Fucoidan Suppresses Hypoxia-Induced Lymphangiogenesis and Lymphatic Metastasis in Mouse Hepatocarcinoma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Effect of Fucoidan on Cell Viability in CoCl2-Treated Hca-F Cells
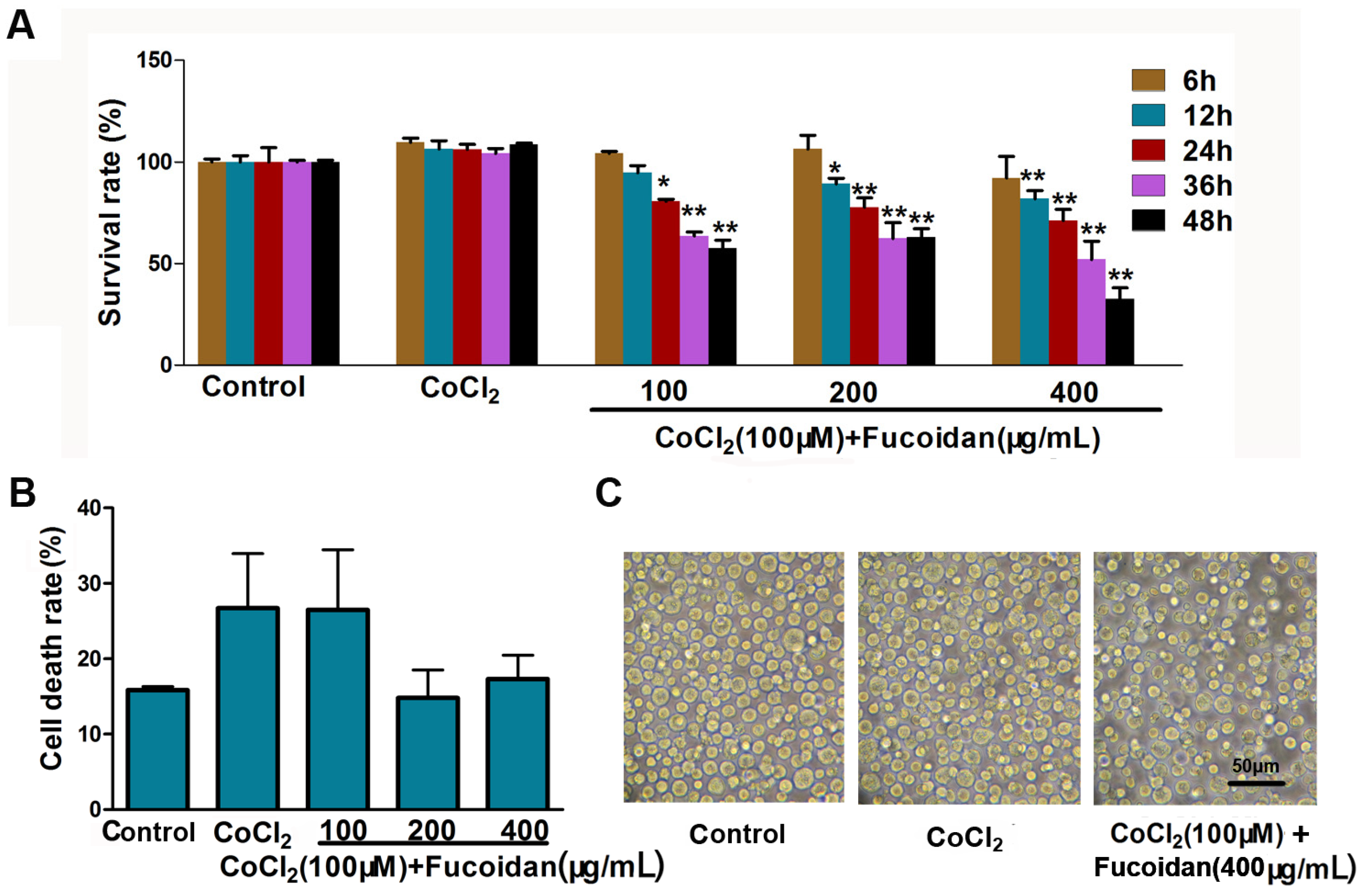
2.2. Fucoidan Downregulates Expression and Activation of HIF-1α in CoCl2-Treated Hca-F Cells

2.3. Fucoidan Inhibits Cell Invasion in CoCl2-Treated Hca-F Cells
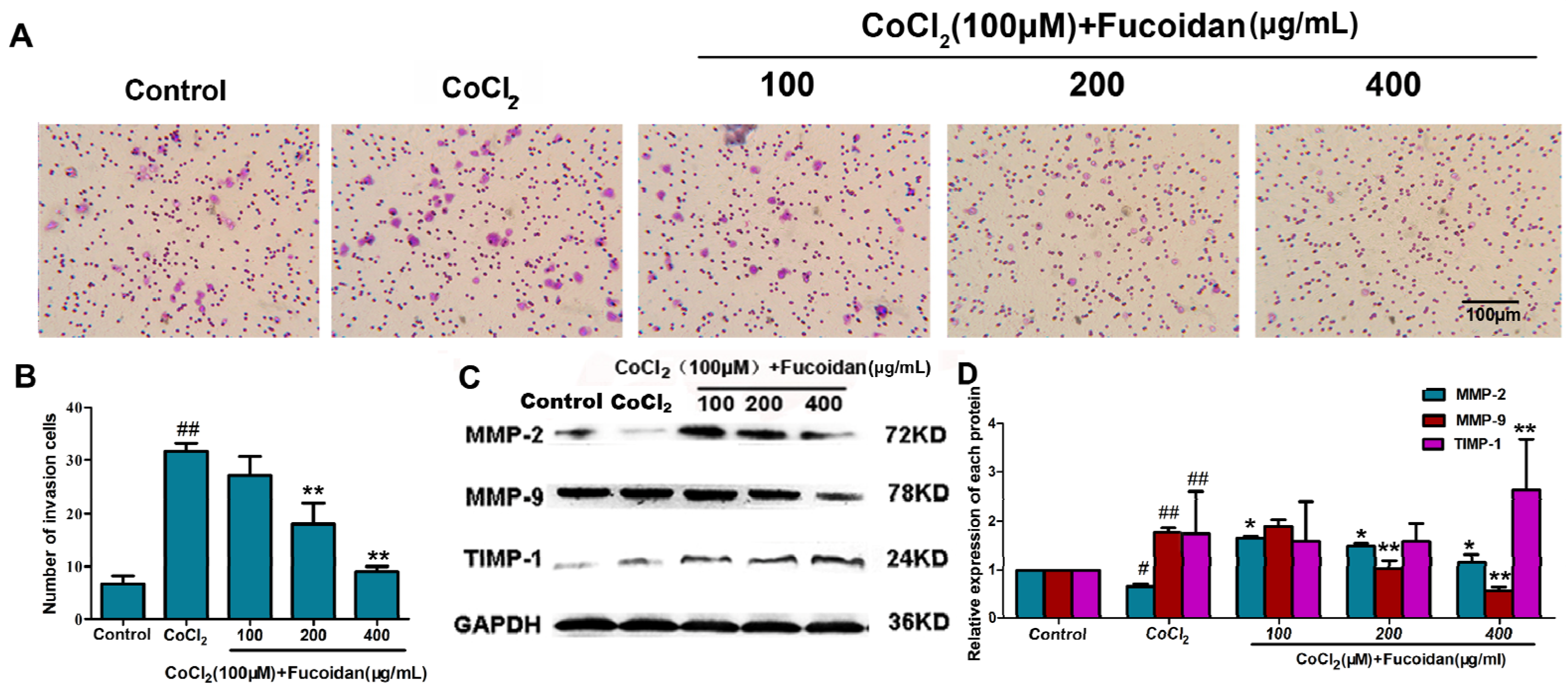
2.4. Fucoidan Inhibits VEGF-C and HGF Production in CoCl2-Treated Hca-F Cells

2.5. Fucoidan Downregulates the Expression of VEGFR-3 and C-Met in CoCl2-Treated Hca-F Cells
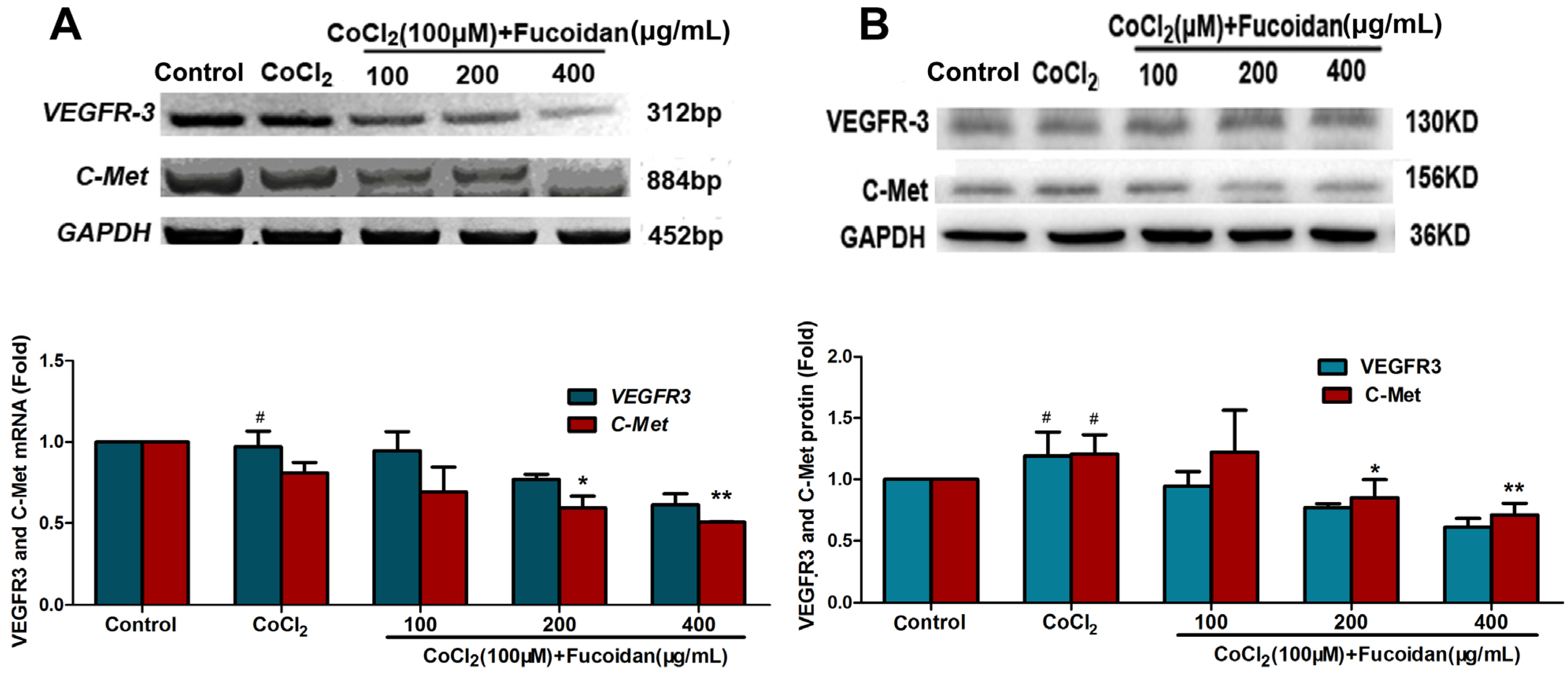
2.6. Fucoidan Modulates Hypoxia-Related Multiple Signaling Pathways
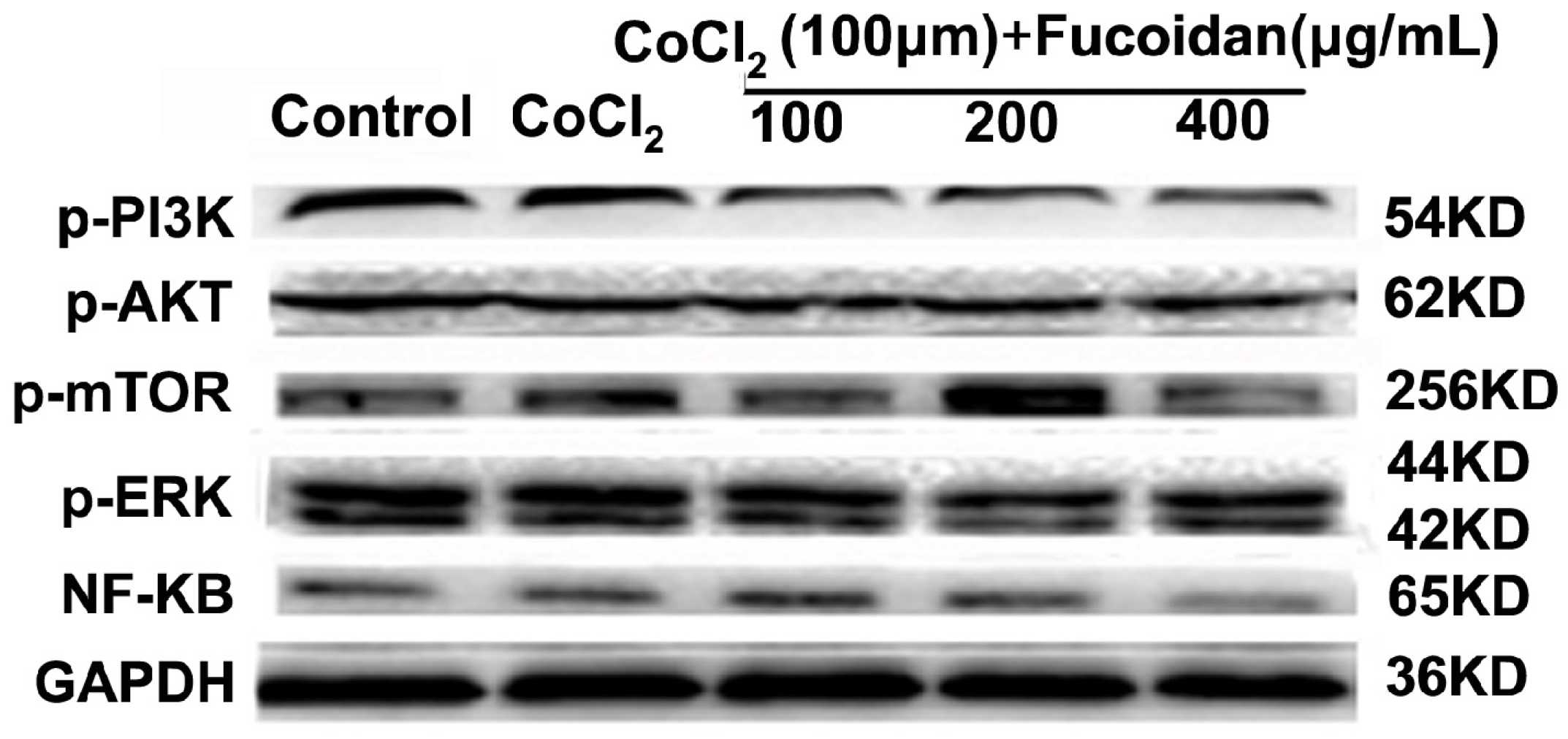

2.7. Fucoidan Inhibits Metastasis of Hca-F Cells in Vivo
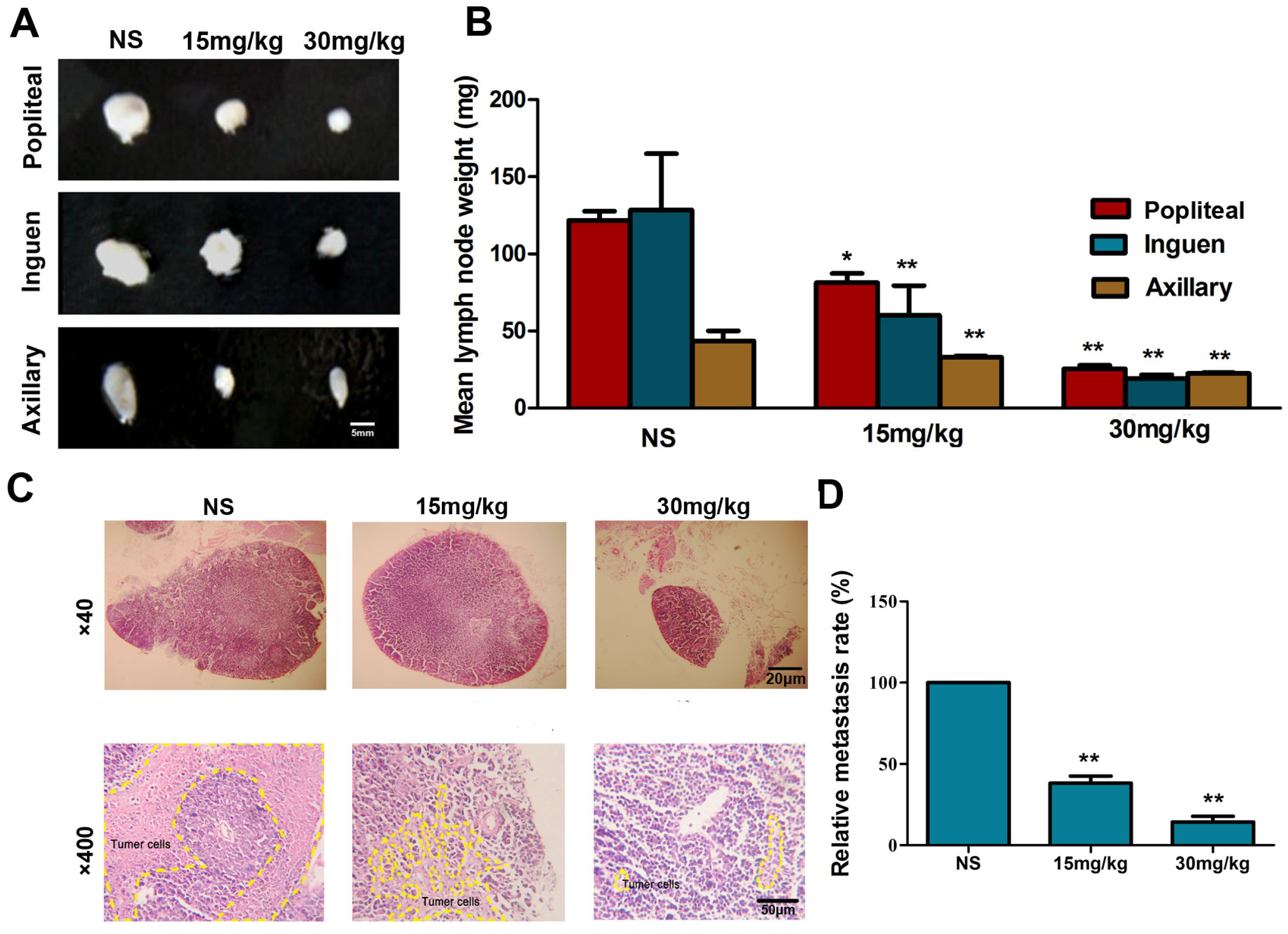
2.8. Fucoidan Inhibits the Expression of HIF-1α and VEGF-C and Lymphangiogenesis in Vivo

2.9. Fucoidan Inhibits Lymphangiogenesis in Vitro
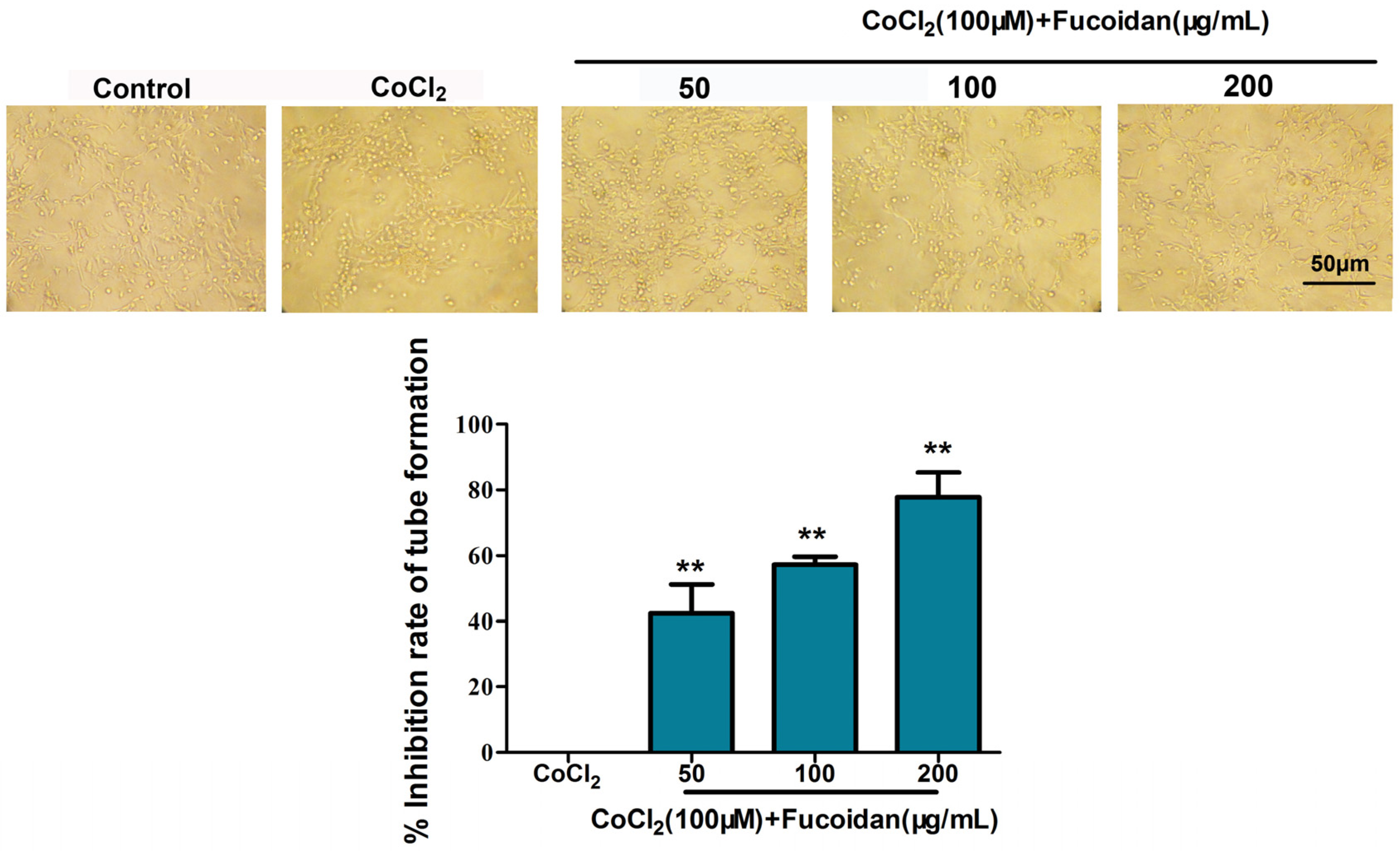
2.10. Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents and Antibodies
3.2. Purification and Analyses of Fucoidan
3.3. Cell Culture and Treatments
3.4. Cell Viability Assay
3.5. Cell Invasion Assay in Vitro
3.6. RT-PCR Analysis
| Gene | Primers Sequence (5′-3′) | Product | |
|---|---|---|---|
| hif-1α | Forward Reverse | AAACCTGGCAATGTCTCC TGCCTTAGCAGTGGTCGT | 350 bp |
| vegfr-3 | Forward Reverse | CTTTCCAATCTCTTCGTCG GAACCGCTGAATCCCAT | 312 bp |
| vegf-c | Forward Reverse | GTCCATCCACCATGCACTTG GCTCATCTACGCTGGACACA | 216 bp |
| hgf | Forward Reverse | GGACCAGCAGACACCACA TTTCCCATTGCCACGATA | 487 bp |
| c-met | Forward Reverse | GTGCCCGAAGTGTAAGTCCA TCTCGTCATGAGCTCCCAGA | 884 bp |
| gapdh | Forward Reverse | ACCACAGTCCATGCCATCAG TCCACCACCCTGTTGCTGTA | 452 bp |
3.7. Western Blotting
3.8. Immunofluorescence Staining
3.9. Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay
3.10. Tumor Metastasis Analysis in Vivo
3.11. Tube Formation Assay
3.12. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Abbreviations
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, K.M.; Heo, D.R.; Lee, J.; Park, J.S.; Baek, M.G.; Yi, J.M.; Kim, H.; Bang, O.S. 5,3′-Dihydroxy-6,7,4′-trimethoxyflavanone exerts its anticancer and antiangiogenesis effects through regulation of the Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in human lung cancer cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2015, 225, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hay, N. The Akt-mTOR tango and its relevance to cancer. Cancer Cell 2005, 8, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalhori, V.; Tornquist, K. MMP2 and MMP9 participate in S1P-induced invasion of follicular ML-1 thyroid cancer cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2015, 404, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandegrift, M.T.; Spzalski, C.; Knobel, D.; Weinstein, A.; Ham, M.; Ezeamuzie, O.; Warren, S.M.; Saadeh, P.B. Acellular dermal matrix-based gene therapy augments graft incorporation. J. Surg. Res. 2015, 195, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semenza, G.L. Targeting HIF-1 for cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 721–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finger, E.C.; Giaccia, A.J. Hypoxia, inflammation and the tumor microenvironment in metastatic disease. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2010, 29, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lunt, S.J.; Chaudary, N.; Hill, R.P. The tumor microenvironment and metastatic disease. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2009, 26, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giaccia, J.M. The unique physiology of solid tumors: Opportunities (and problems) for cancer therapy. Cancer Rev. 1998, 1, 1408–1416. [Google Scholar]
- Kaelin, W.G.; Ratcliffe, P.J. Oxygen sensing by metazoans: The central role of the HIF hydroxylase pathway. Mol. Cell 2008, 30, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majmundar, A.J.; Wong, W.J.; Simon, M.C. Hypoxia-inducible factors and the response to hypoxic stress. Mol. Cell 2010, 40, 294–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, D.; Wang, V.; Wu, J.; Jiang, C.; Wu, J. The role of hypoxia inducible factor-1 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, R.C. Hypoxia and lymphangiogenesis in tumor microenvironment and metastasis. Cancer Lett. 2014, 346, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, R.; Bjorndahl, M.A.; Gallego, M.I. Hepatocyte growth factor is a ymphangiogenic factor with an indirect mechanism of action. Blood 2006, 107, 3531–3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, H.Y.; Olson, O.C.; Joyce, J.A.; Quante, M.; Greten, F.R. 100: IKKβ dependent NF-κB activation suppresses progression of lung metastases during breast carcinogenesis. Eur. J. Cancer 2014, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, N.M.; Lee, B.; Banasr, M.; Elsayed, M.; Duman, R.S. Vascular endothelial growth throuth MEK/ERK- and PI3K/AKT-dependent signaling. Neuropharmacology 2012, 63, 642–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishide, E.; Anzai, H.; Uchida, N. A comparative investigation on the contents of fucose-containing polysaccharides from various Japanese brown algae. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 1987, 53, 1083–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folmer, F.; Jaspars, M.; Dicato, M.; Diederich, M. Photosynthetic marine organisms as a source of anticancer compounds. Phytochem. Rev. 2010, 9, 557–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morya, V.K.; Kim, J.; Kim, E.K. Algal fucoidan: Structural and size-dependent bioactivities and their perspectives. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 93, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomin, V.H.; Mourao, P.A. Structure, biology, evolution, and medical importance of sulfated fucans and galactans. Glycobiology 2008, 18, 1016–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.L.; Wang, P.S.; Wang, H.X. Fucoidan derived from Undaria pinnatifida Induces Apoptosis in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma SMMC-7721 Cells via the ROS-Mediated Mitochondrial Pathway. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1961–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Wang, J.; Chang, A.K. Fucoidan extract derived from Undaria pinnatifida inhibits angiogenesis by human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Phytomedicine 2012, 19, 797–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, R.C.; Wong, J.H.; Chan, Y.S. Antifungal and antiviral products of marine organisms. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 3475–3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, S.G.; Yang, C.; Lee, H.; Lee, B.Y. Molecular characteristics of partially hydrolyzed fucoidans from sporophyll of Undaria pinnatifida and their in vitro anticancer activity. Food Chem. 2010, 119, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.S.; Liu, Z.C.; Liu, X.L. Anti-Metastasis effect of Fucoidan from Undaria pinnatifida Sporophylla in Mouse Hepatocarcinoma Hca-F Cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, K.; Aoki, H.; Nakamura, S. Hydrogel blends of chitin/chitosan, fucoidan and alginate as healing-impaired wound dressings. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jemal, A. Gobal Cancer Statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2011, 61, 69–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.K.; Chen, M.C.; Leong, H.F.; Kuo, Y.L.; Kuo, C.Y; Lee, C.H. Connexin 43 suppresses tumor angiogenesis by down-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor via hypoxic-induced factor-1α. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.Y.; Jeong, K.J.; Lee, J. Hypoxia enhances LPA-induced HIF-1a and VEGF expression: Their inhibition by resveratrol. Cancer Lett. 2007, 258, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Xiao, J.; Yang, Y. COX-2 expression is correlated with VEGF-C, lymphangiogenesis and lymph node metastasis in human cervical cancer. Microvasc. Res. 2011, 82, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lund, A.W.; Duraes, F.V.; Hirosue, S. VEGF-C Promotes Immune Tolerance in B16 Melanomas and Cross-Presentation of Tumor Antigen by Lymph Node Lymphatics. Nat. Rep. 2012, 1, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara, A.; Niwa, M.; Aoki, H.; Kumada, M.; Kunisada, T.; Oyama, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Kozawa, O.; Mori, H. Anew model of retinal photoreceptor cell degeneration induced by a chemical hypoxia-mimicking agent, cobalt chloride. Brain Res. 2006, 1109, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Synytsya, A.; Kim, W.J.; Kim, S.M.; Pohl, R.; Synytsya, A.; Kvasnička, F.; Čopíková, J.; Park, Y.I. Structure and antitumour activity of fucoidan isolated from sporophyll of Korean brown seaweed Undaria pinnatifida. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 81, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuta, M.; Miyashita, M.; Makino, H. Correlation of hypoxia inducible factor-1a with lymphatic metastasis via vascular endothelial growth factor-C in human esophageal cancer. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2005, 78, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Yao, J.; Wang, F. Wogonin inhibits tumor angiogenesis via degradation of HIF-1α protein. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2013, 271, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffers, M.; Fiscella, M.; Webb, C.P. The mutationally activated Met receptor mediates motility and metastasis. Med. Sci. 1998, 95, 14417–14422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego, M.I.; Bierie, B.; Henniqhausen, L. Targeted expression of HGF/SF in mouse mammary epithelium leads to metastatic adenosquamous carcinomas through the activation of multiple signal transduction pathways. Oncogene 2003, 22, 8498–8508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, G.X.; Gai, R.; Chen, Z. The dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor NVP-BEZ235 prevents epithelial-mesenchymal transition induced by hypoxia and TGF-β. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 729, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achen, M.G.; Mann, G.B.; Stacker, S.A. Targeting lymphangiogenesis to prevent tumour metastasis. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 94, 1355–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Karpanen, T.; Alitalo, K. Role of lymphangiogenic factors in tumor metastasis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2004, 1654, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Sun, J.; Hao, L. Modification of glycosylation mediates the invasive properties of murine hepatocarcinoma cell lines to lymph nodes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabrina, M.; Giorgio, S.; Nelson, D.; Marco, B.; Lotta, J.; Marina, Z.; Giancarlo, L.; Daniel, D.; Kari, A.; Oscar, R.B.; et al. Lymphatic Endothelial Tumors Induced by Intraperitoneal Injection of Incomplete Freund’s Adjuvant. Exp. Cell Res. 1999, 246, 368–375. [Google Scholar]
- Ashton, A.W.; Yokota, R.; John, G.; Zhao, S.; Suadicani, S.O.; Spray, D.C.; Anthon, W.J. Inhibition of endothelial cell migration, intercellular communication, and vascular tube formation by thromboxane A2. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 35562–35570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Teng, H.; Yang, Y.; Wei, H.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Ma, Y.; Gao, Z.; Hou, L.; Zou, X. Fucoidan Suppresses Hypoxia-Induced Lymphangiogenesis and Lymphatic Metastasis in Mouse Hepatocarcinoma. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 3514-3530. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13063514
Teng H, Yang Y, Wei H, Liu Z, Liu Z, Ma Y, Gao Z, Hou L, Zou X. Fucoidan Suppresses Hypoxia-Induced Lymphangiogenesis and Lymphatic Metastasis in Mouse Hepatocarcinoma. Marine Drugs. 2015; 13(6):3514-3530. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13063514
Chicago/Turabian StyleTeng, Hongming, Yazong Yang, Hengyun Wei, Zundong Liu, Zhichao Liu, Yanhong Ma, Zixiang Gao, Lin Hou, and Xiangyang Zou. 2015. "Fucoidan Suppresses Hypoxia-Induced Lymphangiogenesis and Lymphatic Metastasis in Mouse Hepatocarcinoma" Marine Drugs 13, no. 6: 3514-3530. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13063514
APA StyleTeng, H., Yang, Y., Wei, H., Liu, Z., Liu, Z., Ma, Y., Gao, Z., Hou, L., & Zou, X. (2015). Fucoidan Suppresses Hypoxia-Induced Lymphangiogenesis and Lymphatic Metastasis in Mouse Hepatocarcinoma. Marine Drugs, 13(6), 3514-3530. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13063514





