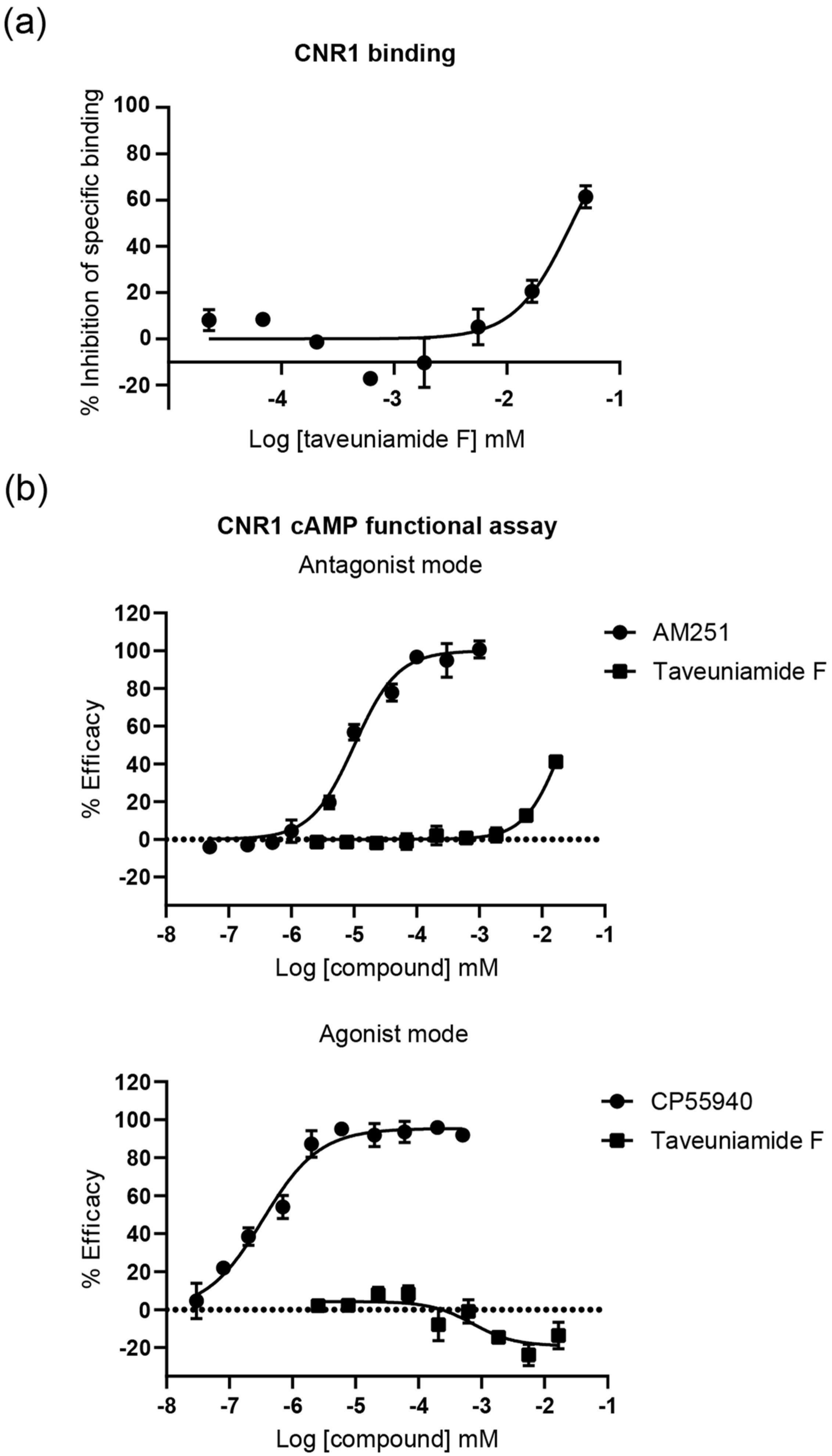
2.3.1. Cannabinoid CNR1 Receptor Binding
2.3.2. CNR1 Functional Response Induced by Taveunimide F (4) through G-Protein-Dependent Pathway
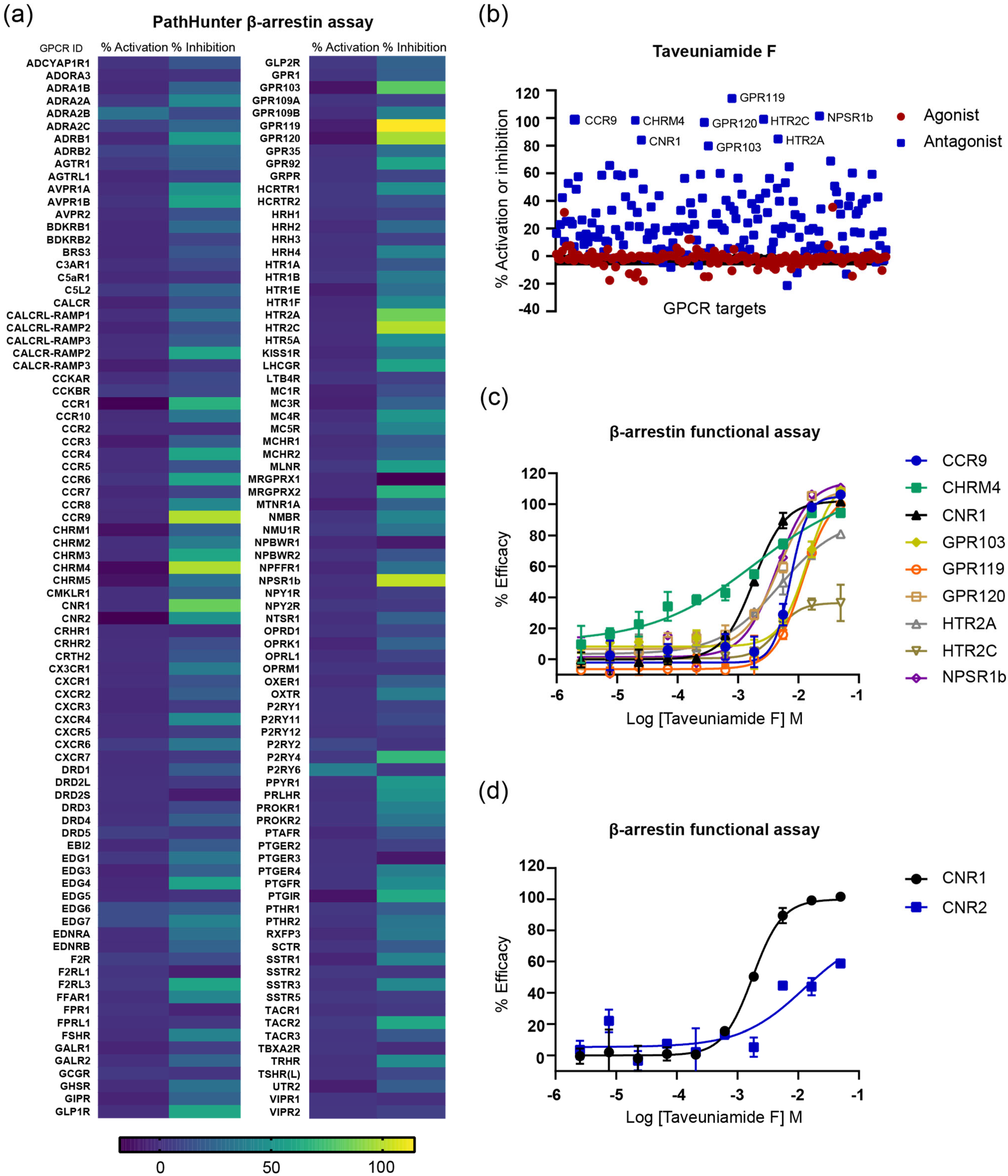
2.3.3. GPCR Target Selectivity Profiling and CNR1 Functional Selectivity Assessment
2.4. Assessment of Taveuniamide F (4) Cytotoxicity in HEK293 Cells
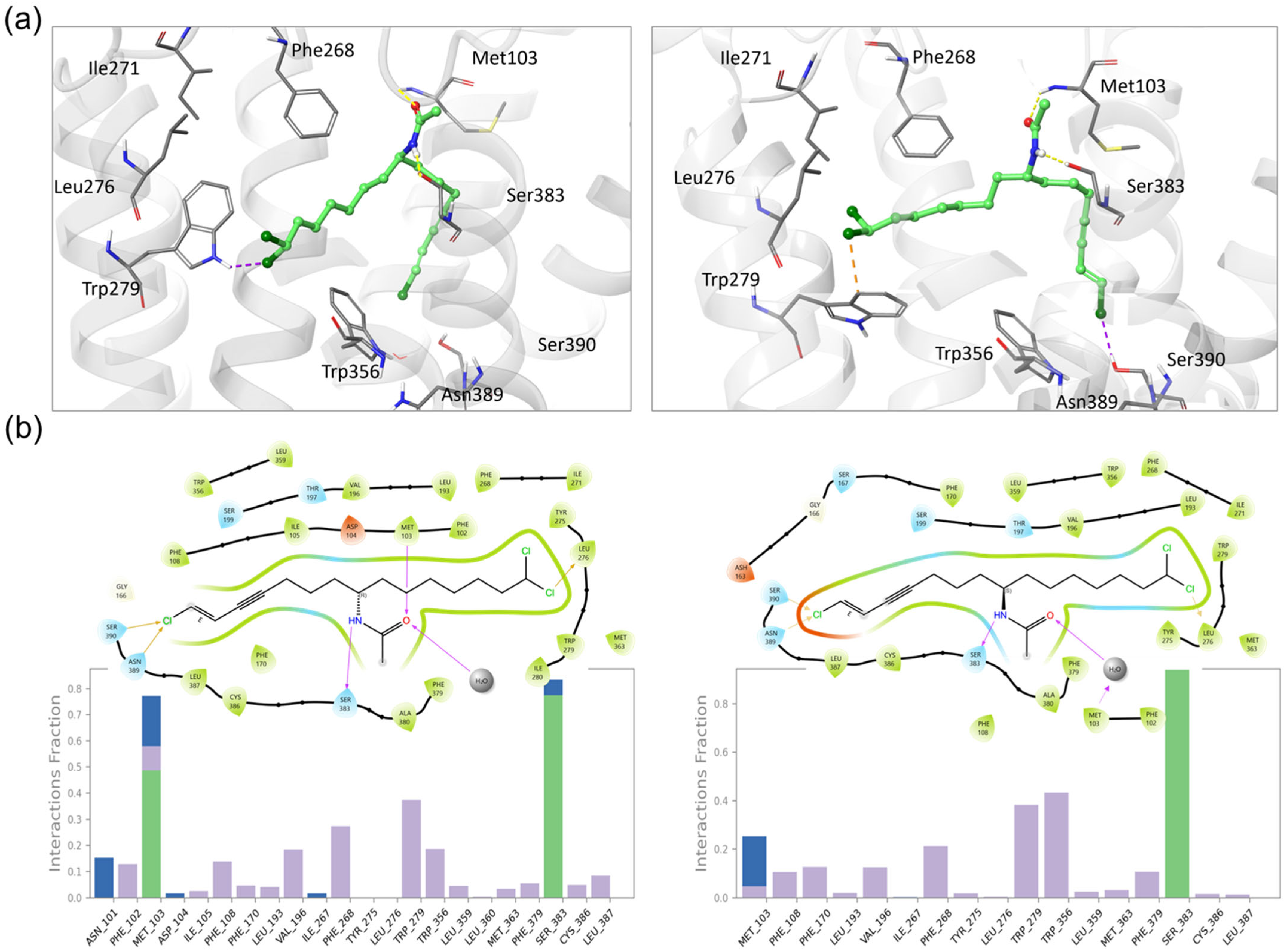
2.5. Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamic Simulations of Taveuniamide F (4) into CNR1
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedure
3.2. Biological Material
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
3.4. Determination of the Absolute Configuration of Taveuniamide F (4)
3.5. Cannabinoid CNR1 Receptor Binding Assay
3.6. cAMP Hunter™ eXpress CNR1 (CB1) CHO-K1 GPCR Assay
3.7. PathHunter β-Arrestin GPCR Profiling
3.8. MTT Cell Viability Assay
3.9. Molecular Modeling and Simulations
4. Conclusions and Outlook
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Farrell, E.K.; Merkler, D.J. Biosynthesis, degradation and pharmacological importance of the fatty acid amides. Drug Discov. Today 2008, 13, 558–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mock, E.D.; Gagestein, B.; van der Stelt, M. Anandamide and other N-acylethanolamines: A class of signaling lipids with therapeutic opportunities. Prog. Lipid Res. 2023, 89, 101194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greger, H. Alkamides: A critical reconsideration of a multifunctional class of unsaturated fatty acid amides. Phytochem. Rev. 2016, 15, 729–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demay, J.; Bernard, C.; Reinhardt, A.; Marie, B. Natural Products from Cyanobacteria: Focus on Beneficial Activities. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, W.; Matthews, J.H.; Paul, V.J.; Luesch, H. Pitiamides A and B, Multifunctional Fatty Acid Amides from Marine Cyanobacteria. Planta Med. 2016, 82, 897–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunnery, J.K.; Engene, N.; Byrum, T.; Cao, Z.; Jabba, S.V.; Pereira, A.R.; Matainaho, T.; Murray, T.F.; Gerwick, W.H. Biosynthetically intriguing chlorinated lipophilic metabolites from geographically distant tropical marine cyanobacteria. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 77, 4198–4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malloy, K.L.; Suyama, T.L.; Engene, N.; Debonsi, H.; Cao, Z.; Matainaho, T.; Spadafora, C.; Murray, T.F.; Gerwick, W.H. Credneramides A and B: Neuromodulatory phenethylamine and isopentylamine derivatives of a vinyl chloride-containing fatty acid from cf. Trichodesmium sp. nov. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, N.A.; Leão, T.; Rankin, M.R.; McCullough, T.M.; Qu, P.; Korobeynikov, A.; Smith, J.L.; Gerwick, L.; Gerwick, W.H. Ketoreductase Domain Dysfunction Expands Chemodiversity: Malyngamide Biosynthesis in the Cyanobacterium Okeania hirsuta. ACS Chem. Biol. 2018, 13, 3385–3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, J.I.; Vansach, T.; Yoshida, W.Y.; Sakamoto, B.; Pörzgen, P.; Horgen, F.D. Halogenated fatty acid amides and cyclic depsipeptides from an eastern Caribbean collection of the cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1573–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, D.J.; Marquez, B.L.; Nogle, L.M.; McPhail, K.; Goeger, D.E.; Roberts, M.A.; Gerwick, W.H. Structure and biosynthesis of the jamaicamides, new mixed polyketide-peptide neurotoxins from the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula. Chem. Biol. 2004, 11, 817–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, J.A.V.; Petitbois, J.G.; Vairappan, C.S.; Umezawa, T.; Matsuda, F.; Okino, T. Columbamides D and E: Chlorinated Fatty Acid Amides from the Marine Cyanobacterium Moorea bouillonii Collected in Malaysia. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 4231–4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, B.; McPhail, K.L.; Ligresti, A.; Di Marzo, V.; Gerwick, W.H. Semiplenamides A-G, fatty acid amides from a Papua New Guinea collection of the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya semiplena. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 1364–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petitbois, J.G.; Casalme, L.O.; Lopez, J.A.V.; Alarif, W.M.; Abdel-Lateff, A.; Al-Lihaibi, S.S.; Yoshimura, E.; Nogata, Y.; Umezawa, T.; Matsuda, F.; et al. Serinolamides and Lyngbyabellins from an Okeania sp. Cyanobacterium Collected from the Red Sea. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 2708–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mevers, E.; Byrum, T.; Gerwick, W.H. Parguerene and precarriebowmide, two classes of lipopeptides from the marine cyanobacterium Moorea producens. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 1810–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, T.R.; Singh, I.P.; Gerwick, W.H. Taveuniamides: New chlorinated toxins from a mixed assemblage of marine cyanobacteria. Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 7025–7033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsini, M.A.; Pannell, L.K.; Erickson, K.L. Polychlorinated acetamides from the cyanobacterium Microcoleus lyngbyaceus. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pretsch, E.; Bühlmann, P.; Badertscher, M. Structure Determination of Organic Compound: Tables of Spectral Data; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, J.B. Organic Structural Spectroscopy; Prentice Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Schedler, D.J.; Li, J.; Ganem, B. Reduction of Secondary Carboxamides to Imines. J. Org. Chem. 1996, 61, 4115–4119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichikawa, A.; Ono, H.; Mikata, Y. Characteristic conformation of Mosher’s amide elucidated using the cambridge structural database. Molecules 2015, 20, 12880–12900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Immadi, S.S.; Wu, Z.; Kendall, D.A. Translational potential of allosteric modulators targeting the cannabinoid CB. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2019, 40, 324–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leo, L.M.; Abood, M.E. CB1 Cannabinoid Receptor Signaling and Biased Signaling. Molecules 2021, 26, 5413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Iyer, M.R.; Godlewski, G.; Jourdan, T.; Liu, J.; Coffey, N.J.; Zawatsky, C.N.; Puhl, H.L.; Wess, J.; Meister, J.; et al. Functional Selectivity of a Biased Cannabinoid-1 Receptor Antagonist. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2021, 4, 1175–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groer, C.E.; Tidgewell, K.; Moyer, R.A.; Harding, W.W.; Rothman, R.B.; Prisinzano, T.E.; Bohn, L.M. An opioid agonist that does not induce mu-opioid receptor—Arrestin interactions or receptor internalization. Mol. Pharmacol. 2007, 71, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felsing, D.E.; Anastasio, N.C.; Miszkiel, J.M.; Gilbertson, S.R.; Allen, J.A.; Cunningham, K.A. Biophysical validation of serotonin 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptor interaction. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0203137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, A.J. Novel cannabinoid receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 152, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira de Souza, C.; Sun, X.; Oh, D. Metabolic Functions of G Protein-Coupled Receptors and β-Arrestin-Mediated Signaling Pathways in the Pathophysiology of Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 715877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Mahri, S.; Malik, S.S.; Al Ibrahim, M.; Haji, E.; Dairi, G.; Mohammad, S. Free Fatty Acid Receptors (FFARs) in Adipose: Physiological Role and Therapeutic Outlook. Cells 2022, 11, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordqvist, A.; Kristensson, L.; Johansson, K.E.; Isaksson da Silva, K.; Fex, T.; Tyrchan, C.; Svensson Henriksson, A.; Nilsson, K. New Hits as Antagonists of GPR103 Identified by HTS. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Prévost, G.; Picot, M.; Le Solliec, M.A.; Arabo, A.; Berrahmoune, H.; El Mehdi, M.; Cherifi, S.; Benani, A.; Nédélec, E.; Gobet, F.; et al. The neuropeptide 26RFa in the human gut and pancreas: Potential involvement in glucose homeostasis. Endocr. Connect. 2019, 8, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Library of Medicine. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/387129 (accessed on 1 February 2023).
- Tapmeier, T.T.; Rahmioglu, N.; Lin, J.; De Leo, B.; Obendorf, M.; Raveendran, M.; Fischer, O.M.; Bafligil, C.; Guo, M.; Harris, R.A.; et al. Neuropeptide S receptor 1 is a nonhormonal treatment target in endometriosis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabd6469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanamiya, R.; Takei, J.; Asano, T.; Tanaka, T.; Sano, M.; Nakamura, T.; Yanaka, M.; Hosono, H.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. Development of Anti-Human CC Chemokine Receptor 9 Monoclonal Antibodies for Flow Cytometry. Monoclon. Antib. Immunodiagn. Immunother. 2021, 40, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, A.C.; Kobilka, B.K.; Gautam, D.; Sexton, P.M.; Christopoulos, A.; Wess, J. Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors: Novel opportunities for drug development. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, T.H.; Sim-Selley, L.J.; Selley, D.E. Cannabinoid CB1 receptor-interacting proteins: Novel targets for central nervous system drug discovery? Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 160, 454–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogueras-Ortiz, C.; Yudowski, G.A. The Multiple Waves of Cannabinoid 1 Receptor Signaling. Mol. Pharmacol. 2016, 90, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Awadhi, F.H.; Gao, B.; Rezaei, M.A.; Kwan, J.C.; Li, C.; Ye, T.; Paul, V.J.; Luesch, H. Discovery, Synthesis, Pharmacological Profiling, and Biological Characterization of Brintonamides A-E, Novel Dual Protease and GPCR Modulators from a Marine Cyanobacterium. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 6364–6378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Z.; Yin, J.; Chapman, K.; Grzemska, M.; Clark, L.; Wang, J.; Rosenbaum, D.M. High-resolution crystal structure of the human CB1 cannabinoid receptor. Nature 2016, 540, 602–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halgren, T.A.; Murphy, R.B.; Friesner, R.A.; Beard, H.S.; Frye, L.L.; Pollard, W.T.; Banks, J.L. Glide: A new approach for rapid, accurate docking and scoring. 2. Enrichment factors in database screening. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 1750–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, W.; Day, T.; Jacobson, M.P.; Friesner, R.A.; Farid, R. Novel procedure for modeling ligand/receptor induced fit effects. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 534–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrödinger LLC. Schrödinger Release 2023-2; Schrödinger LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
| C/H No. | δC, Type | δH (J in Hz) | COSY | HMBC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 128.8, CH | 6.43, d (13.6) | 2 | |
| 2 | 114.0, CH | 5.90, dt (13.6, 2.3) | 1, 5 | |
| 3 | 92.7, C | |||
| 4 | 76.1, C | |||
| 5 | 19.1, CH2 | 2.32, td (7.6, 2.3) | 1, 2, 6 | 1, 3, 4, 6, 7 |
| 6 | 24.8, CH2 | 1.55 | 5, 7a | 7, 8 |
| 7 | 34.4, CH2 | a: 1.41 b: 1.61 | 8, 7b, 6 8, 7a | 5, 8, 9 5, 8, 9 |
| 8 | 48.7, CH | 3.93, dtd (12.7, 8.8, 4.5) | 7a, 7b, 9a, 9b, NH | 9, 10 |
| 9 | 35.3, CH2 | a: 1.33 b: 1.49 | 8, 9b 8, 9a | |
| 10 | 25.5, CH2 | 1.33 | ||
| 11 | 28.8, CH2 | 1.32 | ||
| 12 | 28.0, CH2 | 1.40 | 13 | 10 |
| 13 | 29.4, CH2 | 2.15, dt (7.3, 7.4) | 12, 14 | 12, 14, 15 |
| 14 | 129.8, CH | 5.83, t (7.3) | 13 | |
| 15 | 119.8, C | |||
| 16 | 169.5,C | |||
| 17 | 23.5, CH3 | 1.98, s | 16 | |
| NH | 5.07, d (9.3) | 8 |
| C/H No. | δC, Type | δH (J in Hz) | COSY | HMBC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 128.6, CH | 6.43, d (13.6) | 2, 5 | 2, 4 |
| 2 | 114.0, CH | 5.90, dt (13.6, 2.3) | 1, 5 | 1, 3 |
| 3 | 92.7, C | |||
| 4 | 76.2, C | |||
| 5 | 19.1, CH2 | 2.32, td (7.4, 2.0) | 1, 2, 6 | 1, 3, 4, 6, 7 |
| 6 | 24.8, CH2 | 1.55 | 5, 7a | 5, 7, 8 |
| 7 | 34.4, CH2 | a: 1.41 b: 1.61 | 8, 7b, 6 8, 7a | 5, 8, 9 5, 8, 9 |
| 8 | 48.7, CH | 3.94, dtd (12.7, 8.8, 4.5) | 7a, 7b, 9a, 9b, NH | 9, 10 |
| 9 | 35.3, CH2 | a: 1.34 b: 1.49 | 8, 9b 8, 9a | 8, 10, 11 |
| 10 | 25.5, CH2 | 1.34 | ||
| 11 | 28.9, CH2 | 1.33 | ||
| 12 | 28.4, CH2 | 1.38 | 13 | 11, 10 |
| 13 | 26.2, CH2 | 1.76, dtd (11, 7.8, 5.8) | 12, 14 | 12, 14, 15 |
| 14 | 55.0, CH2 | 2.66, m | 13 | 12, 13, 15 |
| 15 | 100.3, C | |||
| 16 | 169.6, C | |||
| 17 | 23.5, CH3 | 1.98, s | 16 | |
| NH | 5.08, d (9.3) | 8 | 8, 16 |
| C/H No. | δC, Type | δH (J in Hz) | COSY | HMBC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 130.1, C | |||
| 2 | 111.1, CH | 5.93, t (2.3) | 5 | |
| 3 | 98.8, C | |||
| 4 | 74.9, C | |||
| 5 | 19.6, CH2 | 2.40, td (6.8, 2.3) | 2, 6 | 1, 3, 4, 6, 7 |
| 6 | 24.8, CH2 | 1.59 | 5, 7a, 7b | |
| 7 | 34.4, CH2 | a: 1.44 b: 1.66 | 8, 7b, 6 8, 7a, 6 | |
| 8 | 48.8, CH | 3.94, ddq (13.3, 8.9, 4.9) | 7a, 7b, 9a, 9b, NH | |
| 9 | 35.3, CH2 | a: 1.34 b: 1.48 | 8, 9b 8, 9a | |
| 10 | 25.8, CH2 | 1.33 | ||
| 11 | 29.2, CH2 | 1.32 | ||
| 12 | 28.2, CH2 | 1.40 | 13 | 10, 11 |
| 13 | 29.6, CH2 | 2.15, q (7.3) | 12, 14 | 12, 14, 15 |
| 14 | 129.8, CH | 5.84, t (7.4) | 13 | |
| 15 | 119.5, C | |||
| 16 | 169.5, C | |||
| 17 | 23.7, CH3 | 1.98, s | 16 | |
| NH | 5.08, d (9.3) | 8 |
| GPCR Target | IC50 (µM) |
|---|---|
| CNR1 | 1.84 |
| CHRM4 | 1.92 |
| NPSR1b | 4.36 |
| GPR120 | 4.72 |
| HTR2A | 4.83 |
| CCR9 | 7.38 |
| GPR119 | 11.67 |
| GPR103 | 14.07 |
| HTR2C | >50 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elsadek, L.A.; Ellis, E.K.; Seabra, G.; Paul, V.J.; Luesch, H. Chlorinated Enyne Fatty Acid Amides from a Marine Cyanobacterium: Discovery of Taveuniamides L-M and Pharmacological Characterization of Taveuniamide F as a GPCR Antagonist with CNR1 Selectivity. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22010028
Elsadek LA, Ellis EK, Seabra G, Paul VJ, Luesch H. Chlorinated Enyne Fatty Acid Amides from a Marine Cyanobacterium: Discovery of Taveuniamides L-M and Pharmacological Characterization of Taveuniamide F as a GPCR Antagonist with CNR1 Selectivity. Marine Drugs. 2024; 22(1):28. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22010028
Chicago/Turabian StyleElsadek, Lobna A., Emma K. Ellis, Gustavo Seabra, Valerie J. Paul, and Hendrik Luesch. 2024. "Chlorinated Enyne Fatty Acid Amides from a Marine Cyanobacterium: Discovery of Taveuniamides L-M and Pharmacological Characterization of Taveuniamide F as a GPCR Antagonist with CNR1 Selectivity" Marine Drugs 22, no. 1: 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22010028
APA StyleElsadek, L. A., Ellis, E. K., Seabra, G., Paul, V. J., & Luesch, H. (2024). Chlorinated Enyne Fatty Acid Amides from a Marine Cyanobacterium: Discovery of Taveuniamides L-M and Pharmacological Characterization of Taveuniamide F as a GPCR Antagonist with CNR1 Selectivity. Marine Drugs, 22(1), 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22010028