Sargachromenol Isolated from Sargassum horneri Attenuates Glutamate-Induced Neuronal Cell Death and Oxidative Stress through Inhibition of MAPK/NF-κB and Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
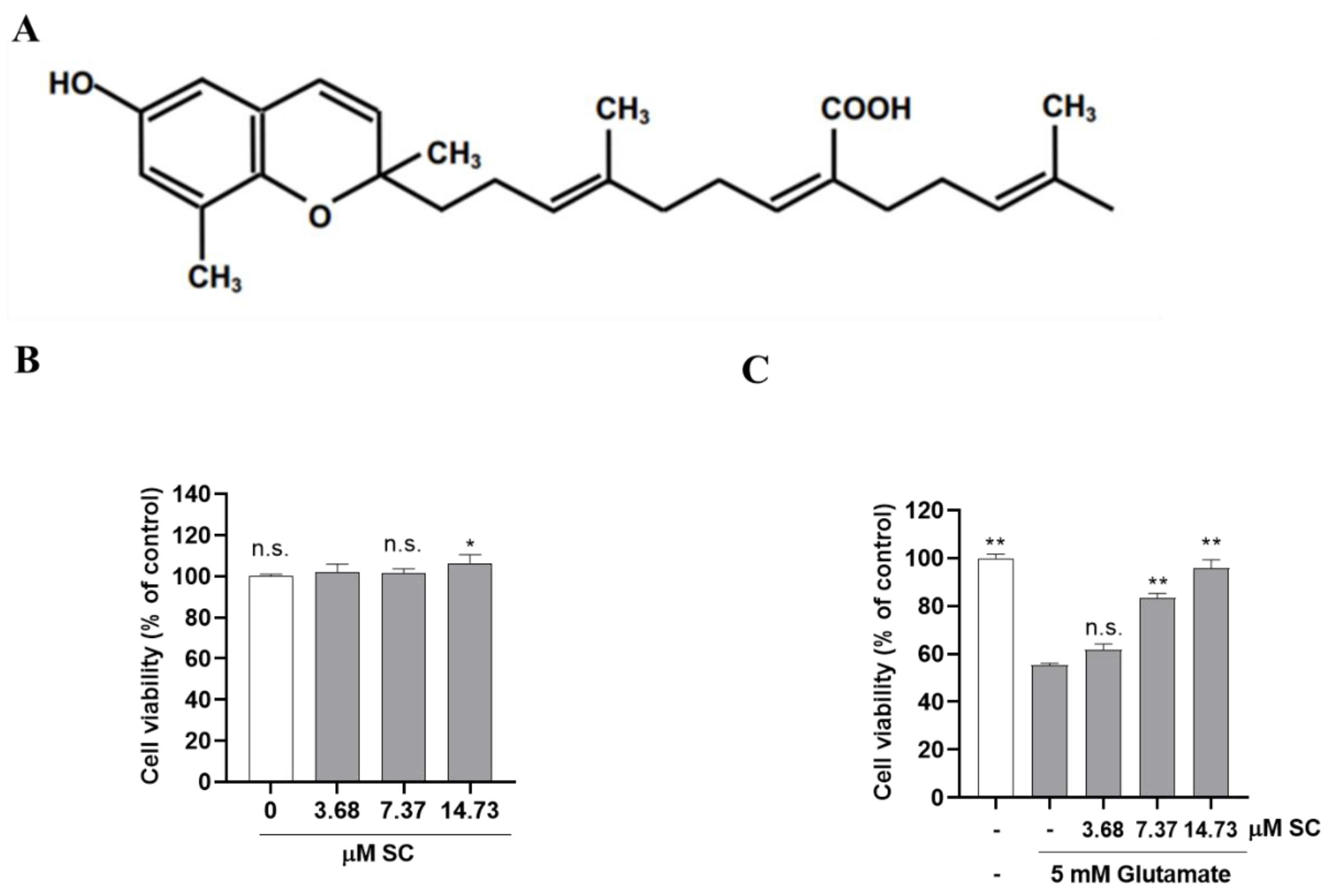
2.1. SC Attenuates Glutamate-Induced Cell Death in Neuronal HT22 Cells
2.2. SC Inhibits Cellular Damage by Modulating the Expression of Apoptosis-Mediated Proteins
2.3. SC Reduces the Production of Intracellular ROS via Inactivation of the Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases (MAPK) Signaling Pathway
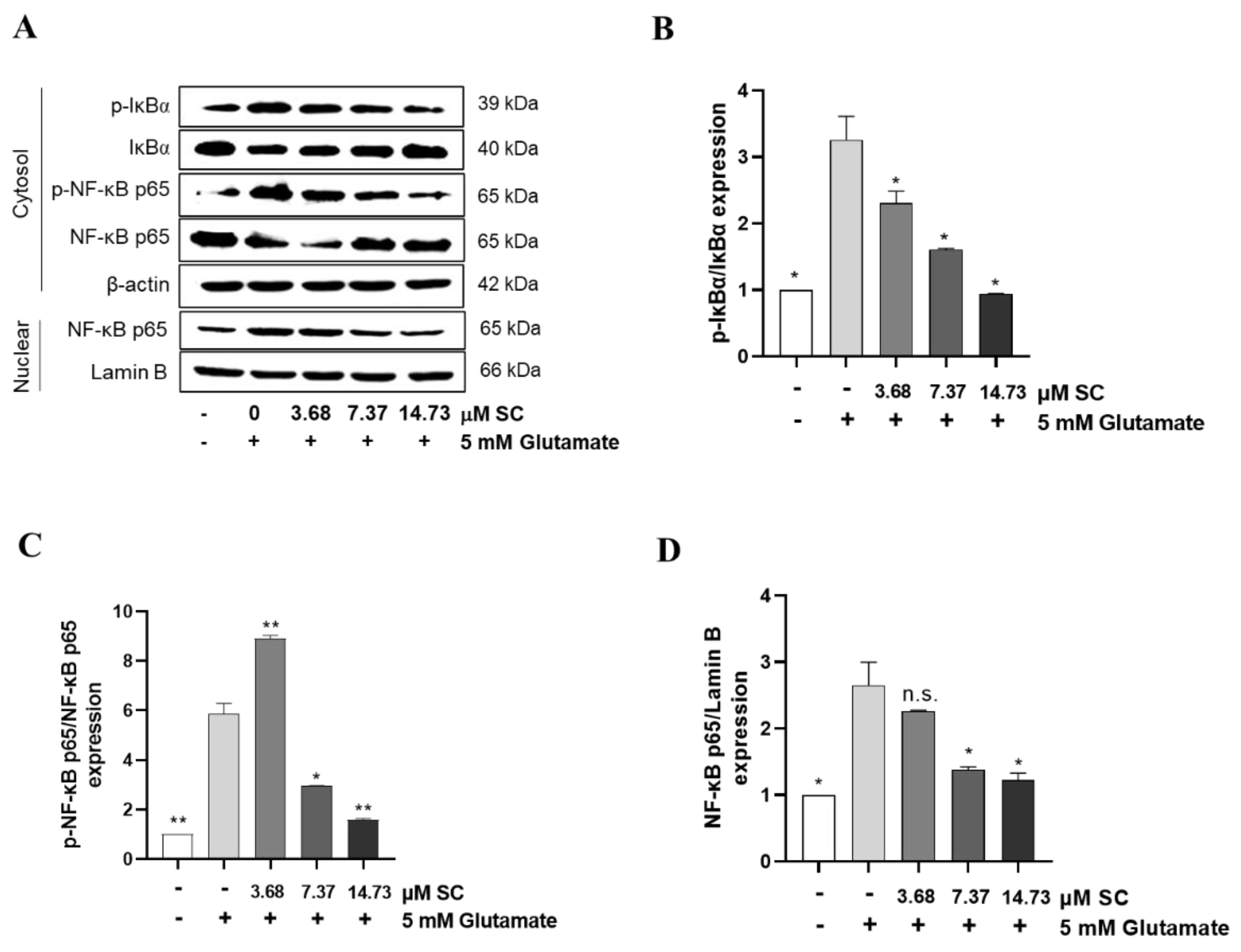
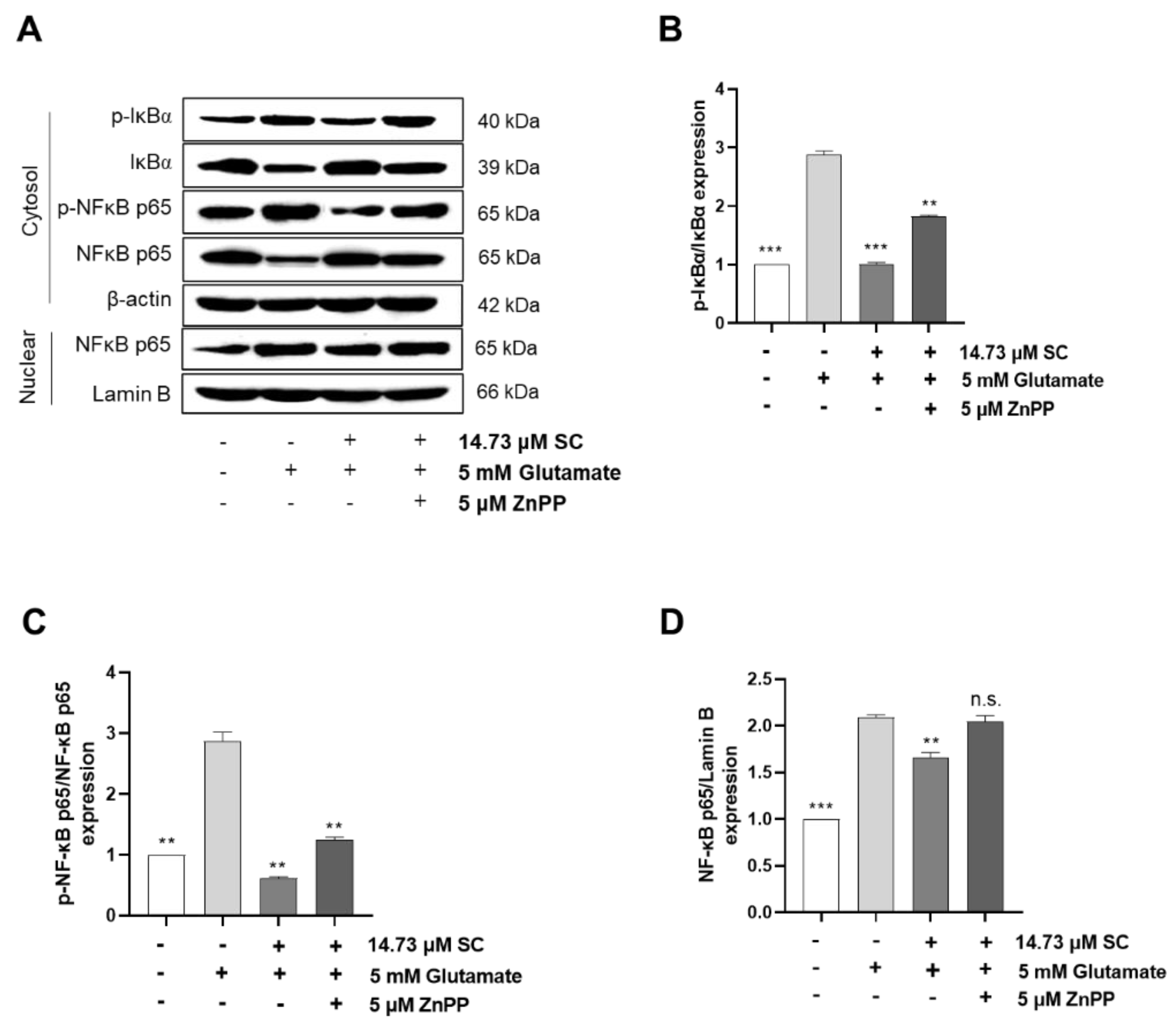
2.4. SC Inhibits the Activation of Nuclear Factor Kappa-Light-Chain-Enhancer of Activated B Cells (NF-κB) Signaling in Glutamate-Treated HT22 Cells
2.5. SC Activates Nuclear Factor Erythroid-2-Related Factor 2 (Nrf2)/Heme Oxygenase 1 (HO-1) Signaling Pathway in Glutamate-Treated HT22 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Cell Viability Assay
4.4. Measurement of Sub-G1 Hypodipolid Cells
4.5. Measurement of Apoptotic Body Formation
4.6. Measurement of Intracellular ROS Production
4.7. Western Blot Assay
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Dugger, B.N.; Dickson, D.W. Pathology of neurodegenerative diseases. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2017, 9, a028035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Platt, S.R. The role of glutamate in central nervous system health and disease—A review. Vet. J. 2007, 173, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezza, H.S.A.; Khadrawyb, Y.A. Glutamate Excitotoxicity and Neurodegeneration. J. Mol. Genet. Med. 2014, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przedborski, S.; Vila, M.; Jackson-Lewis, V. Neurodegeneration: What is it and where are we? J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 111, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Palenzuela Gardon, D.; Cervantes Llanos, M.; Piniella Matamoros, B.; Camacho Rodriguez, H.; Tan, C.Y.; Marín-Prida, J.; Penton-Rol, G. Positive Effects of Phycocyanobilin on Gene Expression in Glutamate-Induced Excitotoxicity in SH-SY5Y Cells and Animal Models of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderklish, P.W.; Bahr, B.A. The pathogenic activation of calpain: A marker and mediator of cellular toxicity and disease states. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2000, 81, 323–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mody, I.; MacDonald, J.F. NMDA receptor-dependent excitotoxicity: The role of intracellular Ca2+ release. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1995, 16, 356–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz-Unal, A.; Korulu, S.; Karabay, A. Neuroprotective strategies against calpain-mediated neurodegeneration. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2015, 11, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, S.; Schubert, D.; Maher, P. Oxytosis: A novel form of programmed cell death. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2001, 1, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pak, M.E.; Choi, B.T. Ethanol extract from asparagus cochinchinensis attenuates glutamate-induced oxidative toxicity in HT22 hippocampal cells. J. Life Sci. 2016, 26, 1458–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoharan, S.; Essa, M.M.; Vinoth, A.; Kowsalya, R.; Manimaran, A.; Selvasundaram, R. Alzheimer’s disease and medicinal plants: An overview. Adv. Neurobiol. 2016, 12, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbalace, M.C.; Malaguti, M.; Giusti, L.; Lucacchini, A.; Hrelia, S.; Angeloni, C. Anti-inflammatory activities of marine algae in neurodegenerative diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Silva, J.; Alves, C.; Freitas, R.; Martins, A.; Pinteus, S.; Ribeiro, J.; Gaspar, H.; Alfonso, A.; Pedrosa, R. Antioxidant and neuroprotective potential of the brown seaweed bifurcaria bifurcata in an in vitro Parkinson’s disease model. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schepers, M.; Martens, N.; Tiane, A.; Vanbrabant, K.; Liu, H.B.; Lutjohann, D.; Mulder, M.; Vanmierlo, T. Edible seaweed-derived constituents: An undisclosed source of neuroprotective compounds. Neural Regen. Res. 2020, 15, 790–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.Y. Antifouling chromanols isolated from brown alga Sargassum horneri. J. Appl. Phycol. 2013, 25, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, M. Marine alga Sargassum horneri component and bone homeostasis: Role in osteoporosis prevention. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. Diet 2013, 2, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Sanjeewa, K.K.A.; Fernando, I.P.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, H.S.; Ahn, G.; Jee, Y.; Jeon, Y.J. In vitro and in vivo anti-inflammatory activities of high molecular weight sulfated polysaccharide; containing fucose separated from Sargassum horneri: Short communication. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 803–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjeewa, K.K.A.; Jayawardena, T.U.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, H.G.; Je, J.G.; Jee, Y.; Jeon, Y.J. Sargassum horneri (Turner) inhibit urban particulate matter-induced inflammation in MH-S lung macrophages via blocking TLRs mediated NF-kappaB and MAPK activation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 249, 112363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, C.K.; Ina, A.; Goto, T.; Kamei, Y. Sargachromenol, a novel nerve growth factor-potentiating substance isolated from Sargassum macrocarpum, promotes neurite outgrowth and survival via distinct signaling pathways in PC12D cells. Neuroscience 2005, 132, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.A.; Ahn, B.N.; Kong, C.S.; Kim, S.K. Protective effect of chromene isolated from Sargassum horneri against UV-A-induced damage in skin dermal fibroblasts. Exp. Dermatol. 2012, 21, 630–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Zhai, Z. Nucleoplasmin regulates chromatin condensation during apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 2778–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourens, M.; Fontanesi, F.; Soto, I.C.; Liu, J.; Barrientos, A. Redox and reactive oxygen species regulation of mitochondrial cytochrome C oxidase biogenesis. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 19, 1940–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Denzer, I.; Muench, G.; Friedland, K. Modulation of mitochondrial dysfunction in neurodegenerative diseases via activation of nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2 by food-derived compounds. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 103, 80–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellezza, I.; Tucci, A.; Galli, F.; Grottelli, S.; Mierla, A.L.; Pilolli, F.; Minelli, A. Inhibition of NF-kappaB nuclear translocation via HO-1 activation underlies alpha-tocopheryl succinate toxicity. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2012, 23, 1583–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyss-Coray, T. Ageing, neurodegeneration and brain rejuvenation. Nature 2016, 539, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prince, M.J.; Wu, F.; Guo, Y.; Gutierrez Robledo, L.M.; O’Donnell, M.; Sullivan, R.; Yusuf, S. The burden of disease in older people and implications for health policy and practice. Lancet 2015, 385, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, E.J.; Kim, G.S.; Jun, M.; Song, K.S. Kaempferol attenuates the glutamate-induced oxidative stress in mouse-derived hippocampal neuronal HT22 cells. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 1395–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorman, A.M. Neuronal cell death in neurodegenerative diseases: Recurring themes around protein handling. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2008, 12, 2263–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lossi, L.; Merighi, A. In vivo cellular and molecular mechanisms of neuronal apoptosis in the mammalian CNS. Prog. Neurobiol. 2003, 69, 287–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, M.; Song, J.H.; Choi, J.; Choi, H.J.; Zhu, B.T. Mechanism of glutamate-induced neurotoxicity in HT22 mouse hippocampal cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 617, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redza-Dutordoir, M.; Averill-Bates, D.A. Activation of apoptosis signalling pathways by reactive oxygen species. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2016, 1863, 2977–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Park, C.; Kim, G.Y.; Park, E.K.; Jeon, Y.J.; Kim, S.; Choi, Y.H. Sargassum serratifolium attenuates RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation and oxidative stress through inhibition of NF-κB and activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. BioSci. Trends 2018, 12, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Son, Y.; Cheong, Y.K.; Kim, N.H.; Chung, H.T.; Kang, D.G.; Pae, H.O. Mitogen-activated protein kinases and reactive oxygen species: How can ros activate mapk pathways? J. Signal Transduct. 2011, 2011, 792639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, C.N.; Tolkovsky, A.M. A role for MAPK/ERK in sympathetic neuron survival: Protection against a p53-dependent, JNK-independent induction of apoptosis by cytosine arabinoside. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 664–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pearson, G.; Robinson, F.; Beers Gibson, T.; Xu, B.E.; Karandikar, M.; Berman, K.; Cobb, M.H. Mitogen-activated protein (map) kinase pathways: Regulation and physiological functions. Endocr. Rev. 2001, 22, 153–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suh, H.W.; Kang, S.; Kwon, K.S. Curcumin attenuates glutamate-induced HT22 cell death by suppressing MAP kinase signaling. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2007, 298, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crampton, S.J.; O’Keeffe, G.W. NF-kappaB: Emerging roles in hippocampal development and function. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 1821–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzi, M.; Spano, P. Distinct roles of diverse nuclear factor-kappaB complexes in neuropathological mechanisms. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 545, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camandola, S.; Mattson, M.P. NF-kappa B as a therapeutic target in neurodegenerative diseases. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2007, 11, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Luan, Y.; Lu, B.; Zhang, H.; Luo, Y.N.; Ge, P. Protection of ischemic postconditioning against neuronal apoptosis induced by transient focal ischemia is associated with attenuation of NF-kappaB/p65 activation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattson, M.P.; Camandola, S. NF-kappaB in neuronal plasticity and neurodegenerative disorders. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 107, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemens, J.A.; Stephenson, D.T.; Dixon, E.P.; Smalstig, E.B.; Mincy, R.E.; Rash, K.S.; Little, S.P. Global cerebral ischemia activates nuclear factor-kappa B prior to evidence of DNA fragmentation. Mol. Brain Res. 1997, 48, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Potrovita, I.; Tarabin, V.; Herrmann, O.; Beer, V.; Weih, F.; Schneider, A.; Schwaninger, M. Neuronal activation of NF-kappaB contributes to cell death in cerebral ischemia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2005, 25, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakai, M.; Qin, Z.H.; Chen, J.F.; Wang, Y.; Chase, T.N. Kainic acid-induced apoptosis in rat striatum is associated with nuclear factor-kappaB activation. J. Neurochem. 2000, 74, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Yang, L.; Hong, L.Z.; Zhao, X.Y.; Zhang, H.L. Direct protection of neurons and astrocytes by matrine via inhibition of the NF-κB signaling pathway contributes to neuroprotection against focal cerebral ischemia. Brain Res. 2012, 1454, 48–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.Y.; Kim, M.R. Neuroprotective effect of carotenoid-rich enteromorpha prolifera extract via trkb/akt pathway against oxidative stress in hippocampal neuronal cells. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K.E.; Park, J.J. Can co-activation of Nrf2 and neurotrophic signaling pathway slow alzheimer’s disease? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, E.-J.; Jayawardena, T.U.; Jang, J.-H.; Fernando, I.P.S.; Jee, Y.; Jeon, Y.-J.; Lee, D.-S.; Lee, J.-M.; Yim, M.-J.; Wang, L.; et al. Sargachromenol Purified from Sargassum horneri Inhibits Inflammatory Responses via Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling in LPS-Stimulated Macrophages. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, E.-J.; Zhang, C.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, J.-Y.; Park, S.-M.; Jung, W.-K.; Ahn, G.; Cha, S.-H. Sargachromenol Isolated from Sargassum horneri Attenuates Glutamate-Induced Neuronal Cell Death and Oxidative Stress through Inhibition of MAPK/NF-κB and Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20110710
Han E-J, Zhang C, Kim H-S, Kim J-Y, Park S-M, Jung W-K, Ahn G, Cha S-H. Sargachromenol Isolated from Sargassum horneri Attenuates Glutamate-Induced Neuronal Cell Death and Oxidative Stress through Inhibition of MAPK/NF-κB and Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(11):710. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20110710
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Eui-Jeong, Chunying Zhang, Hyun-Soo Kim, Ji-Yul Kim, Sang-Muyn Park, Won-Kyo Jung, Ginnae Ahn, and Seon-Heui Cha. 2022. "Sargachromenol Isolated from Sargassum horneri Attenuates Glutamate-Induced Neuronal Cell Death and Oxidative Stress through Inhibition of MAPK/NF-κB and Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway" Marine Drugs 20, no. 11: 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20110710
APA StyleHan, E.-J., Zhang, C., Kim, H.-S., Kim, J.-Y., Park, S.-M., Jung, W.-K., Ahn, G., & Cha, S.-H. (2022). Sargachromenol Isolated from Sargassum horneri Attenuates Glutamate-Induced Neuronal Cell Death and Oxidative Stress through Inhibition of MAPK/NF-κB and Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway. Marine Drugs, 20(11), 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20110710








