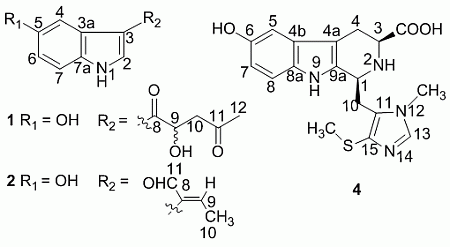
Hainanerectamines A–C, Alkaloids from the Hainan Sponge Hyrtios erecta
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Results and Discussion
| Position | 1 | 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| δC Mult | δH (J in Hz) | δC Mult | δH (J in Hz) | |
| 1 | - | - | - | - |
| 2 | 136.0, CH | 8.19, s | 125.6, CH | 7.05, s |
| 3 | 114.8, qC | - | 105.3, qC | - |
| 3a | 129.1, qC | - | 130.8, qC | - |
| 4 | 107.8, CH | 7.65, d (2.4) | 104.0, CH | 6.58, d (2.4) |
| 5 | 155.0, qC | - | 150.0, qC | - |
| 6 | 114.6, CH | 6.76, dd (8.4, 2.4) | 111.7, CH | 6.65, dd (8.4, 2.4) |
| 7 | 113.9, CH | 7.26, d (8.4) | 111.6, CH | 7.14, d (8.4) |
| 7a | 133.1, qC | - | 126.9, qC | - |
| 8 | 197.5, qC | - | 138.6, qC | - |
| 9 | 72.4, CH | 5.18, dd (8.7, 4.5) | 151.6, CH | 6.80, q (7.3) |
| 10 | 50.4, CH2 | 2.84, dd (16.8, 8.7) | 16.5, CH3 | 1.94, d (7.3) |
| - | 2.95, dd (16.8, 4.5) | - | - | |
| 11 | 209.7, qC | - | 194.9, CH | 9.52, s |
| 12 | 31.3, CH3 | 2.22, s | - | - |
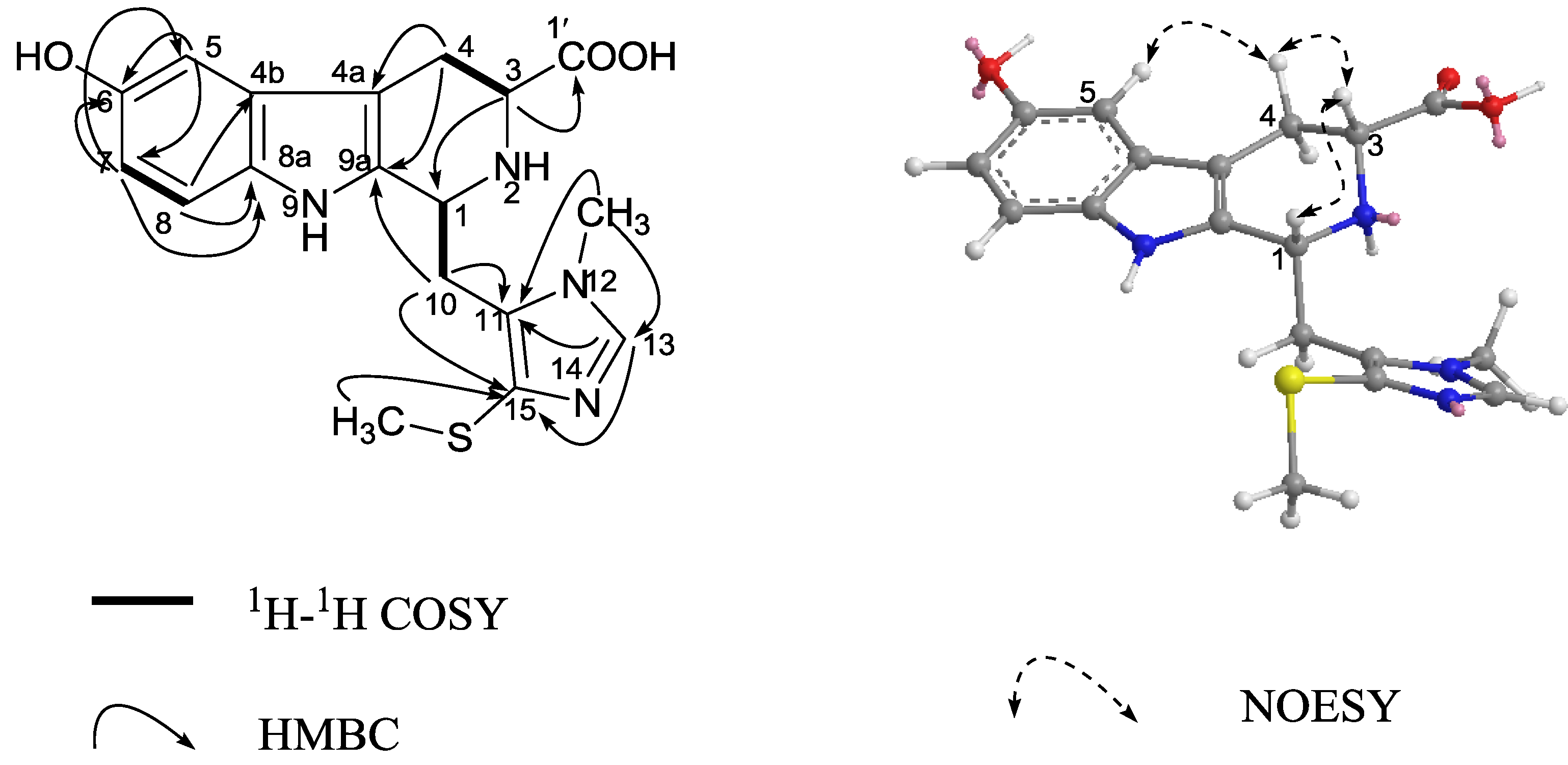
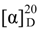 + 4.0 (c 0.05, MeOH)). Its negative ESIMS spectrum displayed a pseudo-molecular ion peak at m/z 246 [M − H]−. The HREIMS experiment established the molecular formula as C13H13NO4 (m/z 247.0835 [M]+, calcd 247.0844), indicating eight degrees of unsaturation. The 1H NMR spectrum of 1 showed downfield signals at δ 8.19 (1H, s, H-2), 7.65 (1H, d, H-4), 7.26 (1H, d, H-7), and 6.76 (1H, dd, H-6) characteristic for a 3,5-disubstituted indole moiety [25]. The 13C NMR spectrum (Table 1) displayed resonances for 13 carbons including six quaternary carbons, five methines, one methylene and one methyl. Substraction of the above elaborated 5-hydroxyl indole moiety from the molecular formula of 1 indicated that the rest part of the molecule (R2), C5H7O2, is composed of two ketons, one oxymethine, one methylene and one methyl. The partial structure 4-hydroxyl-5-oxo-pentan-2-one moiety was readily deduced by the 1H-1H COSY correlations between H-9 and H2-10 and the strong HMBC correlations of H2-10/C-8/C-9 and H3-12/C-10/C-11 (Figure 1), and was further recognized by comparison of the 1H-NMR data of side chain of 1 with those of model compound 9 previously isolated from the sponge Dysidea etberia and Ulosa ruetzler in racemate form [26]. Finally, the location of R2 at C-3 of the indole ring was deduced from the extremely downfield δ value of H-2 (δ 8.19) that implied the presence of a strongly deshielding substituent at C-3. Thus, the planar gross structure of 1 was determined. There is only one chiral center (C-9) in the molecule of 1. To determine its absolute configuration, the modified Mosher’s method [27,28] was applied since hainanerectamine A contains a secondary hydroxyl group at C-9. Thus, compound 1 was esterified separately with (R)- and (S)-MTPA chloride in dry pyridine at room temperature. Unfortunately, we failed to obtain the expected corresponding MTPA esters of 1 due to the decomposition of the molecule during the reaction. Whereas limited amounts of 1 prevent us to try again the Mosher’s reaction. The configuration of hydroxyl group at C-9 of 1 thus remains undefined.
+ 4.0 (c 0.05, MeOH)). Its negative ESIMS spectrum displayed a pseudo-molecular ion peak at m/z 246 [M − H]−. The HREIMS experiment established the molecular formula as C13H13NO4 (m/z 247.0835 [M]+, calcd 247.0844), indicating eight degrees of unsaturation. The 1H NMR spectrum of 1 showed downfield signals at δ 8.19 (1H, s, H-2), 7.65 (1H, d, H-4), 7.26 (1H, d, H-7), and 6.76 (1H, dd, H-6) characteristic for a 3,5-disubstituted indole moiety [25]. The 13C NMR spectrum (Table 1) displayed resonances for 13 carbons including six quaternary carbons, five methines, one methylene and one methyl. Substraction of the above elaborated 5-hydroxyl indole moiety from the molecular formula of 1 indicated that the rest part of the molecule (R2), C5H7O2, is composed of two ketons, one oxymethine, one methylene and one methyl. The partial structure 4-hydroxyl-5-oxo-pentan-2-one moiety was readily deduced by the 1H-1H COSY correlations between H-9 and H2-10 and the strong HMBC correlations of H2-10/C-8/C-9 and H3-12/C-10/C-11 (Figure 1), and was further recognized by comparison of the 1H-NMR data of side chain of 1 with those of model compound 9 previously isolated from the sponge Dysidea etberia and Ulosa ruetzler in racemate form [26]. Finally, the location of R2 at C-3 of the indole ring was deduced from the extremely downfield δ value of H-2 (δ 8.19) that implied the presence of a strongly deshielding substituent at C-3. Thus, the planar gross structure of 1 was determined. There is only one chiral center (C-9) in the molecule of 1. To determine its absolute configuration, the modified Mosher’s method [27,28] was applied since hainanerectamine A contains a secondary hydroxyl group at C-9. Thus, compound 1 was esterified separately with (R)- and (S)-MTPA chloride in dry pyridine at room temperature. Unfortunately, we failed to obtain the expected corresponding MTPA esters of 1 due to the decomposition of the molecule during the reaction. Whereas limited amounts of 1 prevent us to try again the Mosher’s reaction. The configuration of hydroxyl group at C-9 of 1 thus remains undefined.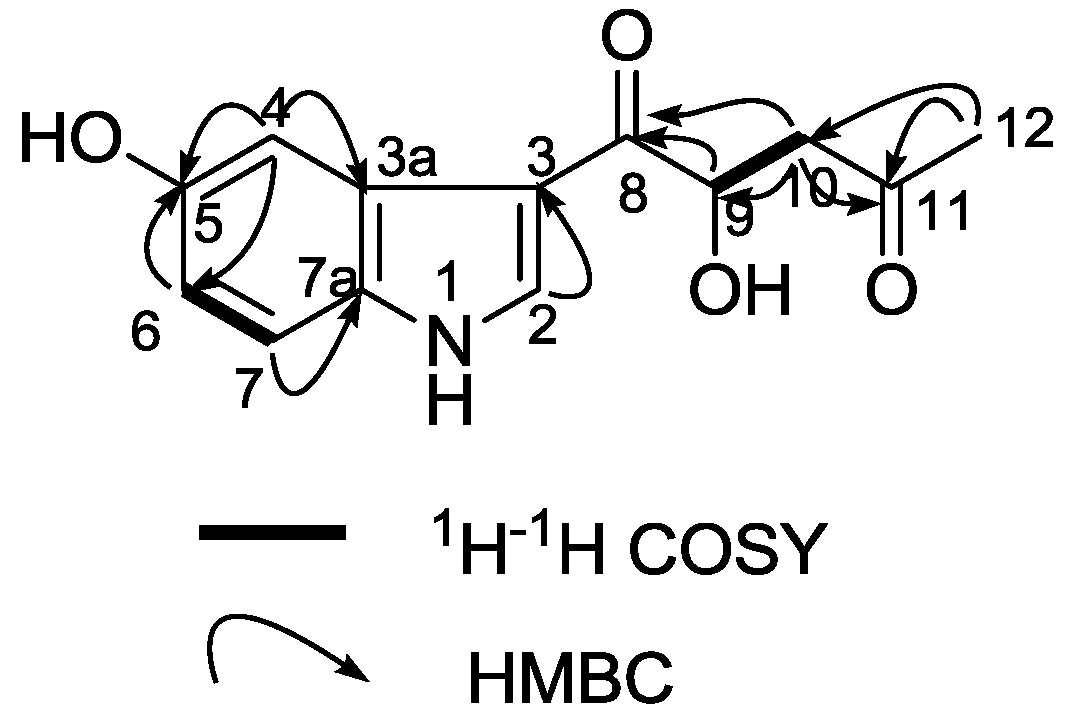

| Position | 3 | 3 b | 4 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δC Mult | δH (J in Hz) | δC Mult | δH (J in Hz) | δC Mult | δH (J in Hz) | |
| 1 | 55.8, CH | 4.80, m | 54.6 | 5.01, br, s | 55.2, CH | 4.72, m |
| 2 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 3 | 60.2, CH | 3.86, m | 59.7 | 4.26, br, d (7.3) | 60.6, CH | 3.70, m |
| 4 | 25.0, CH2 | 3.30, dd (15.3, 4.0) | 24.2 | 3.36, m | 25.7, CH2 | 3.28, dd (15.4, 3.8) |
| - | 2.90, dd (15.3, 13.6) | - | 3.04, dd (15.1, 12.4) | - | 2.96, dd (15.4, 13.8) | |
| 4a | 108.5, qC | - | 107.9 | - | 109.3, qC | - |
| 4b | 128.7, qC | - | 128 | - | 129.1, qC | - |
| 5 | 103.8, CH | 6.82, d (2.1) | 103.4 | 6.86, d (2.3) | 103.8, CH | 6.84, d (2.4) |
| 6 | 152.4, qC | - | 152.2 | - | 152.4, qH | - |
| 7 | 113.7, CH | 6.68, dd (8.7, 2.1) | 113.8 | 6.75, dd (8.7, 2.3) | 113.5, CH | 6.67, dd (8.7, 2.4) |
| 8 | 113.3, CH | 7.17, d (8.7) | 113.1 | 7.22, d (8.7) | 113.2, CH | 7.17, d (8.7) |
| 8a | 133.7, qC | - | 133.4 | - | 133.8, qC | - |
| 9 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 9a | 131.6, qC | - | 129.7 | - | 130.7, qC | - |
| 10 | 31.0, CH2 | 3.48, m | 28.8 | 3.73, br, d (14.2) | 28.4, CH2 | 3.64, m |
| - | 3.18, m | - | 3.36, m | - | 3.24, m | |
| 11 | 136.0, qC | - | 130.7 | - | 130.7, qC | - |
| 12 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 13 | 137.7, CH | 7.68, s | 136.2 | 8.73, s | 141.0, CH | 7.69, s |
| 14 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 15 | 117.2, CH | 7.00, s | 118.6 | 7.27, s | 134.6, qC | - |
| COOH | 174.9, qC | - | 170.6 | - | 176.0, qC | - |
| NCH3 | - | - | - | - | 33.3, CH3 | 3.71, s |
| SCH3 | - | - | - | - | 19.8, CH3 | 2.39, s |
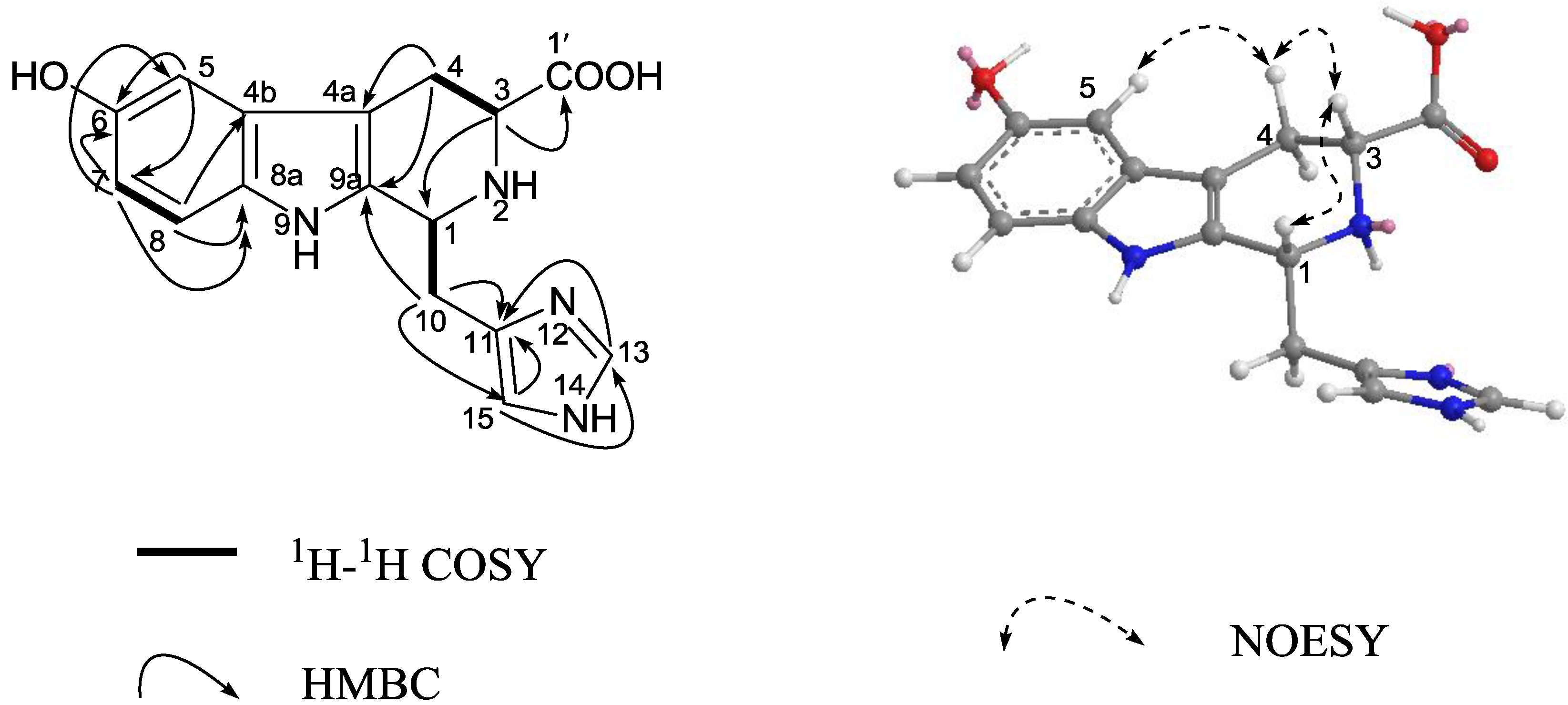
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Animal Material
3.3. Extraction and Separation
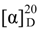 + 4.0 (c 0.05, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 353 (0.7), 307 (3.4), 252 (3.7), 271 (3.6), 213 (4.0) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3405, 2929, 1705, 1629, 1473, 1076 cm−1; EIMS m/z 247 [M]+ (10), 160 (100), 132 (22); HREIMS m/z 247.0835, calcd for C13H13NO4, 247.0844; 1H and 13C NMR see Table 1.
+ 4.0 (c 0.05, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 353 (0.7), 307 (3.4), 252 (3.7), 271 (3.6), 213 (4.0) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3405, 2929, 1705, 1629, 1473, 1076 cm−1; EIMS m/z 247 [M]+ (10), 160 (100), 132 (22); HREIMS m/z 247.0835, calcd for C13H13NO4, 247.0844; 1H and 13C NMR see Table 1.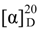 −47 (c 0.06, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 358 (2.7), 286 (3.3), 275 (3.4), 205 (3.9) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3405, 2927, 1626, 1400, 1201, 1084, 625 cm−1; ESIMS m/z 313 [M + H]+; HRESIMS m/z 313.1301, calcd for C16H17N4O3, 313.1301; 1H and 13C NMR data see Table 2.
−47 (c 0.06, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 358 (2.7), 286 (3.3), 275 (3.4), 205 (3.9) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3405, 2927, 1626, 1400, 1201, 1084, 625 cm−1; ESIMS m/z 313 [M + H]+; HRESIMS m/z 313.1301, calcd for C16H17N4O3, 313.1301; 1H and 13C NMR data see Table 2.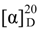 −40 (c 0.06, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 389 (2.8), 358 (2.9), 302 (3.3), 271 (3.5), 204 (4.0) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3423, 1627, 1402, 1201, 1143, 1035, 621 cm−1; ESIMS m/z 373 [M + H]+; HRESIMS m/z 373.1348, calcd for C18H21N4O3S, 373.1334; 1H and 13C NMR see Table 2.
−40 (c 0.06, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 389 (2.8), 358 (2.9), 302 (3.3), 271 (3.5), 204 (4.0) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3423, 1627, 1402, 1201, 1143, 1035, 621 cm−1; ESIMS m/z 373 [M + H]+; HRESIMS m/z 373.1348, calcd for C18H21N4O3S, 373.1334; 1H and 13C NMR see Table 2. 3.4. Biological Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Files
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Supplementary Information
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Youssef, D.T.A.; Yamaki, R.K.; Kelly, M.; Scheuer, P.J. Salmahyrtisol A, a novel cytotoxic sesterterpene from the red sea sponge Hyrtios erecta. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, G.; Matsunaga, S.; Fusetani, N. Three new cytotoxic sesterterpenes from the marine sponge Hyrtios cf. erectus. J. Nat. Prod. 1996, 59, 515–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.E.; Tahir, A.; Andersen, R.J. A new acyclic diketotriterpenoid isolated from the Indonesian marine sponge Hyrtios erectus. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 653–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasu, S.S.; Yeung, B.K.S.; Hamann, M.T.; Scheuer, P.J.; Kelly-Borges, M.; Goins, K. Puupehenone-related metabolites from two Hawaiian sponges, Hyrtios spp. J. Org. Chem. 1995, 60, 7290–7292. [Google Scholar]
- Salmoun, M.; Devijver, C.; Daloze, D.; Braekman, J.C.; Gomez, R.; de Kluijver, M.; van Soest, R.W.M. New sesquiterpene/quinones from two sponges of the genus Hyrtios. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, M.; Aoki, S.; Sakai, H.; Kawazoe, N.; Kihara, N.; Sasaki, T.; Kitagawa, I. Altohyrtin A, a potent anti-tumor macrolide from the Okinawan marine sponge Hyrtios altum. Tetrahedron Lett. 1993, 34, 2795–2798. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, M.; Aoki, S.; Sakai, H.; Hihara, N.; Sasaki, T.; Kitagawa, I. Altohyrtins B and C and 5-desacetylaltohyrtin A, potent cytotoxic macrolide congeners of altohyrtin A, from the Okinawan marine sponge Hyrtios altum. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1993, 41, 989–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettit, G.R.; Cichacz, Z.A.; Gao, F.; Herald, C.L.; Boyd, M.R. Isolation and structure of the remarkable human cancer cell growth inhibitors spongistatins 2 and 3 from an eastern Indian ocean Spongia sp. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1993, 1166–1168. [Google Scholar]
- Pettit, G.R.; Cichacz, Z.A.; Gao, F.; Herald, C.L.; Boyd, M.R.; Schmidt, J.M.; Hooper, J.N.A. Antineoplastic agents. 257. Isolation and structure of spongistatin 1. J. Org. Chem. 1993, 58, 1302–1304. [Google Scholar]
- Pettit, G.R. Progress in the discovery of biosynthetic anticancer drugs. J. Nat. Prod. 1996, 59, 812–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, J.; Murayama, T.; Ishibashi, M.; Kosuge, S.; Takamatsu, M.; Ohizumi, Y.; Kobayashi, H.; Ohta, T.; Nozoe, S.; Sasaki, T. Hyrtiosins A and B, new indole alkaloids from the Okinawan marine sponge Hyrtios erecta. Tetrahedron 1990, 46, 7699–7702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourguet-Kondracki, M.L.; Martin, M.T.; Guyot, M. A new β-carboline alkaloid isolated from the marine sponge Hyrtios erecta. Tetrahedron Lett. 1996, 37, 3457–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmoun, M.; Devijver, C.; Daloze, D.; Braekman, J.C.; van Soest, R.W.M. 5-hydroxytryptamine-derived alkaloids from two marine sponges of the genus Hyrtios. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 1173–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.-G.; Bi, K.-S.; Guo, Y.-W. Hyrtiosins A–E, five new scalarane sesterterpenes from the South China Sea sponge Hyrtios erecta. Helv. Chim. Acta 2005, 88, 1004–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iguchi, K.; Shimada, Y.; Yamada, Y. Hyrtiosal, a new sesterterpenoid with a novel carbon skeleton from the Okinawan marine sponge Hyrtios erectus. J. Org. Chem. 1992, 57, 522–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.-G.; Bi, K.-S.; Li, Z.-Y.; Guo, Y.-W. Crystal structure of hyrtiosal, C25H38O3. New Cryst. Struct. 2004, 219, 415–416. [Google Scholar]
- Cimino, G.; de Stefano, S.; Minale, L. Scalaradial, a third sesterterpene with the tetracarbocyclic skeleton of scalarin, from the sponge Cacospongia mollior. Experientia 1974, 30, 846–847. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs, R.S.; Bober, M.A.; Pinto, J.; Williams, A.B.; Jacobson, P.B.; de Carvalho, M.S. Marine Biotechnology; Attaway, D.H., Zaborsky, O.R., Eds.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1993; Volume 1, pp. 77–99. [Google Scholar]
- Crews, P.; Bescansa, P. Sesterterpenes from a common marine sponge, Hyrtios erecta. J. Nat. Prod. 1986, 49, 1041–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Wang, Q.; Yu, Z.-G.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.-W.; Chen, K.-X.; Shen, X.; Jiang, H.-L. Hyrtiosal, a PTP1B inhibitor from the marine sponge Hyrtios erectus, shows extensive cellular effects on PI3K/AKT activation, glucose transport, and TGFβ/Smad2 signaling. ChemBioChem 2007, 8, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byon, J.C.; Kusari, A.B.; Kusari, J. Protein-tyrosine phosphatase-1B acts as a negative regulator of insulin signal transduction. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 1998, 182, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Shen, L.-L.; Yu, Z.-G.; Chen, J.; Guo, Y.-W.; Tang, Y.; Shen, X.; Jiang, H.-L. Hyrtiosal, from the marine sponge Hyrtios erectus, inhibits HIV-1 integrase binding to viral DNA by a new inhibitor binding site. ChemMedChem 2008, 3, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.-L.; Yu, Z.-G.; Liu, L.-H.; Guo, Y.-W.; Lou, L.-G. Biphasic regulation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases by scalaradial, a secretory phospholipase A2 inhibitor. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2006, 5, 988–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.-L.; Liu, L.-H.; Huang, X.-C.; Guo, Y.-W.; Lou, L.-G. Scalaradial inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor-mediated akt phosphorylation is independent of secretory phospholipase A2. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2005, 314, 1210–1217. [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Uchiyama, T. Formations of (5-hydroxy) indole S-(−)-lactic acid, N-acetyl-5-hydroxy-l-tryptophan, and (5-hydroxy) indole carboxylic acid in the metabolism of tryptophan and 5-hydroxy-tryptophan by chromobacterium violaceum. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1993, 57, 1609–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardellina, J.H., II; Nigh, D.; VanWagenen, B.C. Plant growth regulatory indoles from the sponges Dysidea etheria and Ulosa ruetzleri. J. Nat. Prod. 1986, 49, 1065–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, J.A.; Mosher, H.S. Nuclear magnetic resonance enantiomer regents. Configurational correlations via nuclear magnetic resonance chemical shifts of diastereomeric mandelate, O-methylmandelate, and alpha-methoxy-alpha-trifluoromethylphenylacetate (MTPA) esters. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1973, 95, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtani, I.; Kushmi, T.; Kashman, Y.; Kakisawa, H. A new aspect of the high-field NMR application of Mosher’s method. The absolute configuration of marine triterpene sipholenol A. J. Org. Chem. 1991, 56, 1296–1298. [Google Scholar]
- Yamanokuchi, R.; Imada, K.; Miyazaki, M.; Kato, H.; Watanabe, T.; Fujimuro, M.; Saeki, Y.; Yoshinaga, S.; Terasawa, H.; Iwasaki, N.; et al. Hyrtioreticulins A–E, indole alkaloids inhibiting the ubiquitin-activating enzyme, from the marine sponge Hyrtios reticulates. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 4437–4442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukamoto, S.; Kumamoto University, Kumamoto, Japan. Personal communication, 2014.
- Bialonska, D.; Zjawiony, J. Aplysinopsins-marine indole alkaloids: Chemistry, bioactivity and ecological significance. Mar. Drugs 2009, 7, 166–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.-H.; Peng, W.-L.; Wang, Z.-H.; Xu, A.-L. β-Carboline alkaloids: Biochemical and pharmacological functions. Curr. Med. Chem. 2007, 14, 479–500. [Google Scholar]
- Glover, D.M.; Leibowitz, M.H.; McLean, D.A.; Parry, H. Mutations in aurora prevent centrosome separation leading to the formation of monopolar spindles. Cell 1995, 81, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naruganahalli, K.S.; Lakshmanan, M.; Dastidar, S.G.; Ray, A. Therapeutic potential of Aurora kinase inhibitors in cancer. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2006, 7, 1044–1051. [Google Scholar]
- Gautschi, O.; Mack, P.C.; Davies, A.M.; Lara, P.N., Jr.; Gandara, D.R. Aurora kinase inhibitors: A new class of targeted drugs in cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 2006, 8, 93–98. [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
He, W.-F.; Xue, D.-Q.; Yao, L.-G.; Li, J.-Y.; Li, J.; Guo, Y.-W. Hainanerectamines A–C, Alkaloids from the Hainan Sponge Hyrtios erecta. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 3982-3993. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12073982
He W-F, Xue D-Q, Yao L-G, Li J-Y, Li J, Guo Y-W. Hainanerectamines A–C, Alkaloids from the Hainan Sponge Hyrtios erecta. Marine Drugs. 2014; 12(7):3982-3993. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12073982
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Wen-Fei, Duo-Qing Xue, Li-Gong Yao, Jing-Ya Li, Jia Li, and Yue-Wei Guo. 2014. "Hainanerectamines A–C, Alkaloids from the Hainan Sponge Hyrtios erecta" Marine Drugs 12, no. 7: 3982-3993. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12073982
APA StyleHe, W.-F., Xue, D.-Q., Yao, L.-G., Li, J.-Y., Li, J., & Guo, Y.-W. (2014). Hainanerectamines A–C, Alkaloids from the Hainan Sponge Hyrtios erecta. Marine Drugs, 12(7), 3982-3993. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12073982