Abstract
Soft corals are recognized as an abundant source of diverse secondary metabolites with unique chemical features and physiologic capabilities. However, the discovery of these metabolites is usually hindered by the traditional protocol which requires a large quantity of living tissue for isolation and spectroscopic investigations. In order to overcome this problem, untargeted metabolomics protocols have been developed. The latter have been applied here to study the chemodiversity of common Egyptian soft coral species, using only minute amounts of coral biomass. Spectral similarity networks, based on high-resolution tandem mass spectrometry data, were employed to explore and highlight the metabolic biodiversity of nine Egyptian soft coral species. Species-specific metabolites were highlighted for future prioritization of soft coral species for MS-guided chemical investigation. Overall, 79 metabolites were tentatively assigned, encompassing diterpenes, sesquiterpenes, and sterols. Simultaneously, the methodology assisted in shedding light on newly-overlooked chemical diversity with potential undescribed scaffolds. For instance, glycosylated fatty acids, nitrogenated aromatic compounds, and polyketides were proposed in Sinularia leptoclados, while alkaloidal terpenes and N-acyl amino acids were proposed in both Sarcophyton roseum and Sarcophyton acutum.
1. Introduction
Egypt, with its exclusive geographical location spanning over 3000 km of coastal area, offers numerous distinguishable habitats with abundant biodiversity. The Red Sea is one of the most biodiverse areas, harboring multitudes of corals and sponges [1]. Among coral species worldwide, 40% are inhabitants of the Red Sea [2].
Soft corals represent an outstanding natural resource harboring diverse classes of natural products with a broad spectrum of biological properties [2]. In addition, numerous extracted chemotypes from soft corals have been shown to be primarily involved in chemical defense mechanisms of their producers, as well as their adaptation strategy [3].
Generally, soft corals are known to produce a wide variety of terpenes [4]. Among these, diterpenes are the most prominent metabolites featuring different skeletons such as cembranes, norcembranes, xeniaenes, briaranes, and eunicellins. Cembrane diterpenes, the most explored molecular family, are produced by Sinularia and Lobophytum, and are enriched in Sarcophyton species [5,6,7]. As a result of the promising pharmacological profiles presented by such scaffolds, the possible harnessing of cembrane diterpenes as potential antitumor agents represents significant potential [8,9]. Additionally, eunicellin-based diterpenes have also displayed ecological, agrochemical, and pharmacological significance [10]. This type of diterpenoids is the representative class of the genus Cladiella [11]. Alternatively, soft corals of the genera Sinularia, Nephthea, Lemenalia, and others, are producers of sesquiterpenes and norsesquiterpenes, with highly rearranged skeletons [12].
In addition to the predominant terpenes produced by the corals, they have been recognized to produce other natural product chemotypes. Recently, ribosomal peptides were isolated and identified from scleractinian corals [13], along with acylated glycolipids [14], and alkaloids [15]. However, as the recent genetic investigations of corals suggest [3,16], to date, the reported chemistry merely represents only a fraction of the metabolites that are yet to be discovered.
Recently, advances in metabolomics tools have enabled the development of a comprehensive chart of the metabolic chemical space of living organisms [17]. The exploration of hundreds of metabolites is now feasible with the recent advances in the metabolomic platforms along with the opportunity to compare specimens simultaneously in an untargeted manner, allowing for the recognition of variability and similarity among samples [18].
Recently, untargeted metabolomic approaches in combination with multivariate data analysis were successfully applied to study cembrane diterpenes of different Sarcophyton species growing under different environmental and chemical conditions [2,19,20]. During this study, the superiority of the LC-MS in the discriminative coverage of coral species based on their chemical profiles, became apparent [2]. Subsequently, feature-based molecular networking was employed using the GNPS platform (the Global Natural Products Social Molecular Networking) for the identification of distinct chemical features among different clades of Sarcophyton glaucum [21].
Analogously, our primary aim was to explore and highlight the metabolic biodiversity offered by common Egyptian soft corals with the aid of untargeted metabolomics. Furthermore, species-specific metabolites have been highlighted for the future prioritization of soft coral species for MS-guided chemical investigation. Specimens studied included three Sinularia species (Si. brassica (formerly known as Si. dura), Si. leptoclados, and Si. gardineri), three Sarcophyton species (Sa. roseum (formerly known as Sa. convolutum), Sa. ehrenbergi, and Sa. acutum), along with Cladiella pachyclados, Litophyton mollis (formerly known as Nephthea mollis) and Lobophytum pauciflorum. Molecular networking was consulted to visually dissect the chemical similarities and differences among the specimens through the GNPS platform based on tandem mass spectrometric data (HRMS/MS).
2. Results and Discussion
Since the ultimate objective of this study was to broadly catalog the secondary metabolites of some common Egyptian soft corals with an emphasis on unearthing new chemistries, metabolomic-based indexing was thought to be the best means to interrogate the metabolomes. In concert, several dereplication algorithms have lately emerged to partially address the challenging annotation step in data analysis which contributes to the understanding of the complex metabolomics data sets, potentially revealing previously undiscovered metabolites [22]. In this regard, UPLC-HRMS/MS analysis in conjunction with feature-based molecular networking (FBMN) was harnessed to describe the nature and extent of the chemical diversity of the secondary metabolomes of such a defined set of soft corals.
UPLC-HRMS/MS analysis in the positive ionization mode of the selected Egyptian soft corals revealed distinct chemical profiles as seen in their respective base peak chromatograms (Supplementary Figure S1). The generation of an FBMN using the positive profiles portrayed a global overview of the detected chemical space and the metabolite distribution in the soft corals under investigation [23]. Networks were found that describe 3442 features (represented as nodes), with 1904 connected features in 480 clusters and the rest as singletons (Figure 1). Annotated clusters within the network are shown in boxes (Figure 1) which will be described in detail in terms of class identities in the upcoming sections.
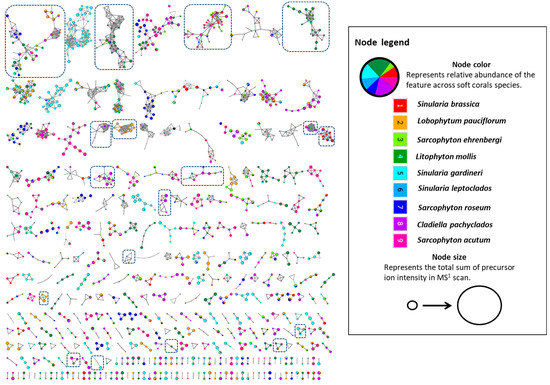
Figure 1.
The feature-based molecular network created using MS/MS data in the positive ionization mode from the soft coral extracts. The network displays nodes as a pie chart to reflect the relative abundance of each ion in each of the extracts.
Metabolite dereplication was principally based on their observed retention times, chemical formulas, and fragmentation behavior. Furthermore, the metabolite identification process was augmented with the FBMN and in silico fragmentation trees proposed by Sirius [24], in conjunction with the MarinLit database (https://marinlit.rsc.org/, accessed on 1 August 2022).
In-depth exploration of the differences between the studied species disclosed the existence of cembrane diterpenes in almost all species. In line with previous reports [11,25], eunicellin diterpenes occurred exclusively in Cladiella pachyclados but are reported here for the first time in Lobophytum pauciflorum (Figure 4). Similarly, sesquiterpenes with rearranged skeletons existed predominantly in Litophyton mollis and were less frequently encountered in Sinularia species (Figure 2).
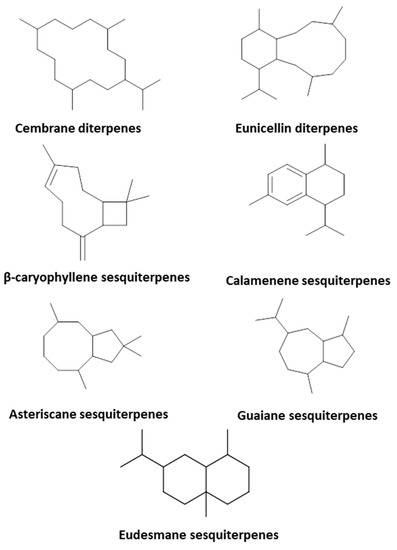
Figure 2.
Diterpene and sesquiterpene skeletons identified in the studied soft coral species.
Overall, 79 metabolites were tentatively assigned, mainly belonging to the terpene class encompassing diterpenes (cembrane and eunicellin types), sesquiterpenes (β-caryophyllene, asteriscane, eudesmane, guaiazulene, and calamenene types), and sterols. Detailed LC and MS information of the annotated metabolites is tabulated in Table S1. However, it is worthy to mention that the relative and/or absolute configuration of the annotated entities cannot be determined unless other appropriate spectroscopic techniques are implemented.
2.1. Cembrane Diterpenes
Detailed analysis of the FBMN uncovered the richness of the soft coral species with cembrane diterpenes (Figure 3). Such entities have previously been obtained from several soft coral genera, including Sarcophyton, Sinularia, Lobophytum, Eunicea, Clavularia, and from other octocorals [26]. Ecologically, cembranoids are thought to act as defensive compounds protecting soft corals from predators, bacteria, and other organisms [26]. In addition, several in vitro studies have documented their broad biological efficacy in anti-inflammatory, anticancer, antibacterial, antiviral, neuroprotective, and cytotoxic assays [26,27]. Interestingly, it was recently discovered that dolphins use these metabolites for self-medication against skin infections by rubbing their skin against specific soft coral species (i.e., Sarcophyton sp.). Tracing this behavior, cembranoid diterpenes (sarcophine/sarcophytolide/sarcophytolide B or C) could be linked as underlying metabolites, since they protect the dolphins from dermal pathogens [28].
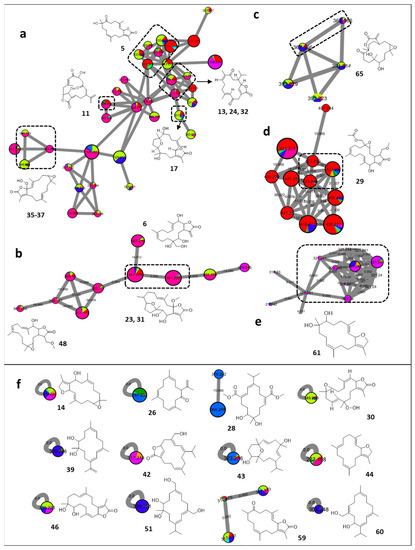
Figure 3.
Annotated cembrane diterpenes and their distribution in the FBMN. Node color corresponds to color codes described in Figure 1.
Manual annotation, supported with GNPS cross-referencing, facilitated the deconvolution of several clusters as cembrane diterpenes and expectedly revealed isomeric structural diversity (Figure 3). Their MS2 spectra showed the typical fragmentation pattern of terpenes with fragments separated by 12–14 Da, besides the common neutral losses of H2O (−18 Da) and CO (−28 Da), depending on the skeleton of the diterpene. In addition, the loss of 71 Da, representing the expulsion of an acyloxy group (C3H5O2), was regarded as a further informative fragment highlighting the γ-lactone ring-derived architectures. While cembranes with a hydroperoxy group showed the successive losses of –OH (17 Da) and –O (16 Da), those decorated with an acetyl group exhibited the typical loss of 42 Da [2]. Although the fragmentation behavior of the cembrane diterpenes was quite similar and showed the same fragments, there were subtle differences in their abundance attributed to their clustering into different groups, or even as single nodes in the MN, with a cosine score of 0.7 [21].
The major cluster of cembrane diterpenes demonstrated their distribution across Sinularia brassica, Sarcophyton ehrenbergi, and Sarcophyton acutum (Figure 3a). The cluster encompassed several isomers of a previously characterized hexahydrohydroxytetramethylcyclotetradecafurandione (5, m/z 333.2067 [M + H]+, C20H28O4) from Sarcophyton ehrenbergi [29]. Three connected features were hypothesized to depict the isomeric features of sarcostolide D [30] (13, 24, and 32, m/z 331.1897 [M + H]+, C20H26O4) and another feature was hypothesized to be sarcoehrenbergilid C [7] (17, m/z 351.2160 [M + H]+, C20H30O5). Within the same cluster, gyrosanolide A (11, m/z 349.2002 [M + H]+, C20H26O4) was proposed as a uniquely morphed cembrane-derived scaffold formerly described in Sinularia gyrosa [31]. In addition, isomers of hydroperoxysarcophine (35 and 37, m/z 349.1998 [M + H]+, C20H28O5), previously reported to occur in the soft corals Sarcophyton infundibuliforma [32] and Lobophytum crassum [33], respectively, were also proposed to be interlinked to the same ion cluster.
Similarly, an additional group of cembrane diterpenes sharing the same distribution pattern among the species (Figure 3b) were uncovered, and were proposed to consist of sinularolide A [34] (6, m/z 367.2111 [M + H]+, C20H30O6), isomers of briaviodiol A [35] (23 and 31, m/z 381.2259 [M + H]+, C21H32O6) and durumolide Q [36] (48, m/z 365.2316 [M + H]+, C21H32O5).
Furthermore, sinulaparvalide A [37] (65, m/z 367.211 [M + H]+, C20H30O6) was proposed as a metabolite of Sarcophyton roseum, and found to be associated with a further set of descendant ions possessing mass differences of +24 and +26 Da. The latter tentative derivatives of 65, which are larger in size, have not been previously described and represent possibly new congeners (Figure 3c).
The Sinularia brassica profile was proposed to harbor an exclusive group of structurally related cembrane diterpenes (Figure 3d), and among them, durumolide O [36] (29, m/z 423.2375 [M + H]+, C21H32O5), was annotated. The associated features were proposed to identify possibly new congeners with variable structural modifications such as dehydration, hydration, hydroxylation, or hydroperoxylation, as implied from the edge connections of −18 Da, +18 Da, +16 Da, or +17 Da, respectively.
Similarly, Cladiella pachyclados appeared to produce numerous isomers of dihydroxydeepoxysarcophytoxide [38] (61, m/z 321.2419 [M + H]+, C20H32O3) (Figure 3e).
2.2. Eunicellin Diterpenes
Alongside the abundant cembrane diterpenes, numerous eunicellin-based scaffolds were annotated exclusively in Cladiella pachyclados and Lobophytum pauciflorum. In line with former investigations [11], eunicellins are recognized as the prevailing terpenes in Cladiella. Eunicellin-derived diterpenes are always found in soft corals as a principal source, in contrast to others such as plants and microbes. Corals, particularly Cladiella, Eunicella, Briareum, and Muricella, are regarded as mega-producing genera of diverse eunicellin diterpenoids [39].
The architecture of eunicellin diterpenes is fundamentally constructed on the basis of a cladiellane diterpene frame and appended with a C-2, C-9 ether bridge to install a tetrahydrofuran ring. Structurally, they are believed to be the descendants of the cembrane diterpenes framed via a 2, 11-cyclization event [39]. As a result of the unusual structural features they can be decorated with, and, in turn, the compelling pharmacological activities, eunicellin diterpenes have captured the interest of both chemists and biologists in diverse chemical biology endeavors [39,40].
The FBMN revealed the presence of multiple clusters coding for the eunicellin terpenes (Figure 4). Their scattered appearance in several clusters was attributed to the relative differences in the abundance of the fragments (Figure S2), as previously mentioned [21].
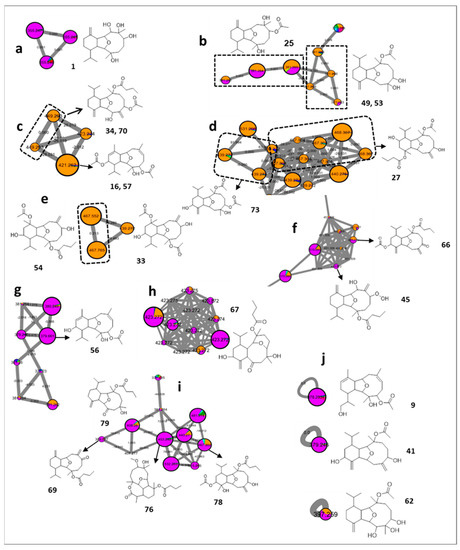
Figure 4.
Annotated eunicellin diterpenes and their distribution in the FBMN. Node color corresponds to color codes described in Figure 1.
The first assigned putative eunicellin diterpene was sclerophytin D [41] (1, m/z 355.2484 [M + H]+, C20H34O5) identified in Cladiella pachyclados (Figure 4a). A further pair of eunicellin-related features were proposed from a cluster mainly derived from Cladiella pachyclados and Lobophytum pauciflorum (Figure 4b). The tentative identification of such ions led to the proposition of the presence of sclerophytin B [42] (25, m/z 381.2627 [M + H]+, C22H36O5) with two additional isomeric forms including the structurally related sclerophytin E [43] (49 and 53, m/z 381.2633 [M + H]+, C22H36O5) (Figure 4b).
Interestingly, the MN unequivocally delineated Lobophytum pauciflorum as a prolific source of eunicellin diterpenes (Figure 4c–e). Cluster 4c was proposed to include astrogorgin B [44] (16 and 57, m/z 421.2581 [M + H]+, C24H36O6), connected with an edge of 28 Da to litophynol A acetate isomers [45] (34 and 70, m/z 449.2890 [M + H]+, C26H40O6), as reflected through their comparative elemental composition (+C2H4). Similarly, cluster 4d was proposed to demonstrate several isomeric forms of pachycladin B [11] (27, m/z 467.2999 [M + H]+, C26H42O7), and cladieunicellin N [46] (73, m/z 439.2684 [M + H]+, C24H38O7), while klysimplexin E [47] (33, m/z 439.2687 [M + H]+, C24H38O7), and klysimplexin C [47] (54, m/z 467.2995 [M + H]+, C26H42O7) constituted cluster 4e.
As expected, the prevalence of the eunicellin diterpene in Cladiella pachyclados was proposed to be exemplified by the known oxylitophynol [45] (45, m/z 423.2748 [M + H]+, C24H38O6), and its characterized peroxy derivative [48] (66, m/z 447.2743 [M + H]+, C26H38O6), which was originally reported from the soft coral Litophyton viscudium (Figure 4f).
In a similar fashion, and foremost in Cladiella pachyclados, three additional clusters were successfully tracked down (Figure 4g,h,i). The first and second groups were proposed to uncover astrogorgin L [44] (56, m/z 379.2471 [M + H]+, C20H35O5), and numerous isomers of cladieunicellin K [49] (67, m/z 423.2742 [M + H]+, C24H38O6), respectively. The third putatively defined set of eunicellin-derived features included litophynin G [50] (69, m/z 389.2682 [M + H]+, C24H36O4), briarellin P [51] (76, m/z 453.2837 [M + H]+, C25H40O7), simplexin P [52] (78, m/z 467.2999 [M + H]+, C26H42O7), and australin G [53] (79, m/z 407.2782 [M + H]+, C24H38O5).
Application of the same strategy on the single nodes also led to the tentative assignment of multiple singletons belonging to Cladiella pachyclados, as hirsutalin G [54] (9, m/z 379.2476 [M + H]+, C22H34O5), klymollin S [55] (41, m/z 379.2474 [M + H]+, C22H34O5), and sclerophytin C [43] (62, m/z 397.2579 [M + H]+, C22H36O6) (Figure 4j).
2.3. Sesquiterpenes
Different from the prevalent diterpenes, which were present in almost all the studied species, sesquiterpenes can only be readily predicted in Litophyton mollis, and sporadically in samples of the genus Sinularia (Figure 5).
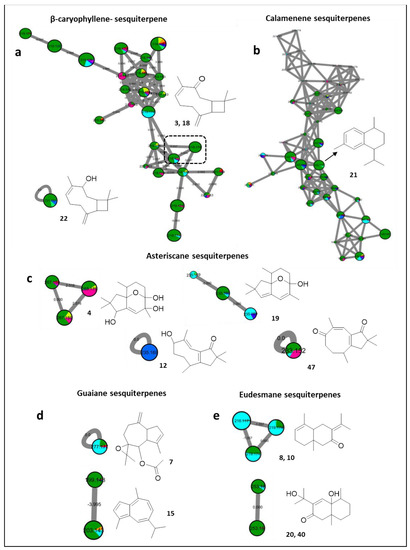
Figure 5.
Annotated sesquiterpenes and their distribution in the FBMN. Node color corresponds to color codes described in Figure 1.
Marine-derived sesquiterpenes embody a vital class of natural products framing countless scaffolds with a diverse array of bioactivity. The biological effects of marine sesquiterpenes were broadly detailed to span antitumor, antibacterial, antiviral, antifungal, immunosuppressive, cytotoxic, and insecticidal activities [56,57].
As illustrated from the FBMN, sesquiterpenes with various carbon skeletons were mostly proposed from the extract of Litophyton mollis. The first instance can be visualized by a group of features, namely, β-caryophyllene-based sesquiterpenes (Figure 5a). Such ions were proposed to include buddledin C/D [58] (3 and 18, m/z 219.1742 [M + H]+, C15H23O) in addition to numerous isomers (Figure 5a), while suberosol C [58] (22, m/z 221.1893 [M + H]+, C15H24O) was deciphered as a self-looped node, and was also found to exist in Sinularia gardineri, and Sinularia leptoclados.
Similarly, a large isomeric diversity was proposed for a calamenene-type sesquiterpene [59] (21, m/z 203.1789 [M + H]+, C15H22), previously characterized as (+)-trans-calamenene from Nephthea erecta (Figure 5b).
Furthermore, the MN suggests the additional occurrence of asteriscane sesquiterpenes in Sarcophyton acutum, Lobophytum pauciflorum, and Sinularia leptoclados (Figure 5c). This includes capillosanane J [60] (4, m/z 269.1748 [M + H]+, C15H24O4) grouped with an unknown pair of dehydrogenated derivatives, and isomers of capillosanane M [60] (19, m/z 235.1686 [M + H]+, C15H22O2), while, both capillosanane D [60] (12, m/z 235.1690 [M + H]+, C15H20O2), occurring exclusively in Lobophytum pauciflorum, and capillosanane F [60] (47, m/z 233.1528 [M + H]+, C15H22O2), appeared as scattered single nodes (Figure 5c).
Moreover, a further family of guaiane sesquiterpenes was proposed, consisting of guaiane spiroazulene 7 [61] (m/z 277.1775 [M + H]+, C17H24O3) and the aromatic cuteazul [62] (15, m/z 199.1478 [M + H]+, C15H18) (Figure 5d). In addition, the presence of eudesmane-based sesquiterpenes, such as isomers of naphthalenones 8 and 10 [63] (m/z 219.1744 [M + H]+, C15H22O), and oxoeudesmendiol [60,64] (20 and 40, m/z 253.1791 [M + H]+, C15H24O3) (Figure 5e), was suggested.
2.4. Sterols
Soft corals, in addition to being a prolific source of bioactive sesquiterpenes and diterpenes, are also known for their biosynthesis of polar polyhydroxy steroids. Typically, coral-derived sterols are structurally characterized by a 3β-hydroxy-Δ5- (or Δ0-) cholestane nucleus embedded with a C8−C10 side chain [65]. Coral-derived oxysterols are believed to be involved in the chemical defense against competitor reef organisms and predators. Therefore, interest is constantly growing to expand their physiological and pharmacological profiles. Moreover, they have demonstrated many biological properties such as cytotoxicity, lowering cholesterol biosynthesis, and inhibition of cancer [66].
The FBMN unearthed the presence of oxysterols in almost all specimens with a typical fragmentation pattern of successive loss of H2O and subsequent loss of the side chain. A major cluster of oxysterols was proposed with prevalence in Lobophytum pauciflorum, and consisted of an epidioxy ergosterol analogue [67] (50, m/z 475.3415 [M + H]+, C29H46O5), previously characterized from Sinularia candidula, nephalsterol B [68] (52, m/z 431.351 [M + H]+, C28H46O3), isomers of hydroxyergostadiene-one [69] (68, m/z 413.3405 [M + H]+, C28H44O2), sarcrasterol [70] (71, m/z 449.3616 [M + H]+, C28H48O4), erectasteroid D [71] (72, m/z 459.3462 [M + H]+, C29H46O4), and hydroxystigmastatrienone [72] (74, m/z 425.3407 [M + H]+, C29H44O2) (Figure 6). The cluster suggested the presence of possible new oxysterol scaffolds with mass differences from the annotated ones of 16 or 17 Da, implying further hydroxylation or hydroperoxylation.
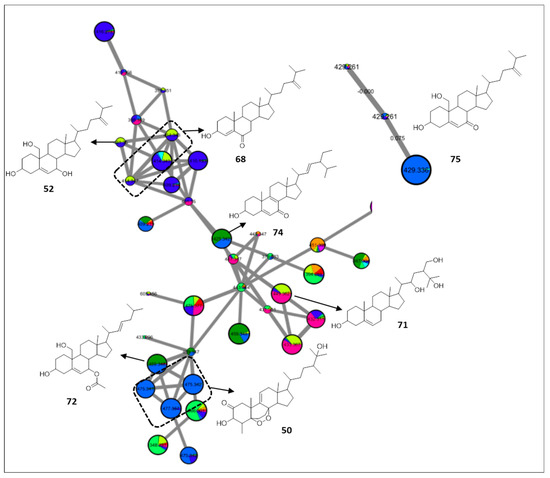
Figure 6.
Annotated sterols and their distribution in the FBMN. Node color corresponds to color codes described in Figure 1.
Lastly, isomers of dihydroxyergostadienone [73] (75, m/z 429.3359 [M + H]+, C28H44O3) were proposed to cluster separately (Figure 6), which could be attributed to the subtle differences in the abundance of the fragment ions as observed with the terpenes metabolites.
2.5. Others
Concurrently, the FBMN and the in-silico fragmentation trees proposed by Sirius, assisted in shedding light on overlooked metabolites with potentially undescribed scaffolds. For instance, glycosylated fatty acids, nitrogenated aromatic compounds, and polyketides were proposed in the Sinularia leptoclados sample. Former studies reported the occurrence of acylated glycolipids in Sinularia species [14]. While marine-derived polyketides have been repeatedly found in various soft coral sources, a growing body of reports point to the coral-associated microorganisms as being the true producers of such chemotypes [74,75]. Additionally, alkaloidal terpenes and N-acyl amino acids were proposed in both Sarcophyton roseum and Sarcophyton acutum. Soft corals are known to produce a variety of N-based congeners such as sphingosines, alkaloidal diterpene, purine, and pyrimidine derivatives [15,76,77]. These metabolites play a vital role in protecting the corals against pathogens and environmental stressors. Furthermore, they determine the distribution of the coral as well as the habitat biodiversity [15,76]. In this vein, sporadic reports have dealt with the isolation and characterization of alkaloidal terpenes from soft corals which could be attributed to the typical protocol usually followed, which requires a large amount of living tissue for the isolation of pure compounds and spectroscopic investigation, especially heteronuclear NMR. Yet, Cladiella, Eunicella, Sinularia, and Lobophytum were reported in the literature as assemblers of alkaloidal scaffolds [15]. Interestingly, the FBMN proposed the novel presence of alkaloidal terpenes in Sarcophyton species for the first time.
Conclusively, the adopted analytical protocol followed in this study proved to be competent and effective for annotating the metabolome of soft corals, allowing the rapid screening of rare and endangered species, and the potential discovery of possible new scaffolds. However, these findings require further chemical investigation for tracing up these potential new scaffolds for their isolation and full characterization.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Soft Coral Material
The soft coral specimens were collected from the Egyptian Red Sea along the coast of Hurghada, and were identified and authenticated by one of the authors (M.A.A.-H.) (Table 1, Figure S3).

Table 1.
Studied soft coral species and their respective collection sites.
The collected soft coral samples were identified based on morphology, colony color, shape, interior, and sclerites, using established identification keys [78,79,80,81,82,83]. Sclerites or spicules were used for the determination of different soft coral species (Figure S4). Sclerites were obtained by dissolving soft coral tissues in 10% sodium hypochlorite [84]. In addition to the sclerites, taxonomy relied on the presence or absence of siphonozooids among the autozooids (dimorphism), especially to differentiate between the genera Sarcophyton and Sinularia; and by the number of the autozooids to differentiate between Sarcophyton species [79,82], where, colony morphology allows the differentiation and definition of the genus. The coral morphology and the surrounding environment and habitat of the collected soft corals were recorded on an underwater slate.
3.2. Chemicals and Reagents
All chemicals for chemical analysis were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (Merck, Kenilworth, NJ, USA).
3.3. Soft Corals Extraction and Sample Preparation for UPLC-MS Analysis
The frozen soft coral specimens (100 g each) were chopped into small pieces and extracted with ethyl acetate (1 L) at room temperature, five times until exhaustion, with respective yields listed in Table 1. The obtained extracts were concentrated under reduced pressure, lyophilized, then kept at −20 °C for further analysis. The lyophilized extracts were prepared for UPLCMS/MS analyses following a previously described protocol [85].
3.4. UPLC–HRMS/MS Analysis
The HRMS/MS analysis was carried out on a MaXis 4G instrument (Bruker Daltonics®, Bremen, Germany) coupled with an Ultimate 3000 HPLC (Thermo Fisher Scientific®, Waltham, MA, USA). A UPLC-method was applied as described in [86]. The separation was carried out on a Nucleoshell 2.7 µm 150 × 2 mm column (Macherey-Nagel®, Düren, Germany), and the range for MS acquisition was 50–1800 Daltons (Da). A capillary voltage of 4500 V, nebulizer gas pressure (nitrogen) of 2 (1.6) bar, ion source temperature of 200 °C, dry gas flow of 9 L/min, and spectral rates of 3 Hz for MS1 and 10 Hz for MS2, were used. For acquiring MS/MS fragmentation, the 10 most intense ions per MS1 were selected for subsequent CID, with stepped CID energy applied. The employed parameters for tandem MS were applied as previously detailed [87].
3.5. Feature-Based Molecular Networking and Compounds Dereplication
Raw data inspection was performed using Compass Data Analysis 4.4 (Bruker Daltonics®). Metaboscape 3.0 (Bruker Daltonics®) was utilized for feature detection, grouping, and alignment, employing the T-ReX 3D (Time aligned Region Complete eXtraction) algorithm [40]. Bucketing was performed with an intensity threshold of 10× 105 and a retention time range from 0.5 to 40 min with a restricted mass range m/z from 190 to 1800. The produced MGF file and the feature quantification table (CSV file) were used in the feature-based molecular networking (FBMN) following the online workflow in GNPS platform (http://gnps.ucsd.edu (accessed on 1 August 2022)) [23]. The parameters, applied for the construction of the FBMN via the GNPS platform, are detailed in Table S2.
Cytoscape version 3.7.1.60 (https://cytoscape.org/, accessed on 15 February 2021) was used for the network visualization. Sirius + CSI:FingerID 4.0.1 was used for the manual putative structures identification [88], assisted by the molecular formula prediction and candidate search with m/z tolerance set to 20 ppm connected to online Pubchem and verified through the MarineLit database (https://marinlit.rsc.org/, accessed on 1 August 2022).
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/md20100630/s1, Figure S1: The base peak chromatograms of the studied soft corals extracts in positive ionization mode; Figure S2: Comparative MS/MS spectra of compounds 9, 41, 62 justifying their de-clustering in the FBMN; Figure S3: Google Earth map showing the location of collection sites; Figure S4: The endoskeleton of the most common genera: (A) Sinularia sp., (B) Sarcophyton sp.; Table S1: Putative compound assignment of the studied soft coral specimens as revealed by UPLC-HRMS/MS analysis; Table S2: Parameters used for the construction of the FBMN via the GNPS platform.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.M.H., T.A.M., H.H.S., M.-E.F.H., T.A.H., M.A.A.-H. and H.G.; methodology, N.M.H., T.A.M., H.H.S., M.A.A.-H. and T.A.H.; formal analysis, N.M.H.; writing—original draft preparation, N.M.H. and H.H.S.; writing—review and editing, M.-E.F.H. and H.G.; supervision, M.-E.F.H. and H.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The FBMN job on GNPS can be accessed at https://gnps.ucsd.edu/ProteoSAFe/status.jsp?task=5c2975ad4ac541f3bf96c564b20d809c (accessed on 1 August 2022).
Acknowledgments
N.M.H. acknowledges the Ministry of Higher Education, Arab Republic of Egypt for being funded with a postdoctoral fellowship.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- DiBattista, J.D.; Roberts, M.B.; Bouwmeester, J.; Bowen, B.W.; Coker, D.J.; Lozano-Cortés, D.F.; Howard Choat, J.; Gaither, M.R.; Hobbs, J.P.A.; Khalil, M.T. A review of contemporary patterns of endemism for shallow water reef fauna in the Red Sea. J. Biogeogr. 2016, 43, 423–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, M.A.; Porzel, A.; Al-Hammady, M.A.; Hegazy, M.-E.F.; Meyer, A.; Mohamed, T.A.; Westphal, H.; Wessjohann, L.A. Soft corals biodiversity in the Egyptian Red Sea: A comparative MS and NMR metabolomics approach of wild and aquarium grown species. J. Proteome Res. 2016, 15, 1274–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scesa, P.D.; Lin, Z.; Schmidt, E.W. Ancient defensive terpene biosynthetic gene clusters in the soft corals. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2022, 18, 659–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegazy, M.E.F.; Mohamed, T.A.; Alhammady, M.A.; Shaheen, A.M.; Reda, E.H.; Elshamy, A.I.; Aziz, M.; Paré, P.W. Molecular architecture and biomedical leads of terpenes from red sea marine invertebrates. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 3154–3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, T.A.; Elshamy, A.I.; Abdel-Tawab, A.M.; AbdelMohsen, M.M.; Ohta, S.; Pare, P.W.; Hegazy, M.-E.F. Oxygenated Cembrene Diterpenes from Sarcophyton convolutum: Cytotoxic Sarcoconvolutum AE. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegazy, M.-E.F.; Eldeen, A.M.G.; Shahat, A.A.; Abdel-Latif, F.F.; Mohamed, T.A.; Whittlesey, B.R.; Paré, P.W. Bioactive hydroperoxyl cembranoids from the Red Sea soft coral Sarcophyton glaucum. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegazy, M.-E.F.; Elshamy, A.I.; Mohamed, T.A.; Hamed, A.R.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Ohta, S.; Paré, P.W. Cembrene diterpenoids with ether linkages from Sarcophyton ehrenbergi: An anti-proliferation and molecular-docking assessment. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, H.; König, G.M. Terpenoids from marine organisms: Unique structures and their pharmacological potential. Phytochem. Rev. 2006, 5, 115–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazy, M.-E.F.; Mohamed, T.A.; Elshamy, A.I.; Hamed, A.R.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Ohta, S.; Umeyama, A.; Paré, P.W.; Efferth, T. Sarcoehrenbergilides D–F: Cytotoxic cembrene diterpenoids from the soft coral Sarcophyton ehrenbergi. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 27183–27189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chill, L.; Berrer, N.; Benayahu, Y.; Kashman, Y. Eunicellin diterpenes from two Kenyan soft corals. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.M.; Khanfar, M.A.; Elnagar, A.Y.; Mohammed, R.; Shaala, L.A.; Youssef, D.T.; Hifnawy, M.S.; El Sayed, K.A. Pachycladins A−E, prostate cancer invasion and migration inhibitory eunicellin-based diterpenoids from the Red Sea soft coral Cladiella pachyclados. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 848–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Munro, M.H.; Northcote, P.T.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2006, 23, 26–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, C.A.; Cooke, I.; Wilson, D.T.; Miller, D.J.; Peigneur, S.; Tytgat, J.; Field, M.; Takjoo, R.; Smout, M.J.; Loukas, A. Newly Discovered Peptides from the Coral Heliofungia actiniformis Show Structural and Functional Diversity. J. Nat. Prod. 2022, 85, 1789–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putra, M.Y.; Ianaro, A.; Panza, E.; Bavestrello, G.; Cerrano, C.; Fattorusso, E.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O. Sinularioside, a triacetylated glycolipid from the Indonesian soft coral Sinularia sp., is an inhibitor of NO release. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 2723–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Yi, X.; Huang, R.; Yan, F.; He, B.; Chen, B. Alkaloids from corals. Chem. Biodivers. 2013, 10, 1435–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhardt, I.; de Rond, T.; Chen, P.Y.-T.; Moore, B.S. Ancient plant-like terpene biosynthesis in corals. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2022, 18, 664–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.E.; Farag, M.A. Expanding Metabolomics Applications to Address Issues in Marine Ecology and Natural Products Chemistry. In Encyclopedia of Marine Biotechnology; Kim, S.-K., Ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; Volume 3, pp. 1827–1842. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos, A.E.F.; Evanno, L.; Poupon, E.; Champy, P.; Beniddir, M.A. Natural products targeting strategies involving molecular networking: Different manners, one goal. RSC Adv. 2019, 36, 960–980. [Google Scholar]
- Farag, M.A.; Meyer, A.; Ali, S.E.; Salem, M.A.; Giavalisco, P.; Westphal, H.; Wessjohann, L.A. Comparative metabolomics approach detects stress-specific responses during coral bleaching in soft corals. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 2060–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, M.A.; Maamoun, A.A.; Meyer, A.; Wessjohann, L.A. Salicylic acid and its derivatives elicit the production of diterpenes and sterols in corals and their algal symbionts: A metabolomics approach to elicitor SAR. Metabolomics 2018, 14, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maloney, K.N.; Botts, R.T.; Davis, T.S.; Okada, B.K.; Maloney, E.M.; Leber, C.A.; Alvarado, O.; Brayton, C.; Caraballo-Rodríguez, A.M.; Chari, J.V. Cryptic species account for the seemingly idiosyncratic secondary metabolism of Sarcophyton glaucum specimens collected in Palau. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfender, J.-L.; Nuzillard, J.-M.; Van Der Hooft, J.J.; Renault, J.-H.; Bertrand, S. Accelerating metabolite identification in natural product research: Toward an ideal combination of liquid chromatography–high-resolution tandem mass spectrometry and NMR profiling, in silico databases, and chemometrics. Anal. Chem. 2018, 91, 704–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nothias, L.-F.; Petras, D.; Schmid, R.; Dührkop, K.; Rainer, J.; Sarvepalli, A.; Protsyuk, I.; Ernst, M.; Tsugawa, H.; Fleischauer, M. Feature-based molecular networking in the GNPS analysis environment. Nat. Methods 2020, 17, 905–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böcker, S.; Dührkop, K. Fragmentation trees reloaded. J. Cheminform. 2016, 8, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dokalahy, E.E.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Farag, M.A. Soft Coral Biodiversity in the Red Sea Family Alcyoniidae: A Biopharmaceutical and Ecological Perspective. In Biodiversity and Chemotaxonomy; Ramawat, K.G., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 55–85. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, I.G.; Miguel, M.G.; Mnif, W. A brief review on new naturally occurring cembranoid diterpene derivatives from the soft corals of the genera Sarcophyton, Sinularia, and Lobophytum since 2016. Molecules 2019, 24, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazy, M.-E.F.; El-Beih, A.A.; Moustafa, A.Y.; Hamdy, A.A.; Alhammady, M.A.; Selim, R.M.; Abdel-Rehim, M.; Paré, P.W. Cytotoxic cembranoids from the Red Sea soft coral Sarcophyton glaucum. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2011, 6, 1809–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morlock, G.E.; Ziltener, A.; Geyer, S.; Tersteegen, J.; Mehl, A.; Schreiner, T.; Kamel, T.; Brümmer, F. Evidence that Indo-Pacific bottlenose dolphins self-medicate with invertebrates in coral reefs. iScience 2022, 25, 104271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkhateeb, A.; El-Beih, A.A.; Gamal-Eldeen, A.M.; Alhammady, M.A.; Ohta, S.; Paré, P.W.; Hegazy, M.-E.F. New terpenes from the Egyptian soft coral Sarcophyton ehrenbergi. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 1977–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.-B.; Shen, Y.-C.; Kuo, Y.-H.; Khalil, A.T. Cembrane diterpenoids from the Taiwanese soft coral Sarcophyton stolidotum. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1141–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.-Y.; Chuang, C.-T.; Wen, Z.-H.; Wang, S.-K.; Chiou, S.-F.; Hsu, C.-H.; Dai, C.-F.; Duh, C.-Y. Bioactive norditerpenoids from the soft coral Sinularia gyrosa. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 3379–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Chen, A.-N.; Shao, C.-L.; Li, L.; Xu, Y.; Quian, P.-Y. Chemical constituents of soft coral Sarcophyton infundibuliforme from the South China Sea. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2011, 39, 853–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.W.; Shi, Y.P.; Li, X.M.; Wang, B.G. A New Cembranoid Diterpene and Other Related Metabolites from the South-China-Sea Soft Coral Lobophytum crassum. Helv. Chim. Acta 2006, 89, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, Z.; van Ofwegen, L.; Proksch, P.; Lin, W. Cytotoxic cembranoid diterpenes from a soft coral Sinularia gibberosa. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 649–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-C.; Huang, I.-C.; Chiang, M.Y.-N.; Hwang, T.-L.; Kung, T.-H.; Lin, C.-S.; Sheu, J.-H.; Sung, P.-J. Briaviodiol A, a new Cembranoid from a softcoral Briareum violacea. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 58, 1666–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.-Y.; Chen, P.-W.; Chen, H.-P.; Wang, S.-K.; Duh, C.-Y. New cembranolides from the Dongsha Atoll soft coral Lobophytum durum. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1307–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Gao, A.-H.; Huang, H.; Li, J.; Mollo, E.; Gavagnin, M.; Cimino, G.; Gu, Y.-C.; Guo, Y.-W. Diterpenoids from the Hainan Soft Coral Sinularia parva. Helv. Chim. Acta 2009, 92, 1341–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Li, X.; Zhao, F.; Cheng, S.; Xiang, Z.; Dong, J.; Huang, K.; Yan, P. Four New 7,8-epoxycembranoids from a Chinese soft coral Lobophytum sp. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2013, 61, 1323–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.-F.; Chen, M.-J.; Liang, D.-E.; Shi, L.-M.; Ying, Y.-M.; Shan, W.-G.; Li, G.-Q.; Zhan, Z.-J. Streptomyces albogriseolus SY67903 produces eunicellin diterpenoids structurally similar to terpenes of the gorgonian Muricella sibogae, the bacterial source. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 1641–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ru, T.; Cai, Y.-S.; Li, H.; Tang, W.; Wang, H.; Guo, Y.-W. Further new eunicellin-based diterpenoids from the Guangxi Weizhou soft coral Cladiella krempfi. Fitoterapia 2018, 131, 200–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.; Sharma, P.; Zektzer, A.S.; Martin, G.E.; Ji, X.; van der Helm, D. Sclerophytin C-F: Isolation and Structures of Four New Diterpenes from the Soft Coral Sclerophytum capitalis. J. Org. Chem. 1989, 54, 1896–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-F.; Chen, W.-F.; Wen, Z.-H.; Hwang, T.-L.; Zhang, Z.-J.; Sung, P.-J. New bioactive Δ11(17)-furanoeunicellins from an octocoral Cladiella sp. Phytochem. Lett. 2019, 33, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, C.B.; Rao, D.S.; Satyanarayana, C.; Rao, D.V.; Kassühlke, K.E.; Faulkner, D.J. New cladiellane diterpenes from the soft coral Cladiella australis of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. J. Nat. Prod. 1994, 57, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, D.; Liu, D.; Deng, Z.; van Ofwegen, L.; Proksch, P.; Lin, W. Antifouling Eunicellin-Type Diterpenoids fom the Gorgonian Astrogorgia sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 1595–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.-S.; Yao, L.-G.; Di Pascale, A.; Irace, C.; Mollo, E.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O.; Guo, Y.-W. Polyoxygenated diterpenoids of the eunicellin-type from the Chinese soft coral Cladiella krempfi. Tetrahedron 2013, 69, 2214–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.-H.; Chen, W.-F.; Wen, Z.-H.; Lu, M.-C.; Wang, W.-H.; Li, J.-J.; Wu, Y.-C.; Sung, P.-J. Cladieunicellins M–Q, new eunicellins from Cladiella sp. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 2144–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.-W.; Wu, Y.-C.; Chiang, M.Y.; Su, J.-H.; Wang, W.-H.; Fan, T.-Y.; Sheu, J.-H. Eunicellin-based diterpenoids from the cultured soft coral Klyxum simplex. Tetrahedron 2009, 65, 7016–7022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwagawa, T.; Kusatsu, T.; Tsuha, K.; Hamada, T.; Okamura, H.; Furukawa, T.; Akiyama, S.-I.; Doe, M.; Morimoto, Y.; Iwase, F.; et al. Cytotoxic eunicellin-type diterpenes from the soft coral Litophyton viscudium. Heterocycles 2011, 83, 2149–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, F.-Y.; Chen, T.-H.; Lu, M.-C.; Chen, W.-F.; Wen, Z.-H.; Kuo, Y.-H.; Sung, P.-J. Cladieunicellins K and L, new eunicellin-based diterpenoids from an octocoral Cladiella sp. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 21781–21789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochi, M.; Yamada, K.; Futatsugi, K.; Kotsuki, H.; Shibata, K. Litophynins F, G, and H, Three New Diterpenoids from a Soft Coral Litophyton sp. Heterocycles 1991, 32, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ospina, C.A.; Rodríguez, A.D.; Ortega-Barria, E.; Capson, T.L. Briarellins J−P and Polyanthellin A: New Eunicellin-Based Diterpenes from the Gorgonian Coral Briareum polyanthes and Their Antimalarial Activity. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.-L.; Su, J.-H.; Huang, C.-Y.; Tai, C.-J.; Sung, P.-J.; Liaw, C.-C.; Sheu, J.-H. Simplexins P–S, eunicellin-based diterpenes from the soft coral Klyxum simplex. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 1203–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.E.; Amlani, A.; Dewi, A.S.; Patrick, B.O.; van Ofwegen, L.; Mui, A.L.-F.; Andersen, R.J. Australin E Isolated from the Soft Coral Cladiella sp. Collected in Pohnpei Activates the Inositol 5-Phosphatase SHIP1. Aust. J. Chem. 2010, 63, 895–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.-W.; Chang, S.-M.; Huang, C.-Y.; Chao, C.-H.; Su, J.-H.; Wen, Z.-H.; Hsu, C.-H.; Dai, C.-F.; Wu, Y.-C.; Sheu, J.-H. Hirsutalins A− H, eunicellin-based diterpenoids from the soft coral Cladiella hirsuta. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1785–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.-C.; Chen, B.-W.; Huang, C.-Y.; Dai, C.-F.; Hwang, T.-L.; Sheu, J.-H. Eunicellin-based diterpenoids from the Formosan soft coral Klyxum molle with inhibitory activity on superoxide generation and elastase release by neutrophils. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 1661–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Bideau, F.; Kousara, M.; Chen, L.; Wei, L.; Dumas, F. Tricyclic sesquiterpenes from marine origin. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 6110–6159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Liu, J.; Leng, X.; Ouyang, H. Chemical diversity and biological activity of secondary metabolites from soft coral genus Sinularia since 2013. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.-H.; Ahmed, A.F.; Sheu, J.-H.; Duh, C.-Y.; Shen, Y.-C.; Wang, L.-T. Suberosols A− D, four new sesquiterpenes with β-caryophyllene skeletons from a Taiwanese gorgonian coral Subergorgia suberosa. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 887–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.-Y.; Huang, Y.-C.; Wen, Z.-H.; Chiou, S.-F.; Wang, S.-K.; Hsu, C.-H.; Dai, C.-F.; Duh, C.-Y. Novel sesquiterpenes and norergosterol from the soft corals Nephthea erecta and Nephthea chabroli. Tetrahedron Lett. 2009, 50, 802–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Chen, W.; Liu, D.; van Ofwegen, L.; Proksch, P.; Lin, W. Asteriscane-type sesquiterpenoids from the soft coral Sinularia capillosa. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 1753–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjaneyulu, A.; Chaturvedula, V.S.P. New Sesqui-and Diterpenoids from the Soft Coral Nephthea chabroli of Indian Coast. Indian J. Chem. Sect. B 2013, 34B, 32. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.-J.; Shao, C.-L.; Chen, M.; Gan, L.-S.; Fang, Y.-C.; Wang, X.-H.; Wang, C.-Y. Ochracenoids A and B, guaiazulene-based analogues from gorgonian Anthogorgia ochracea collected from the South China Sea. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 1569–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coll, J.C.; Bowden, B.F.; Tapiolas, D.M.; Willis, R.H.; Djura, P.; Streamer, M.; Trott, L. Studies of Australian soft corals—XXXV: The terpenoid chemistry of soft corals and its implications. Tetrahedron 1985, 41, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.-Y.; Wang, S.-K.; Wen, Z.-H.; Dai, C.-F.; Duh, C.-Y. Three new eudesmanoids from the Formosan soft coral Nephthea erecta. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2009, 11, 967–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarma, N.S.; Krishna, M.S.; Pasha, S.G.; Rao, T.S.P.; Venkateswarlu, Y.; Parameswaran, P. Marine metabolites: The sterols of soft coral. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 2803–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso-Martínez, F.; José, M.; Díaz-Marrero, A.R.; Darias, J.; D’Croz, L.; Jiménez-Antón, M.D.; Corral, M.J.; García, R.; Alunda, J.M.; Cueto, M. Oxysterols from an octocoral of the genus Gorgonia from the eastern Pacific of Panama. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 38579–38591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Ibrahim, A.; Arafa, A.S. Anti-H5N1 virus metabolites from the Red Sea soft coral, Sinularia candidula. Tetrahedron Lett. 2013, 54, 2377–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duh, C.-Y.; Wang, S.-K.; Chu, M.-J.; Sheu, J.-H. Cytotoxic sterols from the soft coral Nephthea erecta. J. Nat. Prod. 1998, 61, 1022–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoc, N.T.; Huong, P.T.M.; Van Thanh, N.; Chi, N.T.P.; Dang, N.H.; Cuong, N.X.; Nam, N.H.; Thung, D.C.; van Kiem, P.; van Minh, C. Cytotoxic steroids from the Vietnamese soft coral Sinularia conferta. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2017, 65, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.-X.; Yan, S.-J.; Zhang, G.-W.; Su, J.-Y.; Zeng, L.-M. Isolation of new polyhydroxylated sterol from soft coral Sarcophyton crassocaule Mosre. Chem. J. Chin. Univ. 2007, 28, 686–688. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, S.-Y.; Dai, C.-F.; Duh, C.-Y. New 4-methylated and 19-oxygenated steroids from the Formosan soft coral Nephthea erecta. Steroids 2007, 72, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Songzhi, D.; Chunlei, T.; Dingjun, X. Studies on the chemical constituents of the sponge Biemna fortis from the South China Sea. Chin. J. Mar. Drugs 1999, 18, 4–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, W.K.; Che, C.-T. Polyhydroxylated steroids and other constituents of the soft coral Nephthea chabroli. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2003, 51, 1009–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiese, J.; Sabdono, A.; Imhoff, J.F. Corals as source of bacteria with antimicrobial activity. J. Coast. Dev. 2008, 11, 121–130. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Dong, J.-D.; Yang, J.; Luo, X.-M.; Zhang, S. Detection of polyketide synthase and nonribosomal peptide synthetase biosynthetic genes from antimicrobial coral-associated actinomycetes. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2014, 106, 623–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClintock, J.B.; Baker, B.J. Marine Chemical Ecology, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Lakshmi, V.; Kumar, R. Metabolites from Sinularia species. Nat. Prod. Res. 2009, 23, 801–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macfadyen, L. Alcyonaria (Stolonifera, Alcyonacea, Telestacea and Gorgonacea). 1935. Available online: https://biostor.org/reference/175067 (accessed on 1 August 2022).
- Thomson, J.A.; Dean, L.M. The Alcyonacea of the Siboga-Expedition: With an Addendum to the Gorgonacea. In Siboga Expedition, 1899–1900; E.J. Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands, 1931. [Google Scholar]
- Gohar, H.A.F. Studies on the Xeniidae of the Red Sea; Publications of the Marine Biological Station: Ghardaqa (Red Sea), Egypt, 1940. [Google Scholar]
- Reinicke, G.B. Xeniidae des Roten Meeres (Octocorallia, Alcyonacea): Beiträge zur Systematik und Ökologie; Westarp Wissenschaften: Hohenwarsleben, Germany, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Verseveldt, J. A Revision of the Genus Sarcophyton Lesson (Octocorallia, Alcyonacea); Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Fabricius, K.; Alderslade, P. Soft Corals and Sea Fans: A Comprehensive Guide to the Tropical Shallow Water Genera of the Central-West Pacific, the Indian Ocean and the Red Sea; New Litho: Melbourne, Australia, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Benayahu, Y.; Loya, Y.J.T.B.B. Sexual reproduction of a soft coral: Synchronous and brief annual spawning of Sarcophyton glaucum (Quoy & Gaimard, 1833). Biol. Bull. 1986, 170, 32–42. [Google Scholar]
- Hegazi, N.M.; Radwan, R.A.; Ali, S.M.; Saad, H.H. Molecular networking aided metabolomic profiling of beet leaves using three extraction solvents and in relation to its anti-obesity effects. J. Adv. Res. 2020, 24, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazi, N.M.; Saad, H.H.; Marzouk, M.M.; Abdel Rahman, M.F.; El Bishbishy, M.H.; Zayed, A.; Ulber, R.; Ezzat, S.M. Molecular networking leveraging the secondary metabolomes space of Halophila stipulaceae (Forsk.) Aschers. and Thalassia hemprichii (Ehrenb. ex Solms) Asch. in tandem with their chemosystematics and antidiabetic potentials. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, N.; Kapono, C.A.; Lim, Y.W.; Koyama, N.; Vermeij, M.J.; Conrad, D.; Rohwer, F.; Dorrestein, P.C. Mass spectral similarity for untargeted metabolomics data analysis of complex mixtures. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2015, 377, 719–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dührkop, K.; Shen, H.; Meusel, M.; Rousu, J.; Böcker, S. Searching molecular structure databases with tandem mass spectra using CSI: FingerID. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 12580–12585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).