Molecular and Functional Characterization of a Novel Kunitz-Type Toxin-like Peptide in the Giant Triton Snail Charonia tritonis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
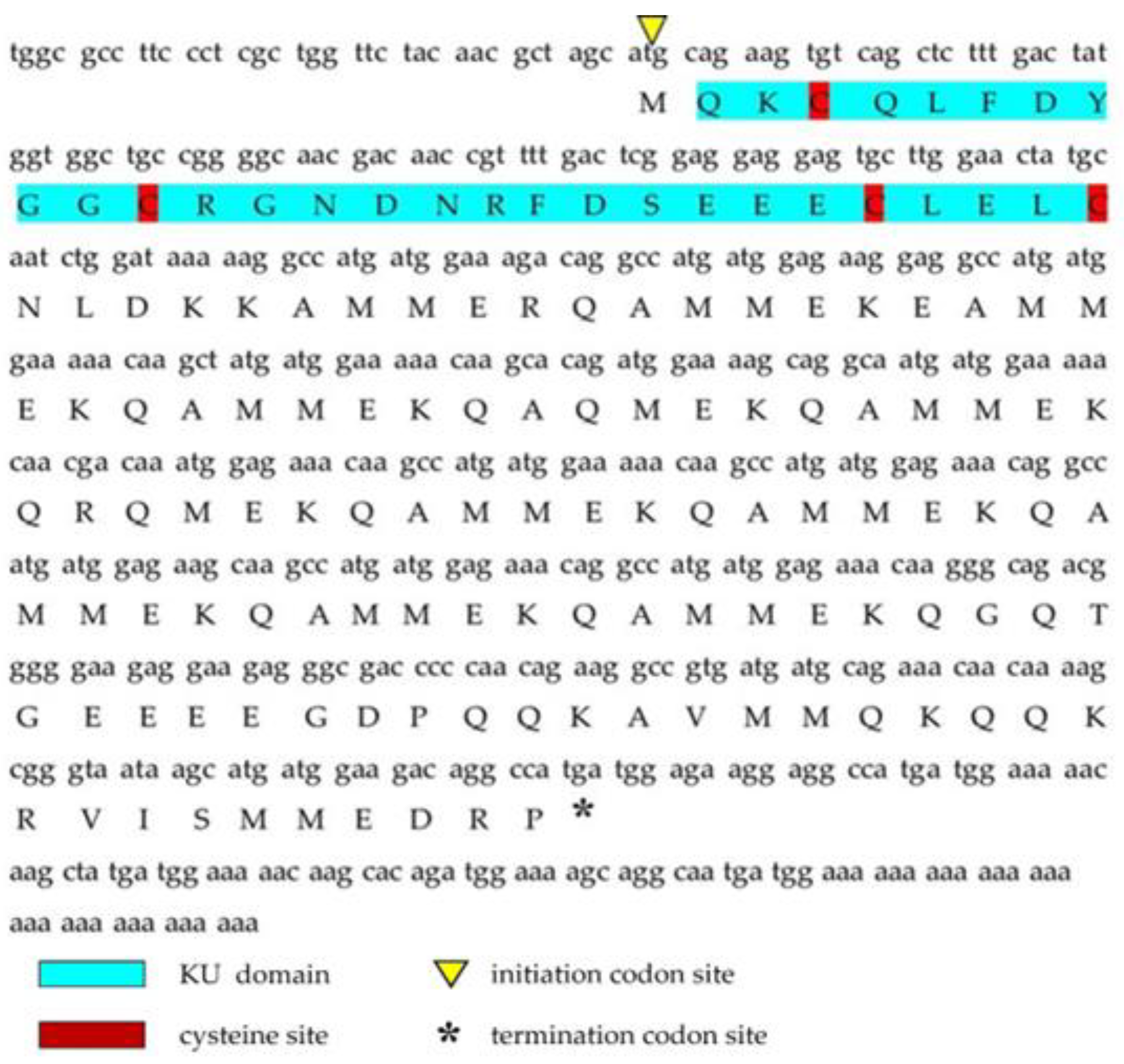
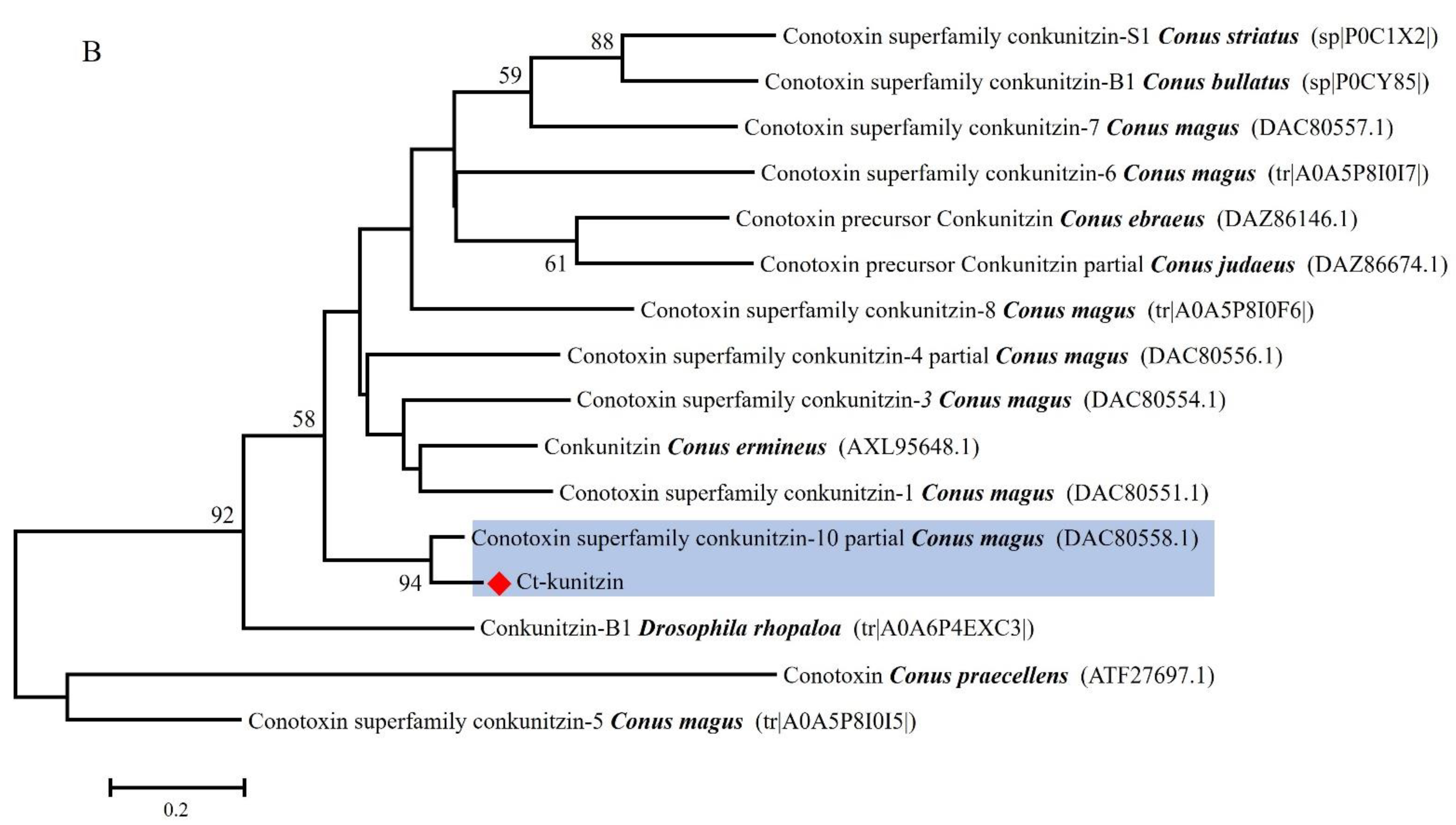
2.1. Sequence Analysis of a Toxin-like Peptide in the Salivary Gland of C. tritonis
2.2. Ct-Kunitzin Expression Analysis
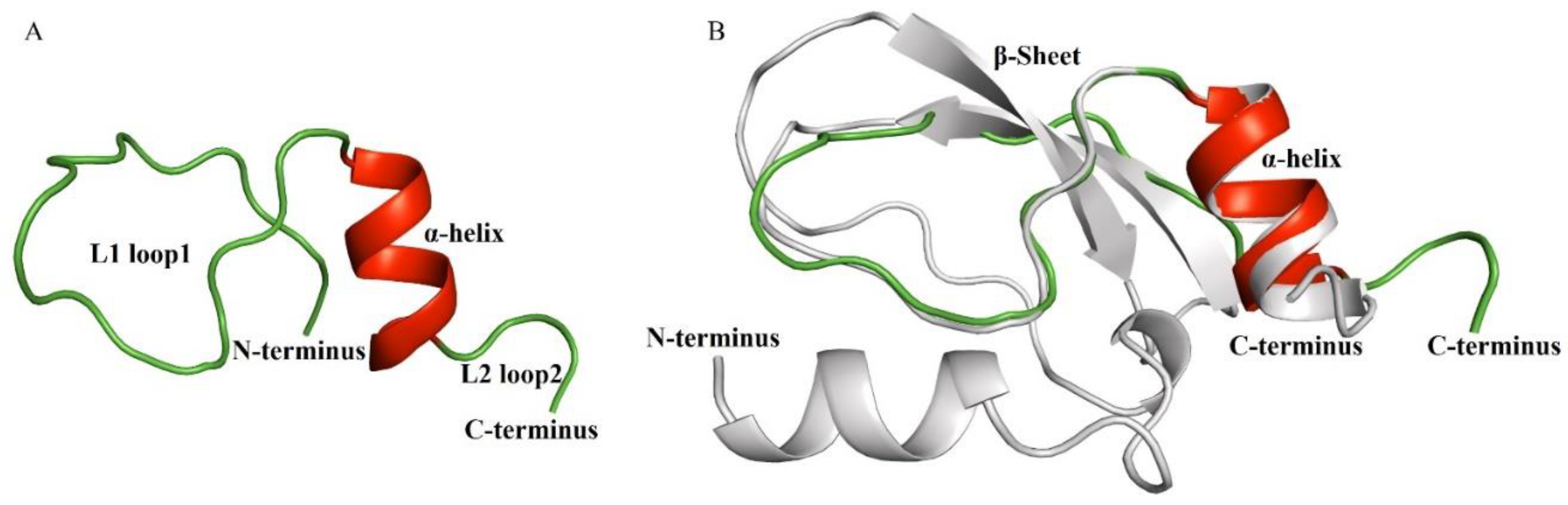
2.3. 3D Structure Determination of Ct-Kunitzin
2.4. Synthesis and Renaturation of the Ct-Kunitzin Peptide
2.5. In Vitro Peptide Activities
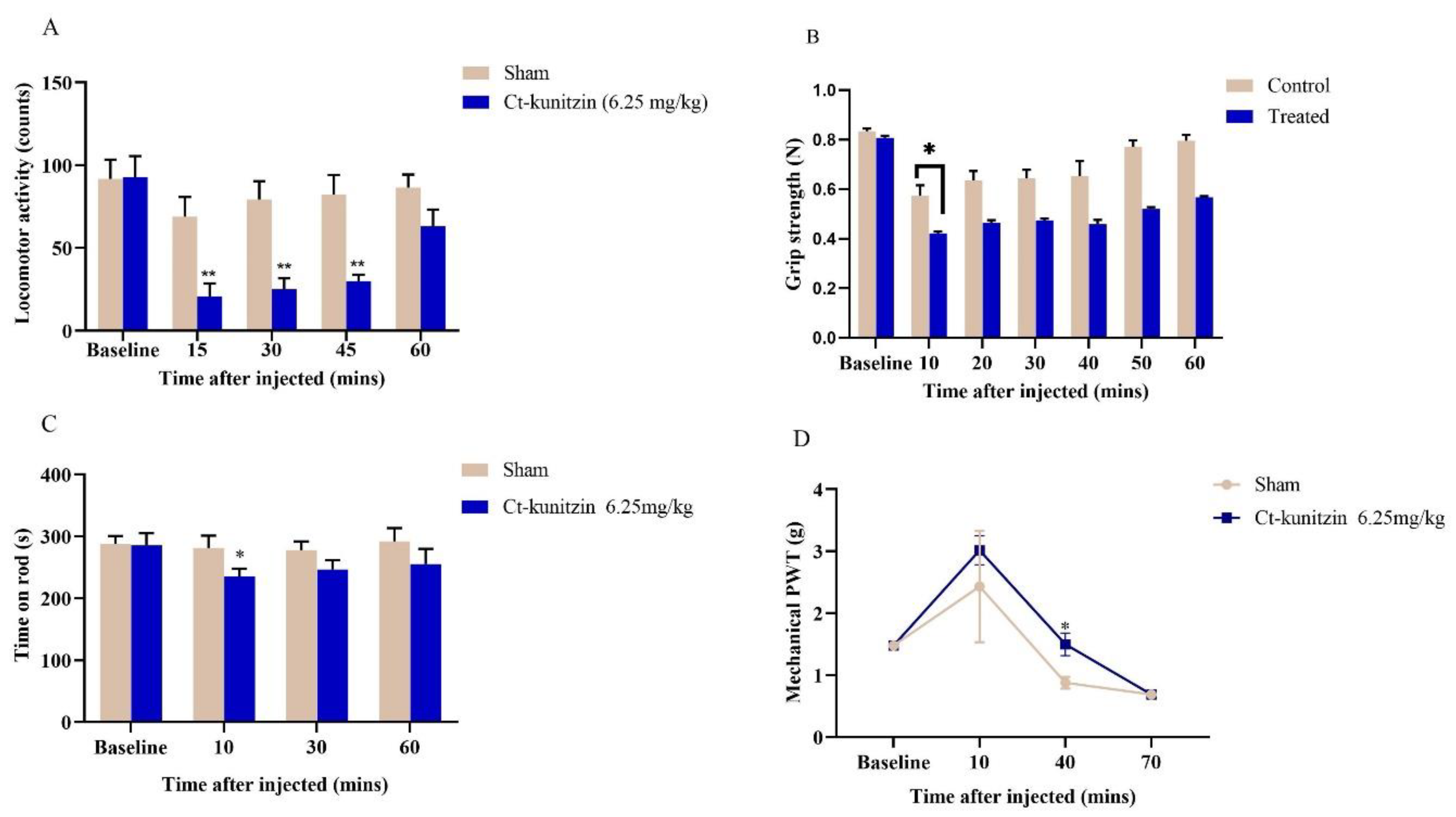
2.5.1. Effects on Motor Coordination
2.5.2. Effects on Pain Thresholds
2.5.3. Effects on Blood Dynamics
2.5.4. Effects on Blood Dynamics
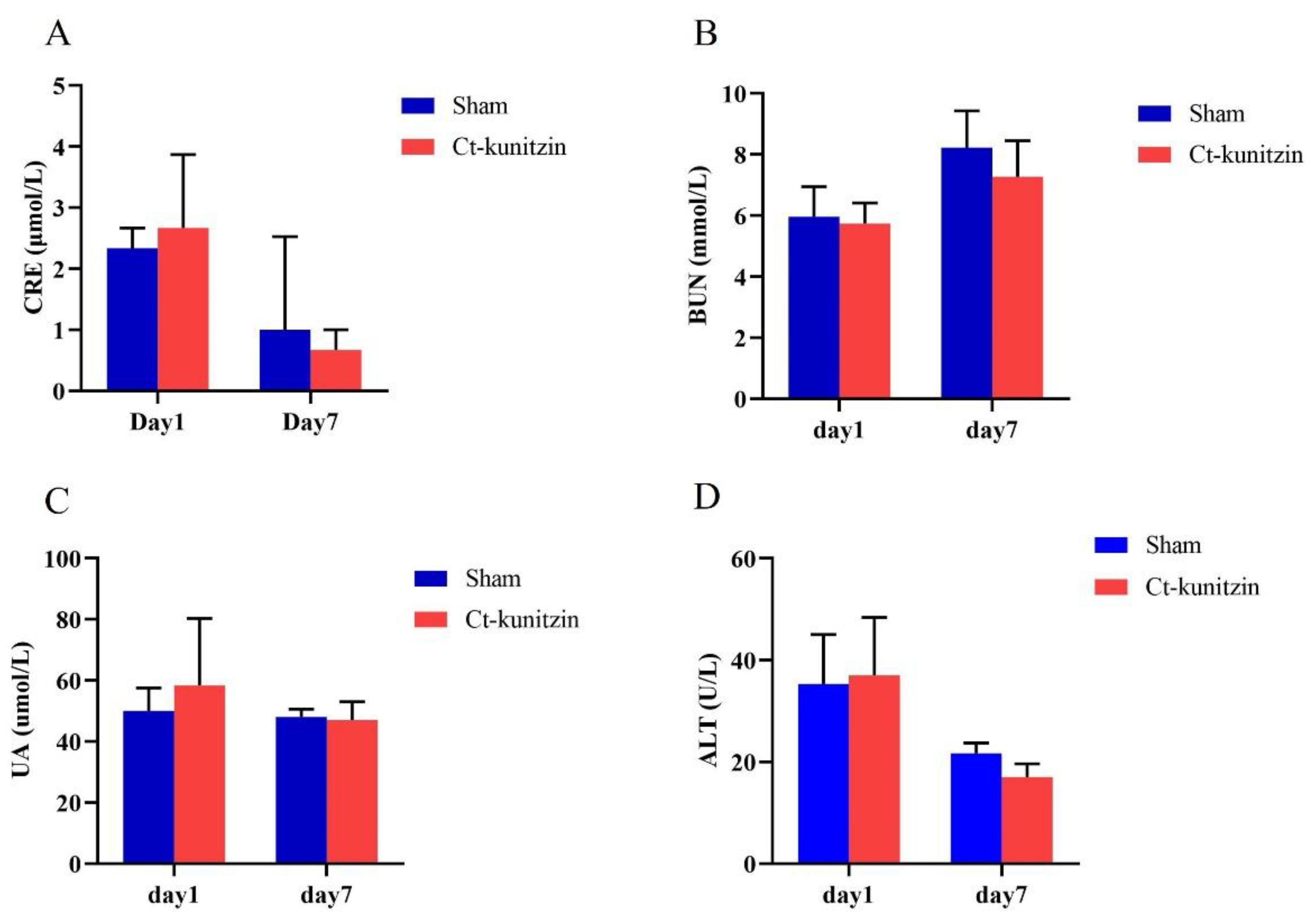
2.5.5. Effects on Vital Organs
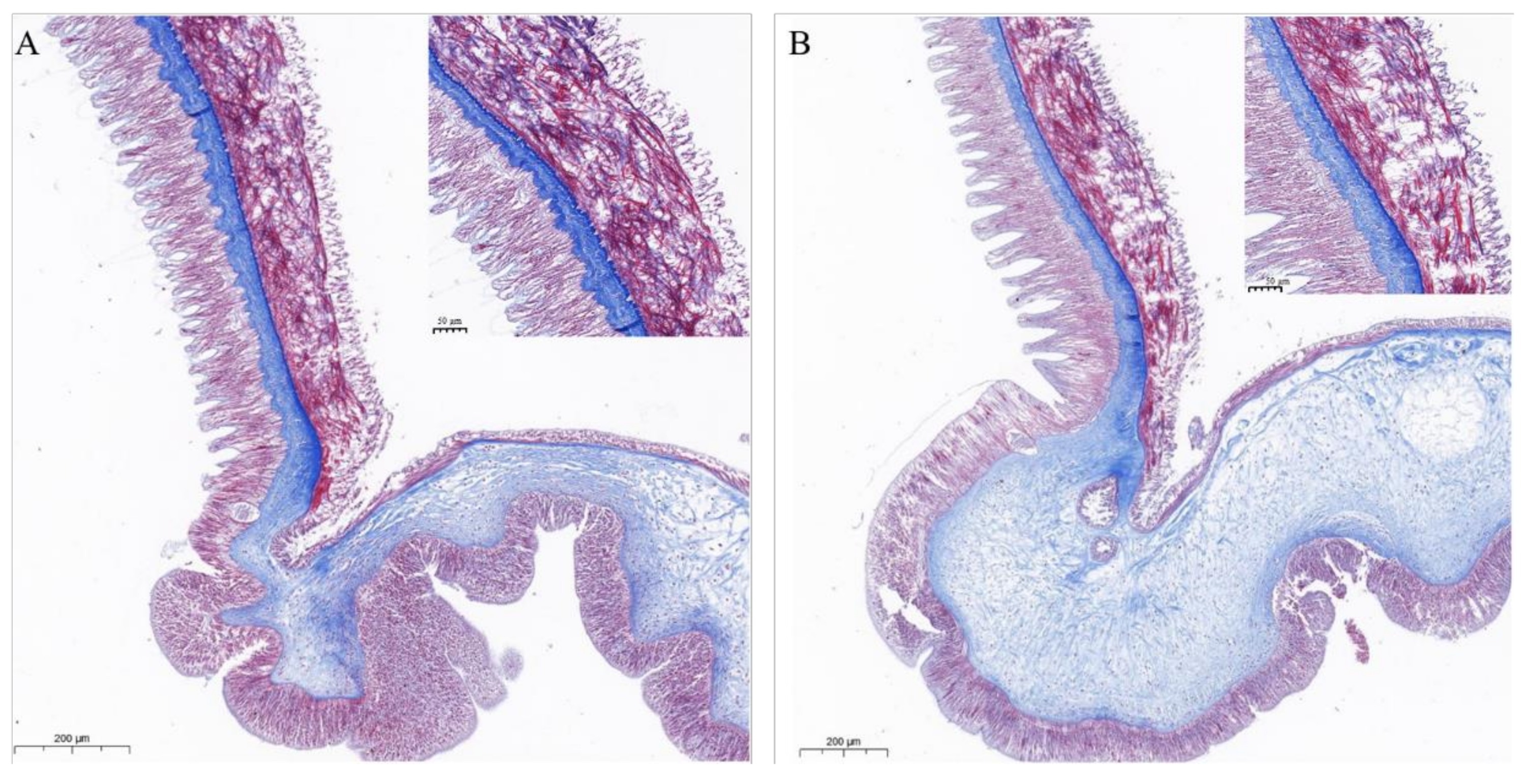
2.5.6. Effects on COTS
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal Materials and Research Ethics
4.2. Methods
4.2.1. Identification of Transcripts Involved in Putative Toxin Gene in C. tritonis Salivary Gland
4.2.2. The 5′ and 3′ Rapid Amplification of cDNA Ends (RACE)
4.2.3. Nucleotide Sequence and Bioinformatics Analyses of the Putative Toxin Gene
4.2.4. qPCR Validation for Tissue Expression Profiles of Toxin-Related Genes
4.2.5. Structural Model Visualization of Ct-Kunitzin
4.2.6. Peptide Synthesis and Renaturation
4.3. In Vitro Peptide Activities
4.3.1. Administration Route
4.3.2. Animal Behaviors
4.3.3. Pain Thresholds
4.3.4. Autopsy and Histopathology
4.3.5. Blood Analysis
4.3.6. Histological Procedures for COTS
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hall, M.R.; Motti, C.A.; Kroon, F. The Potential Role of the Giant Triton Snail, Charonia tritonis (Gastropoda: Ranellidae) in Mitigating Populations of the Crown-of-Thorns Starfish; Reef and Rainforest Research Centre Limited: Cairns, Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.-P.; Xia, J.-J.; Peng, P.-F.; Li, H.-P.; Luo, P.; Hu, C.-Q. Characterization of embryogenesis and early larval development in the Pacific triton, Charonia tritonis (Gastropoda: Caenogastropoda). Invertebr. Reprod. Dev. 2013, 57, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, U.; Wang, T.; Zhao, M.; Motti, C.; Hall, M.; Cummins, S.F. Multiomics analysis of the giant triton snail salivary gland, a crown-of-thorns starfish predator. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, U.; Suwansa-ard, S.; Maikaeo, L.; Motti, C.; Hall, M.; Cummins, S.F. Neuropeptides encoded within a neural transcriptome of the giant triton snail Charonia tritonis, a Crown-of-Thorns Starfish predator. Peptides 2017, 98, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bordon, K.C.F.; Cologna, C.T.; Fornari-Baldo, E.C.; Pinheiro-Júnior, E.L.; Cerni, F.A.; Amorim, F.G.; Anjolette, F.A.P.; Cordeiro, F.A.; Wiezel, G.A.; Cardoso, I.A. From animal poisons and venoms to medicines: Achievements, challenges and perspectives in drug discovery. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzig, V.; Cristofori-Armstrong, B.; Israel, M.R.; Nixon, S.A.; Vetter, I.; King, G.F. Animal toxins—Nature’s evolutionary-refined toolkit for basic research and drug discovery. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 181, 114096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Baelen, A.-C.; Robin, P.; Kessler, P.; Maïga, A.; Gilles, N.; Servent, D. Structural and Functional Diversity of Animal Toxins Interacting with GPCRs. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 811365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, G.F. Venoms as a platform for human drugs: Translating toxins into therapeutics. Expert. Opin. Biol. Ther. 2011, 11, 1469–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triplitt, C.; Chiquette, E. Exenatide: From the Gila monster to the pharmacy. J. Am. Pharm. Assoc. 2006, 46, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanford, M. Intrathecal ziconotide: A review of its use in patients with chronic pain refractory to other systemic or intrathecal analgesics. CNS Drugs 2013, 27, 989–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennington, M.W.; Czerwinski, A.; Norton, R.S. Peptide therapeutics from venom: Current status and potential. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 2738–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Wang, W.; Gao, T.; Huang, L.; Fan, H.; Chen, H.-X. Separation, identification and quantification of associated impurities in cobratide using sheathless CE-MS and CE-UV. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 3845–3851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarcha, E.J.; Olsen, C.M.; Probst, P.; Peckham, D.; Muñoz-Elías, E.J.; Kruger, J.G.; Iadonato, S.P. Safety and pharmacodynamics of dalazatide, a Kv1. 3 channel inhibitor, in the treatment of plaque psoriasis: A randomized phase 1b trial. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180762. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tyagi, A.; Ahmed, T.; Jian, S.; Bajaj, S.; Ong, S.T.; Goay, S.S.M.; Zhao, Y.; Vorobyov, I.; Tian, C.; Chandy, K.G. Rearrangement of a unique Kv1. 3 selectivity filter conformation upon binding of a drug. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2113536119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brust, A.; Croker, D.E.; Colless, B.; Ragnarsson, L.; Andersson, Å.; Jain, K.; Garcia-Caraballo, S.; Castro, J.; Brierley, S.M.; Alewood, P.F. Conopeptide-derived κ-opioid agonists (Conorphins): Potent, selective, and metabolic stable dynorphin A mimetics with antinociceptive properties. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 2381–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolosov, A.; Goodchild, C.S.; Cooke, I. CNSB004 (Leconotide) causes antihyperalgesia without side effects when given intravenously: A comparison with ziconotide in a rat model of diabetic neuropathic pain. Pain Med. 2010, 11, 262–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olubiyi, O.I.; Lu, F.-K.; Calligaris, D.; Jolesz, F.A.; Agar, N.Y. Advances in molecular imaging for surgery. In Image-Guided Neurosurgery; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 407–439. [Google Scholar]
- Dardevet, L.; Rani, D.; Aziz, T.A.E.; Bazin, I.; Sabatier, J.-M.; Fadl, M.; Brambilla, E.; de Waard, M. Chlorotoxin: A helpful natural scorpion peptide to diagnose glioma and fight tumor invasion. Toxins 2015, 7, 1079–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennington, M.W.; Beeton, C.; Galea, C.A.; Smith, B.J.; Chi, V.; Monaghan, K.P.; Garcia, A.; Rangaraju, S.; Giuffrida, A.; Plank, D. Engineering a stable and selective peptide blocker of the Kv1. 3 channel in T lymphocytes. Mol. Pharmacol. 2009, 75, 762–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.C.; Galea, C.A.; Leung, E.W.; Tajhya, R.B.; Beeton, C.; Pennington, M.W.; Norton, R.S. Expression and isotopic labelling of the potassium channel blocker ShK toxin as a thioredoxin fusion protein in bacteria. Toxicon 2012, 60, 840–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-C.; Hsieh, H.J.; Hsieh, C.-H.; Hwang, D.-F. Plancitoxin I from the venom of crown-of-thorns starfish (Acanthaster planci) induces oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum stress associated cytotoxicity in A375. S2 cells. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2015, 99, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, T.; Riedl, R. Paracelsus’ legacy in the faunal realm: Drugs deriving from animal toxins. Drug Discov. Today 2021, 27, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madio, B.; Undheim, E.A.; King, G.F. Revisiting venom of the sea anemone Stichodactyla haddoni: Omics techniques reveal the complete toxin arsenal of a well-studied sea anemone genus. J. Proteom. 2017, 166, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Q.; Kong, X.; Luo, G.; Wu, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, Q.; Tang, C.; Liu, Z. Molecular Diversity of Peptide Toxins in the Venom of Spider Heteropoda pingtungensis as Revealed by cDNA Library and Transcriptome Sequencing Analysis. Toxins 2022, 14, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meiri, N.; Rosenblum, K. Lateral ventricle injection of the protein synthesis inhibitor anisomycin impairs long-term memory in a spatial memory task. Brain Res. 1998, 789, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aridoss, G.; Kim, D.M.; Kim, J.I.; Kang, J.E. Ziconotide (ω-conotoxin MVIIA)—Efficient solid-phase synthesis of a linear precursor peptide and its strategic native folding. Pept. Sci. 2021, 113, e24223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, A.; Herrera, M.; Villalta, M.; Solano, D.; Segura, Á.; Lomonte, B.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; León, G.; Vargas, M. Proteomic and toxinological characterization of the venom of the South African Ringhals cobra Hemachatus haemachatus. J. Proteom. 2018, 181, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgieva, D.; Arni, R.K.; Betzel, C. Proteome analysis of snake venom toxins: Pharmacological insights. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2008, 5, 787–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panagides, N.; Jackson, T.N.; Ikonomopoulou, M.P.; Arbuckle, K.; Pretzler, R.; Yang, D.C.; Ali, S.A.; Koludarov, I.; Dobson, J.; Sanker, B. How the cobra got its flesh-eating venom: Cytotoxicity as a defensive innovation and its co-evolution with hooding, aposematic marking, and spitting. Toxins 2017, 9, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiezel, G.A.; Shibao, P.Y.; Cologna, C.T.; Filho, R.M.; Ueira-Vieira, C.; de Pauw, E.; Quinton, L.; Arantes, E.C. In-depth venome of the Brazilian rattlesnake Crotalus durissus terrificus: An integrative approach combining its venom gland transcriptome and venom proteome. J. Proteom. Res. 2018, 17, 3941–3958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klompen, A.M.; Macrander, J.; Reitzel, A.M.; Stampar, S.N. Transcriptomic analysis of four cerianthid (Cnidaria, Ceriantharia) venoms. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Droctové, L.; Ciolek, J.; Mendre, C.; Chorfa, A.; Huerta, P.; Carvalho, C.; Gouin, C.; Lancien, M.; Stanajic-Petrovic, G.; Braco, L. A new Kunitz-type snake toxin family associated with an original mode of interaction with the vasopressin 2 receptor. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 179, 3470–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladkikh, I.; Peigneur, S.; Sintsova, O.; Pinheiro-Junior, E.L.; Klimovich, A.; Menshov, A.; Kalinovsky, A.; Isaeva, M.; Monastyrnaya, M.; Kozlovskaya, E. Kunitz-type peptides from the sea anemone Heteractis crispa demonstrate potassium channel blocking and anti-inflammatory activities. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dy, C.Y.; Buczek, P.; Imperial, J.S.; Bulaj, G.; Horvath, M.P. Structure of conkunitzin-S1, a neurotoxin and Kunitz-fold disulfide variant from cone snail. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2006, 62, 980–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.; Hao, J.; Luo, X.; Chen, Z. Engineering varied serine protease inhibitors by converting P1 site of BF9, a weakly active Kunitz-type animal toxin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 1190–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Dashevsky, D.; Rokyta, D.; Ghezellou, P.; Fathinia, B.; Shi, Q.; Richardson, M.K.; Fry, B.G. Dynamic genetic differentiation drives the widespread structural and functional convergent evolution of snake venom proteinaceous toxins. BMC Biol. 2022, 20, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreev, Y.A.; Kozlov, S.A.; Koshelev, S.G.; Ivanova, E.A.; Monastyrnaya, M.M.; Kozlovskaya, E.P.; Grishin, E.V. Analgesic compound from sea anemone Heteractis crispa is the first polypeptide inhibitor of vanilloid receptor 1 (TRPV1). J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 23914–23921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamura, K.; Yamada, T.; Kurihara, K.; Tamada, T.; Kuroki, R.; Tanaka, I.; Takahashi, H.; Niimura, N. X-ray and neutron protein crystallographic analysis of the trypsin–BPTI complex. Acta. Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2011, 67, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monastyrnaya, M.; Peigneur, S.; Zelepuga, E.; Sintsova, O.; Gladkikh, I.; Leychenko, E.; Isaeva, M.; Tytgat, J.; Kozlovskaya, E. Kunitz-type peptide HCRG21 from the sea anemone Heteractis crispa is a full antagonist of the TRPV1 receptor. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Báez, A.; Salceda, E.; Fló, M.; Grana, M.; Fernández, C.; Vega, R.; Soto, E. α-Dendrotoxin inhibits the ASIC current in dorsal root ganglion neurons from rat. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 606, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peigneur, S.; Billen, B.; Derua, R.; Waelkens, E.; Debaveye, S.; Béress, L.; Tytgat, J. A bifunctional sea anemone peptide with Kunitz type protease and potassium channel inhibiting properties. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2011, 82, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaev, M.V.; Dorofeeva, N.A.; Komarova, M.S.; Korolkova, Y.V.; Andreev, Y.A.; Mosharova, I.V.; Grishin, E.V.; Tikhonov, D.B.; Kozlov, S.A. TRPV1 activation power can switch an action mode for its polypeptide ligands. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orts, D.J.; Moran, Y.; Cologna, C.T.; Peigneur, S.; Madio, B.; Praher, D.; Quinton, L.; de Pauw, E.; Bicudo, J.E.; Tytgat, J. BcsTx3 is a founder of a novel sea anemone toxin family of potassium channel blocker. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 4839–4852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourão, C.B.; Schwartz, E.F. Protease inhibitors from marine venomous animals and their counterparts in terrestrial venomous animals. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2069–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honma, T.; Kawahata, S.; Ishida, M.; Nagai, H.; Nagashima, Y.; Shiomi, K. Novel peptide toxins from the sea anemone Stichodactyla haddoni. Peptides 2008, 29, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, S.-X.; Zhang, A.-D.; Huang, J.-F. Evolution, expansion and expression of the Kunitz/BPTI gene family associated with long-term blood feeding in Ixodes Scapularis. BMC Evol. Biol. 2012, 12, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Deng, M.; Duan, Z.; Tang, X.; Liang, S. Molecular cloning, bioinformatics analysis and functional characterization of HWTX-XI toxin superfamily from the spider Ornithoctonus huwena. Peptides 2014, 54, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.-H.; He, Q.-Y.; Peng, K.; Diao, J.-B.; Jiang, L.-P.; Tang, X.; Liang, S.-P. Discovery of a distinct superfamily of Kunitz-type toxin (KTT) from tarantulas. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.-Y.; Hu, Y.-T.; Yang, W.-S.; He, Y.-W.; Feng, J.; Wang, B.; Zhao, R.-M.; Ding, J.-P.; Cao, Z.-J.; Li, W.-X. Hg1, novel peptide inhibitor specific for Kv1. 3 channels from first scorpion Kunitz-type potassium channel toxin family. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 13813–13821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Verdaguer, M.; Capera, J.; Serrano-Novillo, C.; Estadella, I.; Sastre, D.; Felipe, A. The voltage-gated potassium channel Kv1. 3 is a promising multitherapeutic target against human pathologies. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2016, 20, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladkikh, I.; Monastyrnaya, M.; Zelepuga, E.; Sintsova, O.; Tabakmakher, V.; Gnedenko, O.; Ivanov, A.; Hua, K.-F.; Kozlovskaya, E. New Kunitz-type HCRG polypeptides from the sea anemone Heteractis crispa. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 6038–6063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remus, J.; Firman, J. Efficacy of lateral ventricular injection of epinephrine, cyproheptadine, or adenosine triphosphate on feed intake in thiamin-deficient turkeys. Poult. Sci. 1991, 70, 2340–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, C.J.; Ramsdell, J.S. Effects of marine algal toxins on thermoregulation in mice. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2005, 27, 727–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, K.; Vilarino, N.; Botana, L.M.; Elliott, C.T. A European perspective on progress in moving away from the mouse bioassay for marine-toxin analysis. TrAc Trends Anal. Chem. 2011, 30, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacPhail, R.; Jarema, K. Prospects on behavioral studies of marine and freshwater toxins. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2005, 27, 695–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aasen, J.A.; Espenes, A.; Hess, P.; Aune, T. Sub-lethal dosing of azaspiracid-1 in female NMRI mice. Toxicon 2010, 56, 1419–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millecamps, M.; Shi, X.Q.; Piltonen, M.; Echeverry, S.; Diatchenko, L.; Zhang, J.; Stone, L.S. The geriatric pain experience in mice: Intact cutaneous thresholds but altered responses to tonic and chronic pain. Neurobiol. Aging 2020, 89, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, R.K.; Nilsson-Todd, L.; Cleren, C.; Léna, I.; Garcia, R.; Finn, D.P. Molecular and electrophysiological changes in the prefrontal cortex–amygdala–dorsal periaqueductal grey pathway during persistent pain state and fear-conditioned analgesia. Physiol. Behav. 2011, 104, 1075–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scuteri, D.; Berliocchi, L.; Rombolà, L.; Morrone, L.A.; Tonin, P.; Bagetta, G.; Corasaniti, M.T. Effects of aging on formalin-induced pain behavior and analgesic activity of gabapentin in C57BL/6 mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, H.; Jiang, S.; Luo, Q.; Han, X.; Xiong, Y.; Xu, Z.; Qiao, R.; Yang, X. Principal component analysis of routine blood test results with Parkinson’s disease: A case-control study. Exp. Gerontol. 2021, 144, 111188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, A.M.; van Vliet, N.; van Vliet, D.; Romani, C.; Huijbregts, S.C.; van der Goot, E.; Hovens, I.B.; van der Zee, E.A.; Kema, I.P.; Heiner-Fokkema, M.R. Correlations of blood and brain biochemistry in phenylketonuria: Results from the Pah-enu2 PKU mouse. Mol. Gen. Metab. 2021, 134, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, A.M.; Salado, I.G.; Perez, D.I.; Brea, J.; Morales-Garcia, J.A.; Gonzalez-Garcia, A.; Cadavid, M.I.; Loza, M.I.; Luque, F.J.; Perez-Castillo, A. Pharmacological tools based on imidazole scaffold proved the utility of pde10a inhibitors for Parkinson’s disease. Future Med. Chem. 2017, 9, 731–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Guo, Q.; Zhai, Y.; Gu, Z. Transcriptomic Insights into the Diversity and Evolution of Myxozoa (Cnidaria, Endocnidozoa) Toxin-like Proteins. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santibáñez-López, C.E.; Ontano, A.Z.; Harvey, M.S.; Sharma, P.P. Transcriptomic analysis of pseudoscorpion venom reveals a unique cocktail dominated by enzymes and protease inhibitors. Toxins 2018, 10, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartigan, A.; Jaimes-Becerra, A.; Okamura, B.; Doonan, L.B.; Ward, M.; Marques, A.C.; Long, P.F. Recruitment of toxin-like proteins with ancestral venom function supports endoparasitic lifestyles of Myxozoa. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Sham | Ct-Kunitzin (6.25 mg/kg) | Sham | Ct-Kunitzin (6.25 mg/kg) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 1 | Day 7 | |||
| MCH (pg) | 15.3 ± 0.6 | 15.9 ± 0.9 | 16.3 ± 1.0 | 16.0 ± 0.6 |
| HGB (g·L−1) | 115 ± 9 | 112 ± 6 | 122 ± 7 | 115 ± 7 |
| MCHC (g·L−1) | 298 ± 3 | 302 ± 15 | 302 ± 13 | 305 ± 6 |
| RBC (1012·L−1) | 7.5 ± 0.6 | 7.1 ± 0.7 | 7.5 ± 0.1 | 7.3 ± 0.6 |
| HCT (L·L−1) | 38.6 ± 3.2 | 37.2 ± 3.3 | 40.4 ± 0.5 | 37.9 ± 2.2 |
| MCV (fL) | 51.6 ± 1.9 | 52.8 ± 0.5 | 53.7 ± 1.0 | 52.4 ± 1.3 |
| RDW (%) | 17.0 ± 0.6 | 18.3 ± 0.9 | 16.5 ± 1.6 | 17.1 ± 2.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, G.; Jia, H.; Luo, L.; Zhang, Y.; Cen, X.; Yao, G.; Zhang, H.; He, M.; Liu, W. Molecular and Functional Characterization of a Novel Kunitz-Type Toxin-like Peptide in the Giant Triton Snail Charonia tritonis. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 686. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20110686
Zhang G, Jia H, Luo L, Zhang Y, Cen X, Yao G, Zhang H, He M, Liu W. Molecular and Functional Characterization of a Novel Kunitz-Type Toxin-like Peptide in the Giant Triton Snail Charonia tritonis. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(11):686. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20110686
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Gege, Huixia Jia, Lei Luo, Yang Zhang, Xitong Cen, Gaoyou Yao, Hua Zhang, Maoxian He, and Wenguang Liu. 2022. "Molecular and Functional Characterization of a Novel Kunitz-Type Toxin-like Peptide in the Giant Triton Snail Charonia tritonis" Marine Drugs 20, no. 11: 686. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20110686
APA StyleZhang, G., Jia, H., Luo, L., Zhang, Y., Cen, X., Yao, G., Zhang, H., He, M., & Liu, W. (2022). Molecular and Functional Characterization of a Novel Kunitz-Type Toxin-like Peptide in the Giant Triton Snail Charonia tritonis. Marine Drugs, 20(11), 686. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20110686






