Chlorella zofingiensis as an Alternative Microalgal Producer of Astaxanthin: Biology and Industrial Potential
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Astaxanthin and Its Applications

3. Sources of Astaxanthin
4. Chlorella zofingiensis as a Potential Producer of Astaxanthin
4.1. Taxonomy
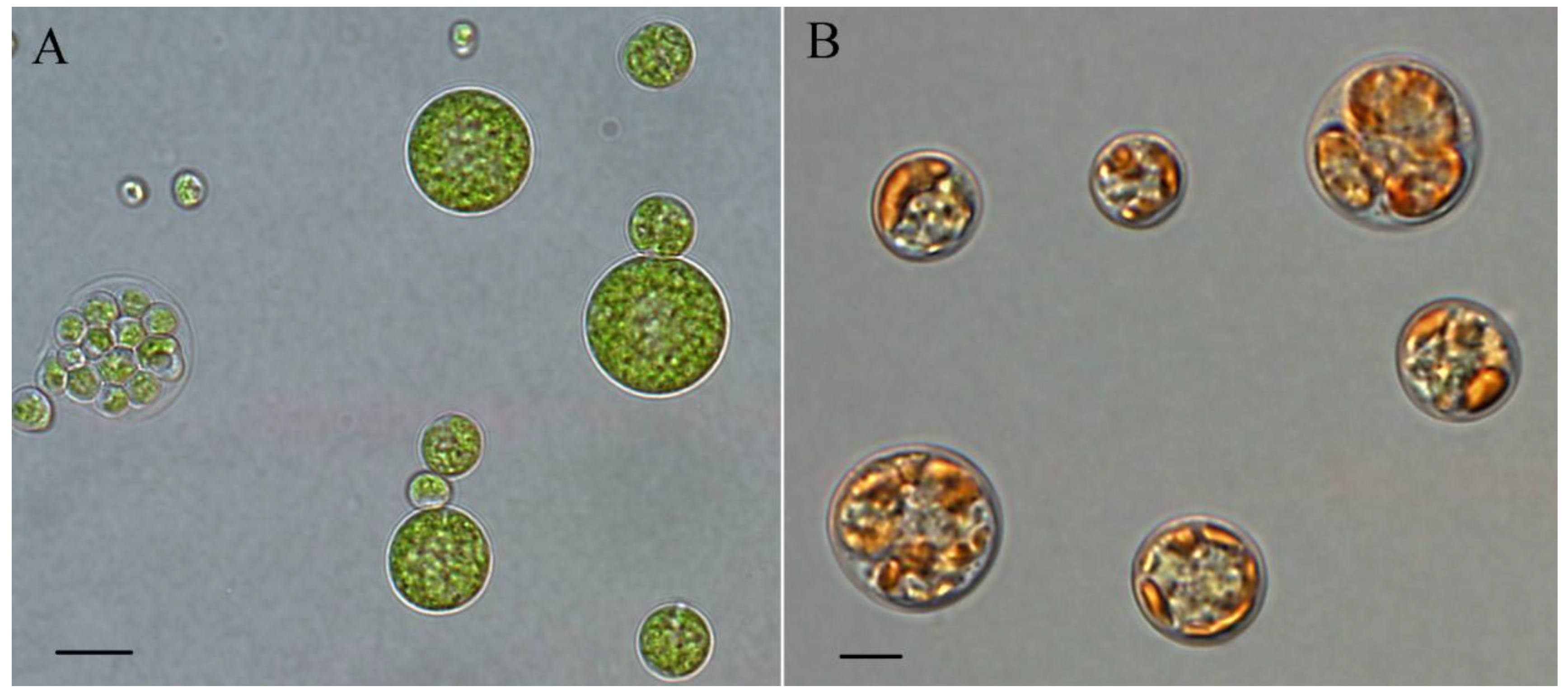

4.2. Pigment Profile
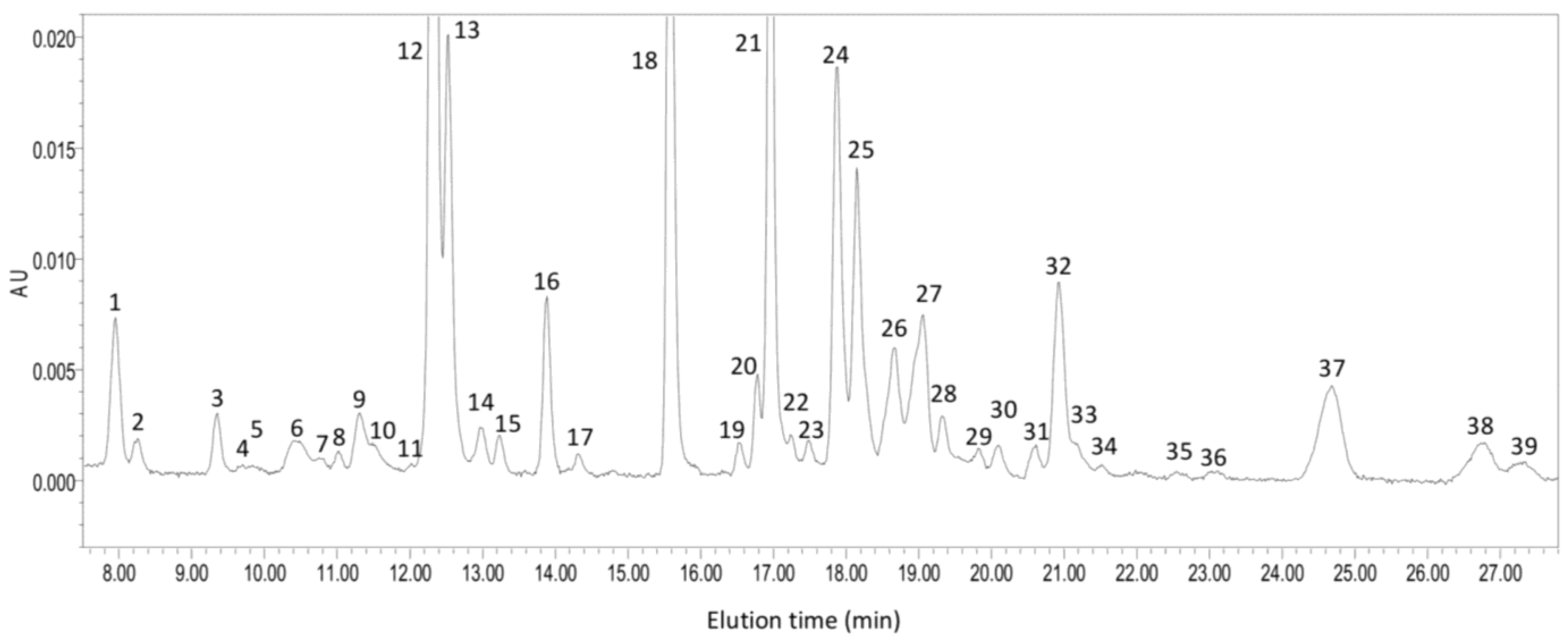
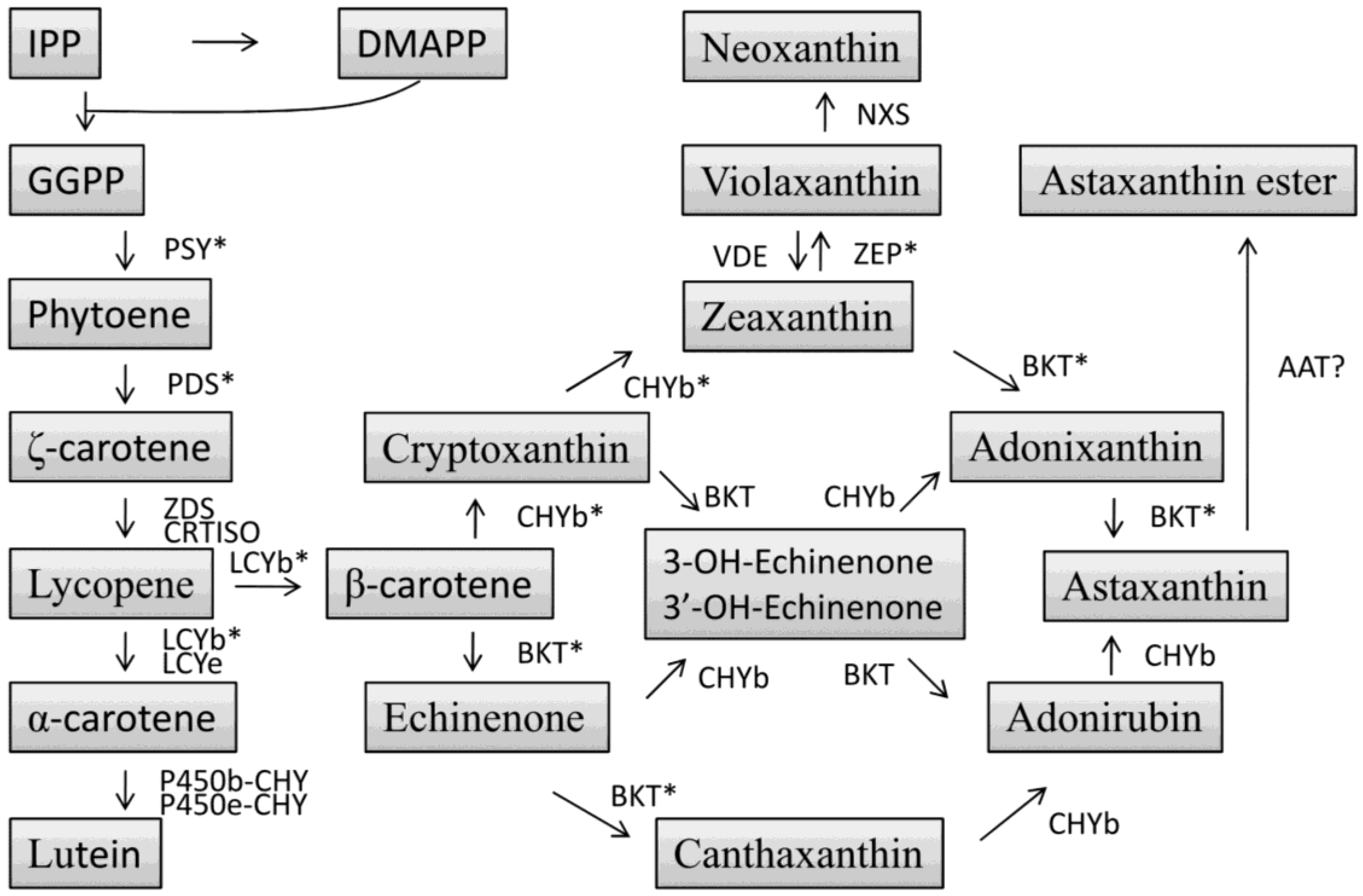
4.3. Carotenoid Biosynthesis
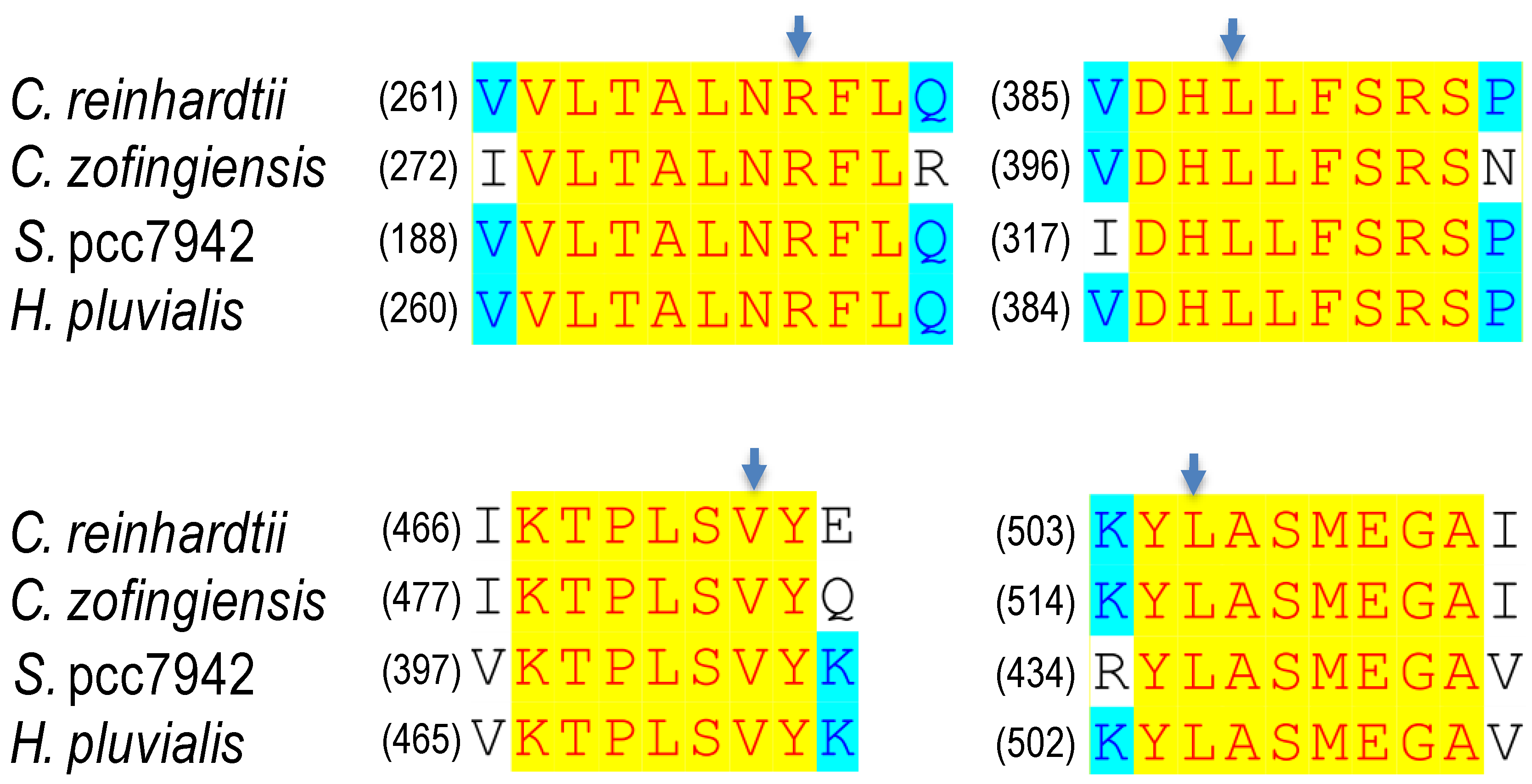
| Organism | Mutation | Desaturation Activity (%) a | Norflurazon Resistance b | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C. zofingiensis | R279P L399P V483G L516R L516F | 32 94 81 67 133 | 18 14 17 28 31 | [69] |
| H. pluvialis | L504R | <100 | 43 | [96] |
| C. reinhardtii | L505R L505F | 80 128 | 24 29 | [92] |
| S. pcc7942 | R195P L320P V403G L436R | 24 91 83 67 | 23 8 15 76 | [93] |
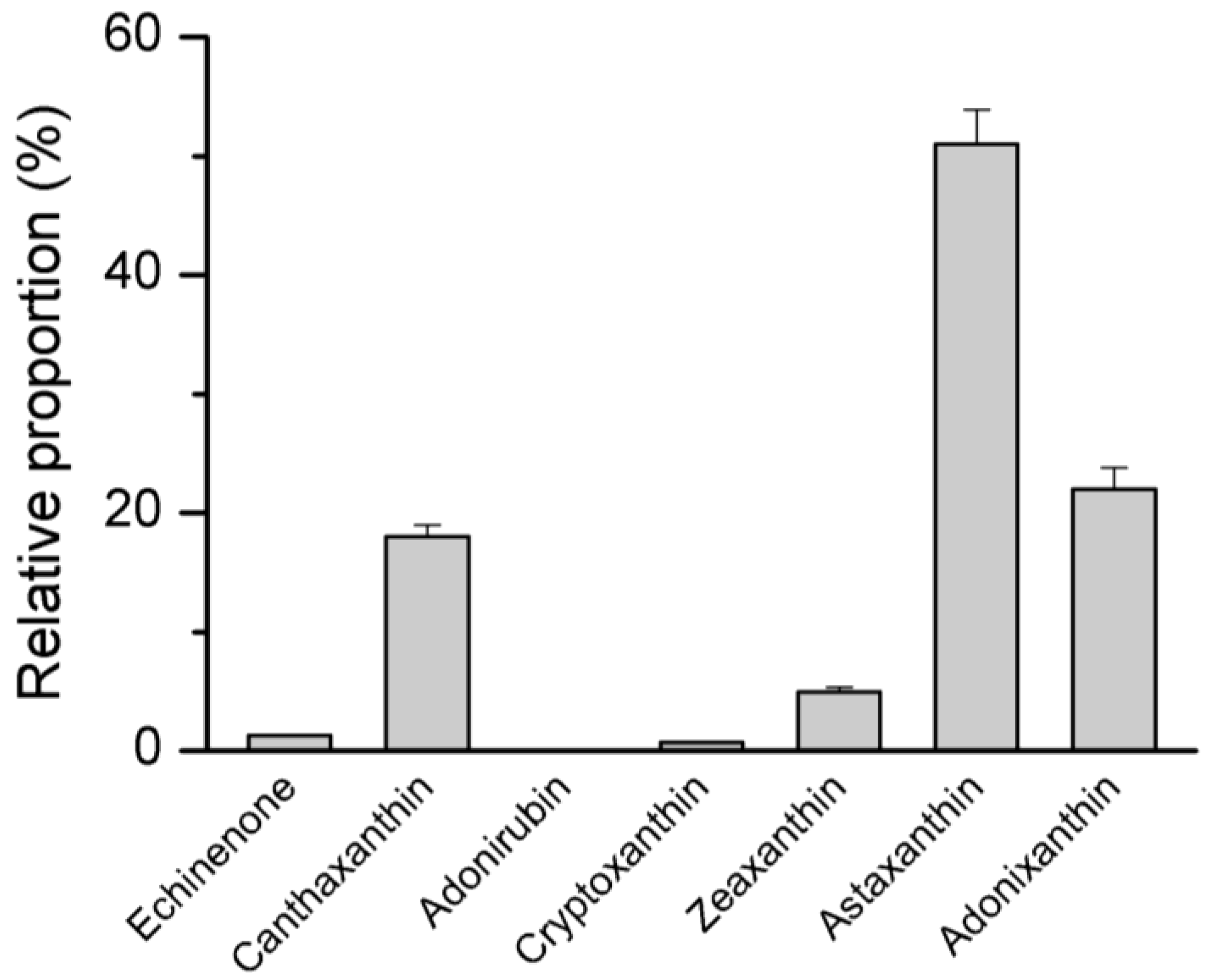
4.4. Factors Affecting Growth and Astaxanthin Production
4.4.1. Nutrients
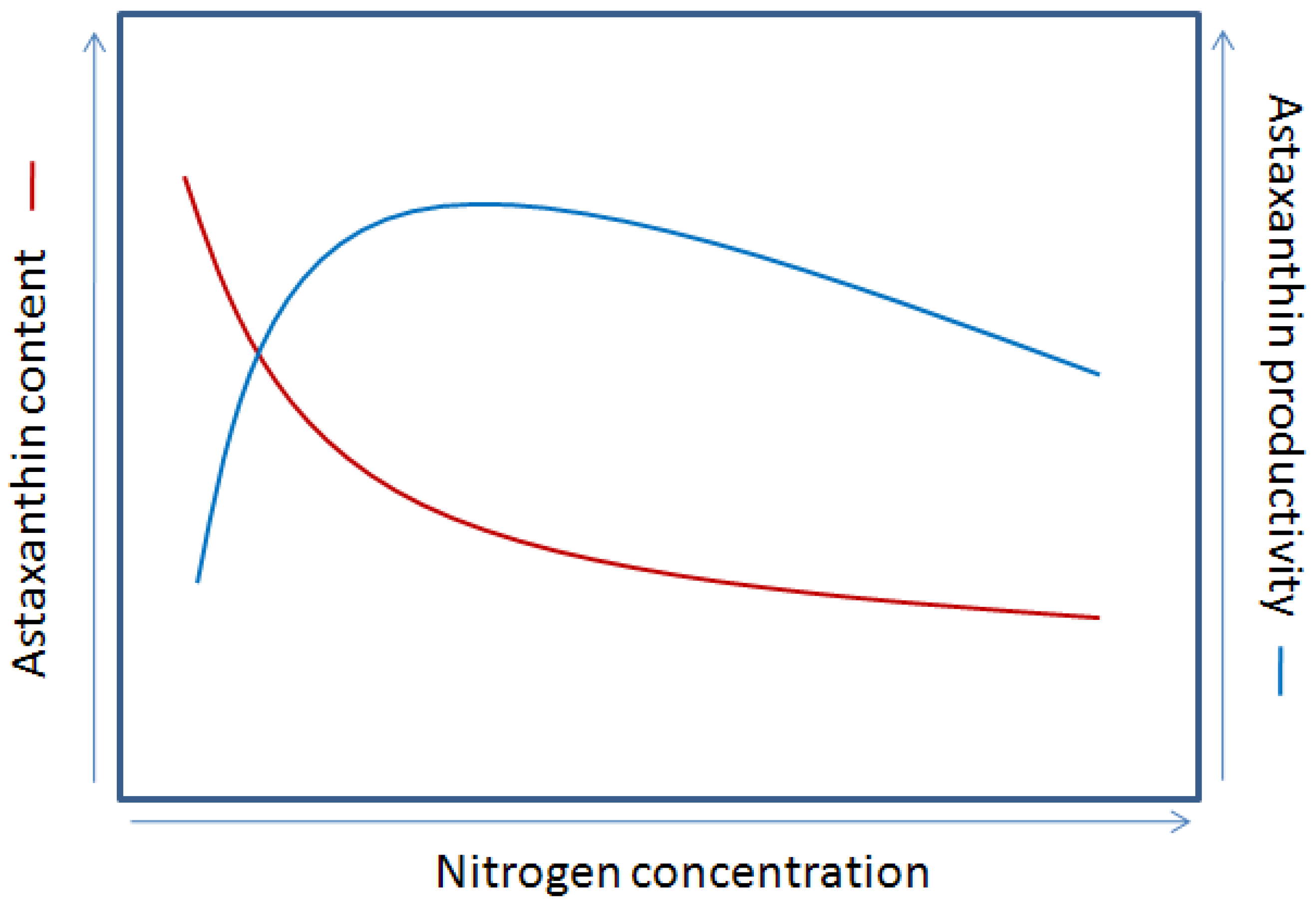
4.4.2. Environmental Factors
4.4.3. Molecular Mechanism of Astaxanthin Biosynthesis
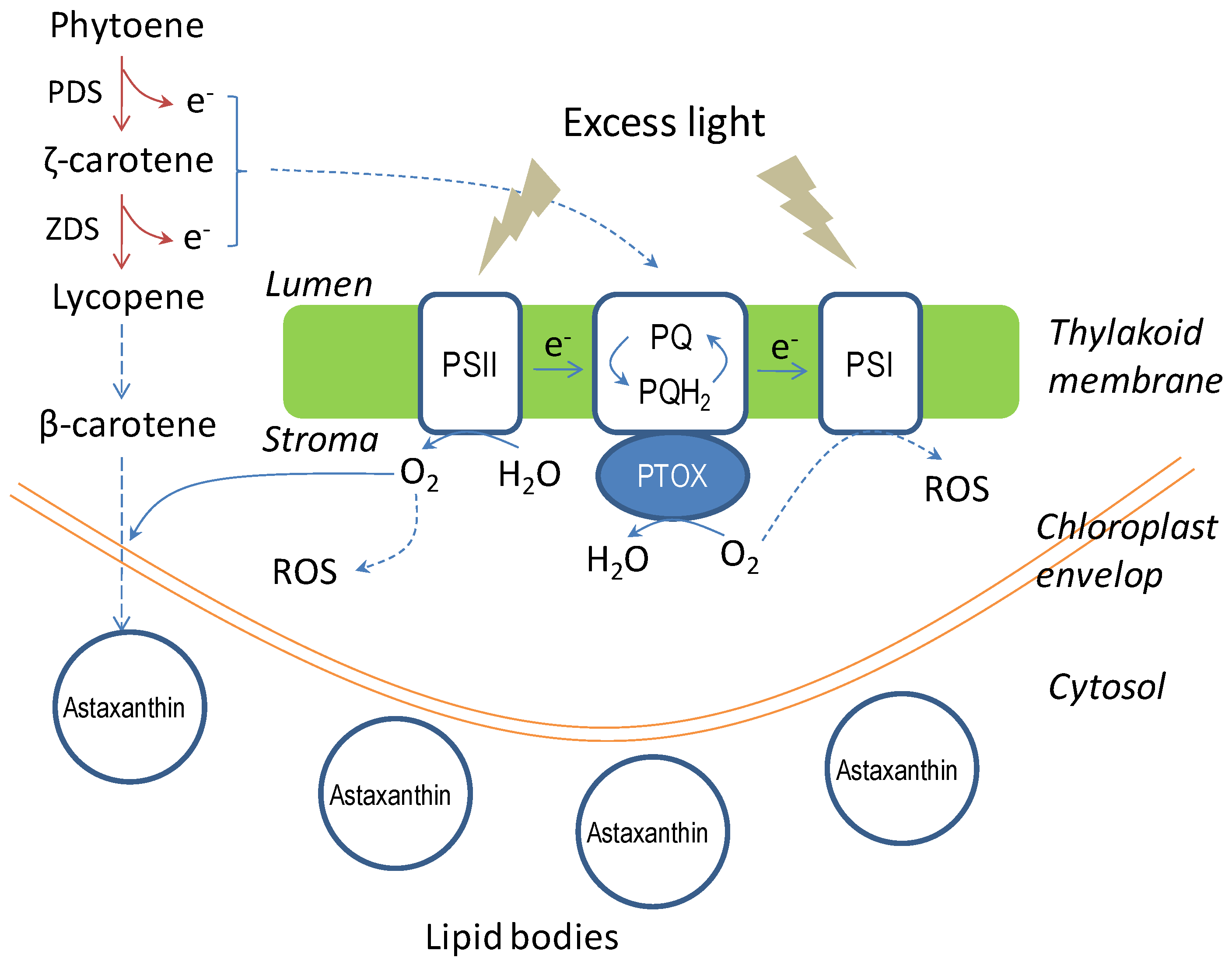
4.5. Mass Cultivation

| Strain | Culture Conditions a | Cell Density (g·L−1) | Biomass Productivity (g·L−1·day−1) | Astaxanthin Content (mg·g−1 Dry Weight) | Astaxanthin Yield (mg·L−1) | Astaxanthin Productivity (mg·L−1·day−1) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C. zofingiensis | |||||||
| CCAP211/14 | P, batch | 6.7 | 0.74 | 3.7 | 24.8 | 2.8 | [11] |
| SAG211/14 | P, batch | - | - | 6.5 | - | 0.8 | [66] |
| ATCC30412 | M, batch | 9.5 | - | 1.3 | 12.5 | - | [104] |
| ATCC30412 | H, batch | 10.2 | - | 1.0 | 10.3 | - | [12] |
| ATCC30412 | H, fed-batch | 53 | 3.5 | 0.69 | 32.4 | 2.2 | [13] |
| ATCC30412 | H, batch | 12.9 | 1.6 | 1.18 | 13.6 | 1.7 | [117] |
| ATCC30412 | H, batch | 10.3 | 2.1 | 1.31 | 13.5 | 2.3 | [7] |
| H, fed-batch | 45.6 | 4.7 | 1.19 | 56.1 | 5.6 | ||
| H. pluvialis | |||||||
| CCAP34/7 | P, batch | 1.6 | 0.02 | 27 | 43.2 | 0.44 | [111] |
| UTEX16 | M, batchM, fed-batch | 2.652.74 | 0.130.14 | 20.123.5 | 53.464.4 | 2.63.2 | [6] |
| CCAP34/7 | P, batch | - | - | 22.7 | - | 2.7 | [66] |
| CCAP34/8 | P, batch | 7.0 | 0.41 | 11.0 | 77 | 4.4 | [120] |
| CCAP34/8 | P, continuous | - | 0.6 | 8 | - | 5.6 | [121] |
| NIES-144 | P, fed-batch | 6.7 | 0.2 | 36 | 390 | 7.2 | [122] |
| CCAP34/8 | P, continuous | 1.5 | 0.7 | 10 | 15 | 7 | [123] |
| X. dendrorhous | |||||||
| ATCC24202 | H, fed-batch | 30 | 5.1 | 0.72 | 21.6 | 3.7 | [124] |
| NRRL Y17268 | H, Batch | 23.2 | 3.4 | 0.45 | 10.4 | 1.5 | [125] |
| ATCC24202 | H, fed-batch | 18.8 | 4.7 | 0.3 | 5.7 | 1.4 | [126] |
| 2A2N b | H, batch | 36 | 7.2 | 1.1 | 39.6 | 7.9 | [127] |
| ZJUT46 b | H, batch | 15.7 | 2.85 | 1.74 | 27.1 | 5.0 | [128] |
| H, fed-batch | 17.7 | 3.2 | 2.0 | 34.4 | 6.4 | [129] | |
| E5042 b | H, batch | 30.7 | 5.4 | 2.5 | 76.8 | 13.5 | [130] |
| VKPM Y2476 b | M, fed-batch | 88 | 9.7 | 4.7 | 420 | 45.6 | [131] |
4.6. Comparison of Astaxanthin Production from C. zofingiensis and Other Organisms
5. Possible Improvements in C. zofingiensis Astaxanthin Production Economics
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pulz, O.; Gross, W. Valuable products from biotechnology of microalgae. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2004, 65, 635–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouveia, L.; Batista, A.P.; Sousa, I.; Raymundo, A.; Bandarra, N.M. Microalgae in novel food products. In Algae: Nutrition, Pollution Control and Energy Sources; Hagen, K.N., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 265–300. [Google Scholar]
- Tafreshi, A.; Shariati, M. Pilot culture of three strains of Dunaliella salina for β-carotene production in open ponds in the central region of Iran. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 22, 1003–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagarde, D.; Beuf, L.; Vermaas, W. Increased production of zeaxanthin and other pigments by application of genetic engineering techniques to Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 64–72. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.-M.; Chen, F. High-yield production of lutein by the green microalga Chlorella protothecoides in heterotrophic fed-batch culture. Biotechnol. Prog. 2002, 18, 723–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.Y.; Geng, Y.H.; Li, Z.K.; Hu, H.J.; Li, Y.G. Production of astaxanthin from Haematococcus in open pond by two-stage growth one-step process. Aquaculture 2009, 295, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Sun, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Gerken, H.; Huang, J.; Chen, F. Utilization of cane molasses towards cost-saving astaxanthin production by a Chlorella zofingiensis mutant. J. Appl. Phycol. 2013, 25, 1447–1456. [Google Scholar]
- Guerin, M.; Huntley, M.E.; Olaizola, M. Haematococcus astaxanthin: Applications for human health and nutrition. Trends Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, P.D.; Bramley, P.M. The biosynthesis and nutritional uses of carotenoids. Prog. Lipid Res. 2004, 43, 228–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambati, R.; Phang, S.-M.; Ravi, S.; Aswathanarayana, R. Astaxanthin: Sources, extraction, stability, biological activities and its commercial applications—A review. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 128–152. [Google Scholar]
- Del Campo, J.A.; Rodriguez, H.; Moreno, J.; Vargas, M.A.; Rivas, J.; Guerrero, M.G. Accumulation of astaxanthin and lutein in Chlorella zofingiensis (Chlorophyta). Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2004, 64, 848–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ip, P.F.; Chen, F. Production of astaxanthin by the green microalga Chlorella zofingiensis in the dark. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 733–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.-T.; Huang, J.-C.; Chen, F. Sugar-based growth, astaxanthin accumulation and carotenogenic transcription of heterotrophic Chlorella zofingiensis (Chlorophyta). Process Biochem. 2008, 43, 1288–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, P.; Deng, Z.; Hu, Z.; Fan, L. Lipid accumulation and growth of Chlorella zofingiensis in flat plate photobioreactors outdoors. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 10577–10584. [Google Scholar]
- Britton, G. Structure and properties of carotenoids in relation to function. FASEB J. 1995, 9, 1551–1558. [Google Scholar]
- Higuera-Ciapara, I.; Félix-Valenzuela, L.; Goycoolea, F.M. Astaxanthin: A review of its chemistry and applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2006, 46, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, R.T.; Cysewski, G.R. Commercial potential for Haematococcus microalgae as a natural source of astaxanthin. Trends Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjerkeng, B.; Peisker, M.; von Schwartzenberg, K.; Ytrestoyl, T.; Asgard, T. Digestibility and muscle retention of astaxanthin in Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar, fed diets with the red yeast Phaffia rhodozyma in comparison with synthetic formulated astaxanthin. Aquaculture 2007, 269, 476–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niamnuy, C.; Devahastin, S.; Soponronnarit, S.; Vijaya Raghavan, G.S. Kinetics of astaxanthin degradation and color changes of dried shrimp during storage. J. Food Eng. 2008, 87, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choubert, G.; Baccaunaud, M. Effect of moist or dry heat cooking procedures on carotenoid retention and colour of fillets of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) fed astaxanthin or canthaxanthin. Food Chem. 2010, 119, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, F.; Synowiecki, J. Isolation and characterization of nutrients and value-added products from snow crab (Chionoecetes opilio) and shrimp (Pandalus borealis) processing discards. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1991, 39, 1527–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storebakken, T.; No, H.K. Pigmentation of rainbow trout. Aquaculture 1992, 100, 209–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storebakken, T.; Goswami, U.C. Plasma carotenoid concentration indicates the availability of dietary astaxanthin for Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar. Aquaculture 1996, 146, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Tian, L.-X.; Liu, Y.-J.; Yang, H.-J.; Ye, C.-X.; Gao, W.; Mai, K.-S. Effect of dietary astaxanthin on growth, survival, and stress tolerance of postlarval shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2009, 40, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ako, H.; Tamaru, C.S. Are feeds for food fish practical for aquarium fish? Int. Aquac. Feed 1999, 2, 30–36. [Google Scholar]
- Kurashige, M.; Okimasu, E.; Inoue, M.; Utsumi, K. Inhibition of oxidative injury of biological-membranes by astaxanthin. Physiol. Chem. Phys. Med. NMR 1990, 22, 27–38. [Google Scholar]
- Palozza, P.; Krinsky, N.I. Astaxanthin and canthaxanthin are potent antioxidants in a membrane model. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1992, 297, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimidzu, N.; Goto, M.; Miki, W. Carotenoids as singlet oxygen quenchers in marine organisms. Fish. Sci. 1996, 62, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naguib, Y.M.A. Antioxidant activities of astaxanthin and related carotenoids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 1150–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupcinskas, L.; Lafolie, P.; Lignell, A.; Kiudelis, G.; Jonaitis, L.; Adamonis, K.; Andersen, L.P.; Wadstron, T. Efficacy of the natural antioxidant astaxanthin in the treatment of functional dyspepsia in patients with or without Helicobacter pylori infection: A prospective, randomized, double blind, and placebo-controlled study. Phytomedicine 2008, 15, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Shibata, T.; Hisaka, S.; Osawa, T. Astaxanthin inhibits reactive oxygen species-mediated cellular toxicity in dopaminergic SH-SY5Y cells via mitochondria-targeted protective mechanism. Brain Res. 2009, 1254, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Liu, J.; Zeng, X.; Huangfu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, M.; Chen, F. Astaxanthin is responsible for antiglycoxidative properties of microalga Chlorella zofingiensis. Food Chem. 2011, 126, 1629–1635. [Google Scholar]
- Santocono, M.; Zurria, M.; Berrettini, M.; Fedeli, D.; Falcioni, G. Lutein, zeaxanthin and astaxanthin protect against DNA damage in SK-N-SH human neuroblastoma cells induced by reactive nitrogen species. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2007, 88, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, N.M.; O’Brien, N.M. Modulatory effects of an algal extract containing astaxanthin on UVA-irradiated cells in culture. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2002, 30, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashkow, F.J.; Watumull, D.G.; Campbell, C.L. Astaxanthin: A novel potential treatment for oxidative stress and inflammation in cardiovascular disease. Am. J. Cardiol. 2008, 101, 58D–68D. [Google Scholar]
- Jyonouchi, H.; Zhang, L.; Tomita, Y. Studies of immunomodulating actions of carotenoids. II. Astaxanthin enhances in vitro antibody production to T-dependent antigens without facilitating polyclonal B-cell activation. Nutr. Cancer 1993, 19, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyonouchi, H.; Sun, S.; Tomita, Y.; Gross, M.D. Astaxanthin, a carotenoid without vitamin A activity, augments antibody responses in cultures Including T-helper cell clones and suboptimal doses of antigen. J. Nutr. 1995, 125, 2483–2492. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, H.; Yanai, H.; Ito, K.; Tomono, Y.; Koikeda, T.; Tsukahara, H.; Tada, N. Administration of natural astaxanthin increases serum HDL-cholesterol and adiponectin in subjects with mild hyperlipidemia. Atherosclerosis 2010, 209, 520–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heu, M.-S.; Kim, J.-S.; Shahidi, F. Components and nutritional quality of shrimp processing by-products. Food Chem. 2003, 82, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, R.L.; Jacobsen, T. Characterization of flash-dried shrimp processing waste. J. Mar. Biotechnol. 1995, 3, 208–209. [Google Scholar]
- Sachindra, N.M.; Mahendrakar, N.S. Process optimization for extraction of carotenoids from shrimp waste with vegetable oils. Bioresour. Technol. 2005, 96, 1195–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachindra, N.M.; Bhaskar, N.; Siddegowda, G.S.; Sathisha, A.D.; Suresh, P.V. Recovery of carotenoids from ensilaged shrimp waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 1642–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, C.M.; Chakrabarti, R.; Surya Sambasivarao, K.R. Enzymatic isolation of carotenoid-protein complex from shrimp head waste and its use as a source of carotenoids. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 41, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handayani, A.D.; Sutrisno; Indraswati, N.; Ismadji, S. Extraction of astaxanthin from giant tiger (Panaeus monodon) shrimp waste using palm oil: Studies of extraction kinetics and thermodynamic. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 4414–4419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, J.; Gutierrez, H.; Gschaedler, A. Optimization of astaxanthin production by Phaffia rhodozyma through factorial design and response surface methodology. J. Biotechnol. 2001, 88, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.G.; Hu, Z.C.; Wang, Z.; Shen, Y.C. Large-scale production of astaxanthin by Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous. Food Bioprod. Process. 2006, 84, 164–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.S.; Wu, J.Y. Optimization of cell growth and carotenoid production of Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous through statistical experiment design. Biochem. Eng. J. 2007, 36, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Sáiz, M.; Fuente, J.; Barredo, J. Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous for the industrial production of astaxanthin. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 88, 645–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, I.; Schewe, H.; Gassel, S.; Jin, C.; Buckingham, J.; Hümbelin, M.; Sandmann, G.; Schrader, J. Biotechnological production of astaxanthin with Phaffia rhodozyma/Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 89, 555–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukibe, K.; Katsuragi, T.; Tani, Y.; Takagi, H. Efficient screening for astaxanthin-overproducing mutants of the yeast Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous by flow cytometry. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2008, 286, 241–248. [Google Scholar]
- Storebakken, T.; Sorensen, M.; Bjerkeng, B.; Hiu, S. Utilization of astaxanthin from red yeast, Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous, in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss: Effects of enzymatic cell wall disruption and feed extrusion temperature. Aquaculture 2004, 236, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, E.A.; An, G.H. Astaxanthin from microbial sources. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 1991, 11, 297–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seybold, A.; Goodwin, T. Occurrence of astaxanthin in the flower petals in Adonis annua L. Nature 1959, 184, 1714–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, V.; Harker, M.; Pecker, I.; Hirschberg, J. Metabolic engineering of astaxanthin production in tobacco flowers. Nat. Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 888–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralley, L.; Enfissi, E.M.A.; Misawa, N.; Schuch, W.; Bramley, P.M.; Fraser, P.D. Metabolic engineering of ketocarotenoid formation in higher plants. Plant J. 2004, 39, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerjets, T.; Sandmann, M.; Zhu, C.; Sandmann, G. Metabolic engineering of ketocarotenoid biosynthesis in leaves and flowers of tobacco species. Biotechnol. J. 2007, 2, 1263–1269. [Google Scholar]
- Hasunuma, T.; Miyazawa, S.I.; Yoshimura, S.; Shinzaki, Y.; Tomizawa, K.I.; Shindo, K.; Choi, S.K.; Misawa, N.; Miyake, C. Biosynthesis of astaxanthin in tobacco leaves by transplastomic engineering. Plant J. 2008, 55, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.-J.; Huang, J.-C.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, Z.-F.; Sandmann, G.; Chen, F. Functional characterization of various algal carotenoid ketolases reveals that ketolating zeaxanthin efficiently is essential for high production of astaxanthin in transgenic Arabidopsis. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 3659–3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerjets, T.; Sandmann, G. Ketocarotenoid formation in transgenic potato. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 3639–3645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, W.L.; Ducreux, L.J.M.; Fraser, P.D.; Millam, S.; Taylor, M.A. Engineering ketocarotenoid biosynthesis in potato tubers. Metab. Eng. 2006, 8, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaraj, J.; Devlin, R.; Punja, Z. Metabolic engineering of novel ketocarotenoid production in carrot plants. Transgenic Res. 2008, 17, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.-C.; Zhong, Y.-J.; Liu, J.; Sandmann, G.; Chen, F. Metabolic engineering of tomato for high-yield production of astaxanthin. Metab. Eng. 2013, 17, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boussiba, S. Carotenogenesis in the green alga Haematococcus pluvialis: Cellular physiology and stress response. Physiol. Plant. 2000, 108, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaizola, M. Commercial production of astaxanthin from Haematococcus pluvialis using 25,000-liter outdoor photobioreactors. J. Appl. Phycol. 2000, 12, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orosa, M.; Torres, E.; Fidalgo, P.; Abalde, J. Production and analysis of secondary carotenoids in green algae. J. Appl. Phycol. 2000, 12, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orosa, M.; Valero, J.F.; Herrero, C.; Abalde, J. Comparison of the accumulation of astaxanthin in Haematococcus pluvialis and other green microalgae under N-starvation and high light conditions. Biotechnol. Lett. 2001, 23, 1079–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hata, N.; Ogbonna, J.C.; Hasegawa, Y.; Taroda, H.; Tanaka, H. Production of astaxanthin by Haematococcus pluvialis in a sequential heterotrophic-photoautotrophic culture. J. Appl. Phycol. 2001, 13, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandesh Kamath, B.; Vidhyavathi, R.; Sarada, R.; Ravishankar, G.A. Enhancement of carotenoids by mutation and stress induced carotenogenic genes in Haematococcus pluvialis mutants. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 8667–8673. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Sun, Z.; Gerken, H.; Huang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, F. Genetic engineering of the green alga Chlorella zofingiensis: A modified norflurazon-resistant phytoene desaturase gene as a dominant selectable marker. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 5069–5079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabregas, J.; Otero, A.; Maseda, A.; Dominguez, A. Two-stage cultures for the production of astaxanthin from Haematococcus pluvialis. J. Biotechnol. 2001, 89, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ip, P.F. Elicitation of astaxanthin biosynthesis in dark-heterotrophic cultures of Chlorella zofingiensis. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China, August 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Imamoglu, E.; Dalay, M.C.; Sukan, F.V. Influences of different stress media and high light intensities on accumulation of astaxanthin in the green alga Haematococcus pluvialis. New Biotechnol. 2009, 26, 199–204. [Google Scholar]
- Osterlie, M.; Bjerkeng, B.; Liaaen-Jensen, S. Accumulation of astaxanthin all-E, 9Z and 13Z geometrical isomers and 3 and 3′ RS optical isomers in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) is selective. J. Nutr. 1999, 129, 391–398. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, F.; Lu, D.; Li, Y.; Zeng, M. Characterization of astaxanthin esters in Haematococcus pluvialis by liquid chromatography-atmospheric pressure chemical ionization mass spectrometry. Anal. Biochem. 2006, 352, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtin, K.; Kuehnle, M.; Rehbein, J.; Schuler, P.; Nicholson, G.; Albert, K. Determination of astaxanthin and astaxanthin esters in the microalgae Haematococcus pluvialis by LC-(APCI)MS and characterization of predominant carotenoid isomers by NMR spectroscopy. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 395, 1613–1622. [Google Scholar]
- Huss, V.A.R.; Frank, C.; Hartmann, E.C.; Hirmer, M.; Kloboucek, A.; Seidel, B.M.; Wenzeler, P.; Kessler, E. Biochemical taxonomy and molecular phylogeny of the genus Chlorella sensu lato (Chlorophyta). J. Phycol. 1999, 35, 587–598. [Google Scholar]
- Krienitz, L.; Bock, C.; Dadheech, P.K.; Pröschold, T. Taxonomic reassessment of the genus Mychonastes (Chlorophyceae, Chlorophyta) including the description of eight new species. Phycologia 2011, 50, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fucikova, K.; Lewis, L.A. Intersection of Chlorella, Muriella and Bracteacoccus: Resurrecting the genus Chromochloris KOL et CHODAT (Chlorophyceae, Chlorophyta). Fottea 2012, 12, 83–93. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, R.E. Phycology, 4th ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Morimura, Y. Synchronous culture of Chlorella. Plant Cell Physiol. 1959, 1, 49–62. [Google Scholar]
- Rise, M.; Cohen, E.; Vishkautsan, M.; Cojocaru, M.; Gottlieb, H.E.; Arad, S.M. Accumulation of secondary carotenoids in Chlorella zofingiensis. J. Plant Physiol. 1994, 144, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunewald, K.; Hirschberg, J.; Hagen, C. Ketocarotenoid biosynthesis outside of plastids in the unicellular green alga Haematococcus pluvialis. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 6023–6029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Huang, J.; Sandmann, G.; Chen, F. High-light and sodium chloride stress differentially regulate the biosynthesis of astaxanthin in Chlorella zofingiensis (Chlorophyceae). J. Phycol. 2009, 45, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschberg, J. Carotenoid biosynthesis in flowering plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2001, 4, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordero, B.; Couso, I.; León, R.; Rodríguez, H.; Vargas, M. Enhancement of carotenoids biosynthesis in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii by nuclear transformation using a phytoene synthase gene isolated from Chlorella zofingiensis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 91, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, P.D.; Romer, S.; Shipton, C.A.; Mills, P.B.; Kiano, J.W.; Misawa, N.; Drake, R.G.; Schuch, W.; Bramley, P.M. Evaluation of transgenic tomato plants expressing an additional phytoene synthase in a fruit-specific manner. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 1092–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.D.; Al-Babili, S.; Kloti, A.; Zhang, J.; Lucca, P.; Beyer, P.; Potrykus, I. Engineering the provitamin A (beta-carotene) biosynthetic pathway into (carotenoid-free) rice endosperm. Science 2000, 287, 303–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couso, I.; Vila, M.; Rodriguez, H.; Vargas, M.A.; León, R. Overexpression of an exogenous phytoene synthase gene in the unicellular alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii leads to an increase in the content of carotenoids. Biotechnol. Prog. 2011, 27, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.C.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.T.; Chen, F. Isolation and characterization of the phytoene desaturase gene as a potential selective marker for genetic engineering of the astaxanthin-producing green alga Chlorella zofingiensis (Chlorophyta). J. Phycol. 2008, 44, 684–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, P.T.; Sharifi, M.N.; Poddar, S.; Dent, R.M.; Niyogi, K.K. Intragenic enhancers and suppressors of phytoene desaturase mutations in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. PLoS One 2012, 7, e42196. [Google Scholar]
- Breitenbach, J.; Zhu, C.F.; Sandmann, G. Bleaching herbicide norflurazon inhibits phytoene desaturase by competition with the cofactors. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 5270–5272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Gerken, H.; Huang, J.; Chen, F. Engineering of an endogenous phytoene desaturase gene as a dominant selectable marker for Chlamydomonas reinhardtii transformation and enhanced biosynthesis of carotenoids. Process Biochem. 2013, 48, 788–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamovitz, D.; Sandmann, G.; Hirschberg, J. Molecular and biochemical-characterization of herbicide-resistant mutants of cyanobacteria reveals that phytoene desaturation is a rate-limiting step in carotenoid biosynthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 17348–17353. [Google Scholar]
- Misawa, N.; Masamoto, K.; Hori, T.; Ohtani, T.; Boger, P.; Sandmann, G. Expression of an Erwinia phytoene desaturase gene not only confers multiple resistance to herbicides interfering with carotenoid biosynthesis but also alters xanthophyll metabolism in transgenic plants. Plant J. 1994, 6, 481–489. [Google Scholar]
- Romer, S.; Fraser, P.D.; Kiano, J.W.; Shipton, C.A.; Misawa, N.; Schuch, W.; Bramley, P.M. Elevation of the provitamin A content of transgenic tomato plants. Nat. Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbrenner, J.; Sandmann, G. Transformation of the green alga Haematococcus pluvialis with a phytoene desaturase for accelerated astaxanthin biosynthesis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 7477–7484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordero, B.F.; Obraztsova, I.; Martin, L.; Couso, I.; Leon, R.; Vargas, M.A.; Rodriguez, H. Isolation and characterization of a lycopene beta-cyclase gene from the astaxanthin-producing green alga Chlorella zofingiensis (Chlorophyta). J. Phycol. 2010, 46, 1229–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, T. The biosynthetic pathway of carotenoids in the astaxanthin-producing green alga Chlorella zofingiensis. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 24, 2927–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.C.; Wang, Y.; Sandmann, G.; Chen, F. Isolation and characterization of a carotenoid oxygenase gene from Chlorella zofingiensis (Chlorophyta). Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 71, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Sun, Z.; Gerken, H.; Chen, F. Employment of a heterotrophic-phototrophic two-stage culture strategy towards improved astaxanthin production in Chlorella zofinginesis. 2014. Unpublished work. [Google Scholar]
- Grunewald, K.; Hagen, C. Beta-carotene is the intermediate exported from the chloroplast during accumulation of secondary carotenoids in Haematococcus pluvialis. J. Appl. Phycol. 2001, 13, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhekisheva, M.; Zarka, A.; Khozin-Goldberg, I.; Cohen, Z.; Boussiba, S. Inhibition of astaxanthin synthesis under high irradiance does not abolish triacylglycerol accumulation in the green alga Haematococcus pluvialis (Chlorophyceae). J. Phycol. 2005, 41, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Huang, J.; Fan, K.W.; Jiang, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Sun, Z.; Chen, F. Production potential of Chlorella zofingienesis as a feedstock for biodiesel. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 8658–8663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ip, P.F.; Wong, K.H.; Chen, F. Enhanced production of astaxanthin by the green microalga Chlorella zofingiensis in mixotrophic culture. Process Biochem. 2004, 39, 1761–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.-M.; Zhang, X.-W.; Chen, F. Heterotrophic production of biomass and lutein by Chlorella protothecoides on various nitrogen sources. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2000, 27, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Sommerfeld, M.; Hu, Q. Screening and characterization of Isochrysis strains and optimization of culture conditions for docosahexaenoic acid production. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 4785–4798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.E.; Yun, Y.S.; Park, J.M. Evaluation of factors promoting astaxanthin production by a unicellular green alga, Haematococcus pluvialis, with fractional factorial design. Biotechnol. Prog. 2002, 18, 1170–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Qin, S. Effects of iron on fatty acid and astaxanthin accumulation in mixotrophic Chromochloris zofingiensis. Biotechnol. Lett. 2013, 35, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, P.D.; Miura, Y.; Misawa, N. In vitro characterization of astaxanthin biosynthetic enzymes. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 6128–6135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbrenner, J.; Linden, H. Light induction of carotenoid biosynthesis genes in the green alga Haematococcus pluvialis: Regulation by photosynthetic redox control. Plant Mol. Biol. 2003, 52, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harker, M.; Tsavalos, A.J.; Young, A.J. Autotrophic growth and carotenoid production of Haematococcus pluvialis in a 30 liter air-lift photobioreactor. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 1996, 82, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.-P. Chlorella: Its Ecology, Structure, Cultivation, Bioprocess and Application; Yi Hsien Publishing: Taipei, Taiwan, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Chisti, Y. Biodiesel from microalgae. Biotechnol. Adv. 2007, 25, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doucha, J.; Lívanský, K. Outdoor open thin-layer microalgal photobioreactor: Potential productivity. J. Appl. Phycol. 2009, 21, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.W.; Richmond, A. Sustainable, high-yielding outdoor mass cultures of Chaetoceros muelleri var. subsalsum and Isochrysis galban in vertical plate reactors. Mar. Biotechnol. 2003, 5, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Gerken, H.; Huang, J.; Hu, Q.; Chen, F. Induced astaxanthin, independent of the de novo fatty acid synthesis, is esterified and accumulates in lipid bodies of the green alga Chlorella zofingiensis. 2014. Unpublished work. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Huang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, F. Molasses-based growth and production of oil and astaxanthin by Chlorella zofingiensis. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 107, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.-Y.; Chen, F. Continuous cultivation of the diatom Nitzschia laevis for eicosapentaenoic acid production: Physiological study and process optimization. Biotechnol. Prog. 2002, 18, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.-Y.; Chen, F. Perfusion culture of the diatom Nitzschia laevis for ultra-high yield of eicosapentaenoic acid. Process Biochem. 2002, 38, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, M.C.G.-M.; Sánchez, E.D.R.; López, J.L.C.; Fernández, F.G.A.; Sevilla, J.M.F.; Rivas, J.; Guerrero, M.G.; Grima, E.M. Comparative analysis of the outdoor culture of Haematococcus pluvialis in tubular and bubble column photobioreactors. J. Biotechnol. 2006, 123, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Rio, E.; Acién, F.G.; García-Malea, M.C.; Rivas, J.; Molina-Grima, E.; Guerrero, M.G. Efficient one-step production of astaxanthin by the microalga Haematococcus pluvialis in continuous culture. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2005, 91, 808–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, R.; Inoue, R.; Shiraishi, H.; Katsuda, T.; Katoh, S. High efficiency production of astaxanthin by autotrophic cultivation of Haematococcus pluvialis in a bubble column photobioreactor. Biochem. Eng. J. 2008, 39, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Malea, M.C.; Acién, F.G.; del Río, E.; Fernández, J.M.; Cerón, M.C.; Guerrero, M.G.; Molina-Grima, E. Production of astaxanthin by Haematococcus pluvialis: Taking the one-step system outdoors. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2009, 102, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamane, Y.; Higashida, K.; Nakashimada, Y.; Kakizono, T.; Nishio, N. Astaxanthin production by Phaffia rhodozyma enhanced in fed-batch culture with glucose and ethanol feeding. Biotechnol. Lett. 1997, 19, 1109–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parajó, J.C.; Santos, V.; Vázquez, M. Production of carotenoids by Phaffia rhodozyma growing on media made from hemicellulosic hydrolysates of Eucalyptus globulus wood. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1998, 59, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriel, D.G.; Chociai, M.B.; Machado, I.M.P.; Fontana, J.D.; Bonfim, T.M.B. Effect of feeding methods on the astaxanthin production by Phaffia rhodozyma in fed-batch process. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2005, 48, 397–401. [Google Scholar]
- An, G.-H.; Jang, B.-G.; Cho, M.-H. Cultivation of the carotenoid-hyperproducing mutant 2A2N of the red yeast Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous (Phaffia rhodozyma) with molasses. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2001, 92, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.-C.; Zheng, Y.-G.; Wang, Z.; Shen, Y.-C. pH control strategy in astaxanthin fermentation bioprocess by Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2006, 39, 586–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Shen, Y. Production of astaxanthin by Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous ZJUT46 with fed-batch fermentation in 2.0 M3 fermentor. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2007, 45, 209–212. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.Q.; Zhang, J.F.; Zheng, Y.G.; Shen, Y.C. Improvement of astaxanthin production by a newly isolated Phaffia rhodozyma mutant with low-energy ion beam implantation. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 104, 861–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Fuente, J.L.; Rodríguez-Sáiz, M.; Schleissner, C.; Díez, B.; Peiro, E.; Barredo, J.L. High-titerproduction of astaxanthin by the semi-industrial fermentation of Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 148, 144–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.Y.; Li, Y.T.; Sommerfeld, M.; Chen, F.; Hu, Q. Enhanced protection against oxidative stress in an astaxanthin-overproduction Haematococcus mutant (Chlorophyceae). Eur. J. Phycol. 2008, 43, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhong, Y.; Sun, Z.; Huang, J.; Sandmann, G.; Chen, F. One amino acid substitution in phytoene desaturase makes Chlorella zofingiensis resistant to norflurazon and enhances the biosynthesis of astaxanthin. Planta 2010, 232, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Sun, Z.; Gerken, H.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, F. Chlorella zofingiensis as an Alternative Microalgal Producer of Astaxanthin: Biology and Industrial Potential. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 3487-3515. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12063487
Liu J, Sun Z, Gerken H, Liu Z, Jiang Y, Chen F. Chlorella zofingiensis as an Alternative Microalgal Producer of Astaxanthin: Biology and Industrial Potential. Marine Drugs. 2014; 12(6):3487-3515. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12063487
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jin, Zheng Sun, Henri Gerken, Zheng Liu, Yue Jiang, and Feng Chen. 2014. "Chlorella zofingiensis as an Alternative Microalgal Producer of Astaxanthin: Biology and Industrial Potential" Marine Drugs 12, no. 6: 3487-3515. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12063487
APA StyleLiu, J., Sun, Z., Gerken, H., Liu, Z., Jiang, Y., & Chen, F. (2014). Chlorella zofingiensis as an Alternative Microalgal Producer of Astaxanthin: Biology and Industrial Potential. Marine Drugs, 12(6), 3487-3515. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12063487






