Theragra chalcogramma Hydrolysate, Rich in Gly-Leu-Pro-Ser-Tyr-Thr, Alleviates Photoaging via Modulating Deposition of Collagen Fibers and Restoration of Extracellular Components Matrix in SD Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Preparation of Low Molecular Weight TCH
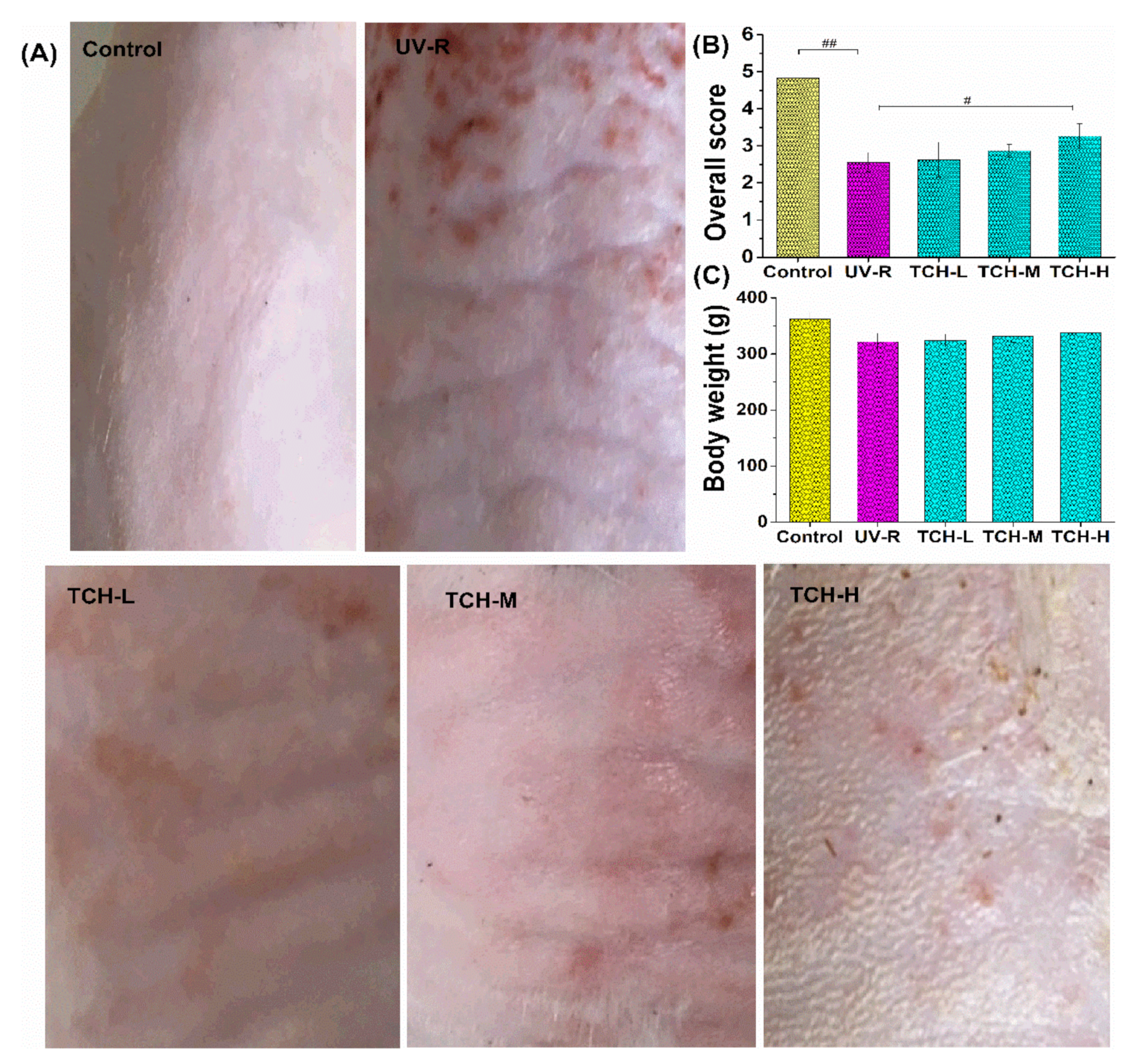
2.2. Effects of TCH on the Appearance and Body Weight in Photoaging Skin
2.3. Effects of TCH on the Barrier Functions in Photoaging Skin of SD Rats
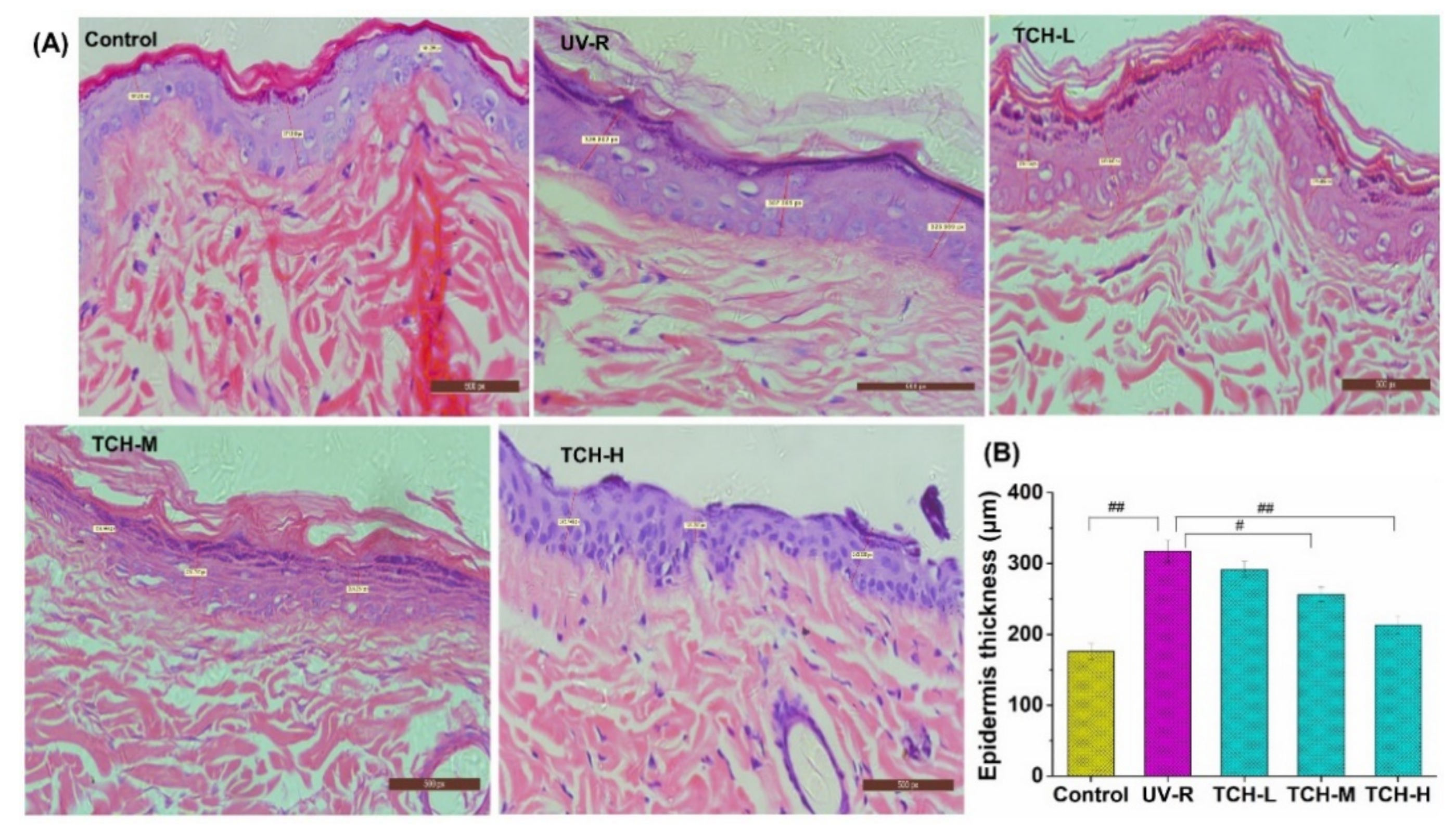
2.4. Effects of TCH on the Pathological Impairments in Photoaging Skin
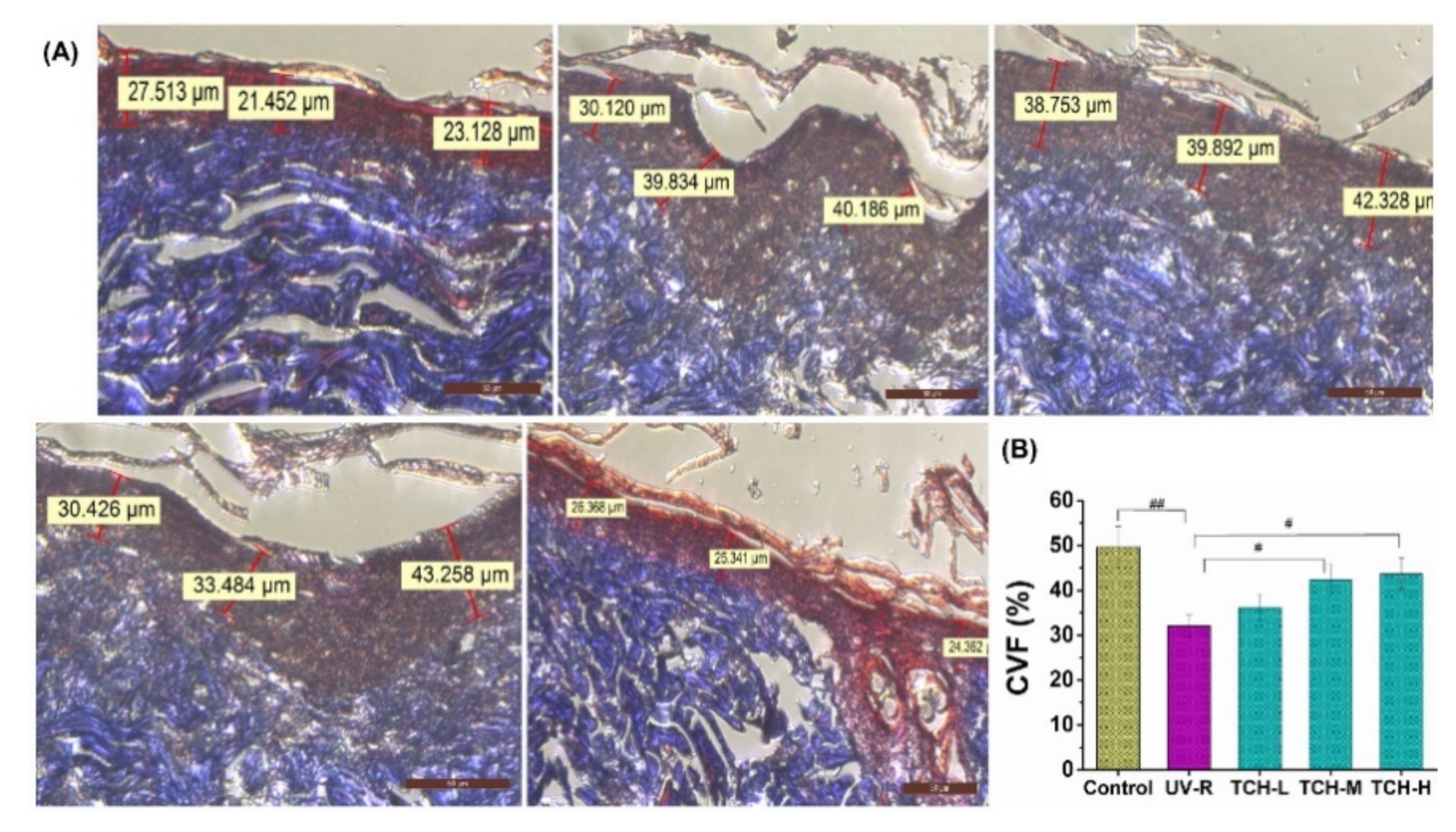
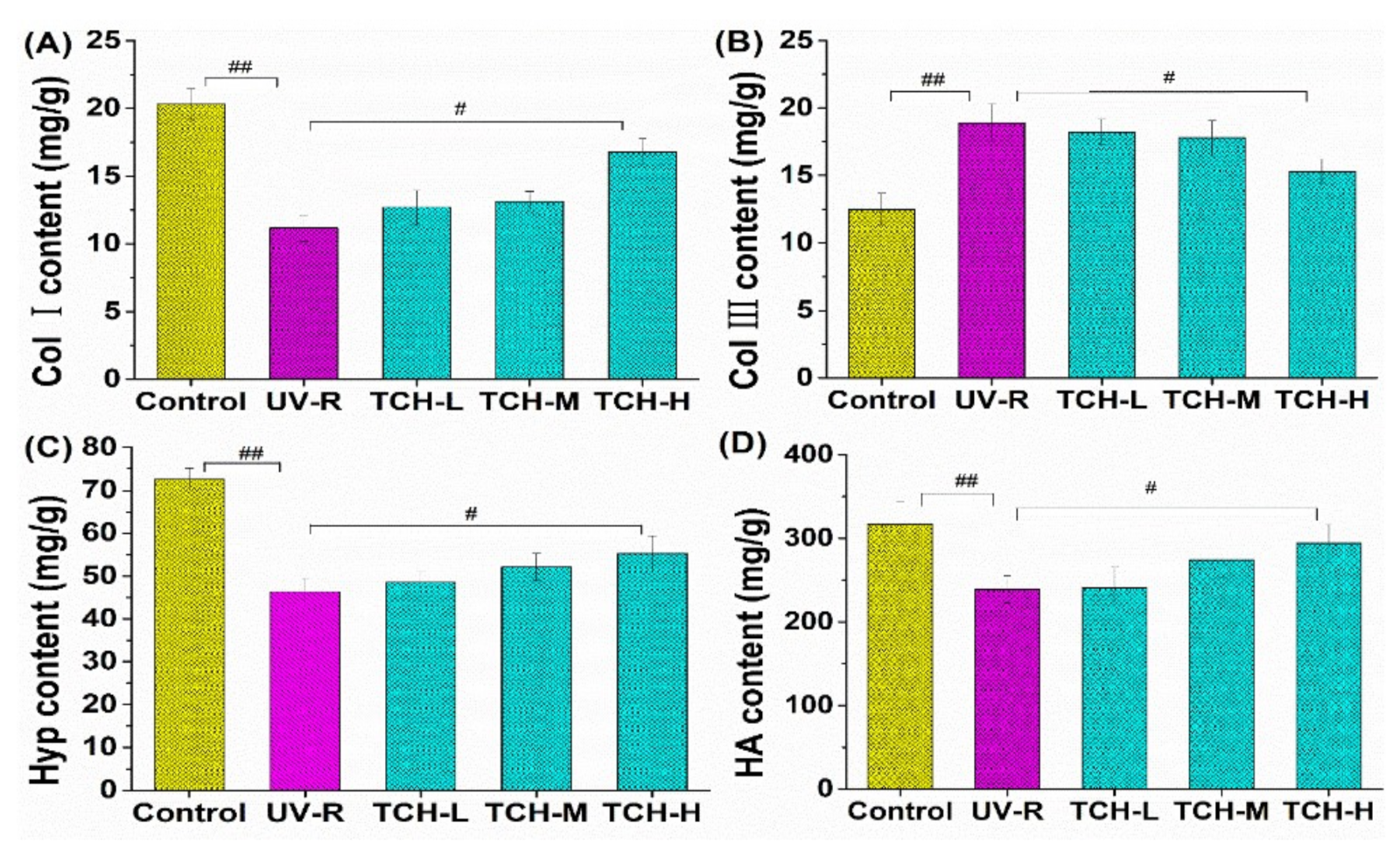
2.5. Effect of TCH on ECM Components
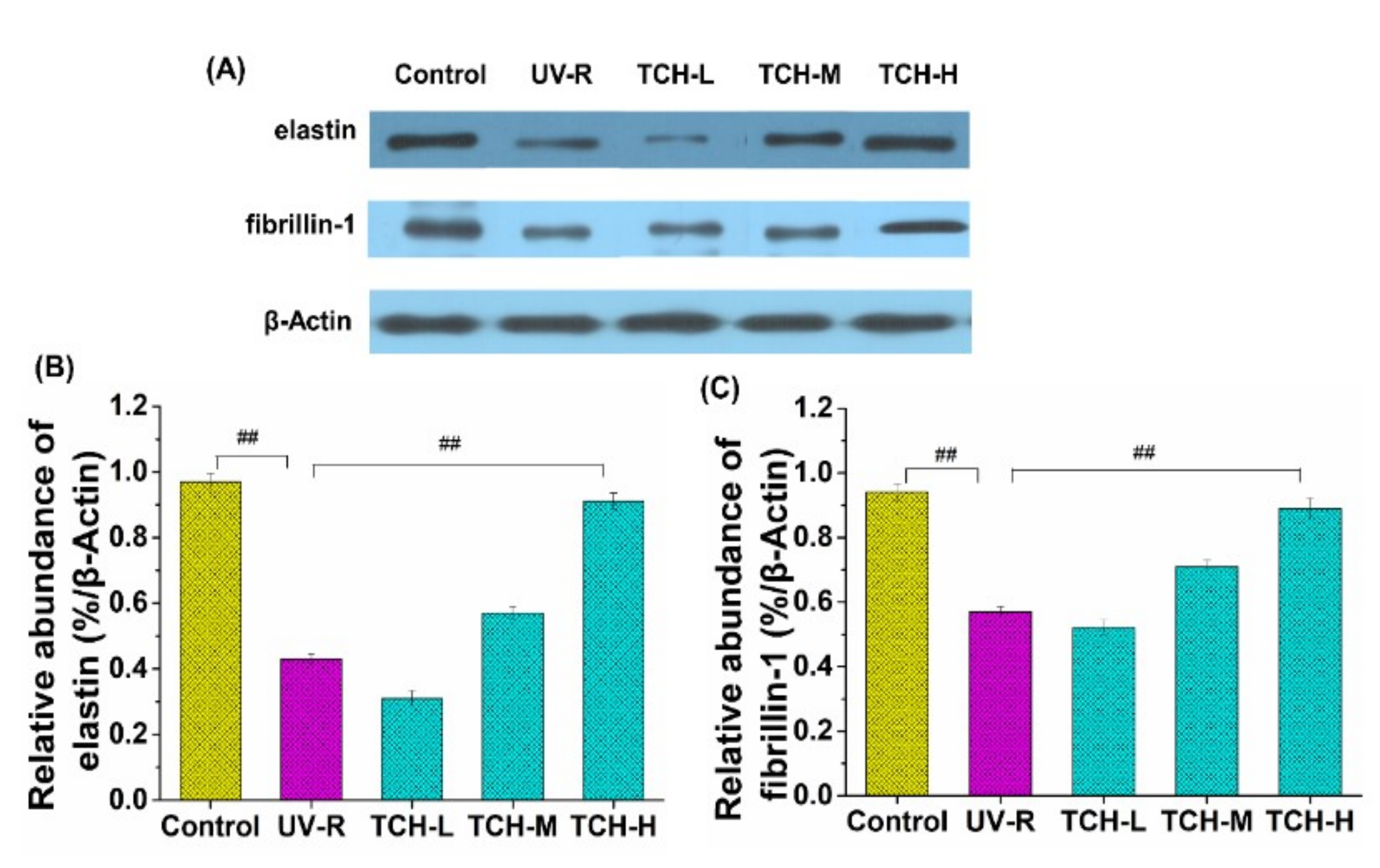
2.6. Effect of TCH on the Level of Elastin and Fibrillin-1
2.7. Effect of TCH on the MMP-1 Activity in Photoaging Skin
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Preparation of TCH
3.2. Materials
3.3. Rats
3.4. Diet
3.5. Establishment of Photoaging Model
3.6. Measurement of Skin Morphology and Barrier Functions
3.7. Determination of ECM Components and MMP-1 Activity
3.8. Western Blotting of Elastin and Fibrillin-1
3.9. Histological Evaluation
3.10. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burke, K.E. Mechanisms of aging and development-A new understanding of environmental damage to the skin and prevention with topical antioxidants. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2018, 172, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Lei, M.; Chang, L.; Xing, Y.; Guo, Y.; Pourzand, C.; Bartsch, J.W.; Chen, J.; Luo, J.; Karisma, V.W.; et al. Bach2 regulates autophagy to modulate UVA-induced photoaging in skin fibroblasts. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 169, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.Y.; Fu, Y.; Dai, H.J.; Wang, Q.; Gao, R.C.; Zhang, Y.H. Recent progress in preventive effect of collagen peptides on photoaging skin and action mechanism. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2022, 11, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanth, M.I.; Gayathri, S.J.; Bhaskar, P.; Krishnan, V.; Balamurugan, K. Understanding the role of p38 and JNK mediated MAPK pathway in response to UV-A induced photoaging in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2020, 205, 11844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.-X.; Yu, X.-T.; Li, W.-J.; Kong, S.-Z.; Liu, Y.-H.; Zhang, X.; Xian, Y.-F.; Zhang, X.-J.; Su, Z.-R.; Lin, Z.-X. Effects of topical application of patchouli alcohol on the UV-induced skin photoaging in mice. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 63, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.H.; Hou, H.; Fan, Y.; Yang, T.T.; Li, B.F. Identification of MMP-1 inhibitory peptides from cod skin gelatin hydrolysates and the inhibition mechanism by MAPK signaling pathway. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 33, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.; Hwang, E.; Seo, S.A.; Zhang, M.Y.; Park, S.Y.; Yi, T.H. Dietary Rosa damascena protects against UVB-induced skin aging by improving collagen synthesis via MMPs reduction through alterations of c-Jun and c-Fos and TGF-β1 stimulation mediated smad2/3 and smad7. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 36, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proksch, E.; Schunck, M.; Zague, V.; Segger, D.; Degwert, J.; Oesser, S. Oral intake of specific bioactive collagen peptides reduce skin wrinkles and increases dermal matrix synthesis. Skin Pharmacol. Phys. 2013, 27, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baroli, B. Penetration of nanoparticles and nanomaterials in the skin: Fiction or reality? J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 21–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundborg, M.; Narangifard, A.; Wennberg, C.L.; Lindahl, E.; Daneholt, B.; Norlén, L. Human skin barrier structure and function analyzed by cryo-EM and molecular dynamics simulation. J. Struct. Biol. 2018, 203, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitak-Arnnop, P.; Hemprich, A.; Dhanuthai, K.; Pausch, N.C. Gold for facial skin care: Fact or fiction? Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2011, 35, 1184–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Z.; Yang, S.; Chen, J.; Li, C.; Zhou, C.; Hong, P.; Sun, S.; Qian, Z.-J. Trehalose against UVB-induced skin photoaging by suppressing MMP expression and enhancing procollagen I synthesis in HaCaT cells. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 74, 104198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, A.; Nosoudi, N.; Karamched, S.; Parasaram, V.; Vyavahar, N. Polyphenol treatments increase elastin and collagen deposition by human dermal fibroblasts; Implications to improve skin health. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2021, 102, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daré, G.R.; Nakamura, V.C.; Ximenes, F.V.; Lautenschlager, O.S.S. Tannic acid, a promising anti-photoaging agent: Evidences of its antioxidant and anti-wrinkle potentials, and its ability to prevent photodamage and MMP-1 expression in L929 fibroblasts exposed to UVB. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 160, 342–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasedya, E.S.; Syafitri, S.M.; Geraldine, B.A.F.D.; Hamdin, C.D.; Frediansyah, A.; Miyake, M.; Kobayashi, D.; Hazama, A.; Sunarpi, H. Photoprotective activity of brown macroalgae Sargassum cristafolium. Biomedicines 2019, 7, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, T.; Hou, H.; Fan, Y.; Wang, S.; Chen, Q.; Si, L.; Li, B. Protective effect of gelatin peptides from pacific cod skin against photoaging by inhibiting the expression of MMPs via, MAPK signaling pathway. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2016, 165, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, M.S.; Kim, C.; Hwang, J.K. Agastache rugosa Kuntze attenuates UVB-induced photoaging in hairless mice through the regulation of MAPK/AP-1 and TGF-beta/Smad Pathways. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 29, 1349–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Kim, D.; Kim, H.J.; Jang, A. Protection effect of donkey hide gelatin hydrolysates on UVB-induced photoaging of human skin fibroblasts. Process Biochem. 2018, 67, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, T.; Okuda, T.; Yasui, N.; Wakaizumi, M.; Ikami, T.; Ikeda, K. Effects of amla extract and collagen peptide on UVB-induced photoaging in hairless mice. J. Funct. Foods 2013, 5, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Koyama, Y.; Nomura, Y. Effects of collagen peptide ingestion on UV-B induced skin damage. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2009, 73, 930–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Je, J.Y.; Park, P.J.; Kim, S.K. Antioxidant activity of a peptide isolated from Alaska pollack (Theragra chalcogramma) frame protein hydrolysate. Food Res. Int. 2005, 38, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.Y.; Li, B.F.; Zhao, X.; Qin, S. Effect of concentration, pH and ionic strength on the kinetic self-assembly of acid-soluble collagen from walleye pollock (Theragra chalcogramma) skin. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 29, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Geng, J.-T.; Thanathornvarakul, N.; Keratimanoch, S.; Üçyol, N.; Okazaki, E.; Osako, K. The influence of processing sequence and frozen storage on the seasoned alaska pollack (Theragra chalcogramma) roe product quality. Food Chem. 2022, 373, 131516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Hu, J.Y.; Wang, S.Q. The role of antioxidants in photoprotection: A critical review. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2012, 67, 1013–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Tian, Q.; Li, L.; Khan, M.N.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, X.; Chen, S. Inhibitory effect of antioxidant peptides derived from pinctada fucata protein on ultraviolet-induced photoaging in mice. J. Funct. Foods 2013, 5, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalamaiah, M.; Ulug, S.K.; Hong, H.; Wu, J.P. Regulatory requirements of bioactive peptides (protein hydrolysates) from food proteins. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 58, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, N.; Jesus GF, A.; Gonçalves AF, N.; de Oliveira, N.S.; Sugai, J.K.; Pessatti, M.L.; Fabregat, T.E.H. Sardine (Sardinella spp.) protein hydrolysate as growth promoter in South American catfish (Rhamdia quelen) feeding: Productive performance, digestive enzymes activity, morphometry and intestinal microbiology. Aquaculture 2019, 500, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, S.Z.; Li, D.D.; Luo, H.; Li, W.J.; Huang, Y.M.; Hu, Z. Anti-photoaging effects of chitosan oligosaccharide in ultraviolet-irradiated hairless mouse skin. Exp. Gerontol. 2018, 103, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Quan, T.H.; Hammerberg, C.J.; Voorhees, J.; Fisher, G.J. A mouse model of skin aging: Fragmentation of dermal collagen fibrils and reduced fibroblast spreading due to expression of human matrix metalloproteinase-1. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2015, 78, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, G.J.; Varani, J.; Voorhees, J.J. Looking older: Fibroblast collapse and therapeutic implications. Arch. Dermatol. 2008, 144, 666–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, G.J.; Quan, T.; Purohit, T.; Shao, Y.; Cho, M.K.; He, T.; Varani, J.; Kang, S.; Voorhees, J.J. Collagen fragmentation promotes oxidative stress and elevates matrix metalloproteinase-1 in fibroblasts in aged human skin. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 174, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Im, A.R.; Kim, H.S.; Hyun, J.W.; Chae, S. Potential for tyndalized lactobacillus acidophilus as an effective component in moisturizing skin and anti-wrinkle products. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 12, 759–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shim, J.H.; Dong, W.S.; Lee, T.R.; Hak, H.K.; Sun, H.J.; Minsoo, N. The retinoic acid-induced up-regulation of insulin-like growth factor 1 and 2 is associated with prolidase-dependent collagen synthesis in UVA-irradiated human dermal equivalents. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2012, 66, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suganuma, K.; Nakajima, H.M.; Imokawa, G. Astaxanthin attenuates the UVA-induced up-regulation of matrix-metalloproteinase-1 and skin fibroblast elastase in human dermal fibroblasts. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2010, 58, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.-S.; Han, M.; Shin, H.S.; Kim, M.-K.; Shin, C.-Y.; Lee, D.H.; Chung, J.H. Perilla frutescens leaves extract ameliorates ultraviolet radiation-induced extracellular matrix damage in human dermal fibroblasts and hairless mice skin. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 195, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobin, D.J. Introduction to skin aging. J. Tissue Viability 2017, 26, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wen, L.; Gao, Q.; Ma, C.W.; Ge, Y.; You, L.; Liu, R.H. Effect of polysaccharides from tremella fuciformis on UV-induced photoaging. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 20, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasushi, Y.; Kei, O.; Yuri, O.; Yasuhiro, S.; Hitoshi, M.; Yoko, F. Efficacy of thermal stimulation on wrinkle removal via the enhancement of collagen synthesis. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2006, 2, S39–S49. [Google Scholar]
- Kawada, C.; Kimura, M.; Masuda, Y.; Nomura, Y. Oral administration of hyaluronan prevents skin dryness and epidermal thickening in ultraviolet irradiated hairless mice. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2015, 153, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, G.J.; Kang, S.; Varani, J.; Bata-Csorgo, Z.; Wan, Y.; Datta, S.; Voorhees, J.J. Mechanisms of photoaging and chronological skin aging. Arch. Dermatol. 2002, 138, 1462–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavinato, M.; Jansen-Dürr, P. Molecular mechanisms of UVB-induced senescence of dermal fibroblasts and its relevance for photoaging of the human skin. Exp. Gerontol. 2017, 94, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, A.; Anna, L.C.; Sewon, K. Photoaging. Dermatol. Clin. 2014, 32, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.F.; Li, D.; Zhao, Z.J.; Wu, J.X.; Zhao, M.M. Regulation by walnut protein hydrolysate on the components and structural degradation of photoaged skin in SD rats. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 6792–6802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inomata, S.J.; Takada, K.; Tsunenaga, M.; Fukuda, M. Possible involvement of gelatinases in basement membrane damage and wrinkle formation in chronically ultraviolet B-exposed hairless mouse. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2003, 120, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takeuchi, H.; Gomi, T.; Shishido, M.; Watanabe, H.; Suenobu, N. Neutrophil elastase contributes to extracellular matrix damage induced by chronic low-dose UV irradiation in a hairless mouse photoaging model. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2010, 60, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.T.; Zhen, J.; Yang, Y.; Gu, J.N.; Wu, S.S.; Liu, Q. Ginsenoside Rg1 ameliorates diabetic cardiomyopathy by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis in a streptozotocin-induced diabetes rat model. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2016, 20, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, D.; Li, C.; Zhao, M. Theragra chalcogramma Hydrolysate, Rich in Gly-Leu-Pro-Ser-Tyr-Thr, Alleviates Photoaging via Modulating Deposition of Collagen Fibers and Restoration of Extracellular Components Matrix in SD Rats. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20040252
Xu D, Li C, Zhao M. Theragra chalcogramma Hydrolysate, Rich in Gly-Leu-Pro-Ser-Tyr-Thr, Alleviates Photoaging via Modulating Deposition of Collagen Fibers and Restoration of Extracellular Components Matrix in SD Rats. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(4):252. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20040252
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Defeng, Caihong Li, and Mouming Zhao. 2022. "Theragra chalcogramma Hydrolysate, Rich in Gly-Leu-Pro-Ser-Tyr-Thr, Alleviates Photoaging via Modulating Deposition of Collagen Fibers and Restoration of Extracellular Components Matrix in SD Rats" Marine Drugs 20, no. 4: 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20040252
APA StyleXu, D., Li, C., & Zhao, M. (2022). Theragra chalcogramma Hydrolysate, Rich in Gly-Leu-Pro-Ser-Tyr-Thr, Alleviates Photoaging via Modulating Deposition of Collagen Fibers and Restoration of Extracellular Components Matrix in SD Rats. Marine Drugs, 20(4), 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20040252





