Fucoidan in Pharmaceutical Formulations: A Comprehensive Review for Smart Drug Delivery Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
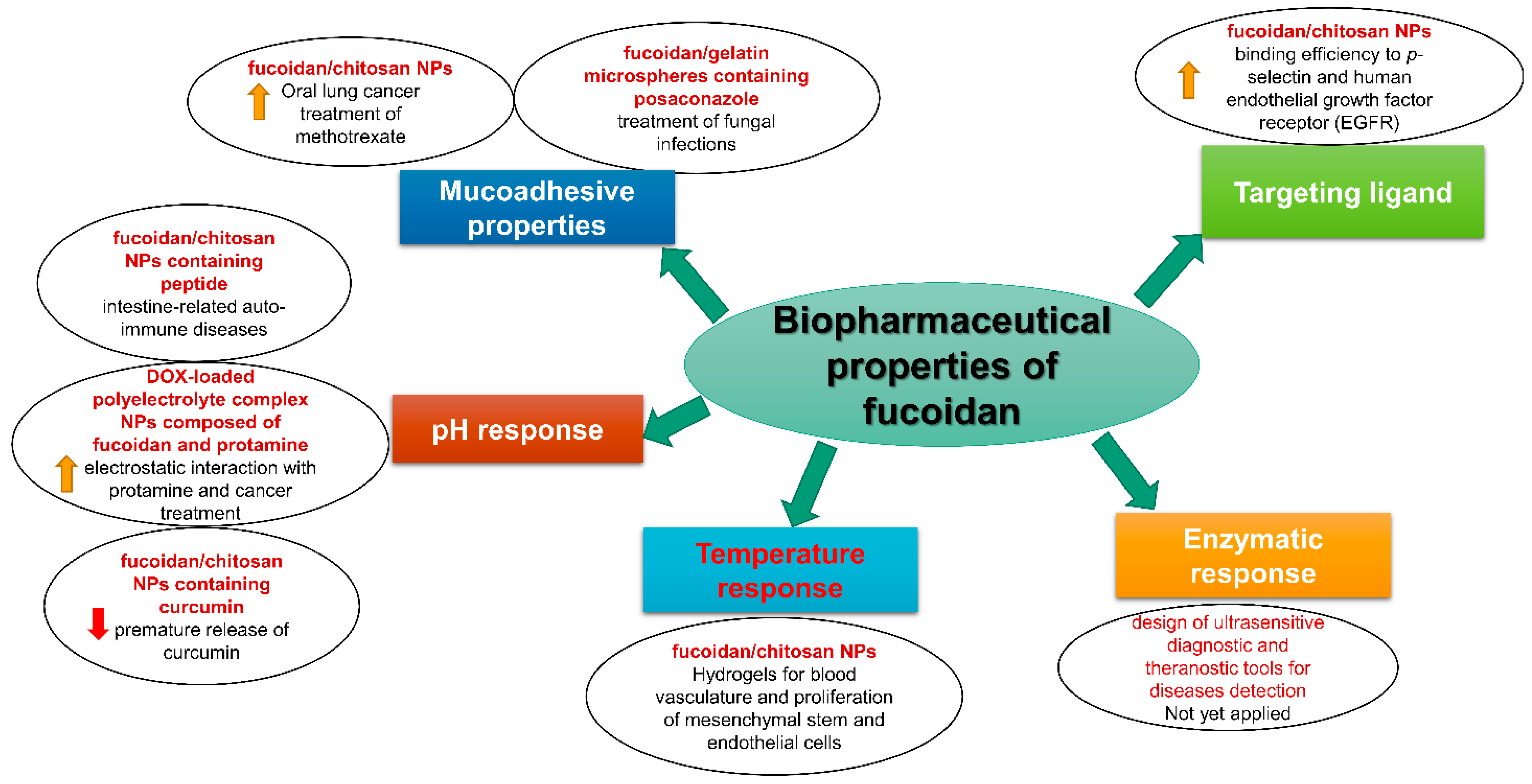
2. Biopharmaceutical Properties of Fucoidan
2.1. Mucoadhesive Properties
2.2. pH Response
2.3. Temperature Response
2.4. Enzymatic Response
2.5. Targeting Ligand
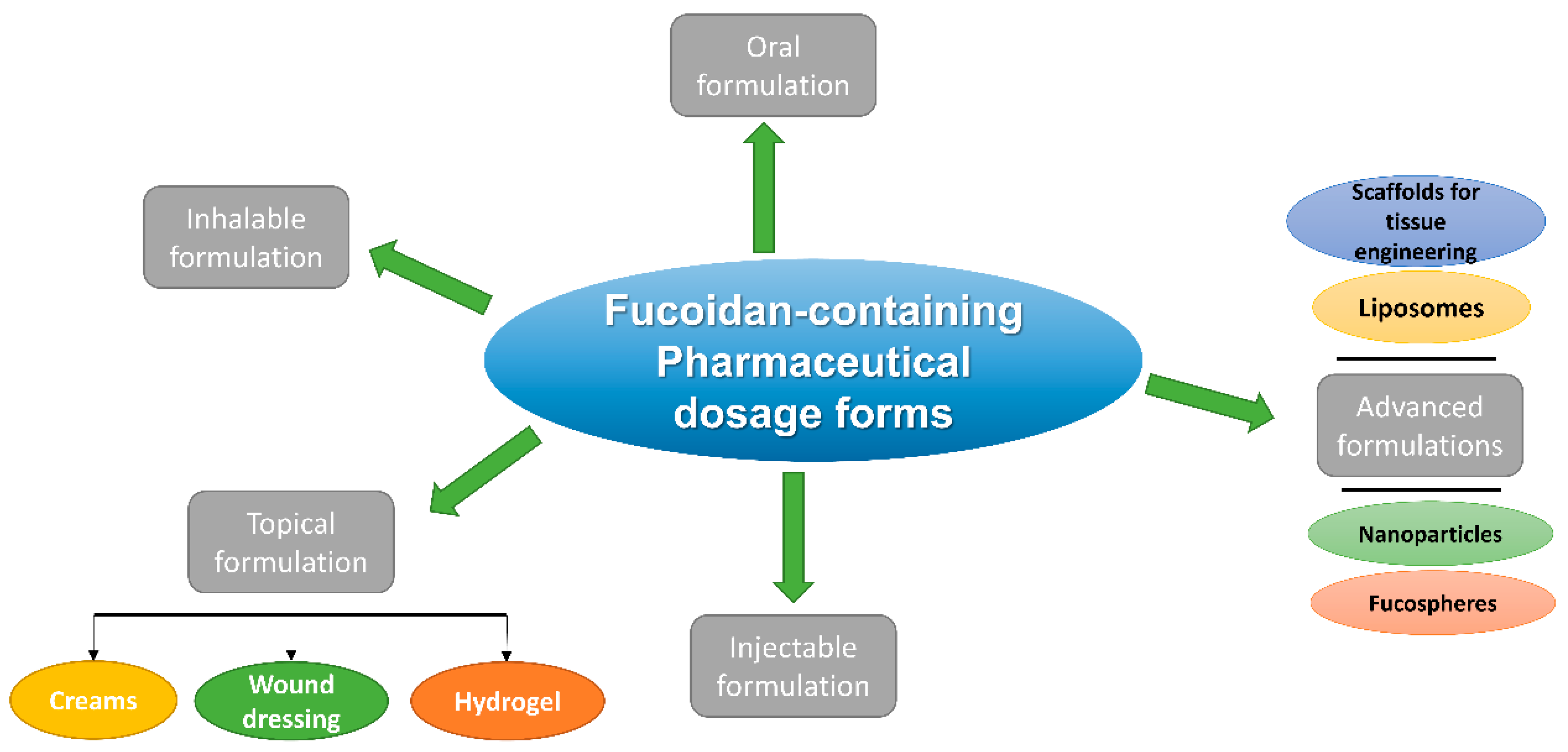
3. Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms of Fucoidan and Their Different Routes of Administration
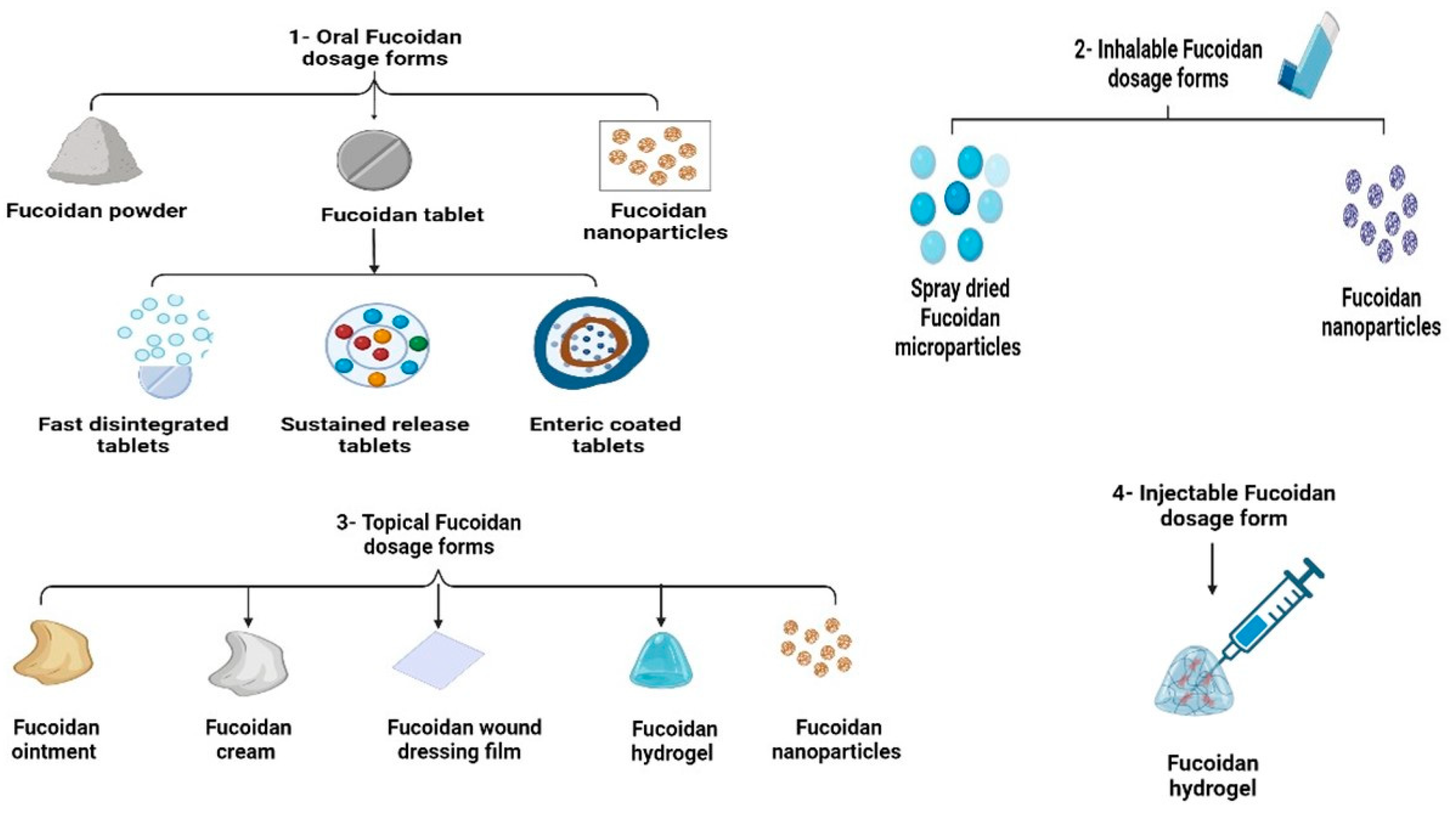
3.1. Oral Fucoidan Formulations
| Tablets | Spray-Dried Microspheres | |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Brown fine powder [55] | Microspheres [59] |
| Taste | Bitter [55] | N/A |
| Solubility | Soluble in water [55] | Soluble in water [59] |
| Mass loss on drying | ≤5% [55] | N/A |
| Mass moisture gain after 1 day | ~4% [55] | N/A |
| Mass moisture gain after 4 days | ~10% [55] | N/A |
| The number of sulfate groups determined by turbidimetry | ≥25% [55] | N/A |
| Bulk density before compression | 0.54 ± 0.06 g/cm3 [55] | 0.45 ± 0.06 [59] |
| Bulk density after compression | 0.80 ± 0.05 g/cm3 [55] | N/A |
| Tapped density | 0.79 ± 0.06 [55] | 0.77 ± 0.19 [59] |
| Compressibility coefficient | 0.05 [55] | N/A |
| Carr index | 32.5 ± 0.8% [55] | N/A |
| Angle of repose | 55 ± 1° [55] | N/A |
| Hausner ratio | 1.48 ± 0.07 [55] | 1.71 ± 0.12 [59] |
| Morphology | Irregular particles [55] | Unloaded microparticles showed smooth surfaces while drug-loaded microparticles showed irregular surfaces [60] |
| Particle diameter | 10 to 500 µm [55] | 1.62 ± 0.8 µm [58] |
3.2. Inhalable Fucoidan Formulations
3.3. Topical Fucoidan Formulations
3.3.1. Fucoidan Creams
3.3.2. Fucoidan Wound Dressing Films
3.3.3. Fucoidan Topical Hydrogels
3.4. Injectable Fucoidan Formulations
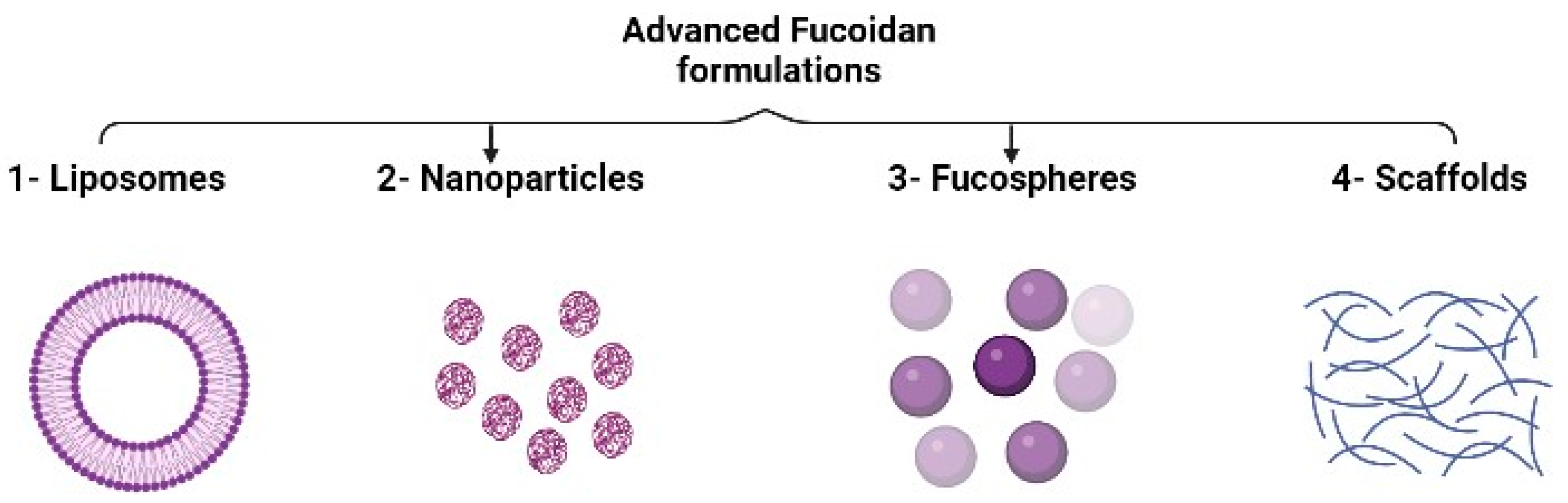
3.5. Advanced Fucoidan Formulations
3.5.1. Liposomes
3.5.2. Nanoparticles
3.5.3. Fucospheres
3.5.4. Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering
4. Fucoidan Pharmacokinetics
5. Scaling up Production of Fucoidan-Based Formulations: Possibilities and Challenges
| Pure Fucoidan Extract | Fucoidan-Based Hydrogel | Fucoidan/Buckwheat Starch Aqueous Paste | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apparent viscosity | Increased at high fucoidan concentration [132]. | Fucoidan has a non-gelling nature, so viscosity is influenced by the addition of another gelling agent, i.e., carrageenan [32]. | Increased at high fucoidan concentration [133]. |
| Type of flow | -Non-Newtonian shear-thinning behavior at low shear rate (1–100 S−1). -A non-Newtonian shear-thickening behavior at high shear rate (100–1000 S−1) [132]. -A Newtonian flow behavior is seen with fucoidan solution extracted from Fucus vesiculosus at concentrations above 2% (w/v) [134]. | Varies according to gelling agent and temperature (especially for thermo-responsive gelling agents) [135]. | -At high a concentration: linear Newtonian flow. -At high a concentration: weak non-Newtonian shear-thinning pseudoplastic flow [133]. |
| Factors affecting viscosity | -Algae species. -Molecular weight. -Degree of branching. The proportion of sulphates and uronic acids. -Temperature and pH. -Presence of ions and additional molecules [25]. | Gelling agent concentration [136]. | Fucoidan concentration [133]. |
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zayed, A.; Dienemann, C.; Giese, C.; Krämer, R.; Ulber, R. An immobilized perylene diimide derivative for fucoidan purification from a crude brown algae extract. Process. Biochem. 2018, 65, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deniaud-Bouët, E.; Hardouin, K.; Potin, P.; Kloareg, B.; Hervé, C. A review about brown algal cell walls and fucose-containing sulfated polysaccharides: Cell wall context, biomedical properties and key research challenges. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 175, 395–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras-esquivel, J.C.; Aguilar, O.; Ramos-de-la-pe, A.M. Structural and bioactive roles of fucoidan in nanogel delivery systems. A review. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2022, 4, 100235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ale, M.T.; Mikkelsen, J.D.; Meyer, A.S. Important determinants for fucoidan bioactivity: A critical review of structure-function relations and extraction methods for fucose-containing sulfated polysaccharides from brown seaweeds. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2106–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catarino, M.D.; Silva, A.M.S.; Cardoso, S.M. Phycochemical constituents and biological activities of Fucus spp. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, H.R.; Biller, P.; Ross, A.B.; Adams, J.M.M. The seasonal variation of fucoidan within three species of brown macroalgae. Algal Res. 2017, 22, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obluchinskaya, E.D.; Pozharitskaya, O.N.; Zakharov, D.V.; Flisyuk, E.V.; Terninko, I.I.; Generalova, Y.E.; Smekhova, I.E.; Shikov, A.N. The Biochemical Composition and Antioxidant Properties of Fucus vesiculosus from the Arctic Region. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benbow, N.L.; Karpiniec, S.; Krasowska, M.; Beattie, D.A. Incorporation of FGF-2 into Pharmaceutical Grade Fucoidan/Chitosan Polyelectrolyte Multilayers. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayani, S.S.; Saravanan, S.; Ravindran, J.; Ramasamy, M.S.; Chitra, J. In vitro anticancer activity of fucoidan extracted from Sargassum cinereum against Caco-2 cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 138, 618–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zayed, A.; Haggag, Y.; Ezzat, S.M.; Salem, M.A.; Ulber, R. Fucoidans as Nanoparticles: Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Applications, 1st ed.; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; ISBN 9780128223512. [Google Scholar]
- Zayed, A.; Finkelmeier, D.; Hahn, T.; Rebers, L.; Shanmugam, A.; Burger-Kentischer, A.; Ulber, R. Characterization and Cytotoxic Activity of Microwave-Assisted Extracted Crude Fucoidans from Different Brown Seaweeds. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozharitskaya, O.N.; Obluchinskaya, E.D.; Shikov, A.N. Mechanisms of Bioactivities of Fucoidan from the Brown Seaweed Fucus vesiculosus L. of the Barents Sea. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sim, S.Y.; Shin, Y.E.; Kim, H.K. Fucoidan from Undaria pinnatifida has anti-diabetic effects by stimulation of glucose uptake and reduction of basal lipolysis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Nutr. Res. 2019, 65, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, M.; Liang, H.; Ji, X.; Liu, Y.; Ge, Y.; Hou, L.; Sun, T. Fucoidan prevent murine autoimmune diabetes via suppression TLR4-signaling pathways, regulation DC/Treg induced immune tolerance and improving gut microecology. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 16, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Guo, C.; Wang, Y.; Su, M.; Huang, W.; Lai, K.P. Preclinical insights into fucoidan as a nutraceutical compound against perfluorooctanoic acid-associated obesity via targeting endoplasmic reticulum stress. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, J.; Ma, S.; Yu, Y.; White, W.L.; Yang, S.; Yang, F.; Lu, J. Fucoidan extracted from Undaria pinnatifida: Source for nutraceuticals/functional foods. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomaa, M.; Hifney, A.F.; Fawzy, M.A.; Abdel-Gawad, K.M. Use of seaweed and filamentous fungus derived polysaccharides in the development of alginate-chitosan edible films containing fucoidan: Study of moisture sorption, polyphenol release and antioxidant properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 82, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.I.; Oh, W.S.; Song, P.H.; Yun, S.; Kwon, Y.S.; Lee, Y.J.; Ku, S.K.; Song, C.H.; Oh, T.H. Anti-photoaging effects of low molecular-weight fucoidan on ultraviolet B-irradiated mice. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, L.; Grenha, A. Sulfated seaweed polysaccharides as multifunctional materials in drug delivery applications. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, S.; Aggarwal, S. Mucoadhesive Polymeric Platform for Drug Delivery; A Comprehensive Review. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2015, 12, 139–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coutinho, A.J.; Costa Lima, S.A.; Afonso, C.M.M.; Reis, S. Mucoadhesive and pH responsive fucoidan-chitosan nanoparticles for the oral delivery of methotrexate. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 158, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marta Szekalska Winnicka, K. The Impact of Gelatin on the Pharmaceutical Characteristics of Fucoidan Microspheres with Posaconazole. Materials 2021, 14, 4087. [Google Scholar]
- Kauscher, U.; Holme, M.N.; Björnmalm, M.; Stevens, M.M. Physical stimuli-responsive vesicles in drug delivery: Beyond liposomes and polymersomes. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 138, 259–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarangi, M.K.; Rao, M.E.B.; Parcha, V.; Yi, D.K.; Nanda, S.S. Marine Polysaccharides for Drug Delivery in Tissue Engineering; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; ISBN 9780128170557. [Google Scholar]
- Citkowska, A.; Szekalska, M.; Winnicka, K. Possibilities of fucoidan utilization in the development of pharmaceutical dosage forms. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbi, S.; Nimal, T.R.; Rajan, V.K.; Baranwal, G.; Biswas, R.; Jayakumar, R.; Sathianarayanan, S. Fucoidan coated ciprofloxacin loaded chitosan nanoparticles for the treatment of intracellular and biofilm infections of Salmonella. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 160, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Huang, Y. Soluble eggshell membrane protein-loaded chitosan/fucoidan nanoparticles for treatment of defective intestinal epithelial cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 131, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.Y.; Li, R.; Hsu, C.H.; Lin, C.W.; Chou, S.C.; Tsai, M.L.; Mi, F.L. Development of a new type of multifunctional fucoidan-based nanoparticles for anticancer drug delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 165, 410–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.C.; Lam, U.I. Chitosan/fucoidan pH sensitive nanoparticles for oral delivery system. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2011, 58, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, S.; Marina, P.F.; Blencowe, A. Thermoresponsive polysaccharides and their thermoreversible physical hydrogel networks. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 207, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Xue, K.; Loh, X.J. Thermo-responsive hydrogels: From recent progress to biomedical applications. Gels 2021, 7, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Tian, J.; Wang, L.; Song, S.; Ai, C.; Janaswamy, S.; Wen, C. Fucoidan hydrogels induced by κ-carrageenan: Rheological, thermal and structural characterization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 191, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, D.; Zhao, A.S.; Su, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.N.; Luo, D.; Gao, Y.; Li, J.A.; Yang, P. An injectable scaffold based on temperature-responsive hydrogel and factor-loaded nanoparticles for application in vascularization in tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res.-Part A 2019, 107, 2123–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, M.; Chen, X. The Novel Medical Thermoresponsive Hydrogel Derived from Chitosan. Curr. Org. Chem. 2018, 22, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, L.A.; Onzi, G.R.; Morawski, A.S.; Pohlmann, A.R.; Guterres, S.S.; Contri, R.V. Chitosan as a coating material for nanoparticles intended for biomedical applications. React. Funct. Polym. 2020, 147, 104459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, B.A.S.; Dufourt, E.C.; Ross, J.; Warner, M.J.; Tanquilut, N.C.; Leung, A.B. Selected Phyto and Marine Bioactive Compounds: Alternatives for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes, 1st ed.; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 55, ISBN 9780444640680. [Google Scholar]
- Mathew, A.P.; Uthaman, S.; Cho, K.H.; Cho, C.S.; Park, I.K. Injectable hydrogels for delivering biotherapeutic molecules. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 110, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köhrmann, A.; Kammerer, U.; Kapp, M.; Dietl, J. Expression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in primary human breast cancer and breast cancer cell lines: New findings and review of the literature. BMC Cancer 2009, 20, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hee, J.M.; Kyong, S.P.; Mi, J.K.; Myeong, S.L.; Seok, H.J.; Imbs, T.I.; Zvyagintseva, T.N.; Ermakova, S.P.; Yong, H.L. Effect of Costaria costata fucoidan on expression of matrix metalloproteinase-1 promoter, mRNA, and protein. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1731–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Rica, R.; Aili, D.; Stevens, M.M. Enzyme-responsive nanoparticles for drug release and diagnostics. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 967–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Katti, P.S.; Gu, Z. Enzyme-responsive nanomaterials for controlled drug delivery. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 12273–12286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Elrahman, A.A.; Mansour, F.R. Targeted magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Preparation, functionalization and biomedical application. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 52, 702–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachelet, L.; Bertholon, I.; Lavigne, D.; Vassy, R.; Jandrot-Perrus, M.; Chaubet, F.; Letourneur, D. Affinity of low molecular weight fucoidan for P-selectin triggers its binding to activated human platelets. BBA-Gen. Subj. 2009, 1790, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Kusaykin, M.I.; Zhang, M.; Bai, X.; Cui, T.; Shi, Y.; Liu, C.; Jia, A. Structural characterization of a P-selectin and EGFR dual-targeting fucoidan from Sargassum fusiforme. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 199, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouzet, F.; Bachelet-Violette, L.; Alsac, J.M.; Suzuki, M.; Meulemans, A.; Louedec, L.; Petiet, A.; Jandrot-Perrus, M.; Chaubet, F.; Michel, J.B.; et al. Radiolabeled Fucoidan as a P-Selectin Targeting Agent for In Vivo Imaging of Platelet-Rich Thrombus and Endothelial Activation. J. Nucl. Med. 2011, 52, 1433–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novoyatleva, T.; Kojonazarov, B.; Owczarek, A.; Veeroju, S.; Rai, N.; Henneke, I.; Böhm, M.; Grimminger, F.; Ghofrani, H.A.; Seeger, W.; et al. Evidence for the fucoidan/P-selectin axis as a therapeutic target in hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 199, 1407–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krylova, N.V.; Ermakova, S.P.; Lavrov, V.F.; Leneva, I.A.; Kompanets, G.G.; Iunikhina, O.V.; Nosik, M.N.; Ebralidze, L.K.; Falynskova, I.N.; Silchenko, A.S.; et al. The Comparative Analysis of Antiviral Activity of Native and Modified Fucoidans from Brown Algae Fucus evanescens In Vitro and In Vivo. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanisamy, S.; Vinosha, M.; Rajasekar, P.; Anjali, R. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules Antibacterial ef fi cacy of a fucoidan fraction (Fu-F2) extracted from Sargassum polycystum. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 125, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biosci, I.J.; Phull, A.; Ali, A.; Ahmed, M.; Zia, M.; Haq, I.; Kim, S.J. In vitro antileishmanial, antibacterial, antifungal and anticancer activity of fucoidan from undaria pinnatifida. Int. J. Biosci. 2017, 6655, 219–227. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.Y.; Lim, S.Y. Fucoidans and bowel health. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, L.; Sun, Z.; Ji, Y.; Wang, D.; Mei, L.; Shen, P.; Li, Z.; Tang, S.; Zhang, H.; et al. Fucoidan as a marine-origin prebiotic modulates the growth and antibacterial ability of Lactobacillus rhamnosus. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 180, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.L.; Tai, C.J.; Huang, C.W.; Chang, F.R.; Wang, J.Y. Efficacy of low-molecular-weight fucoidan as a supplemental therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer patients: A double-blind randomized controlled trial. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitton, J.H.; Stringer, D.N.; Karpiniec, S.S. Therapies from fucoidan: An update. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 5920–5946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, P.H.L.; Lee, B.J.; Tran, T.T.D. Current developments in the oral delivery of fucoidan. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 598, 120371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obluchinskaya, E.D.; Pozharitskaya, O.N.; Flisyuk, E.V.; Shikov, A.N. Optimization of the Composition and Production Technology of Fucoidan Tablets and their Biopharmaceutical Evaluation. Pharm. Chem. J. 2020, 54, 509–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Guo, F.; Hu, J.; Zhang, L.; Xue, C.; Zhang, Z.; Li, B. Antithrombotic activity of oral administered low molecular weight fucoidan from Laminaria Japonica. Thromb. Res. 2016, 144, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuno, M.; Sakaguchi, K.; Sakane, I. Oral administration of fucoidan can exert anti-allergic activity after allergen sensitization by enhancement of galectin-9 secretion in blood. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.J.; Don, T.M.; Lin, C.W.; Mi, F.L. Delivery of berberine using chitosan/fucoidan-taurine conjugate nanoparticles for treatment of defective intestinal epithelial tight junction barrier. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 5677–5697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, L.; Rosa da Costa, A.M.; Lourenço, J.P.; Buttini, F.; Grenha, A. Spray-dried fucoidan microparticles for pulmonary delivery of antitubercular drugs. J. Microencapsul. 2018, 35, 392–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, L.; Rodrigues, S.; da Costa, A.M.R.; Faleiro, M.L.; Buttini, F.; Grenha, A. Inhalable fucoidan microparticles combining two antitubercular drugs with potential application in pulmonary tuberculosis therapy. Polymers 2018, 10, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.; Ngo, D.; Vo, T.; Tran, P. Design of Sustained Release Tablet Containing Fucoidan. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2014, 12, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, L.; Chen, C.; Lin, C.; Ho, Y.; Mi, F. Development of mutlifunctional nanoparticles self-assembled from trimethyl chitosan and fucoidan for enhanced oral delivery of insulin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 126, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, L.C.R.P.; Todaro, V.; do Carmo, F.A.; Frattani, F.S.; de Sousa, V.P.; Rodrigues, C.R.; Sathler, P.C.; Cabral, L.M. A promising oral fucoidan-based antithrombotic nanosystem: Development, activity and safety. 2D Mater. 2018, 29, 165102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.T.-D.; Tran, P.H.-L.; Phan, M.L.-N.; Van, T.V. Colon specific delivery of fucoidan by incorporation of acidifier in enteric coating polymer. Int. J. Pharm. Biosci. Technol. 2013, 9, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.Y.; Wang, C.H. Pulmonary delivery of insulin by liposomal carriers. J. Control. Release 2006, 113, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valente, S.A.; Silva, L.M.; Lopes, G.R.; Sarmento, B.; Coimbra, M.A.; Passos, C.P. Polysaccharide-based formulations as potential carriers for pulmonary delivery—A review of their properties and fates. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 277, 118784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.C.; Li, R.Y.; Chen, J.Y.; Chen, J.K. Biphasic release of gentamicin from chitosan/fucoidan nanoparticles for pulmonary delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 138, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutot, M.; Grassin-Delyle, S.; Salvator, H.; Brollo, M.; Rat, P.; Fagon, R.; Naline, E.; Devillier, P. A marine-sourced fucoidan solution inhibits Toll-like-receptor-3-induced cytokine release by human bronchial epithelial cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 130, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fireman, S.; Toledano, O.; Neimann, K.; Loboda, N.; Dayan, N. A look at emerging delivery systems for topical drug products. Dermatol. Ther. 2011, 24, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharadha, M.; Gowda, D.V.; Vishal Gupta, N.; Akhila, A.R. An overview on topical drug delivery system–updated review. Int. J. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 11, 368–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senni, K.; Gueniche, F.; Foucault-Bertaud, A.; Igondjo-Tchen, S.; Fioretti, F.; Colliec-Jouault, S.; Durand, P.; Guezennec, J.; Godeau, G.; Letourneur, D. Fucoidan a sulfated polysaccharide from brown algae is a potent modulator of connective tissue proteolysis. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2006, 445, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwamoto, K.; Hiragun, T.; Takahagi, S.; Yanase, Y.; Morioke, S.; Mihara, S.; Kameyoshi, Y.; Hide, M. Fucoidan suppresses IgE production in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with atopic dermatitis. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2011, 303, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozharitskaya, O.N.; Shikov, A.N.; Obluchinskaya, E.D.; Vuorela, H. The pharmacokinetics of fucoidan after topical application to rats. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obluchinskaya, E.D.; Pozharitskaya, O.N.; Shikov, A.N. In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Fucoidans from Five Species of Brown Seaweeds. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitton, J.H.; Dell’Acqua, G.; Gardiner, V.A.; Karpiniec, S.S.; Stringer, D.N.; Davis, E. Topical benefits of two fucoidan-rich extracts from marine macroalgae. Cosmetics 2015, 2, 66–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, A.I.; Costa Lima, S.A.; Reis, S. Development of methotrexate loaded fucoidan/chitosan nanoparticles with anti-inflammatory potential and enhanced skin permeation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 124, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J. Topical Application of Fucoidan Improves Atopic Dermatitis Symptoms in NC/Nga Mice. Phytother. Res. 2012, 26, 1898–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, S.; Hamami, A.; Fai, M.; Aththar, A.F.; Zakaria, M.N.Z.; Kharisma, V.D.; Affan, A.; Murtadlo, A.; Tamam, M.B.; Jakhmola, V.; et al. Nano Transdermal Delivery Potential of Fucoidan from Sargassum sp. (Brown Algae) as Chemoprevention Agent for Breast Cancer Treatment. Pharmacogn. J. 2022, 14, 789–795. [Google Scholar]
- Obluchinskaya, E.D.; Pozharitskaya, O.N.; Flisyuk, E.V.; Shikov, A.N. Formulation, optimization and in vivo evaluation of fucoidan-based cream with anti-inflammatory properties. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savencu, I.; Iurian, S.; Porfire, A.; Bogdan, C.; Tomuță, I. Review of advances in polymeric wound dressing films. React. Funct. Polym. 2021, 168, 105059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, L.I.F.; Dias, A.M.A.; Carvalho, E.; De Sousa, H.C. Recent advances on the development of wound dressings for diabetic foot ulcer treatment—A review. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 7093–7114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, K.; Aoki, H.; Nakamura, S.; Nakamura, S.I.; Takikawa, M.; Hanzawa, M.; Kishimoto, S.; Hattori, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Kiyosawa, T.; et al. Hydrogel blends of chitin/chitosan, fucoidan and alginate as healing-impaired wound dressings. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezer, A.D.; Hatipoǧlu, F.; Cevher, E.; Oǧurtan, Z.; Baş, A.L.; Akbuǧa, J. Chitosan film containing fucoidan as a wound dressing for dermal burn healing: Preparation and in vitro/in vivo evaluation. AAPS PharmSciTech 2007, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezer, A.D.; Cevher, E. Topical drug delivery using chitosan nano- and microparticles. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2012, 9, 1129–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sezer, A.D.; Cevher, E.; Hatipoǧlu, F.; Oǧurtan, Z.; Baş, A.L.; Akbuǧa, J. Preparation of fucoidan-chitosan hydrogel and its application as burn healing accelerator on rabbits. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2008, 31, 2326–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali Karami, M.; Sharif Makhmalzadeh, B.; Pooranian, M.; Rezai, A. Preparation and optimization of silibinin-loaded chitosan–fucoidan hydrogel: An in vivo evaluation of skin protection against UVB. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2021, 26, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, S.S.; Venkatesan, J.; Yuvarajan, S.; Rekha, P.D. Self-assembled polyelectrolyte complexes of chitosan and fucoidan for sustained growth factor release from PRP enhance proliferation and collagen deposition in diabetic mice. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2022, 12, 2838–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanmugapriya, K.; Kim, H.; Kang, H.W. Fucoidan-loaded hydrogels facilitates wound healing using photodynamic therapy by in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 247, 116624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klouda, L. Thermoresponsive hydrogels in biomedical applications A seven-year update. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 97, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.T.; Chang, W.T.; Tsai, M.L.; Chen, C.H.; Chen, W.Y.; Mi, F.L. Development of injectable fucoidan and biological macromolecules hybrid hydrogels for intra-articular delivery of platelet-rich plasma. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.L.; Mawad, D.; Dokos, S.; Koshy, P.; Martens, P.J.; Sorrell, C.C. Fucoidan- and carrageenan-based biosynthetic poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogels for controlled permeation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 121, 111821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haggag, Y.; Abu Ras, B.; El-Tanani, Y.; Tambuwala, M.M.; McCarron, P.; Isreb, M.; El-Tanani, M. Co-delivery of a RanGTP inhibitory peptide and doxorubicin using dual-loaded liposomal carriers to combat chemotherapeutic resistance in breast cancer cells. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2020, 17, 1655–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, S.A.; Kwon, M.C.; Han, J.G.; Ha, J.H.; Jin, L.; Jeong, H.S.; Kim, J.C.; You, S.G.; Lee, H.Y. Enhancement of immunomodulatory and anticancer activity of fucoidan by nano encapsulation. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2008, 17, 1254–1260. [Google Scholar]
- Lima Salviano, T.; Dos Santos Macedo, D.C.; de Siqueira Ferraz Carvalho, R.; Pereira, M.A.; de Arruda Barbosa, V.S.; Dos Santos Aguiar, J.; Souto, F.O.; Carvalho da Silva, M.D.P.; Lapa Montenegro Pimentel, L.M.; Correia de Sousa, L.D.Â.; et al. Fucoidan-Coated Liposomes: A Target System to Deliver the Antimicrobial Drug Usnic Acid to Macrophages Infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2021, 17, 1699–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wei, Z.; Xue, C. Physicochemical properties of fucoidan and its applications as building blocks of nutraceutical delivery systems. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 62, 8935–8953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haggag, Y.A.; Yasser, M.; Tambuwala, M.M.; El Tokhy, S.S.; Isreb, M.; Donia, A.A. Repurposing of Guanabenz acetate by encapsulation into long-circulating nanopolymersomes for treatment of triple-negative breast cancer. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 600, 120532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zewail, M.B.; El-Gizawy, S.A.; Osman, M.A.; Haggag, Y.A. Preparation and In vitro characterization of a novel self-nano emulsifying drug delivery system for a fixed-dose combination of candesartan cilexetil and hydrochlorothiazide. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 61, 102320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haggag, Y.A.; Abosalha, A.K.; Tambuwala, M.M.; Osman, E.Y.; El-Gizawy, S.A.; Essa, E.A.; Donia, A.A. Polymeric nanoencapsulation of zaleplon into PLGA nanoparticles for enhanced pharmacokinetics and pharmacological activity. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2021, 42, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, M.A.; Manaa, E.G.; Osama, N.; Aborehab, N.M.; Ragab, M.F.; Haggag, Y.A.; Ibrahim, M.T.; Hamdan, D.I. Coriander (Coriandrum sativum L.) essential oil and oil-loaded nano-formulations as an anti-aging potentiality via TGFβ/SMAD pathway. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haggag, Y.A.; Osman, M.A.; El-Gizawy, S.A.; Goda, A.E.; Shamloula, M.M.; Faheem, A.M.; McCarron, P.A. Polymeric nano-encapsulation of 5-fluorouracil enhances anti-cancer activity and ameliorates side effects in solid Ehrlich Carcinoma-bearing mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 105, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haggag, Y.A.; Matchett, K.B.; Falconer, R.A.; Isreb, M.; Jones, J.; Faheem, A.; McCarron, P.; El-Tanani, M. Novel ran-RCC1 inhibitory peptide-loaded nanoparticles have anti-cancer efficacy in vitro and in vivo. Cancers 2019, 11, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, B.; Mady, O.Y.; Tambuwala, M.M.; Haggag, Y.A. PH-sensitive nanoparticles containing 5-fluorouracil and leucovorin as an improved anti-cancer option for colon cancer. Nanomedicine 2022, 17, 367–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chollet, L.; Saboural, P.; Chauvierre, C.; Villemin, J.; Letourneur, D.; Chaubet, F. Fucoidans in Nanomedicine. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.G.; Venkatesan, J.; Shim, M.S. Selective anticancer therapy using pro-oxidant drug-loaded chitosan–fucoidan nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.W.; Ho, Y.C.; Tsai, T.N.; Tseng, C.L.; Lin, C.; Mi, F.L. Enhancement of the permeability and activities of epigallocatechin gallate by quaternary ammonium chitosan/fucoidan nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 242, 116312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, L.C.; Garcia, T.; Mori, M.; Sandri, G.; Bonferoni, M.C.; Finotelli, P.V.; Cinelli, L.P.; Caramella, C.; Cabral, L.M. Preparation and characterization of polysaccharide-based nanoparticles with anticoagulant activity. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 2975–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etman, S.M.; Abdallah, O.Y.; Elnaggar, Y.S.R. Novel fucoidan based bioactive targeted nanoparticles from Undaria Pinnatifida for treatment of pancreatic cancer. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 145, 390–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, M.J.; Costa, R.R.; Mano, J.F. Marine origin polysaccharides in drug delivery systems. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sezer, A.D.; Akbuğa, J. Comparison on in vitro characterization of fucospheres and chitosan microspheres encapsulated plasmid DNA (pGM-CSF): Formulation design and release characteristics. AAPS PharmSciTech 2009, 10, 1193–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suprunchuk, V.E. Low-molecular-weight fucoidan: Chemical modification, synthesis of its oligomeric fragments and mimetics. Carbohydr. Res. 2019, 485, 107806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezer, A.D.; Akbuǧa, J. Fucosphere-New microsphere carriers for peptide and protein delivery: Preparation and in vitro characterization. J. Microencapsul. 2006, 23, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sezer, A.D.; Akbuǧa, J. The design of biodegradable ofloxacin-based core-shell microspheres: Influence of the formulation parameters on in vitro characterization. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2012, 17, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezer, A.D.; Cevher, E.; Hatipoǧlu, F.; Oǧurtan, Z.; Baş, A.L.; Akbuǧa, J. The use of fucosphere in the treatment of dermal burns in rabbits. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 69, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radvar, E.; Azevedo, H.S. Supramolecular Peptide / Polymer Hybrid Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications. Macromol. Biosci. 2019, 19, e1800221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; McRae, N.L.; McCulloch, D.R.; Boyd-Moss, M.; Barrow, C.J.; Nisbet, D.R.; Stupka, N.; Williams, R.J. Large and Small Assembly: Combining Functional Macromolecules with Small Peptides to Control the Morphology of Skeletal Muscle Progenitor Cells. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 825–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, B.; Venkatesan, J.; Anil, S.; Shim, M.S.; Kim, S.K. Preparation and characterization of chitosan-natural nano hydroxyapatite-fucoidan nanocomposites for bone tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 93, 1479–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Sun, D.; Zhao, X.; Jin, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Q. Microanalysis and preliminary pharmacokinetic studies of a sulfated polysaccharide from Laminaria japonica. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2016, 34, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikov, A.N.; Flisyuk, E.V.; Obluchinskaya, E.D.; Pozharitskaya, O.N. Pharmacokinetics of marine-derived drugs. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Zhang, E.; Hu, B.; Liang, H.; Song, S.; Ji, A. Study on absorption mechanism and tissue distribution of fucoidan. Molecules 2020, 25, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozharitskaya, O.N.; Shikov, A.N.; Faustova, N.M.; Obluchinskaya, E.D.; Kosman, V.M.; Vuorela, H.; Makarov, V.G. Pharmacokinetic and tissue distribution of fucoidan from fucus vesiculosus after oral administration to rats. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravana, P.S.; Cho, Y.J.; Park, Y.B.; Woo, H.C.; Chun, B.S. Structural, antioxidant, and emulsifying activities of fucoidan from Saccharina japonica using pressurized liquid extraction. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 153, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suprunchuk, V. Ultrasonic-treated fucoidan as a promising therapeutic agent. Polim. Med. 2021, 51, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Macquarrie, D.J. Microwave assisted step-by-step process for the production of fucoidan, alginate sodium, sugars and biochar from Ascophyllum nodosum through a biorefinery concept. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 198, 819–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Mikkelsen, M.D.; Nguyen Tran, V.H.; Dieu Trang, V.T.; Rhein-Knudsen, N.; Holck, J.; Rasin, A.B.; Thuy Cao, H.T.; Thanh Van, T.T.; Meyer, A.S. Enzyme-assisted fucoidan extraction from brown macroalgae fucus distichus subsp. Evanescens and saccharina latissima. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flórez-Fernández, N.; Torres, M.D.; González-Muñoz, M.J.; Domínguez, H. Potential of intensification techniques for the extraction and depolymerization of fucoidan. Algal Res. 2018, 30, 128–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Macquarrie, D. Microwave assisted extraction of sulfated polysaccharides (fucoidan) from Ascophyllum nodosum and its antioxidant activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 129, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalak, I.; Chojnacka, K. Algal extracts: Technology and advances. Eng. Life Sci. 2014, 14, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obluchinsksya, E.D.; Makarova, M.N.; Pozharitskaya, O.N.; Shikov, A.N. Effects of Ultrasound Treatment on the Chemical Composition and Anticoagulant Properties of Dry Fucus Extract. Pharm. Chem. J. 2015, 49, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauvierre, C.; Aid-Launais, R.; Aerts, J.; Chaubet, F.; Maire, M.; Chollet, L.; Rolland, L.; Bonafé, R.; Rossi, S.; Bussi, S.; et al. Pharmaceutical development and safety evaluation of a GMP-grade fucoidan for molecular diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowitzka, M.A.; Vonshak, A. Scaling up microalgal cultures to commercial scale. Eur. J. Phycol. 2017, 52, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, A.; Da Silva, T.L. Scale-up Problems for the Large Scale Production of Algae. In Algal Biorefinery: An Integrated Approach; Springer: Kharagpur, India, 2016; pp. 125–149. ISBN 9783319228136. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.; Xue, C.; Chang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Xu, X.; Ge, L.; Liu, G. Structure and rheological characteristics of fucoidan from sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus. Food Chem. 2015, 180, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.L.; Choi, W.S.; You, S.G. Steady and dynamic shear rheology of fucoidan-buckwheat starch mixtures. Starch/Staerke 2009, 61, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hentati, F.; Pierre, G.; Ursu, A.V.; Vial, C.; Delattre, C.; Abdelkafi, S.; Michaud, P. Rheological investigations of water-soluble polysaccharides from the Tunisian brown seaweed Cystoseira compressa. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 103, 105631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, D.N.; Gonçalves, C.; Oliveira, J.M.; Williams, D.S.; Mearns-Spragg, A.; Reis, R.L.; Silva, T.H. Innovative methodology for marine collagen-chitosan-fucoidan hydrogels production, tailoring rheological properties towards biomedical application. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 7016–7029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Zheng, W.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, D.; Sui, K.; Shen, P.; Li, P.; Zhou, Q. Marine polysaccharide-based composite hydrogels containing fucoidan: Preparation, physicochemical characterization, and biocompatible evaluation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 183, 1978–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Haggag, Y.A.; Abd Elrahman, A.A.; Ulber, R.; Zayed, A. Fucoidan in Pharmaceutical Formulations: A Comprehensive Review for Smart Drug Delivery Systems. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21020112
Haggag YA, Abd Elrahman AA, Ulber R, Zayed A. Fucoidan in Pharmaceutical Formulations: A Comprehensive Review for Smart Drug Delivery Systems. Marine Drugs. 2023; 21(2):112. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21020112
Chicago/Turabian StyleHaggag, Yusuf A., Abeer A. Abd Elrahman, Roland Ulber, and Ahmed Zayed. 2023. "Fucoidan in Pharmaceutical Formulations: A Comprehensive Review for Smart Drug Delivery Systems" Marine Drugs 21, no. 2: 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21020112
APA StyleHaggag, Y. A., Abd Elrahman, A. A., Ulber, R., & Zayed, A. (2023). Fucoidan in Pharmaceutical Formulations: A Comprehensive Review for Smart Drug Delivery Systems. Marine Drugs, 21(2), 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21020112







