Protective Effects of Topical Administration of Laminarin in Oxazolone-Induced Atopic Dermatitis-like Skin Lesions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
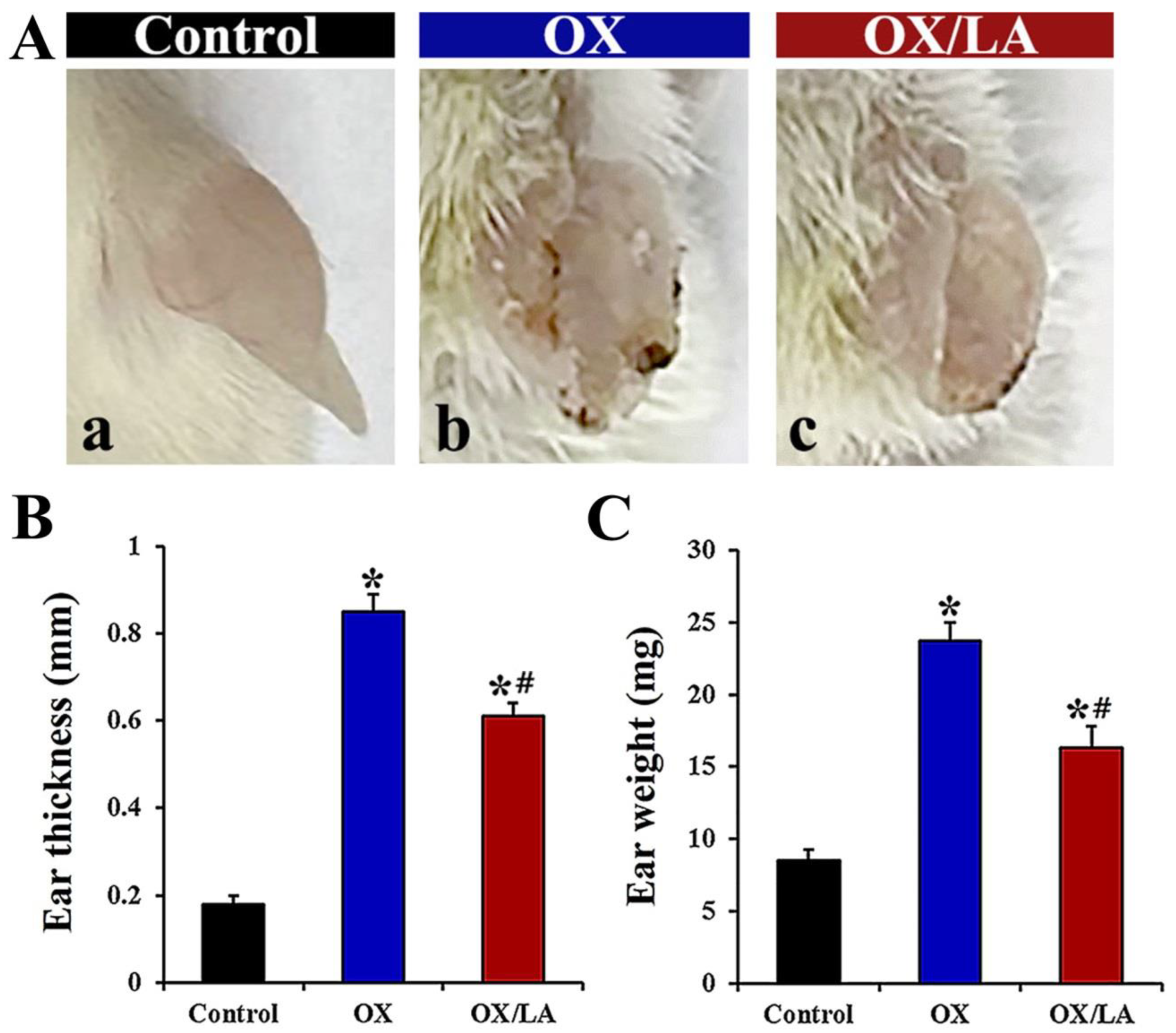
2.1. Effects of LA on OX-Induced Ear Thickness and Weight
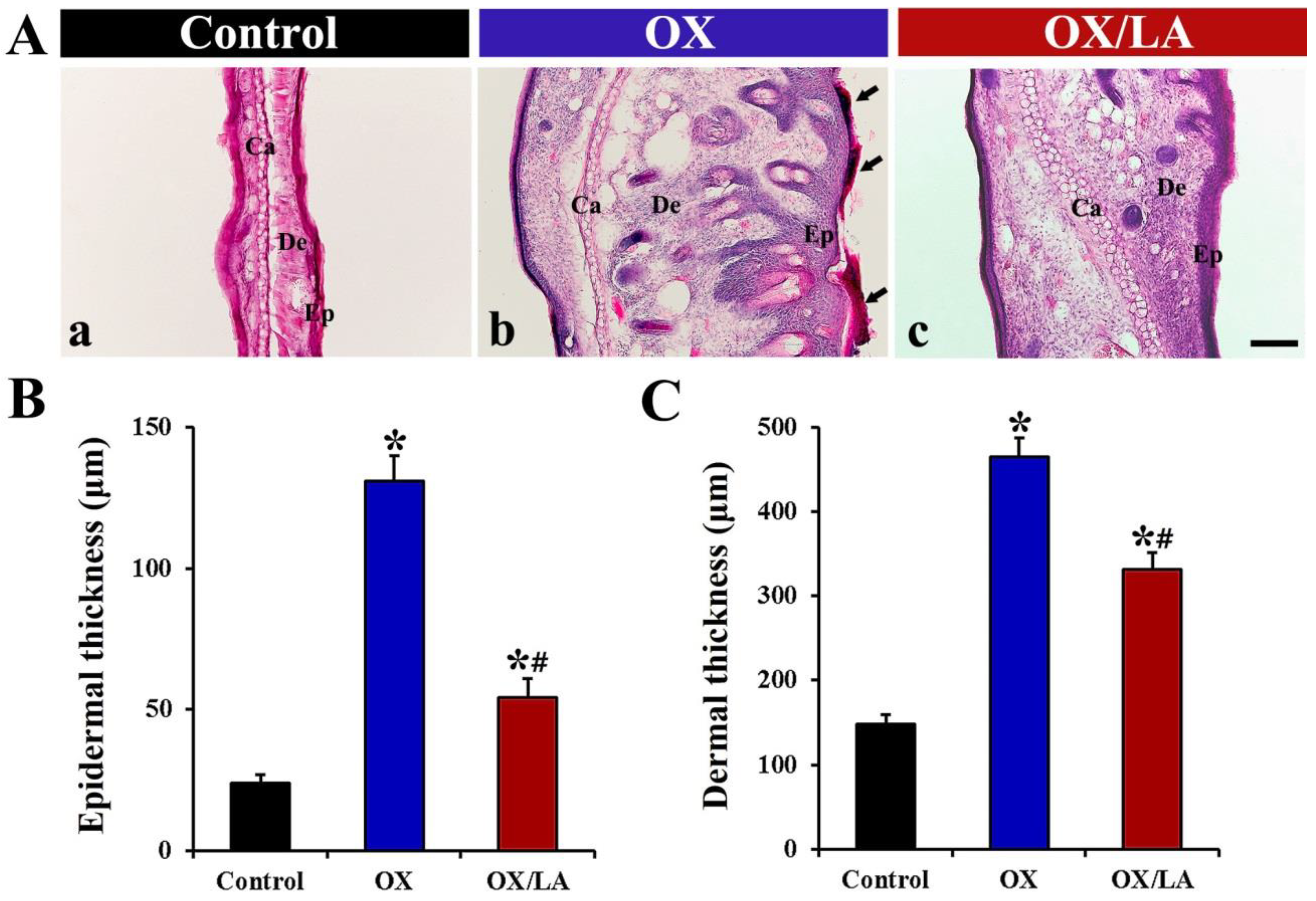
2.2. Effects of LA on OX-Induced Changes in Epidermal and Dermal Thickness
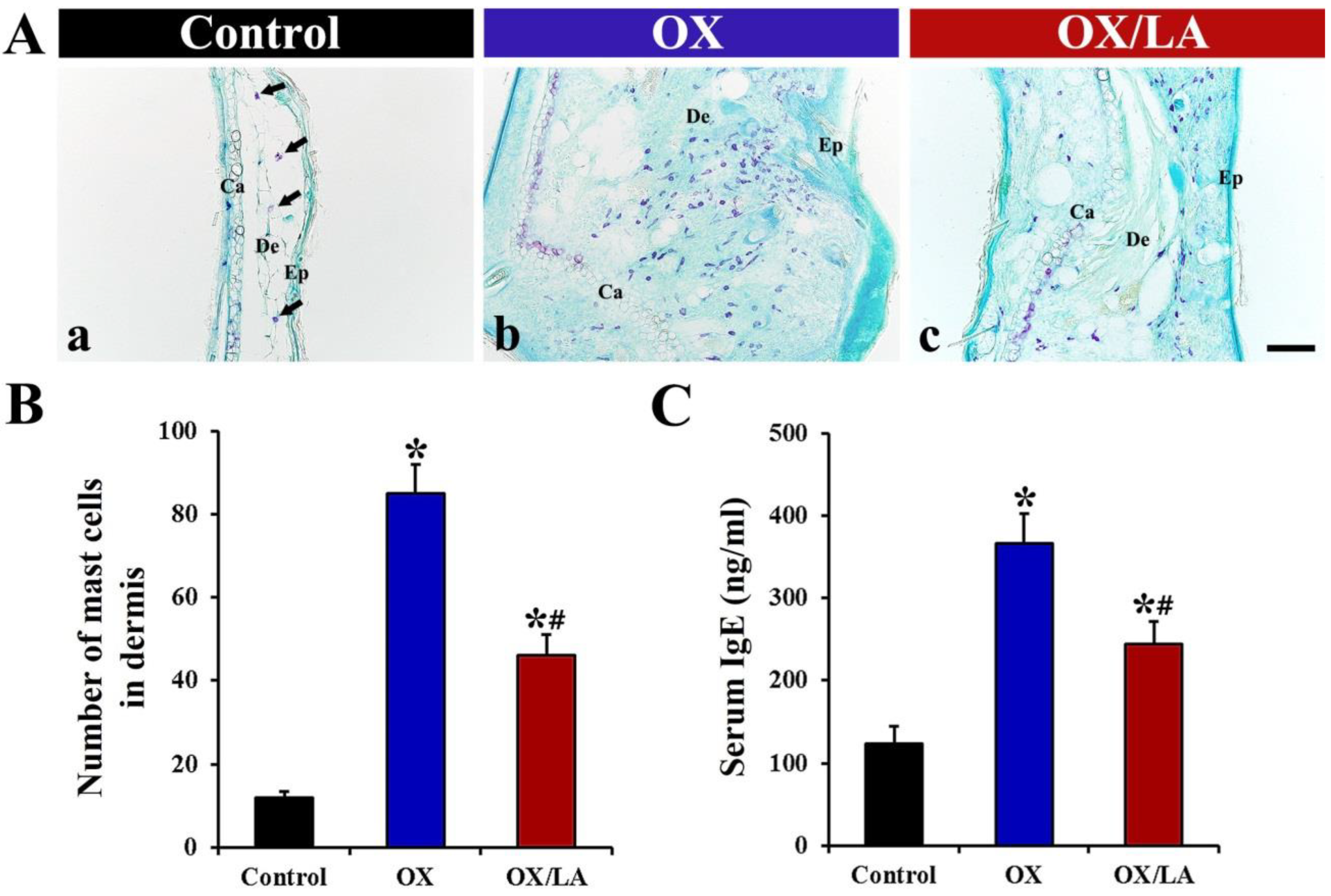
2.3. Effects of LA on OX-Induced Mast Cell Infiltration and Serum Immunoglobulin E (IgE) Level
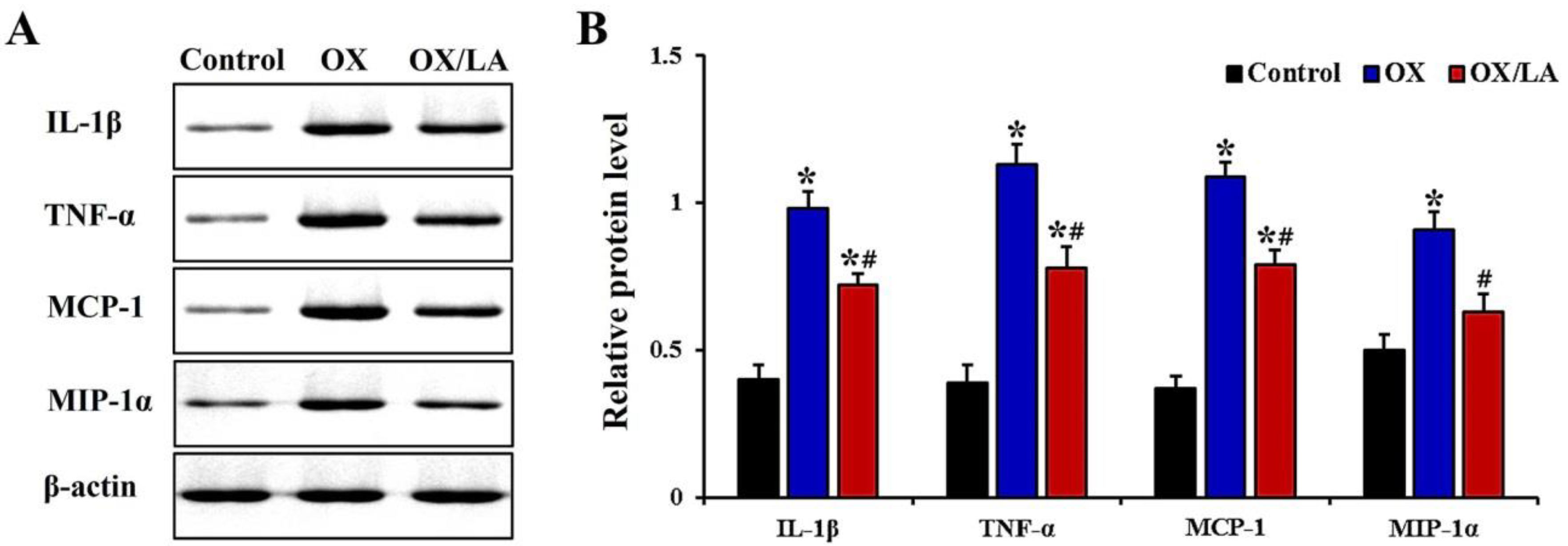
2.4. Effects of LA on OX-Induced Levels of Proinflammatory Cytokines
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
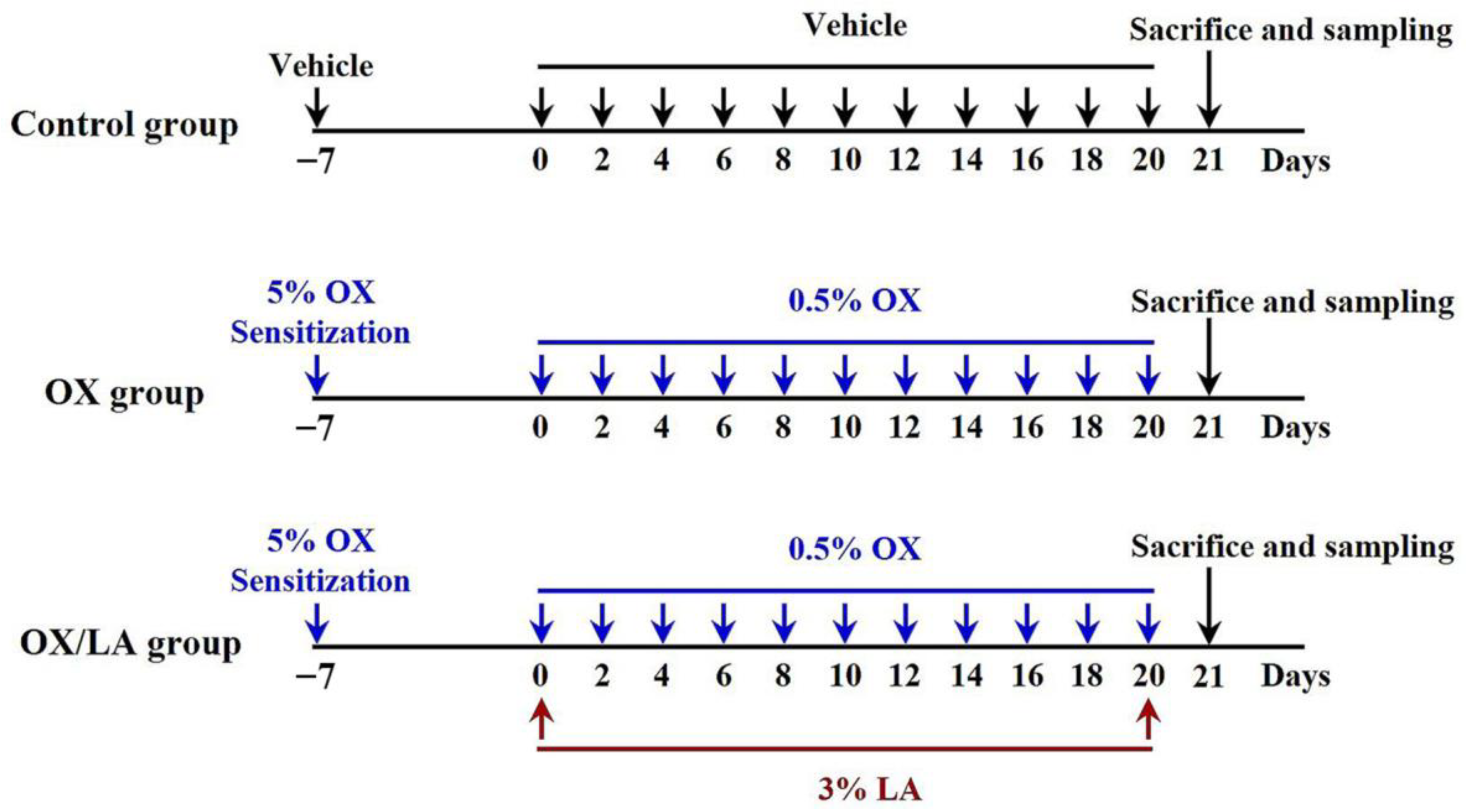
4.2. Experimental Groups and Induction of AD-Like Skin Lesions
4.3. Measurement of Ear Thickness and Weight
4.4. Measurement of IgE
4.5. Tissue Preparation for Histological Examination
4.6. H&E Staining
4.7. Toluidine Blue Staining
4.8. Western Blotting
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boguniewicz, M.; Leung, D.Y. Atopic dermatitis: A disease of altered skin barrier and immune dysregulation. Immunol. Rev. 2011, 242, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, D.Y.; Guttman-Yassky, E. Assessing the current treatment of atopic dermatitis: Unmet needs. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 139, S47–S48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yew, Y.W.; Thyssen, J.P.; Silverberg, J.I. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the regional and age-related differences in atopic dermatitis clinical characteristics. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2019, 80, 390–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Kim, B.E.; Leung, D.Y.M. Pathophysiology of atopic dermatitis: Clinical implications. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2019, 40, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otsuka, A.; Nomura, T.; Rerknimitr, P.; Seidel, J.A.; Honda, T.; Kabashima, K. The interplay between genetic and environmental factors in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 278, 246–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, E.; Gooderham, M.; Torres, T. New topical therapies in development for atopic dermatitis. Drugs 2022, 82, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAleer, M.A.; Jakasa, I.; Stefanovic, N.; McLean, W.H.I.; Kezic, S.; Irvine, A.D. Topical corticosteroids normalize both skin and systemic inflammatory markers in infant atopic dermatitis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2021, 185, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, J.H. Atopic dermatitis in children: When topical steroid treatment “does not work”. BMJ 2021, 372, n297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraswat, A. Topical corticosteroid use in children: Adverse effects and how to minimize them. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2010, 76, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaid, N.A.M.; Sekar, M.; Bonam, S.R.; Gan, S.H.; Lum, P.T.; Begum, M.Y.; Rani, N.N.I.M.; Vaijanathappa, J.; Wu, Y.S.; Subramaniyan, V.; et al. Promising natural products in new drug design, development, and therapy for skin disorders: An overview of scientific evidence and understanding their mechanism of action. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2022, 16, 23–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Pang, Y.; He, Y.; Zhang, X.; Peng, L.; Guo, J.; Zeng, J. A comprehensive review of natural products against atopic dermatitis: Flavonoids, alkaloids, terpenes, glycosides and other compounds. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 140, 111741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neyrinck, A.M.; Mouson, A.; Delzenne, N.M. Dietary supplementation with laminarin, a fermentable marine beta (1-3) glucan, protects against hepatotoxicity induced by lps in rat by modulating immune response in the hepatic tissue. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2007, 7, 1497–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Ahn, J.H.; Lee, T.K.; Park, C.W.; Kim, B.; Lee, J.C.; Kim, D.W.; Shin, M.C.; Cho, J.H.; Lee, C.H.; et al. Laminarin pretreatment provides neuroprotection against forebrain ischemia/reperfusion injury by reducing oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in aged gerbils. Mar. Drug. 2020, 18, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.J.; Graves, B.; Child, R.; Rice, P.J.; Ma, Z.; Lowman, D.W.; Ensley, H.E.; Ryter, K.T.; Evans, J.T.; Williams, D.L. Immunoregulatory activity of the natural product laminarin varies widely as a result of its physical properties. J. Immunol. 2018, 200, 788–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellimi, S.; Maalej, H.; Rekik, D.M.; Benslima, A.; Ksouda, G.; Hamdi, M.; Sahnoun, Z.; Li, S.; Nasri, M.; Hajji, M. Antioxidant, antibacterial and in vivo wound healing properties of laminaran purified from cystoseira barbata seaweed. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 119, 633–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, J.H.; Kim, D.W.; Park, C.W.; Kim, B.; Sim, H.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, T.K.; Lee, J.C.; Yang, G.E.; Her, Y.; et al. Laminarin attenuates ultraviolet-induced skin damage by reducing superoxide anion levels and increasing endogenous antioxidants in the dorsal skin of mice. Mar. Drug. 2020, 18, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorjsembe, B.; Nho, C.W.; Choi, Y.; Kim, J.C. Extract from black soybean cultivar a63 extract ameliorates atopic dermatitis-like skin inflammation in an oxazolone-induced murine model. Molecules 2022, 27, 2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Jegal, H.; Bong, S.K.; Yoon, K.N.; Park, N.J.; Shin, M.S.; Yang, M.H.; Kim, Y.K.; Kim, S.N. Anti-atopic effect of acorn shell extract on atopic dermatitis-like lesions in mice and its active phytochemicals. Biomolecules 2019, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, J.E.; Kim, K.H.; Kang, N.J. Beneficial effects of marine algae-derived carbohydrates for skin health. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pangestuti, R.; Shin, K.H.; Kim, S.K. Anti-photoaging and potential skin health benefits of seaweeds. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.K.; Seo, C.H.; Park, Y. The effects of marine carbohydrates and glycosylated compounds on human health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 6018–6056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.B.; Zhou, X.Y.; Zhao, Z.J.; Li, Q.; Huang, X.Y.; Sun, F.Z. The kunming mouse: As a model for age-related decline in female fertility in human. Zygote 2013, 21, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Xie, L.; Qin, Y.; Liang, W.H.; Mo, M.Q.; Liu, S.L.; Liang, F.; Wang, Y.; Tan, W.; Liang, Y. Effect of laminarin polysaccharide on activity of matrix metalloproteinase in photoaging skin. Zhongguo Zhongyao Zazhi China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2013, 38, 2370–2373. [Google Scholar]
- Ayoub, A.; Pereira, J.M.; Rioux, L.E.; Turgeon, S.L.; Beaulieu, M.; Moulin, V.J. Role of seaweed laminaran from saccharina longicruris on matrix deposition during dermal tissue-engineered production. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 75, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, T.; Ando, T.; Kimura, M.; Wilson, B.S.; Kawakami, Y. Mast cells in atopic dermatitis. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2009, 21, 666–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, K. The role of mast cells in allergic inflammation. Respir. Med. 2012, 106, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theoharides, T.C.; Kempuraj, D.; Tagen, M.; Conti, P.; Kalogeromitros, D. Differential release of mast cell mediators and the pathogenesis of inflammation. Immunol. Rev. 2007, 217, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Kim, D.J.; Nam, S.; Lim, S.; Hwang, J.S.; Park, K.S.; Hong, H.S.; Shin, M.K.; Chung, E.; Son, Y. Manifestation of atopic dermatitis-like skin in tncb-induced nc/nga mice is ameliorated by topical treatment of substance p, possibly through blockade of allergic inflammation. Exp. Dermatol. 2018, 27, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.; Kim, J.C.; Park, N.J.; Bong, S.K.; Lee, S.; Jegal, H.; Jin, L.T.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, Y.K.; Kim, S.N. Eupatilin, an activator of pparα, inhibits the development of oxazolone-induced atopic dermatitis symptoms in balb/c mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 496, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.D.; Kim, T.H.; Park, Y.S.; Ahn, H.J.; Cho, J.J.; Park, C.S. Immune response against 2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene-induced atopic dermatitis-like clinical manifestation is suppressed by spermidine in nc/nga mice. Scand. J. Immunol. 2015, 81, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shornick, L.P.; Bisarya, A.K.; Chaplin, D.D. Il-1beta is essential for langerhans cell activation and antigen delivery to the lymph nodes during contact sensitization: Evidence for a dermal source of il-1beta. Cell Immunol. 2001, 211, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, M.; Sueki, H.; Suzuki, H.; Watanabe, H.; Ohtaki, H.; Shioda, S.; Nakanishi-Ueda, T.; Yasuhara, H.; Sekikawa, K.; Iijima, M. Impaired contact hypersensitivity reaction and reduced production of vascular endothelial growth factor in tumor necrosis factor-alpha gene-deficient mice. J. Dermatol. 2005, 32, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishimoto, T.; Takei, Y.; Yuzawa, Y.; Hanai, K.; Nagahara, S.; Tarumi, Y.; Matsuo, S.; Kadomatsu, K. Downregulation of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 involving short interfering rna attenuates hapten-induced contact hypersensitivity. Mol. Ther. 2008, 16, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.W.; Tedla, N.; Lloyd, A.R.; Wakefield, D.; McNeil, P.H. Mast cell activation and migration to lymph nodes during induction of an immune response in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 102, 1617–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kake, T.; Imai, M.; Takahashi, N. Effects of β-carotene on oxazolone-induced atopic dermatitis in hairless mice. Exp. Dermatol. 2019, 28, 1044–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oka, S.; Wakui, J.; Ikeda, S.; Yanagimoto, S.; Kishimoto, S.; Gokoh, M.; Nasui, M.; Sugiura, T. Involvement of the cannabinoid cb2 receptor and its endogenous ligand 2-arachidonoylglycerol in oxazolone-induced contact dermatitis in mice. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 8796–8805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Park, Y.C.; Kim, K.; Kim, H.; Jeong, H. Histopathologic features in animal model of atopic dermatitis induced by topical application of oxazolone. J. Physiol. Pathol. Korean Med. 2018, 32, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochstim, C.J.; Choi, J.Y.; Lowe, D.; Masood, R.; Rice, D.H. Biofilm detection with hematoxylin-eosin staining. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2010, 136, 453–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.K.; Kim, B.; Kim, D.W.; Ahn, J.H.; Sim, H.; Lee, J.C.; Yang, G.E.; Her, Y.; Park, J.H.; Kim, H.S.; et al. Effects of decursin and angelica gigas nakai root extract on hair growth in mouse dorsal skin via regulating inflammatory cytokines. Molecules 2020, 25, 3697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, T.-K.; Kim, D.W.; Ahn, J.H.; Lee, C.-H.; Lee, J.-C.; Lim, S.S.; Kang, I.J.; Hong, S.; Choi, S.Y.; Won, M.-H.; et al. Protective Effects of Topical Administration of Laminarin in Oxazolone-Induced Atopic Dermatitis-like Skin Lesions. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 669. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20110669
Lee T-K, Kim DW, Ahn JH, Lee C-H, Lee J-C, Lim SS, Kang IJ, Hong S, Choi SY, Won M-H, et al. Protective Effects of Topical Administration of Laminarin in Oxazolone-Induced Atopic Dermatitis-like Skin Lesions. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(11):669. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20110669
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Tae-Kyeong, Dae Won Kim, Ji Hyeon Ahn, Choong-Hyun Lee, Jae-Chul Lee, Soon Sung Lim, Il Jun Kang, Seongkweon Hong, Soo Young Choi, Moo-Ho Won, and et al. 2022. "Protective Effects of Topical Administration of Laminarin in Oxazolone-Induced Atopic Dermatitis-like Skin Lesions" Marine Drugs 20, no. 11: 669. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20110669
APA StyleLee, T.-K., Kim, D. W., Ahn, J. H., Lee, C.-H., Lee, J.-C., Lim, S. S., Kang, I. J., Hong, S., Choi, S. Y., Won, M.-H., & Park, J. H. (2022). Protective Effects of Topical Administration of Laminarin in Oxazolone-Induced Atopic Dermatitis-like Skin Lesions. Marine Drugs, 20(11), 669. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20110669






