Characterization of an α 4/7-Conotoxin LvIF from Conus lividus That Selectively Blocks α3β2 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
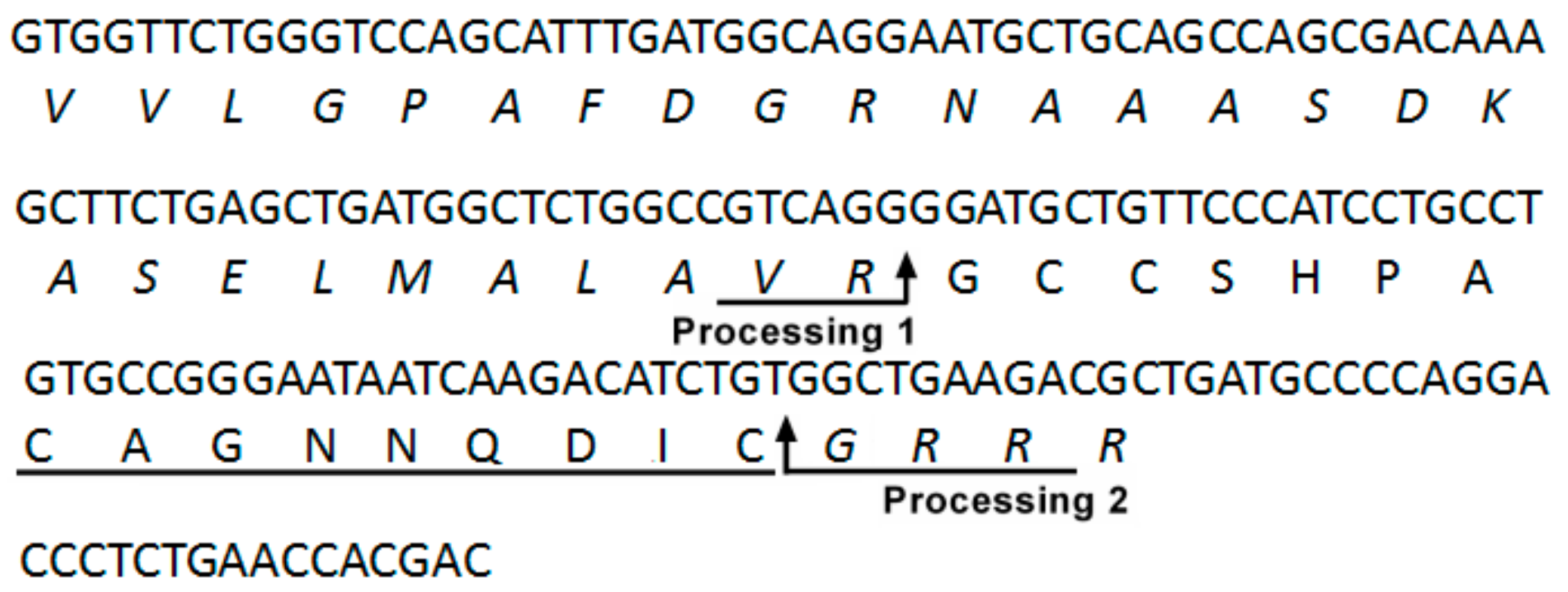
2.1. DNA Cloning and Sequence Analysis of the α-CTx LvIF Precursor
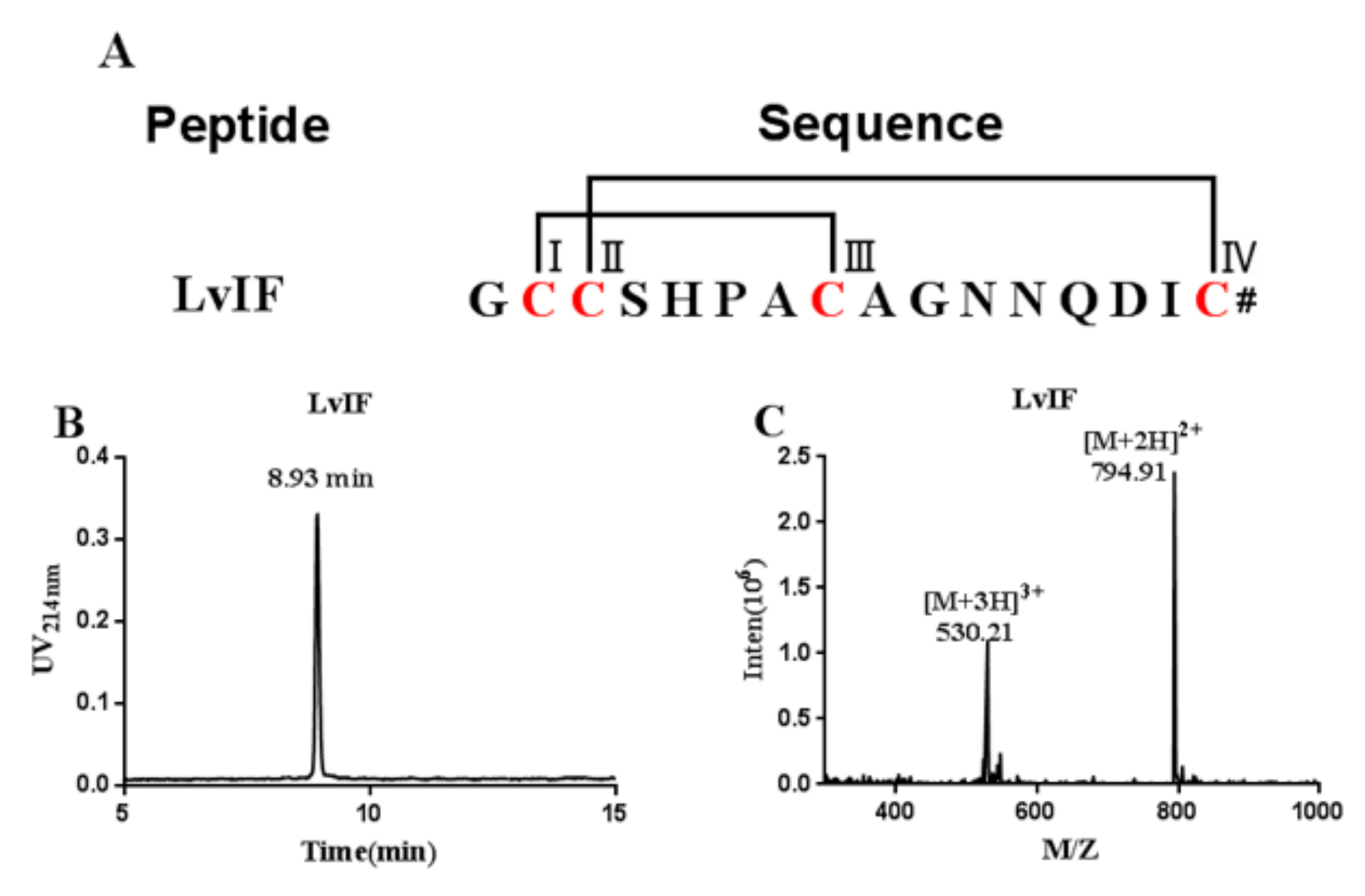
2.2. Oxidative Folding and Identification of α-CTx LvIF
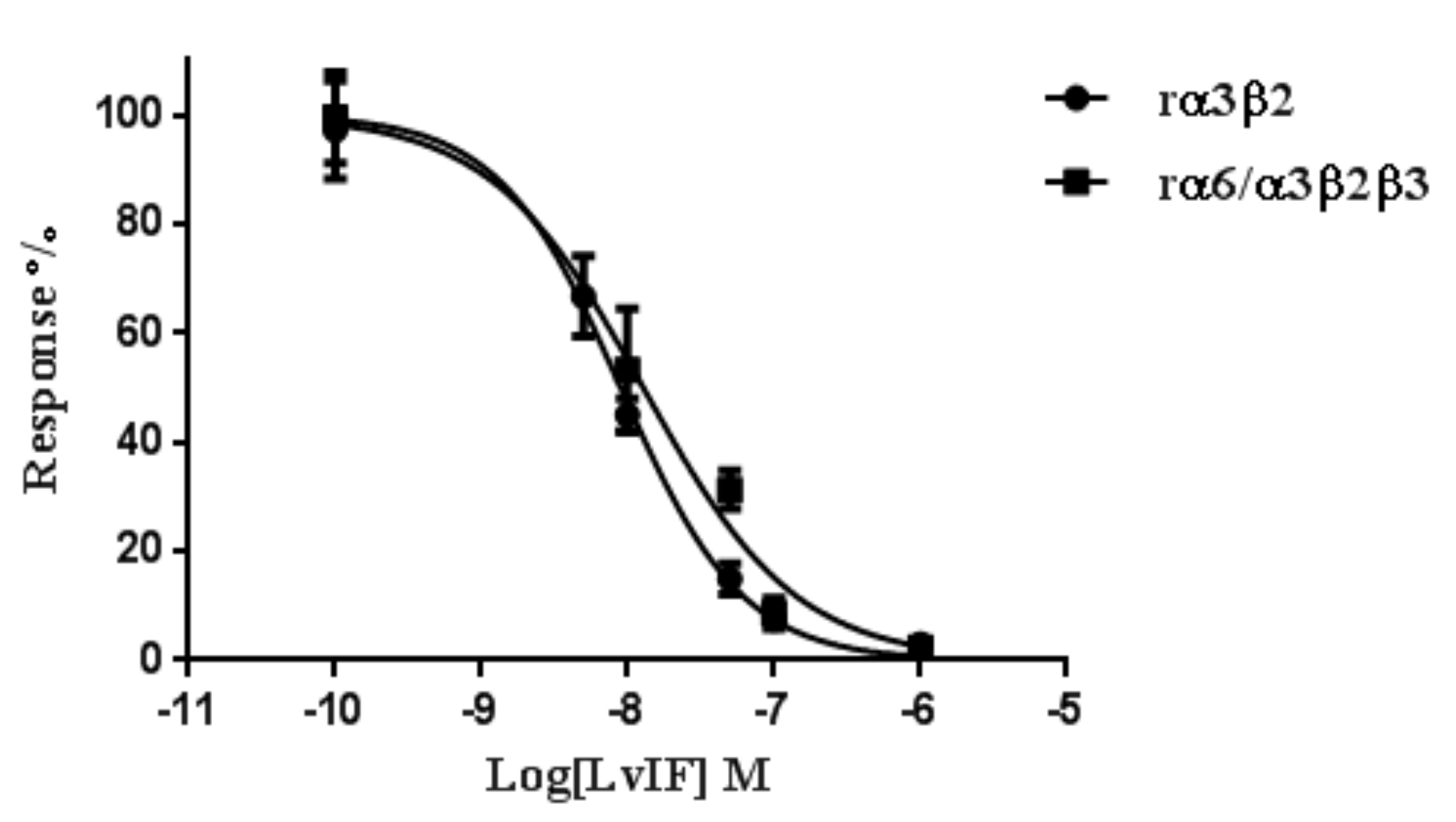
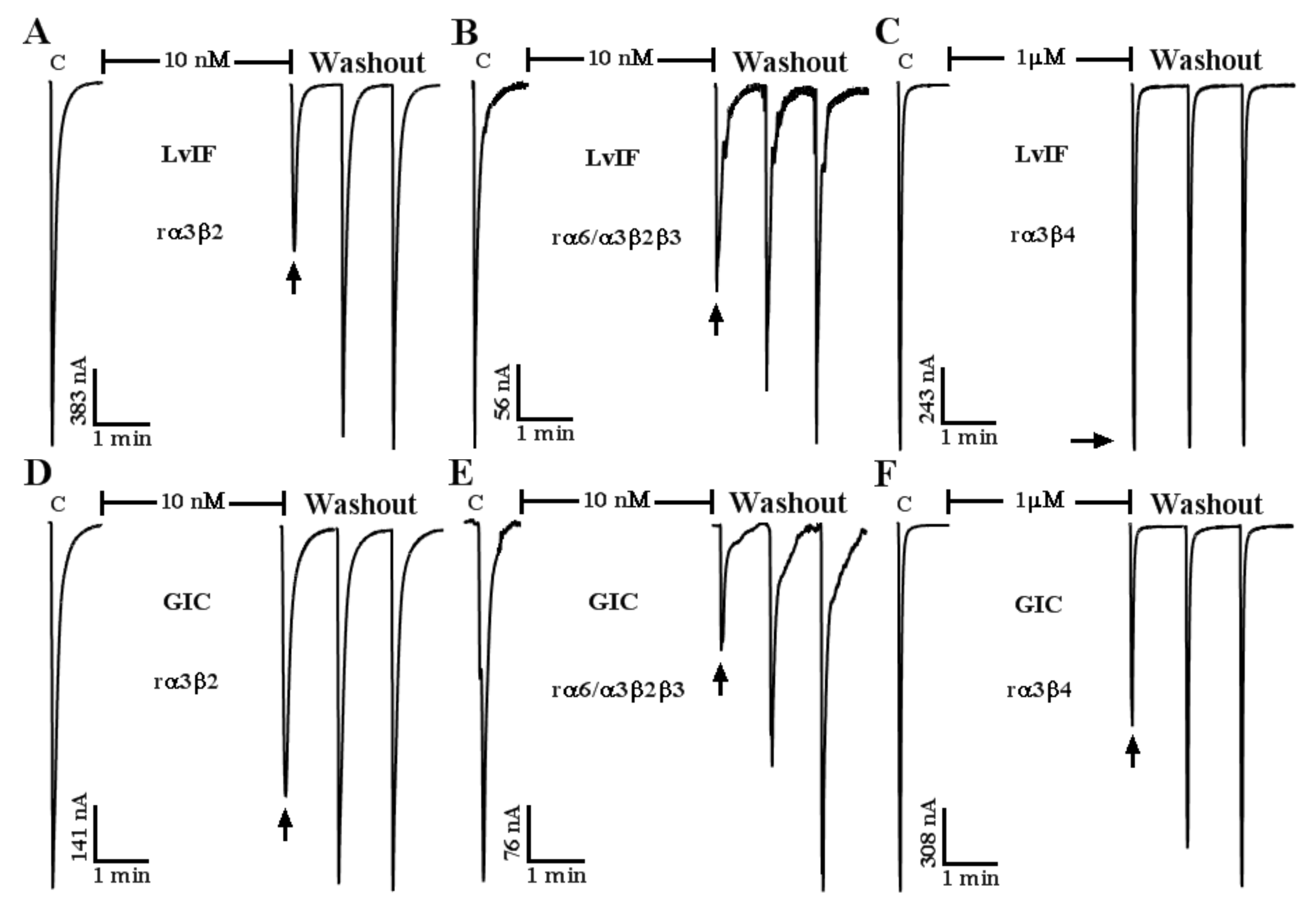
2.3. Effect of α-CTx LvIF on ACh-Evoked nAChR-Mediated Current
2.4. α-CTxs LvIF and MII Compete for Binding to rα3β2 nAChR
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Identification and Sequencing of a Genomic DNA Clone Encoding α-CTx LvIF
4.3. Peptide Synthesis
4.4. cRNA Preparation and Injection
4.5. Electrophysiology
4.6. Data Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hurst, R.; Rollema, H.; Bertrand, D. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: From basic science to therapeutics. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 137, 22–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebbe, E.; Peigneur, S.; Wijesekara, I.; Tytgat, J. Conotoxins Targeting Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors: An Overview. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 2970–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hogg, R.C.; Raggenbass, M.; Bertrand, D. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: From structure to brain function. Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2003, 147, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lyukmanova, E.N.; Shulepko, M.A.; Shenkarev, Z.O.; Bychkov, M.L.; Paramonov, A.S.; Chugunov, A.O.; Kulbatskii, D.S.; Arvaniti, M.; Dolejsi, E.; Schaer, T.; et al. Secreted Isoform of Human Lynx1 (SLURP-2): Spatial Structure and Pharmacology of Interactions with Different Types of Acetylcholine Receptors. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, T.N.T.; Abraham, N.; Lewis, R.J. Structure-Function of Neuronal Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Inhibitors Derived From Natural Toxins. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Zhao, C.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, N.; Du, W.; Dai, Q. Structural and Functional Characterization of a Novel α-Conotoxin Mr1.7 from Conus marmoreus Targeting Neuronal nAChR α3β2, α9α10 and α6/α3β2β3 Subtypes. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 3259–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Young, T.; Wittenauer, S.; McIntosh, J.M.; Vincler, M. Spinal α3β2* nicotinic acetylcholine receptors tonically inhibit the transmission of nociceptive mechanical stimuli. Brain Res. 2008, 1229, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peigneur, S.; Devi, P.; Seldeslachts, A.; Ravichandran, S.; Quinton, L.; Tytgat, J. Structure-Function Elucidation of a New α-Conotoxin, MilIA, from Conus milneedwardsi. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Liang, L.; Ning, H.; Cai, F.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, L.; Dai, Q. Cloning, Synthesis and Functional Characterization of a Novel α-Conotoxin Lt1.3. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lewis, R.J.; Dutertre, S.; Vetter, I.; Christie, M.J.; Dolphin, A.C. Conus Venom Peptide Pharmacology. Pharmacol. Rev. 2012, 64, 259–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Pan, S.; Xu, M.; Zhang, L.; Yu, J.; Yu, J.; Wu, Y.; Fan, Y.; Li, H.; Kasheverov, I.E.; et al. High Selectivity of an α-Conotoxin LvIA Analogue for α3β2 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors Is Mediated by β2 Functionally Important Residues. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 13656–13668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Zhu, X.; Zhangsun, M.; Wu, Y.; Yu, J.; Harvey, P.J.; Kaas, Q.; Zhangsun, D.; Craik, D.J.; Luo, S. Engineered Conotoxin Differentially Blocks and Discriminates Rat and Human α7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 5620–5631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, S.; Zhangsun, D.; Harvey, P.J.; Kaas, Q.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Hu, Y.; Li, X.; Tsetlin, V.I.; Christensen, S.; et al. Cloning, synthesis, and characterization of αO-conotoxin GeXIVA, a potent α9α10 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E4026–E4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Post, M.R.; Tender, G.S.; Lester, H.A.; Dougherty, D.A. Secondary Ammonium Agonists Make Dual Cation-π Interactions in α4β2 Nicotinic Receptors. Eneuro 2017, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boulter, J.; Luyten, W.; Evans, K.; Mason, P.; Ballivet, M.; Goldman, D.; Stengelin, S.; Martin, G.; Heinemann, S.; Patrick, J. Isolation of a clone coding for the alpha-subunit of a mouse acetylcholine receptor. J. Neurosci. 1985, 5, 2545–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hone, A.J.; McIntosh, J.M.; Azam, L.; Lindstrom, J.; Lucero, L.; Whiteaker, P.; Passas, J.; Blázquez, J.; Albillos, A. α-Conotoxins Identify the α3β4* Subtype as the Predominant Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Expressed in Human Adrenal Chromaffin Cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 2015, 88, 881–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moretti, M.; Vailati, S.; Zoli, M.; Lippi, G.; Riganti, L.; Longhi, R.; Viegi, A.; Clementi, F.; Gotti, C. Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Subtypes Expression during Rat Retina Development and Their Regulation by Visual Experience. Mol. Pharmacol. 2004, 66, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hernandez, S.C.; Vicini, S.; Xiao, Y.; Dávila-García, M.I.; Yasuda, R.P.; Wolfe, B.B.; Kellar, K.J. The Nicotinic Receptor in the Rat Pineal Gland Is an α3β4 Subtype. Mol. Pharmacol. 2004, 66, 978–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, A.-H.; Brandstaetter, H.; Nevin, S.T.; Tan, C.; Clark, R.J.; Adams, D.J.; Alewood, P.F.; Craik, D.J.; Daly, N.L. Structure of α-conotoxin BuIA: Influences of disulfide connectivity on structural dynamics. BMC Struct. Biol. 2007, 7, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- AlSharari, S.D.; Carroll, F.I.; McIntosh, J.M.; Damaj, M.I. The Antinociceptive Effects of Nicotinic Partial Agonists Varenicline and Sazetidine-A in Murine Acute and Tonic Pain Models. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2012, 342, 742–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abraham, N.; Healy, M.; Ragnarsson, L.; Brust, A.; Alewood, P.F.; Lewis, R.J. Structural mechanisms for α-conotoxin activity at the human α3β4 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cuny, H.; Kompella, S.; Tae, H.; Yu, R.; Adams, D.J. Key structural determinants in the agonist binding loops of human beta2 and beta4 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunits contribute to alpha 3 beta 4 subtype selectivity of alpha-conotoxins. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 23779–23792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McIntosh, J.M.; Azam, L.; Staheli, S.; Dowell, C.; Lindstrom, J.M.; Kuryatov, A.; Garrett, J.E.; Marks, M.J.; Whiteaker, P. Analogs of α-Conotoxin MII Are Selective for α6-Containing Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2004, 65, 944–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hone, A.J.; Kaas, Q.; Kearns, I.; Hararah, F.; Gajewiak, J.; Christensen, S.; Craik, D.J.; McIntosh, J.M. Computational and Functional Mapping of Human and Rat α6β4 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors Reveals Species-Specific Ligand-Binding Motifs. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 1685–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhangsun, D.; Zhu, X.; Wu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Kaas, Q.; Craik, D.J.; McIntosh, J.M.; Luo, S. Key Residues in the Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor β2 Subunit Contribute to α-Conotoxin LvIA Binding. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 9855–9862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shiembob, D.L.; Roberts, R.L.; Luetje, C.W.; McIntosh, J.M. Determinants of α-Conotoxin BuIA Selectivity on the Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor β Subunit. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 11200–11207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McIntosh, J.M.; Plazas, P.V.; Watkins, M.; Gomez-Casati, M.E.; Olivera, B.M.; Elgoyhen, A.B. A Novel α-Conotoxin, PeIA, Cloned from Conus pergrandis, Discriminates between Rat α9α10 and α7 Nicotinic Cholinergic Receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 30107–30112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McIntosh, J.M.; Dowell, C.; Watkins, M.; Garrett, J.E.; Yoshikami, D.; Olivera, B.M. α-Conotoxin GIC from Conus geographus, a Novel Peptide Antagonist of Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 33610–33615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sandall, D.W.; Satkunanathan, N.; Keays, D.A.; Polidano, M.A.; Liping, X.; Pham, V.; Down, J.G.; Khalil, Z.; Livett, B.G.; Gayler, K.R. A Novel α-Conotoxin Identified by Gene Sequencing Is Active in Suppressing the Vascular Response to Selective Stimulation of Sensory Nerves in vivo. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 6904–6911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, C.; Liu, J.; Peng, C.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Tang, S.; Wang, L.; Dong, M.; Chen, S.; et al. Diversity and evolution of conotoxins based on gene expression profiling of Conus litteratus. Genomics 2006, 88, 809–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kompella, S.N.; Cuny, H.; Hung, A.; Adams, D.J. Molecular Basis for Differential Sensitivity of α-Conotoxin RegIIA at Rat and Human Neuronal Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2015, 88, 993–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franco, A.; Kompella, S.N.; Akondi, K.B.; Melaun, C.; Daly, N.L.; Luetje, C.W.; Alewood, P.F.; Craik, D.J.; Adams, D.J.; Marí, F. RegIIA: An α4/7-conotoxin from the venom of Conus regius that potently blocks α3β4 nAChRs. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 83, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Zhangsun, D.; Schroeder, C.I.; Zhu, X.; Hu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Weltzin, M.M.; Eberhard, S.; Kaas, Q.; Craik, D.J.; et al. A novel α4/7-conotoxin LvIA from Conus lividus that selectively blocks α3β2 vs. α6/α3β2β3 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. FASEB J. 2014, 28, 1842–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dowell, C.; Olivera, B.M.; Garrett, J.E.; Staheli, S.T.; Watkins, M.; Kuryatov, A.; Yoshikami, D.; Lindstrom, J.M.; McIntosh, J.M. α-Conotoxin PIA Is Selective for α6 Subunit-Containing Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 8445–8452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhu, X.; Harvey, P.J.; Kaas, Q.; Zhangsun, D.; Craik, D.J.; Luo, S. Single Amino Acid Substitution in α-Conotoxin TxID Reveals a Specific α3β4 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Antagonist. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 9256–9265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiram, P.A.; McIntosh, J.M.; Sine, S.M. Pairwise Interactions between Neuronal α7Acetylcholine Receptors and α-Conotoxin PnIB. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 4889–4896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bren, N.; Sine, S.M. Hydrophobic Pairwise Interactions Stabilize α-Conotoxin MI in the Muscle Acetylcholine Receptor Binding Site. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 12692–12700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chi, S.-W.; Kim, D.-H.; Olivera, B.M.; Michael McIntosh, J.; Han, K.-H. Solution conformation of alpha-conotoxin GIC, a novel potent antagonist of alpha3beta2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Biochem. J. 2004, 380, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuny, H.; Yu, R.; Tae, H.S.; Kompella, S.N.; Adams, D.J. α-Conotoxins active at α3-containing nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and their molecular determinants for selective inhibition. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 175, 1855–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turner, M.W.; Marquart, L.A.; Phillips, P.D.; McDougal, O.M. Mutagenesis of α-Conotoxins for Enhancing Activity and Selectivity for Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. Toxins 2019, 11, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, S.; Zhangsun, D.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Hu, Y.; McIntyre, M.; Christensen, S.; Akcan, M.; Craik, D.J.; McIntosh, J.M. Characterization of a Novel α-Conotoxin from Conus textile That Selectively Targets α6/α3β2β3 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 894–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, J.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, L.; Kudryavtsev, D.; Kasheverov, I.; Lei, Y.; Zhangsun, D.; Tsetlin, V.; Luo, S. Species specificity of rat and human α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors towards different classes of peptide and protein antagonists. Neuropharmacology 2018, 139, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Akondi, K.B.; Zhangsun, D.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Hu, Y.; Christensen, S.; Dowell, C.; Daly, N.L.; Craik, D.J.; et al. Atypical α-Conotoxin LtIA from Conus litteratus Targets a Novel Microsite of the α3β2 Nicotinic Receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 12355–12366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, B.; Xu, M.; Zhu, X.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhangsun, D.; Hu, Y.; Xiang, S.-H.; Kasheverov, I.E.; Tsetlin, V.I.; et al. From crystal structure of α-conotoxin GIC in complex with Ac-AChBP to molecular determinants of its high selectivity for α3β2 nAChR. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kompella, S.N.; Hung, A.; Clark, R.J.; Marí, F.; Adams, D.J. Alanine Scan of α-Conotoxin RegIIA Reveals a Selective α3β4 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Antagonist. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 1039–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuryatov, A.; Lindstrom, J. Expression of Functional Human α6β2β3* Acetylcholine Receptors in Xenopus laevis Oocytes Achieved through Subunit Chimeras and Concatamers. Mol. Pharmacol. 2011, 79, 126–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gyanda, R.; Banerjee, J.; Chang, Y.-P.; Phillips, A.M.; Toll, L.; Armishaw, C.J. Oxidative folding and preparation of α-conotoxins for use in high-throughput structure-activity relationship studies. J. Pept. Sci. 2013, 19, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, J.; Li, R.; Ren, J.; Zhangsun, D.; Zhu, X.; Wu, Y.; Luo, S. Alanine-Scanning Mutagenesis of α-Conotoxin GI Reveals the Residues Crucial for Activity at the Muscle Acetylcholine Receptor. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Li, X.; Zhangsun, D.; Yu, G.; Su, R.; Luo, S. The α9α10 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Antagonist αO-Conotoxin GeXIVA[1,2] Alleviates and Reverses Chemotherapy-Induced Neuropathic Pain. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, S.; Kulak, J.M.; Cartier, G.E.; Jacobsen, R.B.; Yoshikami, D.; Olivera, B.M.; McIntosh, J.M. α-Conotoxin AuIB Selectively Blocks α3β4 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors and Nicotine-Evoked Norepinephrine Release. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 8571–8579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- You, S.; Li, X.; Xiong, J.; Zhu, X.; Zhangsun, D.; Zhu, X.; Luo, S. α-Conotoxin TxIB: A Uniquely Selective Ligand for α6/α3β2β3 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Attenuates Nicotine-Induced Conditioned Place Preference in Mice. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borghese, C.M. Sites of Excitatory and Inhibitory Actions of Alcohols on Neuronal 2 4 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2003, 307, 42–52. [Google Scholar]
- Khiroug, S.S.; Khiroug, L.; Yakel, J.L. Rat nicotinic acetylcholine receptor α2β2 channels: Comparison of functional properties with α4β2 channels in Xenopus oocytes. Neuroscience 2004, 124, 817–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhangsun, D.; Zhu, X.; Kaas, Q.; Wu, Y.; Craik, D.J.; McIntosh, J.M.; Luo, S. αO-Conotoxin GeXIVA disulfide bond isomers exhibit differential sensitivity for various nicotinic acetylcholine receptors but retain potency and selectivity for the human α9α10 subtype. Neuropharmacology 2017, 127, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
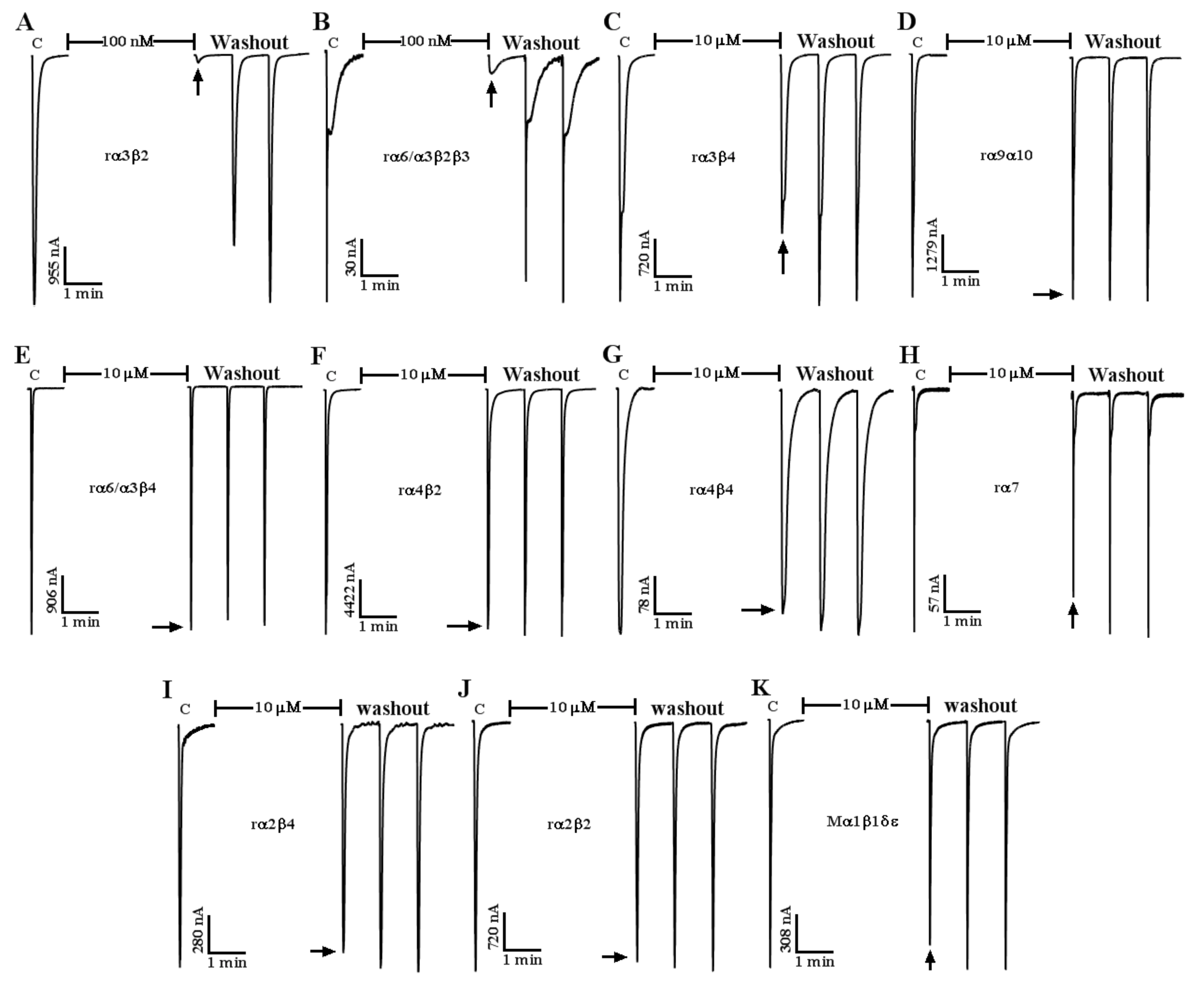


| Subtype | IC50 (nM) a | Hill Slope a |
|---|---|---|
| rα3β2 | 8.98 (7.73–10.43) | 1.0 (0.9–1.2) |
| rα6/α3β2β3 | 14.43 (10.24–20.39) | 1.0 (0.7–1.1) |
| mα1β1δε | >10,000 b | |
| rα2β2 | >10,000 b | |
| rα2β4 | >10,000 b | |
| rα3β4 | >10,000 b | |
| rα4β4 | >10,000 b | |
| rα4β2 | >10,000 b | |
| rα6/α3β4 | >10,000 b | |
| rα7 | >10,000 b | |
| rα9α10 | >10,000 b |
| α-CTx | Organism | Sequence a | Target b | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LvIF | C. lividus | GCCSHPACAGNNQDIC# | rα3β2 > rα6/α3β2β3 | This work |
| RegIIA | C. regius | GCCSHPACNVNNPHIC# | rα3β2 > rα7 > rα6/rα3β2β3 > rα3β4 > rα6/α3β4 | [22] |
| MII | C. magus | GCCSNPVCHLEHSNLC# | rα6/α3β2β3 > rα3β2 > rα6/α3β4 | [23,24] |
| LvIA | C. lividus | GCCSHPACNVDHPEIC# | rα3β2 > rα6/α3β2β3 > rα6/α3β4 > rα3β4 | [11,25] |
| BuIA | C. bullatus | GCCSTPPCAVLY---C# | rα2β2 > rα2β4 > rα4β4 > rα3β2 > rα3β4 > rα6/α3β4 > rα6/α3β2β3 | [26] |
| PeIA | C. pergrandis | GCCSHPACSVNHPELC# | rα9α10 > rα6/α3β2β3 > rα3β2 > rα6/α3β4 > rα3β4 | [27] |
| GIC | C. geographus | GCCSHPACAGNNQHIC# | rα6/α3β2β3 ≥ rα3β2 > rα4β2 > rα3β4 | This work |
| hα6/α3β2β3 ≈ hα3β2 > hα4β2 > hα3β4 | [28,29,30] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, M.; Yu, J.; Zhu, X.; Zhangsun, D.; Luo, S. Characterization of an α 4/7-Conotoxin LvIF from Conus lividus That Selectively Blocks α3β2 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 398. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19070398
Guo M, Yu J, Zhu X, Zhangsun D, Luo S. Characterization of an α 4/7-Conotoxin LvIF from Conus lividus That Selectively Blocks α3β2 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor. Marine Drugs. 2021; 19(7):398. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19070398
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Man, Jinpeng Yu, Xiaopeng Zhu, Dongting Zhangsun, and Sulan Luo. 2021. "Characterization of an α 4/7-Conotoxin LvIF from Conus lividus That Selectively Blocks α3β2 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor" Marine Drugs 19, no. 7: 398. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19070398
APA StyleGuo, M., Yu, J., Zhu, X., Zhangsun, D., & Luo, S. (2021). Characterization of an α 4/7-Conotoxin LvIF from Conus lividus That Selectively Blocks α3β2 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor. Marine Drugs, 19(7), 398. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19070398








